49154625bfaa481eaed565a5d22cee27.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
Nervous System AP Biology 20032004

Why do animals need a nervous system? § What characteristics do animals need in a nervous system? u fast u accurate u reset quickly Remember… think about Poor bunny! the bunny… Regents Biology 2003 -
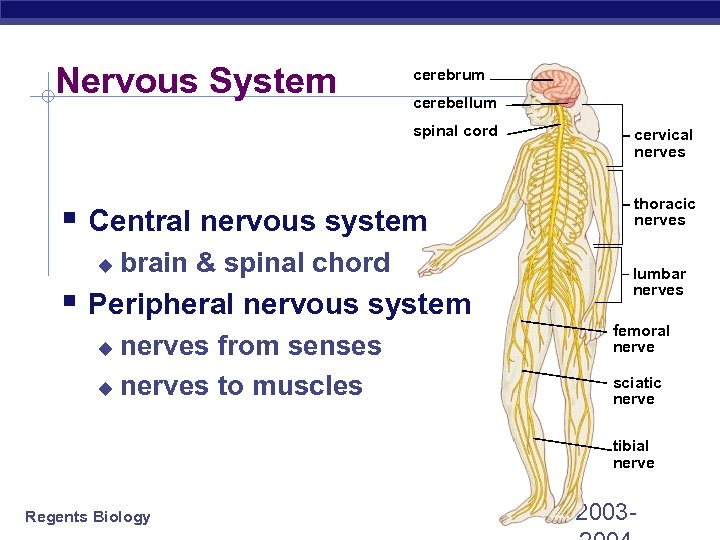
Nervous System cerebrum cerebellum spinal cord § Central nervous system u brain & spinal chord § Peripheral nervous system nerves from senses u nerves to muscles u cervical nerves thoracic nerves lumbar nerves femoral nerve sciatic nerve tibial nerve Regents Biology 2003 -
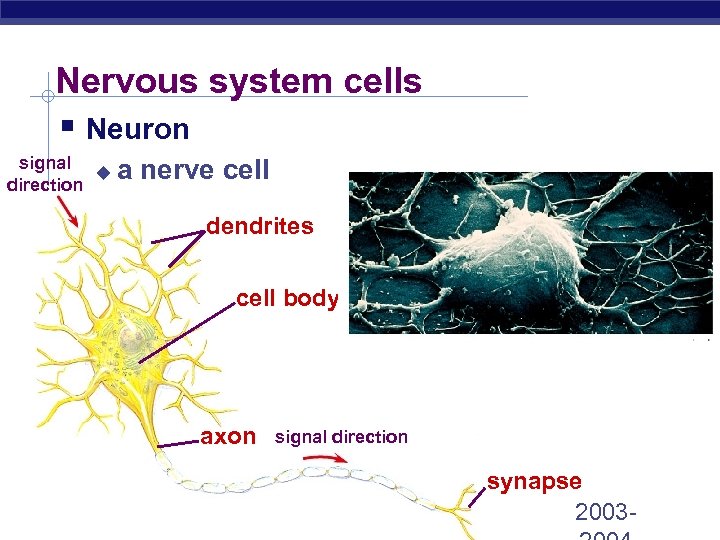
Nervous system cells § Neuron signal u direction a nerve cell dendrites cell body axon Regents Biology signal direction synapse 2003 -

