90f397879fc093b7f769dd848e5736af.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
Nervous System Regents Biology

Why do animals need a nervous system? What characteristics do animals need in a nervous system? u fast u accurate u reset quickly Remember… think about Poor bunny! the bunny… Regents Biology
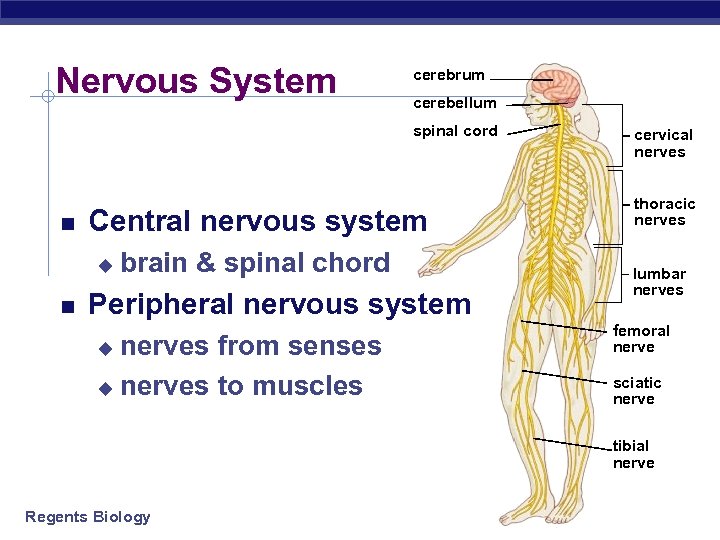
Nervous System cerebrum cerebellum spinal cord Central nervous system u brain & spinal chord Peripheral nervous system nerves from senses u nerves to muscles u cervical nerves thoracic nerves lumbar nerves femoral nerve sciatic nerve tibial nerve Regents Biology
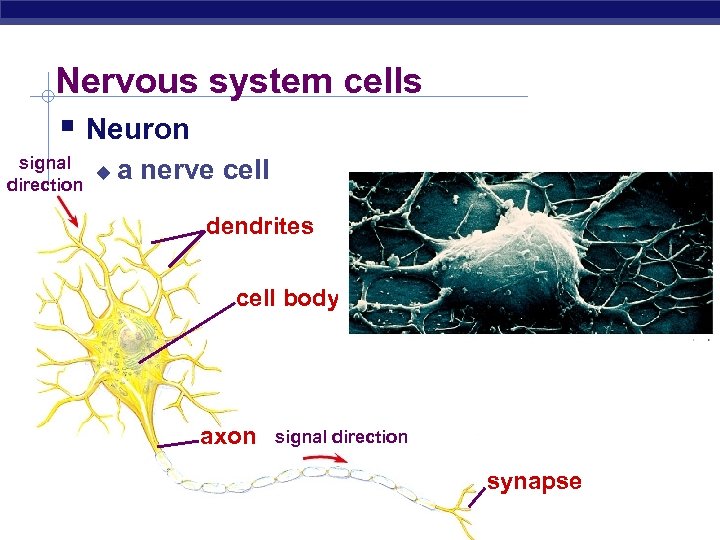
Nervous system cells § Neuron signal u direction a nerve cell dendrites cell body axon signal direction synapse Regents Biology
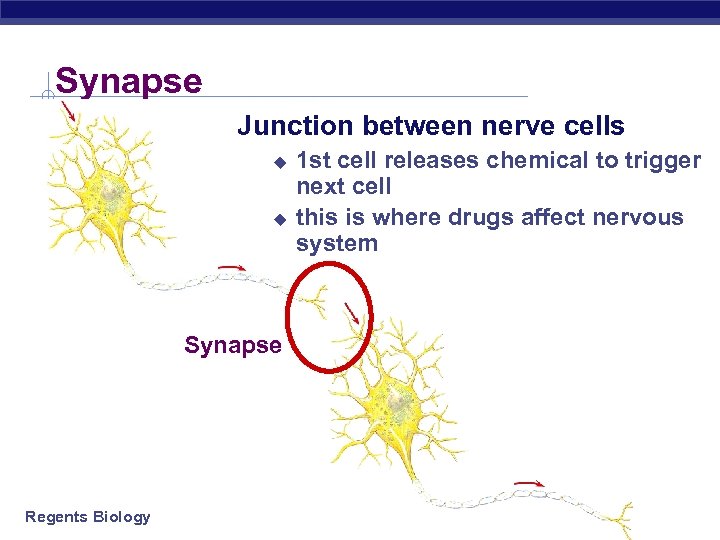
Synapse Junction between nerve cells u u Synapse Regents Biology 1 st cell releases chemical to trigger next cell this is where drugs affect nervous system
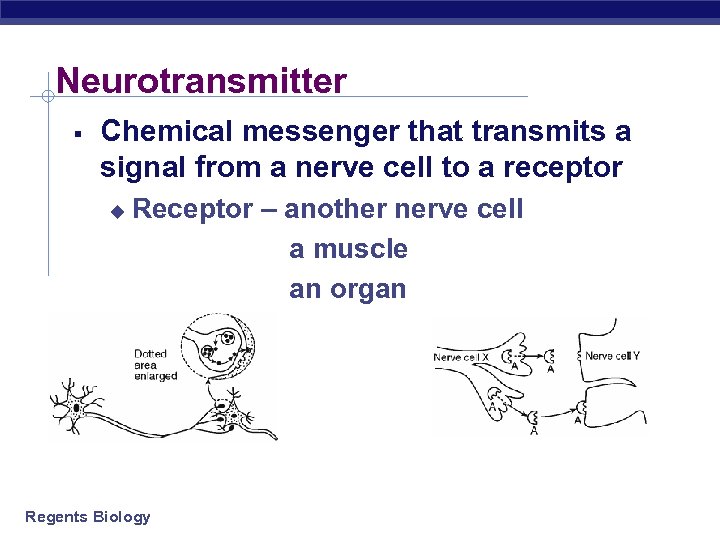
