831b7107fa033cdfc92bac80bfa9e814.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
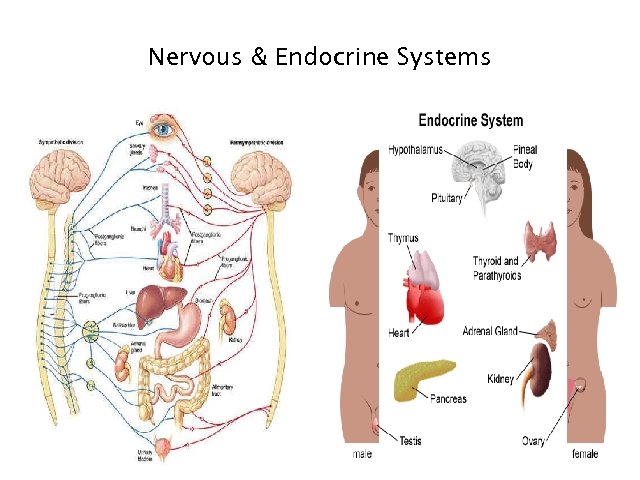 Nervous & Endocrine Systems 1
Nervous & Endocrine Systems 1
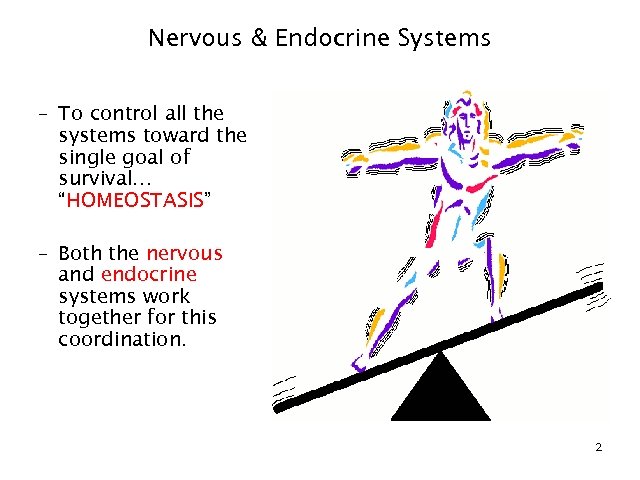 Nervous & Endocrine Systems – To control all the systems toward the single goal of survival… “HOMEOSTASIS” – Both the nervous and endocrine systems work together for this coordination. 2
Nervous & Endocrine Systems – To control all the systems toward the single goal of survival… “HOMEOSTASIS” – Both the nervous and endocrine systems work together for this coordination. 2
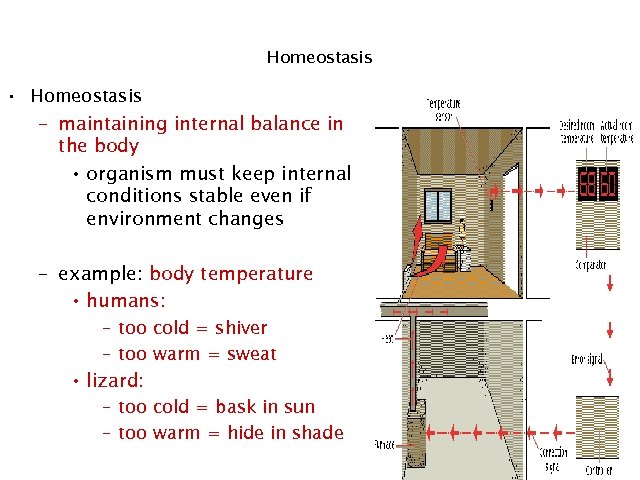 Homeostasis • Homeostasis – maintaining internal balance in the body • organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes – example: body temperature • humans: – too • lizard: – too cold = shiver warm = sweat cold = bask in sun warm = hide in shade 3
Homeostasis • Homeostasis – maintaining internal balance in the body • organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes – example: body temperature • humans: – too • lizard: – too cold = shiver warm = sweat cold = bask in sun warm = hide in shade 3
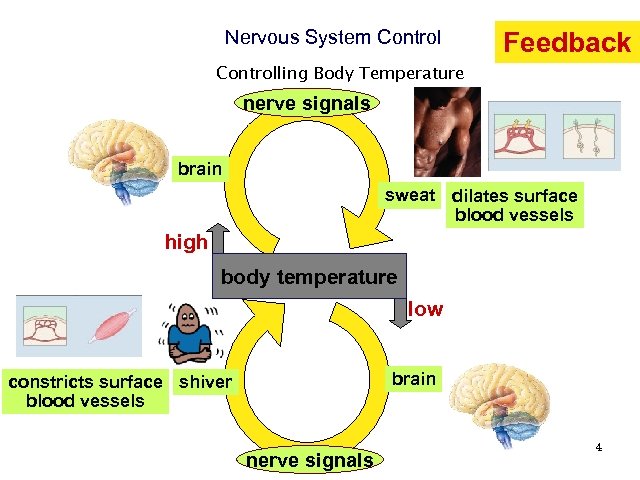 Nervous System Control Feedback Controlling Body Temperature nerve signals brain sweat dilates surface blood vessels high body temperature low brain constricts surface shiver blood vessels nerve signals 4
Nervous System Control Feedback Controlling Body Temperature nerve signals brain sweat dilates surface blood vessels high body temperature low brain constricts surface shiver blood vessels nerve signals 4