Fun facts about neurons § Most specialized cell in § animals Longest cell u blue whale neuron § 10 -30 meters u giraffe axon § 5 meters u human neuron § 1 -2 meters Nervous system allows for 1 millisecond response time Regents Biology 2003 -
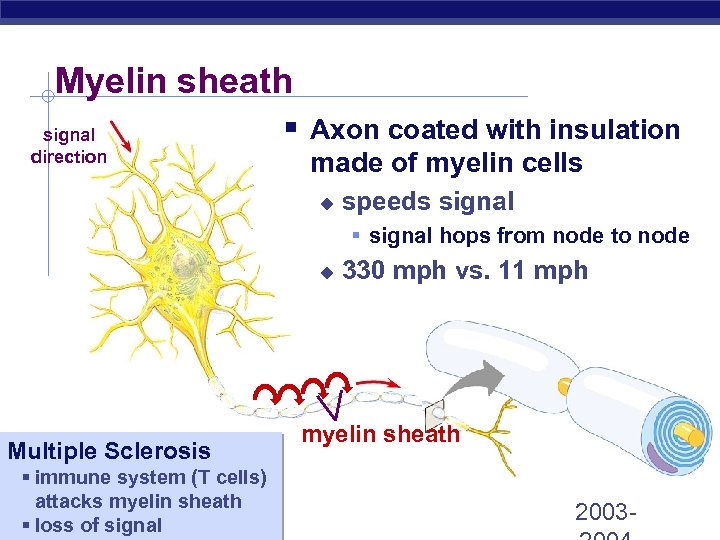
Myelin sheath signal direction § Axon coated with insulation made of myelin cells u speeds signal § signal hops from node to node u Multiple Sclerosis § immune system (T cells) attacks myelin sheath Regents Biology § loss of signal 330 mph vs. 11 mph myelin sheath 2003 -
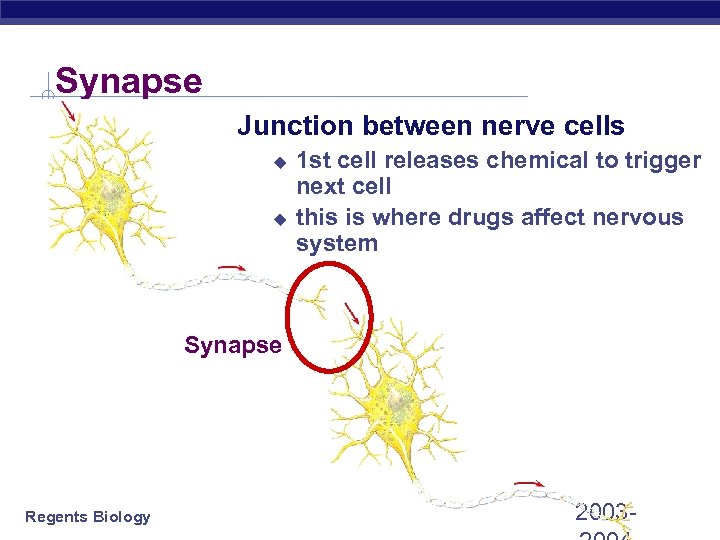
Synapse Junction between nerve cells u u 1 st cell releases chemical to trigger next cell this is where drugs affect nervous system Synapse Regents Biology 2003 -