Neurotransmitter § Chemical messenger that transmits a signal from a nerve cell to a receptor u Receptor – another nerve cell a muscle an organ Regents Biology
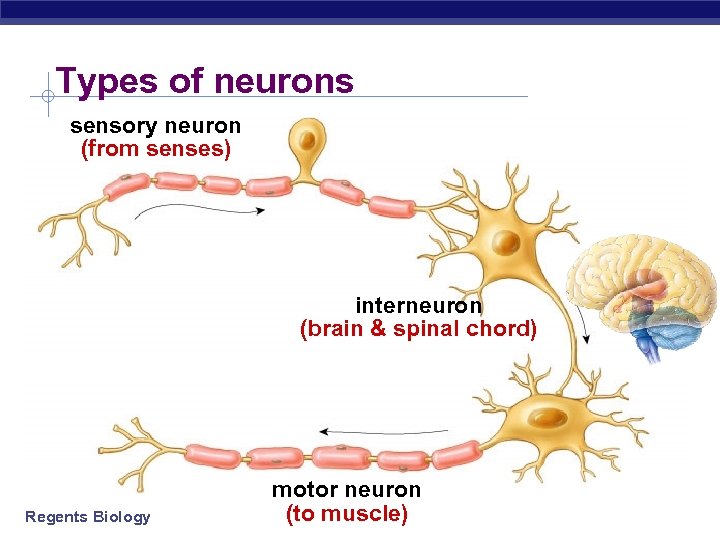
Types of neurons sensory neuron (from senses) interneuron (brain & spinal chord) Regents Biology motor neuron (to muscle)
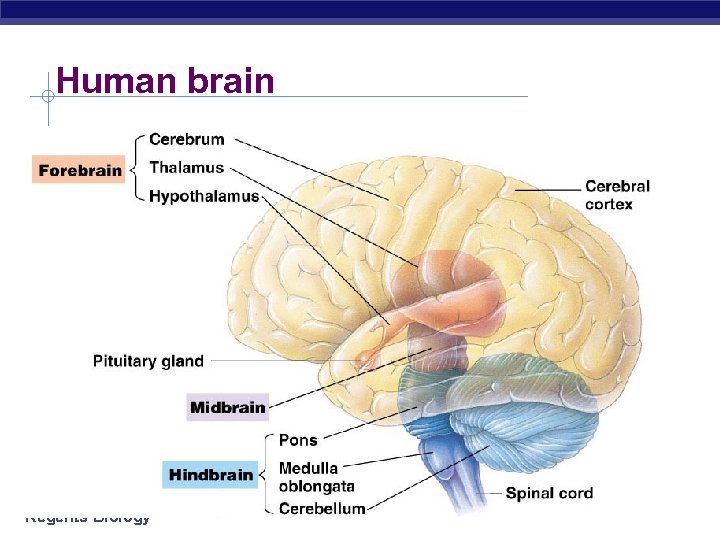
Human brain Regents Biology
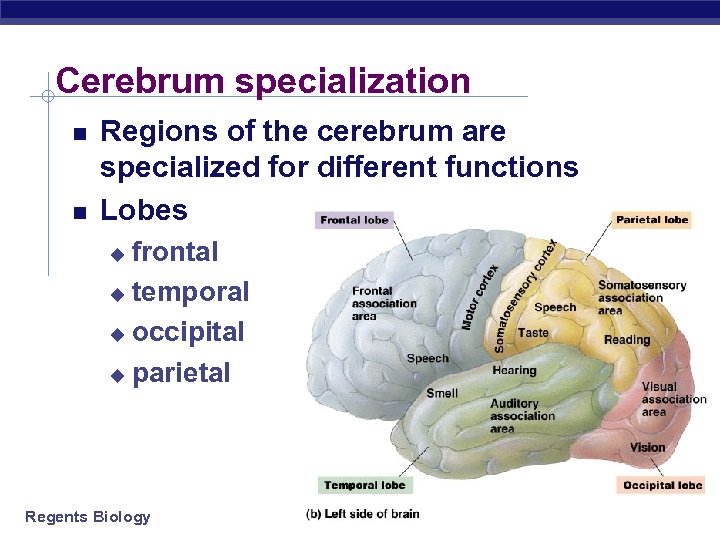
Cerebrum specialization Regions of the cerebrum are specialized for different functions Lobes frontal u temporal u occipital u parietal u Regents Biology
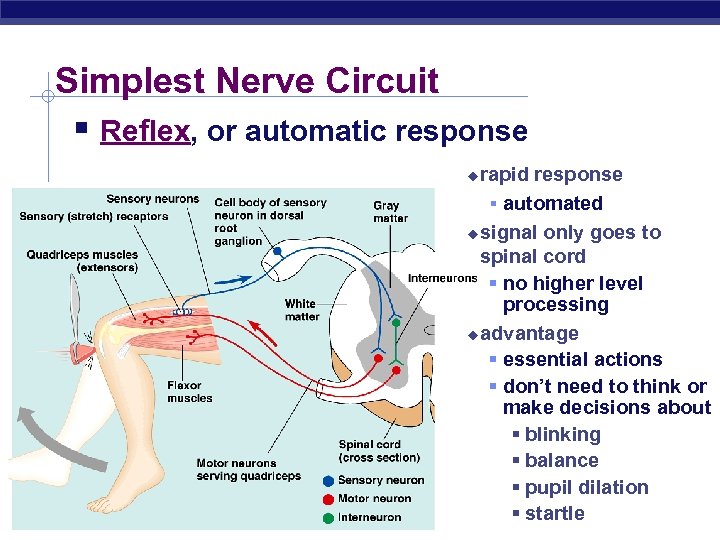
Simplest Nerve Circuit § Reflex, or automatic response rapid response § automated u signal only goes to spinal cord § no higher level processing u advantage § essential actions § don’t need to think or make decisions about § blinking § balance § pupil dilation § startle u Regents Biology
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis Regents Biology

