7517a95047cb00ebbb32f5d67e3ed9cf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 88
 Network Management and Network Operations I have a network, now what? Abha Ahuja
Network Management and Network Operations I have a network, now what? Abha Ahuja
 Outline What is network management? n Fault Management n • Fault detection and tracking • Basic Network Operations • What are typical network problems? n Other parts of network management ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 2
Outline What is network management? n Fault Management n • Fault detection and tracking • Basic Network Operations • What are typical network problems? n Other parts of network management ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 2
 Outline (con) n Network Management Tools • what do I need? • what is available? • Pros and Cons of various tools n A day in the life of Merit’s NOC ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 3
Outline (con) n Network Management Tools • what do I need? • what is available? • Pros and Cons of various tools n A day in the life of Merit’s NOC ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 3
 Network Management - What is it? Making sure the network is up, running and performing well n Parts of Network Management n • • • fault management performance management security management trouble tracking statistics and accounting ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 4
Network Management - What is it? Making sure the network is up, running and performing well n Parts of Network Management n • • • fault management performance management security management trouble tracking statistics and accounting ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 4
 Who is Merit? Educational and Research Institution based in Michigan, U. S. n Affiliated with University of Michigan n Run State-wide ISP - Mich. Net n • 300+ routers • 24/7 Network Operations Center ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 5
Who is Merit? Educational and Research Institution based in Michigan, U. S. n Affiliated with University of Michigan n Run State-wide ISP - Mich. Net n • 300+ routers • 24/7 Network Operations Center ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 5
 Fault Management one of the most important parts of network management n detect network problems n • transient/persistent • failure/overload – examples: router down, serial link down detect server problems n isolating problems n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 6
Fault Management one of the most important parts of network management n detect network problems n • transient/persistent • failure/overload – examples: router down, serial link down detect server problems n isolating problems n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 6
 Fault Management (con) n reporting mechanism • link to help desk • notify on-call personnel setup & control alarm procedures n repair/recovery procedures n ticket system n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 7
Fault Management (con) n reporting mechanism • link to help desk • notify on-call personnel setup & control alarm procedures n repair/recovery procedures n ticket system n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 7
 Fault Management - Fault Detection n Who notices a problem with the network? • Network Operations Center w/ 24 x 7 operations staff – open trouble ticket to track problem – preliminary troubleshooting – escalate to engineer or call carrier ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 8
Fault Management - Fault Detection n Who notices a problem with the network? • Network Operations Center w/ 24 x 7 operations staff – open trouble ticket to track problem – preliminary troubleshooting – escalate to engineer or call carrier ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 8
 Fault Management Fault Detection (con) n How can you tell if there is a problem with the network? • Network Monitoring Tools – common utilities Õ ping Õ traceroute Õ snmp • Report state or unreachability – detect node down – routing problems ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 9
Fault Management Fault Detection (con) n How can you tell if there is a problem with the network? • Network Monitoring Tools – common utilities Õ ping Õ traceroute Õ snmp • Report state or unreachability – detect node down – routing problems ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 9
 Fault Management Fault Detection (con) • “Alert” shows up for NOC – rover – spectrum – NOCol – HP Openview – other • Other methods – customer complaint via phone/email – another ISP notices problem ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 10
Fault Management Fault Detection (con) • “Alert” shows up for NOC – rover – spectrum – NOCol – HP Openview – other • Other methods – customer complaint via phone/email – another ISP notices problem ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 10
 Fault Detection Example Using Rover n Rover = network monitoring system • http: //www. merit. edu/internet. tools/rover/ Keep it Simple n add nodes and tests to hostfile n run Display to see status n NOC notices alert on board for failed node n • opens ticket • investigates ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 11
Fault Detection Example Using Rover n Rover = network monitoring system • http: //www. merit. edu/internet. tools/rover/ Keep it Simple n add nodes and tests to hostfile n run Display to see status n NOC notices alert on board for failed node n • opens ticket • investigates ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 11
 Fault Management Ticket System (Why all the fuss? ) Very Important! n Need mechanism to track: n • failures • current status of outage • carrier ticket #s ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 12
Fault Management Ticket System (Why all the fuss? ) Very Important! n Need mechanism to track: n • failures • current status of outage • carrier ticket #s ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 12
 Fault Management Ticket Systems (Why all the fuss? ) n system provides for: • • • short term memory & communication scheduling and work assignment referrals and dispatching oversight statistical analysis long term accountability ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 13
Fault Management Ticket Systems (Why all the fuss? ) n system provides for: • • • short term memory & communication scheduling and work assignment referrals and dispatching oversight statistical analysis long term accountability ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 13
 Fault Management Ticket Systems (Why all the fuss? ) Goal: make your NOC the communication and coordination center! n Central repository for all information n • current status • troubleshooting information n Engineers can coordinate their work through the NOC ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 14
Fault Management Ticket Systems (Why all the fuss? ) Goal: make your NOC the communication and coordination center! n Central repository for all information n • current status • troubleshooting information n Engineers can coordinate their work through the NOC ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 14
 Fault Management - Ticket Usage create a ticket on ALL calls n create a ticket on ALL problems n create a ticket for ALL scheduled events n copy of ticket mailed to reporter and mailing list(s) n all milestones in resolution of problem create a new ticket entry with reference to original n ticket stays "open" until problem resolved according to problem reporter n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 15
Fault Management - Ticket Usage create a ticket on ALL calls n create a ticket on ALL problems n create a ticket for ALL scheduled events n copy of ticket mailed to reporter and mailing list(s) n all milestones in resolution of problem create a new ticket entry with reference to original n ticket stays "open" until problem resolved according to problem reporter n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 15
