81b022b0b5f70349412ed932c90be266.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75

NCBI Field. Guide NCBI Molecular Biology Resources A Field Guide Part 2 January 12, 2007
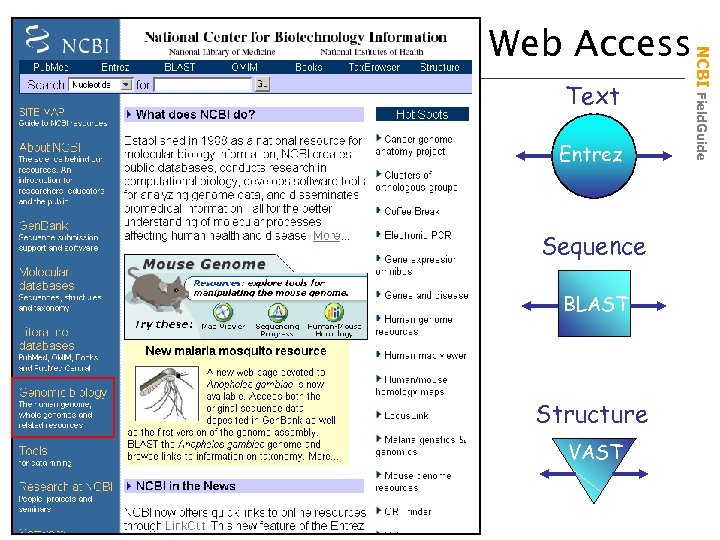
Text Entrez Sequence BLAST Structure VAST NCBI Field. Guide Web Access
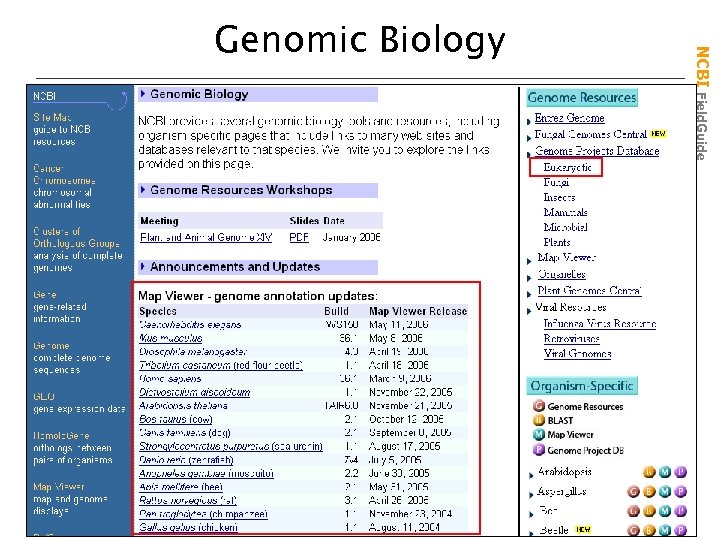
NCBI Field. Guide Genomic Biology
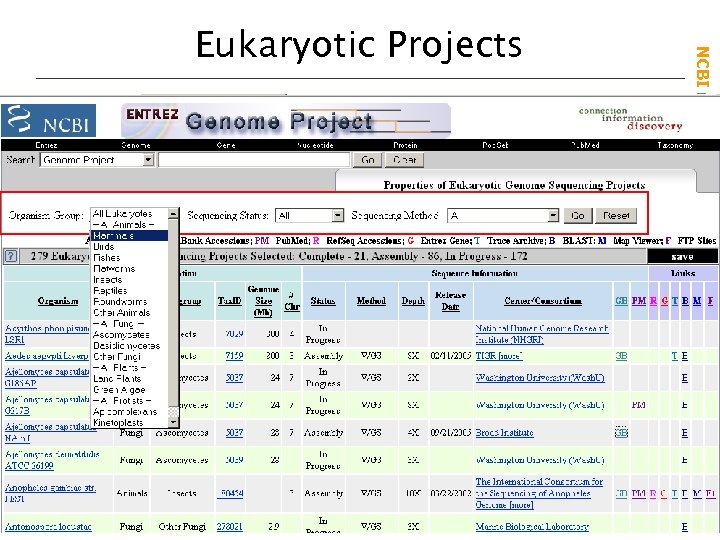
NCBI Field. Guide Eukaryotic Projects
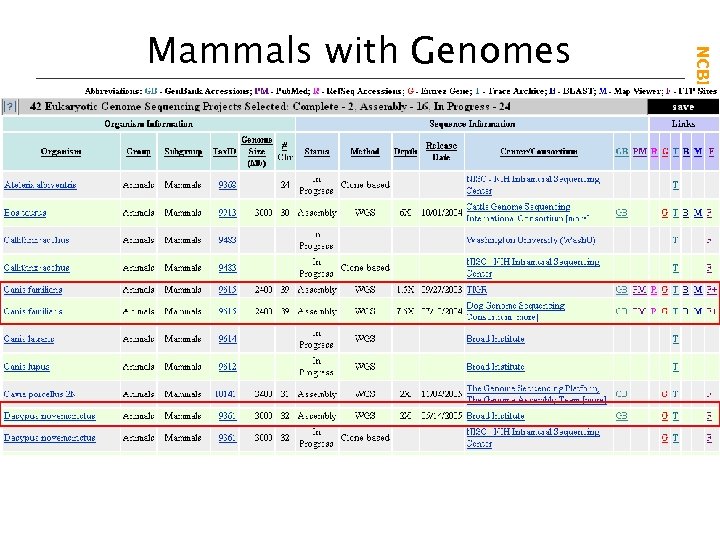
NCBI Field. Guide Mammals with Genomes
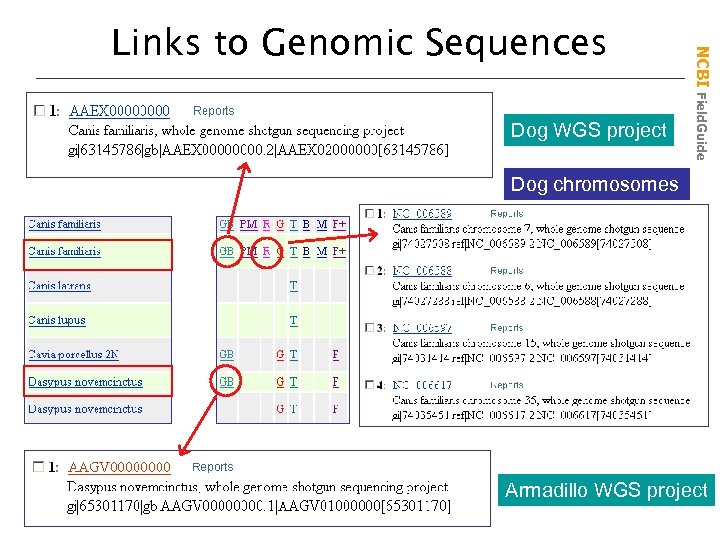
Dog WGS project NCBI Field. Guide Links to Genomic Sequences Dog chromosomes Armadillo WGS project
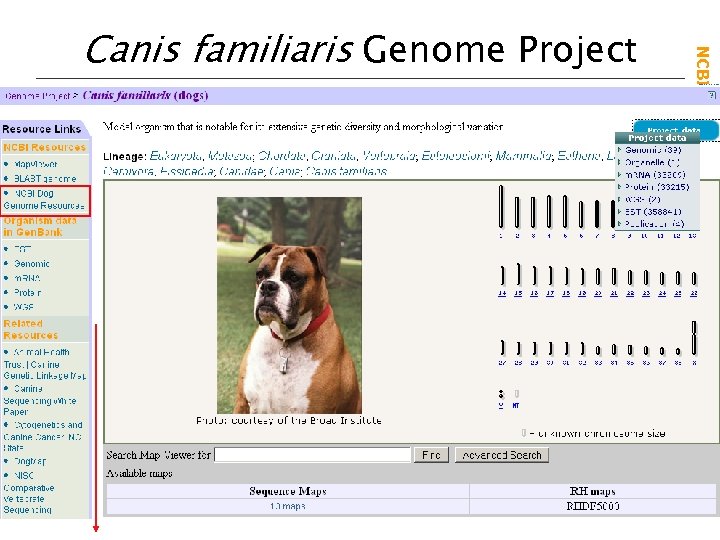
NCBI Field. Guide Canis familiaris Genome Project