Homeostasis u maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called “dynamic equilibrium” u example: body temperature humans: w too cold = shiver w too warm = sweat Regents Biology

Regulation How we maintain homeostasis u nervous system u nerve signals control body functions endocrine system hormones chemical signals control body functions Regents Biology
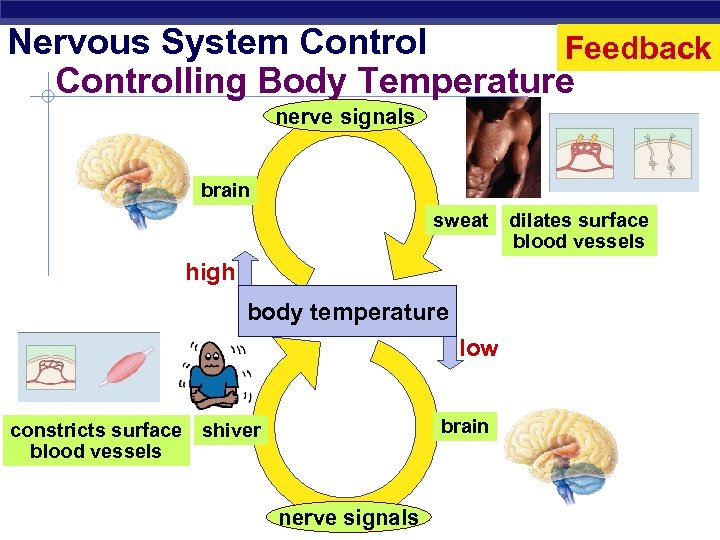
Nervous System Control Feedback Controlling Body Temperature nerve signals brain sweat high body temperature low brain constricts surface shiver blood vessels Regents Biology nerve signals dilates surface blood vessels

Hormones Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to cells in other parts of body u communication needed to coordinate whole body u maintaining homeostasis u Regents Biology growth hormones
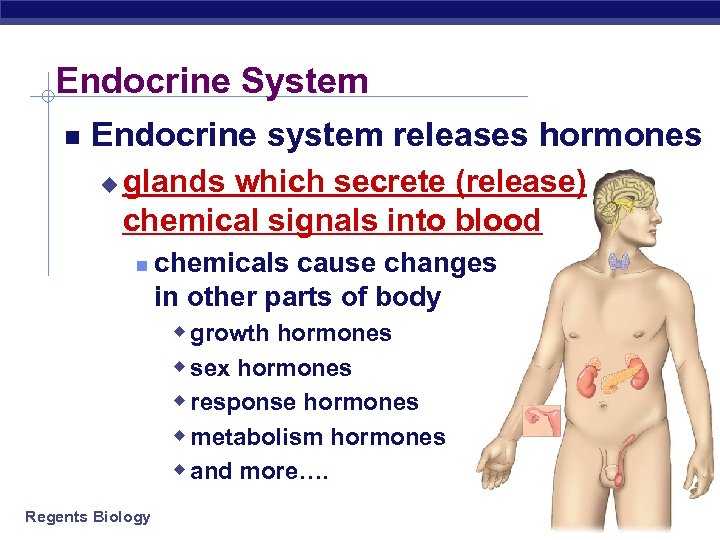
Endocrine System Endocrine system releases hormones u glands which secrete (release) chemical signals into blood Regents Biology chemicals cause changes in other parts of body w growth hormones w sex hormones w response hormones w metabolism hormones w and more….
