8d692b9a27dceaff54d3e0a10a935236.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Network Processors and Web Servers CS 213 LECTURE 17 From: IBM Technical Report
Intel® IXP 2 XXX Network Processor Architecture and Programming Prof. Laxmi Bhuyan Computer Science UC Riverside
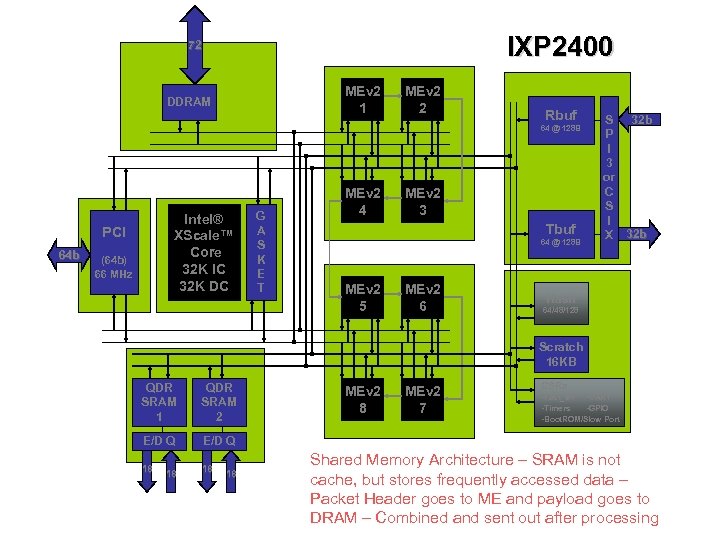
IXP 2400 72 MEv 2 1 DDRAM MEv 2 2 Rbuf 64 @ 128 B Intel® XScale™ Core 32 K IC 32 K DC PCI 64 b (64 b) 66 MHz G A S K E T MEv 2 4 MEv 2 3 Tbuf 64 @ 128 B MEv 2 5 MEv 2 6 32 b S P I 3 or C S I X 32 b Hash 64/48/128 Scratch 16 KB QDR SRAM 1 QDR SRAM 2 E/D Q 18 18 CSRs E/D Q 18 18 MEv 2 7 -Fast_wr -UART -Timers -GPIO -Boot. ROM/Slow Port Shared Memory Architecture – SRAM is not cache, but stores frequently accessed data – Packet Header goes to ME and payload goes to DRAM – Combined and sent out after processing
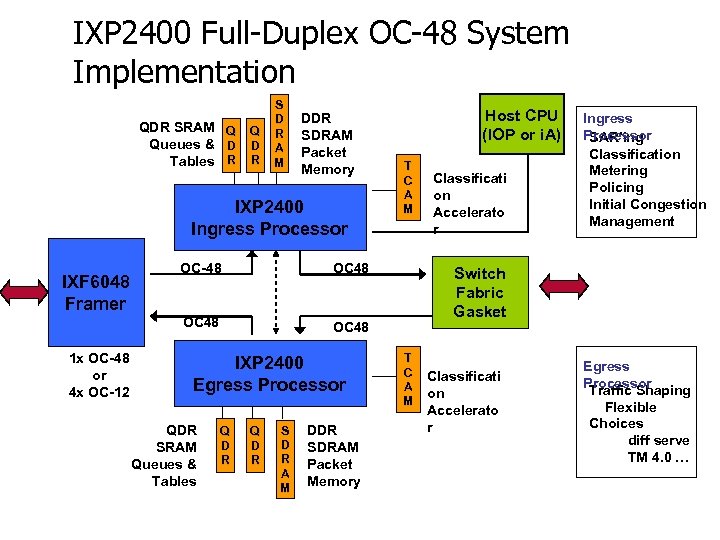
