68839eba57005698e76141cf2b6c3918.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 130
 Net. CDF 4 Reformatting Toolkit (N 4 RT): BUFR and GRIB 2 Tailoring Critical Design Review September 14, 2009 Prepared By: Tom King 1, Zhaohui Cheng 1, Larisa Koval 1, and Yi Song 2, 1 PSGS, 2 IMSG 1
Net. CDF 4 Reformatting Toolkit (N 4 RT): BUFR and GRIB 2 Tailoring Critical Design Review September 14, 2009 Prepared By: Tom King 1, Zhaohui Cheng 1, Larisa Koval 1, and Yi Song 2, 1 PSGS, 2 IMSG 1
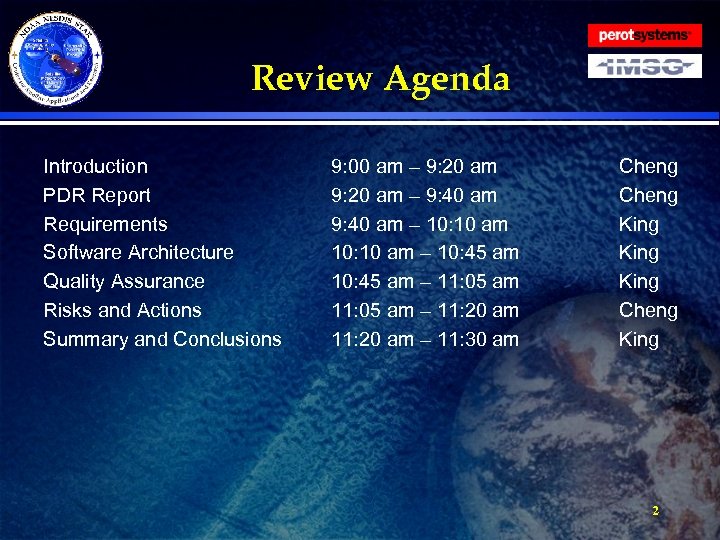 Review Agenda Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 9: 00 am – 9: 20 am – 9: 40 am – 10: 10 am – 10: 45 am – 11: 05 am – 11: 20 am – 11: 30 am Cheng King Cheng King 2
Review Agenda Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 9: 00 am – 9: 20 am – 9: 40 am – 10: 10 am – 10: 45 am – 11: 05 am – 11: 20 am – 11: 30 am Cheng King Cheng King 2
 Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 3
Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 3
 Introduction Presented by Zhaohui Cheng NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 4
Introduction Presented by Zhaohui Cheng NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 4
 Introduction · Project Background » IJPS » NPP/NPOESS » NDE · Project Objectives · Integrated Product Team · Project Plan · Entry and Exit Criteria 5
Introduction · Project Background » IJPS » NPP/NPOESS » NDE · Project Objectives · Integrated Product Team · Project Plan · Entry and Exit Criteria 5
 Project Background NPP/NPOESS • NPP and NPOESS, a joint Military/NOAA/NASA effort, is the next series of polar-orbiting satellites dedicated to among other things, operational meteorology. The objective of the NPOESS mission is to ensure continuity, improvement and availability of operational observations from an afternoon polar orbit (1: 30 pm). • Instrument packages on NPOESS: » Cr. IS, ATMS, VIIRS, OMPS, SEM, CERES, MIS • NPP is the first of five missions with launch dates of ≈2011, ≈2013, ≈2016, ≈2018, ≈ 2020, respectively. 6
Project Background NPP/NPOESS • NPP and NPOESS, a joint Military/NOAA/NASA effort, is the next series of polar-orbiting satellites dedicated to among other things, operational meteorology. The objective of the NPOESS mission is to ensure continuity, improvement and availability of operational observations from an afternoon polar orbit (1: 30 pm). • Instrument packages on NPOESS: » Cr. IS, ATMS, VIIRS, OMPS, SEM, CERES, MIS • NPP is the first of five missions with launch dates of ≈2011, ≈2013, ≈2016, ≈2018, ≈ 2020, respectively. 6
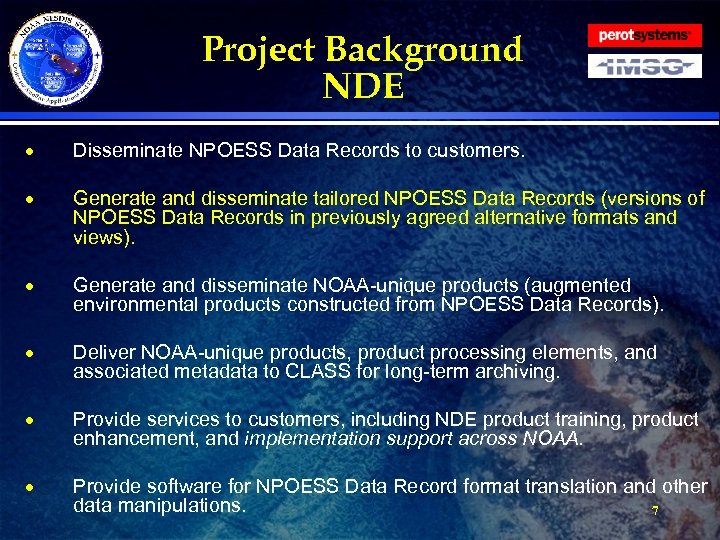 Project Background NDE · Disseminate NPOESS Data Records to customers. · Generate and disseminate tailored NPOESS Data Records (versions of NPOESS Data Records in previously agreed alternative formats and views). · Generate and disseminate NOAA-unique products (augmented environmental products constructed from NPOESS Data Records). · Deliver NOAA-unique products, product processing elements, and associated metadata to CLASS for long-term archiving. · Provide services to customers, including NDE product training, product enhancement, and implementation support across NOAA. · Provide software for NPOESS Data Record format translation and other data manipulations. 7
Project Background NDE · Disseminate NPOESS Data Records to customers. · Generate and disseminate tailored NPOESS Data Records (versions of NPOESS Data Records in previously agreed alternative formats and views). · Generate and disseminate NOAA-unique products (augmented environmental products constructed from NPOESS Data Records). · Deliver NOAA-unique products, product processing elements, and associated metadata to CLASS for long-term archiving. · Provide services to customers, including NDE product training, product enhancement, and implementation support across NOAA. · Provide software for NPOESS Data Record format translation and other data manipulations. 7
 Project Objectives · To build a software package that will tailor NPOESS and NDE products from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR and GRIB 2 formats in support of NDE’s overall tailoring efforts. · The Net. CDF 4 Reformatting Toolkit (N 4 RT) must be designed so it can easily be modified/expanded to incorporate the tailoring of new products. » Flexible » Extendable · The software must be able run within the NDE system architecture and operate within the NDE functional guidelines. · Output product formats and content must meet the needs of NOAA customers. 8
Project Objectives · To build a software package that will tailor NPOESS and NDE products from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR and GRIB 2 formats in support of NDE’s overall tailoring efforts. · The Net. CDF 4 Reformatting Toolkit (N 4 RT) must be designed so it can easily be modified/expanded to incorporate the tailoring of new products. » Flexible » Extendable · The software must be able run within the NDE system architecture and operate within the NDE functional guidelines. · Output product formats and content must meet the needs of NOAA customers. 8
 Project Objectives Phase 1 Products · Products to Reformat » » » » » ATMS Radiances Cr. IS Radiances Nadir Profile and Total Column Ozone (OMPS) VIIRS Radiances Aerosol Optical Thickness Sea Surface Temperature Snow Cover (Currently Tabled) Vegetation Index (Currently Tabled) Polar Winds (Possibly New) Green Vegetation Fraction (Possibly New) 9
Project Objectives Phase 1 Products · Products to Reformat » » » » » ATMS Radiances Cr. IS Radiances Nadir Profile and Total Column Ozone (OMPS) VIIRS Radiances Aerosol Optical Thickness Sea Surface Temperature Snow Cover (Currently Tabled) Vegetation Index (Currently Tabled) Polar Winds (Possibly New) Green Vegetation Fraction (Possibly New) 9
 Integrated Product Team · IPT Lead: Walter Wolf (STAR) · IPT Backup Lead: AK Sharma (OSDPD) · NESDIS team: » STAR: Walter Wolf, Hank Drahos, Jaime Daniels, Yi Song, Thomas King, Larisa Koval » OSDPD: Dave Benner, AK Sharma, Ricky Irving » OSD: Tom Schott, Jim Yoe » Data Center: Lei Shi (NCDC) · User team » Lead: Jim Heil (NWS), Stephen Lord (NWS /NCEP/EMC), John Derber (NWS/NCEP/EMC), Jeff Ator (NWS/NCEP/NCO), Lars Peter-Riishojgaard (JCSDA), Tony Mc. Nally (ECMWF), Fiona Hilton (UK-Met) » Others: International NWP users, NWP FOs, Climate Users · Product Oversight Panel: ZPOP, EPOP, ICAPOP, CAL/NAVPOP 10
Integrated Product Team · IPT Lead: Walter Wolf (STAR) · IPT Backup Lead: AK Sharma (OSDPD) · NESDIS team: » STAR: Walter Wolf, Hank Drahos, Jaime Daniels, Yi Song, Thomas King, Larisa Koval » OSDPD: Dave Benner, AK Sharma, Ricky Irving » OSD: Tom Schott, Jim Yoe » Data Center: Lei Shi (NCDC) · User team » Lead: Jim Heil (NWS), Stephen Lord (NWS /NCEP/EMC), John Derber (NWS/NCEP/EMC), Jeff Ator (NWS/NCEP/NCO), Lars Peter-Riishojgaard (JCSDA), Tony Mc. Nally (ECMWF), Fiona Hilton (UK-Met) » Others: International NWP users, NWP FOs, Climate Users · Product Oversight Panel: ZPOP, EPOP, ICAPOP, CAL/NAVPOP 10
 Project Stakeholders · NOAA National Weather Service » Weather Forecast Offices » National Center for Environmental Prediction · Department of Defense » NRL » FNMOC » AFWA · Global NWP » » » EUMETSAT ECMWF UK Meteo France CMC 11
Project Stakeholders · NOAA National Weather Service » Weather Forecast Offices » National Center for Environmental Prediction · Department of Defense » NRL » FNMOC » AFWA · Global NWP » » » EUMETSAT ECMWF UK Meteo France CMC 11
 Project Plan · Year 1 – Design and Development (2008 – 2009) » Verify Requirements – Work with customers to verify product requirements – Discuss with the current developers of similar translators to determine what is required in their output files » Design the Net. CDF 4 reformatting toolkit; » Conduct PDR » Develop BUFR tables and GRIB 2 formats with the product teams for Phase 1 products » Work with NDE to determine the interface between the Level 1 B and the Level 2 NPP products and the reformatter » Conduct CDR 12
Project Plan · Year 1 – Design and Development (2008 – 2009) » Verify Requirements – Work with customers to verify product requirements – Discuss with the current developers of similar translators to determine what is required in their output files » Design the Net. CDF 4 reformatting toolkit; » Conduct PDR » Develop BUFR tables and GRIB 2 formats with the product teams for Phase 1 products » Work with NDE to determine the interface between the Level 1 B and the Level 2 NPP products and the reformatter » Conduct CDR 12
 Net. CDF 4 Reformatter: System Design and Development for Phase 1 13
Net. CDF 4 Reformatter: System Design and Development for Phase 1 13
 Project Plan · Year 2 –Transition to Pre-Operations of Phase 1 Products (2009 – 2010) » Set up infrastructure to implement the readers and writers for the data formats » Implement BUFR tables and GRIB 2 formats for the Phase 1 products on the NDE hardware » Conduct Test Readiness Review for Phase 1 products » Transition and test system within the NDE environment » Conduct Code Review for Phase 1 products 14
Project Plan · Year 2 –Transition to Pre-Operations of Phase 1 Products (2009 – 2010) » Set up infrastructure to implement the readers and writers for the data formats » Implement BUFR tables and GRIB 2 formats for the Phase 1 products on the NDE hardware » Conduct Test Readiness Review for Phase 1 products » Transition and test system within the NDE environment » Conduct Code Review for Phase 1 products 14
 Project Plan · Year 3 – Transition to Operations of Phase 1 Products (2010 – 2011) » Evaluate with NDE and OSDPD the implementation of the Reformatting Toolkit within the NDE data handling system » Conduct System Readiness Review for Phase 1 products » Transition pre-operational Phase 1 product reformatting system to operations 15
Project Plan · Year 3 – Transition to Operations of Phase 1 Products (2010 – 2011) » Evaluate with NDE and OSDPD the implementation of the Reformatting Toolkit within the NDE data handling system » Conduct System Readiness Review for Phase 1 products » Transition pre-operational Phase 1 product reformatting system to operations 15
 Phase 1 Transition to Operations 16
Phase 1 Transition to Operations 16
 Project Plan – Schedule · Schedule (Milestones) » » » Project begins – 07/01/08 Preliminary Design Review – 04/14/09 (10/21/08) Critical Design Review – 09/14/09 (03/19/09) Test Readiness Review – 04/14/10 (02/25/09) Code Unit Test Review – 05/12/10 (01/29/10) System Readiness Review – 01/31/11 (04/20/10) – Waive or shift to NDE 17
Project Plan – Schedule · Schedule (Milestones) » » » Project begins – 07/01/08 Preliminary Design Review – 04/14/09 (10/21/08) Critical Design Review – 09/14/09 (03/19/09) Test Readiness Review – 04/14/10 (02/25/09) Code Unit Test Review – 05/12/10 (01/29/10) System Readiness Review – 01/31/11 (04/20/10) – Waive or shift to NDE 17
 Entry Criteria · PDR Completed and the following items reviewed: » » Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions · Requirements Allocation Document - Updated · PDR Report » The PDR Report (PDRR) is a standard artifact of the STAR EPL process. The PDR report is produced after the PDR. It contains: – Actions – Comments – Revision of the PDR » PDR Report for this project contains 13 items for review. These will be discussed in the next section. 18
Entry Criteria · PDR Completed and the following items reviewed: » » Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions · Requirements Allocation Document - Updated · PDR Report » The PDR Report (PDRR) is a standard artifact of the STAR EPL process. The PDR report is produced after the PDR. It contains: – Actions – Comments – Revision of the PDR » PDR Report for this project contains 13 items for review. These will be discussed in the next section. 18
 Exit Criteria · Conduct the CDR · The CDR Report (CDRR) is a standard artifact of the STAR EPL process. The CDR report is produced after the CDR. It contains: » Actions » Comments » Revision of the CDR 19
Exit Criteria · Conduct the CDR · The CDR Report (CDRR) is a standard artifact of the STAR EPL process. The CDR report is produced after the CDR. It contains: » Actions » Comments » Revision of the CDR 19
 Summary of Review Objectives · Review the Project Schedule and Plans · Review of the PDR Report · Review the Requirements · Review Software Architecture · Review Quality Assurance · Identify Risks and Actions 20
Summary of Review Objectives · Review the Project Schedule and Plans · Review of the PDR Report · Review the Requirements · Review Software Architecture · Review Quality Assurance · Identify Risks and Actions 20
 Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 21
Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 21
 PDR Report Presented by Zhaohui Cheng NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 22
PDR Report Presented by Zhaohui Cheng NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 22
 PDR Risk · Risk 1: NPOESS product formats and content are still changing, especially for VIIRS · Assessment: Low · Impact: May have to revise software several time during development to adjust to new formats, names, and types. · Likelihood: High · Mitigation: Work through the NPOESS Data Format Working Group to obtain information on format and algorithm updates. Monitor the latest copies of the NPOESS Common Data Format Control Books (CDFCB) for any updates. Maintain contact with customers to inform them of any upstream product changes. Make the code design flexible so that changes in the upstream products translate into the minimum amount code revision. · Status: Open 23
PDR Risk · Risk 1: NPOESS product formats and content are still changing, especially for VIIRS · Assessment: Low · Impact: May have to revise software several time during development to adjust to new formats, names, and types. · Likelihood: High · Mitigation: Work through the NPOESS Data Format Working Group to obtain information on format and algorithm updates. Monitor the latest copies of the NPOESS Common Data Format Control Books (CDFCB) for any updates. Maintain contact with customers to inform them of any upstream product changes. Make the code design flexible so that changes in the upstream products translate into the minimum amount code revision. · Status: Open 23
 PDR Risk · Risk 2: The roles and responsibilities regarding who shall generate the set of required SPSRB documents for NDE has not yet been decided. · Assessment: Low · Impact: Difficult to budget time needed for the team to generate documentation. · Likelihood: Moderate · Mitigation: This issue, and that of document content, is being worked by Maurice Mc. Hugh, STAR, NDE, OSD, and OSDPD personnel. Reformatting Toolkit developers intend to participate in these meetings and discussions. · Status: Open 24
PDR Risk · Risk 2: The roles and responsibilities regarding who shall generate the set of required SPSRB documents for NDE has not yet been decided. · Assessment: Low · Impact: Difficult to budget time needed for the team to generate documentation. · Likelihood: Moderate · Mitigation: This issue, and that of document content, is being worked by Maurice Mc. Hugh, STAR, NDE, OSD, and OSDPD personnel. Reformatting Toolkit developers intend to participate in these meetings and discussions. · Status: Open 24
 PDR Risk · Risk 3: There are small variations in the types of platforms and the versions of the compilers · Assessment: Low · Impact: May obtain different results using different compilers. · Likelihood: Moderate · Mitigation: Reformatting Toolkit developers will work with NDE during system tests in the integration and production phase to ensure that those results match the results from the units. The BCR process (mentioned earlier) should help to resolve these issues early on in development. · Status: Open 25
PDR Risk · Risk 3: There are small variations in the types of platforms and the versions of the compilers · Assessment: Low · Impact: May obtain different results using different compilers. · Likelihood: Moderate · Mitigation: Reformatting Toolkit developers will work with NDE during system tests in the integration and production phase to ensure that those results match the results from the units. The BCR process (mentioned earlier) should help to resolve these issues early on in development. · Status: Open 25
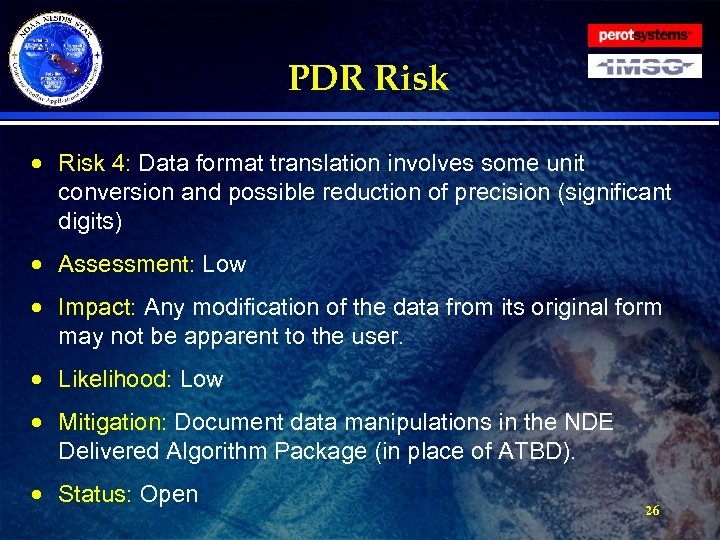 PDR Risk · Risk 4: Data format translation involves some unit conversion and possible reduction of precision (significant digits) · Assessment: Low · Impact: Any modification of the data from its original form may not be apparent to the user. · Likelihood: Low · Mitigation: Document data manipulations in the NDE Delivered Algorithm Package (in place of ATBD). · Status: Open 26
PDR Risk · Risk 4: Data format translation involves some unit conversion and possible reduction of precision (significant digits) · Assessment: Low · Impact: Any modification of the data from its original form may not be apparent to the user. · Likelihood: Low · Mitigation: Document data manipulations in the NDE Delivered Algorithm Package (in place of ATBD). · Status: Open 26