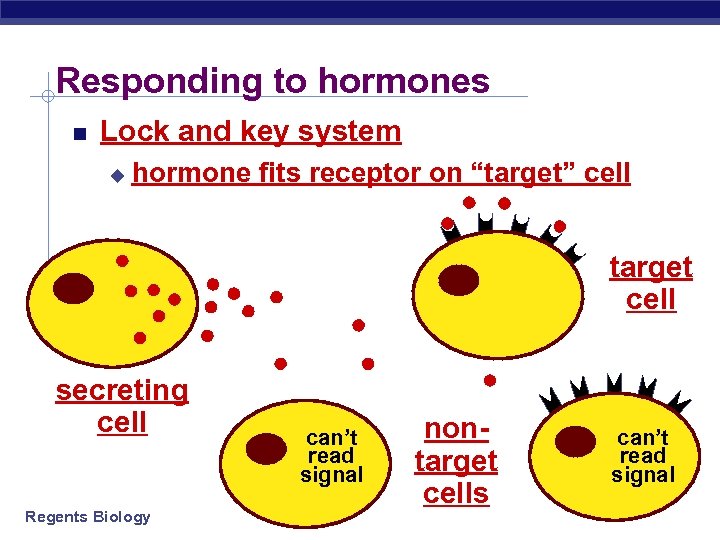
Responding to hormones Lock and key system u hormone fits receptor on “target” cell target cell secreting cell Regents Biology can’t read signal nontarget cells can’t read signal
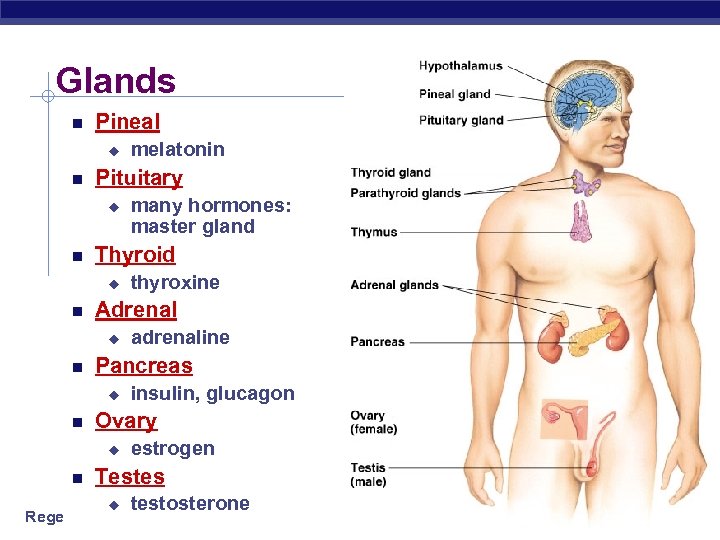
Glands Pineal u Pituitary u insulin, glucagon Ovary u adrenaline Pancreas u thyroxine Adrenal u many hormones: master gland Thyroid u melatonin estrogen Testes u testosterone Regents Biology
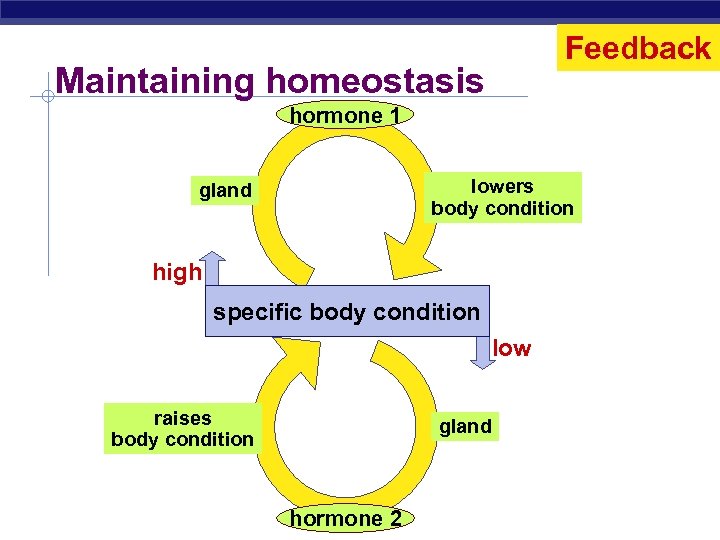
Feedback Maintaining homeostasis hormone 1 lowers body condition gland high specific body condition low raises body condition Regents Biology gland hormone 2
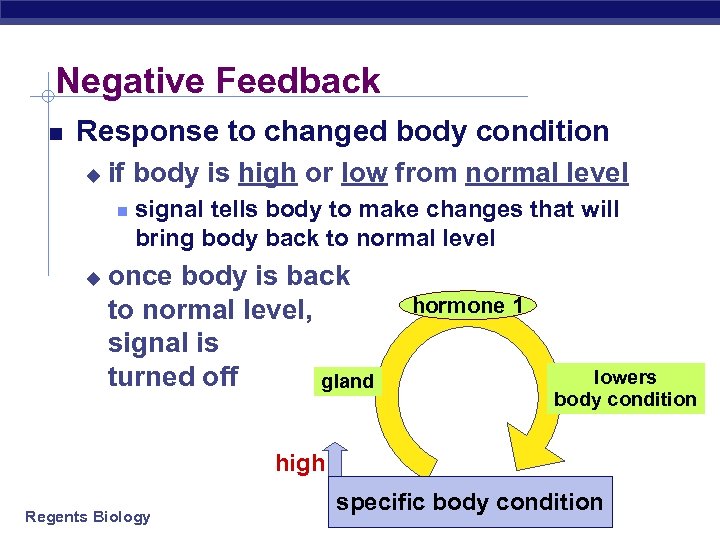
Negative Feedback Response to changed body condition u if body is high or low from normal level u signal tells body to make changes that will bring body back to normal level once body is back to normal level, signal is turned off gland hormone 1 lowers body condition high Regents Biology specific body condition
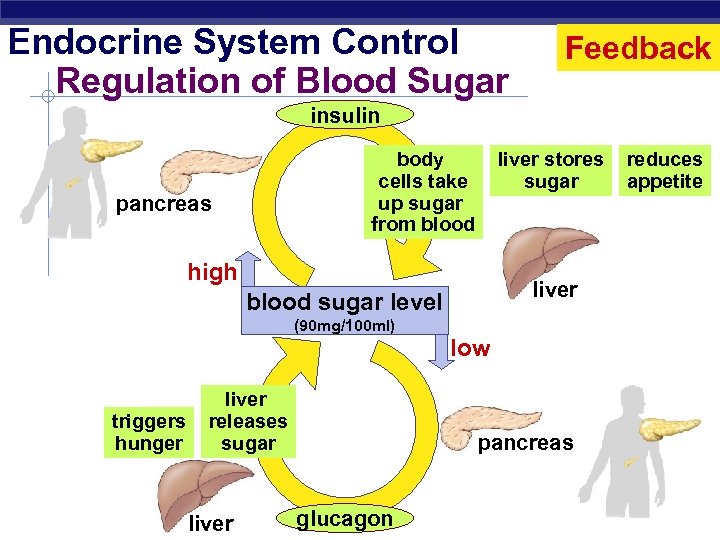