• Traditional Gen. Bank Divisions; Keyword: WGS • 12 -digit Accessions (eg. AABC 0000) • 424 Projects • 299 Taxa – 203 bacteria – 91 eukaryotes • 40 fungi • 34 animals NCBI Field. Guide Whole Genome Shotgun Projects

? NCBI Field. Guide From WGS to Ref. Seq
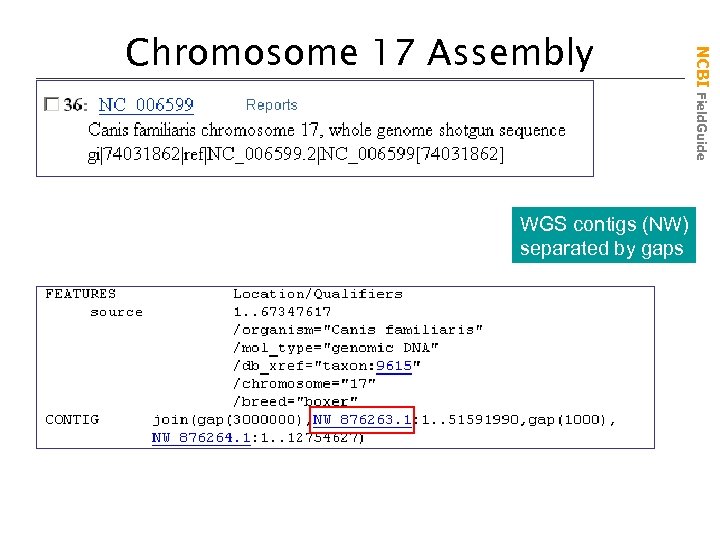
WGS contigs (NW) separated by gaps NCBI Field. Guide Chromosome 17 Assembly
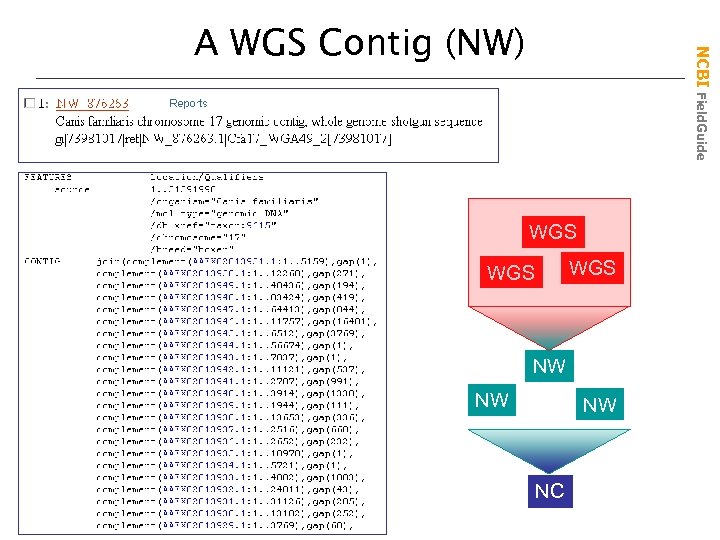
NCBI Field. Guide A WGS Contig (NW) WGS WGS NW NW NW NC
![Search Gene for thyroid peroxidase (TPO) tpo [sym] AND canis familiaris [organism] [gene/protein name] Search Gene for thyroid peroxidase (TPO) tpo [sym] AND canis familiaris [organism] [gene/protein name]](https://present5.com/presentation/81b022b0b5f70349412ed932c90be266/image-12.jpg)
