Aigerim Sakanova business system.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
Netherlands Business System (Holland) Aigerim Sakanova

Structuring Belarus Ukraine Turkey 1. Overview 2. Industry Sectors 3. Economic Regions 4. Major Factors in the Economy 5. Basic income 6. Financial Structures 7. Export 8. Import 9. Business Structures 10. Business Etiquette 11. International Business Relations Georgia Uzbekistan Kyrgyzstan Azerbaijan Armenia 12. Communication Styles Tajikistan 13. Conclusion Turkmenistan Mongolia China
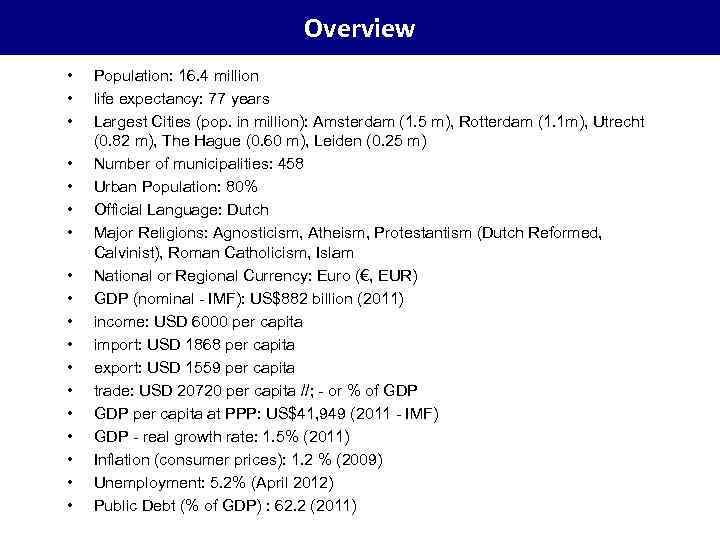
Overview • • • • • Population: 16. 4 million life expectancy: 77 years Largest Cities (pop. in million): Amsterdam (1. 5 m), Rotterdam (1. 1 m), Utrecht (0. 82 m), The Hague (0. 60 m), Leiden (0. 25 m) Number of municipalities: 458 Urban Population: 80% Official Language: Dutch Major Religions: Agnosticism, Atheism, Protestantism (Dutch Reformed, Calvinist), Roman Catholicism, Islam National or Regional Currency: Euro (€, EUR) GDP (nominal - IMF): US$882 billion (2011) income: USD 6000 per capita import: USD 1868 per capita export: USD 1559 per capita trade: USD 20720 per capita //; - or % of GDP per capita at PPP: US$41, 949 (2011 - IMF) GDP - real growth rate: 1. 5% (2011) Inflation (consumer prices): 1. 2 % (2009) Unemployment: 5. 2% (April 2012) Public Debt (% of GDP) : 62. 2 (2011)
Belarus Ukraine Mongolia Georgia Armenia. Azerbaijan Uzbekistan Turkey Kyrgyzstan Tajikistan Turkmenistan China
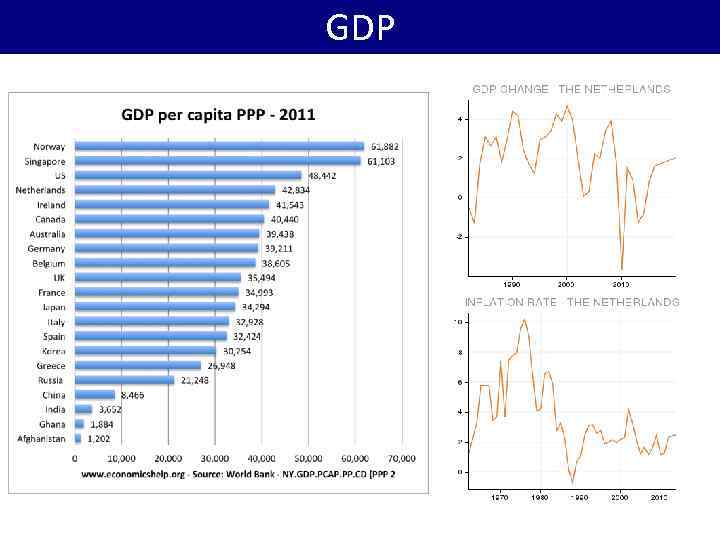
GDP Belarus Ukraine Mongolia Georgia Armenia. Azerbaijan Uzbekistan Turkey Kyrgyzstan Tajikistan Turkmenistan China