Endocrine System Control Regulation of Blood Sugar Feedback insulin liver stores sugar body cells take up sugar from blood pancreas high liver blood sugar level (90 mg/100 ml) low triggers hunger Regents Biology liver releases sugar liver pancreas glucagon reduces appetite
Endocrine System Hormones & Reproduction Regents Biology 2009 -2010
Sex & Growth Hormones Large scale body changes u how do they work turn genes on start new processes in the body by turning genes on that were lying “dormant” Regents Biology
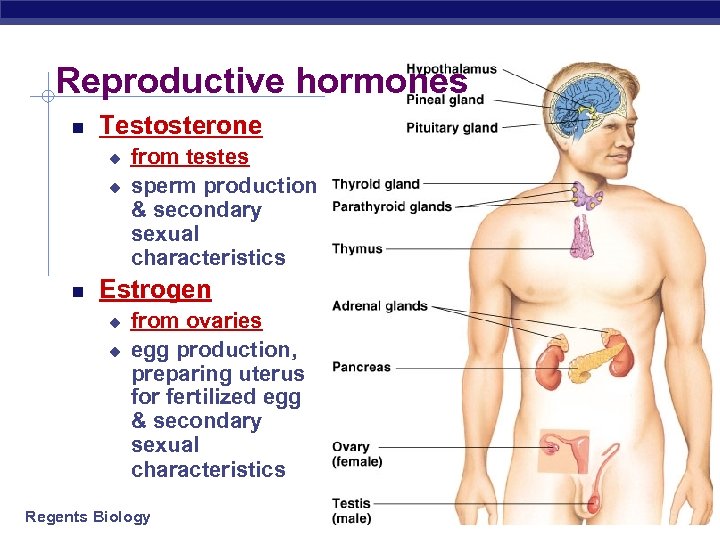
Reproductive hormones Testosterone u u from testes sperm production & secondary sexual characteristics Estrogen u u from ovaries egg production, preparing uterus for fertilized egg & secondary sexual characteristics Regents Biology
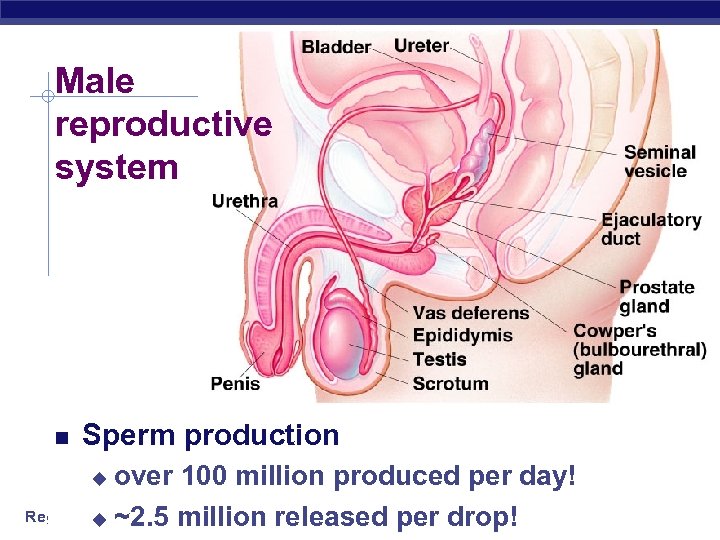
Male reproductive system Sperm production over 100 million produced per day! Regents u ~2. 5 million released per drop! Biology u
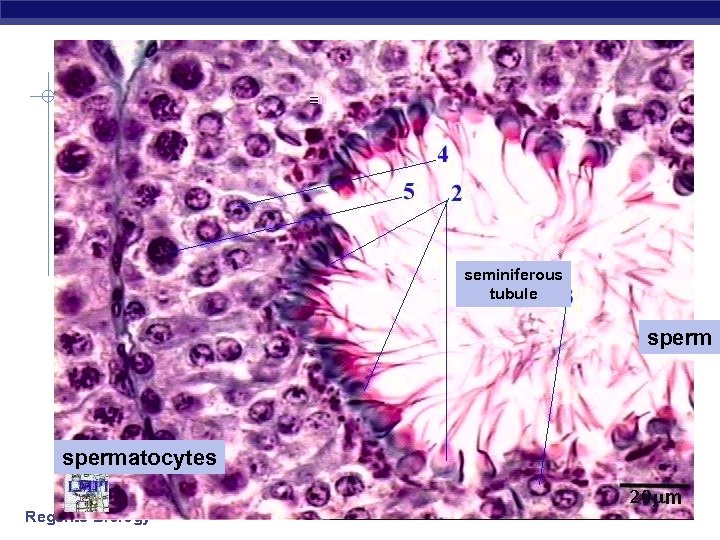
seminiferous tubule spermatocytes Regents Biology
