ad1df230b60d952dbf583248485c0589.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Network Defenses CS 432 - Security in Computing Copyright © 2005, 2007 by Scott Orr and the Trustees of Indiana University
Network Defenses CS 432 - Security in Computing Copyright © 2005, 2007 by Scott Orr and the Trustees of Indiana University
 References n Security in Computing, 3 rd Ed. n Chapter 7 (pgs. 425 -457)
References n Security in Computing, 3 rd Ed. n Chapter 7 (pgs. 425 -457)
 Section Overview n Distributed Authentication n Session Encryption n Virtual Private Networks n Service Protection
Section Overview n Distributed Authentication n Session Encryption n Virtual Private Networks n Service Protection
 Distributed Authentication n Trusted hosts sharing a common DB of account and system information Network Information Systems (NIS) NT Domains n n n Single domain Trust relationships between domains Active Directory Services (ADS) Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Single Sign-Ons
Distributed Authentication n Trusted hosts sharing a common DB of account and system information Network Information Systems (NIS) NT Domains n n n Single domain Trust relationships between domains Active Directory Services (ADS) Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Single Sign-Ons
 Impersonation Countermeasures n n n User Education Policies and Procedures Two Factor Authentication What you know (password) n What you have (token) n n Replace applications with encryption enhanced versions (i. e. Secure Shell)
Impersonation Countermeasures n n n User Education Policies and Procedures Two Factor Authentication What you know (password) n What you have (token) n n Replace applications with encryption enhanced versions (i. e. Secure Shell)