IXP 2400 Full-Duplex OC-48 System Implementation QDR SRAM Q Queues & D Tables R Q D R S D R A M DDR SDRAM Packet Memory IXP 2400 Ingress Processor 1 x OC-48 or 4 x OC-12 T C A M OC 48 IXF 6048 Framer OC-48 Host CPU (IOP or i. A) OC 48 IXP 2400 Egress Processor QDR SRAM Queues & Tables Q D R S D R A M DDR SDRAM Packet Memory Classificati on Accelerato r Ingress Processor SAR’ing Classification Metering Policing Initial Congestion Management Switch Fabric Gasket T C A M Classificati on Accelerato r Egress Processor Traffic Shaping Flexible Choices diff serve TM 4. 0 …
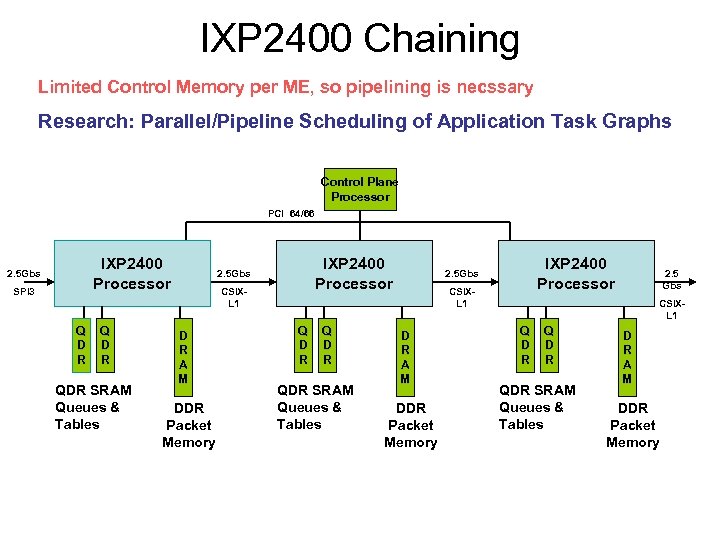
IXP 2400 Chaining Limited Control Memory per ME, so pipelining is necssary Research: Parallel/Pipeline Scheduling of Application Task Graphs Control Plane Processor PCI 64/66 IXP 2400 Processor 2. 5 Gbs SPI 3 Q D R QDR SRAM Queues & Tables IXP 2400 Processor 2. 5 Gbs CSIXL 1 D R A M DDR Packet Memory 2. 5 Gbs CSIXL 1 Q D R QDR SRAM Queues & Tables D R A M DDR Packet Memory