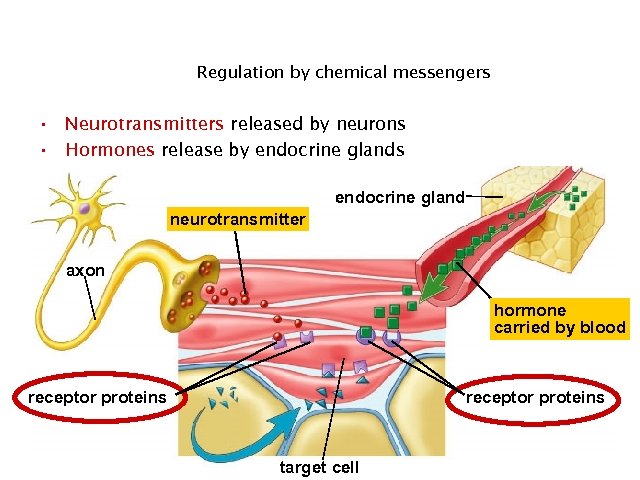 Regulation by chemical messengers • Neurotransmitters released by neurons • Hormones release by endocrine glands endocrine gland neurotransmitter axon hormone carried by blood receptor proteins 5 target cell
Regulation by chemical messengers • Neurotransmitters released by neurons • Hormones release by endocrine glands endocrine gland neurotransmitter axon hormone carried by blood receptor proteins 5 target cell
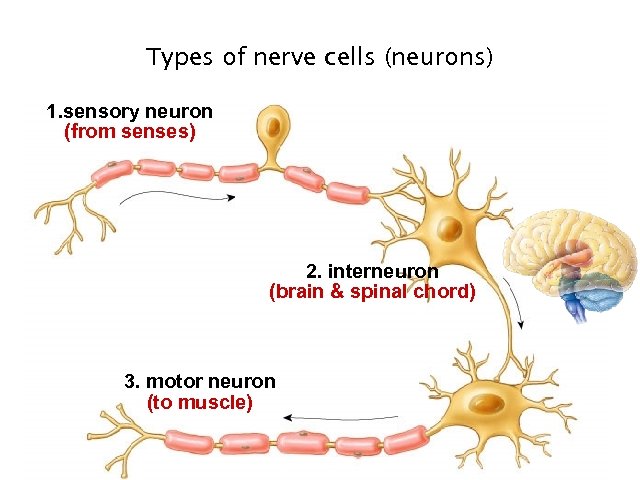 Types of nerve cells (neurons) 1. sensory neuron (from senses) 2. interneuron (brain & spinal chord) 3. motor neuron (to muscle) 6
Types of nerve cells (neurons) 1. sensory neuron (from senses) 2. interneuron (brain & spinal chord) 3. motor neuron (to muscle) 6
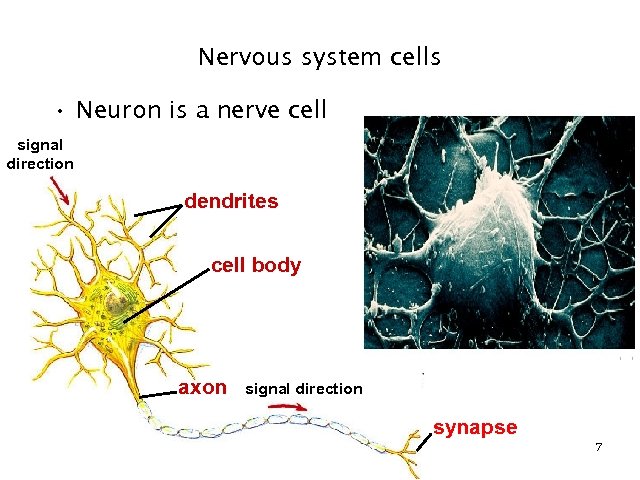 Nervous system cells • Neuron is a nerve cell signal direction dendrites cell body axon signal direction synapse 7
Nervous system cells • Neuron is a nerve cell signal direction dendrites cell body axon signal direction synapse 7
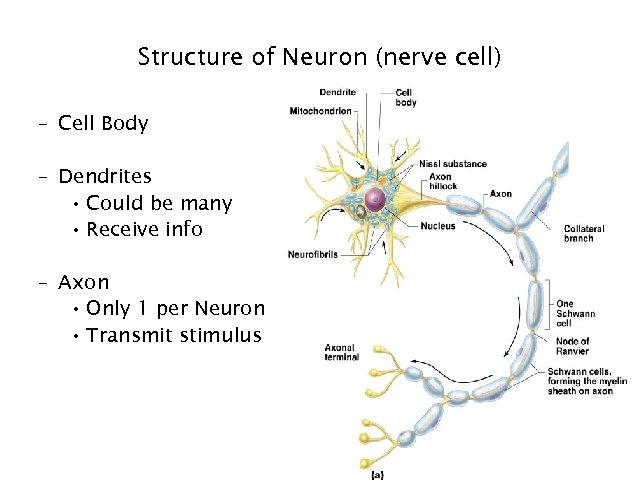 Structure of Neuron (nerve cell) – Cell Body – Dendrites • Could be many • Receive info – Axon • Only 1 per Neuron • Transmit stimulus 8
Structure of Neuron (nerve cell) – Cell Body – Dendrites • Could be many • Receive info – Axon • Only 1 per Neuron • Transmit stimulus 8
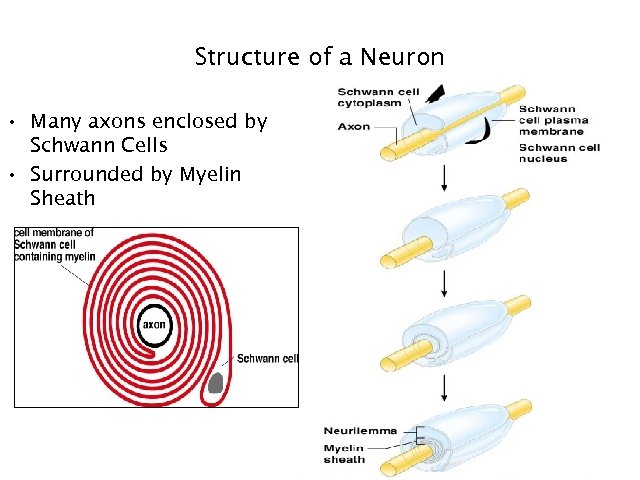 Structure of a Neuron • Many axons enclosed by Schwann Cells • Surrounded by Myelin Sheath 9
Structure of a Neuron • Many axons enclosed by Schwann Cells • Surrounded by Myelin Sheath 9
