0114ce32fbdf9b1abb3b249885215d95.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 NEERAJ KUMAR , AVTAR , (students) JITENDER MEHLA (Research Scholar) , NDRI and Dr. S. K. Sood , Senior scientist, NDRI, Karnal
NEERAJ KUMAR , AVTAR , (students) JITENDER MEHLA (Research Scholar) , NDRI and Dr. S. K. Sood , Senior scientist, NDRI, Karnal
 CONTENTS q q q Introduction History DNA vaccines Vs Traditional vaccines How DNA vaccine is made Methods of delivery How DNA vaccine works q q q q Advantages Disadvantages Current clinical trials Safety issues Future of DNA vaccines Conclusion References
CONTENTS q q q Introduction History DNA vaccines Vs Traditional vaccines How DNA vaccine is made Methods of delivery How DNA vaccine works q q q q Advantages Disadvantages Current clinical trials Safety issues Future of DNA vaccines Conclusion References
 INTRODUCTION r r DNA vaccine is DNA sequence used as a vaccine. This DNA Sequence code for antigenic protein of pathogen. As this DNA inserted into cells it is translated to form antigenic protein. As this protein is foreign to cells , so immune response raised against this protein. In this way , DNA vaccine provide immunity against that pathogen.
INTRODUCTION r r DNA vaccine is DNA sequence used as a vaccine. This DNA Sequence code for antigenic protein of pathogen. As this DNA inserted into cells it is translated to form antigenic protein. As this protein is foreign to cells , so immune response raised against this protein. In this way , DNA vaccine provide immunity against that pathogen.
 HISTORY In 1990, University of Wisconsin, Jon Wolff found that injection of DNA plasmids produce a protein response in mice. q In 1993, Merck Research Laboratories, Dr. Margaret Liu found that intramuscular injection of DNA from influenzae virus into mice produced complete immune response q In 1996, trials involving T-cell lymphoma, influenzae & herpes simplex virus were started q
HISTORY In 1990, University of Wisconsin, Jon Wolff found that injection of DNA plasmids produce a protein response in mice. q In 1993, Merck Research Laboratories, Dr. Margaret Liu found that intramuscular injection of DNA from influenzae virus into mice produced complete immune response q In 1996, trials involving T-cell lymphoma, influenzae & herpes simplex virus were started q
 DNA vaccines Vs Traditional vaccines DNA vaccines q q Uses only the DNA from infectious organisms. Avoid the risk of using actual infectious organism. Provide both Humoral & Cell mediated immunity Refrigeration is not required Traditional vaccines q q Uses weakened or killed form of infectious organism. Create possible risk of the vaccine being fatal. Provide primarily Humoral immunity Usually requires Refrigeration.
DNA vaccines Vs Traditional vaccines DNA vaccines q q Uses only the DNA from infectious organisms. Avoid the risk of using actual infectious organism. Provide both Humoral & Cell mediated immunity Refrigeration is not required Traditional vaccines q q Uses weakened or killed form of infectious organism. Create possible risk of the vaccine being fatal. Provide primarily Humoral immunity Usually requires Refrigeration.