Industry sectors Main Industries: agro industries, metal and engineering products, electronic machinery and equipment, chemicals, petroleum, construction, microelectronics, fishing Main Exports: machinery and equipment, chemicals, fuels; foodstuffs Main Imports: machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, fuels, foodstuffs, clothing Main Trading Partners: Germany, Belgium, France, UK, USA, China, Italy
Economic Regions The Netherlands has a wealthy and free economy, which depends heavily on foreign trade. Its economy is noted for stable international industrial relations, moderate unemployment and inflation rates, a significant national current account balance surplus, and an important role as a European transportation hub. Industrial activity is predominantly in food stuffs processing, chemicals, oil and gas refining, and electrical machinery. Netherlands’ economy also benefits from the presence of one of the largest natural gas fields. With oil and energy prices projected to go up, the Netherlands can expect fast paced growth in times to come. All these factors make Holland even more attractive for investors. Netherlands’ economy is the 16 th largest one in the world with a GDP that is 4% higher than the EU average. The Netherlands is located in North West Europe and is bordered by the North Sea, Belgium and Germany. Holland, due to its stability, has been able to attract a lot of FDI as well. In 2009, the total FDI amount stood at $661 billion, higher than the 2008 level of $644. 6 billion. The country ranked seventh in the world in terms of FDI volume. The Netherlands, with a rather prosperous economy, is one of the biggest investors in the USA as well. Its FDI abroad amounted to $866. 1 billion in 2009, an increase from the 2008 level of $843. 7 billions.

Major factors in the economy • The Netherlands's economy is predominantly manufacturing-based. Services account for 73. 98% of the GDP and employs 71. 50% of the population. Manufacturing and industry accounts for 24. 37% of GDP and employs 15. 30% of the population. Agriculture accounts for 1. 65% of GDP and employs 2. 50% of the population. • Government revenue in the Netherlands was 47. 55% of GDP in 2013, while government spending was 48. 07% of GDP. Government debt in the Netherlands, as a percent of GDP, was 35. 34% in 2013.

Major factors in the economy • The Netherlands trade is the main support system for the economy. Netherlands’ location also means that the nation is closest to the European regions that have the maximum population density. In fact, almost 160 million people stay within a 300 mile radius of the Netherlands, giving the country many regions to trade with. Almost 80% of Netherlands’ exports are to European nations and nearly 70% of its imports come from European nations as well. The Netherlands trades with a positive trade balance. As the nation enjoys a massive contribution through trade, it is an ardent supporter of open trade, along with the US.
Basic income Airports: (2013) The largest airport by far is Amsterdam Airport Schiphol, which is one of the largest in Europe. Smaller airports with scheduled passenger service are Rotterdam The Hague Airport , Eindhoven Airport and Maastricht Aachen Airport. The total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) but may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc. ) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control. • • • ü ü ü ü ü Airports by year chart Airports rank chart Airports - comparative map Airports - with paved runways Airports - with unpaved runways Heliports Pipelines Railways Roadways Waterways Merchant marine Ports and terminals

Financial Structures In general, the annual report contains the following documents: • A directors’ report presenting a fair view of the financial position, results and future plans of the company; • Financial statements comprising (I) a balance sheet, (II) a profit and loss account, (III) a cash-flow statement, and (IV) notes to the balance sheet and profit and loss account; • Other information, including the auditors’ report. Small company Medium-sized company Large company Net turnover (in EUR millions) < 8. 8 >8. 8 and < 35 > 35 Total assets (in EUR millions) < 4. 4 > 4. 4 and < 17. 5 > 17. 5 Employees < 50 > 50 and < 250 > 250 28 Pw. C
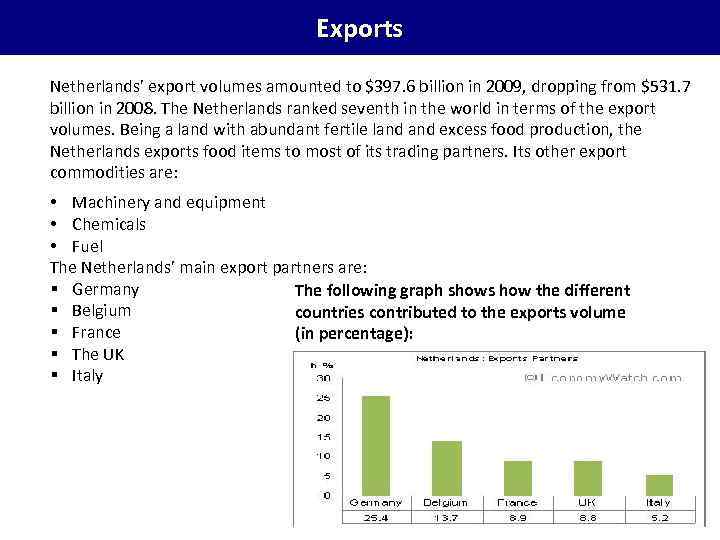
Exports Netherlands’ export volumes amounted to $397. 6 billion in 2009, dropping from $531. 7 billion in 2008. The Netherlands ranked seventh in the world in terms of the export volumes. Being a land with abundant fertile land excess food production, the Netherlands exports food items to most of its trading partners. Its other export commodities are: • Machinery and equipment • Chemicals • Fuel The Netherlands’ main export partners are: § Germany The following graph shows how the different § Belgium countries contributed to the exports volume § France (in percentage): § The UK § Italy