Search Gene for thyroid peroxidase (TPO) tpo [sym] AND canis familiaris [organism] [gene/protein name] (if [sym] doesn’t work) Only 1 record! Why not start all your NCBI searches this way? NCBI Field. Guide Let’s Do a Search!
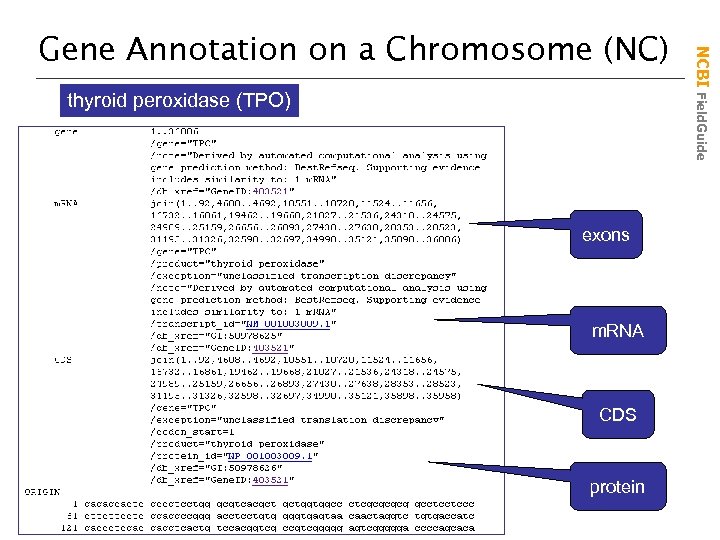
thyroid peroxidase (TPO) exons m. RNA CDS protein NCBI Field. Guide Gene Annotation on a Chromosome (NC)
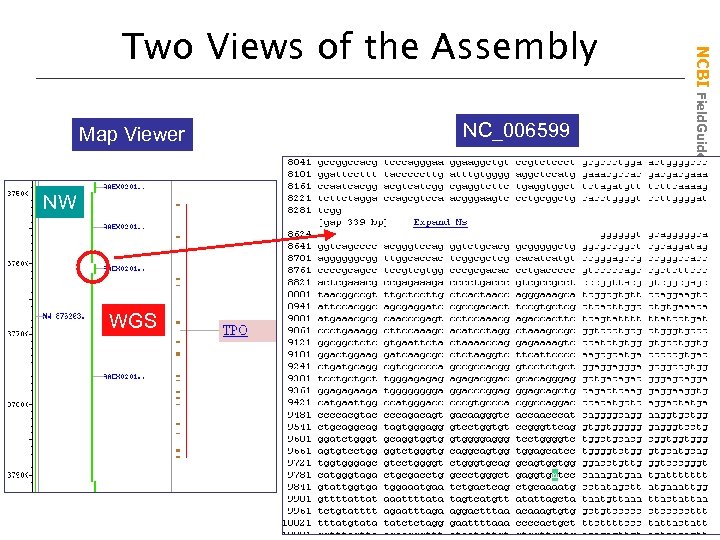
Map Viewer NW WGS NC_006599 NCBI Field. Guide Two Views of the Assembly
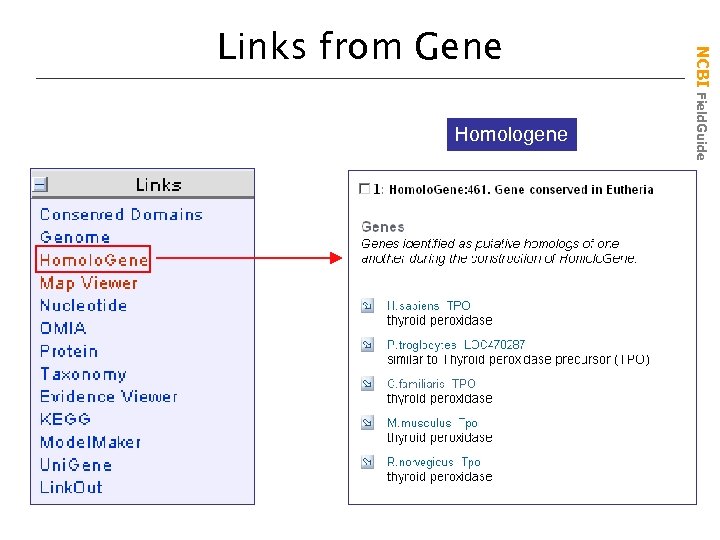
Homologene NCBI Field. Guide Links from Gene
![If your organism is not in Gene… • WGS sequences in Entrez Nucleotide (wgs[prop]) If your organism is not in Gene… • WGS sequences in Entrez Nucleotide (wgs[prop])](https://present5.com/presentation/81b022b0b5f70349412ed932c90be266/image-16.jpg)