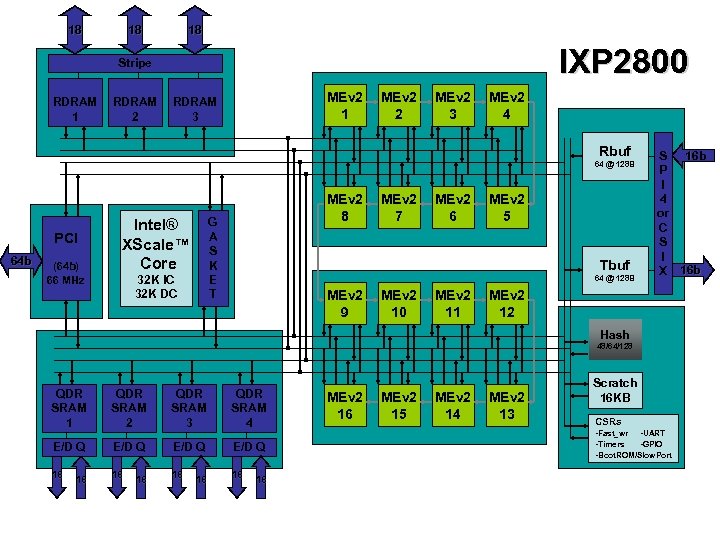
18 18 18 IXP 2800 Stripe RDRAM 1 RDRAM 2 MEv 2 1 RDRAM 3 MEv 2 2 MEv 2 3 MEv 2 4 Rbuf 64 @ 128 B PCI 64 b (64 b) 66 MHz MEv 2 8 G A S K E T Intel® XScale™ Core 32 K IC 32 K DC MEv 2 7 MEv 2 6 MEv 2 5 Tbuf 64 @ 128 B MEv 2 9 MEv 2 10 MEv 2 11 16 b S P I 4 or C S I X 16 b MEv 2 12 Hash 48/64/128 QDR SRAM 1 QDR SRAM 2 QDR SRAM 3 QDR SRAM 4 E/D Q 18 18 MEv 2 16 MEv 2 15 MEv 2 14 MEv 2 13 Scratch 16 KB CSRs -Fast_wr -UART -Timers -GPIO -Boot. ROM/Slow. Port
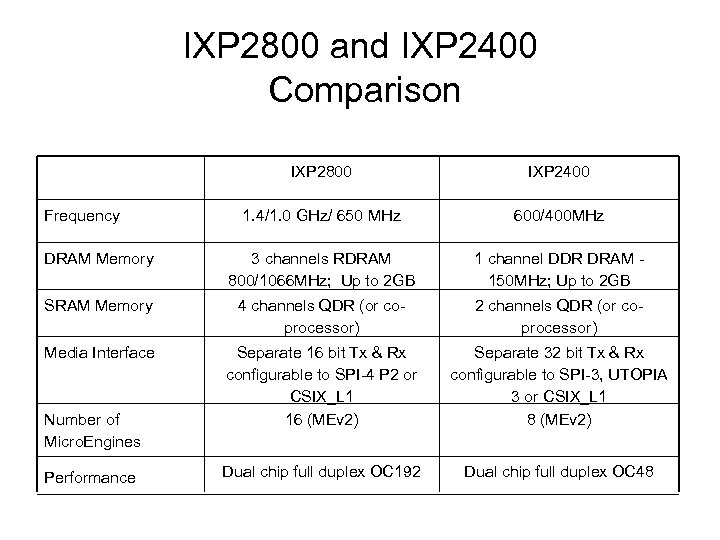
IXP 2800 and IXP 2400 Comparison IXP 2800 IXP 2400 1. 4/1. 0 GHz/ 650 MHz 600/400 MHz DRAM Memory 3 channels RDRAM 800/1066 MHz; Up to 2 GB 1 channel DDR DRAM 150 MHz; Up to 2 GB SRAM Memory 4 channels QDR (or coprocessor) 2 channels QDR (or coprocessor) Media Interface Separate 16 bit Tx & Rx configurable to SPI-4 P 2 or CSIX_L 1 16 (MEv 