 Fault Management - Ticket Example n sample opening ticket TT 0000033975 has been OPENED. Here is the trouble ticket contents: Create-date : 06/09/99 12: 46: 42 Ticket ID : TT 0000033975 Node + : rs 2. mae-west. rsng. net Equipment Type : host NOC Customer : RA Trouble Reported : Unreachable Next Action : Investigate Next Action Date : 06/09/99 12: 46: 42 Outage type : unscheduled Source of Report : Noc/rover. Status Assigned-to : Noc Contact Name : rsng Group Member : Contact pager#/email address : Contact Phone : . Carrier Ticket History : Carrier Phone : Ticket information log : 06/09/99 12: 46: 42 noc-op toppingb@facesofdeath. ns. itd. umich. edu said. . . : 11 Wed 12: 23 rs 2 MW_O/C 198. 32. 136. 2 PING ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 16
Fault Management - Ticket Example n sample opening ticket TT 0000033975 has been OPENED. Here is the trouble ticket contents: Create-date : 06/09/99 12: 46: 42 Ticket ID : TT 0000033975 Node + : rs 2. mae-west. rsng. net Equipment Type : host NOC Customer : RA Trouble Reported : Unreachable Next Action : Investigate Next Action Date : 06/09/99 12: 46: 42 Outage type : unscheduled Source of Report : Noc/rover. Status Assigned-to : Noc Contact Name : rsng Group Member : Contact pager#/email address : Contact Phone : . Carrier Ticket History : Carrier Phone : Ticket information log : 06/09/99 12: 46: 42 noc-op toppingb@facesofdeath. ns. itd. umich. edu said. . . : 11 Wed 12: 23 rs 2 MW_O/C 198. 32. 136. 2 PING ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 16
 Fault Management - Ticket Example n sample progress ticket TT 0000033975 has been MODIFIED. changed: Here are the fields that have been Copy. Of. Time : 5 TTC Temp : 0 Ticket information log : toppingb@facesofdeath. ns. itd. umich. edu said. . . While I was investigating this, Debbie from UUNet called (via Merit main number) to tell us they were seeing it down. She can be reached at xxx-xxxx. The UUNet ticket is xxxxx. . ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 17
Fault Management - Ticket Example n sample progress ticket TT 0000033975 has been MODIFIED. changed: Here are the fields that have been Copy. Of. Time : 5 TTC Temp : 0 Ticket information log : toppingb@facesofdeath. ns. itd. umich. edu said. . . While I was investigating this, Debbie from UUNet called (via Merit main number) to tell us they were seeing it down. She can be reached at xxx-xxxx. The UUNet ticket is xxxxx. . ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 17
 Fault Management - Ticket Example n sample closing ticket • includes previous ticket contents plus resolution T 0000033975 has been CLOSED. Here is the trouble ticket contents: 01/15/99 12: 50: 06 noc-op mgf@wonka. ns. itd. umich. edu said. . . Email response from Abha suggesting contacting peers directly -- see internal log. 01/15/99 14: 25: 22 noc-op aubinc@augustus 2. ns. itd. umich. edu said. . . The alerts cleared shortly before 14: 00. I called MCI/Worldcom for an update, and found out their ticket was closed. According to them the outage was due solely to a power problem. Closing. Last-modified-by Modified-date Submitter ahuja@merit. edu : noc-op : 01/15/99 14: 25: 22 : btracy Network Management and Network Operations 18
Fault Management - Ticket Example n sample closing ticket • includes previous ticket contents plus resolution T 0000033975 has been CLOSED. Here is the trouble ticket contents: 01/15/99 12: 50: 06 noc-op mgf@wonka. ns. itd. umich. edu said. . . Email response from Abha suggesting contacting peers directly -- see internal log. 01/15/99 14: 25: 22 noc-op aubinc@augustus 2. ns. itd. umich. edu said. . . The alerts cleared shortly before 14: 00. I called MCI/Worldcom for an update, and found out their ticket was closed. According to them the outage was due solely to a power problem. Closing. Last-modified-by Modified-date Submitter ahuja@merit. edu : noc-op : 01/15/99 14: 25: 22 : btracy Network Management and Network Operations 18
 Fault Management - typical failures n Node unpingable • no ip connectivity to router • possible reasons: – serial link down Õ telco call – router down/hardware problem Õ engineer call – routing problem Õ troubleshoot with traceroute Õ routeviews machine ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 19
Fault Management - typical failures n Node unpingable • no ip connectivity to router • possible reasons: – serial link down Õ telco call – router down/hardware problem Õ engineer call – routing problem Õ troubleshoot with traceroute Õ routeviews machine ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 19
 Performance Management evaluate the behavior of network elements n information used in planning n – interface stats – throughput – error rates – software stats – usage – queues – system load – disk space – percent availability ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 20
Performance Management evaluate the behavior of network elements n information used in planning n – interface stats – throughput – error rates – software stats – usage – queues – system load – disk space – percent availability ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 20
 Security Management tends to be host-based n protect your stats, data and NOC info n protect other services n security required to operate network and protect managed objects n security services n • Kerberos • PGP key server • secure time ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 21
Security Management tends to be host-based n protect your stats, data and NOC info n protect other services n security required to operate network and protect managed objects n security services n • Kerberos • PGP key server • secure time ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 21
 Security Management (con) n security tools • • • n cops - host configuration checker (www. cert. org) swatch - email reports of activity on machine tcpwrappers ssh/skey tripwire distribute security information • bug reports – CERT advisories • bug fixes • intruder alerts ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 22
Security Management (con) n security tools • • • n cops - host configuration checker (www. cert. org) swatch - email reports of activity on machine tcpwrappers ssh/skey tripwire distribute security information • bug reports – CERT advisories • bug fixes • intruder alerts ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 22
 Security Management (con) n reporting procedure for security events • e. g. break-ins • abuse email address for customers to report complaints (abuse@your-isp. net) n control internal and external gateways • control firewalls (external and internal) security logs n privacy issues a conflict n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 23
Security Management (con) n reporting procedure for security events • e. g. break-ins • abuse email address for customers to report complaints (abuse@your-isp. net) n control internal and external gateways • control firewalls (external and internal) security logs n privacy issues a conflict n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 23
 Security Management n Network based security • Types of attacks – DOS - Denial of Service Õ ping floods Õ smurf Õ attacks that make your network unusable – Spoofing Õ packets with “spoofed” source address ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 24
Security Management n Network based security • Types of attacks – DOS - Denial of Service Õ ping floods Õ smurf Õ attacks that make your network unusable – Spoofing Õ packets with “spoofed” source address ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 24
 What types of problems? Blocking and tracing denial of service attacks n Tracing incoming forged packets back to their source n Blocking outgoing forged packets n Most other security problems are not specific to backbone operators n Deal with complaints n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 25
What types of problems? Blocking and tracing denial of service attacks n Tracing incoming forged packets back to their source n Blocking outgoing forged packets n Most other security problems are not specific to backbone operators n Deal with complaints n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 25