If your organism is not in Gene… • WGS sequences in Entrez Nucleotide (wgs[prop]) – remember the armadillo! • Uni. Gene : gene-based clusters of c. DNAs and ESTs • Trace Archive NCBI Field. Guide Beyond Gene
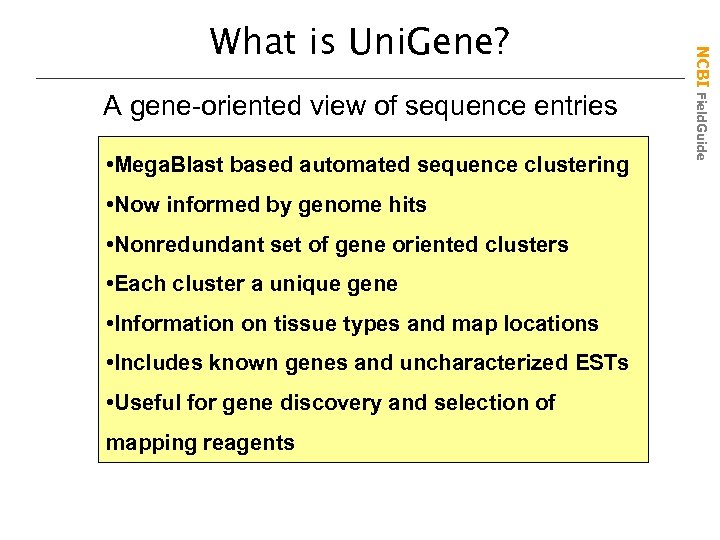
A gene-oriented view of sequence entries • Mega. Blast based automated sequence clustering • Now informed by genome hits • Nonredundant set of gene oriented clusters • Each cluster a unique gene • Information on tissue types and map locations • Includes known genes and uncharacterized ESTs • Useful for gene discovery and selection of mapping reagents NCBI Field. Guide What is Uni. Gene?
