5ce2a60ace6409fe31e45afe085bf42a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Network Management - Introduction
Network Management - Introduction
 References n Communications Network Management, Kornel Terplan Prentice Hall 1992, 2 nd ed. n Managing Inter networks with SNMP Mark A. Miller, M& T books 1999, 3 rd ed. n SNMP, SNMPv 2, SNMPv 3 and RMON 1 & 2, William Stallings, 3 rd ed. Addison Wiley 1999 n Telecommunications Network Management into the 21 st century : techniques, standards, technologies, and applications, New York : IEEE Press
References n Communications Network Management, Kornel Terplan Prentice Hall 1992, 2 nd ed. n Managing Inter networks with SNMP Mark A. Miller, M& T books 1999, 3 rd ed. n SNMP, SNMPv 2, SNMPv 3 and RMON 1 & 2, William Stallings, 3 rd ed. Addison Wiley 1999 n Telecommunications Network Management into the 21 st century : techniques, standards, technologies, and applications, New York : IEEE Press
 References - contd n How to Manage your Network Using SNMP, Marshall T. Rose and Keith Mc. Cloghrie n The Simple Book, Marshall T. Rose n A Practical Guide to SNMPv 3 and Network 8. Management, David Zeltserman, Prentice Hall. Network Management – Principles and Practice, Mani Subramanian, Adddison Wesley Press Network Management, A Practical Perspective, Allan Leinwand Karen Fang Conroy, Addison Wesley
References - contd n How to Manage your Network Using SNMP, Marshall T. Rose and Keith Mc. Cloghrie n The Simple Book, Marshall T. Rose n A Practical Guide to SNMPv 3 and Network 8. Management, David Zeltserman, Prentice Hall. Network Management – Principles and Practice, Mani Subramanian, Adddison Wesley Press Network Management, A Practical Perspective, Allan Leinwand Karen Fang Conroy, Addison Wesley
 Introduction n What is Network Management? Managing Networks - is the network n Performing optimally n Troubleshooting n Reconfiguring - configuration n Expanding n Secure n Accounting, Usage n Planning
Introduction n What is Network Management? Managing Networks - is the network n Performing optimally n Troubleshooting n Reconfiguring - configuration n Expanding n Secure n Accounting, Usage n Planning
 What if no NM? n What is the latest configuration? n What are the systems and what is their capacity? n Not up to speed? Where is the bottleneck? n High delays under certain conditions? Why is it happening? n Permissions, access? n Security?
What if no NM? n What is the latest configuration? n What are the systems and what is their capacity? n Not up to speed? Where is the bottleneck? n High delays under certain conditions? Why is it happening? n Permissions, access? n Security?
 Strategic Importance of Network and Network Management n 1970 s – decade of centralized networks n 1980 s – n More LANs n Interconnected LANs n Distributed computing
Strategic Importance of Network and Network Management n 1970 s – decade of centralized networks n 1980 s – n More LANs n Interconnected LANs n Distributed computing
 Contd. n Current n Gigabit speeds n SONET n WANs n Web based technologies n Various architectures n Wireless proliferation
Contd. n Current n Gigabit speeds n SONET n WANs n Web based technologies n Various architectures n Wireless proliferation
 NM Functional Groupings
