 Network Analysis Applications for Qualitative Content Analysis Data
Network Analysis Applications for Qualitative Content Analysis Data
 What is Network Analysis? Ø A way of thinking sociologically Ø A body of sociological theory Ø A body of research findings Ø A form of quantitative-qualitative analysis Ø A set of analytical tools for analysis
What is Network Analysis? Ø A way of thinking sociologically Ø A body of sociological theory Ø A body of research findings Ø A form of quantitative-qualitative analysis Ø A set of analytical tools for analysis
 A Different Way of Thinking Ø Approach is holistic—whole networks Ø Focus is on relations between units Ø Organize data differently Ø Ask different questions l about the overall state of the network l about the nature of particular relations Ø Use different quantitative measures
A Different Way of Thinking Ø Approach is holistic—whole networks Ø Focus is on relations between units Ø Organize data differently Ø Ask different questions l about the overall state of the network l about the nature of particular relations Ø Use different quantitative measures
 Two Types of Network Analysis Ø One kind theorizes about social structure l l uses network data to test hypotheses also uses simulated data to test hypotheses Ø The other kind is exploratory l l uses real data to figure out what is going on often uses visual network diagrams Ø Exploratory approach flexible, accessible
Two Types of Network Analysis Ø One kind theorizes about social structure l l uses network data to test hypotheses also uses simulated data to test hypotheses Ø The other kind is exploratory l l uses real data to figure out what is going on often uses visual network diagrams Ø Exploratory approach flexible, accessible
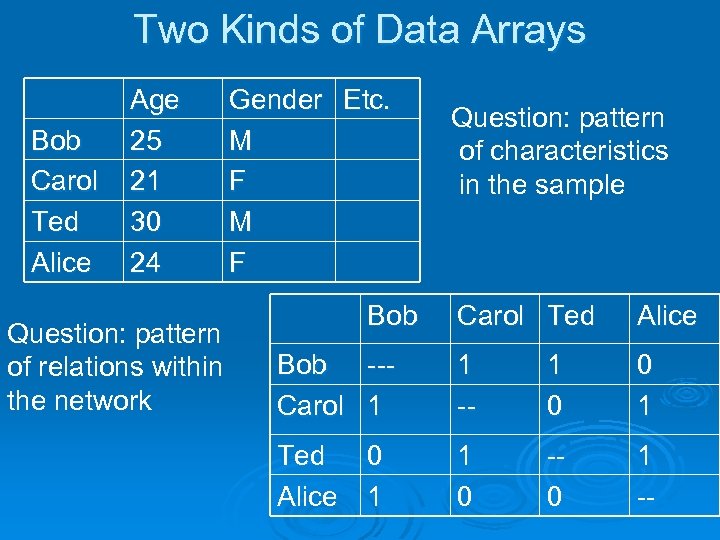 Two Kinds of Data Arrays Bob Carol Ted Alice Age 25 21 30 24 Gender Etc. M F Question: pattern of relations within the network Bob Question: pattern of characteristics in the sample Carol Ted Alice Bob --Carol 1 1 -- 1 0 0 1 Ted Alice 1 0 -0 1 -- 0 1
Two Kinds of Data Arrays Bob Carol Ted Alice Age 25 21 30 24 Gender Etc. M F Question: pattern of relations within the network Bob Question: pattern of characteristics in the sample Carol Ted Alice Bob --Carol 1 1 -- 1 0 0 1 Ted Alice 1 0 -0 1 -- 0 1
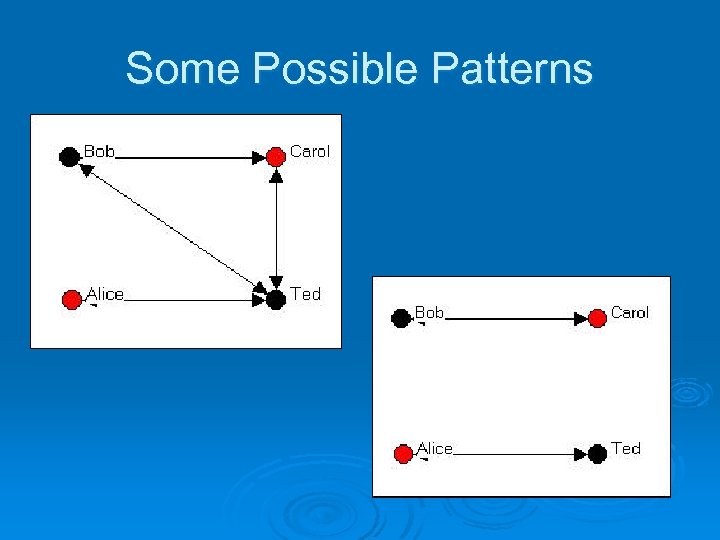 Some Possible Patterns
Some Possible Patterns
 Network Language Ø NODES---the individual units l l people groups nations companies Ø TIES—the relations between the units l l l Can be present/absent (Are X and Y linked? ) Can be directional (Does X like Y? ) Can be quantified (# of links, amount of trade)
Network Language Ø NODES---the individual units l l people groups nations companies Ø TIES—the relations between the units l l l Can be present/absent (Are X and Y linked? ) Can be directional (Does X like Y? ) Can be quantified (# of links, amount of trade)
 Nature of Network Data Ø Populations, not samples preferred l l Do not use probabilistic statistics Use matrix algebra as mathematical base Ø Ego-centric Networks—all ties from one node l l Only direct ties to ego Trace ties of those linked to ego Ø Full networks—all ties between all nodes l l can limit network to make this feasible can some times use snowball to trace network