 PDR Risk · Risk 6: Risk on NDVI and snow mask. Test GRIB 2 functionality before/for CDR. · Assessment: Moderate · Impact: Failure to meet the requirement to have demonstrated GRIB 2 tailoring capability. · Likelihood: Low · Mitigation: RAD/Requirements meeting before CDR. · Status: Open 27
PDR Risk · Risk 6: Risk on NDVI and snow mask. Test GRIB 2 functionality before/for CDR. · Assessment: Moderate · Impact: Failure to meet the requirement to have demonstrated GRIB 2 tailoring capability. · Likelihood: Low · Mitigation: RAD/Requirements meeting before CDR. · Status: Open 27
 PDR Risk · Risk 8: Requirement to write tailoring into GRIB 2 VIIRS snow cover and vegetation index. Need to insure that view point M. EK is known and understood by EMC director. · Assessment: Moderate · Impact: User (EMC) does not receive the product they requested. · Likelihood: Moderate · Mitigation: Yoe/Schott to contact M. EK and coordinate w/s Lord/EMC/JCSDA before decisions (i. e. snow cover and vegetation index may decide differently) · Status: Open · Comments: Has this been done? If so, it can be closed. 28
PDR Risk · Risk 8: Requirement to write tailoring into GRIB 2 VIIRS snow cover and vegetation index. Need to insure that view point M. EK is known and understood by EMC director. · Assessment: Moderate · Impact: User (EMC) does not receive the product they requested. · Likelihood: Moderate · Mitigation: Yoe/Schott to contact M. EK and coordinate w/s Lord/EMC/JCSDA before decisions (i. e. snow cover and vegetation index may decide differently) · Status: Open · Comments: Has this been done? If so, it can be closed. 28
 PDR Risk · Risk 9: NWS and other NWP users will want ATMS/Cr. IS spectral response functions. They will also want OMPS key calibration functions. This information appears to be contained In ITAR document that we cannot share with foreign users. · Assessment: Moderate · Impact: Users will not be able to use the data. · Likelihood: High · Mitigation: NDE should work with IPO to determine if we can receive and release that ATMS, Cr. IS and OMPS SPF and KCF data to foreign NWP users. It is our understanding that the information is in ITAR documentation · Status: Open · Comments: We recommend closing this risk since it is not a risk to the Tailoring project. It is a user need that would be best addressed by IPO. 29
PDR Risk · Risk 9: NWS and other NWP users will want ATMS/Cr. IS spectral response functions. They will also want OMPS key calibration functions. This information appears to be contained In ITAR document that we cannot share with foreign users. · Assessment: Moderate · Impact: Users will not be able to use the data. · Likelihood: High · Mitigation: NDE should work with IPO to determine if we can receive and release that ATMS, Cr. IS and OMPS SPF and KCF data to foreign NWP users. It is our understanding that the information is in ITAR documentation · Status: Open · Comments: We recommend closing this risk since it is not a risk to the Tailoring project. It is a user need that would be best addressed by IPO. 29
 PDR Risk · Risk 11: A lot of effort would be imposed on projects/NDE to convert to Net. CDF 4 (depend heavily on NDE schedule for the conversion to Net. CDF 4). · Assessment: Low · Impact: Increased schedule pressure on NDE Product Teams. · Likelihood: Low · Mitigation: Make converter tool flexible to accept other formats not just Net. CDF 4. Those formats should include: 1) project formats (MIRS, NUCAPS, Ozone etc. ) 2) HDF 5 format from IDPS. This is not a risk for the Tailoring project. This is an NDE or Product Team risk. · Status: Open · Comments: We recommend closing this since it is not a risk to the Tailoring project. It’s a risk to NDE and the Product Teams. 30
PDR Risk · Risk 11: A lot of effort would be imposed on projects/NDE to convert to Net. CDF 4 (depend heavily on NDE schedule for the conversion to Net. CDF 4). · Assessment: Low · Impact: Increased schedule pressure on NDE Product Teams. · Likelihood: Low · Mitigation: Make converter tool flexible to accept other formats not just Net. CDF 4. Those formats should include: 1) project formats (MIRS, NUCAPS, Ozone etc. ) 2) HDF 5 format from IDPS. This is not a risk for the Tailoring project. This is an NDE or Product Team risk. · Status: Open · Comments: We recommend closing this since it is not a risk to the Tailoring project. It’s a risk to NDE and the Product Teams. 30
 PDR Risk · Risk 12: Timelines gets tight If we have to convert HDF 5, project format to Net. CDF 4 and then to other format. · Assessment: Moderate · Impact: Users may receive their product later than desired. · Likelihood: NA · Mitigation: Asses timeliness issue (due to added conversion step). · Status: Open · Comments: We recommend closing this since it is not a risk to the Tailoring project. It’s a risk to NDE and the Product Teams. 31
PDR Risk · Risk 12: Timelines gets tight If we have to convert HDF 5, project format to Net. CDF 4 and then to other format. · Assessment: Moderate · Impact: Users may receive their product later than desired. · Likelihood: NA · Mitigation: Asses timeliness issue (due to added conversion step). · Status: Open · Comments: We recommend closing this since it is not a risk to the Tailoring project. It’s a risk to NDE and the Product Teams. 31
 PDR Comment · Review Item 5: Requirement section: traceability to L 1 requirements is a strength. This section mingles project requirements, system requirements and assumptions. · Mitigation: In the RAD and PDR, clearly identify assumptions up-front, including expectations of the NDE system. Remove "NDE shall…" requirements. NDE team will validate assumption and assume new requirements if necessary. · Comments: The PDR and RAD have been revised to identify only the Tailoring project’s requirements. The language in the requirements analysis has been modified to express the project’s understanding of NDE’s roles. 32
PDR Comment · Review Item 5: Requirement section: traceability to L 1 requirements is a strength. This section mingles project requirements, system requirements and assumptions. · Mitigation: In the RAD and PDR, clearly identify assumptions up-front, including expectations of the NDE system. Remove "NDE shall…" requirements. NDE team will validate assumption and assume new requirements if necessary. · Comments: The PDR and RAD have been revised to identify only the Tailoring project’s requirements. The language in the requirements analysis has been modified to express the project’s understanding of NDE’s roles. 32
 PDR Comment · Review Item 7: Set up a meeting with Tom Schott on new aerosol product requirements/requests. · Comments: Has this been done? 33
PDR Comment · Review Item 7: Set up a meeting with Tom Schott on new aerosol product requirements/requests. · Comments: Has this been done? 33
 PDRR – Item 10 · Review Item 10: Minor terminology and details. 1) IPs: Not all IPs are created equal. DIPs: Delivered IPs (OMPS NP O 3 Profile). RIPS: Retained IPs 2) O 3 POP is now Atmospheric Chemistry POP. 3) OMPS Total Ozone Algorithm is multiple triplet Not v 8 primary. Output fields are equivalent to v 8 on GOME-2. · Mitigation: 1) Not existence of DIPs. Current OMPS DIP is v 6. 2) Change in POP list. 3) Get sample EDR compare fields to GOME-2 v 8 PMF · Comments: The PDR has been updated to contain the enhanced IP definitions and ozone algorithm version. 34
PDRR – Item 10 · Review Item 10: Minor terminology and details. 1) IPs: Not all IPs are created equal. DIPs: Delivered IPs (OMPS NP O 3 Profile). RIPS: Retained IPs 2) O 3 POP is now Atmospheric Chemistry POP. 3) OMPS Total Ozone Algorithm is multiple triplet Not v 8 primary. Output fields are equivalent to v 8 on GOME-2. · Mitigation: 1) Not existence of DIPs. Current OMPS DIP is v 6. 2) Change in POP list. 3) Get sample EDR compare fields to GOME-2 v 8 PMF · Comments: The PDR has been updated to contain the enhanced IP definitions and ozone algorithm version. 34
 PDR Comment · Review Item 13: Good idea to have placeholder for additional quality flags (for land mask etc. ). Filling them depends on timelines. Why not the same thing is done to ATMS BUFR table. · Mitigation: Plan for placeholders of additional quality flags for ATMS radiance BUFR table. The need maybe there but not expressed. · Comments: There already spare bit fields in the ATMS BUFR quality flag fields if new ATMS quality flags become available. With respect to the tailoring software, it’s not within the scope of this project to assess data quality such that we generate and add to the BUFR our own new quality information. 35
PDR Comment · Review Item 13: Good idea to have placeholder for additional quality flags (for land mask etc. ). Filling them depends on timelines. Why not the same thing is done to ATMS BUFR table. · Mitigation: Plan for placeholders of additional quality flags for ATMS radiance BUFR table. The need maybe there but not expressed. · Comments: There already spare bit fields in the ATMS BUFR quality flag fields if new ATMS quality flags become available. With respect to the tailoring software, it’s not within the scope of this project to assess data quality such that we generate and add to the BUFR our own new quality information. 35
 PDRR Summary · There are 9 risks and 4 comments at this time. · 5 risks are rated as low, 4 as moderate. · We recommend closing 3 of the risks. · 6 risks will remain open. · An additional risk may be closed depending upon the status of progress (meetings Yoe/Schott and EMC). 36
PDRR Summary · There are 9 risks and 4 comments at this time. · 5 risks are rated as low, 4 as moderate. · We recommend closing 3 of the risks. · 6 risks will remain open. · An additional risk may be closed depending upon the status of progress (meetings Yoe/Schott and EMC). 36
 Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 37
Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 37
 Requirements Presented by Thomas King NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 38
Requirements Presented by Thomas King NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 38
 Requirements Overview · SPSRB Requirements were presented to the developers in a document entitled: “Level 1 Requirements for a Net. CDF 4 Reformatting Tool” (Version 1. 5). · Product requirements have been added to those from the SPSRB and are presented here as well. These additional requirements were obtained in a series of meetings between the developers, EMC (the customer) and the heritage product teams. · Using all of this information a Requirements Allocation Document (RAD) has been generated for the Reformatting Toolkit project. · Text highlighted in yellow indicates requirements that have been updated or refined since the PDR. 39
Requirements Overview · SPSRB Requirements were presented to the developers in a document entitled: “Level 1 Requirements for a Net. CDF 4 Reformatting Tool” (Version 1. 5). · Product requirements have been added to those from the SPSRB and are presented here as well. These additional requirements were obtained in a series of meetings between the developers, EMC (the customer) and the heritage product teams. · Using all of this information a Requirements Allocation Document (RAD) has been generated for the Reformatting Toolkit project. · Text highlighted in yellow indicates requirements that have been updated or refined since the PDR. 39
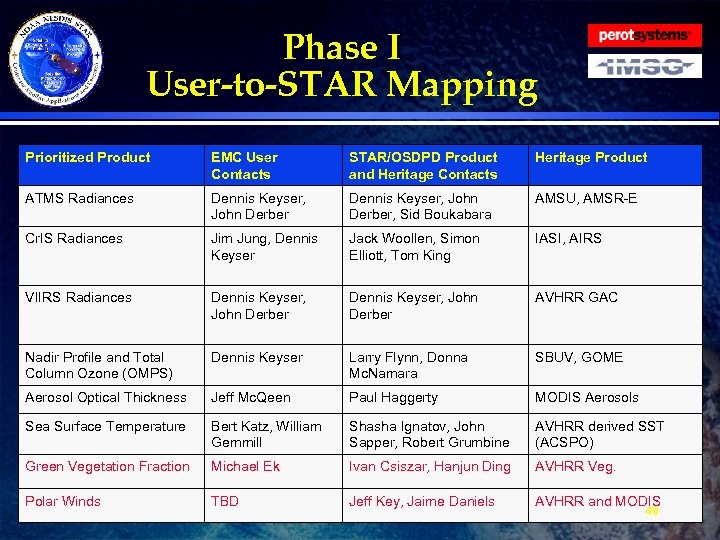 Phase I User-to-STAR Mapping Prioritized Product EMC User Contacts STAR/OSDPD Product and Heritage Contacts Heritage Product ATMS Radiances Dennis Keyser, John Derber Dennis Keyser, John Derber, Sid Boukabara AMSU, AMSR-E Cr. IS Radiances Jim Jung, Dennis Keyser Jack Woollen, Simon Elliott, Tom King IASI, AIRS VIIRS Radiances Dennis Keyser, John Derber Dennis Keyser, John Derber AVHRR GAC Nadir Profile and Total Column Ozone (OMPS) Dennis Keyser Larry Flynn, Donna Mc. Namara SBUV, GOME Aerosol Optical Thickness Jeff Mc. Qeen Paul Haggerty MODIS Aerosols Sea Surface Temperature Bert Katz, William Gemmill Shasha Ignatov, John Sapper, Robert Grumbine AVHRR derived SST (ACSPO) Green Vegetation Fraction Michael Ek Ivan Csiszar, Hanjun Ding AVHRR Veg. Polar Winds TBD Jeff Key, Jaime Daniels AVHRR and MODIS 40
Phase I User-to-STAR Mapping Prioritized Product EMC User Contacts STAR/OSDPD Product and Heritage Contacts Heritage Product ATMS Radiances Dennis Keyser, John Derber Dennis Keyser, John Derber, Sid Boukabara AMSU, AMSR-E Cr. IS Radiances Jim Jung, Dennis Keyser Jack Woollen, Simon Elliott, Tom King IASI, AIRS VIIRS Radiances Dennis Keyser, John Derber Dennis Keyser, John Derber AVHRR GAC Nadir Profile and Total Column Ozone (OMPS) Dennis Keyser Larry Flynn, Donna Mc. Namara SBUV, GOME Aerosol Optical Thickness Jeff Mc. Qeen Paul Haggerty MODIS Aerosols Sea Surface Temperature Bert Katz, William Gemmill Shasha Ignatov, John Sapper, Robert Grumbine AVHRR derived SST (ACSPO) Green Vegetation Fraction Michael Ek Ivan Csiszar, Hanjun Ding AVHRR Veg. Polar Winds TBD Jeff Key, Jaime Daniels AVHRR and MODIS 40
 Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software · Requirement: STAR shall deliver to NDE a reformatting toolkit capable of translating NESDIS Net. CDF 4 data products into NCEP-accepted data formats (i. e. , BUFR and/or GRIB 2). » Requirement: The toolkit shall be capable of reformatting the NPP tailoring prioritized phase 1 product list. 41
Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software · Requirement: STAR shall deliver to NDE a reformatting toolkit capable of translating NESDIS Net. CDF 4 data products into NCEP-accepted data formats (i. e. , BUFR and/or GRIB 2). » Requirement: The toolkit shall be capable of reformatting the NPP tailoring prioritized phase 1 product list. 41
 Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: The toolkit shall provide its capabilities such that it may be run automatically within an operational system, especially within the NDE environment. – The Toolkit shall compile and run on the NDE IBM AIX P 5 series hardware. – The Toolkit shall interact with the NDE Data Handling System (DHS). – The Toolkit shall be able to read a Production Control File (PCF). – The Toolkit shall handle and return errors according to NDE/STAR standard codes. – The Toolkit shall be able to write a (Product Status File) PSF. » Requirement: The toolkit shall consist of modular components that can be tested independently. – The code shall consist of a single compiled program that parses arguments and logically assigns tasks to a family of hierarchically structured tailoring subroutines. – Data shall be stored in allocatable data structures. 42
Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: The toolkit shall provide its capabilities such that it may be run automatically within an operational system, especially within the NDE environment. – The Toolkit shall compile and run on the NDE IBM AIX P 5 series hardware. – The Toolkit shall interact with the NDE Data Handling System (DHS). – The Toolkit shall be able to read a Production Control File (PCF). – The Toolkit shall handle and return errors according to NDE/STAR standard codes. – The Toolkit shall be able to write a (Product Status File) PSF. » Requirement: The toolkit shall consist of modular components that can be tested independently. – The code shall consist of a single compiled program that parses arguments and logically assigns tasks to a family of hierarchically structured tailoring subroutines. – Data shall be stored in allocatable data structures. 42
 Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: STAR shall include one update to the reformatting toolkit within its initial project plan. » Requirement: STAR shall propose additional updates to the reformatting toolkit at a future Annual Review for Satellite Product Development that will address the NDE Phase 2 products. » Requirement: STAR shall use the standard set of NCEP software libraries for BUFR and GRIB 2 in the reformatting toolkit. » Requirement: STAR shall update the reformatting toolkit when NCEP updates its BUFR and GRIB 2 libraries. – Updates shall be made when there are updates to the versions of the Net. CDF 4 library being used by NDE. 43
Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: STAR shall include one update to the reformatting toolkit within its initial project plan. » Requirement: STAR shall propose additional updates to the reformatting toolkit at a future Annual Review for Satellite Product Development that will address the NDE Phase 2 products. » Requirement: STAR shall use the standard set of NCEP software libraries for BUFR and GRIB 2 in the reformatting toolkit. » Requirement: STAR shall update the reformatting toolkit when NCEP updates its BUFR and GRIB 2 libraries. – Updates shall be made when there are updates to the versions of the Net. CDF 4 library being used by NDE. 43
 Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: STAR shall coordinate with the NDE Project before proposing any enhancements to add other standard format translations to the toolkit at the Annual Review for Satellite Product Development. » Requirement: The output from the toolkit shall be compared with the input. » Requirement: The translation toolkit shall convert from the new format back into Net. CDF 4. » Requirement: The reformatting software shall log each transaction’s control information, including: the calling application, the type of transaction requested, the start and end times, and completion status codes. – The Reformatting Toolkit software shall generate run logs and return NDE/STAR standard (agreed upon) error codes to the DHS. 44
Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: STAR shall coordinate with the NDE Project before proposing any enhancements to add other standard format translations to the toolkit at the Annual Review for Satellite Product Development. » Requirement: The output from the toolkit shall be compared with the input. » Requirement: The translation toolkit shall convert from the new format back into Net. CDF 4. » Requirement: The reformatting software shall log each transaction’s control information, including: the calling application, the type of transaction requested, the start and end times, and completion status codes. – The Reformatting Toolkit software shall generate run logs and return NDE/STAR standard (agreed upon) error codes to the DHS. 44
 Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: Applications running under either Linux or AIX Operating Systems shall be able to provide the reformatting toolkit data and be able to accept the data from the toolkit for further processing (e. g. , dissemination). » Requirement: The toolkit parameters (e. g. , how to use the service) shall be well documented. – Reformatting Toolkit Developers shall provide documentation in the form of a tailored Delivered Algorithm Package (DAP). » Requirement: The messages provided by the toolkit in the event of failure to perform a requested service shall be comprehensible by untrained operators. – Reformatting Toolkit shall use the standard set of error return codes developed by NDE for code running within the DHS. 45
Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: Applications running under either Linux or AIX Operating Systems shall be able to provide the reformatting toolkit data and be able to accept the data from the toolkit for further processing (e. g. , dissemination). » Requirement: The toolkit parameters (e. g. , how to use the service) shall be well documented. – Reformatting Toolkit Developers shall provide documentation in the form of a tailored Delivered Algorithm Package (DAP). » Requirement: The messages provided by the toolkit in the event of failure to perform a requested service shall be comprehensible by untrained operators. – Reformatting Toolkit shall use the standard set of error return codes developed by NDE for code running within the DHS. 45
 Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: The messages provided by the toolkit in the event of failure to perform a requested service shall include diagnostic details needed for troubleshooting. – All messaging shall be directed to a run log file. These messages shall be documented in the Reformatting Toolkit tailored DAP. » Requirement: STAR shall coordinate development of the reformatting toolkit with the NDE contractors and assist the NDE contractors with the integration of the toolkit within each of the environments of the NDE processing system. » Requirement: Toolkit code shall adhere to the STAR coding standards. » Requirement: Performance shall be measured on a product level. 46
Functional Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Software » Requirement: The messages provided by the toolkit in the event of failure to perform a requested service shall include diagnostic details needed for troubleshooting. – All messaging shall be directed to a run log file. These messages shall be documented in the Reformatting Toolkit tailored DAP. » Requirement: STAR shall coordinate development of the reformatting toolkit with the NDE contractors and assist the NDE contractors with the integration of the toolkit within each of the environments of the NDE processing system. » Requirement: Toolkit code shall adhere to the STAR coding standards. » Requirement: Performance shall be measured on a product level. 46
 Program Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Project · Requirement: STAR shall provide monthly project status reports to OSDPD and OSD. · Requirement: Earned Value Management shall be performed on the project. · Requirement: STAR shall update the project plan on an annual basis and submit it to the Annual Review of Satellite Product Development for funding consideration. · Requirement: The toolkit shall be implemented and tested six months before the NPP launch to ensure NDE readiness. 47
Program Requirements: Reformatting Toolkit Project · Requirement: STAR shall provide monthly project status reports to OSDPD and OSD. · Requirement: Earned Value Management shall be performed on the project. · Requirement: STAR shall update the project plan on an annual basis and submit it to the Annual Review of Satellite Product Development for funding consideration. · Requirement: The toolkit shall be implemented and tested six months before the NPP launch to ensure NDE readiness. 47
 Product Requirements: Cr. IS Radiances · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor the NUCAPS thinned Cr. IS Radiances from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » The Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to create a BUFR table for the NUCAPS thinned radiances based on AIRS and IASI. » The table shall use delayed replication for storing the radiances. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The BUFR format shall allow for the storage of negative radiances. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 48
Product Requirements: Cr. IS Radiances · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor the NUCAPS thinned Cr. IS Radiances from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » The Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to create a BUFR table for the NUCAPS thinned radiances based on AIRS and IASI. » The table shall use delayed replication for storing the radiances. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The BUFR format shall allow for the storage of negative radiances. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 48
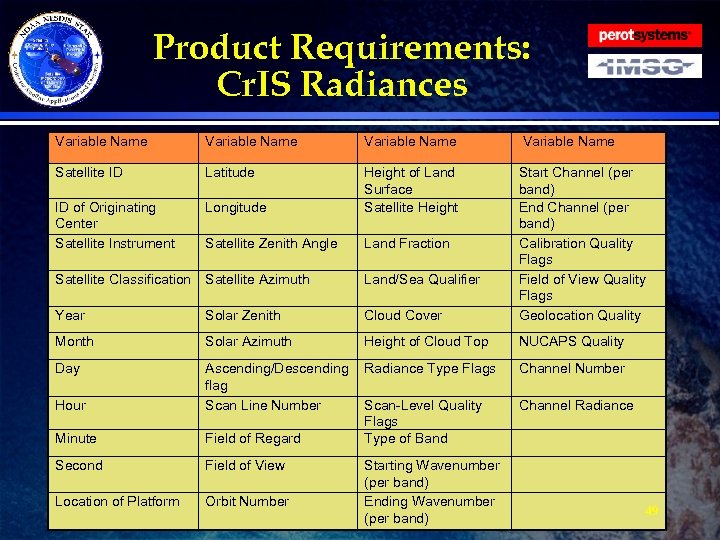 Product Requirements: Cr. IS Radiances Variable Name Satellite ID Latitude ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Longitude Height of Land Surface Satellite Height Satellite Zenith Angle Land Fraction Satellite Classification Satellite Azimuth Land/Sea Qualifier Year Solar Zenith Cloud Cover Start Channel (per band) End Channel (per band) Calibration Quality Flags Field of View Quality Flags Geolocation Quality Month Solar Azimuth Height of Cloud Top NUCAPS Quality Day Minute Ascending/Descending Radiance Type Flags flag Scan Line Number Scan-Level Quality Flags Field of Regard Type of Band Second Field of View Location of Platform Orbit Number Hour Starting Wavenumber (per band) Ending Wavenumber (per band) Channel Number Channel Radiance 49
Product Requirements: Cr. IS Radiances Variable Name Satellite ID Latitude ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Longitude Height of Land Surface Satellite Height Satellite Zenith Angle Land Fraction Satellite Classification Satellite Azimuth Land/Sea Qualifier Year Solar Zenith Cloud Cover Start Channel (per band) End Channel (per band) Calibration Quality Flags Field of View Quality Flags Geolocation Quality Month Solar Azimuth Height of Cloud Top NUCAPS Quality Day Minute Ascending/Descending Radiance Type Flags flag Scan Line Number Scan-Level Quality Flags Field of Regard Type of Band Second Field of View Location of Platform Orbit Number Hour Starting Wavenumber (per band) Ending Wavenumber (per band) Channel Number Channel Radiance 49
 Product Requirements: ATMS Radiances · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor the NPOESS ATMS SDR and TDR data from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » The ATMS BUFR file shall contain, from all channels, the antenna and brightness temperatures, associated Quality Flags, and the geolocation data at native resolution (not resampled) data. » The Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC and the MIRS team to create an ATMS BUFR table. The ATMS BUFR file shall be based on what is currently provided for AMSU and MHS. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 50
Product Requirements: ATMS Radiances · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor the NPOESS ATMS SDR and TDR data from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » The ATMS BUFR file shall contain, from all channels, the antenna and brightness temperatures, associated Quality Flags, and the geolocation data at native resolution (not resampled) data. » The Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC and the MIRS team to create an ATMS BUFR table. The ATMS BUFR file shall be based on what is currently provided for AMSU and MHS. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 50
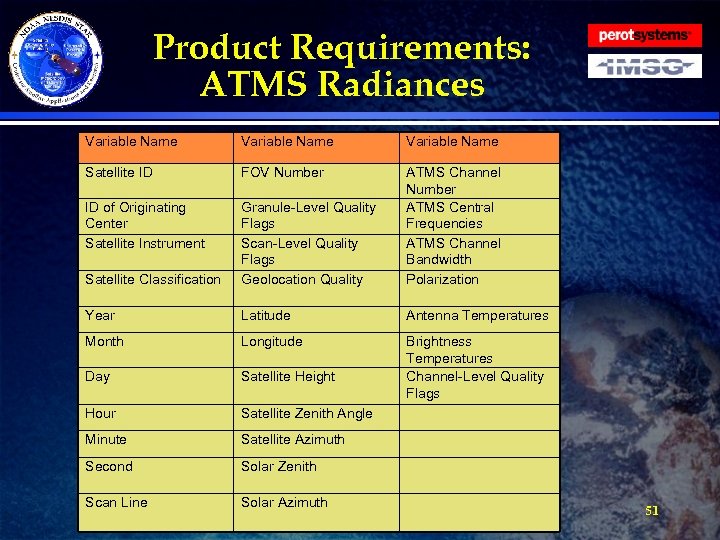 Product Requirements: ATMS Radiances Variable Name Satellite ID FOV Number ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Satellite Classification Granule-Level Quality Flags Scan-Level Quality Flags Geolocation Quality ATMS Channel Number ATMS Central Frequencies ATMS Channel Bandwidth Polarization Year Latitude Antenna Temperatures Month Longitude Day Satellite Height Brightness Temperatures Channel-Level Quality Flags Hour Satellite Zenith Angle Minute Satellite Azimuth Second Solar Zenith Scan Line Solar Azimuth 51
Product Requirements: ATMS Radiances Variable Name Satellite ID FOV Number ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Satellite Classification Granule-Level Quality Flags Scan-Level Quality Flags Geolocation Quality ATMS Channel Number ATMS Central Frequencies ATMS Channel Bandwidth Polarization Year Latitude Antenna Temperatures Month Longitude Day Satellite Height Brightness Temperatures Channel-Level Quality Flags Hour Satellite Zenith Angle Minute Satellite Azimuth Second Solar Zenith Scan Line Solar Azimuth 51
 Product Requirements: OMPS Ozone · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NPOESS OMPS Ozone products from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » The product shall contain OMPS Nadir Profile and Total Column (multiple triplet algorithm, not v 8, but output is equivalent to v 8 according to Larry Flynn). » The Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to develop an OMPS BUFR table based on that currently used for GOME and SBUV. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » This file’s content is currently under development. 52
Product Requirements: OMPS Ozone · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NPOESS OMPS Ozone products from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » The product shall contain OMPS Nadir Profile and Total Column (multiple triplet algorithm, not v 8, but output is equivalent to v 8 according to Larry Flynn). » The Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to develop an OMPS BUFR table based on that currently used for GOME and SBUV. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » This file’s content is currently under development. 52
 Product Requirements: VIIRS SST · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NPOESS VIIRS SST products from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » Product shall contain Skin SST, Bulk SST, Quality Flags, Cloud Mask, and geolocation data. » Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to create a BUFR table for the VIIRS SST product. » The VIIRS SST BUFR table shall be derived from that currently being used for the AVHRR derived SST (from ACSPO - Advanced Clear-Sky Processor for Oceans). » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 53
Product Requirements: VIIRS SST · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NPOESS VIIRS SST products from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » Product shall contain Skin SST, Bulk SST, Quality Flags, Cloud Mask, and geolocation data. » Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to create a BUFR table for the VIIRS SST product. » The VIIRS SST BUFR table shall be derived from that currently being used for the AVHRR derived SST (from ACSPO - Advanced Clear-Sky Processor for Oceans). » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 53
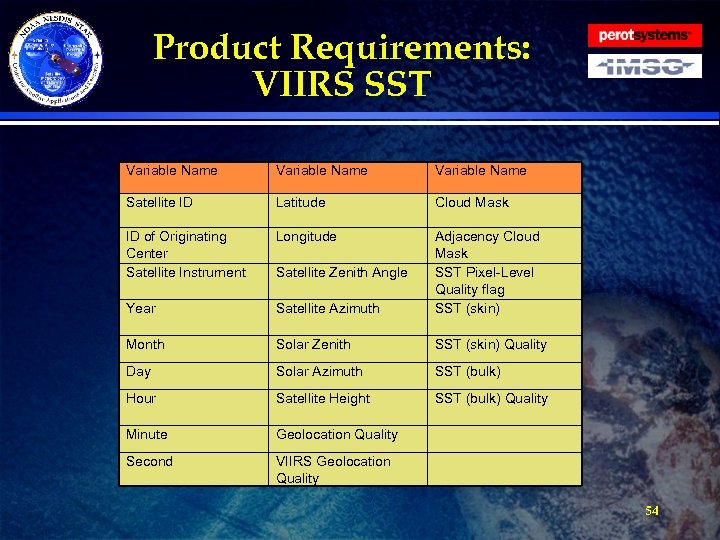 Product Requirements: VIIRS SST Variable Name Satellite ID Latitude Cloud Mask ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Longitude Year Satellite Azimuth Adjacency Cloud Mask SST Pixel-Level Quality flag SST (skin) Month Solar Zenith SST (skin) Quality Day Solar Azimuth SST (bulk) Hour Satellite Height SST (bulk) Quality Minute Geolocation Quality Second VIIRS Geolocation Quality Satellite Zenith Angle 54
Product Requirements: VIIRS SST Variable Name Satellite ID Latitude Cloud Mask ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Longitude Year Satellite Azimuth Adjacency Cloud Mask SST Pixel-Level Quality flag SST (skin) Month Solar Zenith SST (skin) Quality Day Solar Azimuth SST (bulk) Hour Satellite Height SST (bulk) Quality Minute Geolocation Quality Second VIIRS Geolocation Quality Satellite Zenith Angle 54
 Product Requirements: VIIRS Radiances · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NPOESS VIIRS Radiances from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » Each BUFR file will contain the VIIRS data for a single band (Imagery band, Moderate band, or Day/Night band resolution). » Coverage will be global. » Each of the 3 file types will use the same VIIRS BUFR table. » The product shall contain the land cloud mask if it doesn’t take too long for the IDPS to generate those EDRs. » Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to create a VIIRS BUFR table derived from that used earlier for the GAC AVHRR. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 55
Product Requirements: VIIRS Radiances · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NPOESS VIIRS Radiances from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » Each BUFR file will contain the VIIRS data for a single band (Imagery band, Moderate band, or Day/Night band resolution). » Coverage will be global. » Each of the 3 file types will use the same VIIRS BUFR table. » The product shall contain the land cloud mask if it doesn’t take too long for the IDPS to generate those EDRs. » Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to create a VIIRS BUFR table derived from that used earlier for the GAC AVHRR. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 55
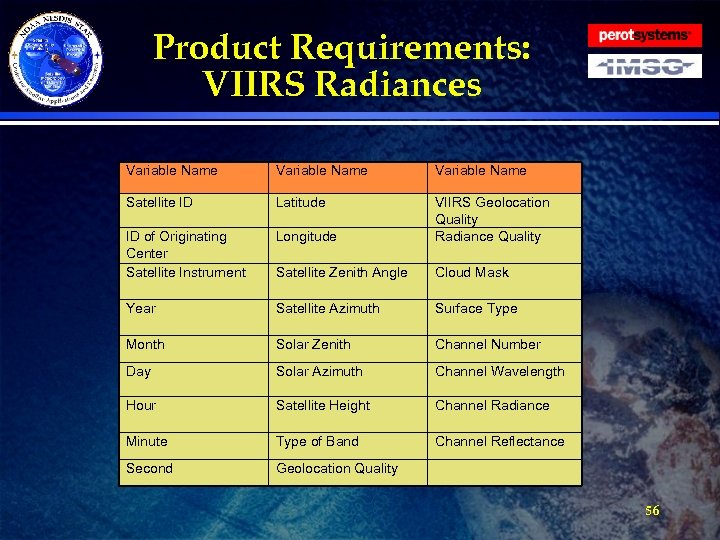 Product Requirements: VIIRS Radiances Variable Name Satellite ID Latitude ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Longitude VIIRS Geolocation Quality Radiance Quality Satellite Zenith Angle Cloud Mask Year Satellite Azimuth Surface Type Month Solar Zenith Channel Number Day Solar Azimuth Channel Wavelength Hour Satellite Height Channel Radiance Minute Type of Band Channel Reflectance Second Geolocation Quality 56
Product Requirements: VIIRS Radiances Variable Name Satellite ID Latitude ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Longitude VIIRS Geolocation Quality Radiance Quality Satellite Zenith Angle Cloud Mask Year Satellite Azimuth Surface Type Month Solar Zenith Channel Number Day Solar Azimuth Channel Wavelength Hour Satellite Height Channel Radiance Minute Type of Band Channel Reflectance Second Geolocation Quality 56
 Product Requirements: Aerosol Optical Thickness · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NPOESS Aerosol Optical Thickness (AOT) from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » The product shall contain the AOT, wavelength of AOT, and Aerosol Size. » Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to develop the AOT BUFR table based on what has already been done for MODIS. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 57
Product Requirements: Aerosol Optical Thickness · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NPOESS Aerosol Optical Thickness (AOT) from Net. CDF 4 into BUFR for EMC. » The product shall contain the AOT, wavelength of AOT, and Aerosol Size. » Reformatting Toolkit developers shall work with EMC to develop the AOT BUFR table based on what has already been done for MODIS. » BUFR messages shall be smaller than 50 KB. » The file shall contain the following data fields (see table next slide): 57
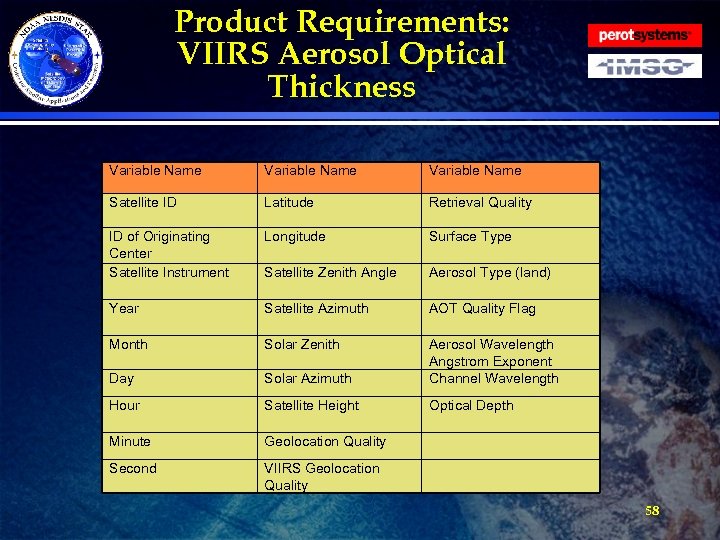 Product Requirements: VIIRS Aerosol Optical Thickness Variable Name Satellite ID Latitude Retrieval Quality ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Longitude Surface Type Satellite Zenith Angle Aerosol Type (land) Year Satellite Azimuth AOT Quality Flag Month Solar Zenith Day Solar Azimuth Aerosol Wavelength Angstrom Exponent Channel Wavelength Hour Satellite Height Optical Depth Minute Geolocation Quality Second VIIRS Geolocation Quality 58
