4c3e21310e536093545cfccf6f91dd2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
 Needs and expectations for the ISO 9001 2015 renewal Juhani Anttila, Academician International Academy for Quality (IAQ) Helsinki, Finland juhani. anttila@telecon. fi , ww. Quality. Integration. biz 1 September, 2014 These pages are licensed under the Creative Commons 3. 0 License http: //creativecommons. org/licenses/by/3. 0 (Mention the origin)
Needs and expectations for the ISO 9001 2015 renewal Juhani Anttila, Academician International Academy for Quality (IAQ) Helsinki, Finland juhani. anttila@telecon. fi , ww. Quality. Integration. biz 1 September, 2014 These pages are licensed under the Creative Commons 3. 0 License http: //creativecommons. org/licenses/by/3. 0 (Mention the origin)
 35 years ISO 9000 standardization, Five generations ISO 9000 standards Technical committee ISO/TC 176 formed in 1979. Five generation of the ISO 9000 series standards: • ISO 8402: 1986, and ISO 9000/9001/9002/9003/9004: 1987 • ISO 9000/9001/9002/9003/9004: 1994 • ISO 9000/9001/9004: 2000 • ISO 9000: 2005, ISO 9001: 2008, and ISO 9004: 2009 • ISO 9001: 2015 and ISO 9004: 20? ? In addition to prepare standards for quality management, the work in committee ISO/TC 176 has an important role in the worldwide quality discipline and social collaboration of the professionals. 2 4315/14. 9. 2014/jan 2012
35 years ISO 9000 standardization, Five generations ISO 9000 standards Technical committee ISO/TC 176 formed in 1979. Five generation of the ISO 9000 series standards: • ISO 8402: 1986, and ISO 9000/9001/9002/9003/9004: 1987 • ISO 9000/9001/9002/9003/9004: 1994 • ISO 9000/9001/9004: 2000 • ISO 9000: 2005, ISO 9001: 2008, and ISO 9004: 2009 • ISO 9001: 2015 and ISO 9004: 20? ? In addition to prepare standards for quality management, the work in committee ISO/TC 176 has an important role in the worldwide quality discipline and social collaboration of the professionals. 2 4315/14. 9. 2014/jan 2012
 Requirements for the ISO 9001 revision 2015 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 3 4316/14. 9. 2014/jan Strategic objectives of the ISO 9000 responsible committee ISO/TC 176/SC 2 Systematic review on ISO 9001: 2008 Worldwide user survey of the ISO 9001 and 9004 standards Analysis of the quality management concepts for considering the future ISO 9000 work Design specification: Challenging targets to meet the needs and expectations of modern organizations Renewed quality management principles (QMPs) ISO Directives Annex SL: High level structure, identical core text, common terms and core definitions in the management system standards Emphasized a harmonized risk management approach with the ISO 31000
Requirements for the ISO 9001 revision 2015 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 3 4316/14. 9. 2014/jan Strategic objectives of the ISO 9000 responsible committee ISO/TC 176/SC 2 Systematic review on ISO 9001: 2008 Worldwide user survey of the ISO 9001 and 9004 standards Analysis of the quality management concepts for considering the future ISO 9000 work Design specification: Challenging targets to meet the needs and expectations of modern organizations Renewed quality management principles (QMPs) ISO Directives Annex SL: High level structure, identical core text, common terms and core definitions in the management system standards Emphasized a harmonized risk management approach with the ISO 31000
 Design specification for the ISO 9001 revision 2015 The revision will: a) Take account of changes in quality management systems practices and technology since the last major revision to ISO 9001 (in the year 2000) and to provide a stable core set of requirements for the next 10 years or more. b) Ensure that requirements in this standard reflect the changes in the increasingly complex, demanding, and dynamic environments in which organizations operate. c) Ensure that requirements are stated to facilitate effective implementation by organizations and effective conformity assessment by 1 st, 2 nd and 3 rd parties. d) Ensure that the How well have these requirements been realized in the standard is adequate to provide confidence in those organizations meeting the standard’s requirements 4 xxxx/14. 9. 2014/jan