2) Separate 32 bit Tx & Rx configurable to SPI-3, UTOPIA 3 or CSIX_L 1 8 (MEv 2) Dual chip full duplex OC 192 Dual chip full duplex OC 48 Frequency Number of Micro. Engines Performance
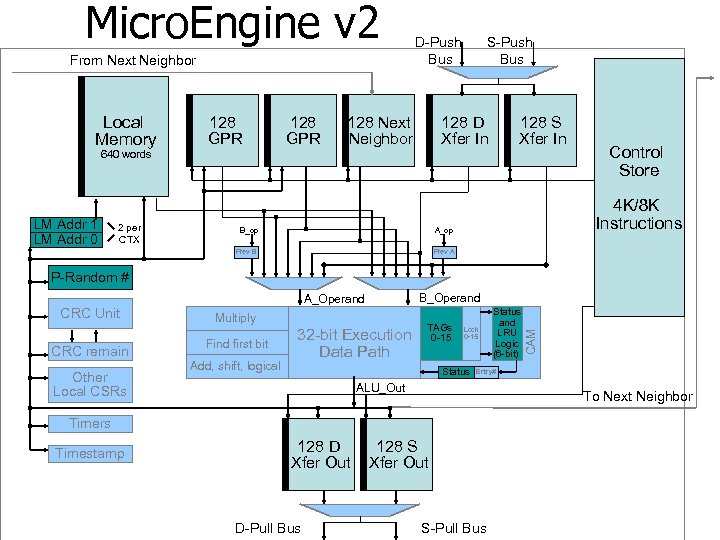
Micro. Engine v 2 From Next Neighbor Local Memory 128 GPR D-Push Bus 128 Next Neighbor S-Push Bus 128 D Xfer In 128 S Xfer In 640 words LM Addr 1 LM Addr 0 2 per CTX B_op 4 K/8 K Instructions A_op Prev B Control Store Prev A P-Random # CRC remain Other Local CSRs Multiply Find first bit Add, shift, logical 32 -bit Execution Data Path TAGs 0 -15 Lock 0 -15 Status Entry# ALU_Out To Next Neighbor Timers Timestamp 128 D Xfer Out D-Pull Bus Status and LRU Logic (6 -bit) CAM CRC Unit B_Operand A_Operand 128 S Xfer Out S-Pull Bus

Microengine v 2 Features – Part 1 • • Clock Rates – IXP 2400 – 600/400 MHz – IXP 2800 - 1. 4/1. 