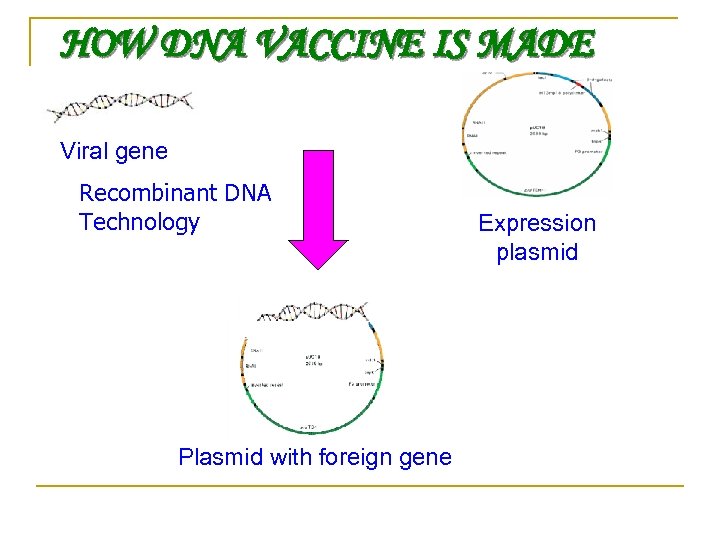 HOW DNA VACCINE IS MADE Viral gene Recombinant DNA Technology Plasmid with foreign gene Expression plasmid
HOW DNA VACCINE IS MADE Viral gene Recombinant DNA Technology Plasmid with foreign gene Expression plasmid
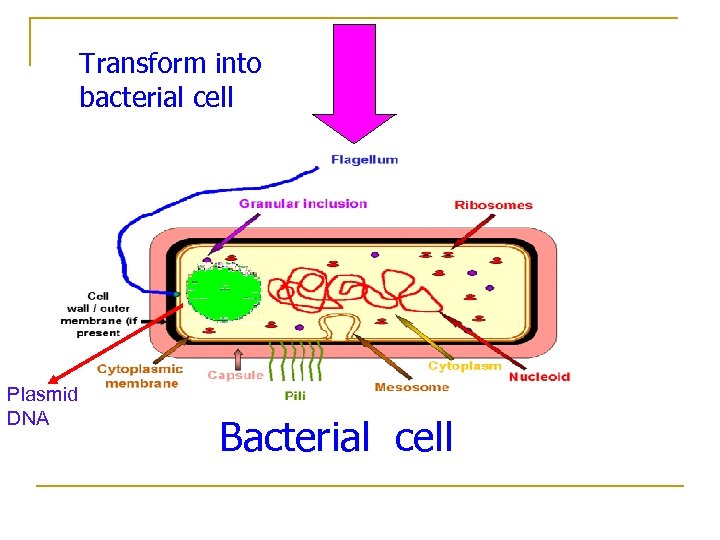 Transform into bacterial cell Plasmid DNA Bacterial cell
Transform into bacterial cell Plasmid DNA Bacterial cell
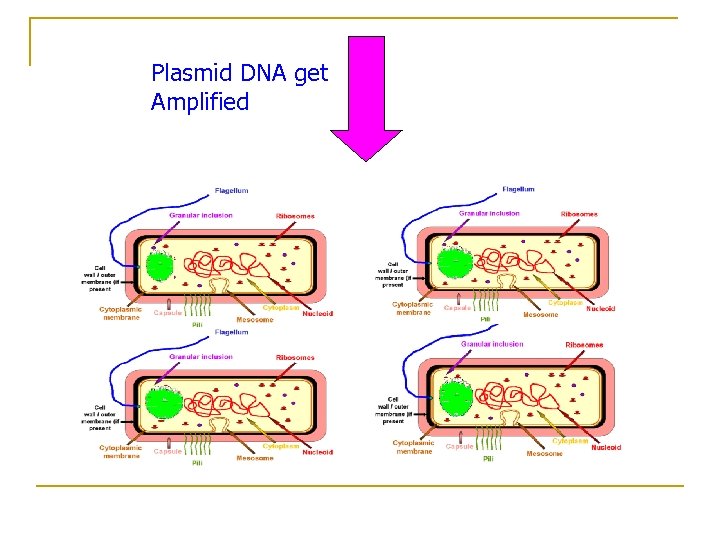 Plasmid DNA get Amplified
Plasmid DNA get Amplified