Design specification for the ISO 9001 revision 2015 The revision will: a) Take account of changes in quality management systems practices and technology since the last major revision to ISO 9001 (in the year 2000) and to provide a stable core set of requirements for the next 10 years or more. b) Ensure that requirements in this standard reflect the changes in the increasingly complex, demanding, and dynamic environments in which organizations operate. c) Ensure that requirements are stated to facilitate effective implementation by organizations and effective conformity assessment by 1 st, 2 nd and 3 rd parties. d) Ensure that the How well have these requirements been realized in the standard is adequate to provide confidence in those organizations meeting the standard’s requirements 4 xxxx/14. 9. 2014/jan
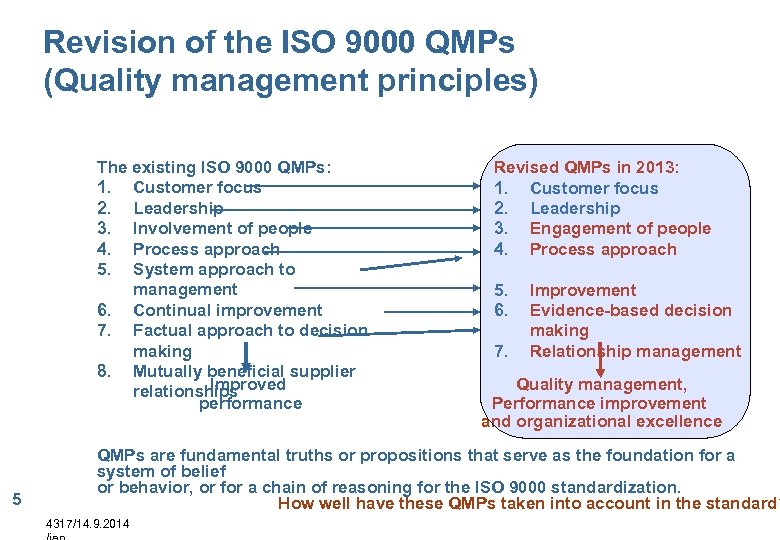 Revision of the ISO 9000 QMPs (Quality management principles) The existing ISO 9000 QMPs: 1. Customer focus 2. Leadership 3. Involvement of people 4. Process approach 5. System approach to management 6. Continual improvement 7. Factual approach to decision making 8. Mutually beneficial supplier Improved relationships performance 5 Revised QMPs in 2013: 1. Customer focus 2. Leadership 3. Engagement of people 4. Process approach 5. 6. 7. Improvement Evidence-based decision making Relationship management Quality management, Performance improvement and organizational excellence QMPs are fundamental truths or propositions that serve as the foundation for a system of belief or behavior, or for a chain of reasoning for the ISO 9000 standardization. How well have these QMPs taken into account in the standard? 4317/14. 9. 2014
Revision of the ISO 9000 QMPs (Quality management principles) The existing ISO 9000 QMPs: 1. Customer focus 2. Leadership 3. Involvement of people 4. Process approach 5. System approach to management 6. Continual improvement 7. Factual approach to decision making 8. Mutually beneficial supplier Improved relationships performance 5 Revised QMPs in 2013: 1. Customer focus 2. Leadership 3. Engagement of people 4. Process approach 5. 6. 7. Improvement Evidence-based decision making Relationship management Quality management, Performance improvement and organizational excellence QMPs are fundamental truths or propositions that serve as the foundation for a system of belief or behavior, or for a chain of reasoning for the ISO 9000 standardization. How well have these QMPs taken into account in the standard? 4317/14. 9. 2014
 The common structure for all management system requirements standards supports business integration 6 Required contents for the discipline XXX management in an organization: E. g. quality 4. Context of the organization 7. Support is a XXX 4. 1 Understanding of the 7. 1 Resources organization and its context 7. 2 Competence discipline. 4. 2 Understanding the needs 7. 3 Awareness and expectations of 7. 4 Communication interested parties 7. 5 Documented information 4. 3 Determining the scope of the 7. 5. 1 General XXX management system 7. 5. 2 Creating and updating 4. 4 XXX management system 7. 5. 3 Control of documented 5. Leadership Information 5. 1 Leadership and commitment 8. Operation 5. 2 Policy 8. 1 Operational planning and 5. 3 Organizational roles, control responsibilities and 9. Performance evaluation authorities 9. 1 Monitoring, measurement, 6 Planning analysis and evaluation 6. 1 Actions to address risks and 9. 2 Internal Audit opportunities 9. 3 Management review 6. 2 XXX objectives and planning 10. Improvement to achieve them 10. 1 Nonconformity and corrective action Factually this a general structure for any business management. All XXX 10. 2 Continual improvement aspects are standardized and implemented to organization’s business processes according to this structure. How well have this structure realized in the standard te 4318/14. 9. 2014/jan (Ref. : ISO Directives Annex SL )