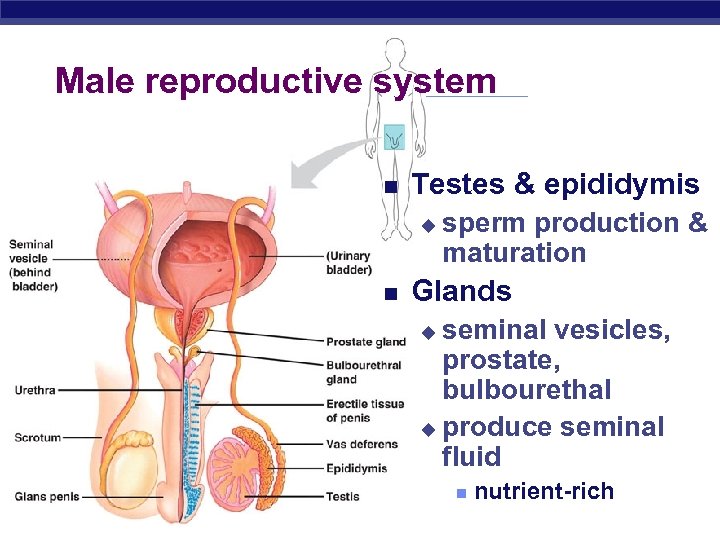
Male reproductive system Testes & epididymis u sperm production & maturation Glands seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethal u produce seminal fluid u Regents Biology nutrient-rich
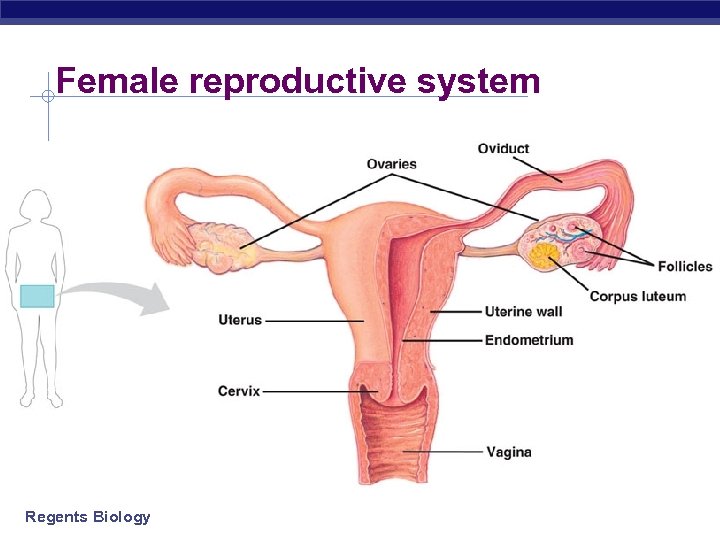
Female reproductive system Regents Biology

DO NOW How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis in the body? Regents Biology
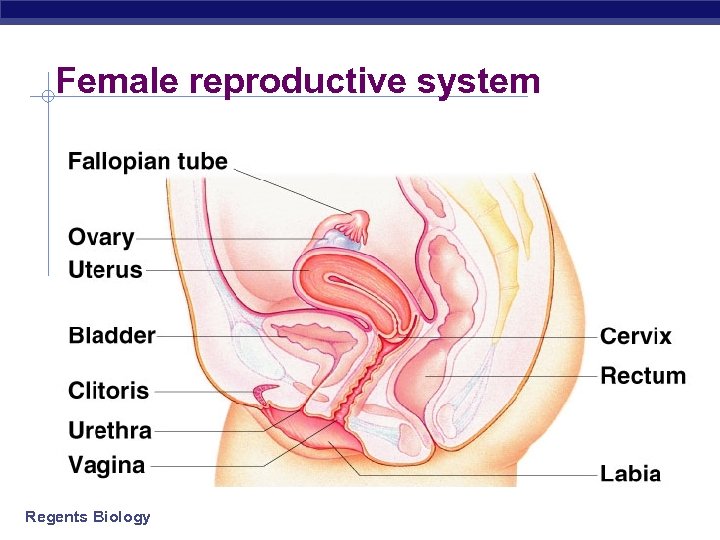
Female reproductive system Regents Biology
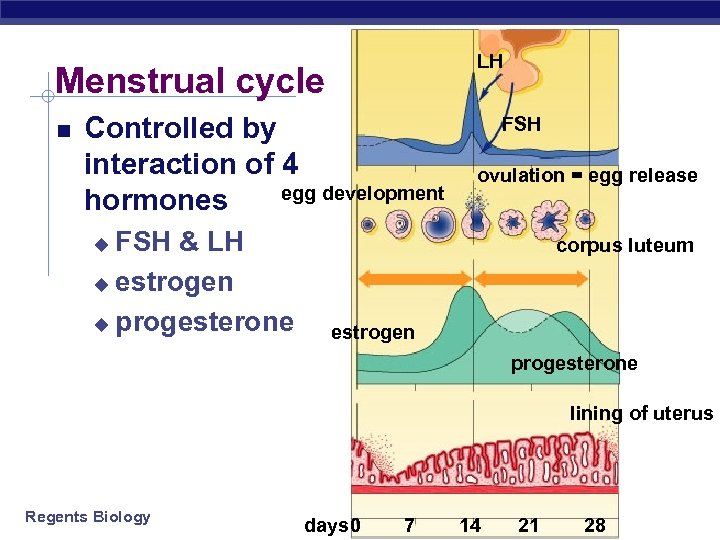
LH Menstrual cycle Controlled by interaction of 4 egg development hormones FSH & LH u estrogen u progesterone FSH ovulation = egg release corpus luteum u estrogen progesterone lining of uterus Regents Biology days 0 7 14 21 28
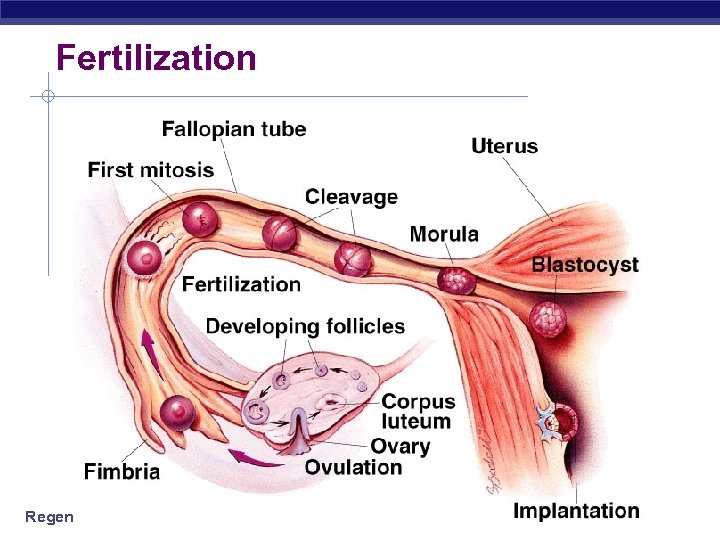
Fertilization Regents Biology

https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=_5 Ov g. QW 6 FG 4 Regents Biology
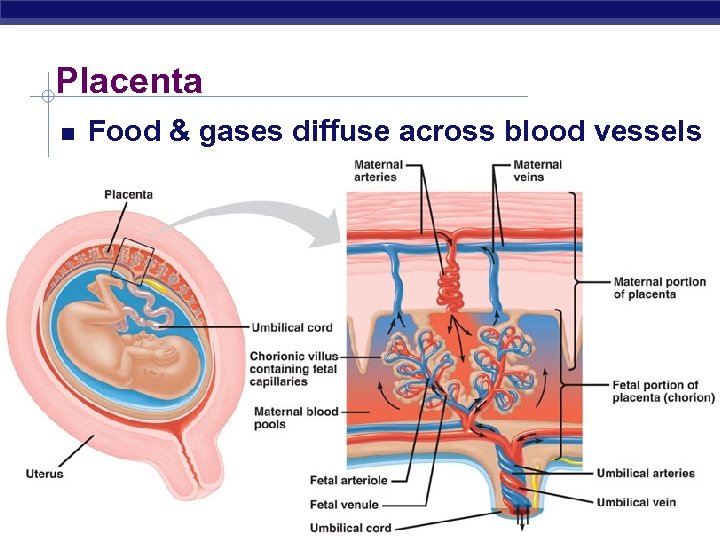
Placenta Food & gases diffuse across blood vessels Regents Biology
