c4242ec51407a8fcdbf22672fc58205f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 8

. NET Remoting A Distributed Application Cookbook

Agenda • Brief overview of Remoting • Technicalities for creating a distributed application based on Remoting • Examples will be uploaded to the course site
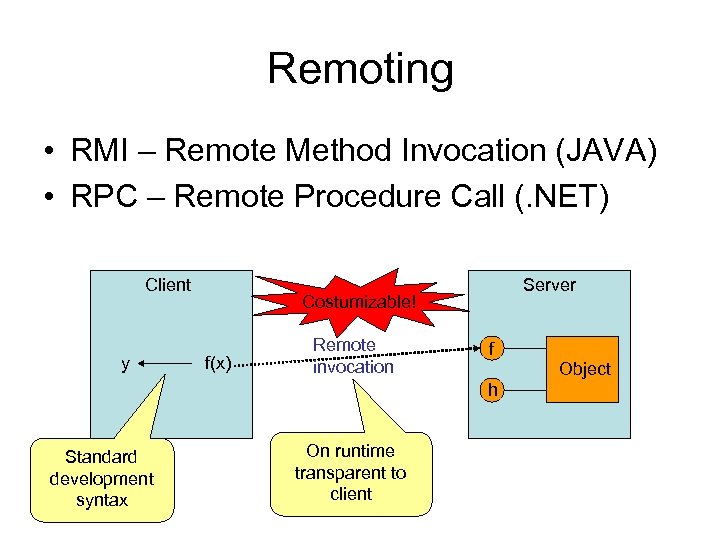
Remoting • RMI – Remote Method Invocation (JAVA) • RPC – Remote Procedure Call (. NET) Client y Server Costumizable! f(x) Remote invocation f h Standard development syntax On runtime transparent to client Object
Step 1 – Miscellaneous • Create three modules – A client module • Holds client code • Will ultimately run the client process (console application) – A server module • Holds server code • Will ultimately run the server process (console application) – A common library • This module contains all the declarationsdefinitions that are common to the client and the server (DLL)
Step 2 – Creating the remote object - In the common library module Declare an interface exposing your remote objects methods - In the server module, declare the object’s class extending Marshal. By. Ref. Object and implementing the interface

Step 3 – Hosting the object • The object is hosted in the server process • Programmatically: Soap. Server. Formatter. Sink. Provider server = new Soap. Server. Formatter. Sink. Provider(); server. Type. Filter. Level = System. Runtime. Serialization. Formatters. Type. Filter. Level. Full; IDictionary prop = new Hashtable(); prop["port"] = 9999; Channel. Services. Register. Channel(new Http. Channel(prop, null, server), false); Remoting. Configuration. Register. Well. Known. Service. Type( Type. Get. Type("Server. Program, Server"), "Service", Well. Known. Object. Mode. Singleton); • Using a configuration file

Step 4 – Instantiation at the client • The object is instantiated and accessed in the client process • Programmatically: Soap. Server. Formatter. Sink. Provider server = new Soap. Server. Formatter. Sink. Provider(); server. Type. Filter. Level = System. Runtime. Serialization. Formatters. Type. Filter. Level. Full; IDictionary prop = new Hashtable(); prop["port"] = 0; //listens on an arbitrary port Channel. Services. Register. Channel(new Http. Channel(prop, null, server), false); Common. IService service = (Common. IService)Activator. Get. Object(typeof(Common. IService), "http: //localhost: 9999/Service"); • Using a configuration file

Custom Sinks • A class implemeting the sink – Extend Base. Channel. Sink. With. Properties – Implement IClient. Channel. Sink or Iserver. Channel. Sink – Implement IMessage. Sink if placed before the formater sink • A sink provider class – Implementing IClient. Channel. Sink. Provider or IServer. Channel. Sink. Provider – Actually passed to the channel
c4242ec51407a8fcdbf22672fc58205f.ppt