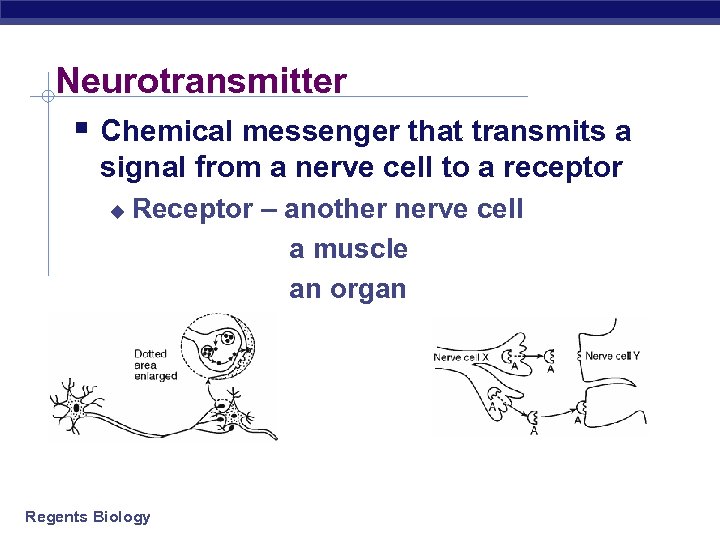
Neurotransmitter § Chemical messenger that transmits a signal from a nerve cell to a receptor u Receptor – another nerve cell a muscle an organ Regents Biology
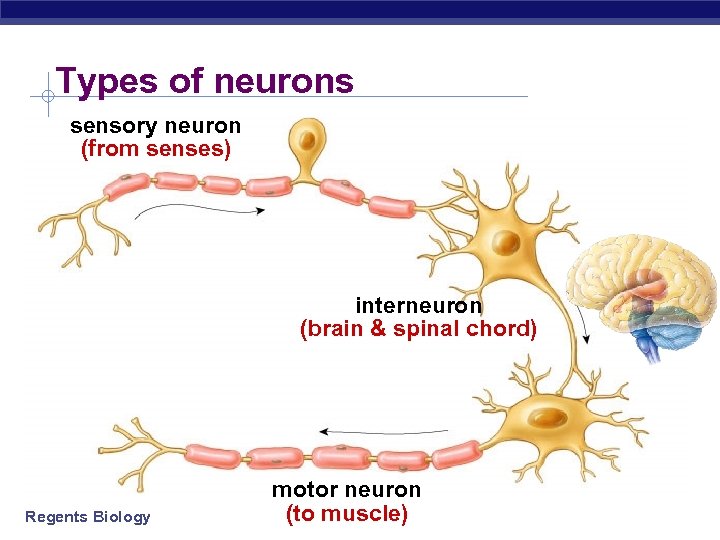
Types of neurons sensory neuron (from senses) interneuron (brain & spinal chord) Regents Biology motor neuron (to muscle)
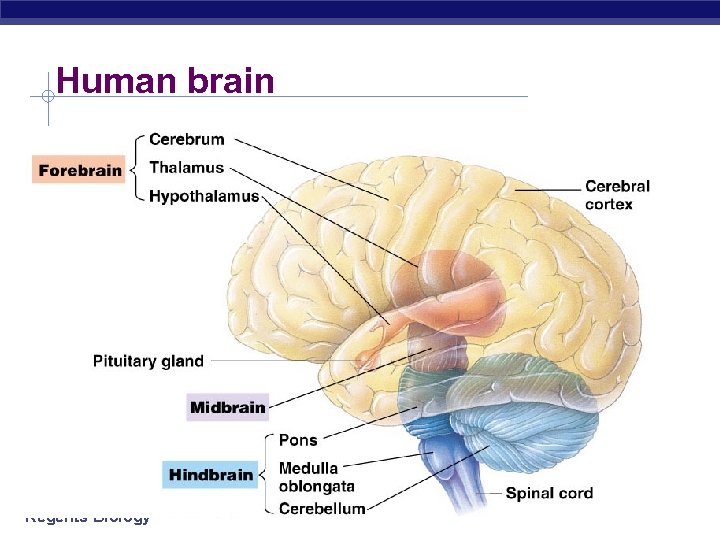
Human brain Regents Biology
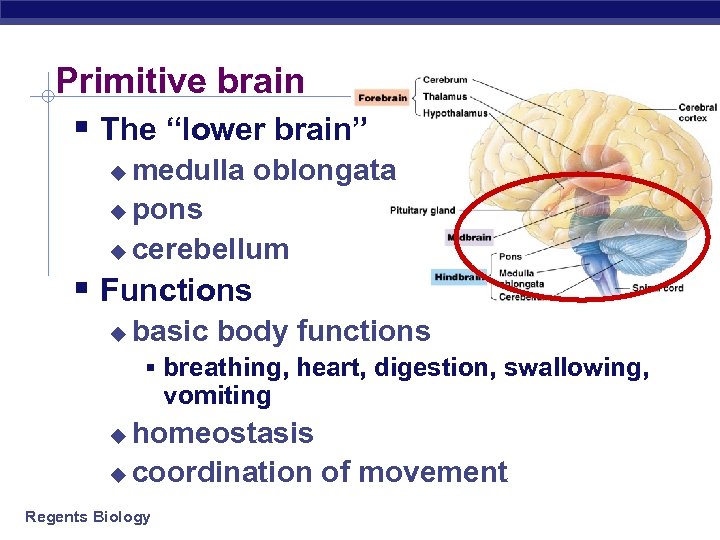
Primitive brain § The “lower brain” medulla oblongata u pons u cerebellum u § Functions u basic body functions § breathing, heart, digestion, swallowing, vomiting homeostasis u coordination of movement u Regents Biology
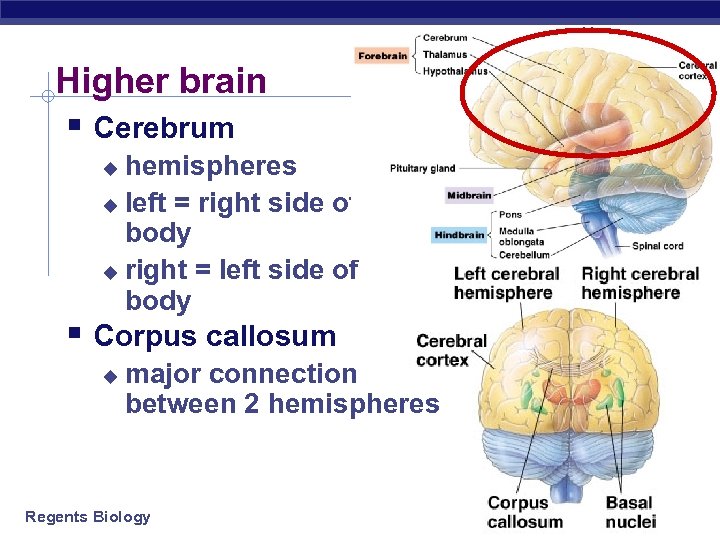