 smurf n attacker sends many ping request packets: • from forged (victim) source address • to broadcast address on “amplifier” network many ping responses from systems on amplifier network n attacker on dialup modem can saturate victim’s T 1 using a T 3 -connected amplifier n http: //users. quadrunner. com/chuegen/smurf/ n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 26
smurf n attacker sends many ping request packets: • from forged (victim) source address • to broadcast address on “amplifier” network many ping responses from systems on amplifier network n attacker on dialup modem can saturate victim’s T 1 using a T 3 -connected amplifier n http: //users. quadrunner. com/chuegen/smurf/ n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 26
 Protection against smurf n configure “no directed-broadcast” on all interfaces • so you can’t be used as an amplifier trace forged packets back, hop by hop n block outgoing forged packets from your customers n limit the bandwidth that can be used by ICMP traffic n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 27
Protection against smurf n configure “no directed-broadcast” on all interfaces • so you can’t be used as an amplifier trace forged packets back, hop by hop n block outgoing forged packets from your customers n limit the bandwidth that can be used by ICMP traffic n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 27
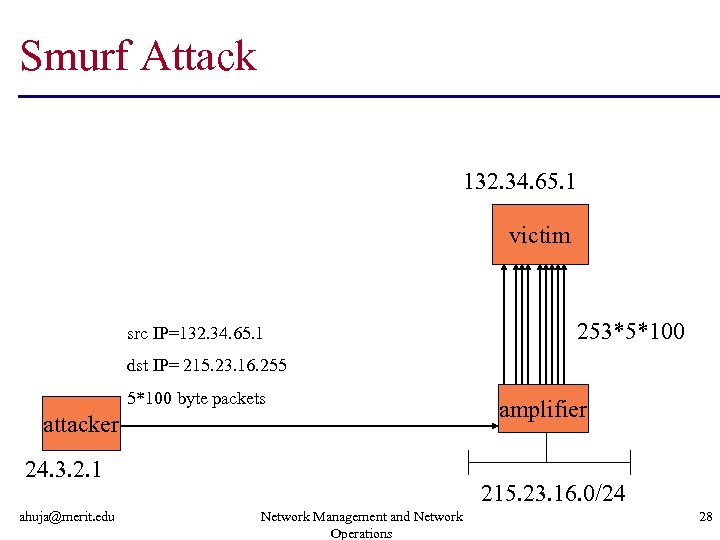 Smurf Attack 132. 34. 65. 1 victim src IP=132. 34. 65. 1 253*5*100 dst IP= 215. 23. 16. 255 5*100 byte packets attacker 24. 3. 2. 1 ahuja@merit. edu amplifier 215. 23. 16. 0/24 Network Management and Network Operations 28
Smurf Attack 132. 34. 65. 1 victim src IP=132. 34. 65. 1 253*5*100 dst IP= 215. 23. 16. 255 5*100 byte packets attacker 24. 3. 2. 1 ahuja@merit. edu amplifier 215. 23. 16. 0/24 Network Management and Network Operations 28
 SYN flooding attacker sends many TCP SYN packet from forged source address n victim sends SYN+ACK packets to invalid address n • gets no response • connection hangs in half open state • wastes OS resources, possibly crashing system ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 29
SYN flooding attacker sends many TCP SYN packet from forged source address n victim sends SYN+ACK packets to invalid address n • gets no response • connection hangs in half open state • wastes OS resources, possibly crashing system ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 29
 Protection against SYN flooding n Make operating system more robust • not a backbone problem, except on routers Trace and block forged packets n Limit bandwidth that can be used by TCP SYN traffic n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 30
Protection against SYN flooding n Make operating system more robust • not a backbone problem, except on routers Trace and block forged packets n Limit bandwidth that can be used by TCP SYN traffic n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 30
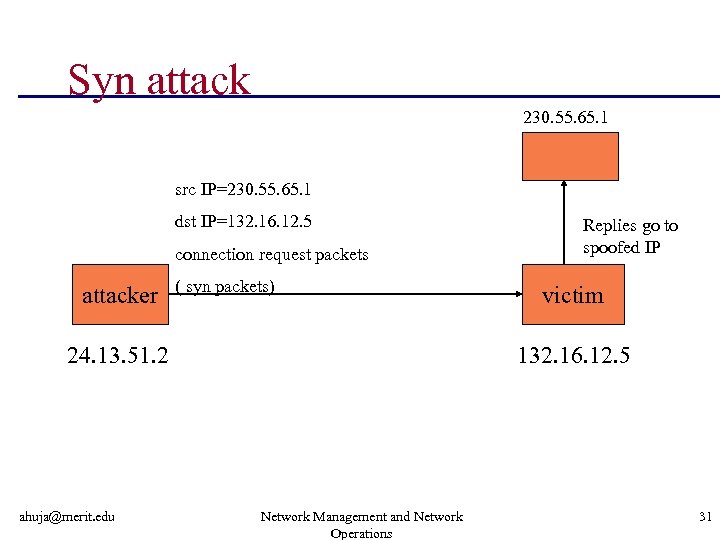 Syn attack 230. 55. 65. 1 src IP=230. 55. 65. 1 dst IP=132. 16. 12. 5 connection request packets attacker ( syn packets) 24. 13. 51. 2 ahuja@merit. edu Replies go to spoofed IP victim 132. 16. 12. 5 Network Management and Network Operations 31
Syn attack 230. 55. 65. 1 src IP=230. 55. 65. 1 dst IP=132. 16. 12. 5 connection request packets attacker ( syn packets) 24. 13. 51. 2 ahuja@merit. edu Replies go to spoofed IP victim 132. 16. 12. 5 Network Management and Network Operations 31
 Notice a pattern? Forged packets n Need a way of preventing customers from sending forged packets n Need a way of tracing where forged packets really come from n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 32
Notice a pattern? Forged packets n Need a way of preventing customers from sending forged packets n Need a way of tracing where forged packets really come from n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 32
 Tracing forged packets Start on router near victim n Find how packets get to that router n Repeat on next router n Continue until edge of your AS n Ask next AS to trace further n Need cooperation n IMPORTANT - Should have a 24 hour security contact! n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 33
Tracing forged packets Start on router near victim n Find how packets get to that router n Repeat on next router n Continue until edge of your AS n Ask next AS to trace further n Need cooperation n IMPORTANT - Should have a 24 hour security contact! n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 33
 Security Management n Protecting your network • traffic shapers – use CAR to limit ICMP traffic • anti-spoofing filters – RFC 2267 (Network Ingress Filtering) – for singly-homed customers ÕIF packet's source address from within your network ÕTHEN forward as appropriate ÕIF packet's source address is anything else ÕTHEN deny packet – Filter on the outbound ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 34
Security Management n Protecting your network • traffic shapers – use CAR to limit ICMP traffic • anti-spoofing filters – RFC 2267 (Network Ingress Filtering) – for singly-homed customers ÕIF packet's source address from within your network ÕTHEN forward as appropriate ÕIF packet's source address is anything else ÕTHEN deny packet – Filter on the outbound ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 34
 Preventing forged packets from customers packet filters! n you know what IP addresses are used (at east for dialup and statically routed customers) n make a filter for each customer that denies other source addresses n very recent cisco code has “ip verify sourceaddress” n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 35
Preventing forged packets from customers packet filters! n you know what IP addresses are used (at east for dialup and statically routed customers) n make a filter for each customer that denies other source addresses n very recent cisco code has “ip verify sourceaddress” n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 35
 Preventing forged packets from you to outside world n you might know all the IP addresses that are used in your AS • if your connections to the outside world and your transit arrangements are not too complicated make a filter that denies other source addresses n apply that filter to all links from you to other Ases n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 36
Preventing forged packets from you to outside world n you might know all the IP addresses that are used in your AS • if your connections to the outside world and your transit arrangements are not too complicated make a filter that denies other source addresses n apply that filter to all links from you to other Ases n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 36
 Configuration and Name Management n track network vitals • ip addresses, interfaces, console phone numbers, etc NOC needs valid contact info for nodes n network state information n • network topology • operation status of network elements – including resources • network element configuration ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 37
Configuration and Name Management n track network vitals • ip addresses, interfaces, console phone numbers, etc NOC needs valid contact info for nodes n network state information n • network topology • operation status of network elements – including resources • network element configuration ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 37
 Configuration and Name Management n control network elements • start/stop • modification of network attributes • addition of new features n configuration modification • allocation and addition of network resources • reconfiguration if dictated by link outages ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 38
Configuration and Name Management n control network elements • start/stop • modification of network attributes • addition of new features n configuration modification • allocation and addition of network resources • reconfiguration if dictated by link outages ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 38
 Configuration and Name Management n inventory management • database of network elements • history of changes & problems n directory maintenance • all hosts & applications • nameserver database n host and service naming coordination • "Information is not information if you can't find it" ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 39