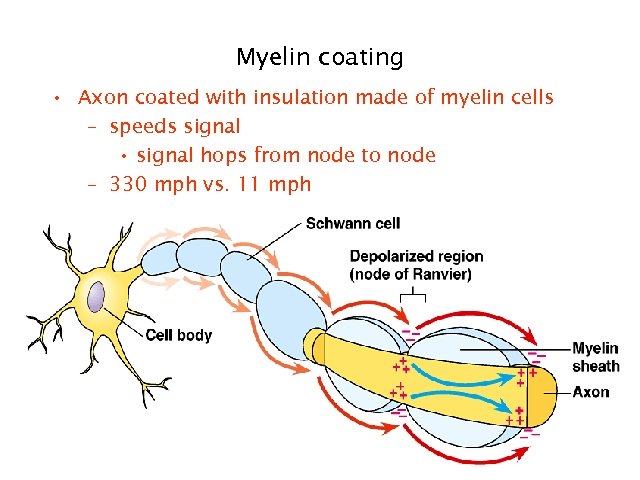 Myelin coating • Axon coated with insulation made of myelin cells – speeds signal • signal hops from node to node – 330 mph vs. 11 mph 10
Myelin coating • Axon coated with insulation made of myelin cells – speeds signal • signal hops from node to node – 330 mph vs. 11 mph 10
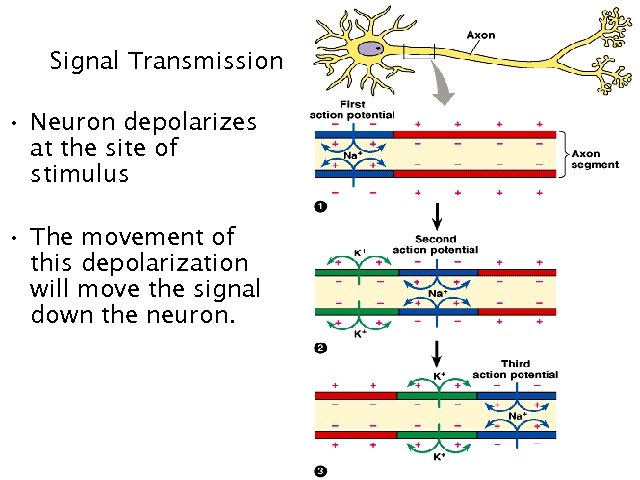 Signal Transmission • Neuron depolarizes at the site of stimulus • The movement of this depolarization will move the signal down the neuron. 11
Signal Transmission • Neuron depolarizes at the site of stimulus • The movement of this depolarization will move the signal down the neuron. 11
 Steps in Nerve Impulse Transmission 1. Stimulus makes cell membrane permeable to Na+ ions. 2. Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron changing the membrane potential 3. Cell membrane is depolarized an action potential is generated. 4. Cell membrane becomes permeable to K+ ions. 5. K+ ions diffuse out of the cell. 6. Cell membrane is repolarized. 8. Concentration of Na+ and K+ reestablished by Na-K pump. 12
Steps in Nerve Impulse Transmission 1. Stimulus makes cell membrane permeable to Na+ ions. 2. Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron changing the membrane potential 3. Cell membrane is depolarized an action potential is generated. 4. Cell membrane becomes permeable to K+ ions. 5. K+ ions diffuse out of the cell. 6. Cell membrane is repolarized. 8. Concentration of Na+ and K+ reestablished by Na-K pump. 12
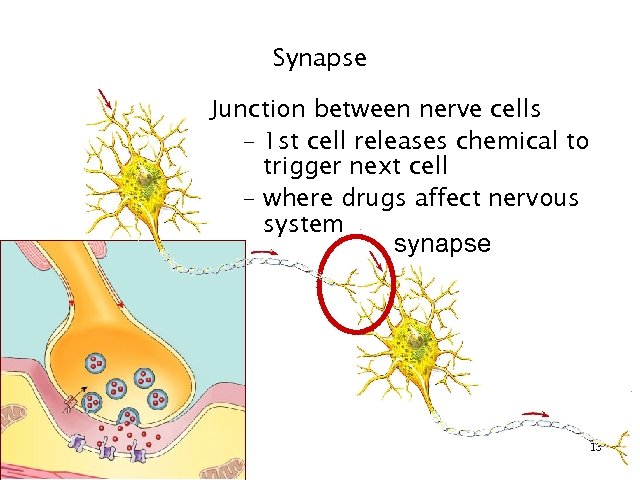 Synapse Junction between nerve cells – 1 st cell releases chemical to trigger next cell – where drugs affect nervous system synapse 13