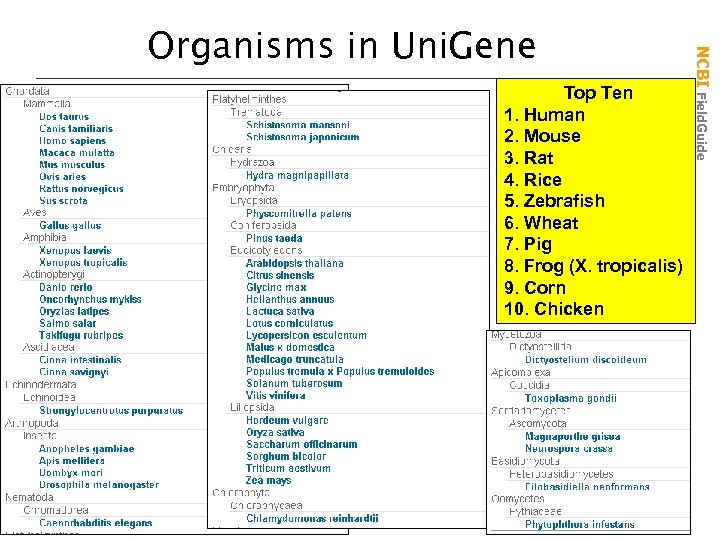
Top Ten 1. Human 2. Mouse 3. Rat 4. Rice 5. Zebrafish 6. Wheat 7. Pig 8. Frog (X. tropicalis) 9. Corn 10. Chicken NCBI Field. Guide Organisms in Uni. Gene
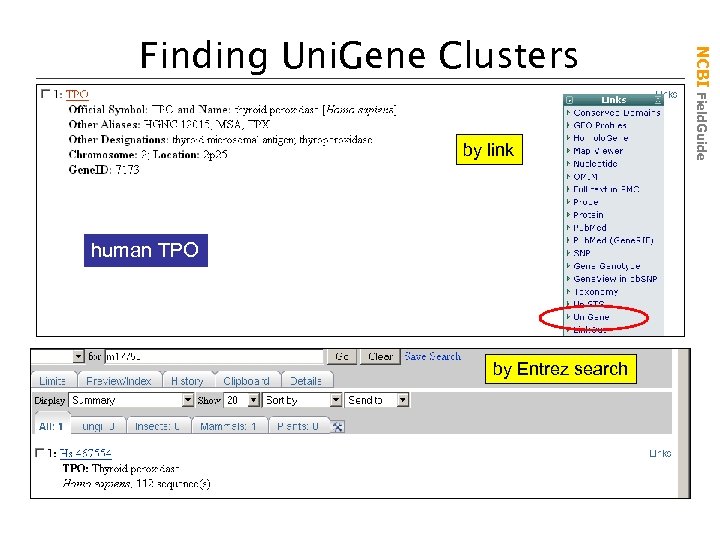
by link human TPO by Entrez search NCBI Field. Guide Finding Uni. Gene Clusters
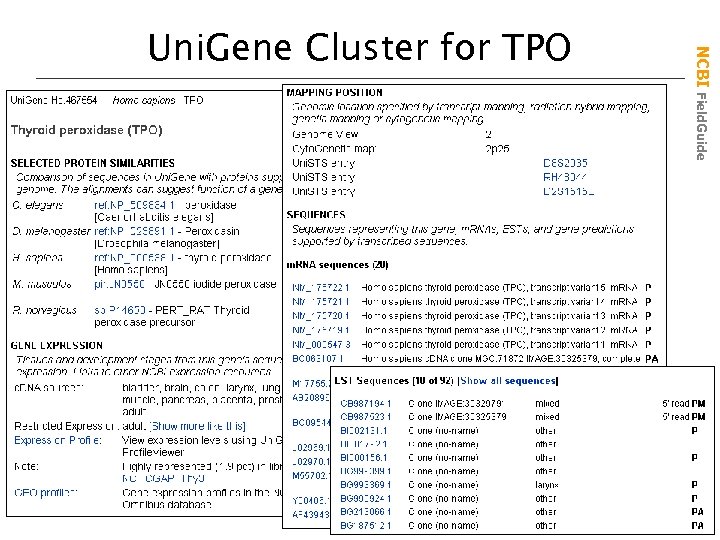
NCBI Field. Guide Uni. Gene Cluster for TPO
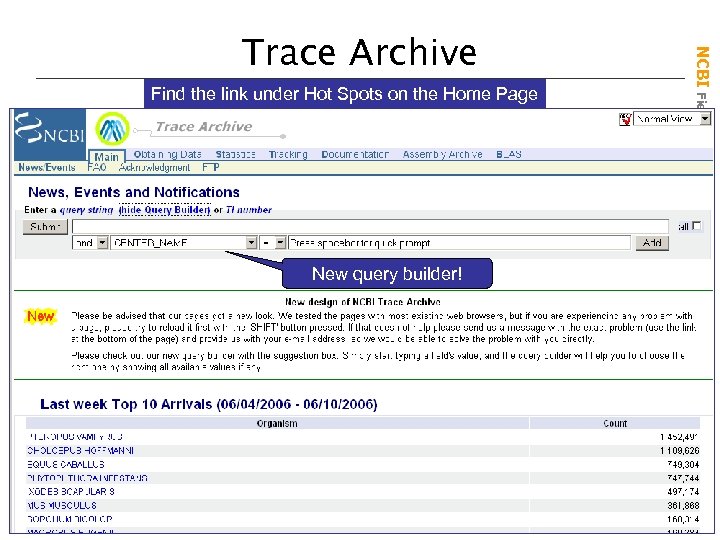
Find the link under Hot Spots on the Home Page New query builder! NCBI Field. Guide Trace Archive
NCBI Field. Guide Short-tailed opossum traces
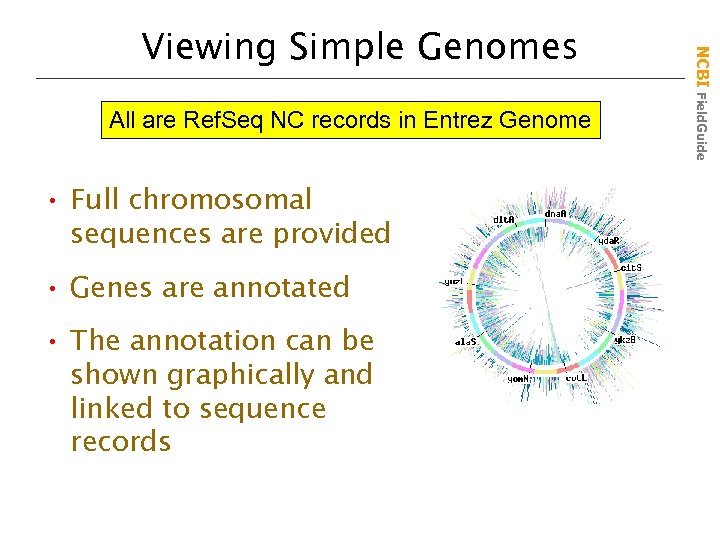