0 GHz/ 650 MHz Control Store – IXP 2400 – 4 K Instruction store – IXP 2800 – 8 K Instruction store Configurable to 4 or 8 threads – Each thread has its own program counter, registers, signal and wakeup events – Generalized Thread Signaling (15 signals per thread) Local Storage Options – 256 GPRs – 256 Transfer Registers – 128 Next Neighbor Registers – 640 - 32 bit words of local memory
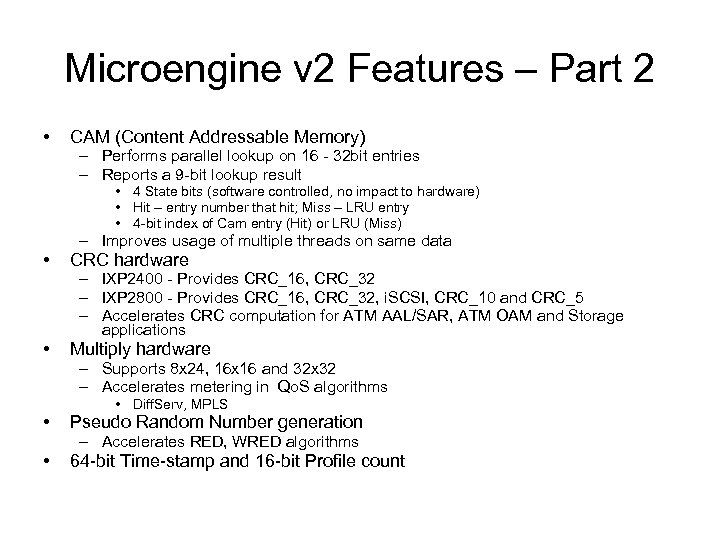
Microengine v 2 Features – Part 2 • CAM (Content Addressable Memory) – Performs parallel lookup on 16 - 32 bit entries – Reports a 9 -bit lookup result • 4 State bits (software controlled, no impact to hardware) • Hit – entry number that hit; Miss – LRU entry • 4 -bit index of Cam entry (Hit) or LRU (Miss) – Improves usage of multiple threads on same data • CRC hardware • Multiply hardware – IXP 2400 - Provides CRC_16, CRC_32 – IXP 2800 - Provides CRC_16, CRC_32, i. SCSI, CRC_10 and CRC_5 – Accelerates CRC computation for ATM AAL/SAR, ATM OAM