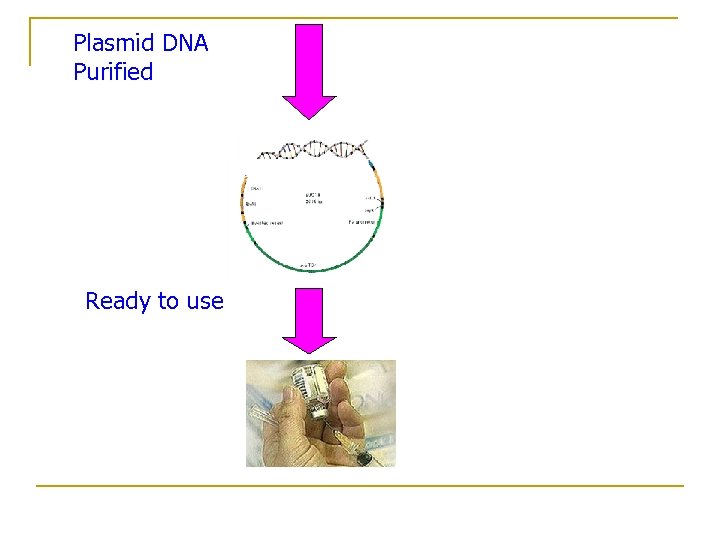 Plasmid DNA Purified Ready to use
Plasmid DNA Purified Ready to use
 METHODS OF DELIVERY q Syringe delivery: Either intramuscularly or Intradermally
METHODS OF DELIVERY q Syringe delivery: Either intramuscularly or Intradermally
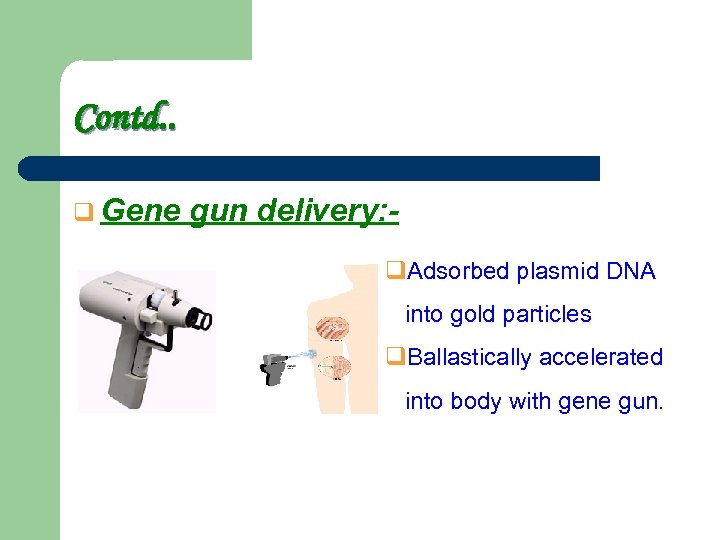 Contd. . q Gene gun delivery: q. Adsorbed plasmid DNA into gold particles q. Ballastically accelerated into body with gene gun.
Contd. . q Gene gun delivery: q. Adsorbed plasmid DNA into gold particles q. Ballastically accelerated into body with gene gun.