Configuration and Name Management n inventory management • database of network elements • history of changes & problems n directory maintenance • all hosts & applications • nameserver database n host and service naming coordination • "Information is not information if you can't find it" ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 39
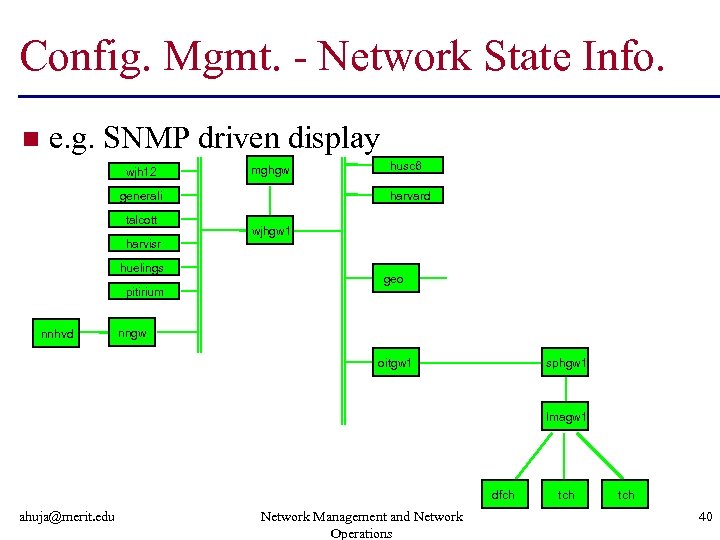 Config. Mgmt. - Network State Info. n e. g. SNMP driven display wjh 12 mghgw generali talcott harvisr huelings pitirium nnhvd husc 6 harvard wjhgw 1 geo nngw oitgw 1 sphgw 1 lmagw 1 dfch ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations tch 40
Config. Mgmt. - Network State Info. n e. g. SNMP driven display wjh 12 mghgw generali talcott harvisr huelings pitirium nnhvd husc 6 harvard wjhgw 1 geo nngw oitgw 1 sphgw 1 lmagw 1 dfch ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations tch 40
 Network Management Tools many use SNMP n ping n traceroute n References: n • • • MON - http: //www. kernel. org/software/mon/ NOCol - ftp: //ftp. navya. com/pub/vikas/nocol. tar. gz Sysmon - ftp: //puck. nether. net/pub/jared Rover - http: //www. merit. edu/~rover Concord - http: //www. concord. com ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 41
Network Management Tools many use SNMP n ping n traceroute n References: n • • • MON - http: //www. kernel. org/software/mon/ NOCol - ftp: //ftp. navya. com/pub/vikas/nocol. tar. gz Sysmon - ftp: //puck. nether. net/pub/jared Rover - http: //www. merit. edu/~rover Concord - http: //www. concord. com ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 41
 What is SNMP? (the quick version. . . ) Simple Network Management Protocol n query - response system n • can obtain status from a device • standard queries • enterprise specific n uses database defined in MIB • management information base ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 42
What is SNMP? (the quick version. . . ) Simple Network Management Protocol n query - response system n • can obtain status from a device • standard queries • enterprise specific n uses database defined in MIB • management information base ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 42
 What do we use SNMP for? n query routers for: • • n in and out bytes per second CPU load uptime BGP peer session status query hosts for: • network status ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 43
What do we use SNMP for? n query routers for: • • n in and out bytes per second CPU load uptime BGP peer session status query hosts for: • network status ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 43
 SNMP Network Management Tools n mrtg (http//: www. ee. ethz. ch/~oetiker/webtools/mrtg • why we like it – simple to use and configure – quickly determine spikes/drops in traffic Õ ping floods n • in/out bps • uptime • supplement to monitoring tools http: //israel. t 1. isocws. isoc. org/mrtg/7200 ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 44
SNMP Network Management Tools n mrtg (http//: www. ee. ethz. ch/~oetiker/webtools/mrtg • why we like it – simple to use and configure – quickly determine spikes/drops in traffic Õ ping floods n • in/out bps • uptime • supplement to monitoring tools http: //israel. t 1. isocws. isoc. org/mrtg/7200 ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 44
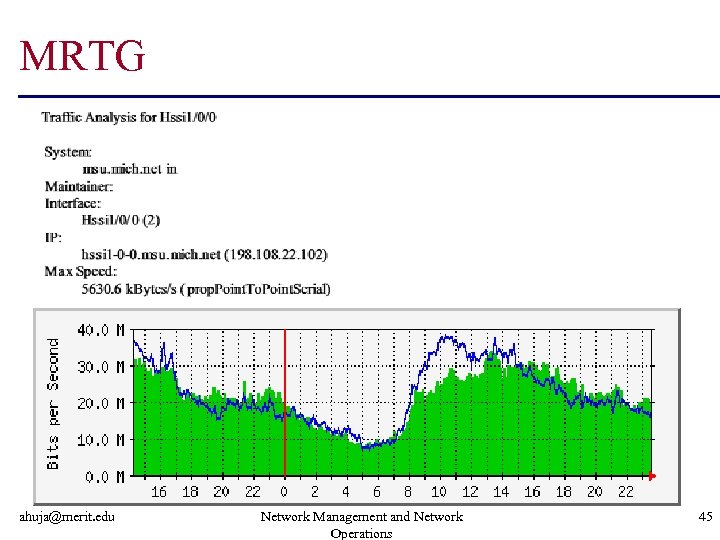 MRTG ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 45
MRTG ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 45
 Spectrum commercial package n Used by various networks n configurable alarms n GUI interface - view network topology n auto-discovery n difficult to use n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 46
Spectrum commercial package n Used by various networks n configurable alarms n GUI interface - view network topology n auto-discovery n difficult to use n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 46
 Netscarf/Scion free n snmp collector and analyzer package n • collects snmp data • display on web pages n http: //www. merit. net/~netscarf ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 47
Netscarf/Scion free n snmp collector and analyzer package n • collects snmp data • display on web pages n http: //www. merit. net/~netscarf ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 47
 Other Network Tools n netflow • • cflowd (http: //www. caida. org/Tools/Cflowd) collects flow information from cisco routers AS to AS information src and destination ip and port information useful for accounting and statistics how much of my traffic is port 80? how much of my traffic goes to AS 237? ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 48
Other Network Tools n netflow • • cflowd (http: //www. caida. org/Tools/Cflowd) collects flow information from cisco routers AS to AS information src and destination ip and port information useful for accounting and statistics how much of my traffic is port 80? how much of my traffic goes to AS 237? ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 48
 Netflow examples n Top ten lists (or top five) ##### Top 5 AS's based on number of bytes ####### src. AS dst. AS pkts bytes 6461 237 4473872 3808572766 237 22977795 3180337999 3549 237 6457673 2816009078 2548 237 5215912 2457515319 ##### Top 5 Nets based on number of bytes ###### Net Matrix -----number of net entries: 931777 SRCNET/MASK DSTNET/MASK PKTS 165. 123. 0. 0/16 35. 8. 0. 0/13 745858 207. 126. 96. 0/19 198. 108. 98. 0/24 708205 206. 183. 224. 0/19 198. 108. 16. 0/22 740218 35. 8. 0. 0/13 128. 32. 0. 0/16 671980 ##### Top 10 Ports ####### input port packets bytes 119 10863322 2808194019 80 36073210 862839291 20 1079075 1100961902 7648 1146864 419882753 25 1532439 97294492 ahuja@merit. edu BYTES 1036296098 907577874 861538792 467274801 output packets bytes 5712783 427304556 17312202 1387817094 614910 62754268 1147081 414663212 2158042 722584770 Network Management and Network Operations 49
Netflow examples n Top ten lists (or top five) ##### Top 5 AS's based on number of bytes ####### src. AS dst. AS pkts bytes 6461 237 4473872 3808572766 237 22977795 3180337999 3549 237 6457673 2816009078 2548 237 5215912 2457515319 ##### Top 5 Nets based on number of bytes ###### Net Matrix -----number of net entries: 931777 SRCNET/MASK DSTNET/MASK PKTS 165. 123. 0. 0/16 35. 8. 0. 0/13 745858 207. 126. 96. 0/19 198. 108. 98. 0/24 708205 206. 183. 224. 0/19 198. 108. 16. 0/22 740218 35. 8. 0. 0/13 128. 32. 0. 0/16 671980 ##### Top 10 Ports ####### input port packets bytes 119 10863322 2808194019 80 36073210 862839291 20 1079075 1100961902 7648 1146864 419882753 25 1532439 97294492 ahuja@merit. edu BYTES 1036296098 907577874 861538792 467274801 output packets bytes 5712783 427304556 17312202 1387817094 614910 62754268 1147081 414663212 2158042 722584770 Network Management and Network Operations 49
 More Tools! n http: //www. caida. org/Tools/ • OC 3 Mon/Coral n http: //www. merit. edu/~ipma • Route. Tracker • IRRj • ASExplorer http: //www. geektools. com/ n http: //www. merit. edu/ipma/tools/other. html n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 50
More Tools! n http: //www. caida. org/Tools/ • OC 3 Mon/Coral n http: //www. merit. edu/~ipma • Route. Tracker • IRRj • ASExplorer http: //www. geektools. com/ n http: //www. merit. edu/ipma/tools/other. html n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 50
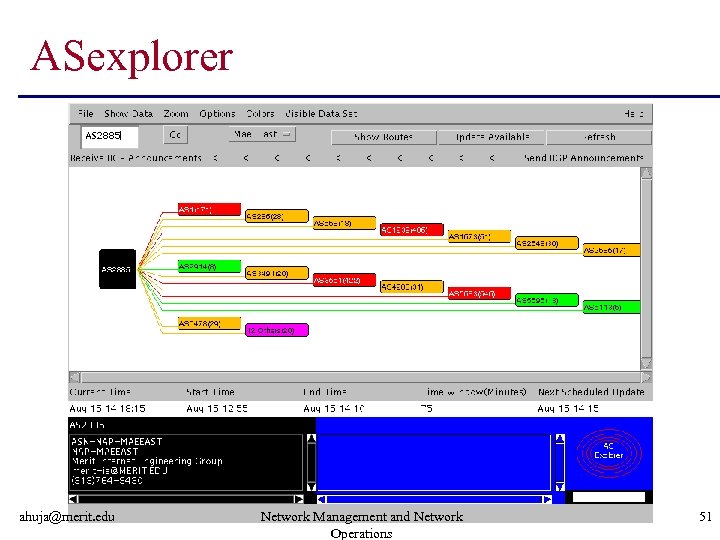 ASexplorer ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 51
ASexplorer ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 51
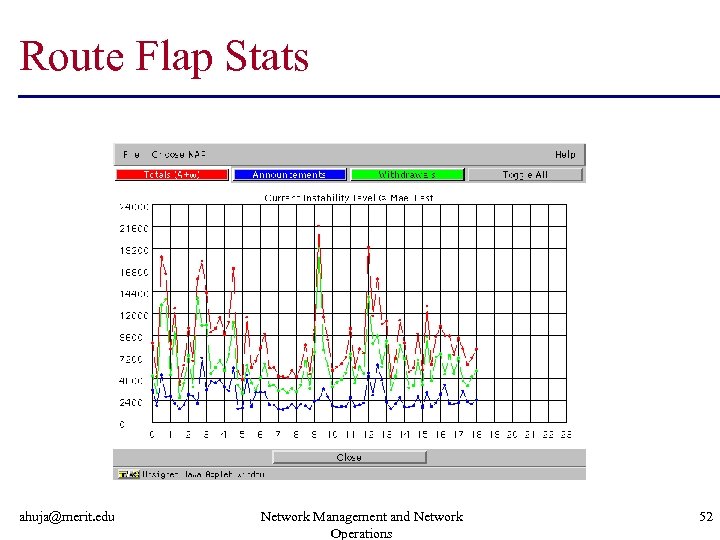 Route Flap Stats ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 52
Route Flap Stats ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 52