and Storage applications – Supports 8 x 24, 16 x 16 and 32 x 32 – Accelerates metering in Qo. S algorithms • Diff. Serv, MPLS • Pseudo Random Number generation • 64 -bit Time-stamp and 16 -bit Profile count – Accelerates RED, WRED algorithms
Intel® XScale™ Core Overview • High-performance, Low-power, 32 -bit Embedded RISC processor • Clock rate – IXP 2400 600 MHz – IXP 2800 700/500/325 MHz • • • 32 Kbyte instruction cache 32 Kbyte data cache 2 Kbyte mini-data cache Write buffer Memory management unit
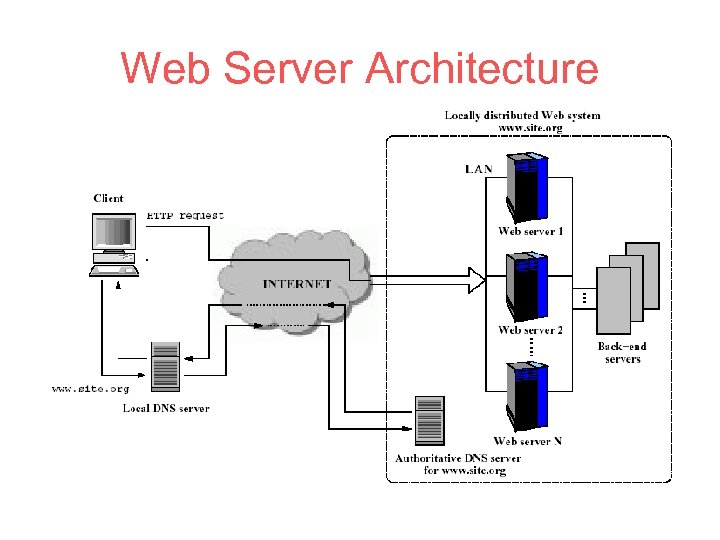
Web Server Architecture
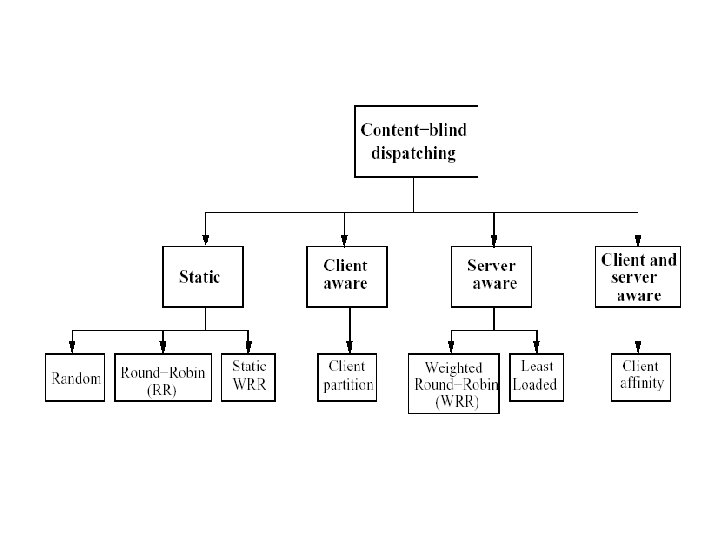
Dispatching Algorithms Strategies to select the target server of the web clusters • Static: Fastest solution to prevent web server bottleneck, but do not consider the current state of the servers • Dynamic: Outperform static algorithms by using intelligent decisions, but collecting state information