Synapse Junction between nerve cells – 1 st cell releases chemical to trigger next cell – where drugs affect nervous system synapse 13
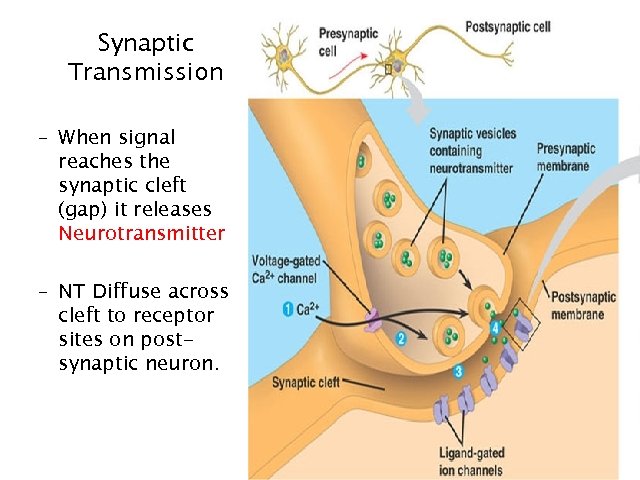 Synaptic Transmission – When signal reaches the synaptic cleft (gap) it releases Neurotransmitter – NT Diffuse across cleft to receptor sites on postsynaptic neuron. 14
Synaptic Transmission – When signal reaches the synaptic cleft (gap) it releases Neurotransmitter – NT Diffuse across cleft to receptor sites on postsynaptic neuron. 14
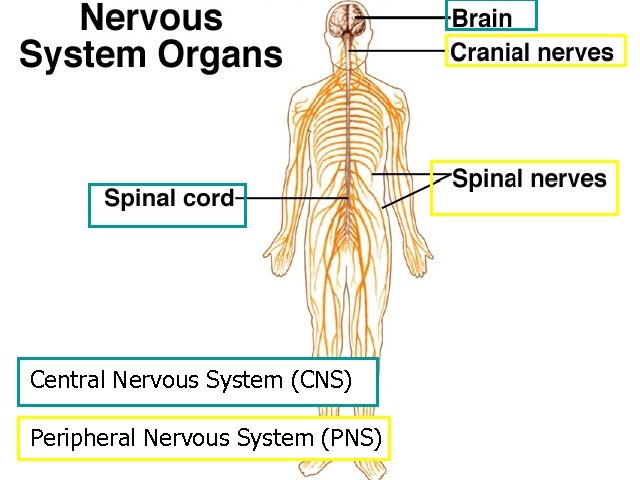 Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 15
Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 15
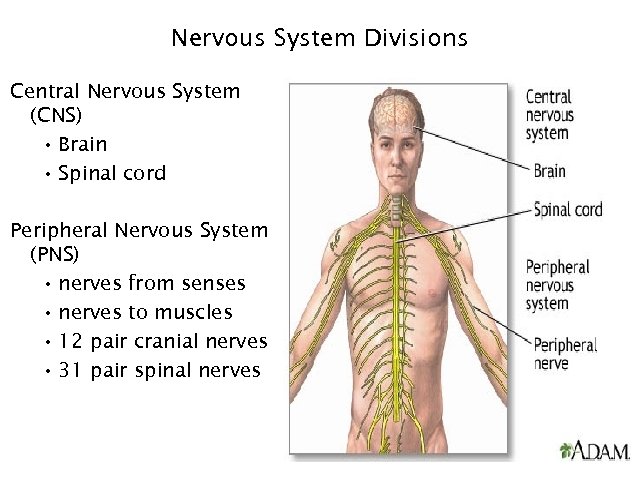 Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) • Brain • Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • nerves from senses • nerves to muscles • 12 pair cranial nerves • 31 pair spinal nerves 16
Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) • Brain • Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • nerves from senses • nerves to muscles • 12 pair cranial nerves • 31 pair spinal nerves 16
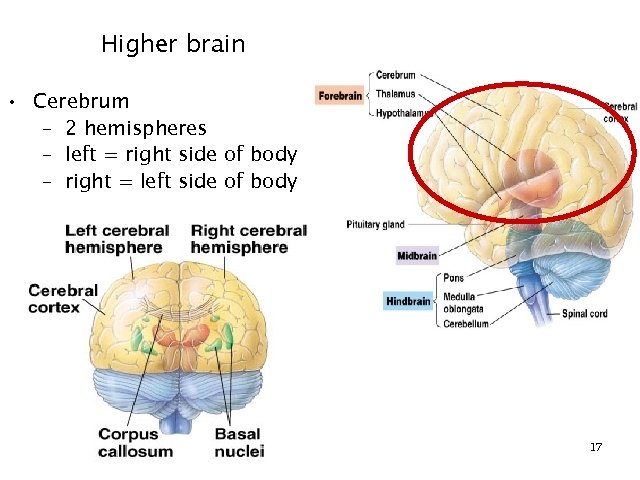 Higher brain • Cerebrum – 2 hemispheres – left = right side of body – right = left side of body 17
Higher brain • Cerebrum – 2 hemispheres – left = right side of body – right = left side of body 17
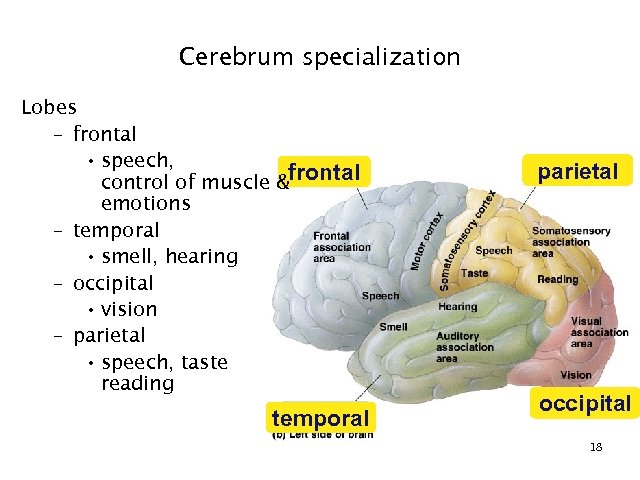 Cerebrum specialization Lobes – frontal • speech, control of muscle &frontal emotions – temporal • smell, hearing – occipital • vision – parietal • speech, taste reading temporal parietal occipital 18