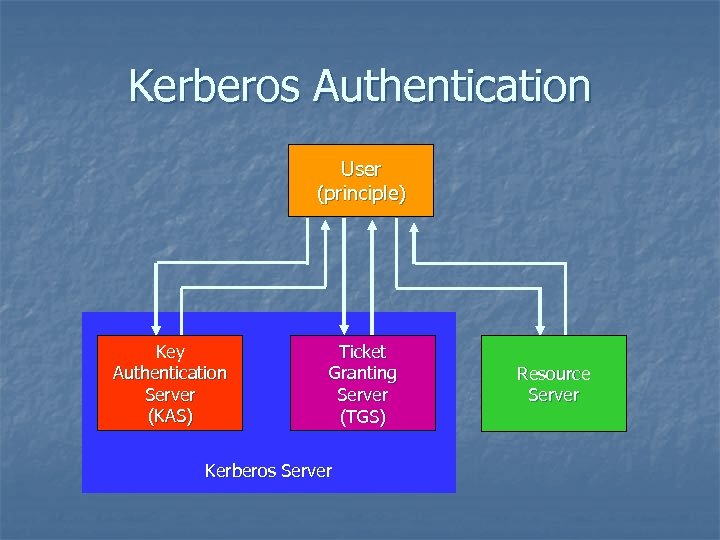 Kerberos Authentication User (principle) Key Authentication Server (KAS) Ticket Granting Server (TGS) Kerberos Server Resource Server
Kerberos Authentication User (principle) Key Authentication Server (KAS) Ticket Granting Server (TGS) Kerberos Server Resource Server
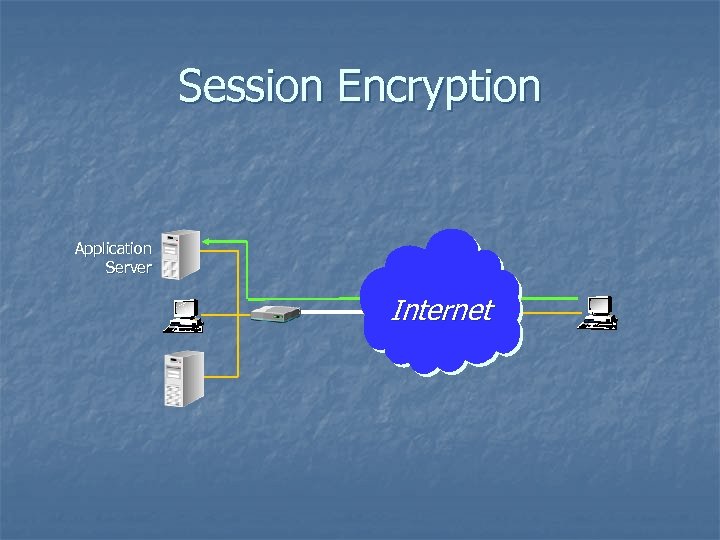 Session Encryption Application Server Internet
Session Encryption Application Server Internet
 Secure Socket Layer n Separate algorithms based on task Encryption n Authentication n Data Integrity n SSL Hello n n n Efficient – Caches Master Secret key Certificate-based authentication
Secure Socket Layer n Separate algorithms based on task Encryption n Authentication n Data Integrity n SSL Hello n n n Efficient – Caches Master Secret key Certificate-based authentication
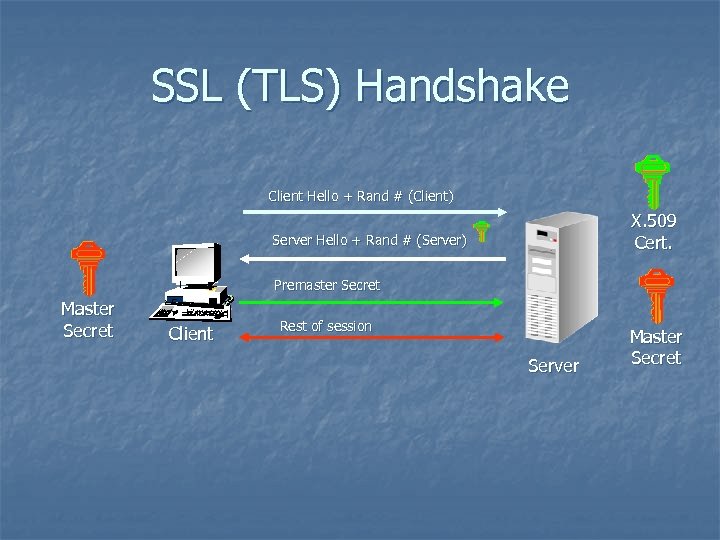 SSL (TLS) Handshake Client Hello + Rand # (Client) X. 509 Cert. Server Hello + Rand # (Server) Premaster Secret Master Secret Client Rest of session Server Master Secret
SSL (TLS) Handshake Client Hello + Rand # (Client) X. 509 Cert. Server Hello + Rand # (Server) Premaster Secret Master Secret Client Rest of session Server Master Secret
 X 509 Certificates Version Serial Number Algorithm Info Issuer Period Subject’s Public Key Issuer Signature Source: Web Security and Commerce Simson Garfinkel and Gene Spafford
X 509 Certificates Version Serial Number Algorithm Info Issuer Period Subject’s Public Key Issuer Signature Source: Web Security and Commerce Simson Garfinkel and Gene Spafford
 Certificate Types n n Server Certificates Personal Certificates Software Publisher Certificates Certificate Authority Certificates