and analyzing them cause expensive overheads Requirements: (1) Low computational complexity (2) Full compatibility with web standards (3) state information must be readily available without much overhead
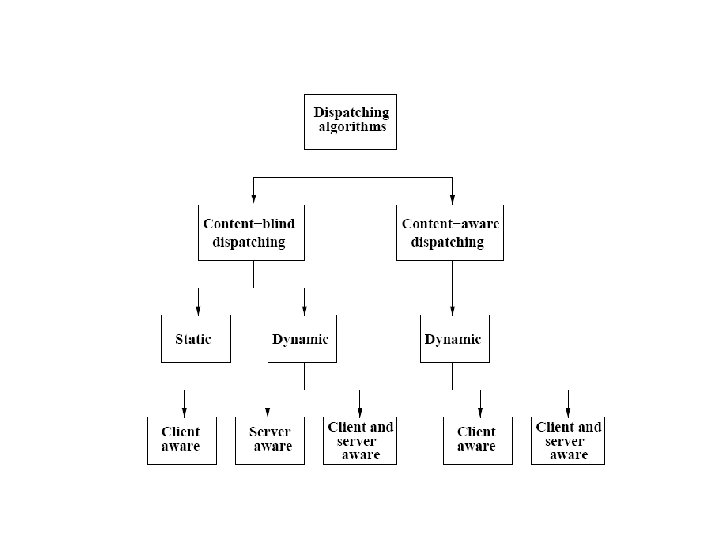
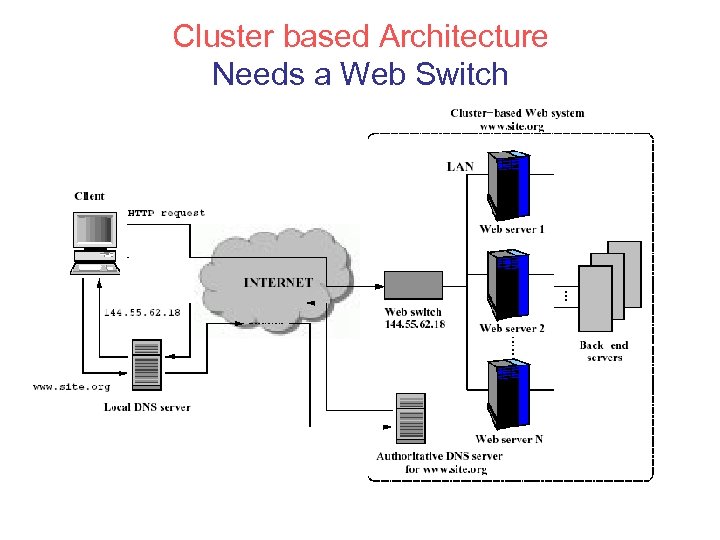
Cluster based Architecture Needs a Web Switch
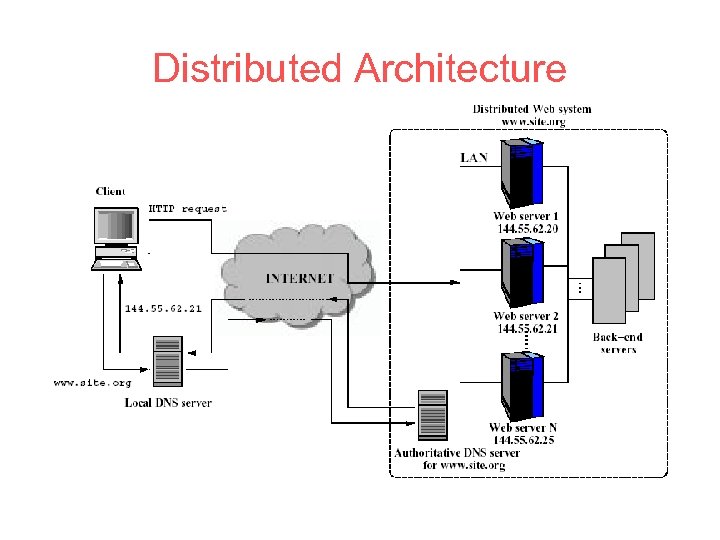
Distributed Architecture
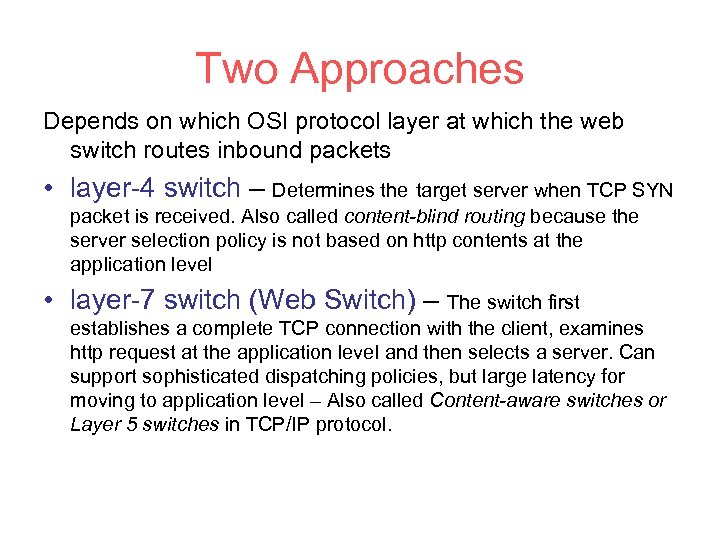
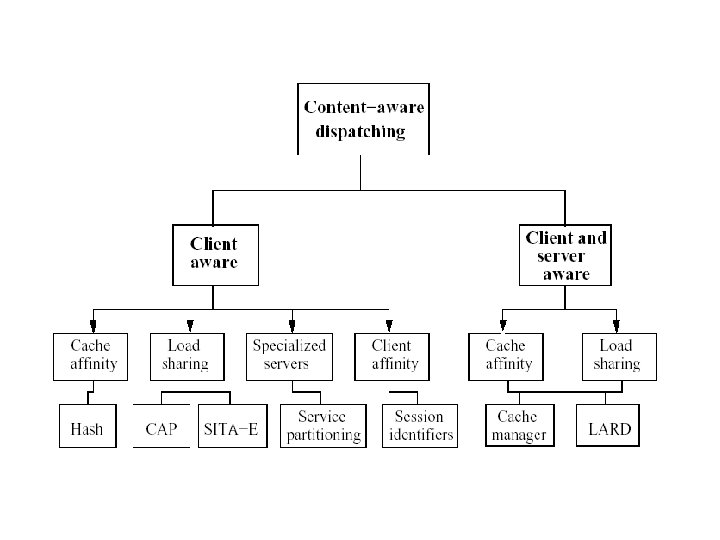
Two Approaches Depends on which OSI protocol layer at which the web switch routes inbound packets • layer-4 switch – Determines the target server when TCP SYN packet is received. Also called content-blind routing because the server selection policy is not based on http contents at the application level • layer-7 switch (Web Switch) – The switch first establishes a complete TCP connection with the client, examines http request at the