The common structure for all management system requirements standards supports business integration 6 Required contents for the discipline XXX management in an organization: E. g. quality 4. Context of the organization 7. Support is a XXX 4. 1 Understanding of the 7. 1 Resources organization and its context 7. 2 Competence discipline. 4. 2 Understanding the needs 7. 3 Awareness and expectations of 7. 4 Communication interested parties 7. 5 Documented information 4. 3 Determining the scope of the 7. 5. 1 General XXX management system 7. 5. 2 Creating and updating 4. 4 XXX management system 7. 5. 3 Control of documented 5. Leadership Information 5. 1 Leadership and commitment 8. Operation 5. 2 Policy 8. 1 Operational planning and 5. 3 Organizational roles, control responsibilities and 9. Performance evaluation authorities 9. 1 Monitoring, measurement, 6 Planning analysis and evaluation 6. 1 Actions to address risks and 9. 2 Internal Audit opportunities 9. 3 Management review 6. 2 XXX objectives and planning 10. Improvement to achieve them 10. 1 Nonconformity and corrective action Factually this a general structure for any business management. All XXX 10. 2 Continual improvement aspects are standardized and implemented to organization’s business processes according to this structure. How well have this structure realized in the standard te 4318/14. 9. 2014/jan (Ref. : ISO Directives Annex SL )
 Risk management in the ISO 9001: 2015 The new ISO 9001 standard makes risk-based thinking more explicit than the previous ones and this covers the whole standard including requirements for the establishment, implementation, maintenance and continual improvement of the quality management system. Organizations must decide how the necessary risk management is to be applied to the entire organization, at its different areas and levels, at any time, as well as to specific functions, projects and activities. Standard ISO 31000 provides guidelines on formal risk management and recommends how the organization can develop, implement and continuously improve a framework whose purpose is to integrate the process for managing risk into the organization's overall governance, strategy and planning, management, reporting processes, policies, values and culture. realized and allocated in the stand How well have risk management items 7 4319/14. 9. 2014/jan
Risk management in the ISO 9001: 2015 The new ISO 9001 standard makes risk-based thinking more explicit than the previous ones and this covers the whole standard including requirements for the establishment, implementation, maintenance and continual improvement of the quality management system. Organizations must decide how the necessary risk management is to be applied to the entire organization, at its different areas and levels, at any time, as well as to specific functions, projects and activities. Standard ISO 31000 provides guidelines on formal risk management and recommends how the organization can develop, implement and continuously improve a framework whose purpose is to integrate the process for managing risk into the organization's overall governance, strategy and planning, management, reporting processes, policies, values and culture. realized and allocated in the stand How well have risk management items 7 4319/14. 9. 2014/jan
 Pros and cons of the general international standa 8 All standardization has positive and proactive aims: • Improved business performance and confidence, and quality of products • Decreased operational costs • Improved communication between people and organizations Pros of general Cons of general standardization: • There is uneven and unbalanced groups of • Broad acceptance and voluntary people participating the standardization distribution of the texts work. • Extensive expertise in • Management of the standardization is weak. preparing and commenting • Only communally interesting issues are the standards accepted to the final standard texts mainly due to • Wide commitment and the consensus principle. recognition • Influence of the strong and active individuals • No restrictions for and lobbying. innovative implementation • Only trivial means to implement the standard clauses may be considered in the standards. • Handling of the inadequacies, inconsistencies All general international standards have seriousissues in the standard text is superficial. and other problems mainly due to the normal standardization processes and • Standardization process is very slow. particularly the consensus practices. • Participating highlight their own responsibility Organizations applying the standards should in standardization is expensive. of business leaders and experts and clarify, correct, and complete general standards and find creative solutions in their implementations in order to achieve business 4320/14. 9. 2014/jan benefits.