 Looking Glass Tools n http: //www. merit. edu/~ipma/tools/lookingglass. html route-views. oregon-ix. net>show ip bgp 35. 0. 0. 0 BGP routing table entry for 35. 0. 0. 0/8, version 56135569 Paths: (17 available, best #12) 11537 237 198. 32. 8. 252 from 198. 32. 8. 252 Origin incomplete, localpref 100, valid, external Community: 11537: 900 11537: 950 2914 5696 237 129. 250. 0. 3 (inaccessible) from 129. 250. 0. 3 Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external Community: 2914: 420 2914 5696 237 129. 250. 0. 1 (inaccessible) from 129. 250. 0. 1 Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external Community: 2914: 420 3561 237 237 204. 70. 4. 89 from 204. 70. 4. 89 Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external 267 1225 237 204. 42. 253 from 204. 42. 253 Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external Community: 267: 1225: 237 ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 53
Looking Glass Tools n http: //www. merit. edu/~ipma/tools/lookingglass. html route-views. oregon-ix. net>show ip bgp 35. 0. 0. 0 BGP routing table entry for 35. 0. 0. 0/8, version 56135569 Paths: (17 available, best #12) 11537 237 198. 32. 8. 252 from 198. 32. 8. 252 Origin incomplete, localpref 100, valid, external Community: 11537: 900 11537: 950 2914 5696 237 129. 250. 0. 3 (inaccessible) from 129. 250. 0. 3 Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external Community: 2914: 420 2914 5696 237 129. 250. 0. 1 (inaccessible) from 129. 250. 0. 1 Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external Community: 2914: 420 3561 237 237 204. 70. 4. 89 from 204. 70. 4. 89 Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external 267 1225 237 204. 42. 253 from 204. 42. 253 Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external Community: 267: 1225: 237 ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 53
 More Looking Glass Tools Traceroute servers n http: //www. merit. edu/ipma/tools/trace. html n Query: trace Addr : www. isoc. org Translating "www. isoc. org". . . domain server (206. 205. 242. 132) [OK] Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to info. isoc. org (198. 6. 250. 9) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 iad 1 -core 2 -fa 5 -0 -0. atlas. digex. net (165. 117. 129. 2) 0 msec 4 msec dca 5 -core 2 -s 5 -0 -0. atlas. digex. net (165. 117. 53. 41) 0 msec 4 msec 0 msec dca 5 -core 1 -fa 5 -1 -0. atlas. digex. net (165. 117. 56. 117) 4 msec 0 msec 4 msec Hssi 3 -1 -0. BR 1. DCA 1. ALTER. NET (209. 116. 159. 98) 0 msec 4 msec 101. ATM 2 -0. XR 1. DCA 1. ALTER. NET (146. 188. 160. 226) [AS 701] 4 msec 0 msec 4 msec 195. ATM 7 -0. XR 1. TCO 1. ALTER. NET (146. 188. 160. 102) [AS 701] 4 msec 0 msec 193. ATM 8 -0 -0. GW 1. TCO 1. ALTER. NET (146. 188. 160. 33) [AS 701] 4 msec charlie. isoc. org (198. 6. 250. 1) [AS 701] 8 msec info. isoc. org (198. 6. 250. 9) [AS 701] 8 msec * 12 msec ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 54
More Looking Glass Tools Traceroute servers n http: //www. merit. edu/ipma/tools/trace. html n Query: trace Addr : www. isoc. org Translating "www. isoc. org". . . domain server (206. 205. 242. 132) [OK] Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to info. isoc. org (198. 6. 250. 9) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 iad 1 -core 2 -fa 5 -0 -0. atlas. digex. net (165. 117. 129. 2) 0 msec 4 msec dca 5 -core 2 -s 5 -0 -0. atlas. digex. net (165. 117. 53. 41) 0 msec 4 msec 0 msec dca 5 -core 1 -fa 5 -1 -0. atlas. digex. net (165. 117. 56. 117) 4 msec 0 msec 4 msec Hssi 3 -1 -0. BR 1. DCA 1. ALTER. NET (209. 116. 159. 98) 0 msec 4 msec 101. ATM 2 -0. XR 1. DCA 1. ALTER. NET (146. 188. 160. 226) [AS 701] 4 msec 0 msec 4 msec 195. ATM 7 -0. XR 1. TCO 1. ALTER. NET (146. 188. 160. 102) [AS 701] 4 msec 0 msec 193. ATM 8 -0 -0. GW 1. TCO 1. ALTER. NET (146. 188. 160. 33) [AS 701] 4 msec charlie. isoc. org (198. 6. 250. 1) [AS 701] 8 msec info. isoc. org (198. 6. 250. 9) [AS 701] 8 msec * 12 msec ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 54
 Accounting Management what do you account for? n if you count packets sent n • it can inhibit anonymous ftp & web sites • Qo. S differences in the future n want to charge "user" of service • application dependent determination of "user" n if count hosts • is a PC equal to a mainframe? • cost? ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 55
Accounting Management what do you account for? n if you count packets sent n • it can inhibit anonymous ftp & web sites • Qo. S differences in the future n want to charge "user" of service • application dependent determination of "user" n if count hosts • is a PC equal to a mainframe? • cost? ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 55
 Accounting, Cont. usage-based billing may become common as telcos take over Internet service providers n when "little provider" meets "big provider”, Qo. S. . . n fred's bits to go MCI UNET NAP PSI SPRINT ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 56
Accounting, Cont. usage-based billing may become common as telcos take over Internet service providers n when "little provider" meets "big provider”, Qo. S. . . n fred's bits to go MCI UNET NAP PSI SPRINT ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 56
 getoctets simple traffic stats collector n cron-driven shell procedure n • get-octets router 1 router 2 router 3 • figures out interface list for each router n then gets • if. In. Octets, if. Out. Octets, if. In. Ucast. Pkts, if. Out. Ucast. Pkts • if. In. NUcast. Pkts, if. Out. NUcast. Pkts, system. sys. Up. Time n ftp: //ndtl. harvard. edu/pub/SNMPoll/octets. tar • needs cmu snmp package ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 57
getoctets simple traffic stats collector n cron-driven shell procedure n • get-octets router 1 router 2 router 3 • figures out interface list for each router n then gets • if. In. Octets, if. Out. Octets, if. In. Ucast. Pkts, if. Out. Ucast. Pkts • if. In. NUcast. Pkts, if. Out. NUcast. Pkts, system. sys. Up. Time n ftp: //ndtl. harvard. edu/pub/SNMPoll/octets. tar • needs cmu snmp package ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 57
 getoctets, contd. n makes separate stats file for each interface • example filename: 128. 103. 1. 2. WJHgw 1 n example data 1997, 06, 23, 160, 09, 1, 00, 02, 37, EDT, 1764089502, 1045789221, 99138769, 92200835, 10, 628226, 758006814 1997, 06, 23, 160, 09, 1, 00, 22, 37, EDT, 1766362487, 1047093977, 99151676, 92213338, 10, 628281, 758126831 1997, 06, 23, 160, 09, 1, 00, 42, 36, EDT, 1768439726, 1048266407, 99163118, 92224546, 10, 628342, 758246748 n processing a bit hard • must deal with counter wrap & router reboots • sample period must be < 59 min for an Ethernet n link utilization calculation complex • must include link encapsulation etc ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 58
getoctets, contd. n makes separate stats file for each interface • example filename: 128. 103. 1. 2. WJHgw 1 n example data 1997, 06, 23, 160, 09, 1, 00, 02, 37, EDT, 1764089502, 1045789221, 99138769, 92200835, 10, 628226, 758006814 1997, 06, 23, 160, 09, 1, 00, 22, 37, EDT, 1766362487, 1047093977, 99151676, 92213338, 10, 628281, 758126831 1997, 06, 23, 160, 09, 1, 00, 42, 36, EDT, 1768439726, 1048266407, 99163118, 92224546, 10, 628342, 758246748 n processing a bit hard • must deal with counter wrap & router reboots • sample period must be < 59 min for an Ethernet n link utilization calculation complex • must include link encapsulation etc ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 58
 getoctets, processing n Up. Date routine • bug in 32 bit versions of perl (gives bad results) n example output week ending 1997. 06. 01 ahuja@merit. edu millions of bits per second peak in peak out 95% in 95% out 5. 0976 0. 9330 1. 3389 0. 4104 Network Management and Network Operations millions of octets in out total 18782 13752 32534 59
getoctets, processing n Up. Date routine • bug in 32 bit versions of perl (gives bad results) n example output week ending 1997. 06. 01 ahuja@merit. edu millions of bits per second peak in peak out 95% in 95% out 5. 0976 0. 9330 1. 3389 0. 4104 Network Management and Network Operations millions of octets in out total 18782 13752 32534 59
 Accounting, Cont. usage-based billing may become common as telcos take over Internet service providers n when "little provider" meets "big provider”, Qo. S. . . n fred's bits to go MCI UNET NAP PSI SPRINT ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 60
Accounting, Cont. usage-based billing may become common as telcos take over Internet service providers n when "little provider" meets "big provider”, Qo. S. . . n fred's bits to go MCI UNET NAP PSI SPRINT ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 60