NM Functional Groupings
 Network Dependency n Business n Commercial n Education n Research n Defense n Integration of these sectors
Network Dependency n Business n Commercial n Education n Research n Defense n Integration of these sectors
 Network Dependency n Failure of networks n Inefficient operation n Heavy Downtime costs and Loss
Network Dependency n Failure of networks n Inefficient operation n Heavy Downtime costs and Loss
 Factors affecting NM systems
Factors affecting NM systems
 Complexity of Network Management by Human effort Automated tools Large networks - heterogeneous equipment § cost and complexity higher § need for standardized tools management Staff
Complexity of Network Management by Human effort Automated tools Large networks - heterogeneous equipment § cost and complexity higher § need for standardized tools management Staff
 Is NM crucial? n Better control – higher level of network performance n Better performance – higher productivity n Higher productivity – financial stability and improvement n (Continuous improvements in network management necessary)
Is NM crucial? n Better control – higher level of network performance n Better performance – higher productivity n Higher productivity – financial stability and improvement n (Continuous improvements in network management necessary)
 contd n How to cope with new applications? n New Systems? n Controlling complexity n Improving services n Balancing needs n Reduce downtime n Controlling costs
contd n How to cope with new applications? n New Systems? n Controlling complexity n Improving services n Balancing needs n Reduce downtime n Controlling costs
 NM? CEO: n financial management of the corporate communications network USER n Availability n Reliability n Performance n Stability n Security n Simplicity in accounting
NM? CEO: n financial management of the corporate communications network USER n Availability n Reliability n Performance n Stability n Security n Simplicity in accounting
 Critical Success Factors for NM n Process and procedures n Steps and guidelines on how to use the necessary tools to execute network management n Instruments n Hardware & software for data collection and processing n Human Resources n NM personnel
Critical Success Factors for NM n Process and procedures n Steps and guidelines on how to use the necessary tools to execute network management n Instruments n Hardware & software for data collection and processing n Human Resources n NM personnel
 Process and Procedures n Configuration Management n Fault Management n Performance Management n Security Management n Accounting n Planning
Process and Procedures n Configuration Management n Fault Management n Performance Management n Security Management n Accounting n Planning
 Configuration Management n Middle and long range activities for controlling n physical, electrical and logical inventories n maintaining vendor files n supporting provisioning and order processing n managing changes n distributing software
Configuration Management n Middle and long range activities for controlling n physical, electrical and logical inventories n maintaining vendor files n supporting provisioning and order processing n managing changes n distributing software