Product Requirements: VIIRS Aerosol Optical Thickness Variable Name Satellite ID Latitude Retrieval Quality ID of Originating Center Satellite Instrument Longitude Surface Type Satellite Zenith Angle Aerosol Type (land) Year Satellite Azimuth AOT Quality Flag Month Solar Zenith Day Solar Azimuth Aerosol Wavelength Angstrom Exponent Channel Wavelength Hour Satellite Height Optical Depth Minute Geolocation Quality Second VIIRS Geolocation Quality 58
 Product Requirements: VIIRS Polar Winds · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NDE-generated Polar Winds product from Net. CDF 4 to BUFR format for EMC. · Additional requirements for this product will be forthcoming. 59
Product Requirements: VIIRS Polar Winds · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NDE-generated Polar Winds product from Net. CDF 4 to BUFR format for EMC. · Additional requirements for this product will be forthcoming. 59
 Product Requirements: Green Vegetation Index · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NDE-generated Green Vegetation Index products from Net. CDF 4 to GRIB 2 format for EMC. · Additional requirements for this product will be forthcoming. 60
Product Requirements: Green Vegetation Index · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall tailor NDE-generated Green Vegetation Index products from Net. CDF 4 to GRIB 2 format for EMC. · Additional requirements for this product will be forthcoming. 60
 Interface Requirements · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use thinned Cr. IS radiances (~300 channels) files from NUCAPS as an input for generating the Cr. IS radiance BUFR files. These files shall be in compliant Net. CDF 4 and shall already contain the thinned SDR and geolocation information. · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS ATMS TDR and SDR files and associated Geolocation files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the ATMS radiance BUFR files. · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS OMPS Total Column Ozone EDR files and OMPS Nadir Profile IP files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the OMPS Ozone BUFR files. 61
Interface Requirements · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use thinned Cr. IS radiances (~300 channels) files from NUCAPS as an input for generating the Cr. IS radiance BUFR files. These files shall be in compliant Net. CDF 4 and shall already contain the thinned SDR and geolocation information. · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS ATMS TDR and SDR files and associated Geolocation files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the ATMS radiance BUFR files. · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS OMPS Total Column Ozone EDR files and OMPS Nadir Profile IP files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the OMPS Ozone BUFR files. 61
 Interface Requirements · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS VIIRS radiance SDR files and associated Geolocation files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the VIIRS radiance BUFR files. » Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall receive the NPOESS VIIRS IP Cloud Mask Product to obtain the cloud and land mask for the VIIRS radiance BUFR files. · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS Aerosol Optical Thickness EDR files and associated Geolocation files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the Aerosol Optical Thickness EDR BUFR files. · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS SST EDR files and associated Geolocation files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the SST BUFR files. 62
Interface Requirements · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS VIIRS radiance SDR files and associated Geolocation files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the VIIRS radiance BUFR files. » Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall receive the NPOESS VIIRS IP Cloud Mask Product to obtain the cloud and land mask for the VIIRS radiance BUFR files. · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS Aerosol Optical Thickness EDR files and associated Geolocation files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the Aerosol Optical Thickness EDR BUFR files. · Requirement: The Reformatting Toolkit shall use the NPOESS SST EDR files and associated Geolocation files tailored into Net. CDF 4 as an input for generating the SST BUFR files. 62
 Requirements Summary · The Reformatting Toolkit developers have met with NDE and all the users of the original Phase I NDE tailored products. · All Reformatting Toolkit project, functional, and product requirements have been captured and documented in the Reformatting Toolkit RAD. · As development continues, the detailed product requirements shall continue to be refined. 63
Requirements Summary · The Reformatting Toolkit developers have met with NDE and all the users of the original Phase I NDE tailored products. · All Reformatting Toolkit project, functional, and product requirements have been captured and documented in the Reformatting Toolkit RAD. · As development continues, the detailed product requirements shall continue to be refined. 63
 Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 64
Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 64
 Software Architecture Presented by Thomas King PSGS 65
Software Architecture Presented by Thomas King PSGS 65
 Reformatting Toolkit Architecture · Hardware Environment » » · Data Files » » » · Development and Unit testing Test Product Distribution System Testing and Integration Production File Formats Input Files Static/Ancillary Files Output Files Run Files Software Description » External Interfaces » System Level » Unit Level 66
Reformatting Toolkit Architecture · Hardware Environment » » · Data Files » » » · Development and Unit testing Test Product Distribution System Testing and Integration Production File Formats Input Files Static/Ancillary Files Output Files Run Files Software Description » External Interfaces » System Level » Unit Level 66
 Reformatting Toolkit Development Hardware · Reformatting Toolkit Development Hardware - Unit tests, and Cr. IS/ATMS simulation data generation will be conducted on the IASI development machine at NSOF. This machine is maintained under the ESPC maintenance contract. » » » IBM P 570 (AIX 5. 3) 6 TB disk space 16 CPU 2 GB memory/CPU IBM XL Version 7. 0 C/C++ IBM XL Version 10. 1 Fortran 77/90 67
Reformatting Toolkit Development Hardware · Reformatting Toolkit Development Hardware - Unit tests, and Cr. IS/ATMS simulation data generation will be conducted on the IASI development machine at NSOF. This machine is maintained under the ESPC maintenance contract. » » » IBM P 570 (AIX 5. 3) 6 TB disk space 16 CPU 2 GB memory/CPU IBM XL Version 7. 0 C/C++ IBM XL Version 10. 1 Fortran 77/90 67
 Reformatting Toolkit Development Hardware · Additional Development Hardware - Reformatting Toolkit testing may be conducted at STAR on AIX. This machine was purchased with ground systems money. It will be located at NCWCP, and maintained by STAR IT. » » IBM P 570 3 TB disk space 16 CPU 2 GB memory/CPU · Configuration management of Reformatting Toolkit code will be conducted in the STAR Collaborative Environment on STAR Linux hardware running IBM Clear Case. 68
Reformatting Toolkit Development Hardware · Additional Development Hardware - Reformatting Toolkit testing may be conducted at STAR on AIX. This machine was purchased with ground systems money. It will be located at NCWCP, and maintained by STAR IT. » » IBM P 570 3 TB disk space 16 CPU 2 GB memory/CPU · Configuration management of Reformatting Toolkit code will be conducted in the STAR Collaborative Environment on STAR Linux hardware running IBM Clear Case. 68
 Reformatting Toolkit Test Product Distribution · STAR Data Server - Reformatting Toolkit test products will be available on a distribution server at STAR (ftp 2. orbit. nesdis. noaa. gov). » » Linux 3. 2 TB disk space Access via anonymous ftp Products available on a near real time basis · This server will make available test BUFR and GRIB 2 files containing simulated data, BUFR tables, and any additional resources. · The first finalized version of a Cr. IS test BUFR file was made available to EMC (Jeff Ator and Dennis Keyser) April 15, 2009. · Cr. IS test BUFR files were made available to users on a near real time basis on June 19, 2009. · Yong Chen at the JCSDA began accessing the Cr. IS test BUFR files on July 14, 2009. A BUFR table and reader subroutine were also provided. 69
Reformatting Toolkit Test Product Distribution · STAR Data Server - Reformatting Toolkit test products will be available on a distribution server at STAR (ftp 2. orbit. nesdis. noaa. gov). » » Linux 3. 2 TB disk space Access via anonymous ftp Products available on a near real time basis · This server will make available test BUFR and GRIB 2 files containing simulated data, BUFR tables, and any additional resources. · The first finalized version of a Cr. IS test BUFR file was made available to EMC (Jeff Ator and Dennis Keyser) April 15, 2009. · Cr. IS test BUFR files were made available to users on a near real time basis on June 19, 2009. · Yong Chen at the JCSDA began accessing the Cr. IS test BUFR files on July 14, 2009. A BUFR table and reader subroutine were also provided. 69
 Reformatting Toolkit Integration and Production Hardware · NDE SADIE – The Reformatting Toolkit system testing and integration will be conducted on the SADIE integration platform working with NDE integration personnel. This hardware is located at NSOF and is maintained under the ESPC maintenance contract. » » » IBM P 561 (AIX 5. 3) 50 TB disk space 16 CPUs 2 GB/CPU IBM XL Version 9. 0 C/C++ IBM XL Version 11. 1 Fortran 77/90 70
Reformatting Toolkit Integration and Production Hardware · NDE SADIE – The Reformatting Toolkit system testing and integration will be conducted on the SADIE integration platform working with NDE integration personnel. This hardware is located at NSOF and is maintained under the ESPC maintenance contract. » » » IBM P 561 (AIX 5. 3) 50 TB disk space 16 CPUs 2 GB/CPU IBM XL Version 9. 0 C/C++ IBM XL Version 11. 1 Fortran 77/90 70
 Reformatting Toolkit Integration and Production Hardware · NDE Test/Production Hardware - After successful system tests, our understanding is that NDE plans to check the code into configuration management and then promote it to the Test/Production machine. This machine will be located at NSOF. It has not yet been acquired. » » IBM P 570 (AIX 5. 3) TBD Disk space TBD CPUs TBD GB/CPU 71
Reformatting Toolkit Integration and Production Hardware · NDE Test/Production Hardware - After successful system tests, our understanding is that NDE plans to check the code into configuration management and then promote it to the Test/Production machine. This machine will be located at NSOF. It has not yet been acquired. » » IBM P 570 (AIX 5. 3) TBD Disk space TBD CPUs TBD GB/CPU 71
 Net. CDF 4 File Format Information · Net. CDF (Network Common Data Form) is a machine independent binary format that was developed by UCAR (University Corporation for Atmospheric Research). · The latest version of Net. CDF is version 4. Version 4 is built on top of HDF version 5. · Unlike BUFR and GRIB, it was not designed with a particular meteorological application so its records are not designed to assume any particular geographic reference. · Data are stored as arrays making it useful for storing sequentially organized data such as satellite data. 72
Net. CDF 4 File Format Information · Net. CDF (Network Common Data Form) is a machine independent binary format that was developed by UCAR (University Corporation for Atmospheric Research). · The latest version of Net. CDF is version 4. Version 4 is built on top of HDF version 5. · Unlike BUFR and GRIB, it was not designed with a particular meteorological application so its records are not designed to assume any particular geographic reference. · Data are stored as arrays making it useful for storing sequentially organized data such as satellite data. 72
 Net. CDF 4 File Format Information · The CF (Climate and Forecast) Convention defines metadata that are included in the same file as the data (thus making the file "self-describing"), that provide a definitive description of what the data in each variable represents, and of the spatial and temporal properties of the data. Examples of CF metadata include specification of: » Coordinate systems information needed to locate data in space and time » Standard names for quantities to determine whether data from different sources are comparable » Information about grids, such as grid cell bounds and cell averaging methods · The actual structure of data storage in Net. CDF is not known or visible to the user. The user must access the data solely through the Net. CDF APIs. 73
Net. CDF 4 File Format Information · The CF (Climate and Forecast) Convention defines metadata that are included in the same file as the data (thus making the file "self-describing"), that provide a definitive description of what the data in each variable represents, and of the spatial and temporal properties of the data. Examples of CF metadata include specification of: » Coordinate systems information needed to locate data in space and time » Standard names for quantities to determine whether data from different sources are comparable » Information about grids, such as grid cell bounds and cell averaging methods · The actual structure of data storage in Net. CDF is not known or visible to the user. The user must access the data solely through the Net. CDF APIs. 73
 BUFR File Format Information · BUFR (Binary Universal Form for the Representation of meteorological data ) is a machine dependent form of binary file. · The format is standardized by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Commission for Basic Systems (BUFR FM 94). · The current standard is version 4, although version 3 is still an accepted version for operations. · It is used primarily to store station data and was designed as a format for transmission. 74
BUFR File Format Information · BUFR (Binary Universal Form for the Representation of meteorological data ) is a machine dependent form of binary file. · The format is standardized by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Commission for Basic Systems (BUFR FM 94). · The current standard is version 4, although version 3 is still an accepted version for operations. · It is used primarily to store station data and was designed as a format for transmission. 74
 BUFR File Format Information · Each BUFR product file is constructed from a static table that contains BUFR descriptors. · BUFR “descriptors” are used to indicate the exact meaning and storage structure of the data values. · A set of WMO master BUFR tables defines all standard descriptors. This makes the format self-describing. · For example, radiance can be described as: » » » · Table B descriptor: 0 -14 -045 Description: channel radiance Units: W m-2 sr-1 cm-1 Scale, Offset, Bit storage: 0 0 11 Mnemonic: CHRAD If a particular type of data cannot be described using an existing descriptor, a new descriptor may be proposed. Doing so requires our NOAA representative to WMO (currently Jeff Ator) to present the change at the bi-annual WMO meeting. 75
BUFR File Format Information · Each BUFR product file is constructed from a static table that contains BUFR descriptors. · BUFR “descriptors” are used to indicate the exact meaning and storage structure of the data values. · A set of WMO master BUFR tables defines all standard descriptors. This makes the format self-describing. · For example, radiance can be described as: » » » · Table B descriptor: 0 -14 -045 Description: channel radiance Units: W m-2 sr-1 cm-1 Scale, Offset, Bit storage: 0 0 11 Mnemonic: CHRAD If a particular type of data cannot be described using an existing descriptor, a new descriptor may be proposed. Doing so requires our NOAA representative to WMO (currently Jeff Ator) to present the change at the bi-annual WMO meeting. 75
 BUFR File Format Information · A BUFR message is composed of six sections, numbered zero through five. » SECTION 0 - Indicator Section contains “BUFR”, length of message, edition number. » SECTION 1 - Identification Section contains length of section and identification of message. » SECTION 2 - Optional Section; if used, it may contain arbitrary data in any form wished for by the creator of the message (this is only advisable for local use). » SECTION 3 - Data Description Section contains a sequence of so-called descriptors that define the form and contents of the BUFR data product. » SECTION 4 - Data Section; a bit-stream containing the message's core data and meta-data values as laid out by Section 3. » SECTION 5 - End Section “ 7777”. · A given BUFR file may contain multiple BUFR messages. The table determines only the structure of the message, not the number of messages or the size of the BUFR records; that is determined by the 76 user’s software.