 Accounting, Cont. n could do settlements based in routing information • try to minimize size of routing tables n Telco model • everyone shares in revenue • call an 800 number from a pay phone – 800 destinations pay phone owner • receive a long distance call to your own switch – you get free for local delivery ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 61
Accounting, Cont. n could do settlements based in routing information • try to minimize size of routing tables n Telco model • everyone shares in revenue • call an 800 number from a pay phone – 800 destinations pay phone owner • receive a long distance call to your own switch – you get free for local delivery ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 61
 Importance of Network Statistics Accounting n Troubleshooting n Long-term trend analysis n Capacity Planning n Two different types n • active measurement • passive measurement n Management Tools have statistical functionality ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 62
Importance of Network Statistics Accounting n Troubleshooting n Long-term trend analysis n Capacity Planning n Two different types n • active measurement • passive measurement n Management Tools have statistical functionality ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 62
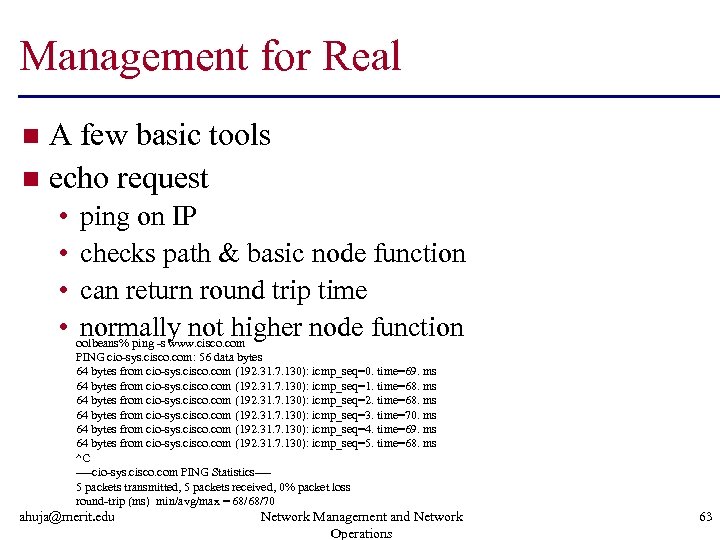 Management for Real A few basic tools n echo request n • • ping on IP checks path & basic node function can return round trip time normally not higher node function oolbeans% ping -s www. cisco. com PING cio-sys. cisco. com: 56 data bytes 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=0. time=69. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=1. time=68. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=2. time=68. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=3. time=70. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=4. time=69. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=5. time=68. ms ^C ----cio-sys. cisco. com PING Statistics---5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 68/68/70 ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 63
Management for Real A few basic tools n echo request n • • ping on IP checks path & basic node function can return round trip time normally not higher node function oolbeans% ping -s www. cisco. com PING cio-sys. cisco. com: 56 data bytes 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=0. time=69. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=1. time=68. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=2. time=68. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=3. time=70. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=4. time=69. ms 64 bytes from cio-sys. cisco. com (192. 31. 7. 130): icmp_seq=5. time=68. ms ^C ----cio-sys. cisco. com PING Statistics---5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 68/68/70 ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 63
 Management for Real, Cont. n traceroute - finds path to node with delays • detect reachability • detect routing problems – example of routing loop (next slide) ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 64
Management for Real, Cont. n traceroute - finds path to node with delays • detect reachability • detect routing problems – example of routing loop (next slide) ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 64
![dfalk@unagi [Thu 15: 07] 5 /usr/home/jdfalk>traceroute -m 255 www. monkeys. com traceroute to www. dfalk@unagi [Thu 15: 07] 5 /usr/home/jdfalk>traceroute -m 255 www. monkeys. com traceroute to www.](https://present5.com/presentation/7517a95047cb00ebbb32f5d67e3ed9cf/image-65.jpg) dfalk@unagi [Thu 15: 07] 5 /usr/home/jdfalk>traceroute -m 255 www. monkeys. com traceroute to www. monkeys. com (207. 212. 142. 41), 255 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 thermal-detonator. explosive. net (209. 133. 38. 1) 3. 428 ms 2. 032 ms 2. 915 ms 2 explosive-gate. bungi. com (207. 126. 96. 81) 14. 158 ms 6. 082 ms 6. 239 ms 3 above-gw 1. above. net (207. 126. 96. 249) 18. 889 ms 23. 423 ms 13. 275 ms 4 core 2 -main. sjc. above. net (207. 126. 96. 133) 20. 749 ms 22. 295 ms 26. 260 ms 5 pbnap. ibm. net (198. 32. 128. 49) 31. 658 ms 21. 513 ms 10. 753 ms 6 sfra 1 sr 1 -4 -0 -0. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 13. 5) 22. 046 ms 46. 370 ms 11. 730 ms 7 sfo-pacbell-pop-sc. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 225. 9) 14. 978 ms 31. 752 ms 15. 835 ms 8 ded 1 -fa 0 -1 -0. pbi. net (216. 102. 176. 229) 16. 619 ms 26. 949 ms 14. 992 ms 9 pbi. scrm 01. foothill. net (206. 13. 15. 82) 47. 453 ms 41. 492 ms 55. 562 ms 10 inyo. E 0. foothill. net (206. 170. 175. 12) 25. 009 ms 42. 198 ms 46. 245 ms 11 fhaub. foothill. net (207. 212. 142. 2) 26. 434 ms 26. 344 ms 28. 052 ms 12 aub 2 -aub. foothill. net (207. 212. 142. 18) 124. 096 ms 101. 107 ms 116. 097 ms 13 yellowstone. foothill. net (209. 77. 125. 7) 60. 986 ms 65. 366 ms 62. 531 ms 14 black. foothill. net (209. 77. 125. 5) 54. 999 ms 54. 907 ms 75. 083 ms 15 den-edge-03. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 2. 81) 60. 018 ms 65. 658 ms 70. 363 ms 16 den-core-01. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 16. 101) 74. 909 ms 65. 983 ms 53. 476 ms 17 kcm-core-01. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 5. 49) 122. 825 ms 122. 386 ms 109. 227 ms 18 chi-core-03. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 5. 209) 105. 897 ms 124. 867 ms * 19 chi-brdr-01. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 20. 66) 157. 154 ms 135. 603 ms 112. 038 ms 20 ameritech-nap. ibm. net (198. 32. 130. 48) 97. 206 ms 287. 921 ms 118. 020 ms 21 scha 1 br 2 -0 -0 -0. il. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 34. 162) 127. 120 ms 94. 150 ms 108. 502 ms 22 sfra 1 br 2 -at-2 -0 -1 -4. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 230. 238) 121. 666 ms 106. 453 ms 137. 678 ms 23 sfra 1 sr 1 -12 -0 -0. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 13. 9) 134. 660 ms 121. 347 ms 134. 990 ms 24 sfo-pacbell-pop-sc. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 225. 9) 110. 007 ms 118. 412 ms 25 ded 1 -fa 0 -1 -0. pbi. net (216. 102. 176. 229) 110. 922 ms 121. 757 ms 120. 744 ms 26 pbi. scrm 01. foothill. net (206. 13. 15. 82) 168. 531 ms 120. 297 ms 126. 005 ms 27 inyo. E 0. foothill. net (206. 170. 175. 12) 139. 673 ms 132. 929 ms 127. 300 ms 28 fhaub. foothill. net (207. 212. 142. 2) 141. 649 ms 122. 945 ms 129. 213 ms ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 65
dfalk@unagi [Thu 15: 07] 5 /usr/home/jdfalk>traceroute -m 255 www. monkeys. com traceroute to www. monkeys. com (207. 212. 142. 41), 255 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 thermal-detonator. explosive. net (209. 133. 38. 1) 3. 428 ms 2. 032 ms 2. 915 ms 2 explosive-gate. bungi. com (207. 126. 96. 81) 14. 158 ms 6. 082 ms 6. 239 ms 3 above-gw 1. above. net (207. 126. 96. 249) 18. 889 ms 23. 423 ms 13. 275 ms 4 core 2 -main. sjc. above. net (207. 126. 96. 133) 20. 749 ms 22. 295 ms 26. 260 ms 5 pbnap. ibm. net (198. 32. 128. 49) 31. 658 ms 21. 513 ms 10. 753 ms 6 sfra 1 sr 1 -4 -0 -0. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 13. 5) 22. 046 ms 46. 370 ms 11. 730 ms 7 sfo-pacbell-pop-sc. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 225. 9) 14. 978 ms 31. 752 ms 15. 835 ms 8 ded 1 -fa 0 -1 -0. pbi. net (216. 102. 176. 229) 16. 619 ms 26. 949 ms 14. 992 ms 9 pbi. scrm 01. foothill. net (206. 13. 15. 82) 47. 453 ms 41. 492 ms 55. 562 ms 10 inyo. E 0. foothill. net (206. 170. 175. 12) 25. 009 ms 42. 198 ms 46. 245 ms 11 fhaub. foothill. net (207. 212. 142. 2) 26. 434 ms 26. 344 ms 28. 052 ms 12 aub 2 -aub. foothill. net (207. 212. 142. 18) 124. 096 ms 101. 107 ms 116. 097 ms 13 yellowstone. foothill. net (209. 77. 125. 7) 60. 986 ms 65. 366 ms 62. 531 ms 14 black. foothill. net (209. 77. 125. 5) 54. 999 ms 54. 907 ms 75. 083 ms 15 den-edge-03. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 2. 81) 60. 018 ms 65. 658 ms 70. 363 ms 16 den-core-01. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 16. 101) 74. 909 ms 65. 