 Fault Management n Dynamically maintain network service level n High availability n Quick recognition of problems & performance degradation n Log control & information distribution n Fault Isolation n Reconfigure / Modify to minimize impact n Repair /Replace failed components
Fault Management n Dynamically maintain network service level n High availability n Quick recognition of problems & performance degradation n Log control & information distribution n Fault Isolation n Reconfigure / Modify to minimize impact n Repair /Replace failed components
 Performance Management n Ongoing evaluation of network – service level maintenance n Identify bottlenecks (potential) n Check level of capacity/ utilisation? n Check delays n Check for unusual network behaviour
Performance Management n Ongoing evaluation of network – service level maintenance n Identify bottlenecks (potential) n Check level of capacity/ utilisation? n Check delays n Check for unusual network behaviour
 Security n Ongoing protection of network n Protection of Network Components n Entry to network n Access to Services n Transfer of information from network n Risk analysis – minimizing n Implementing security plans n Monitoring Success of strategies
Security n Ongoing protection of network n Protection of Network Components n Entry to network n Access to Services n Transfer of information from network n Risk analysis – minimizing n Implementing security plans n Monitoring Success of strategies
 Accounting n Process of n Collecting n Interpreting n Reporting on n Costing and charging oriented information on resource usage n Processing of accounting records, bill verifications, charge back procedures
Accounting n Process of n Collecting n Interpreting n Reporting on n Costing and charging oriented information on resource usage n Processing of accounting records, bill verifications, charge back procedures
 contd n Resources subject to accounting n Communication facilities n Hardware usage n Software usage n Other services n Security and Accounting depend on Company Policies
contd n Resources subject to accounting n Communication facilities n Hardware usage n Software usage n Other services n Security and Accounting depend on Company Policies
 Planning n Off line management, based on collected statistics, corporate level decisions, network designers, user requirements & demands n Involves dimensioning a networks n Depends on n n n Network traffic Resource utilization Networking requirements Technological trade-offs Estimated growth – technology Growth of user population
Planning n Off line management, based on collected statistics, corporate level decisions, network designers, user requirements & demands n Involves dimensioning a networks n Depends on n n n Network traffic Resource utilization Networking requirements Technological trade-offs Estimated growth – technology Growth of user population
 Monitoring and Control n Network Monitoring n Observing and Analysing the status and behaviour of the end-systems, intermediate systems and sub-networks n Three major functions n Design monitoring mechanism n Access information for monitoring n Apply monitored information