BUFR File Format Information · A BUFR message is composed of six sections, numbered zero through five. » SECTION 0 - Indicator Section contains “BUFR”, length of message, edition number. » SECTION 1 - Identification Section contains length of section and identification of message. » SECTION 2 - Optional Section; if used, it may contain arbitrary data in any form wished for by the creator of the message (this is only advisable for local use). » SECTION 3 - Data Description Section contains a sequence of so-called descriptors that define the form and contents of the BUFR data product. » SECTION 4 - Data Section; a bit-stream containing the message's core data and meta-data values as laid out by Section 3. » SECTION 5 - End Section “ 7777”. · A given BUFR file may contain multiple BUFR messages. The table determines only the structure of the message, not the number of messages or the size of the BUFR records; that is determined by the 76 user’s software.
 GRIB 2 File Format Information · GRIB (Gridded Binary) is a binary machine independent format used and generated (as forecast output) by NWP. · GRIB (like BUFR) is standardized by the WMO’s Commission for Basic Systems (GRIB FM 92 -IX, described in WMO Manual on Codes No. 306). · The latest version of GRIB is Edition 2 although Edition 1 is still widely used. · It is designed for storing gridded data. 77
GRIB 2 File Format Information · GRIB (Gridded Binary) is a binary machine independent format used and generated (as forecast output) by NWP. · GRIB (like BUFR) is standardized by the WMO’s Commission for Basic Systems (GRIB FM 92 -IX, described in WMO Manual on Codes No. 306). · The latest version of GRIB is Edition 2 although Edition 1 is still widely used. · It is designed for storing gridded data. 77
 GRIB 2 File Format Information · A GRIB file can contain many different variables on different grids. · Like BUFR, these names are standardized in tables by WMO so the file is self-describing. · For example, if you want write temperature, in Octet 11 of section 4 of the GRIB 2 you set: » GRIB Code for Temperature: 0 » Abbrev: TMP » Units: Kelvin 78
GRIB 2 File Format Information · A GRIB file can contain many different variables on different grids. · Like BUFR, these names are standardized in tables by WMO so the file is self-describing. · For example, if you want write temperature, in Octet 11 of section 4 of the GRIB 2 you set: » GRIB Code for Temperature: 0 » Abbrev: TMP » Units: Kelvin 78
 GRIB 2 File Format Information · A GRIB 2 file contains the following sections: » SECTION 0 - Indicator Section contains “GRIB”, Discipline, GRIB Edition number, length of message. » SECTION 1 - Identification Section contains length of section, section number, message characteristics. » SECTION 2 - (Local Use Section) – optional; length of section, section number, additional local use info. » SECTION 3 - Grid Definition Section contains definition of grid and geometry of data. » SECTION 4 - Product Definition Section (repeated) contains description of the nature of the data. » SECTION 5 - Data Representation Section (repeated) contains description of how the data values are represented. » SECTION 6 - Bit-map Section (repeated) contains an indication of presence or absence of data at each grid point. » SECTION 7 - Data Section contains the data. » SECTION 8 - End Section “ 7777”. · Sequences of GRIB sections 2 to 7, 3 to 7, or sections 4 to 7 may be repeated within a single GRIB message. 79
GRIB 2 File Format Information · A GRIB 2 file contains the following sections: » SECTION 0 - Indicator Section contains “GRIB”, Discipline, GRIB Edition number, length of message. » SECTION 1 - Identification Section contains length of section, section number, message characteristics. » SECTION 2 - (Local Use Section) – optional; length of section, section number, additional local use info. » SECTION 3 - Grid Definition Section contains definition of grid and geometry of data. » SECTION 4 - Product Definition Section (repeated) contains description of the nature of the data. » SECTION 5 - Data Representation Section (repeated) contains description of how the data values are represented. » SECTION 6 - Bit-map Section (repeated) contains an indication of presence or absence of data at each grid point. » SECTION 7 - Data Section contains the data. » SECTION 8 - End Section “ 7777”. · Sequences of GRIB sections 2 to 7, 3 to 7, or sections 4 to 7 may be repeated within a single GRIB message. 79
 Reformatting Toolkit Data · The tables on the following slides show all the Reformatting Toolkit input and output. The input data files are those required by the Reformatting Toolkit software to produce the Phase I tailored products. · All input data must be CF compliant Net. CDF 4 format. · Ancillary/Static files, such as the BUFR tables are listed. » They will be delivered as part of the DAP » Described more thoroughly in the CDR · All output will be in either BUFR or GRIB 2 format. 80
Reformatting Toolkit Data · The tables on the following slides show all the Reformatting Toolkit input and output. The input data files are those required by the Reformatting Toolkit software to produce the Phase I tailored products. · All input data must be CF compliant Net. CDF 4 format. · Ancillary/Static files, such as the BUFR tables are listed. » They will be delivered as part of the DAP » Described more thoroughly in the CDR · All output will be in either BUFR or GRIB 2 format. 80
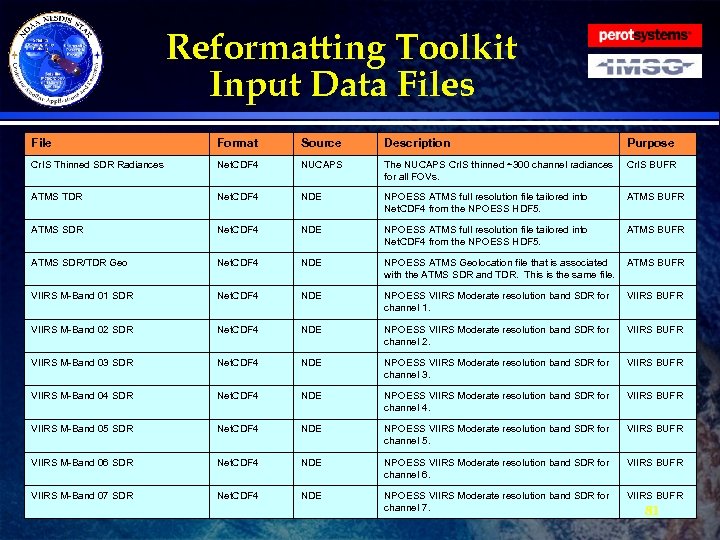 Reformatting Toolkit Input Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose Cr. IS Thinned SDR Radiances Net. CDF 4 NUCAPS The NUCAPS Cr. IS thinned ~300 channel radiances for all FOVs. Cr. IS BUFR ATMS TDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS ATMS full resolution file tailored into Net. CDF 4 from the NPOESS HDF 5. ATMS BUFR ATMS SDR/TDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS ATMS Geolocation file that is associated with the ATMS SDR and TDR. This is the same file. ATMS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 01 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 1. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 02 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 2. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 03 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 3. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 04 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 4. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 05 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 5. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 06 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 6. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 07 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 7. VIIRS BUFR 81
Reformatting Toolkit Input Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose Cr. IS Thinned SDR Radiances Net. CDF 4 NUCAPS The NUCAPS Cr. IS thinned ~300 channel radiances for all FOVs. Cr. IS BUFR ATMS TDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS ATMS full resolution file tailored into Net. CDF 4 from the NPOESS HDF 5. ATMS BUFR ATMS SDR/TDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS ATMS Geolocation file that is associated with the ATMS SDR and TDR. This is the same file. ATMS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 01 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 1. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 02 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 2. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 03 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 3. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 04 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 4. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 05 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 5. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 06 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 6. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 07 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 7. VIIRS BUFR 81
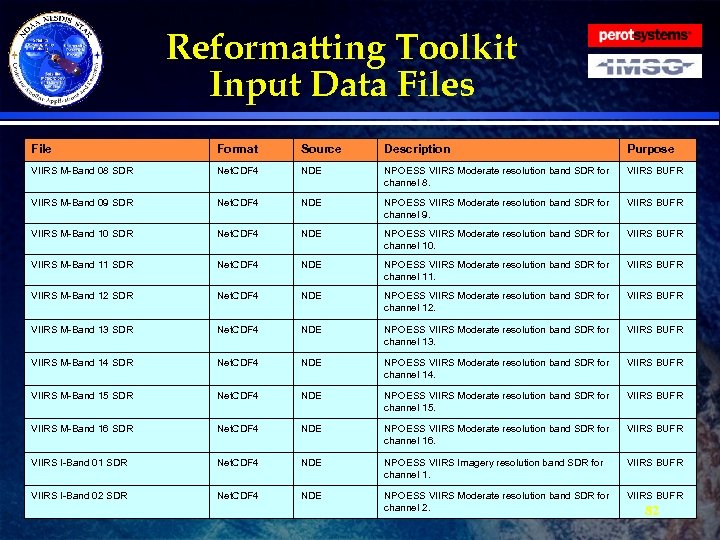 Reformatting Toolkit Input Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose VIIRS M-Band 08 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 8. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 09 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 9. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 10 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 10. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 11 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 11. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 12 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 12. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 13 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 13. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 14 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 14. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 15 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 15. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 16 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 16. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band 01 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Imagery resolution band SDR for channel 1. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band 02 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 2. VIIRS BUFR 82
Reformatting Toolkit Input Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose VIIRS M-Band 08 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 8. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 09 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 9. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 10 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 10. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 11 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 11. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 12 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 12. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 13 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 13. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 14 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 14. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 15 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 15. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band 16 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 16. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band 01 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Imagery resolution band SDR for channel 1. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band 02 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 2. VIIRS BUFR 82
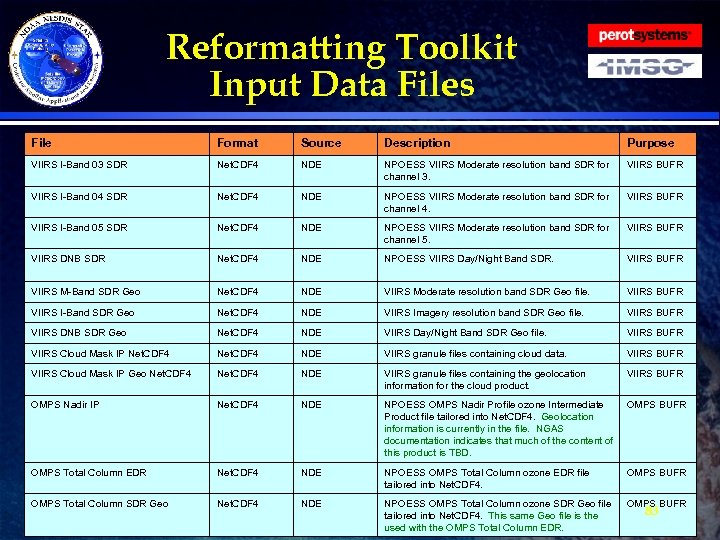 Reformatting Toolkit Input Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose VIIRS I-Band 03 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 3. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band 04 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 4. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band 05 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 5. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS DNB SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Day/Night Band SDR. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band SDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR Geo file. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band SDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS Imagery resolution band SDR Geo file. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS DNB SDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS Day/Night Band SDR Geo file. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS Cloud Mask IP Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS granule files containing cloud data. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS Cloud Mask IP Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS granule files containing the geolocation information for the cloud product. VIIRS BUFR OMPS Nadir IP Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS OMPS Nadir Profile ozone Intermediate Product file tailored into Net. CDF 4. Geolocation information is currently in the file. NGAS documentation indicates that much of the content of this product is TBD. OMPS BUFR OMPS Total Column EDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS OMPS Total Column ozone EDR file tailored into Net. CDF 4. OMPS BUFR OMPS Total Column SDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS OMPS Total Column ozone SDR Geo file tailored into Net. CDF 4. This same Geo file is the used with the OMPS Total Column EDR. OMPS BUFR 83