 HOW DNA VACCINE WORKS BY TWO PATHWAYS ENDOGENOUS : - Antigenic Protein is presented by cell in which it is produced EXOGENOUS : - Antigenic Protein is formed in one cell but presented by different cell
HOW DNA VACCINE WORKS BY TWO PATHWAYS ENDOGENOUS : - Antigenic Protein is presented by cell in which it is produced EXOGENOUS : - Antigenic Protein is formed in one cell but presented by different cell
 HOW DNA VACCINES WORK + Muscle Cells Plasmid DNA
HOW DNA VACCINES WORK + Muscle Cells Plasmid DNA
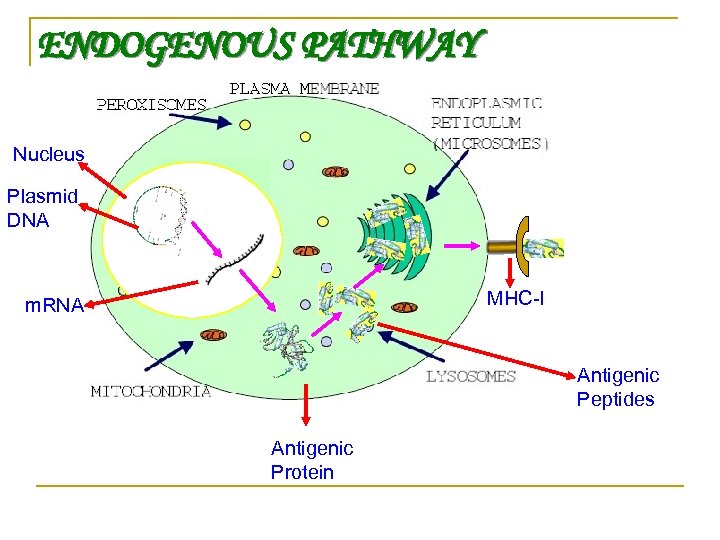 ENDOGENOUS PATHWAY Nucleus Plasmid DNA MHC-I m. RNA Antigenic Peptides Antigenic Protein
ENDOGENOUS PATHWAY Nucleus Plasmid DNA MHC-I m. RNA Antigenic Peptides Antigenic Protein
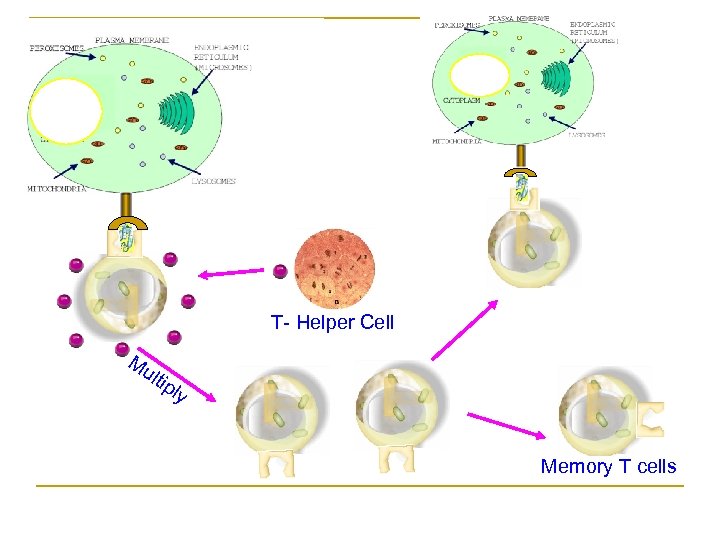 T- Helper Cell Mu ltip ly Memory T cells
T- Helper Cell Mu ltip ly Memory T cells
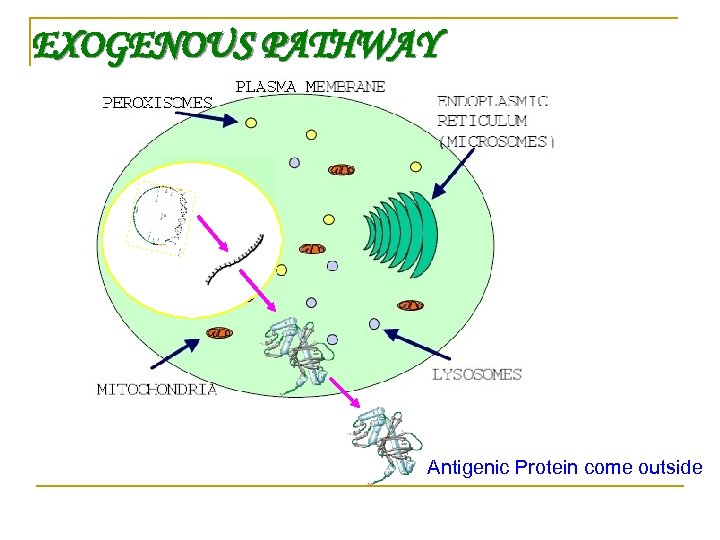 EXOGENOUS PATHWAY Antigenic Protein come outside
EXOGENOUS PATHWAY Antigenic Protein come outside
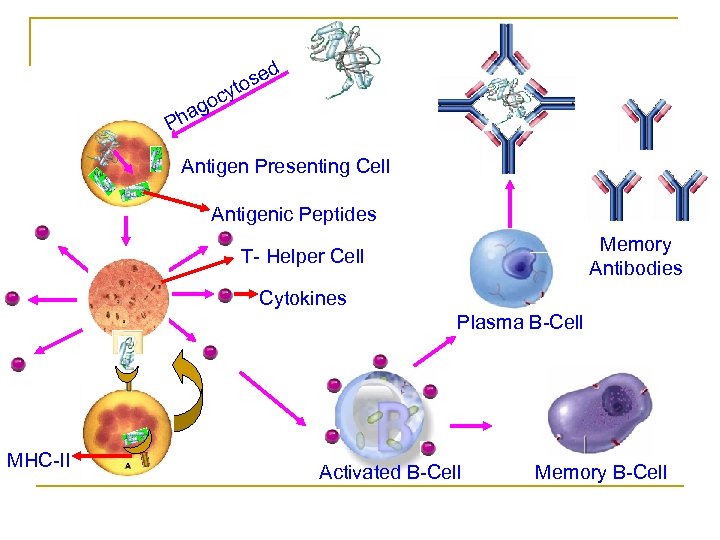 d e tos y c go a Ph Antigen Presenting Cell Antigenic Peptides Memory Antibodies T- Helper Cell Cytokines Plasma B-Cell MHC-II Activated B-Cell Memory B-Cell
d e tos y c go a Ph Antigen Presenting Cell Antigenic Peptides Memory Antibodies T- Helper Cell Cytokines Plasma B-Cell MHC-II Activated B-Cell Memory B-Cell
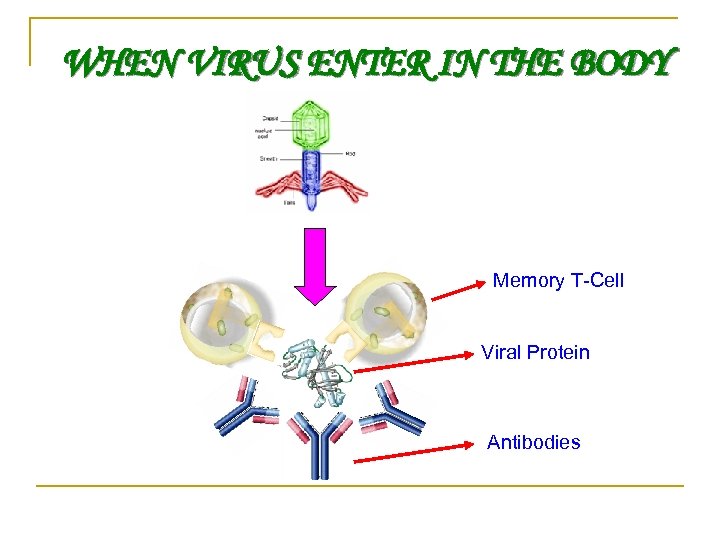 WHEN VIRUS ENTER IN THE BODY Memory T-Cell Viral Protein Antibodies
WHEN VIRUS ENTER IN THE BODY Memory T-Cell Viral Protein Antibodies
 ADVANTAGES q Elicit both Humoral & cell mediated immunity q Focused on Antigen of interest q Long term immunity q Refrigeration is not required q Stable for storage