Higher brain § Cerebrum hemispheres u left = right side of body u right = left side of body u § Corpus callosum u major connection between 2 hemispheres Regents Biology
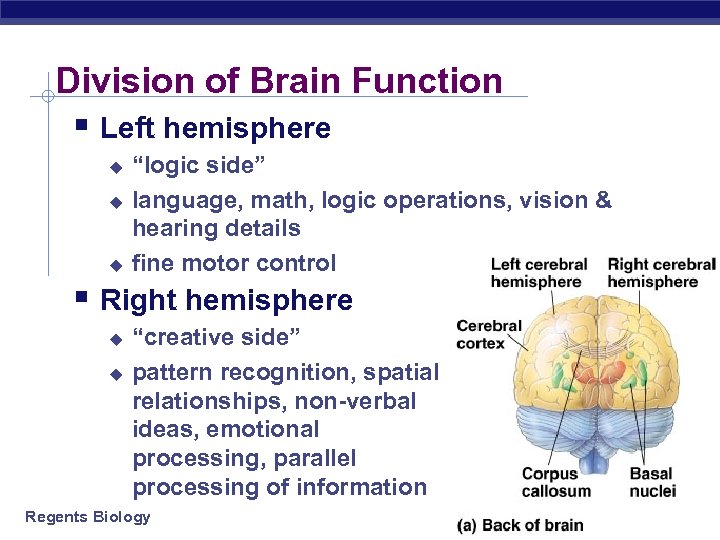
Division of Brain Function § Left hemisphere u u u “logic side” language, math, logic operations, vision & hearing details fine motor control § Right hemisphere u u “creative side” pattern recognition, spatial relationships, non-verbal ideas, emotional processing, parallel processing of information Regents Biology 2003 -
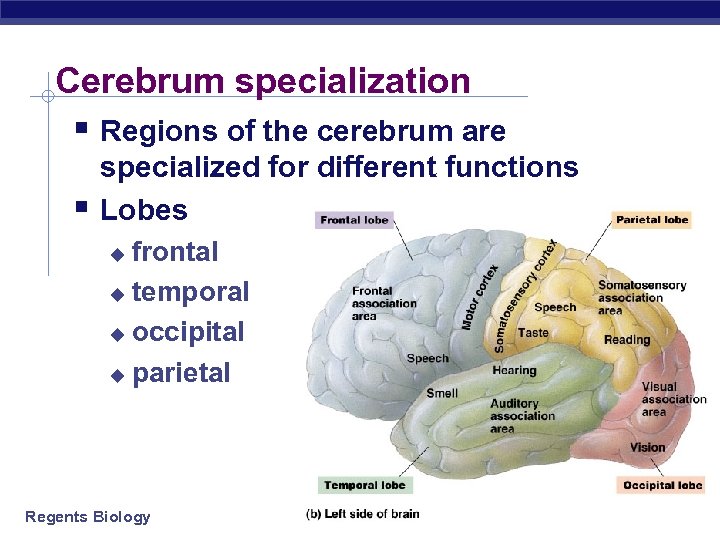
Cerebrum specialization § Regions of the cerebrum are § specialized for different functions Lobes frontal u temporal u occipital u parietal u Regents Biology
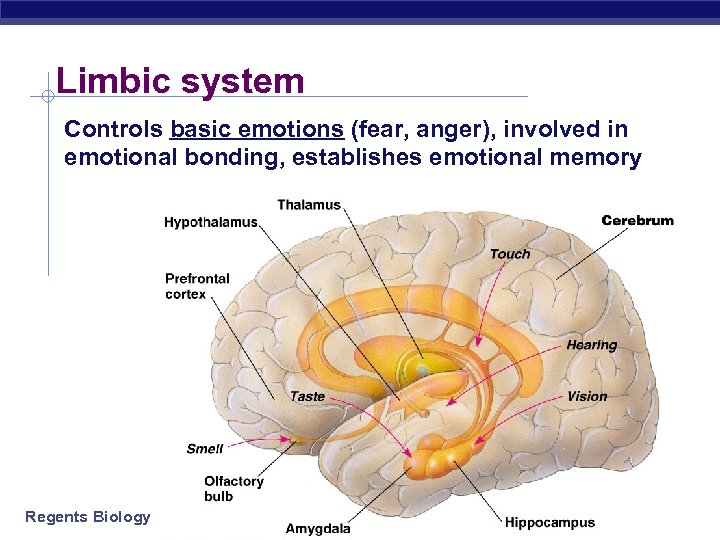
Limbic system Controls basic emotions (fear, anger), involved in emotional bonding, establishes emotional memory Regents Biology 2003 -