Certificate Types n n Server Certificates Personal Certificates Software Publisher Certificates Certificate Authority Certificates
 Public Key Infrastructure n n Certificate Authorities Registration Authorities Certificate Distribution System Key Escrow
Public Key Infrastructure n n Certificate Authorities Registration Authorities Certificate Distribution System Key Escrow
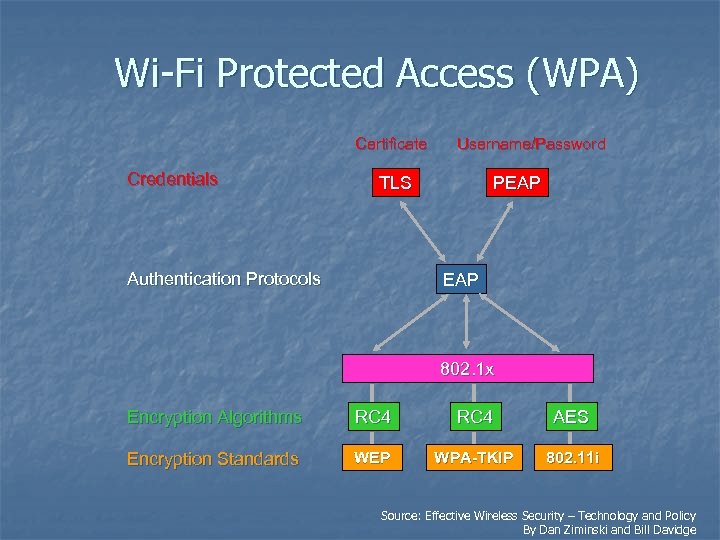 Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Certificate Credentials Username/Password TLS Authentication Protocols PEAP 802. 1 x Encryption Algorithms RC 4 AES Encryption Standards WEP WPA-TKIP 802. 11 i Source: Effective Wireless Security – Technology and Policy By Dan Ziminski and Bill Davidge
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Certificate Credentials Username/Password TLS Authentication Protocols PEAP 802. 1 x Encryption Algorithms RC 4 AES Encryption Standards WEP WPA-TKIP 802. 11 i Source: Effective Wireless Security – Technology and Policy By Dan Ziminski and Bill Davidge
 802. 1 x EAP-TLS Authentication Client digital cert From XYZ CA Station Supplicant Access Point Authenticator RADIUS Server Authorizer Server Digital cert From XYZ CA Source: Effective Wireless Security – Technology and Policy By Dan Ziminski and Bill Davidge
802. 1 x EAP-TLS Authentication Client digital cert From XYZ CA Station Supplicant Access Point Authenticator RADIUS Server Authorizer Server Digital cert From XYZ CA Source: Effective Wireless Security – Technology and Policy By Dan Ziminski and Bill Davidge
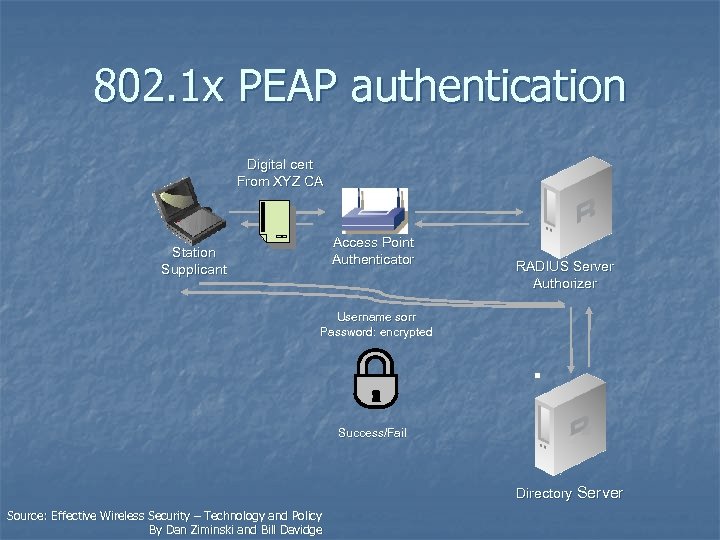 802. 1 x PEAP authentication Digital cert From XYZ CA Access Point Authenticator Station Supplicant RADIUS Server Authorizer Username sorr Password: encrypted Success/Fail Directory Server Source: Effective Wireless Security – Technology and Policy By Dan Ziminski and Bill Davidge
