31cacdb2423d0cceca429e7edbd1e1dc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Needs Assessment
Needs Assessment
 Program Evaluation Types • • Evaluation of Need Evaluation of Process Evaluation of Outcome Evaluation of Efficiency
Program Evaluation Types • • Evaluation of Need Evaluation of Process Evaluation of Outcome Evaluation of Efficiency
 Programs for Class Discussion • Sexual assault companions • Mediation center in New River Valley • After school academic and activity center
Programs for Class Discussion • Sexual assault companions • Mediation center in New River Valley • After school academic and activity center
 What is a Need? • Discrepancy between actual level and – – – An ideal A norm A minimum A desired state An expected state • A need is something that people must have to be in a satisfactory state (Scriven & Roth, 1990)
What is a Need? • Discrepancy between actual level and – – – An ideal A norm A minimum A desired state An expected state • A need is something that people must have to be in a satisfactory state (Scriven & Roth, 1990)
 Analysis of Need Four Key Questions • What are we trying to accomplish? • Why do we think there is a need for our program? • Is there an actual need for our program? • Is our idea for a program practical?
Analysis of Need Four Key Questions • What are we trying to accomplish? • Why do we think there is a need for our program? • Is there an actual need for our program? • Is our idea for a program practical?
 Analysis of Need What are We Trying to Accomplish? • Do we have a particular need in mind or are we trolling for unmet needs in general? • Is the dog wagging the tail or is the tail wagging the dog? • What is the real goal? – To help others? – To help our agency survive? – To justify our job?
Analysis of Need What are We Trying to Accomplish? • Do we have a particular need in mind or are we trolling for unmet needs in general? • Is the dog wagging the tail or is the tail wagging the dog? • What is the real goal? – To help others? – To help our agency survive? – To justify our job?
 Analysis of Need Why Do We Think There is a Need? • • Normative Need Felt Need Expressed Need Comparative Need
Analysis of Need Why Do We Think There is a Need? • • Normative Need Felt Need Expressed Need Comparative Need
 Analysis of Need Is There an Actual Need for our Program? • Is there actually a problem or unmet need? • Are there existing programs trying to solve the problem? • Are their enough potential clients to justify a program?
Analysis of Need Is There an Actual Need for our Program? • Is there actually a problem or unmet need? • Are there existing programs trying to solve the problem? • Are their enough potential clients to justify a program?
 Analysis of Need Is the Program Practical? • • Will people participate in the program? Are the barriers insurmountable? Do we have the expertise? Do we have the funding?
Analysis of Need Is the Program Practical? • • Will people participate in the program? Are the barriers insurmountable? Do we have the expertise? Do we have the funding?
 Resource Analysis • Funding – How much • Staff – Number – Skills – Availability • Physical resources – – Office space Phones Computers Vehicles
Resource Analysis • Funding – How much • Staff – Number – Skills – Availability • Physical resources – – Office space Phones Computers Vehicles
 Identifying Potential Stakeholders • • Funding sources Administrators Staff Community groups Politicians Businesses Unions Current, past, and future clients
Identifying Potential Stakeholders • • Funding sources Administrators Staff Community groups Politicians Businesses Unions Current, past, and future clients
 Needs Assessment Methods • • Existing data Archival research Surveys Interviews – – Individual Focus groups Nominal groups Delphi technique
Needs Assessment Methods • • Existing data Archival research Surveys Interviews – – Individual Focus groups Nominal groups Delphi technique
 Police Suicide Example
Police Suicide Example
 Our Basic Research Question • Do law enforcement personnel have higher suicide rates than the general public? • If so, – is it something about the people who go into law enforcement (e. g. , demographics, personality)? – is it something about the job (e. g. , stress, availability of guns, alienation)? – is it an interaction between the two?
Our Basic Research Question • Do law enforcement personnel have higher suicide rates than the general public? • If so, – is it something about the people who go into law enforcement (e. g. , demographics, personality)? – is it something about the job (e. g. , stress, availability of guns, alienation)? – is it an interaction between the two?