983 ms 53. 476 ms 17 kcm-core-01. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 5. 49) 122. 825 ms 122. 386 ms 109. 227 ms 18 chi-core-03. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 5. 209) 105. 897 ms 124. 867 ms * 19 chi-brdr-01. inet. qwest. net (205. 171. 20. 66) 157. 154 ms 135. 603 ms 112. 038 ms 20 ameritech-nap. ibm. net (198. 32. 130. 48) 97. 206 ms 287. 921 ms 118. 020 ms 21 scha 1 br 2 -0 -0 -0. il. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 34. 162) 127. 120 ms 94. 150 ms 108. 502 ms 22 sfra 1 br 2 -at-2 -0 -1 -4. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 230. 238) 121. 666 ms 106. 453 ms 137. 678 ms 23 sfra 1 sr 1 -12 -0 -0. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 13. 9) 134. 660 ms 121. 347 ms 134. 990 ms 24 sfo-pacbell-pop-sc. ca. us. ibm. net (165. 87. 225. 9) 110. 007 ms 118. 412 ms 25 ded 1 -fa 0 -1 -0. pbi. net (216. 102. 176. 229) 110. 922 ms 121. 757 ms 120. 744 ms 26 pbi. scrm 01. foothill. net (206. 13. 15. 82) 168. 531 ms 120. 297 ms 126. 005 ms 27 inyo. E 0. foothill. net (206. 170. 175. 12) 139. 673 ms 132. 929 ms 127. 300 ms 28 fhaub. foothill. net (207. 212. 142. 2) 141. 649 ms 122. 945 ms 129. 213 ms ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 65
 Management for Real, Cont. network monitors/analyzers n local systems n • take unit to problem • don't depend on working network • wide range of cost & function n remote systems • leave unit on problem or key network • remote control & viewing of information n privacy & security issues ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 66
Management for Real, Cont. network monitors/analyzers n local systems n • take unit to problem • don't depend on working network • wide range of cost & function n remote systems • leave unit on problem or key network • remote control & viewing of information n privacy & security issues ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 66
 Management for Real, Cont. n management agents • SNMP agents in all "gateway" devices • SNMP agents in all servers • binary + "analog" reports n need something that knows what it is looking at it ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 67
Management for Real, Cont. n management agents • SNMP agents in all "gateway" devices • SNMP agents in all servers • binary + "analog" reports n need something that knows what it is looking at it ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 67
 Management for Real n Which tools should I use? What do I really need? • Keep it simple! • Need to consider engineers working remotely • Don’t want to spend too much time maintaining the tool (it should be helping you!) • Different tools for NOC and engineers • Different tools for statistics • RELIABILITY! ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 68
Management for Real n Which tools should I use? What do I really need? • Keep it simple! • Need to consider engineers working remotely • Don’t want to spend too much time maintaining the tool (it should be helping you!) • Different tools for NOC and engineers • Different tools for statistics • RELIABILITY! ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 68
 Monitoring n simple monitoring tools do 95% of task • e. g. ftp: //ndtl. harvard. edu/pub/SNMPoll • e. g. http: //www. merit. edu/internet. tools/rover/ n monitor should be both poll & trap based for best reliability • but just polling will do better than just traps • and will work fine other than response latency n simple, terse, messages on problems ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 69
Monitoring n simple monitoring tools do 95% of task • e. g. ftp: //ndtl. harvard. edu/pub/SNMPoll • e. g. http: //www. merit. edu/internet. tools/rover/ n monitor should be both poll & trap based for best reliability • but just polling will do better than just traps • and will work fine other than response latency n simple, terse, messages on problems ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 69
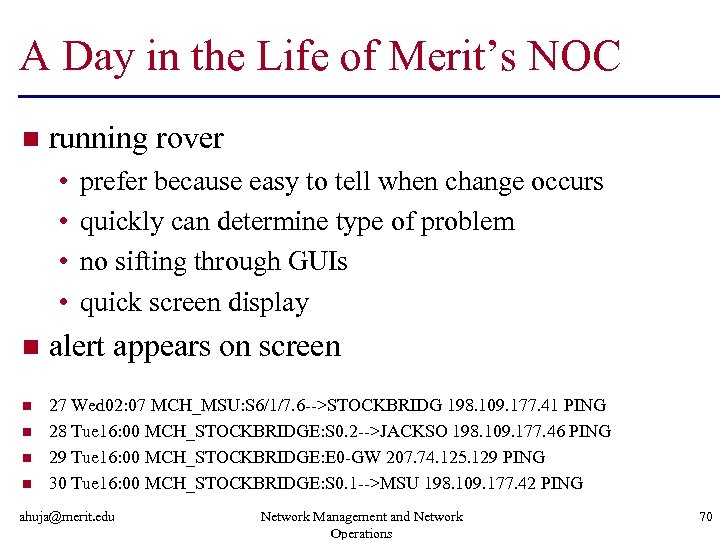 A Day in the Life of Merit’s NOC n running rover • • prefer because easy to tell when change occurs quickly can determine type of problem no sifting through GUIs quick screen display n alert appears on screen n 27 Wed 02: 07 MCH_MSU: S 6/1/7. 6 -->STOCKBRIDG 198. 109. 177. 41 PING 28 Tue 16: 00 MCH_STOCKBRIDGE: S 0. 2 -->JACKSO 198. 109. 177. 46 PING 29 Tue 16: 00 MCH_STOCKBRIDGE: E 0 -GW 207. 74. 125. 129 PING 30 Tue 16: 00 MCH_STOCKBRIDGE: S 0. 1 -->MSU 198. 109. 177. 42 PING n n n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 70
A Day in the Life of Merit’s NOC n running rover • • prefer because easy to tell when change occurs quickly can determine type of problem no sifting through GUIs quick screen display n alert appears on screen n 27 Wed 02: 07 MCH_MSU: S 6/1/7. 6 -->STOCKBRIDG 198. 109. 177. 41 PING 28 Tue 16: 00 MCH_STOCKBRIDGE: S 0. 2 -->JACKSO 198. 109. 177. 46 PING 29 Tue 16: 00 MCH_STOCKBRIDGE: E 0 -GW 207. 74. 125. 129 PING 30 Tue 16: 00 MCH_STOCKBRIDGE: S 0. 1 -->MSU 198. 109. 177. 42 PING n n n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 70
 A Day in the Life of Merit’s NOC open ticket n investigate n • the two most important questions: – can you ping it? – can you trace to it? • get to the node from somewhere else in the network? • dial-in to the router? • serial line problem? call telco n If necessary, escalate to engineer ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 71
A Day in the Life of Merit’s NOC open ticket n investigate n • the two most important questions: – can you ping it? – can you trace to it? • get to the node from somewhere else in the network? • dial-in to the router? • serial line problem? call telco n If necessary, escalate to engineer ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 71
 Another example - Sluggishness customer calls NOC - reports sluggishness n open ticket n investigate n • check mrtg – more traffic now than normal? • use netflow to determine what type of traffic – possible denial of service attack • circuit problem? – call telco to test n always call customer. Management and Network okay to close back to get Network ahuja@merit. edu Operations 72
Another example - Sluggishness customer calls NOC - reports sluggishness n open ticket n investigate n • check mrtg – more traffic now than normal? • use netflow to determine what type of traffic – possible denial of service attack • circuit problem? – call telco to test n always call customer. Management and Network okay to close back to get Network ahuja@merit. edu Operations 72
 Another example - DOS Customer reports possible Denial of Service n Open ticket n Investigate n • notice a large amount of packets from one destination? – log onto router – ip accounting – sho ip route cache flow • install packet filter • report to offending ISP ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 73
Another example - DOS Customer reports possible Denial of Service n Open ticket n Investigate n • notice a large amount of packets from one destination? – log onto router – ip accounting – sho ip route cache flow • install packet filter • report to offending ISP ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 73
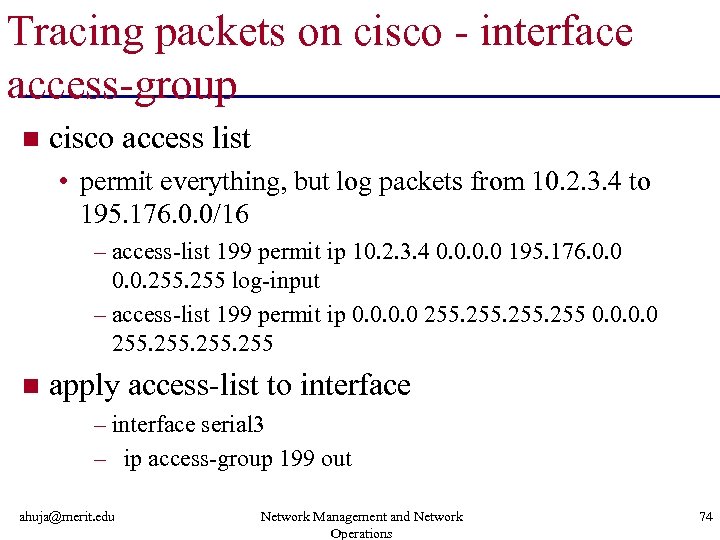 Tracing packets on cisco - interface access-group n cisco access list • permit everything, but log packets from 10. 2. 3. 4 to 195. 176. 0. 0/16 – access-list 199 permit ip 10. 2. 3. 4 0. 0 195. 176. 0. 0. 255 log-input – access-list 199 permit ip 0. 0 255 n apply access-list to interface – interface serial 3 – ip access-group 199 out ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 74
Tracing packets on cisco - interface access-group n cisco access list • permit everything, but log packets from 10. 2. 3. 4 to 195. 176. 0. 0/16 – access-list 199 permit ip 10. 2. 3. 4 0. 0 195. 176. 0. 0. 255 log-input – access-list 199 permit ip 0. 0 255 n apply access-list to interface – interface serial 3 – ip access-group 199 out ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 74
 Tracing packets on cisco - debug ip packet n cisco access list • permit packets from 10. 2. 3. 4 to 195. 176. 0. 0/16, deny others – access-list 199 permit ip 10. 2. 3. 4 0. 0 195. 176. 0. 0. 255 log-input – access-list 199 deny ip 0. 0 255 n use access-list with “debug ip packet” – debug ip packet 199 ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 75