application level and then selects a server. Can support sophisticated dispatching policies, but large latency for moving to application level – Also called Content-aware switches or Layer 5 switches in TCP/IP protocol.
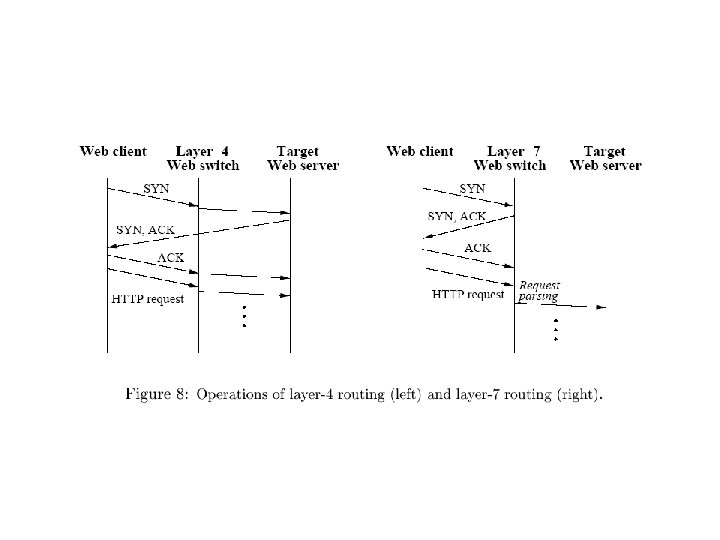
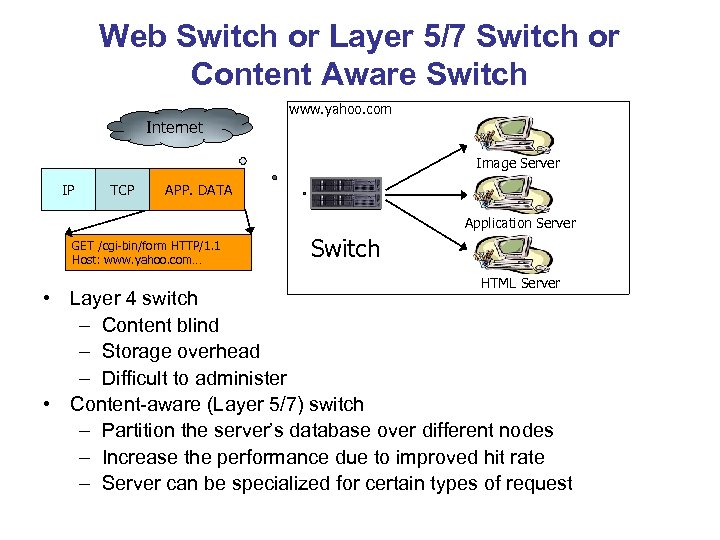
Web Switch or Layer 5/7 Switch or Content Aware Switch www. yahoo. com Internet Image Server IP TCP APP. DATA Application Server GET /cgi-bin/form HTTP/1. 1 Host: www. yahoo. com… Switch HTML Server • Layer 4 switch – Content blind – Storage overhead – Difficult to administer • Content-aware (Layer 5/7) switch – Partition the server’s database over different nodes – Increase the performance due to improved hit rate – Server can be specialized for certain types of request
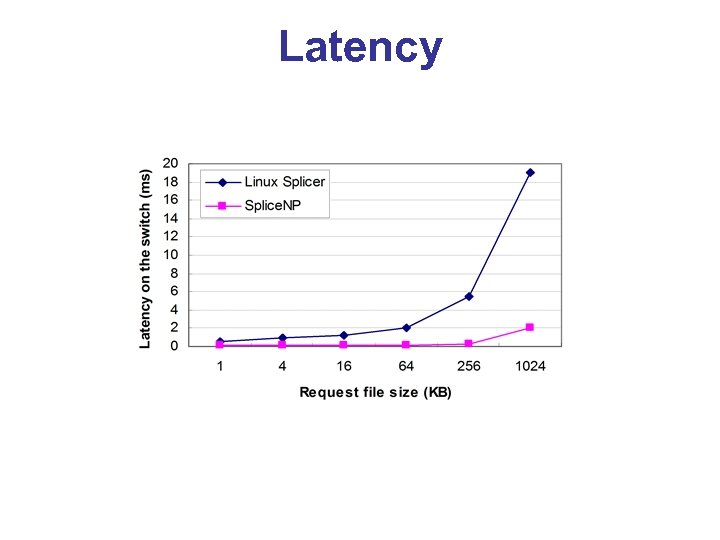
Latency
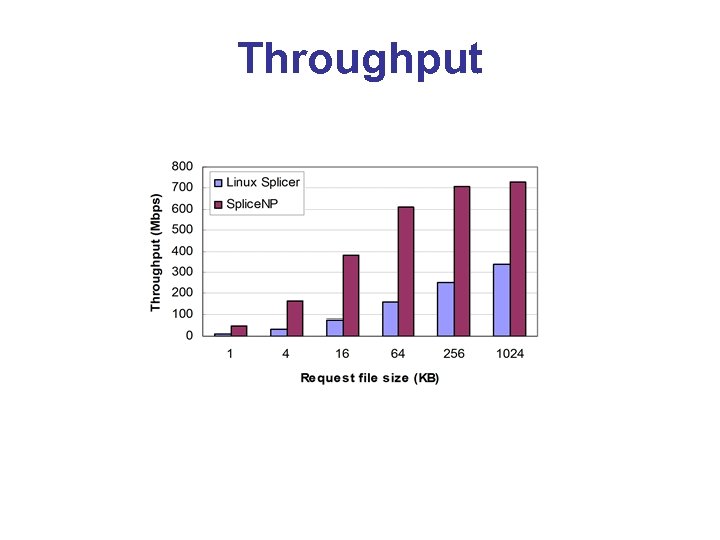
Throughput
8d692b9a27dceaff54d3e0a10a935236.ppt