ADVANTAGES q Elicit both Humoral & cell mediated immunity q Focused on Antigen of interest q Long term immunity q Refrigeration is not required q Stable for storage
 DISADVANTAGES q Limited to protein immunogen only q Extended immunostimulation leads to chronic inflammation q Some antigen require processing which sometime does not occur
DISADVANTAGES q Limited to protein immunogen only q Extended immunostimulation leads to chronic inflammation q Some antigen require processing which sometime does not occur
 CURRENT CLINICAL TRIALS q June 2006, DNA vaccine examined on horse Horse acquired immunity against west nile viruses q August 2007, DNA vaccination against multiple Sclerosis was reported as being effective
CURRENT CLINICAL TRIALS q June 2006, DNA vaccine examined on horse Horse acquired immunity against west nile viruses q August 2007, DNA vaccination against multiple Sclerosis was reported as being effective

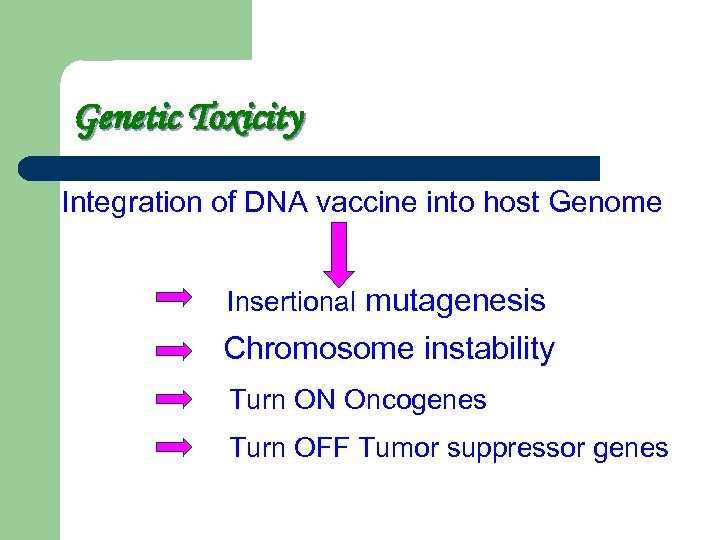 Genetic Toxicity Integration of DNA vaccine into host Genome Insertional mutagenesis Chromosome instability Turn ON Oncogenes Turn OFF Tumor suppressor genes
Genetic Toxicity Integration of DNA vaccine into host Genome Insertional mutagenesis Chromosome instability Turn ON Oncogenes Turn OFF Tumor suppressor genes
 Over Expression of DNA vaccine Acute or chronic inflammatory responses Destruction of normal tisues
Over Expression of DNA vaccine Acute or chronic inflammatory responses Destruction of normal tisues
 Generation of Autoimmune diseases Anti DNA Antibodies Autoimmune diseases Autoimmune Myositis