All are Ref. Seq NC records in Entrez Genome • Full chromosomal sequences are provided • Genes are annotated • The annotation can be shown graphically and linked to sequence records NCBI Field. Guide Viewing Simple Genomes
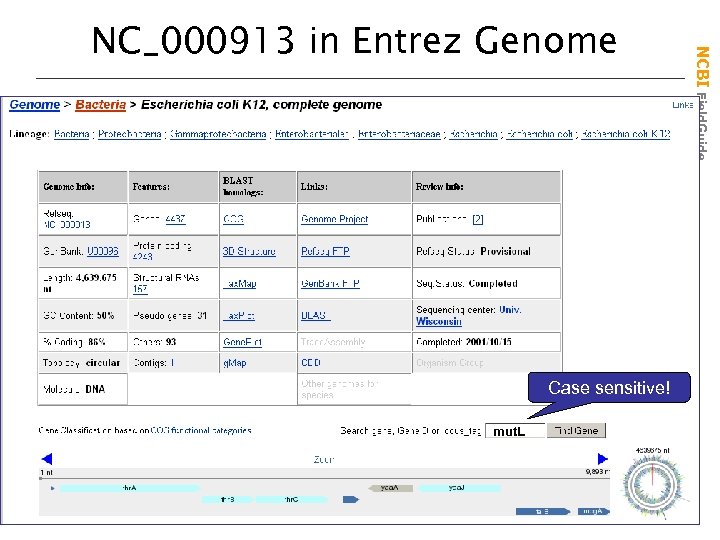
Case sensitive! mut. L NCBI Field. Guide NC_000913 in Entrez Genome
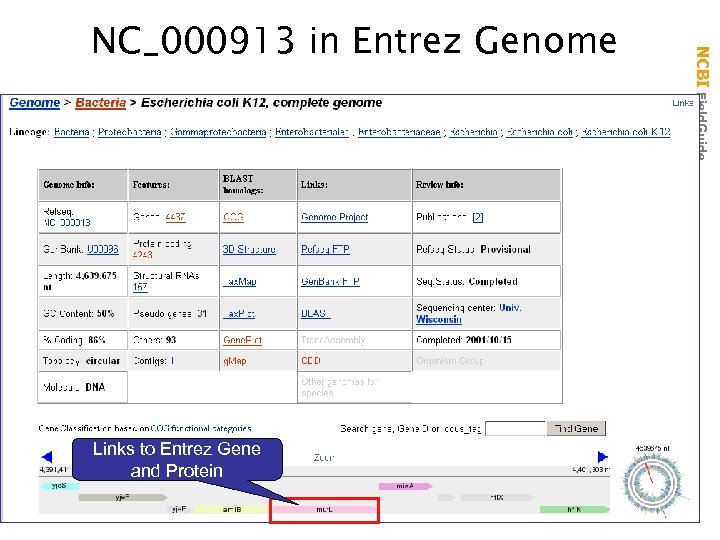
Links to Entrez Gene and Protein NCBI Field. Guide NC_000913 in Entrez Genome
NCBI Map Viewer • Map Viewer Home Page – Shows all supported organisms – Provides links to genomic BLAST • Genome Overview Page – Provides links to individual chromosomes – Shows hits on a genome graphically • Chromosome Viewing