Pros and cons of the general international standa 8 All standardization has positive and proactive aims: • Improved business performance and confidence, and quality of products • Decreased operational costs • Improved communication between people and organizations Pros of general Cons of general standardization: • There is uneven and unbalanced groups of • Broad acceptance and voluntary people participating the standardization distribution of the texts work. • Extensive expertise in • Management of the standardization is weak. preparing and commenting • Only communally interesting issues are the standards accepted to the final standard texts mainly due to • Wide commitment and the consensus principle. recognition • Influence of the strong and active individuals • No restrictions for and lobbying. innovative implementation • Only trivial means to implement the standard clauses may be considered in the standards. • Handling of the inadequacies, inconsistencies All general international standards have seriousissues in the standard text is superficial. and other problems mainly due to the normal standardization processes and • Standardization process is very slow. particularly the consensus practices. • Participating highlight their own responsibility Organizations applying the standards should in standardization is expensive. of business leaders and experts and clarify, correct, and complete general standards and find creative solutions in their implementations in order to achieve business 4320/14. 9. 2014/jan benefits.
 Standardization, a linking factor between science and practice Science Standardizatio n Practice An activity giving solutions for repetitive application, to problems essentially in the spheres of science, technology and economics, aimed at the achievement of the optimum degree of order in a given context. Generally, the activity consists of the processes of formulating, issuing and implementing standards. (ISO Guide 2) 9 Standard A technical specification or other document available to the public, drawn up with the cooperation and consensus or general approval of all interests affected by it, based on the consolidated results of science, technology and experience, aimed at the promotion of optimum community benefits and approved by a standardization body (ISO Guide 2) 4073/2. 8. 2013/jan
Standardization, a linking factor between science and practice Science Standardizatio n Practice An activity giving solutions for repetitive application, to problems essentially in the spheres of science, technology and economics, aimed at the achievement of the optimum degree of order in a given context. Generally, the activity consists of the processes of formulating, issuing and implementing standards. (ISO Guide 2) 9 Standard A technical specification or other document available to the public, drawn up with the cooperation and consensus or general approval of all interests affected by it, based on the consolidated results of science, technology and experience, aimed at the promotion of optimum community benefits and approved by a standardization body (ISO Guide 2) 4073/2. 8. 2013/jan
 Implementing the ISO 9000 series of standards The ISO 9000 standards series for quality management systems (QMS) is it is an ensemble of: • ISO 9000: Fundamentals and vocabulary • ISO 9001: Requirements • ISO 9004: Managing for the sustained success of an organization Different parts of the series form a complementary whole. Starting point for implementing ISO 9001 is the organization itself, its business needs, and its QMS: • ISO 9001 presents requirements for organizations’ QMS • QMSs should be created by organizations themselves. QMSs have not been specified in any standards. 10 4321/14. 9. 2014/jan
Implementing the ISO 9000 series of standards The ISO 9000 standards series for quality management systems (QMS) is it is an ensemble of: • ISO 9000: Fundamentals and vocabulary • ISO 9001: Requirements • ISO 9004: Managing for the sustained success of an organization Different parts of the series form a complementary whole. Starting point for implementing ISO 9001 is the organization itself, its business needs, and its QMS: • ISO 9001 presents requirements for organizations’ QMS • QMSs should be created by organizations themselves. QMSs have not been specified in any standards. 10 4321/14. 9. 2014/jan