Reformatting Toolkit Input Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose VIIRS I-Band 03 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 3. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band 04 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 4. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band 05 SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR for channel 5. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS DNB SDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS VIIRS Day/Night Band SDR. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS M-Band SDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS Moderate resolution band SDR Geo file. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS I-Band SDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS Imagery resolution band SDR Geo file. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS DNB SDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS Day/Night Band SDR Geo file. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS Cloud Mask IP Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS granule files containing cloud data. VIIRS BUFR VIIRS Cloud Mask IP Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE VIIRS granule files containing the geolocation information for the cloud product. VIIRS BUFR OMPS Nadir IP Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS OMPS Nadir Profile ozone Intermediate Product file tailored into Net. CDF 4. Geolocation information is currently in the file. NGAS documentation indicates that much of the content of this product is TBD. OMPS BUFR OMPS Total Column EDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS OMPS Total Column ozone EDR file tailored into Net. CDF 4. OMPS BUFR OMPS Total Column SDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS OMPS Total Column ozone SDR Geo file tailored into Net. CDF 4. This same Geo file is the used with the OMPS Total Column EDR. OMPS BUFR 83
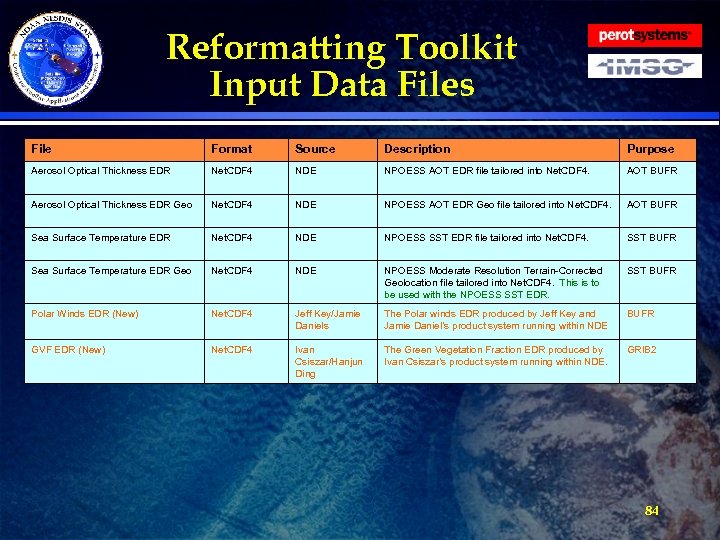 Reformatting Toolkit Input Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose Aerosol Optical Thickness EDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS AOT EDR file tailored into Net. CDF 4. AOT BUFR Aerosol Optical Thickness EDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS AOT EDR Geo file tailored into Net. CDF 4. AOT BUFR Sea Surface Temperature EDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS SST EDR file tailored into Net. CDF 4. SST BUFR Sea Surface Temperature EDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS Moderate Resolution Terrain-Corrected Geolocation file tailored into Net. CDF 4. This is to be used with the NPOESS SST EDR. SST BUFR Polar Winds EDR (New) Net. CDF 4 Jeff Key/Jamie Daniels The Polar winds EDR produced by Jeff Key and Jamie Daniel’s product system running within NDE BUFR GVF EDR (New) Net. CDF 4 Ivan Csiszar/Hanjun Ding The Green Vegetation Fraction EDR produced by Ivan Csiszar’s product system running within NDE. GRIB 2 84
Reformatting Toolkit Input Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose Aerosol Optical Thickness EDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS AOT EDR file tailored into Net. CDF 4. AOT BUFR Aerosol Optical Thickness EDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS AOT EDR Geo file tailored into Net. CDF 4. AOT BUFR Sea Surface Temperature EDR Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS SST EDR file tailored into Net. CDF 4. SST BUFR Sea Surface Temperature EDR Geo Net. CDF 4 NDE NPOESS Moderate Resolution Terrain-Corrected Geolocation file tailored into Net. CDF 4. This is to be used with the NPOESS SST EDR. SST BUFR Polar Winds EDR (New) Net. CDF 4 Jeff Key/Jamie Daniels The Polar winds EDR produced by Jeff Key and Jamie Daniel’s product system running within NDE BUFR GVF EDR (New) Net. CDF 4 Ivan Csiszar/Hanjun Ding The Green Vegetation Fraction EDR produced by Ivan Csiszar’s product system running within NDE. GRIB 2 84
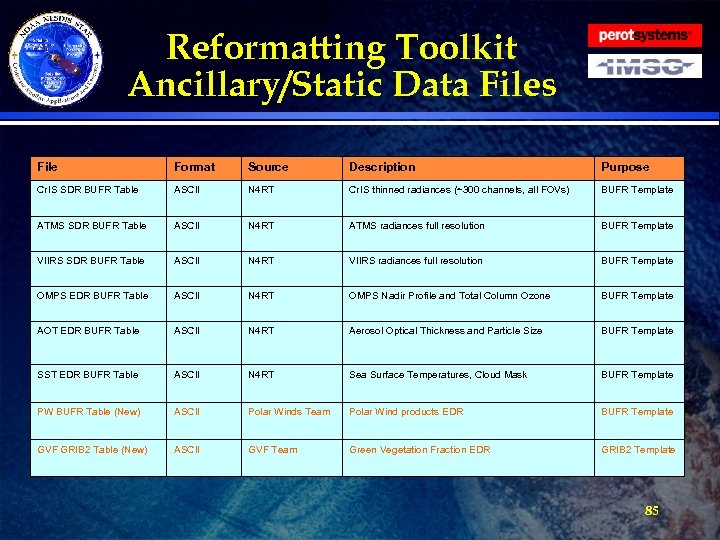 Reformatting Toolkit Ancillary/Static Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose Cr. IS SDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT Cr. IS thinned radiances (~300 channels, all FOVs) BUFR Template ATMS SDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT ATMS radiances full resolution BUFR Template VIIRS SDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT VIIRS radiances full resolution BUFR Template OMPS EDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT OMPS Nadir Profile and Total Column Ozone BUFR Template AOT EDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT Aerosol Optical Thickness and Particle Size BUFR Template SST EDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT Sea Surface Temperatures, Cloud Mask BUFR Template PW BUFR Table (New) ASCII Polar Winds Team Polar Wind products EDR BUFR Template GVF GRIB 2 Table (New) ASCII GVF Team Green Vegetation Fraction EDR GRIB 2 Template 85
Reformatting Toolkit Ancillary/Static Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose Cr. IS SDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT Cr. IS thinned radiances (~300 channels, all FOVs) BUFR Template ATMS SDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT ATMS radiances full resolution BUFR Template VIIRS SDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT VIIRS radiances full resolution BUFR Template OMPS EDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT OMPS Nadir Profile and Total Column Ozone BUFR Template AOT EDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT Aerosol Optical Thickness and Particle Size BUFR Template SST EDR BUFR Table ASCII N 4 RT Sea Surface Temperatures, Cloud Mask BUFR Template PW BUFR Table (New) ASCII Polar Winds Team Polar Wind products EDR BUFR Template GVF GRIB 2 Table (New) ASCII GVF Team Green Vegetation Fraction EDR GRIB 2 Template 85
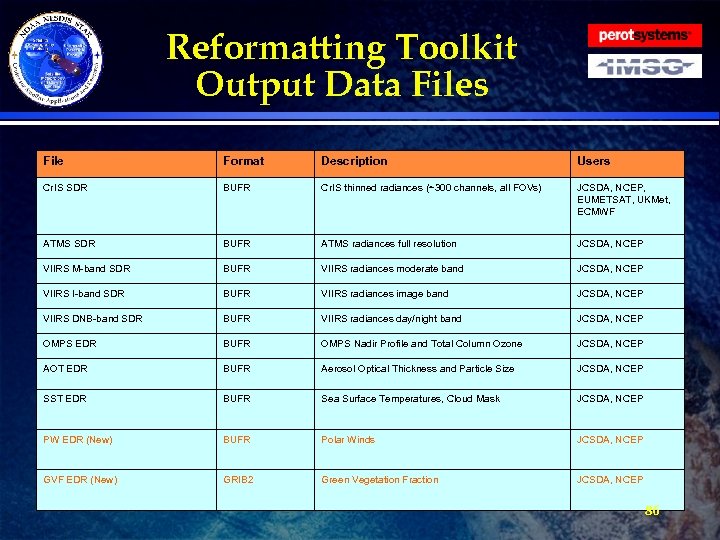 Reformatting Toolkit Output Data Files File Format Description Users Cr. IS SDR BUFR Cr. IS thinned radiances (~300 channels, all FOVs) JCSDA, NCEP, EUMETSAT, UKMet, ECMWF ATMS SDR BUFR ATMS radiances full resolution JCSDA, NCEP VIIRS M-band SDR BUFR VIIRS radiances moderate band JCSDA, NCEP VIIRS I-band SDR BUFR VIIRS radiances image band JCSDA, NCEP VIIRS DNB-band SDR BUFR VIIRS radiances day/night band JCSDA, NCEP OMPS EDR BUFR OMPS Nadir Profile and Total Column Ozone JCSDA, NCEP AOT EDR BUFR Aerosol Optical Thickness and Particle Size JCSDA, NCEP SST EDR BUFR Sea Surface Temperatures, Cloud Mask JCSDA, NCEP PW EDR (New) BUFR Polar Winds JCSDA, NCEP GVF EDR (New) GRIB 2 Green Vegetation Fraction JCSDA, NCEP 86
Reformatting Toolkit Output Data Files File Format Description Users Cr. IS SDR BUFR Cr. IS thinned radiances (~300 channels, all FOVs) JCSDA, NCEP, EUMETSAT, UKMet, ECMWF ATMS SDR BUFR ATMS radiances full resolution JCSDA, NCEP VIIRS M-band SDR BUFR VIIRS radiances moderate band JCSDA, NCEP VIIRS I-band SDR BUFR VIIRS radiances image band JCSDA, NCEP VIIRS DNB-band SDR BUFR VIIRS radiances day/night band JCSDA, NCEP OMPS EDR BUFR OMPS Nadir Profile and Total Column Ozone JCSDA, NCEP AOT EDR BUFR Aerosol Optical Thickness and Particle Size JCSDA, NCEP SST EDR BUFR Sea Surface Temperatures, Cloud Mask JCSDA, NCEP PW EDR (New) BUFR Polar Winds JCSDA, NCEP GVF EDR (New) GRIB 2 Green Vegetation Fraction JCSDA, NCEP 86
 Reformatting Toolkit Run Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose PCF ASCII NUCAPS The PCF file containing all the required input parameters for the N 4 RT driver script. Driver input N 4 RT Run Log ASCII N 4 RT The N 4 RT log file containing all the standard error and standard output from a given run. Diagnostic N 4 RT Main Resource ASCII N 4 RT The internal control file required by the N 4 RT executable main program. Executable input PSF ASCII N 4 RT The Process Status File containing only the successfully generated output files. Driver output list 87
Reformatting Toolkit Run Data Files File Format Source Description Purpose PCF ASCII NUCAPS The PCF file containing all the required input parameters for the N 4 RT driver script. Driver input N 4 RT Run Log ASCII N 4 RT The N 4 RT log file containing all the standard error and standard output from a given run. Diagnostic N 4 RT Main Resource ASCII N 4 RT The internal control file required by the N 4 RT executable main program. Executable input PSF ASCII N 4 RT The Process Status File containing only the successfully generated output files. Driver output list 87
 Reformatting Toolkit Software: External Interfaces · The Reformatting Toolkit system will be run via the execution of a single driver script that will be invoked, monitored, and managed by the NDE DHS Product Generation Manager. · Execution of the script will be event-driven (i. e. the arrival of a required input file whose type is predefined in the Reformatting Toolkit production rules given to NDE). · An invocation of Reformatting Toolkit by the NDE DHS will be used to perform a single file-tofile (e. g. granule-to-granule) translation (as opposed to reformatting many files as once). · Our understanding is that NDE plans to run the driver script in a working directory. All Reformatting Toolkit output will be produced in this same working directory. · The driver script will require an input PCF file containing parameters such as: » » The input and output file names Input and output product type IDs (e. g. ATMS radiances) The type of conversion required (e. g. Net. CDF 4 to BUFR) BUFR or GRIB 2 tables 88
Reformatting Toolkit Software: External Interfaces · The Reformatting Toolkit system will be run via the execution of a single driver script that will be invoked, monitored, and managed by the NDE DHS Product Generation Manager. · Execution of the script will be event-driven (i. e. the arrival of a required input file whose type is predefined in the Reformatting Toolkit production rules given to NDE). · An invocation of Reformatting Toolkit by the NDE DHS will be used to perform a single file-tofile (e. g. granule-to-granule) translation (as opposed to reformatting many files as once). · Our understanding is that NDE plans to run the driver script in a working directory. All Reformatting Toolkit output will be produced in this same working directory. · The driver script will require an input PCF file containing parameters such as: » » The input and output file names Input and output product type IDs (e. g. ATMS radiances) The type of conversion required (e. g. Net. CDF 4 to BUFR) BUFR or GRIB 2 tables 88
 Reformatting Toolkit Software: External Interfaces · The driver script will run, parse the PCF content, run the compiled conversion code, handle program output and errors, direct required error codes to the DHS via an output log (and through the driver script’s return code), and generate a PSF. · If there are errors, our understanding is that NDE plans to save the contents of the run in a forensics repository. · Our understanding is that NDE plans to manage and direct error status to the operators from the DHS system. · Our understanding is that NDE plans to manage all distribution through the NDE DDS and the short term storage of tailored data on the SAN. 89
Reformatting Toolkit Software: External Interfaces · The driver script will run, parse the PCF content, run the compiled conversion code, handle program output and errors, direct required error codes to the DHS via an output log (and through the driver script’s return code), and generate a PSF. · If there are errors, our understanding is that NDE plans to save the contents of the run in a forensics repository. · Our understanding is that NDE plans to manage and direct error status to the operators from the DHS system. · Our understanding is that NDE plans to manage all distribution through the NDE DDS and the short term storage of tailored data on the SAN. 89
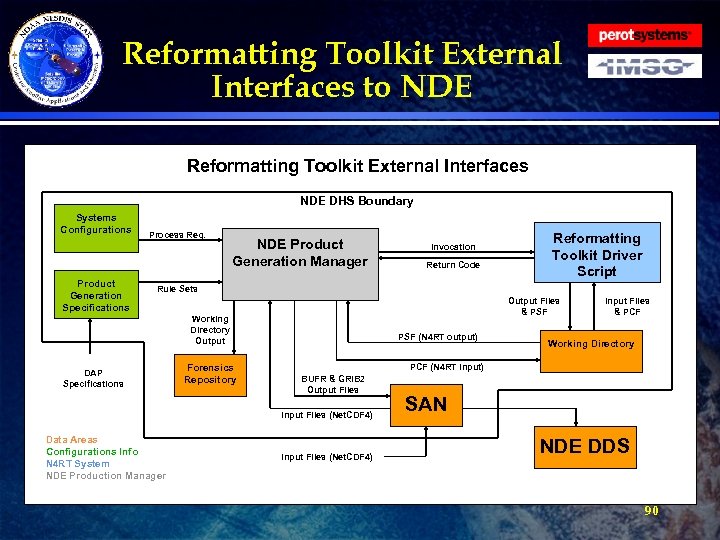 Reformatting Toolkit External Interfaces to NDE Reformatting Toolkit External Interfaces NDE DHS Boundary Systems Configurations Product Generation Specifications Process Req. NDE Product Generation Manager Invocation Return Code Reformatting Toolkit Driver Script Rule Sets Output Files & PSF Working Directory Output DAP Specifications Forensics Repository PSF (N 4 RT output) Working Directory PCF (N 4 RT input) BUFR & GRIB 2 Output Files Input Files (Net. CDF 4) Data Areas Configurations Info N 4 RT System NDE Production Manager Input Files & PCF Input Files (Net. CDF 4) SAN NDE DDS 90
Reformatting Toolkit External Interfaces to NDE Reformatting Toolkit External Interfaces NDE DHS Boundary Systems Configurations Product Generation Specifications Process Req. NDE Product Generation Manager Invocation Return Code Reformatting Toolkit Driver Script Rule Sets Output Files & PSF Working Directory Output DAP Specifications Forensics Repository PSF (N 4 RT output) Working Directory PCF (N 4 RT input) BUFR & GRIB 2 Output Files Input Files (Net. CDF 4) Data Areas Configurations Info N 4 RT System NDE Production Manager Input Files & PCF Input Files (Net. CDF 4) SAN NDE DDS 90