Monitoring and Control n Network Monitoring n Observing and Analysing the status and behaviour of the end-systems, intermediate systems and sub-networks n Three major functions n Design monitoring mechanism n Access information for monitoring n Apply monitored information
 Types of monitored information n Static Information n Related to current network configuration n Infrequent information change n Dynamic Information n Related to events n Statistical n Derived from dynamic information
Types of monitored information n Static Information n Related to current network configuration n Infrequent information change n Dynamic Information n Related to events n Statistical n Derived from dynamic information
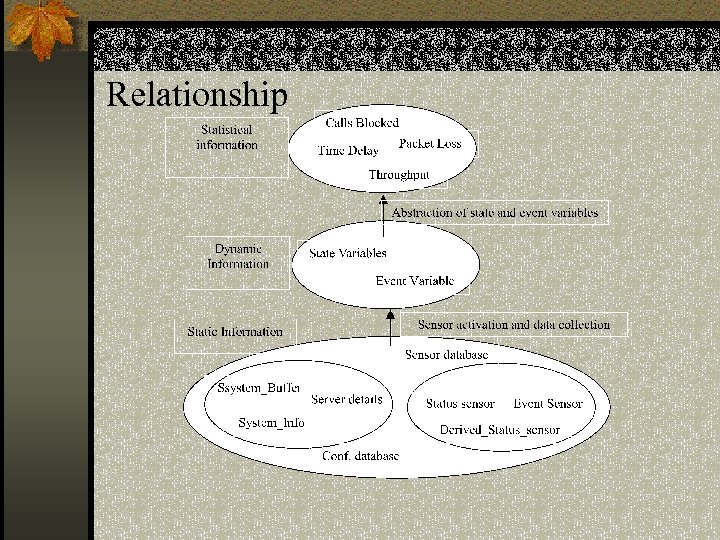 Relationship
Relationship
 Monitoring and Control n Network Control n Modifying parameters and causing actions to be taken by the end systems, intermediate systems, sub-networks
Monitoring and Control n Network Control n Modifying parameters and causing actions to be taken by the end systems, intermediate systems, sub-networks
 Physical and Logical Network management n Physical n Problem detection n Failure notification on n Physical entities – Circuits – Devices – Multiplexers etc
Physical and Logical Network management n Physical n Problem detection n Failure notification on n Physical entities – Circuits – Devices – Multiplexers etc
 Contd. n Logical n Monitoring and management of n Logical Connections n Session awareness n Traffic flow monitoring
Contd. n Logical n Monitoring and management of n Logical Connections n Session awareness n Traffic flow monitoring
 In summary NM n NM is continuing process n Data identification n Extraction n Collection n Maintenance n Analysis n Interpretation n For Control and Management
In summary NM n NM is continuing process n Data identification n Extraction n Collection n Maintenance n Analysis n Interpretation n For Control and Management
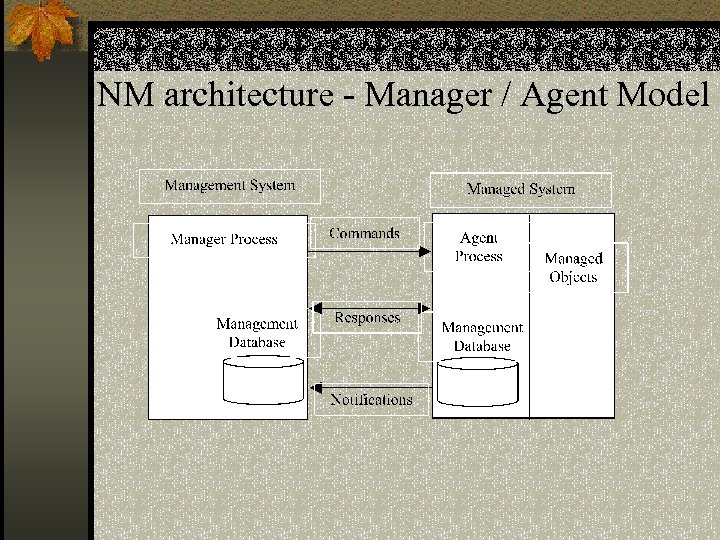 NM architecture - Manager / Agent Model
NM architecture - Manager / Agent Model
 Contd. . n Management System n Houses a Manager Application n Management Database n Manager Application n Interface between Network manager (human) and the devices being managed n Could be GUI based n There could be a number of manager applications and Management Systems
Contd. . n Management System n Houses a Manager Application n Management Database n Manager Application n Interface between Network manager (human) and the devices being managed n Could be GUI based n There could be a number of manager applications and Management Systems
 Contd. . n Managed System n Has the Agent process n Managed Objects n Management Database n Management Information Database n There could be a number of Managed Systems
Contd. . n Managed System n Has the Agent process n Managed Objects n Management Database n Management Information Database n There could be a number of Managed Systems
 Contd. . n Agent Process n Collects statistics on communication and network related activities n Store statistics locally n Respond to commands from network n Transmit collected statistics to network control centre n Change a parameter n Provide status information n Generate artificial traffic pattern to perform a test