Cerebrum specialization Lobes – frontal • speech, control of muscle &frontal emotions – temporal • smell, hearing – occipital • vision – parietal • speech, taste reading temporal parietal occipital 18
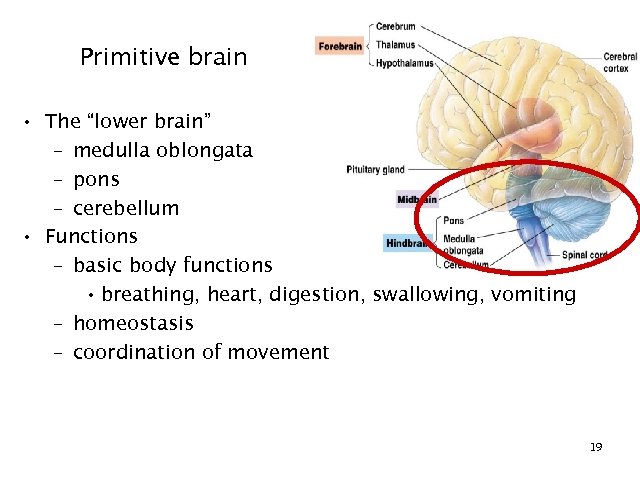 Primitive brain • The “lower brain” – medulla oblongata – pons – cerebellum • Functions – basic body functions • breathing, heart, digestion, swallowing, vomiting – homeostasis – coordination of movement 19
Primitive brain • The “lower brain” – medulla oblongata – pons – cerebellum • Functions – basic body functions • breathing, heart, digestion, swallowing, vomiting – homeostasis – coordination of movement 19
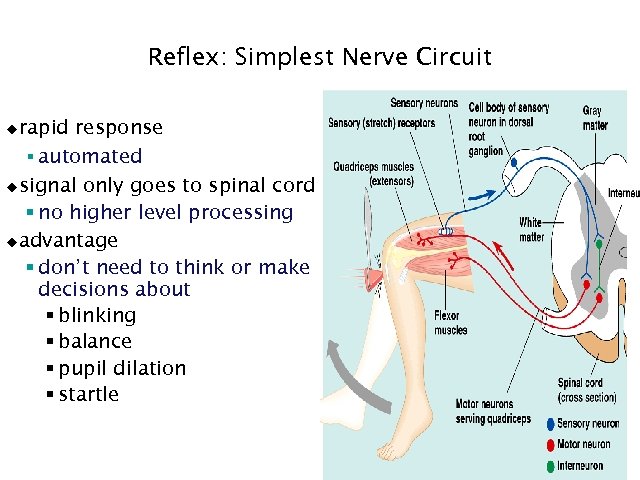 Reflex: Simplest Nerve Circuit rapid response § automated usignal only goes to spinal cord § no higher level processing uadvantage § don’t need to think or make decisions about § blinking § balance § pupil dilation § startle u 20
Reflex: Simplest Nerve Circuit rapid response § automated usignal only goes to spinal cord § no higher level processing uadvantage § don’t need to think or make decisions about § blinking § balance § pupil dilation § startle u 20
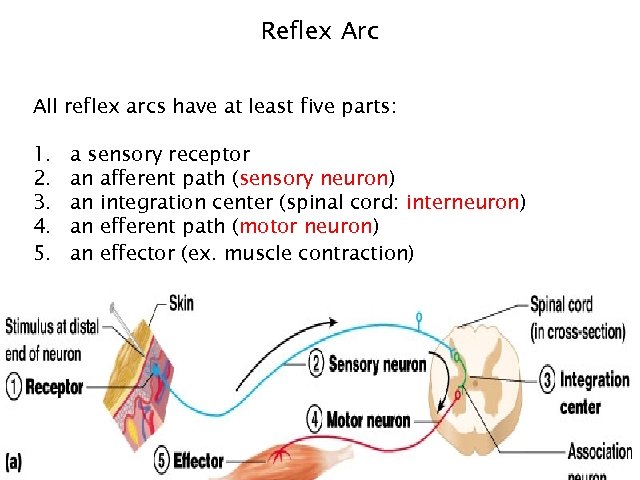 Reflex Arc All reflex arcs have at least five parts: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. a sensory receptor an afferent path (sensory neuron) an integration center (spinal cord: interneuron) an efferent path (motor neuron) an effector (ex. muscle contraction) 21
Reflex Arc All reflex arcs have at least five parts: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. a sensory receptor an afferent path (sensory neuron) an integration center (spinal cord: interneuron) an efferent path (motor neuron) an effector (ex. muscle contraction) 21