 Reformatting Toolkit Software: System Level · The Reformatting Toolkit driver script will be a single Perl script that acts as a wrapper for the compiled Reformatting Toolkit code. » There will be no hard coded paths in the script. All needed information regarding locations of files will come through the PCF. » All system calls have their return values checked so the exits are graceful and informative. » All standard out and standard error will be directed to a single log file that can be read by NDE for obtaining any error or warning messages. » The driver script will translate the low-level program errors into the high-level numerical error codes expected by the PGM. » The Perl script will generate an internal control file for the main Reformatting Toolkit program. 91
Reformatting Toolkit Software: System Level · The Reformatting Toolkit driver script will be a single Perl script that acts as a wrapper for the compiled Reformatting Toolkit code. » There will be no hard coded paths in the script. All needed information regarding locations of files will come through the PCF. » All system calls have their return values checked so the exits are graceful and informative. » All standard out and standard error will be directed to a single log file that can be read by NDE for obtaining any error or warning messages. » The driver script will translate the low-level program errors into the high-level numerical error codes expected by the PGM. » The Perl script will generate an internal control file for the main Reformatting Toolkit program. 91
 Reformatting Toolkit Software: System Level · The PCF content (nominal mode): » » » » Input Net. CDF 4 file(s) Output BUFR file Output GRIB 2 file Direction of conversion (eg. NC to BF) Input and output product types Input/Output BUFR table Input/Output GRIB 2 table · The PCF content (test mode): » » » Input BUFR or input GRIB 2 Output Net. CDF 4 file Direction of conversion (e. g. BF to NC) Input and output product types NC templates if (Net. CDF 4 is an output type) 92
Reformatting Toolkit Software: System Level · The PCF content (nominal mode): » » » » Input Net. CDF 4 file(s) Output BUFR file Output GRIB 2 file Direction of conversion (eg. NC to BF) Input and output product types Input/Output BUFR table Input/Output GRIB 2 table · The PCF content (test mode): » » » Input BUFR or input GRIB 2 Output Net. CDF 4 file Direction of conversion (e. g. BF to NC) Input and output product types NC templates if (Net. CDF 4 is an output type) 92
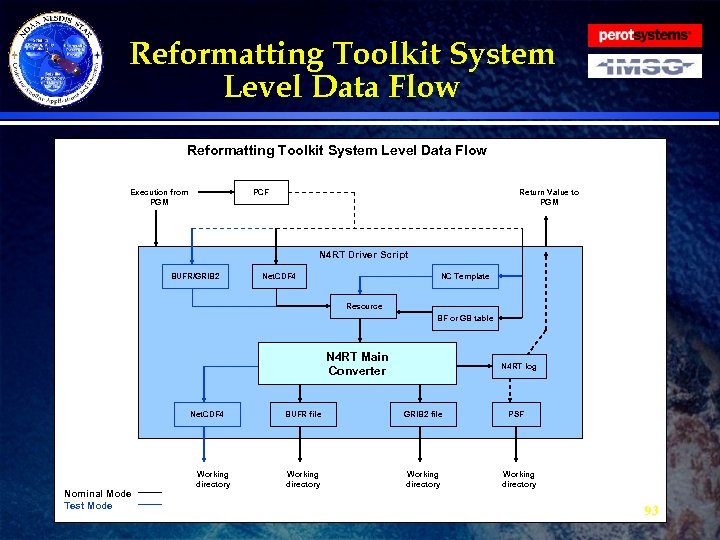 Reformatting Toolkit System Level Data Flow Execution from PGM PCF Return Value to PGM N 4 RT Driver Script BUFR/GRIB 2 Net. CDF 4 NC Template Resource BF or GB table N 4 RT Main Converter Net. CDF 4 Nominal Mode Test Mode Working directory N 4 RT log BUFR file GRIB 2 file Working directory PSF Working directory 93
Reformatting Toolkit System Level Data Flow Execution from PGM PCF Return Value to PGM N 4 RT Driver Script BUFR/GRIB 2 Net. CDF 4 NC Template Resource BF or GB table N 4 RT Main Converter Net. CDF 4 Nominal Mode Test Mode Working directory N 4 RT log BUFR file GRIB 2 file Working directory PSF Working directory 93
 Reformatting Toolkit Software: Unit Level · The Reformatting Toolkit main program will be a single main C++ program containing all the predefined data structures required by the code. Lowerlevels will be in Fortran 90. Why this approach? » C++ main program will give the system flexibility for having to plug into future types of architectures. » APIs for BUFR are only Fortran 77. » Much of the code being reused is already in Fortran 90. » Many users tend to request readers in Fortran 90. · In the Reformatting Toolkit main program, all data structures will be declared and a series of cases statements will direct the program flow based on the type of input files and the direction of conversion. · The Reformatting Toolkit subroutines at the next level down (and at all subsequent levels) will be in Fortran 90. This next level will manage: » Allocation, initialization, deallocation of data structures. » They are designed for overseeing specific product definitions and conversions. 94
Reformatting Toolkit Software: Unit Level · The Reformatting Toolkit main program will be a single main C++ program containing all the predefined data structures required by the code. Lowerlevels will be in Fortran 90. Why this approach? » C++ main program will give the system flexibility for having to plug into future types of architectures. » APIs for BUFR are only Fortran 77. » Much of the code being reused is already in Fortran 90. » Many users tend to request readers in Fortran 90. · In the Reformatting Toolkit main program, all data structures will be declared and a series of cases statements will direct the program flow based on the type of input files and the direction of conversion. · The Reformatting Toolkit subroutines at the next level down (and at all subsequent levels) will be in Fortran 90. This next level will manage: » Allocation, initialization, deallocation of data structures. » They are designed for overseeing specific product definitions and conversions. 94
 Reformatting Toolkit Software: Unit Level · The lowest-level Reformatting Toolkit subroutines: » Perform the actual reading and writing of the specific file types. » Directly call the library APIs for BUFR, GRIB 2, and Net. CDF 4. · General Reformatting Toolkit compiled code characteristics: » The status of all functions are checked to allow for graceful and informative exits. » No paths are hard coded in the compiled code. » The are no system calls from within the compiled code. » All code will be compiled as 64 bit to utilize the IBM architecture. » All code will be “mostly statically” linked (i. e. only system libraries like libc. a and the 64 -bit UNIX kernel will be dynamically linked). 95
Reformatting Toolkit Software: Unit Level · The lowest-level Reformatting Toolkit subroutines: » Perform the actual reading and writing of the specific file types. » Directly call the library APIs for BUFR, GRIB 2, and Net. CDF 4. · General Reformatting Toolkit compiled code characteristics: » The status of all functions are checked to allow for graceful and informative exits. » No paths are hard coded in the compiled code. » The are no system calls from within the compiled code. » All code will be compiled as 64 bit to utilize the IBM architecture. » All code will be “mostly statically” linked (i. e. only system libraries like libc. a and the 64 -bit UNIX kernel will be dynamically linked). 95
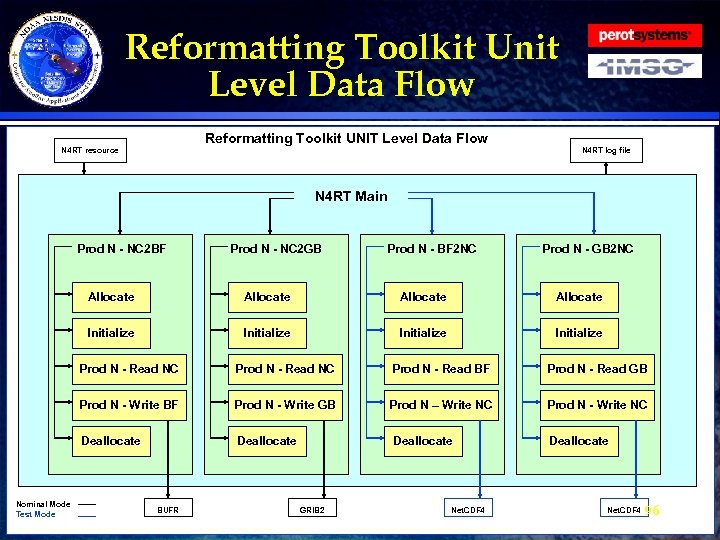 Reformatting Toolkit Unit Level Data Flow Reformatting Toolkit UNIT Level Data Flow N 4 RT resource N 4 RT log file N 4 RT Main Prod N - NC 2 BF Prod N - NC 2 GB Prod N - BF 2 NC Prod N - GB 2 NC Allocate Initialize Prod N - Read NC Prod N - Read BF Prod N - Read GB Prod N - Write BF Prod N - Write GB Prod N – Write NC Prod N - Write NC Deallocate Nominal Mode Test Mode Prod N - Read NC Deallocate BUFR Deallocate GRIB 2 Net. CDF 4 Deallocate Net. CDF 4 96
Reformatting Toolkit Unit Level Data Flow Reformatting Toolkit UNIT Level Data Flow N 4 RT resource N 4 RT log file N 4 RT Main Prod N - NC 2 BF Prod N - NC 2 GB Prod N - BF 2 NC Prod N - GB 2 NC Allocate Initialize Prod N - Read NC Prod N - Read BF Prod N - Read GB Prod N - Write BF Prod N - Write GB Prod N – Write NC Prod N - Write NC Deallocate Nominal Mode Test Mode Prod N - Read NC Deallocate BUFR Deallocate GRIB 2 Net. CDF 4 Deallocate Net. CDF 4 96
 Reformatting Toolkit Software: Libraries · BUFR Library » NCEP BUFRLIB library (available on the NCEP website) » Code is all Fortran 77 » Compiled as 64 bit · GRIB 2 Library » NCEP GRIB 2 Encoder/Decoder library (available on the NCEP website) » Code is available in C and Fortran 90 » Compiled as 64 bit · Net. CDF 4 Library version 4. 0 » Available from Unidata website » Compiled as 64 bit · Reformatting Toolkit developers will coordinate with NDE and the product teams to make sure that all parties are using compatible libraries. 97
Reformatting Toolkit Software: Libraries · BUFR Library » NCEP BUFRLIB library (available on the NCEP website) » Code is all Fortran 77 » Compiled as 64 bit · GRIB 2 Library » NCEP GRIB 2 Encoder/Decoder library (available on the NCEP website) » Code is available in C and Fortran 90 » Compiled as 64 bit · Net. CDF 4 Library version 4. 0 » Available from Unidata website » Compiled as 64 bit · Reformatting Toolkit developers will coordinate with NDE and the product teams to make sure that all parties are using compatible libraries. 97
 Software Architecture Summary · Reformatting Toolkit software development, testing, and operation will be conducted on comparable IBM hardware at NSOF and STAR. · The Reformatting Toolkit code will run as a stand-alone unit within the NDE DHS. · The code will be modular to allow for easy reuse of code and expansion to accommodate new products. · The code will use only the official releases and NDE compatible versions of the Net. CDF 4, BUFR, and GRIB 2 libraries. · A Reformatting Toolkit Prototype DAP shall be delivered at the end of September 2009. 98
Software Architecture Summary · Reformatting Toolkit software development, testing, and operation will be conducted on comparable IBM hardware at NSOF and STAR. · The Reformatting Toolkit code will run as a stand-alone unit within the NDE DHS. · The code will be modular to allow for easy reuse of code and expansion to accommodate new products. · The code will use only the official releases and NDE compatible versions of the Net. CDF 4, BUFR, and GRIB 2 libraries. · A Reformatting Toolkit Prototype DAP shall be delivered at the end of September 2009. 98
 Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 99
Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 99
 Quality Assurance Presented by Thomas King PSGS 100
Quality Assurance Presented by Thomas King PSGS 100
 Quality Assurance Background · STAR is using the Capability Maturity Model Integrated (CMMI) to improve processes and practices for development and the transfer of research to operations. · The STAR Enterprise Life Cycle (EPL) merges the CMMI and SPSRB standards. · IASI and NUCAPS are both pathfinder projects (CMMI Level 3). The IASI system has been transitioned to operations successfully. · The Reformatting Toolkit algorithm development will follow the same process but tailored to the scale of the project. 101
Quality Assurance Background · STAR is using the Capability Maturity Model Integrated (CMMI) to improve processes and practices for development and the transfer of research to operations. · The STAR Enterprise Life Cycle (EPL) merges the CMMI and SPSRB standards. · IASI and NUCAPS are both pathfinder projects (CMMI Level 3). The IASI system has been transitioned to operations successfully. · The Reformatting Toolkit algorithm development will follow the same process but tailored to the scale of the project. 101
 Quality Assurance – Project Implemented Tailored STAR EPL Reviews · The Reformatting Toolkit Preliminary Design Review (April 2009) » » · The Reformatting Toolkit Critical Design Review (September 2009) » · Will present the unit test plan to demonstrate that the toolkit is ready to be run in the Test Environment. A Code Unit Test Review (May 2010) » · To finalize requirements and to verify that the chosen design is able to meet those requirements. An Reformatting Toolkit Test Readiness Review (April 2010) » · Will present the initial draft of the requirements and discuss a proposed design. An Reformatting Toolkit Requirements Allocation Document (RAD) has been made available to Reformatting Toolkit stakeholders. It will be updated throughout the lifecycle of the project. Will be conducted to ensure that the Reformatting Toolkit software is able to fulfill the functional software requirements. The Reformatting Toolkit System Readiness Review (January 2011) » Has requested to be waived because Reformatting Toolkit will be run within the 102 NDE system.
Quality Assurance – Project Implemented Tailored STAR EPL Reviews · The Reformatting Toolkit Preliminary Design Review (April 2009) » » · The Reformatting Toolkit Critical Design Review (September 2009) » · Will present the unit test plan to demonstrate that the toolkit is ready to be run in the Test Environment. A Code Unit Test Review (May 2010) » · To finalize requirements and to verify that the chosen design is able to meet those requirements. An Reformatting Toolkit Test Readiness Review (April 2010) » · Will present the initial draft of the requirements and discuss a proposed design. An Reformatting Toolkit Requirements Allocation Document (RAD) has been made available to Reformatting Toolkit stakeholders. It will be updated throughout the lifecycle of the project. Will be conducted to ensure that the Reformatting Toolkit software is able to fulfill the functional software requirements. The Reformatting Toolkit System Readiness Review (January 2011) » Has requested to be waived because Reformatting Toolkit will be run within the 102 NDE system.