Tracing packets on cisco - debug ip packet n cisco access list • permit packets from 10. 2. 3. 4 to 195. 176. 0. 0/16, deny others – access-list 199 permit ip 10. 2. 3. 4 0. 0 195. 176. 0. 0. 255 log-input – access-list 199 deny ip 0. 0 255 n use access-list with “debug ip packet” – debug ip packet 199 ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 75
 Limiting bandwidth access-list matches a class of traffic (e. g. ICMP) n use bandwidth management techniques to limit amount of traffic in that class n • cisco CAR or traffic-shaping ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 76
Limiting bandwidth access-list matches a class of traffic (e. g. ICMP) n use bandwidth management techniques to limit amount of traffic in that class n • cisco CAR or traffic-shaping ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 76
 Things to Look For duplicate addresses n network/link load n router/bridge n • • • CPU load errors drops!! interface resets collisions (if CSMA/CD network) ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 77
Things to Look For duplicate addresses n network/link load n router/bridge n • • • CPU load errors drops!! interface resets collisions (if CSMA/CD network) ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 77
 Things to Do (Defensive) Filter!!! Filter! n Use the Internet Routing Registry! n • register your routes • register your policy • configure your routers off of the database! – tools available – http: //www. isi. edu/ra/RATool. Set n use the Route Servers! ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 78
Things to Do (Defensive) Filter!!! Filter! n Use the Internet Routing Registry! n • register your routes • register your policy • configure your routers off of the database! – tools available – http: //www. isi. edu/ra/RATool. Set n use the Route Servers! ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 78
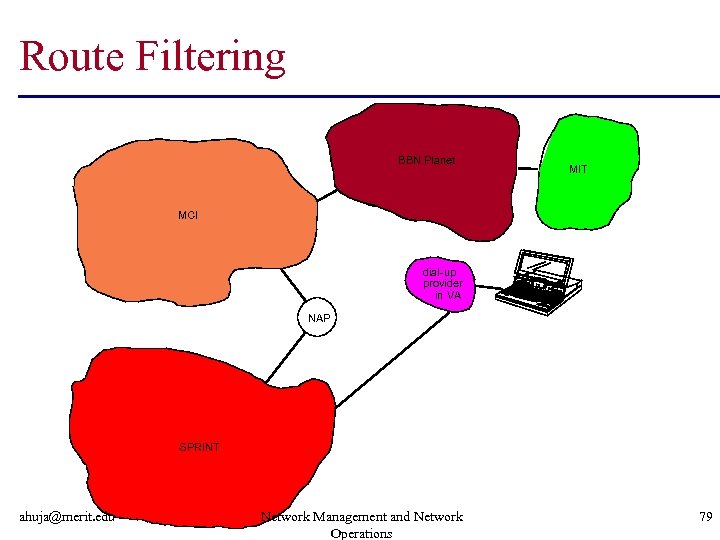 Route Filtering BBN Planet MIT MCI dial-up provider in VA NAP SPRINT ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 79
Route Filtering BBN Planet MIT MCI dial-up provider in VA NAP SPRINT ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 79
 Things Not to Do tunnel n complex routing n reconfig on the fly n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 80
Things Not to Do tunnel n complex routing n reconfig on the fly n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 80
 Problems n we are early in the internet management game • there is still a lot to learn n prices still high for functionality • many new NMSs will be on the market soon, will help lower price and expand capabilities data networks are not "plug and play" with large scale n nefarious people n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 81
Problems n we are early in the internet management game • there is still a lot to learn n prices still high for functionality • many new NMSs will be on the market soon, will help lower price and expand capabilities data networks are not "plug and play" with large scale n nefarious people n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 81
 More Problems not so good at provoking simple, easy to understand, warning to non-gurus n should have database & logic about when to cry wolf n • critical vs, noncritical device, access restrictions, who to call when needs to be usable by "normal" people n needs to say when users will complain n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 82
More Problems not so good at provoking simple, easy to understand, warning to non-gurus n should have database & logic about when to cry wolf n • critical vs, noncritical device, access restrictions, who to call when needs to be usable by "normal" people n needs to say when users will complain n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 82
 Even more Problems training your Network Operations Staff n keeping your database up-to-date n • router configs • contact information n communication with the telco ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 83
Even more Problems training your Network Operations Staff n keeping your database up-to-date n • router configs • contact information n communication with the telco ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 83
 More things you can do! n secure your router • tacacs • radius • restrict login and snmp access n enable syslog logging • security • debugging ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 84
More things you can do! n secure your router • tacacs • radius • restrict login and snmp access n enable syslog logging • security • debugging ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 84
 More things you can do! n Filtering • • generate your filters off of the IRR anti-spoofing filters filter private networks (RFC 1918) recommended filter list – http: //www. merit. edu/ipma/docs/help. html ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 85
More things you can do! n Filtering • • generate your filters off of the IRR anti-spoofing filters filter private networks (RFC 1918) recommended filter list – http: //www. merit. edu/ipma/docs/help. html ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 85
 More things you can do! n educate your NOC • provide adequate documentation • escalation procedures n register your routers in DNS • traceroutes easier to follow coolbeans% traceroute www. above. net traceroute to www. above. net (207. 126. 96. 163), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 eth 0 -2. michnet 1. mich. net (198. 108. 61. 1) 1. 074 ms 0. 888 ms 0. 696 ms 2 hssi 1 -0 -0. msu. mich. net (198. 108. 22. 102) 77. 602 ms 75. 356 ms 12. 437 ms 3 aads. above. net (198. 32. 130. 71) 9. 981 ms 15. 098 ms 11. 342 ms 4 chicago-core 1. ord. above. net (209. 249. 0. 129) 9. 634 ms 9. 834 ms 9. 590 ms 5 sjc-chicago-oc 3. above. net (209. 249. 0. 125) 71. 261 ms 71. 232 ms 71. 305 ms 6 main 2 -core 1 -oc 3 -3. sjc. above. net (209. 133. 31. 97) 123. 499 ms 71. 512 ms 71. 8 7 www. above. net (207. 126. 96. 163) 72. 861 ms 72. 624 ms 74. 529 ms ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 86
More things you can do! n educate your NOC • provide adequate documentation • escalation procedures n register your routers in DNS • traceroutes easier to follow coolbeans% traceroute www. above. net traceroute to www. above. net (207. 126. 96. 163), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 eth 0 -2. michnet 1. mich. net (198. 108. 61. 1) 1. 074 ms 0. 888 ms 0. 696 ms 2 hssi 1 -0 -0. msu. mich. net (198. 108. 22. 102) 77. 602 ms 75. 356 ms 12. 437 ms 3 aads. above. net (198. 32. 130. 71) 9. 981 ms 15. 098 ms 11. 342 ms 4 chicago-core 1. ord. above. net (209. 249. 0. 129) 9. 634 ms 9. 834 ms 9. 590 ms 5 sjc-chicago-oc 3. above. net (209. 249. 0. 125) 71. 261 ms 71. 232 ms 71. 305 ms 6 main 2 -core 1 -oc 3 -3. sjc. above. net (209. 133. 31. 97) 123. 499 ms 71. 512 ms 71. 8 7 www. above. net (207. 126. 96. 163) 72. 861 ms 72. 624 ms 74. 529 ms ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 86
 More things you can do! n Prevent excessive route-flapping • enable route-flap dampening • use CIDR • use filters ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 87
More things you can do! n Prevent excessive route-flapping • enable route-flap dampening • use CIDR • use filters ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 87
 References http: //www. merit. edu/ipma/docs/isp. html n http: //www. nanog. org n http: //www. caida. org n http: //www. nlanr. net n http: //www. cisco. com n http: //www. amazing. com/internet/ n http: //www. isp-resource. com/ n http: //www. merit. edu/ipma n http: //www. ripe. net n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 88
References http: //www. merit. edu/ipma/docs/isp. html n http: //www. nanog. org n http: //www. caida. org n http: //www. nlanr. net n http: //www. cisco. com n http: //www. amazing. com/internet/ n http: //www. isp-resource. com/ n http: //www. merit. edu/ipma n http: //www. ripe. net n ahuja@merit. edu Network Management and Network Operations 88