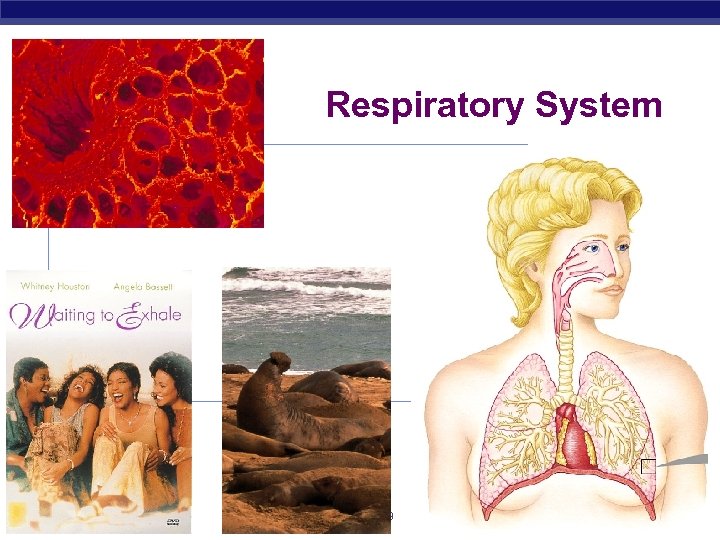
Respiratory System Regents Biology 2008 -2009

Why do we need a respiratory system? Need O 2 in for cellular respiration u make ATP u Need CO 2 out u food waste product O 2 Regents Biology ATP CO 2
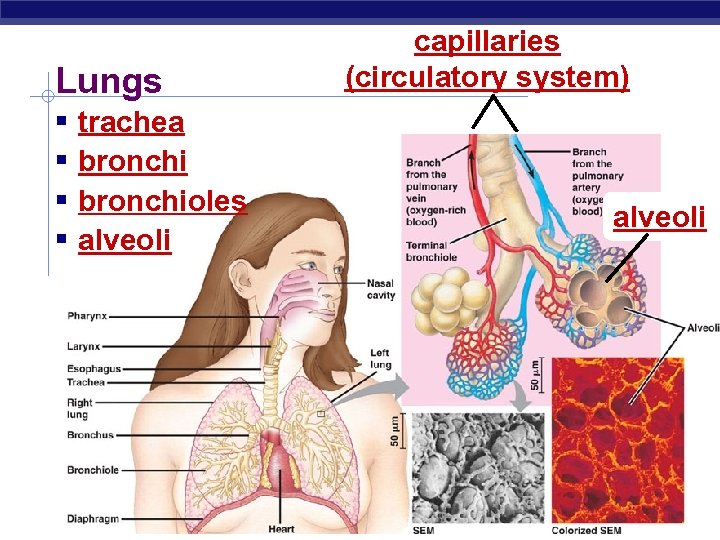
Lungs § trachea § bronchioles § alveoli Regents Biology capillaries (circulatory system) alveoli
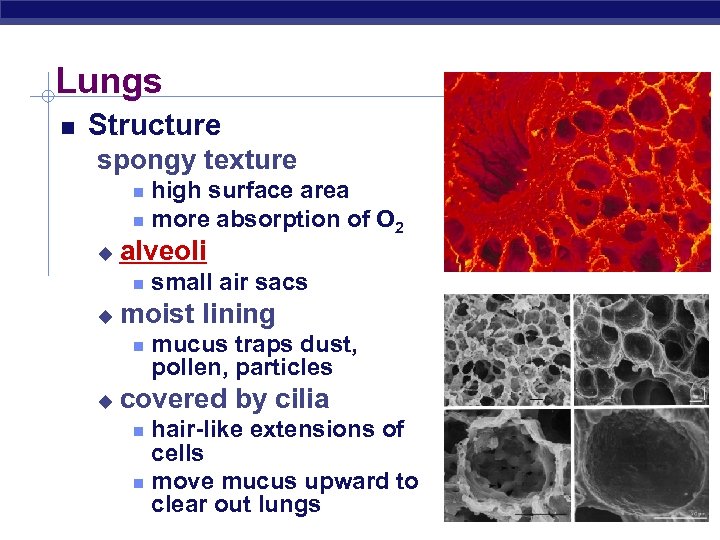
Lungs Structure spongy texture high surface area more absorption of O 2 u alveoli u moist lining u small air sacs mucus traps dust, pollen, particles covered by cilia hair-like extensions of cells move mucus upward to clear out lungs Regents Biology
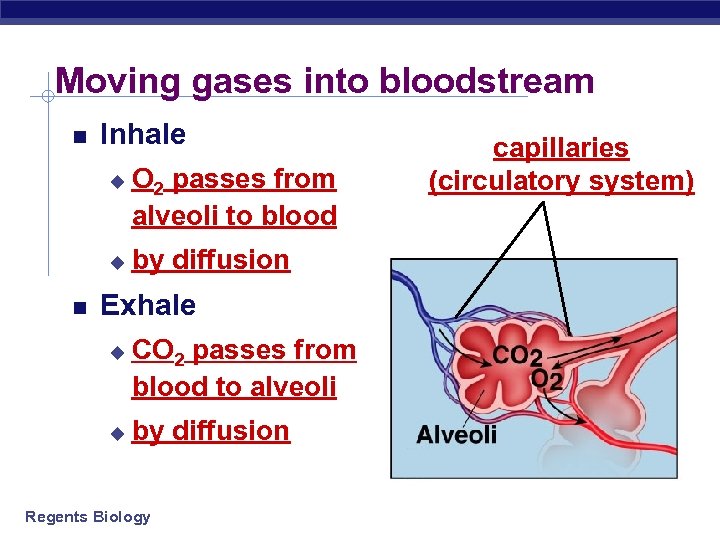
Moving gases into bloodstream Inhale u u O 2 passes from alveoli to blood by diffusion Exhale u u CO 2 passes from blood to alveoli by diffusion Regents Biology capillaries (circulatory system)
Excretory System Kidneys Regents Biology 2008 -2009
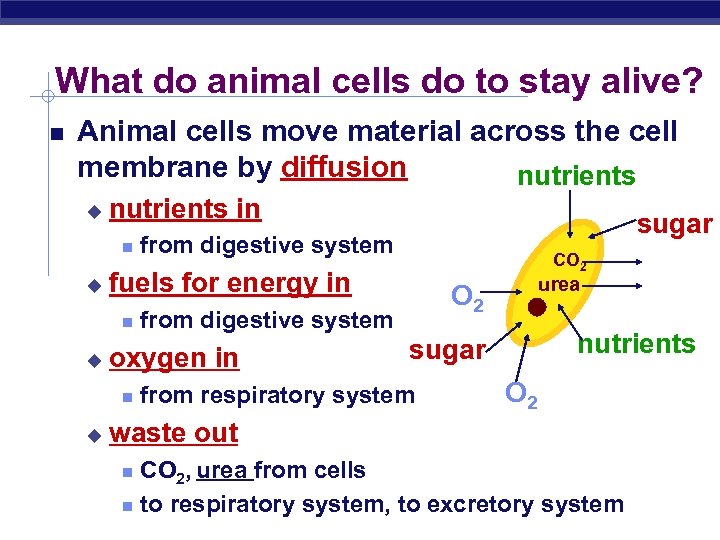