Page – Allows interactive views of annotation details – Provides numerous maps unique to each genome NCBI Field. Guide Viewing Complex Genomes
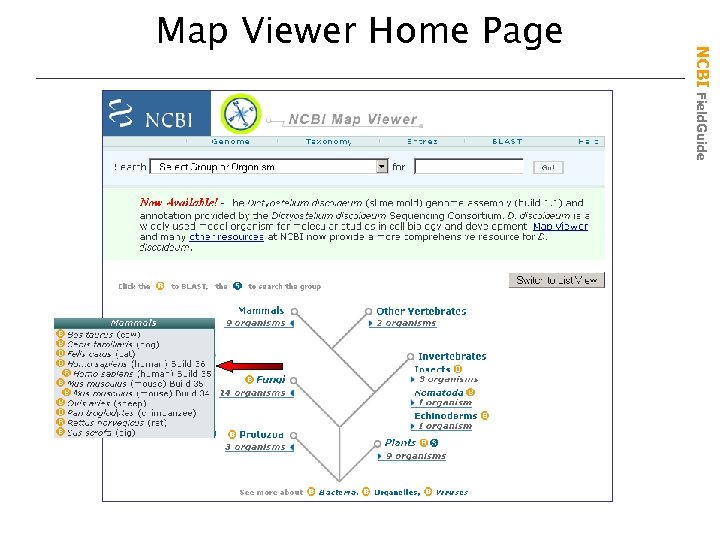
NCBI Field. Guide Map Viewer Home Page
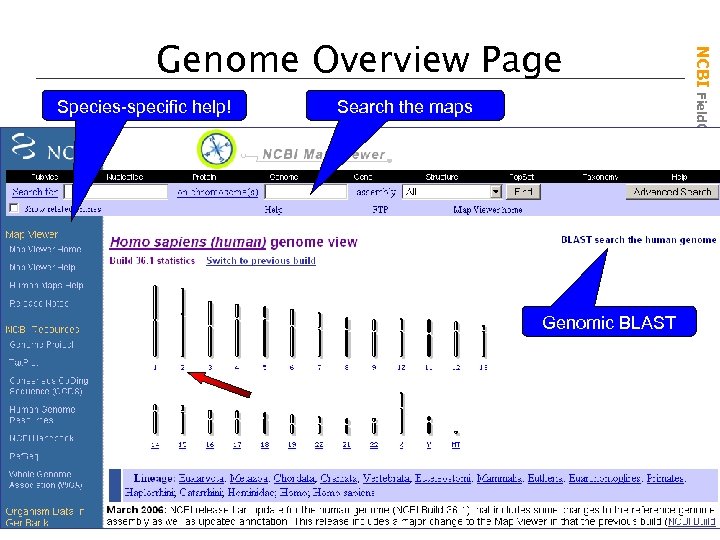
Species-specific help! Search the maps Genomic BLAST NCBI Field. Guide Genome Overview Page
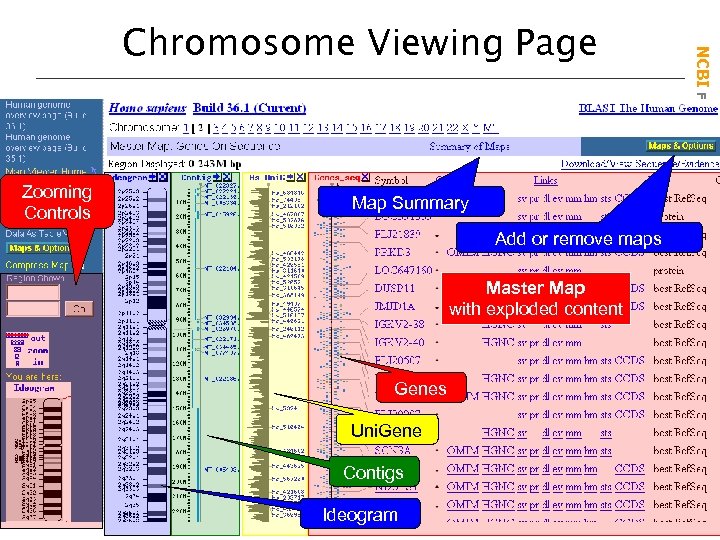
Zooming Controls Map Summary Add or remove maps Master Map with exploded content Genes Uni. Gene Contigs Ideogram NCBI Field. Guide Chromosome Viewing Page
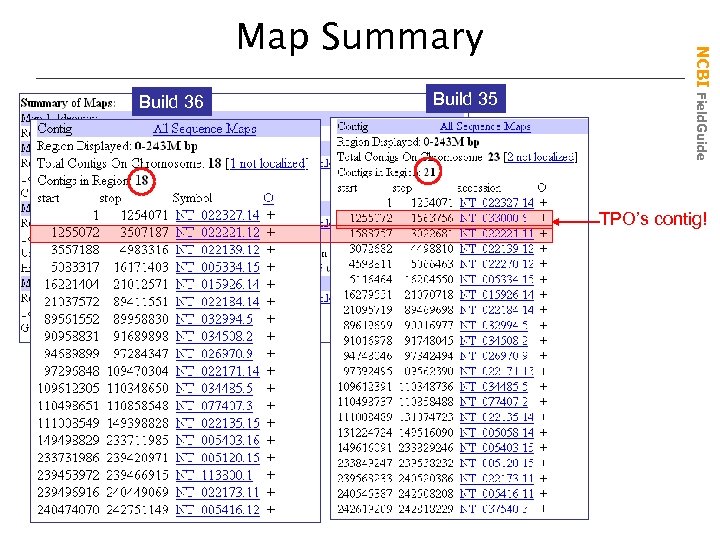
Build 36 Build 35 NCBI Field. Guide Map Summary TPO’s contig!