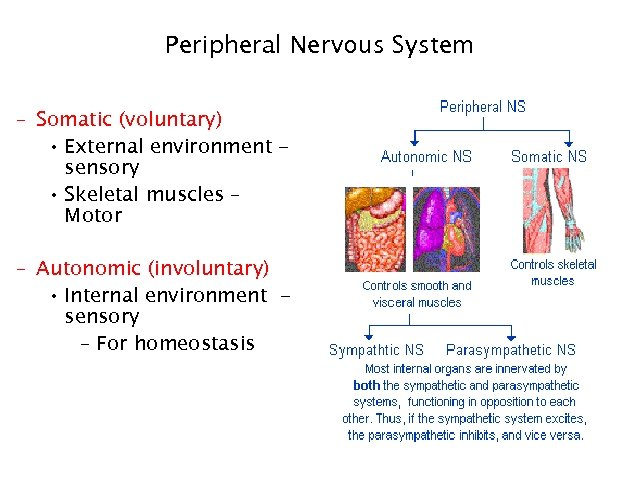 Peripheral Nervous System – Somatic (voluntary) • External environment sensory • Skeletal muscles – Motor – Autonomic (involuntary) • Internal environment sensory – For homeostasis 22
Peripheral Nervous System – Somatic (voluntary) • External environment sensory • Skeletal muscles – Motor – Autonomic (involuntary) • Internal environment sensory – For homeostasis 22
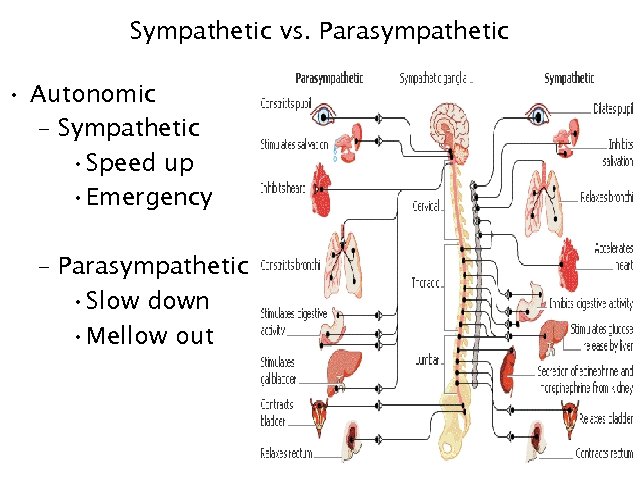 Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic • Autonomic – Sympathetic • Speed up • Emergency – Parasympathetic • Slow down • Mellow out 23
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic • Autonomic – Sympathetic • Speed up • Emergency – Parasympathetic • Slow down • Mellow out 23
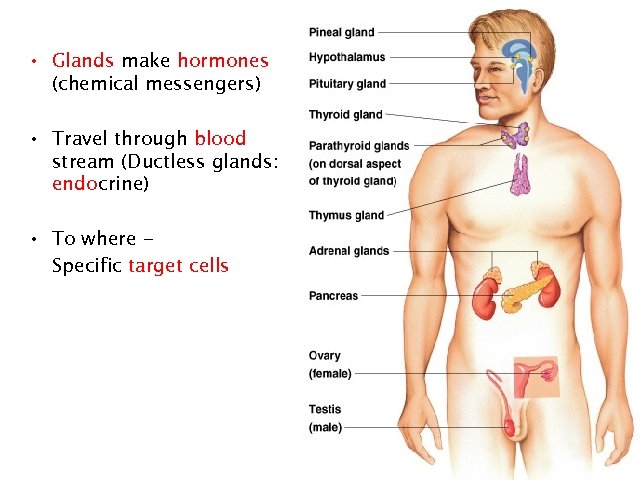 • Glands make hormones (chemical messengers) • Travel through blood stream (Ductless glands: endocrine) • To where Specific target cells 24
• Glands make hormones (chemical messengers) • Travel through blood stream (Ductless glands: endocrine) • To where Specific target cells 24
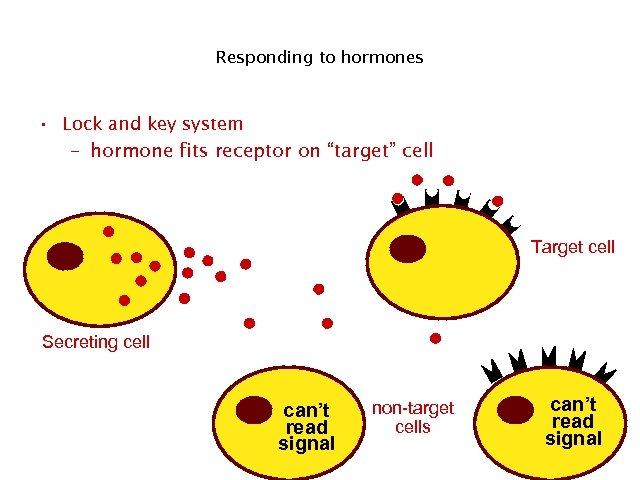 Responding to hormones • Lock and key system – hormone fits receptor on “target” cell Target cell Secreting cell can’t read signal non-target cells can’t read signal 25
Responding to hormones • Lock and key system – hormone fits receptor on “target” cell Target cell Secreting cell can’t read signal non-target cells can’t read signal 25