 Configuration Management (CM) · CM Tool (IBM Rational Clear. Case, Version 7. 0 ) » Has been purchased and implemented in the Collaborative Environment. · CM personnel have been identified. · CM training: » Administrator training completed. » Developers will be trained by the CM administrator. · We will be using a modified version of the CM plan developed for GOES-R framework being developed at STAR. 103
Configuration Management (CM) · CM Tool (IBM Rational Clear. Case, Version 7. 0 ) » Has been purchased and implemented in the Collaborative Environment. · CM personnel have been identified. · CM training: » Administrator training completed. » Developers will be trained by the CM administrator. · We will be using a modified version of the CM plan developed for GOES-R framework being developed at STAR. 103
 STAR Coding Standards · Coding standards guidelines and quick references are available. · Provide a common list of abbreviations. · Adhere to the standards throughout the development life cycle. · Have checklists available for developers to keep track of the delivery status of the code. 104
STAR Coding Standards · Coding standards guidelines and quick references are available. · Provide a common list of abbreviations. · Adhere to the standards throughout the development life cycle. · Have checklists available for developers to keep track of the delivery status of the code. 104
 Quality Assurance – Software · A prototype version of the Toolkit will be tested on the NDE hardware as part of the NDE Build Content Reviews during the fall of 2009. · All code development is being conducted on a platform that is nearly identical to the test and production target platforms using the same compilers and operating system. · Only the official releases of the NCEP BUFRLIB, GRIB 2, and Net. CDF 4 libraries will be used in the software. · STAR code checking tools will be used to minimize coding bugs and to ensure that Reformatting Toolkit code meets STAR coding standards. · The status of all system calls and intrinsic functions are checked. · Unit tests will have the Reformatting Toolkit generate BUFR and GRIB 2 products from Net. CDF 4 files. These BUFR and GRIB 2 files will be directed back into the Reformatting Toolkit to generate new Net. CDF 4 files. » » The contents of the new and original Net. CDF 4 files will be compared to demonstrate that went in matches with what came back out. Customers will have access to test data products to verify that values appear reasonable and that precision is not being lost in the format conversions. 105
Quality Assurance – Software · A prototype version of the Toolkit will be tested on the NDE hardware as part of the NDE Build Content Reviews during the fall of 2009. · All code development is being conducted on a platform that is nearly identical to the test and production target platforms using the same compilers and operating system. · Only the official releases of the NCEP BUFRLIB, GRIB 2, and Net. CDF 4 libraries will be used in the software. · STAR code checking tools will be used to minimize coding bugs and to ensure that Reformatting Toolkit code meets STAR coding standards. · The status of all system calls and intrinsic functions are checked. · Unit tests will have the Reformatting Toolkit generate BUFR and GRIB 2 products from Net. CDF 4 files. These BUFR and GRIB 2 files will be directed back into the Reformatting Toolkit to generate new Net. CDF 4 files. » » The contents of the new and original Net. CDF 4 files will be compared to demonstrate that went in matches with what came back out. Customers will have access to test data products to verify that values appear reasonable and that precision is not being lost in the format conversions. 105
 Quality Assurance – Software · An official (tailored) DAP will be delivered: » » » » » All Reformatting Toolkit code and system files Test plans Test data sets Error messaging/handling PCF format Production rules Product file specifications Data flow diagrams Estimates of resource usage ATBD has been waived – However, all modifications to data will be identified and document » Delivery memo 106
Quality Assurance – Software · An official (tailored) DAP will be delivered: » » » » » All Reformatting Toolkit code and system files Test plans Test data sets Error messaging/handling PCF format Production rules Product file specifications Data flow diagrams Estimates of resource usage ATBD has been waived – However, all modifications to data will be identified and document » Delivery memo 106
 Quality Assurance – Products · Reformatting Toolkit developers will work with EMC, NRL, FNMOC, GMAO, EUMETSAT, and UK Met users to ensure that the proper BUFR descriptors are used in the BUFR and GRIB 2 tables and that, whenever possible, they are WMO approved (as opposed to local). » Chosen descriptors must work with NCEP BUFRLIB. · Reformatting Toolkit developers will work with EMC, heritage product developers, and NPOESS operational algorithm teams to ensure consistency with heritage products with respect to format and content. · Reformatting Toolkit developers will make BUFR tables and test products (BUFR and GRIB 2) available to users before the operational products are made available. This will allow for preliminary product content validation. » Cr. IS and ATMS are currently being simulated at STAR. » For the other products such as VIIRS, we are working with the IPO (Joe Zajic), the NPP Test Data Working Group (TDWG), and NDE to obtain simulated products. 107
Quality Assurance – Products · Reformatting Toolkit developers will work with EMC, NRL, FNMOC, GMAO, EUMETSAT, and UK Met users to ensure that the proper BUFR descriptors are used in the BUFR and GRIB 2 tables and that, whenever possible, they are WMO approved (as opposed to local). » Chosen descriptors must work with NCEP BUFRLIB. · Reformatting Toolkit developers will work with EMC, heritage product developers, and NPOESS operational algorithm teams to ensure consistency with heritage products with respect to format and content. · Reformatting Toolkit developers will make BUFR tables and test products (BUFR and GRIB 2) available to users before the operational products are made available. This will allow for preliminary product content validation. » Cr. IS and ATMS are currently being simulated at STAR. » For the other products such as VIIRS, we are working with the IPO (Joe Zajic), the NPP Test Data Working Group (TDWG), and NDE to obtain simulated products. 107
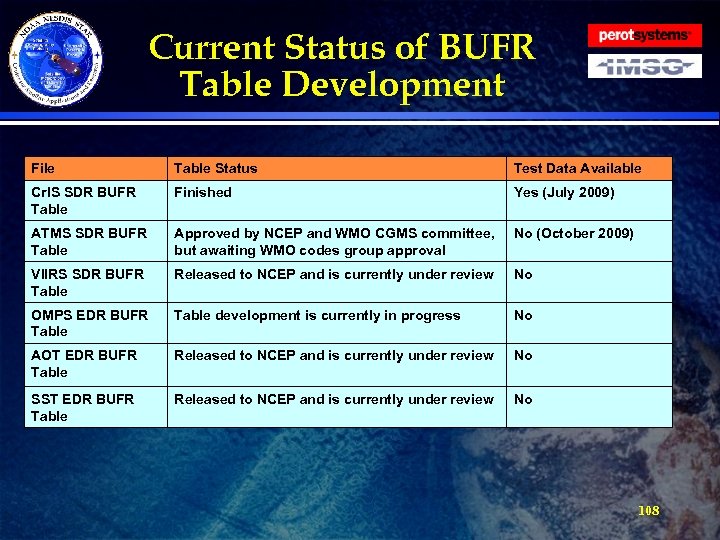 Current Status of BUFR Table Development File Table Status Test Data Available Cr. IS SDR BUFR Table Finished Yes (July 2009) ATMS SDR BUFR Table Approved by NCEP and WMO CGMS committee, but awaiting WMO codes group approval No (October 2009) VIIRS SDR BUFR Table Released to NCEP and is currently under review No OMPS EDR BUFR Table development is currently in progress No AOT EDR BUFR Table Released to NCEP and is currently under review No SST EDR BUFR Table Released to NCEP and is currently under review No 108
Current Status of BUFR Table Development File Table Status Test Data Available Cr. IS SDR BUFR Table Finished Yes (July 2009) ATMS SDR BUFR Table Approved by NCEP and WMO CGMS committee, but awaiting WMO codes group approval No (October 2009) VIIRS SDR BUFR Table Released to NCEP and is currently under review No OMPS EDR BUFR Table development is currently in progress No AOT EDR BUFR Table Released to NCEP and is currently under review No SST EDR BUFR Table Released to NCEP and is currently under review No 108
 Quality Assurance – Archive and Maintenance · Archive Plan » Reformatting toolkit will be integrated into NDE system and made available to CLASS by NDE » Product archive requirements are addressed within product development projects – NPOESS program office works with CLASS to archive x. DRs – NOAA Unique Product (NUP) projects work with CLASS as required · Long Term Maintenance Plan » The reformatting toolkit will be maintained by the OSDPD staff » STAR system developers will be available 109
Quality Assurance – Archive and Maintenance · Archive Plan » Reformatting toolkit will be integrated into NDE system and made available to CLASS by NDE » Product archive requirements are addressed within product development projects – NPOESS program office works with CLASS to archive x. DRs – NOAA Unique Product (NUP) projects work with CLASS as required · Long Term Maintenance Plan » The reformatting toolkit will be maintained by the OSDPD staff » STAR system developers will be available 109
 Quality Assurance – Documentation and Metadata · Documentation/Metadata Plan » The Documentation will include those sections of the SPRSB documents that are decided to be the responsibility of the project teams. The decisions regarding who is responsible for writing the different parts of these documents are being made in a series of ongoing meetings involving the Standards Working Group, NDE, and the STAR Product Teams. » When agreement has been made, the Tailoring project’s requirements will be updated to include generation of the necessary portions of these documents. » Given the current trajectory of this group’s work, we anticipate involvement in the creation of the following documents: – SMM (System Maintenance Manual) – UM (User’s Manual) – DDD (Data Description Document) – SDD (System Description Document) – No MDD (Metadata Description Document) – No OM (Operations Manual) » Additional CMMI documents: – RAD (Requirements Allocation Document) » NDE Documents: – DAP (Testing information is contained within here) 110
Quality Assurance – Documentation and Metadata · Documentation/Metadata Plan » The Documentation will include those sections of the SPRSB documents that are decided to be the responsibility of the project teams. The decisions regarding who is responsible for writing the different parts of these documents are being made in a series of ongoing meetings involving the Standards Working Group, NDE, and the STAR Product Teams. » When agreement has been made, the Tailoring project’s requirements will be updated to include generation of the necessary portions of these documents. » Given the current trajectory of this group’s work, we anticipate involvement in the creation of the following documents: – SMM (System Maintenance Manual) – UM (User’s Manual) – DDD (Data Description Document) – SDD (System Description Document) – No MDD (Metadata Description Document) – No OM (Operations Manual) » Additional CMMI documents: – RAD (Requirements Allocation Document) » NDE Documents: – DAP (Testing information is contained within here) 110
 Quality Assurance Summary · Quality assurance plan will consist of: » Project reviews at which stakeholders are encouraged to participate. » Ongoing interaction with customers, heritage product developers, operations, NDE, and the SPSRB. » Adhering to STAR/NDE software standards and use of standard libraries only. » Software unit tests shall be presented in the TRR. » Documentation of the Reformatting Toolkit code operation, production rules, and software tests will be in the DAP. » Documentation of requirements will be in the Reformatting Toolkit RAD. » Early release of BUFR and GRIB 2 products, tables, and additional resources will allow for customer validation of products. 111
Quality Assurance Summary · Quality assurance plan will consist of: » Project reviews at which stakeholders are encouraged to participate. » Ongoing interaction with customers, heritage product developers, operations, NDE, and the SPSRB. » Adhering to STAR/NDE software standards and use of standard libraries only. » Software unit tests shall be presented in the TRR. » Documentation of the Reformatting Toolkit code operation, production rules, and software tests will be in the DAP. » Documentation of requirements will be in the Reformatting Toolkit RAD. » Early release of BUFR and GRIB 2 products, tables, and additional resources will allow for customer validation of products. 111
 Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 112
Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 112
 Risks and Actions Presented by Zhaohui Cheng NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 113
Risks and Actions Presented by Zhaohui Cheng NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 113
 Risk and Actions · The status of risks from the PDR Report were reported earlier in this CDR, but will be summarized here. · The status of any new risks since the PDR will be reported here as well. 114
Risk and Actions · The status of risks from the PDR Report were reported earlier in this CDR, but will be summarized here. · The status of any new risks since the PDR will be reported here as well. 114
 Risk Summary · Risk 1: NPOESS product formats and content are still changing. » Mitigation: Work and maintain contact with NPOESS DFWG and customers. · Risk 2: Roles and responsibilities for SPSRB documents. » Mitigation: Work with Maurice Mc. Hugh and SPSRB Standard Group. · Risk 3: Variations in platforms and compilers. » Mitigation: Delivery of prototypes and coordination with NDE on system tests. · Risk 4: Data format translation impacts (unit conversion & precision) » Mitigation: Document any translation of data in the DAP. 115
Risk Summary · Risk 1: NPOESS product formats and content are still changing. » Mitigation: Work and maintain contact with NPOESS DFWG and customers. · Risk 2: Roles and responsibilities for SPSRB documents. » Mitigation: Work with Maurice Mc. Hugh and SPSRB Standard Group. · Risk 3: Variations in platforms and compilers. » Mitigation: Delivery of prototypes and coordination with NDE on system tests. · Risk 4: Data format translation impacts (unit conversion & precision) » Mitigation: Document any translation of data in the DAP. 115
 Risk Summary · Risk 6: GRIB 2 functionality not demonstrated. » Mitigation: Test GRIB 2 capability by generating NDVI GRIB 2 file. · Risk 8: Need to verify with EMC management regarding NDVI and Snow Cover. » Mitigation: Tom Schott meet with Steve Lord. · Risk 9: User access to spectral response and calibration. » Mitigation: IPO to work with NPOESS contractor. 116
Risk Summary · Risk 6: GRIB 2 functionality not demonstrated. » Mitigation: Test GRIB 2 capability by generating NDVI GRIB 2 file. · Risk 8: Need to verify with EMC management regarding NDVI and Snow Cover. » Mitigation: Tom Schott meet with Steve Lord. · Risk 9: User access to spectral response and calibration. » Mitigation: IPO to work with NPOESS contractor. 116
 Risk Summary · Risk 11: Effort imposed on product teams to generate Net. CDF 4. » Mitigation: Issue is for NDE and product teams to resolve. · Risk 12: Schedule risk associated with product teams having to convert formats. » Mitigation: Issue is for NDE and product teams to resolve. 117
Risk Summary · Risk 11: Effort imposed on product teams to generate Net. CDF 4. » Mitigation: Issue is for NDE and product teams to resolve. · Risk 12: Schedule risk associated with product teams having to convert formats. » Mitigation: Issue is for NDE and product teams to resolve. 117
 Risk and Actions Summary · There are currently 9 risks identified for the Reformatting Toolkit project. These carry over from the PDR. · There are no new risks at this time. · We believe that 3 of these can be closed. · 6 risks remain open. · An additional risk (risk #8) may be closed depending on status. 118
Risk and Actions Summary · There are currently 9 risks identified for the Reformatting Toolkit project. These carry over from the PDR. · There are no new risks at this time. · We believe that 3 of these can be closed. · 6 risks remain open. · An additional risk (risk #8) may be closed depending on status. 118
 Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 119
Review Outline · · · · Introduction PDR Report Requirements Software Architecture Quality Assurance Risks and Actions Summary and Conclusions 119
 Summary and Conclusions Presented by Thomas King NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 120
Summary and Conclusions Presented by Thomas King NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 120
 Review Objectives Have Been Addressed · The Project Mission and Schedule has been reviewed. · The PDR Report has been reviewed. · The Project Requirements have been reviewed. · Software architecture, hardware, data, and interfaces have been reviewed. · Plans for quality assurance have been reviewed. · Risks and Actions have been reviewed. 121
Review Objectives Have Been Addressed · The Project Mission and Schedule has been reviewed. · The PDR Report has been reviewed. · The Project Requirements have been reviewed. · Software architecture, hardware, data, and interfaces have been reviewed. · Plans for quality assurance have been reviewed. · Risks and Actions have been reviewed. 121
 Current Status · The Cr. IS BUFR table is finished and test BUFR data are available on the STAR ftp 2 server via anonymous ftp. · The ATMS BUFR table has been reviewed by EMC (Dennis Keyser & Jeff Ator), EUMETSAT (Simon Elliott), ECMWF(Milan Dragosavac), UKMet (Nigel Atkinson) and the WMO CGMS science committee. It is awaiting WMO approval. · VIIRS radiance, SST, and AOT tables have been delivered to EMC and are currently under review. · OMPS BUFR table is in progress. · A prototype of the code has been created. There is an NDE compatible Perl driver (with PCF, PSF, and log generation). » » · A Fortran executable can currently convert Cr. IS between Net. CDF 4 and BUFR (in both directions). ATMS read/write BUFR capability is being added at this time. We anticipate delivery of a prototype to NDE at the end of September 2009. Reformatting Toolkit developers will be working with Joe Zajic (IPO) to obtain access to simulated VIIRS products at NSOF. 122
Current Status · The Cr. IS BUFR table is finished and test BUFR data are available on the STAR ftp 2 server via anonymous ftp. · The ATMS BUFR table has been reviewed by EMC (Dennis Keyser & Jeff Ator), EUMETSAT (Simon Elliott), ECMWF(Milan Dragosavac), UKMet (Nigel Atkinson) and the WMO CGMS science committee. It is awaiting WMO approval. · VIIRS radiance, SST, and AOT tables have been delivered to EMC and are currently under review. · OMPS BUFR table is in progress. · A prototype of the code has been created. There is an NDE compatible Perl driver (with PCF, PSF, and log generation). » » · A Fortran executable can currently convert Cr. IS between Net. CDF 4 and BUFR (in both directions). ATMS read/write BUFR capability is being added at this time. We anticipate delivery of a prototype to NDE at the end of September 2009. Reformatting Toolkit developers will be working with Joe Zajic (IPO) to obtain access to simulated VIIRS products at NSOF. 122
 Next Steps · Code development phase is ongoing » Delivery of prototype DAP to NDE » Delivery of ATMS test BUFR files to EMC » Obtain WMO approval of ATMS, VIIRS, OMPS, SST, and AOT BUFR tables » Obtain VIIRS test data · Test Readiness Review (April 2010) 123
Next Steps · Code development phase is ongoing » Delivery of prototype DAP to NDE » Delivery of ATMS test BUFR files to EMC » Obtain WMO approval of ATMS, VIIRS, OMPS, SST, and AOT BUFR tables » Obtain VIIRS test data · Test Readiness Review (April 2010) 123
 Open Discussion · The review is now open for free discussion 124
Open Discussion · The review is now open for free discussion 124
 Backup Slides 125
Backup Slides 125
 Project Background Terminology · Raw Data Records (RDRs) · Sensor Data Records (SDRs) · Temperature Data Records (TDRs) · Environmental Data Records (EDRs) · Intermediate Products (IPs) 126
Project Background Terminology · Raw Data Records (RDRs) · Sensor Data Records (SDRs) · Temperature Data Records (TDRs) · Environmental Data Records (EDRs) · Intermediate Products (IPs) 126
 Project Background Terminology · Raw Data Records (RDRs) » Full resolution, digital sensor data, time-referenced and locatable in earth coordinates with absolute radiometric and geometric calibration coefficients appended, but not applied, to the data. 127
Project Background Terminology · Raw Data Records (RDRs) » Full resolution, digital sensor data, time-referenced and locatable in earth coordinates with absolute radiometric and geometric calibration coefficients appended, but not applied, to the data. 127
 Project Background Terminology · Sensor Data Records (SDRs) » Data record produced when an algorithm is used to convert RDRs to geolocated, calibrated detected fluxes with associated ephemeris data. Calibration, ephemeris, and any other ancillary data necessary to convert the sensor units back to sensor raw data (counts) are included. 128
Project Background Terminology · Sensor Data Records (SDRs) » Data record produced when an algorithm is used to convert RDRs to geolocated, calibrated detected fluxes with associated ephemeris data. Calibration, ephemeris, and any other ancillary data necessary to convert the sensor units back to sensor raw data (counts) are included. 128
 Project Background Terminology · Temperature Data Records (TDRs) » Calibrated antenna temperature records from a microwave instrument such as ATMS. · Environmental Data Records (EDRs) » Data records produced when an algorithm is used to convert SDRs to geophysical parameters (including ancillary parameters, e. g. , cloud clear radiation, etc. ). 129
Project Background Terminology · Temperature Data Records (TDRs) » Calibrated antenna temperature records from a microwave instrument such as ATMS. · Environmental Data Records (EDRs) » Data records produced when an algorithm is used to convert SDRs to geophysical parameters (including ancillary parameters, e. g. , cloud clear radiation, etc. ). 129
 Project Background Terminology · Intermediate Products (IPs) » There are 2 types of IPS – DIPs: These are “Delivered IPs” meaning that these files will be made available to NPOESS customers via the IDPS. – RIPs: These are “Retained IPs” meaning that these files will be retained within the IDPS and to released to customers. 130
Project Background Terminology · Intermediate Products (IPs) » There are 2 types of IPS – DIPs: These are “Delivered IPs” meaning that these files will be made available to NPOESS customers via the IDPS. – RIPs: These are “Retained IPs” meaning that these files will be retained within the IDPS and to released to customers. 130