What do animal cells do to stay alive? Animal cells move material across the cell membrane by diffusion nutrients u nutrients in u CO 2 urea O 2 from digestive system oxygen in u from digestive system fuels for energy in u sugar nutrients sugar from respiratory system O 2 waste out CO 2, urea from cells to respiratory system, to excretory system Regents Biology
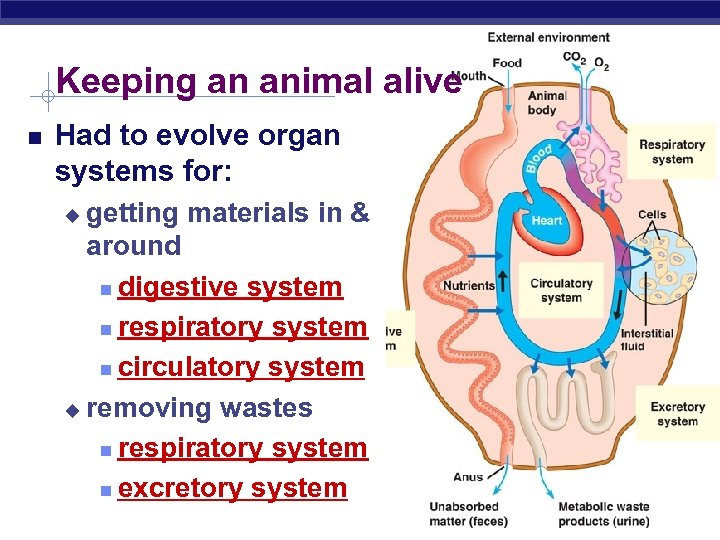
Keeping an animal alive Had to evolve organ systems for: getting materials in & around digestive system respiratory system circulatory system u removing wastes respiratory system excretory system u Regents Biology
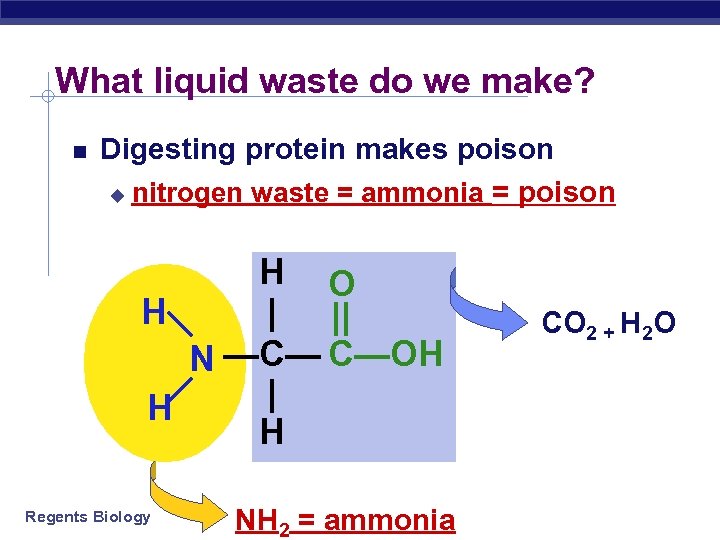
What liquid waste do we make? Digesting protein makes poison u nitrogen waste = ammonia = poison H O | || H N —C— C—OH | H H Regents Biology NH 2 = ammonia CO 2 + H 2 O
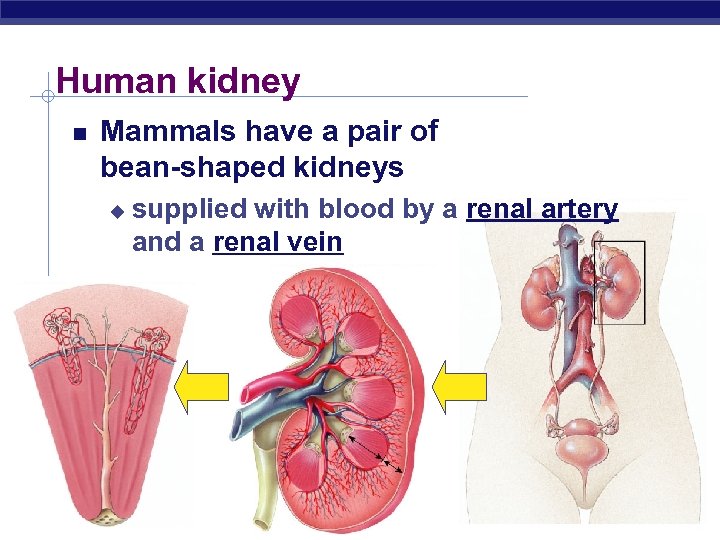
Human kidney Mammals have a pair of bean-shaped kidneys u supplied with blood by a renal artery and a renal vein Regents Biology
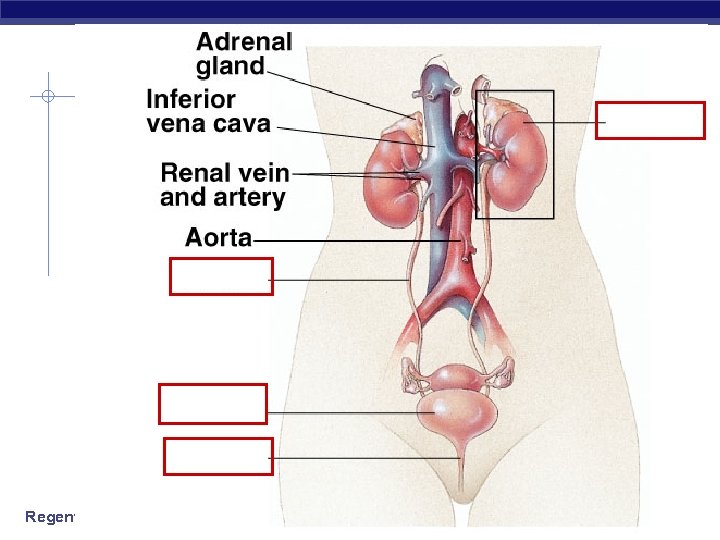
Bladder Regents Biology
90f397879fc093b7f769dd848e5736af.ppt