Nature of Network Data Ø Populations, not samples preferred l l Do not use probabilistic statistics Use matrix algebra as mathematical base Ø Ego-centric Networks—all ties from one node l l Only direct ties to ego Trace ties of those linked to ego Ø Full networks—all ties between all nodes l l can limit network to make this feasible can some times use snowball to trace network
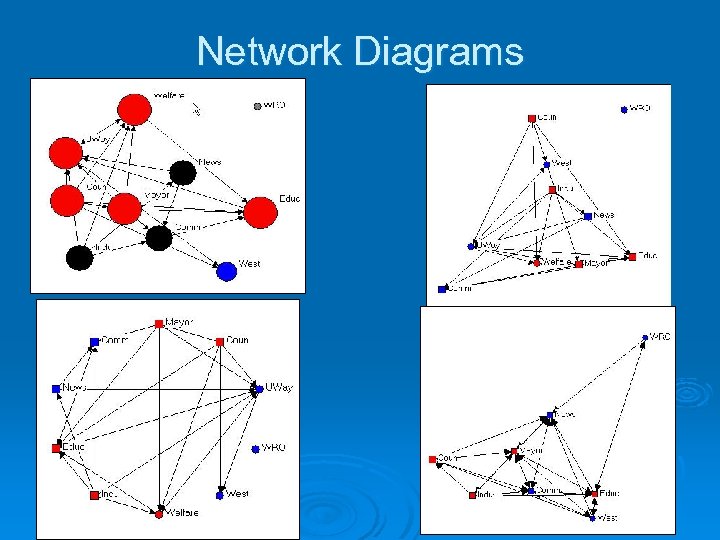 Network Diagrams
Network Diagrams
 Some Network Measures Ø Density Ø Connectivity Ø Reachability Ø Distance Ø Reciprocity Ø Clustering Ø Hierarchy Ø Cliques
Some Network Measures Ø Density Ø Connectivity Ø Reachability Ø Distance Ø Reciprocity Ø Clustering Ø Hierarchy Ø Cliques
 Using with Content Analysis Ø Your data may include “relations” already l l l website links or reports in the data ties between people, groups, or other units “grammatical” relations Ø You may be able to create relational data l l construct it from your Access database add external data or more codes Ø You might just want to diagram relations
Using with Content Analysis Ø Your data may include “relations” already l l l website links or reports in the data ties between people, groups, or other units “grammatical” relations Ø You may be able to create relational data l l construct it from your Access database add external data or more codes Ø You might just want to diagram relations
 Form of Network Data Enter directly in the network programs, UCINET, PAJEK, or NETDRAW (included in UCINET) Ø Import from an Excel spreadsheet (flat file matrix) Ø l l Ø Move data from Access to Excel Then import into UCINET Enter usual data array with other variables l l UCINET can turn it into a matrix for you You then can add the relations to the matrix Output a text file and format it for UCINET Ø UCINET can export into PAJEK format or Netdraw Ø
Form of Network Data Enter directly in the network programs, UCINET, PAJEK, or NETDRAW (included in UCINET) Ø Import from an Excel spreadsheet (flat file matrix) Ø l l Ø Move data from Access to Excel Then import into UCINET Enter usual data array with other variables l l UCINET can turn it into a matrix for you You then can add the relations to the matrix Output a text file and format it for UCINET Ø UCINET can export into PAJEK format or Netdraw Ø
 Network Resources Ø UCINET software: (free trial, $25 for students) Hanneman, Robert A. and Mark Riddle. 2005. Introduction to social network methods. Riverside, CA: University of California, Riverside ( Free tutorial, published in digital form at http: //faculty. ucr. edu/~hanneman/ ) Ø Pajek: network analysis and visualization: http: //vlado. fmf. uni-lj. si/pub/networks/pajek/ (free Ø software, buy better manual)
Network Resources Ø UCINET software: (free trial, $25 for students) Hanneman, Robert A. and Mark Riddle. 2005. Introduction to social network methods. Riverside, CA: University of California, Riverside ( Free tutorial, published in digital form at http: //faculty. ucr. edu/~hanneman/ ) Ø Pajek: network analysis and visualization: http: //vlado. fmf. uni-lj. si/pub/networks/pajek/ (free Ø software, buy better manual)