Contd. . n Agent Process n Collects statistics on communication and network related activities n Store statistics locally n Respond to commands from network n Transmit collected statistics to network control centre n Change a parameter n Provide status information n Generate artificial traffic pattern to perform a test
 Contd. . n Agent Process n Send messages to the Manager Process when local conditions undergo significant changes n Notifications
Contd. . n Agent Process n Send messages to the Manager Process when local conditions undergo significant changes n Notifications
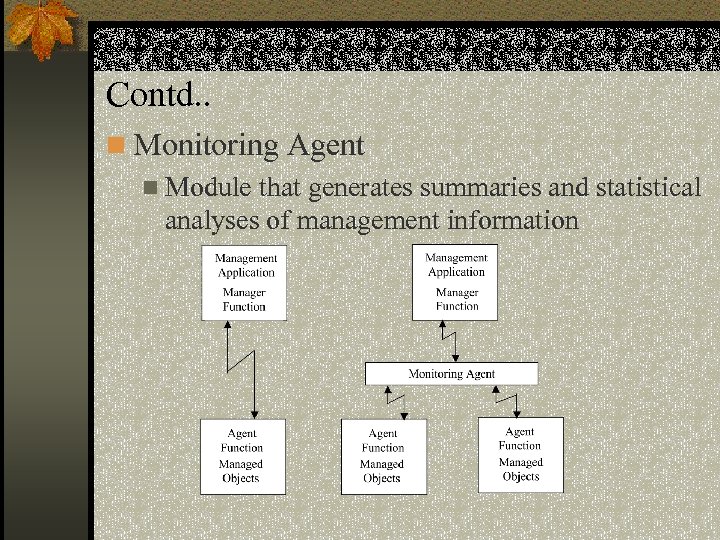 Contd. . n Monitoring Agent n Module that generates summaries and statistical analyses of management information
Contd. . n Monitoring Agent n Module that generates summaries and statistical analyses of management information
 Managed Objects n Entities which need to be monitored and controlled n TCP connection n Packets n Time n CPU n Link
Managed Objects n Entities which need to be monitored and controlled n TCP connection n Packets n Time n CPU n Link
 Management Information Base (MIB) n MIB is a virtual data Information base. It is compiled into the manager and Agent application. It is static n Management database contains the measured values associated with the Managed object. It is dynamic
Management Information Base (MIB) n MIB is a virtual data Information base. It is compiled into the manager and Agent application. It is static n Management database contains the measured values associated with the Managed object. It is dynamic
 MIB structure n Tree structure with root n Branches – managed objects by logical categories n leaves – managed objects
MIB structure n Tree structure with root n Branches – managed objects by logical categories n leaves – managed objects
 Management Protocol n Sets up communication protocol between manager, agents and managed objects n Commands n Responses n Notifications
Management Protocol n Sets up communication protocol between manager, agents and managed objects n Commands n Responses n Notifications
 Techniques of monitoring n Polling n Request-response interaction n Manager queries for variables n Agent responds n Request reports with matching criteria
Techniques of monitoring n Polling n Request-response interaction n Manager queries for variables n Agent responds n Request reports with matching criteria
 Techniques of monitoring n Event Reporting n Agent Initiated n Manager is listener n Periodic Events n On occurrence of significant or unusual event
Techniques of monitoring n Event Reporting n Agent Initiated n Manager is listener n Periodic Events n On occurrence of significant or unusual event
 Polling or Event Reporting n Either or combination n Amount of traffic generated n Robustness in critical situations n Time delay in notification n Amount of processing in managed devices
Polling or Event Reporting n Either or combination n Amount of traffic generated n Robustness in critical situations n Time delay in notification n Amount of processing in managed devices
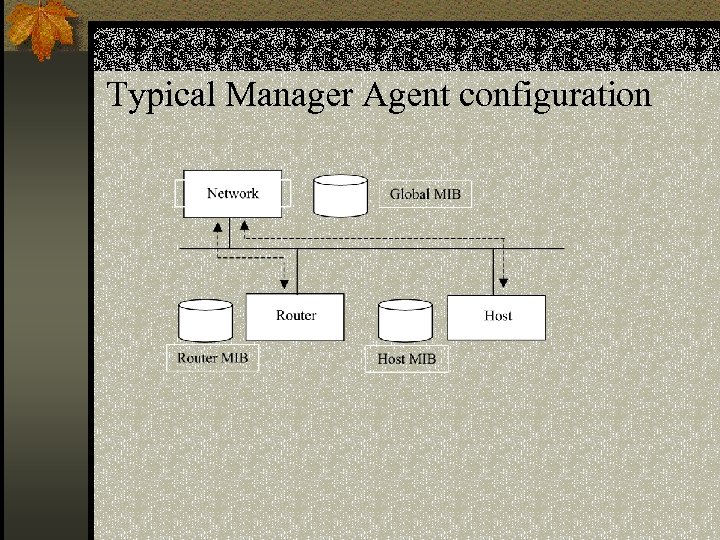 Typical Manager Agent configuration
Typical Manager Agent configuration
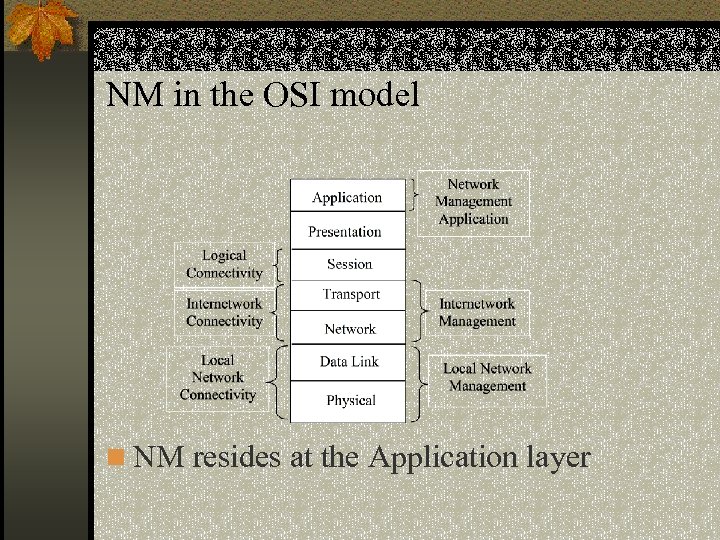 NM in the OSI model n NM resides at the Application layer
NM in the OSI model n NM resides at the Application layer