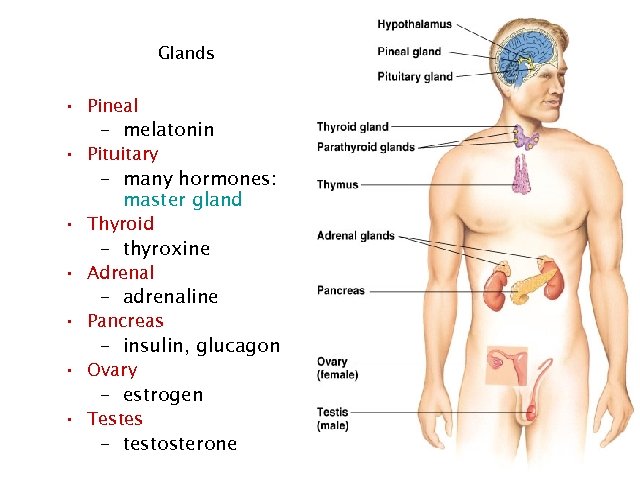 Glands • Pineal – melatonin • Pituitary – many hormones: master gland • Thyroid – thyroxine • Adrenal – adrenaline • Pancreas – insulin, glucagon • Ovary – estrogen • Testes – testosterone 26
Glands • Pineal – melatonin • Pituitary – many hormones: master gland • Thyroid – thyroxine • Adrenal – adrenaline • Pancreas – insulin, glucagon • Ovary – estrogen • Testes – testosterone 26
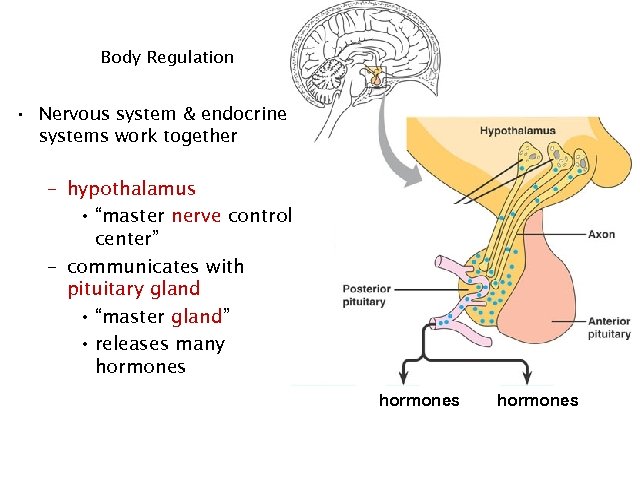 Body Regulation • Nervous system & endocrine systems work together – hypothalamus • “master nerve control center” – communicates with pituitary gland • “master gland” • releases many hormones 27
Body Regulation • Nervous system & endocrine systems work together – hypothalamus • “master nerve control center” – communicates with pituitary gland • “master gland” • releases many hormones 27
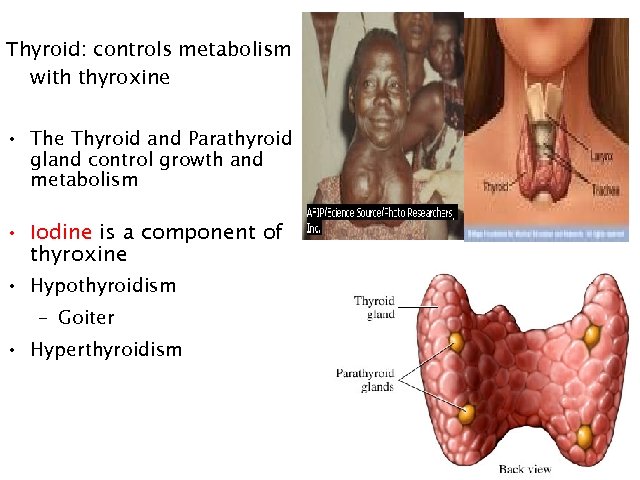 Thyroid: controls metabolism with thyroxine • The Thyroid and Parathyroid gland control growth and metabolism • Iodine is a component of thyroxine • Hypothyroidism – Goiter • Hyperthyroidism 28
Thyroid: controls metabolism with thyroxine • The Thyroid and Parathyroid gland control growth and metabolism • Iodine is a component of thyroxine • Hypothyroidism – Goiter • Hyperthyroidism 28
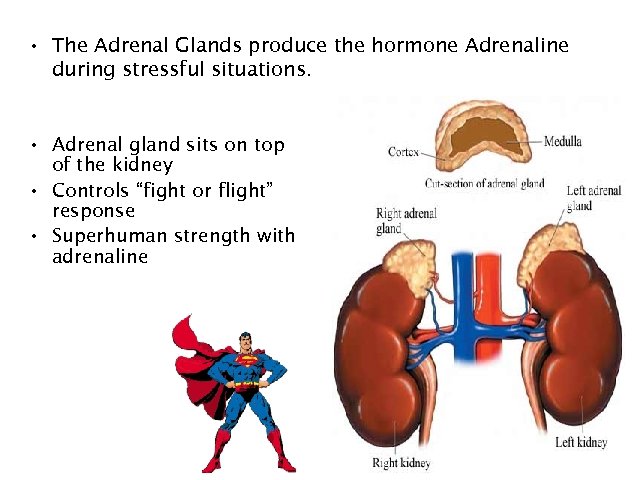 • The Adrenal Glands produce the hormone Adrenaline during stressful situations. • Adrenal gland sits on top of the kidney • Controls “fight or flight” response • Superhuman strength with adrenaline 29
• The Adrenal Glands produce the hormone Adrenaline during stressful situations. • Adrenal gland sits on top of the kidney • Controls “fight or flight” response • Superhuman strength with adrenaline 29