Generation of Autoimmune diseases Anti DNA Antibodies Autoimmune diseases Autoimmune Myositis
 Antibiotic Resistance Plasmid used is resistance to antibiotics for selection Raise the resistance to same antibiotic in the host
Antibiotic Resistance Plasmid used is resistance to antibiotics for selection Raise the resistance to same antibiotic in the host
 FUTURE PROSPECTS q Plasmid with multiple genes provide immunity against many diseases in one booster q DNA vaccines against infectious diseases such as AIDS, Rabies, Malaria can be available
FUTURE PROSPECTS q Plasmid with multiple genes provide immunity against many diseases in one booster q DNA vaccines against infectious diseases such as AIDS, Rabies, Malaria can be available
 CONCLUSION DNA vaccines are in their early phase. There are no DNA vaccines in market at present. But this just the beginning. DNA vaccines are going to be the vaccines of next generation.
CONCLUSION DNA vaccines are in their early phase. There are no DNA vaccines in market at present. But this just the beginning. DNA vaccines are going to be the vaccines of next generation.
 References q q q q www. medscape. com www. wikipedia. org www. sciencedirect. com www. nature. com www. biokenyon. com www. biolife. com Immunology by Kuby 6 th Edition Immunology by Tizard 4 th Edition
References q q q q www. medscape. com www. wikipedia. org www. sciencedirect. com www. nature. com www. biokenyon. com www. biolife. com Immunology by Kuby 6 th Edition Immunology by Tizard 4 th Edition
 THANK YOU
THANK YOU
 Queries ?
Queries ?