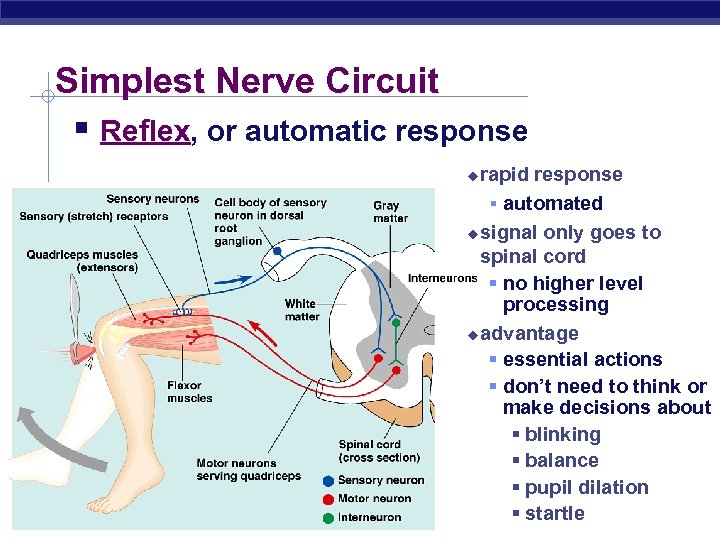
Simplest Nerve Circuit § Reflex, or automatic response rapid response § automated u signal only goes to spinal cord § no higher level processing u advantage § essential actions § don’t need to think or make decisions about § blinking § balance § pupil dilation § startle u Regents Biology
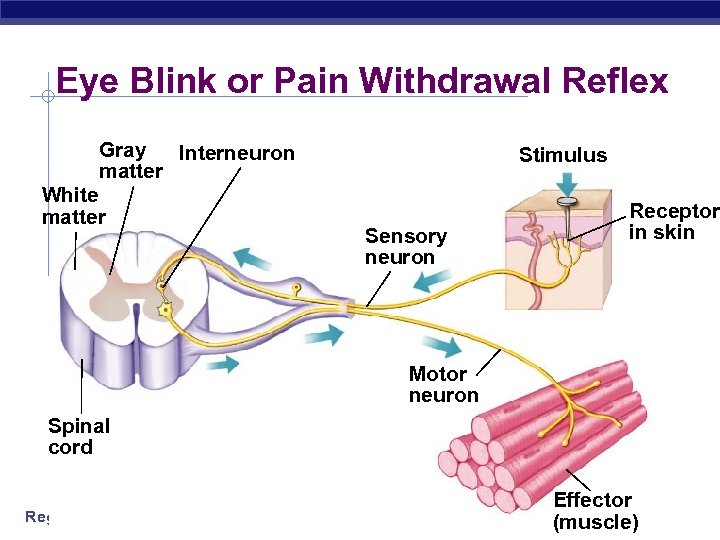
Eye Blink or Pain Withdrawal Reflex Gray Interneuron matter White matter Stimulus Sensory neuron Receptor in skin Motor neuron Spinal cord Regents Biology Effector (muscle)
cerebrum cerebellum spinal cord cervical nerves thoracic nerves lumbar nerves femoral nerve Any Questions? ? sciatic nerve tibial nerve AP Biology 20032004
49154625bfaa481eaed565a5d22cee27.ppt