 Our Goals • Establish law enforcement suicide rate – look at published research – look at media accounts – collect new data • Compare to national norms – general population – control for age, sex, race • Establish a profile of officers who commit suicide
Our Goals • Establish law enforcement suicide rate – look at published research – look at media accounts – collect new data • Compare to national norms – general population – control for age, sex, race • Establish a profile of officers who commit suicide
 Suicide Rates • Determining Rates – Department record approach – Death certificate approach – “Hmm, let me think” approach • Calculating Rates – Rate per 100, 000 – Proportionate Mortality Ratios (PMR)
Suicide Rates • Determining Rates – Department record approach – Death certificate approach – “Hmm, let me think” approach • Calculating Rates – Rate per 100, 000 – Proportionate Mortality Ratios (PMR)
 At first glance, police have a high suicide rate • FOP Study (1995) – 12 per 100, 000 in general population – 22 per 100, 000 in law enforcement population • Newspaper Articles – 300 police suicides per year – police rate twice that of general public
At first glance, police have a high suicide rate • FOP Study (1995) – 12 per 100, 000 in general population – 22 per 100, 000 in law enforcement population • Newspaper Articles – 300 police suicides per year – police rate twice that of general public
 At second glance… Determining the Police Suicide Rate • FOP study • USA Today article • Review of published literature – obtained number of sworn personnel – computed suicide rates • Collection of new data from the Roanoke and New River Valleys • Review of newspaper articles
At second glance… Determining the Police Suicide Rate • FOP study • USA Today article • Review of published literature – obtained number of sworn personnel – computed suicide rates • Collection of new data from the Roanoke and New River Valleys • Review of newspaper articles
 Our best estimate of the law enforcement rate is …. 18. 1 • Five sources – – – 22. 0 16. 3 37. 1 18. 6 10. 0 FOP study USA Today Media sources Published research Roanoke Valley • Studies weighted by – size of department – number of years over which data were collected
Our best estimate of the law enforcement rate is …. 18. 1 • Five sources – – – 22. 0 16. 3 37. 1 18. 6 10. 0 FOP study USA Today Media sources Published research Roanoke Valley • Studies weighted by – size of department – number of years over which data were collected
 Comparison to population is a bit more tricky (1996) • Race by sex • Overall – 11. 7 • Sex – male 19. 3 – female 4. 4 • Race – white – black 12. 7 6. 5 – – WM WF BM BF 20. 9 4. 8 11. 4 2. 0 • Age 25 -54 – – WM WF BM BF 25. 6 6. 3 13. 5 2. 9
Comparison to population is a bit more tricky (1996) • Race by sex • Overall – 11. 7 • Sex – male 19. 3 – female 4. 4 • Race – white – black 12. 7 6. 5 – – WM WF BM BF 20. 9 4. 8 11. 4 2. 0 • Age 25 -54 – – WM WF BM BF 25. 6 6. 3 13. 5 2. 9
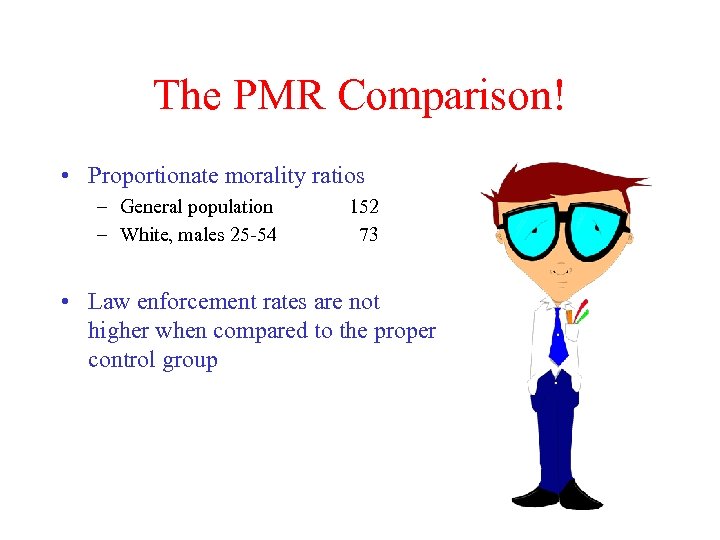 The PMR Comparison! • Proportionate morality ratios – General population – White, males 25 -54 152 73 • Law enforcement rates are not higher when compared to the proper control group
The PMR Comparison! • Proportionate morality ratios – General population – White, males 25 -54 152 73 • Law enforcement rates are not higher when compared to the proper control group
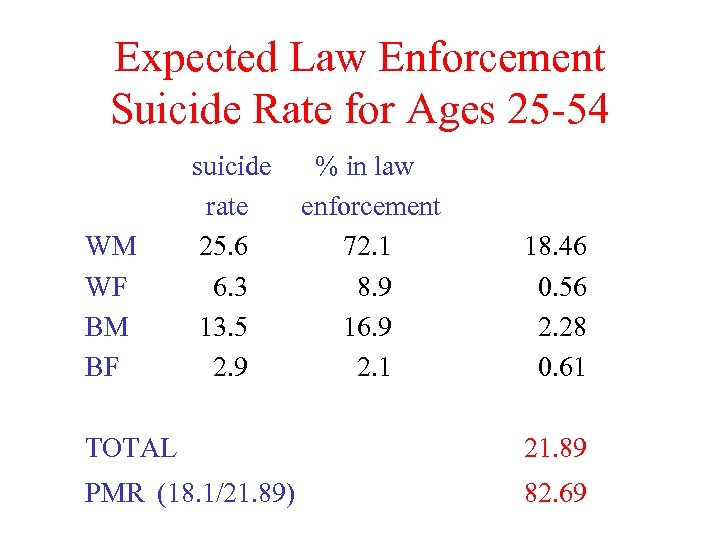 Expected Law Enforcement Suicide Rate for Ages 25 -54 WM WF BM BF suicide rate 25. 6 6. 3 13. 5 2. 9 % in law enforcement 72. 1 8. 9 16. 9 2. 1 18. 46 0. 56 2. 28 0. 61 TOTAL 21. 89 PMR (18. 1/21. 89) 82. 69
Expected Law Enforcement Suicide Rate for Ages 25 -54 WM WF BM BF suicide rate 25. 6 6. 3 13. 5 2. 9 % in law enforcement 72. 1 8. 9 16. 9 2. 1 18. 46 0. 56 2. 28 0. 61 TOTAL 21. 89 PMR (18. 1/21. 89) 82. 69
 Summary • The police suicide rate of 18. 1 is higher than the rate found in the general population • This higher rate can be completely accounted for by sex, race, and age • After accounting for these demographics, the police suicide rate is lower than that of the comparable general population • Police-specific interventions will probably not yield significant decreases in police suicide
Summary • The police suicide rate of 18. 1 is higher than the rate found in the general population • This higher rate can be completely accounted for by sex, race, and age • After accounting for these demographics, the police suicide rate is lower than that of the comparable general population • Police-specific interventions will probably not yield significant decreases in police suicide