Imports According to the 2009 statistics, the Netherland imported a total volume of $358. 9 billion, dropping substantially from $474. 8 billion in 2008. The Netherlands ranked eighth in the world in terms of import volumes. With huge natural resources, the Netherlands requires machines to process them and therefore machinery dominates its imports. Other import commodities include: • Transport equipment • Chemicals • Fuels • Foodstuffs • Clothing The Netherlands’ main import partners are The following graph shows how the different § Germany countries contribute in the import volumes: § China § Belgium § The US § The UK § Russia § France

Business structures Structures that do not have a separate legal entity With these business structures, you are personally responsible for the debts or losses of the business: • Sole trader (eenmanszaak) • General partnership (vennootschap onder firma, VOF) • Ordinary partnership (maatschap) Business forms that have a separate legal entity With these business forms, you are responsible up to the amounts you have invested. Like an individual, a business structure with a separate legal entity has independent rights and obligations: • Private limited company (besloten vennootschap, BV) • Association (vereniging) • Foundation (stichting) • Freelancers It is important to note that freelancers (ZZP-ers) occupy a different position.

Business etiquette Dutch people tend to view themselves as modest, tolerant, independent and selfreliant. They value education, tolerance, hard work, ambition and ability. The Dutch have an aversion to the non-essential. Dutch manners are frank, with a nononsense attitude; informality combined with adherence to basic etiquette. For foreigners not used to this, the Dutch may seem somewhat harsh or impolite at first. However, it soon becomes apparent that the Dutch way of working is also honest, efficient and friendly. The Dutch are proud of their cultural heritage, rich history in art and music and involvement in international affairs.

Tax & HRS covers all services with regard to tax consultancy, legal consultancy and human resources. Tax & HRS helps companies, individuals and organizations with their tax strategy, planning and compliance, and provides a wide variety of advisory services in the area of taxation. This Line of Service also has Human Resources specialists in place who advise on such matters as remuneration structures, pension plans, and cross-border staff exchanges.

International Business relations The foreign policy of the Netherlands is based on four basic commitments: to the Atlantic cooperation, to European integration, to international development and to international law. While historically the Netherlands was a neutral state, since the second World War it became a member of a large number of international organisations. The Dutch economy is very open and relies on international trade. One of the more controversial international issues surrounding the Netherlands is its liberal policy towards soft drugs and position of the Netherlands as one of the major exporters of hard drugs. During and after its Golden Age, the Dutch built up a commercial and colonial empire, which fell apart quickly after the Second World War; the historical ties inherited from its colonial past still influence the foreign relations of the Netherlands. Countries partnership: Ø Ø Ø Ø Albania Armenia Austria Belgium Bulgaria Czech Republic Denmark Estonia

Communication styles • The Dutch have a very direct and informal communication style, which may appear rude or angry to those from cultures that place more emphasis on formality and 'face saving. ’ It is not the Dutch person's intent to offend. Similarly, their sense of humor may appear strong to some, and few topics are forbidden. • The Dutch do not often initiate conversation with a stranger. The Dutch greet each other with a handshake upon the first introduction and share their first and last names. After the initial meeting, they nod and say hello to one another as friends but generally do not shake hands again. In Amsterdam, kissing close friends on the cheek three times is acceptable when greeting. Some Dutch may simply shake hands and say their surname. They may also answer the telephone by saying their surname. In a business setting, one should use courtesy titles (Mevrouw for women, Meneer of Meneer for men) followed by a surname.

Conclusion The central geographical position of the Netherlands and its outstanding infrastructure make it the ideal gateway to start expanding your business to (mainland) Europe. • The Netherlands acts as the logistics hub for Europe through the Rotterdam port (Europe’s largest) and Amsterdam Airport Schiphol (named best European airport for 2013), both with renowned service levels. • The Netherlands features one of the most highly educated, flexible and motivated workforces in Europe. • Due to its exceptional amount of bilateral investment treaties, the Netherlands is a secure place from which to make your investments. • The Dutch political/financial climate has been very stable for decades. • The Netherlands has the eighth position of cleanest countries in the world with respect to the perceived level of public sector corruption. • According to the Global Enabling Trade Report 2014 of the World Economic Forum, the Netherlands ranks third out of 138 countries in the Enabling Trade Index 2014.

Thank you for attention!
Aigerim Sakanova business system.pptx