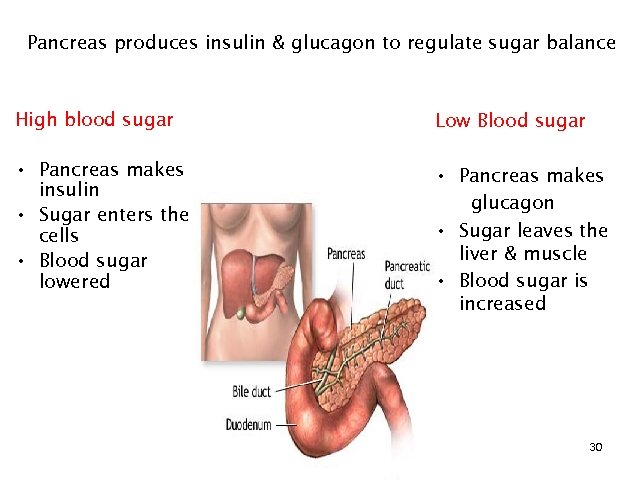 Pancreas produces insulin & glucagon to regulate sugar balance High blood sugar Low Blood sugar • Pancreas makes insulin • Sugar enters the cells • Blood sugar lowered • Pancreas makes glucagon • Sugar leaves the liver & muscle • Blood sugar is increased 30
Pancreas produces insulin & glucagon to regulate sugar balance High blood sugar Low Blood sugar • Pancreas makes insulin • Sugar enters the cells • Blood sugar lowered • Pancreas makes glucagon • Sugar leaves the liver & muscle • Blood sugar is increased 30
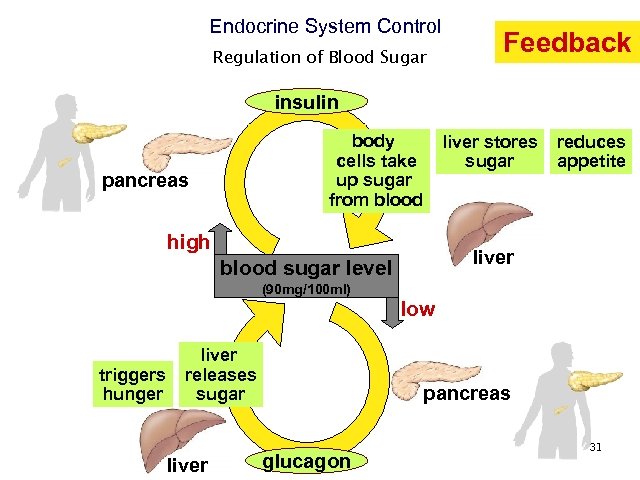 Endocrine System Control Regulation of Blood Sugar Feedback insulin body cells take up sugar from blood pancreas liver stores sugar high reduces appetite liver blood sugar level (90 mg/100 ml) low triggers hunger liver releases sugar liver pancreas glucagon 31
Endocrine System Control Regulation of Blood Sugar Feedback insulin body cells take up sugar from blood pancreas liver stores sugar high reduces appetite liver blood sugar level (90 mg/100 ml) low triggers hunger liver releases sugar liver pancreas glucagon 31
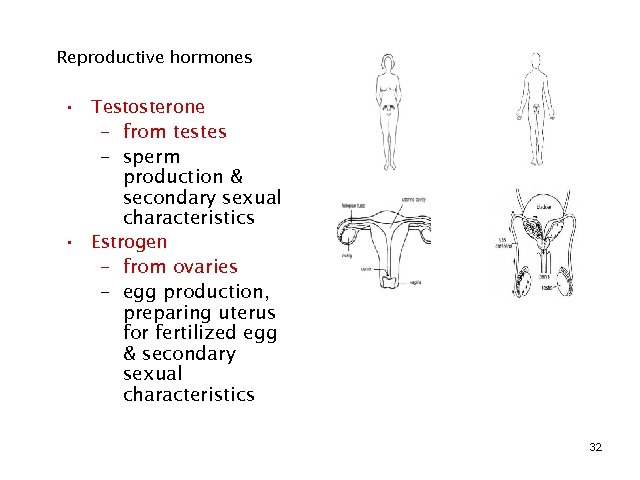 Reproductive hormones • Testosterone – from testes – sperm production & secondary sexual characteristics • Estrogen – from ovaries – egg production, preparing uterus for fertilized egg & secondary sexual characteristics 32
Reproductive hormones • Testosterone – from testes – sperm production & secondary sexual characteristics • Estrogen – from ovaries – egg production, preparing uterus for fertilized egg & secondary sexual characteristics 32