802. 1 x PEAP authentication Digital cert From XYZ CA Access Point Authenticator Station Supplicant RADIUS Server Authorizer Username sorr Password: encrypted Success/Fail Directory Server Source: Effective Wireless Security – Technology and Policy By Dan Ziminski and Bill Davidge
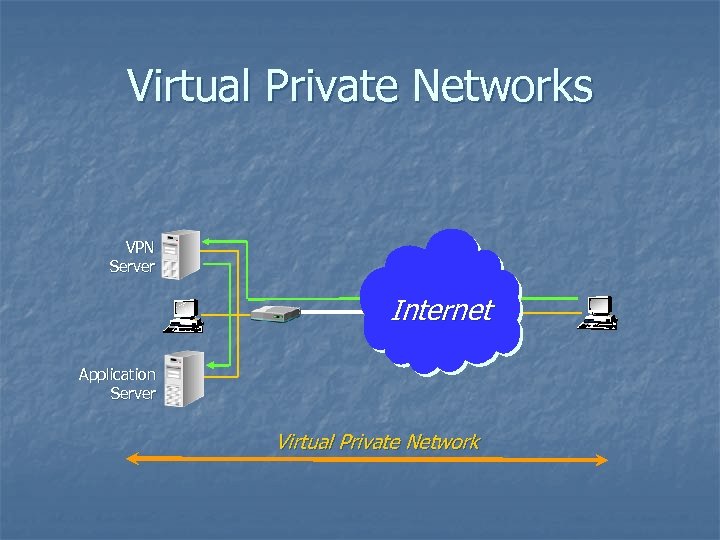 Virtual Private Networks VPN Server Internet Application Server Virtual Private Network
Virtual Private Networks VPN Server Internet Application Server Virtual Private Network
 Point to Point Tunneling Protocol n Based on Point to Point Protocol (PPP) n Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) n IP Hdr GRE Hdr Encrypted GRE Body PPP IP TCP Data § Weaknesses § Poor Encryption § Session handshaking done in clear
Point to Point Tunneling Protocol n Based on Point to Point Protocol (PPP) n Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) n IP Hdr GRE Hdr Encrypted GRE Body PPP IP TCP Data § Weaknesses § Poor Encryption § Session handshaking done in clear
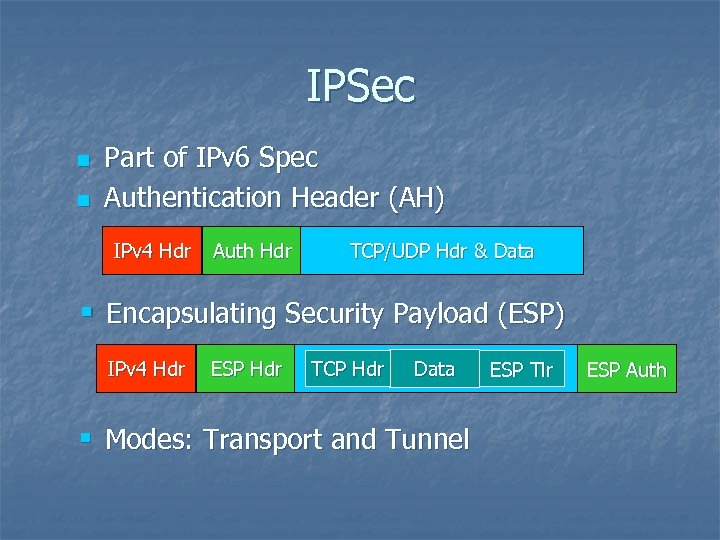 IPSec n n Part of IPv 6 Spec Authentication Header (AH) IPv 4 Hdr Auth Hdr TCP/UDP Hdr & Data § Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) IPv 4 Hdr ESP Hdr Encrypted Payload Tlr TCP Hdr Data ESP § Modes: Transport and Tunnel ESP Auth
IPSec n n Part of IPv 6 Spec Authentication Header (AH) IPv 4 Hdr Auth Hdr TCP/UDP Hdr & Data § Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) IPv 4 Hdr ESP Hdr Encrypted Payload Tlr TCP Hdr Data ESP § Modes: Transport and Tunnel ESP Auth
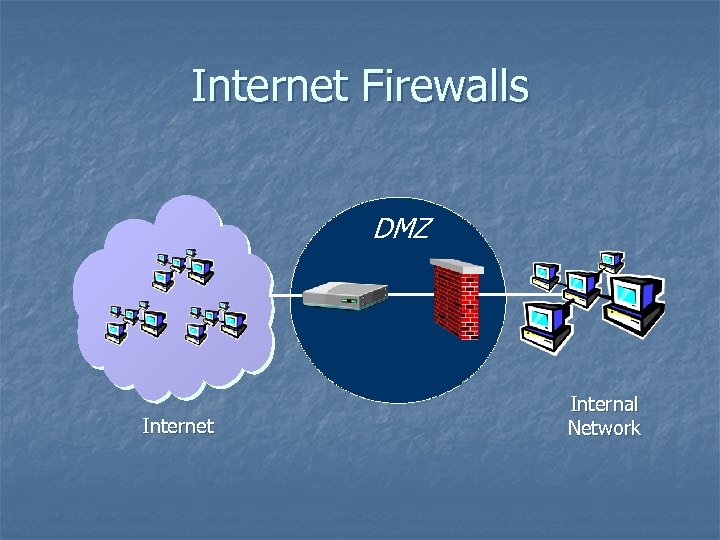 Internet Firewalls DMZ Internet Internal Network
Internet Firewalls DMZ Internet Internal Network