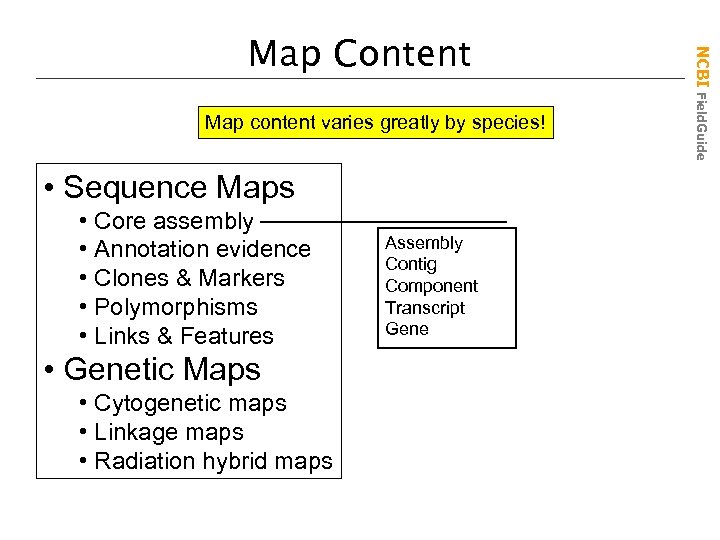
Map content varies greatly by species! • Sequence Maps • Core assembly • Annotation evidence • Clones & Markers • Polymorphisms • Links & Features • Genetic Maps • Cytogenetic maps • Linkage maps • Radiation hybrid maps Assembly Contig Component Transcript Gene NCBI Field. Guide Map Content
NCBI Field. Guide View the Assembly near TPO
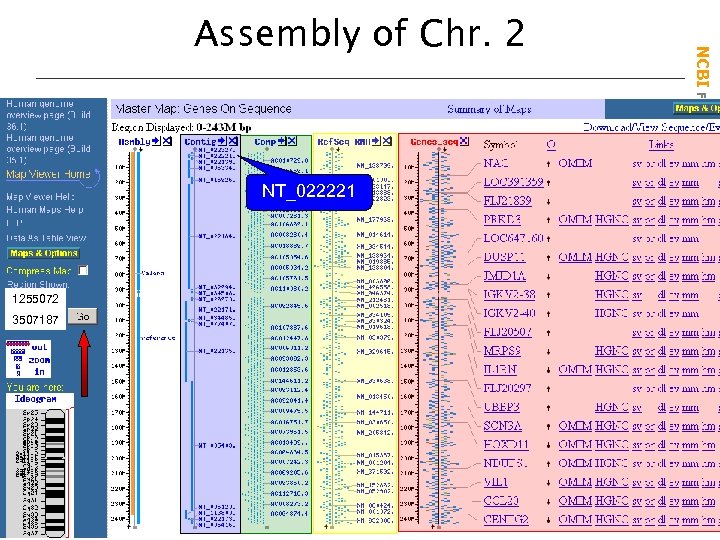
NT_022221 1255072 3507187 NCBI Field. Guide Assembly of Chr. 2
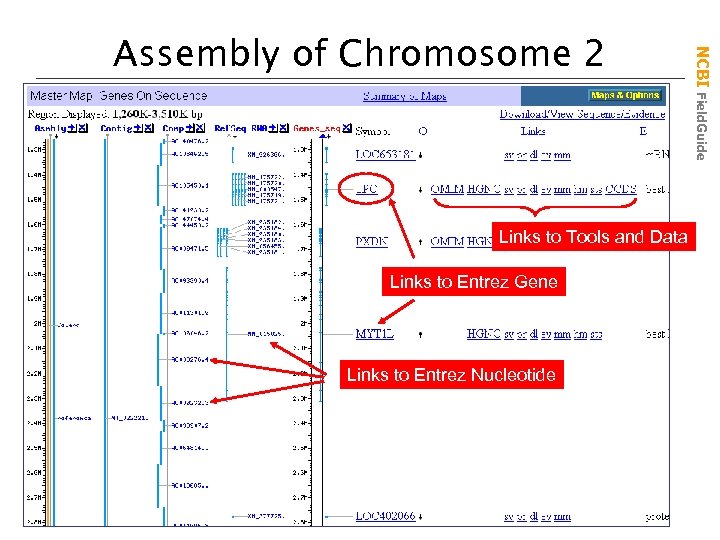
Links to Tools and Data Links to Entrez Gene Links to Entrez Nucleotide NCBI Field. Guide Assembly of Chromosome 2
Why do we need similarity searching? è To identify and annotate sequences with… • incomplete (or no) annotations (Gen. Bank) • incorrect annotations è To assemble genomes è To explore evolutionary relationships by… • finding homologous molecules • developing phylogenetic trees NOTE: Similar sequences may NOT have similar function! NCBI Field. Guide Searching with Sequences
• • • Widely used similarity search tool Heuristic approach based on Smith Waterman algorithm Finds best local alignments Provides statistical significance All combinations (DNA/Protein) query and database. – – – DNA vs DNA translation vs Protein vs DNA translation • www, standalone, and network clients NCBI Field. Guide Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
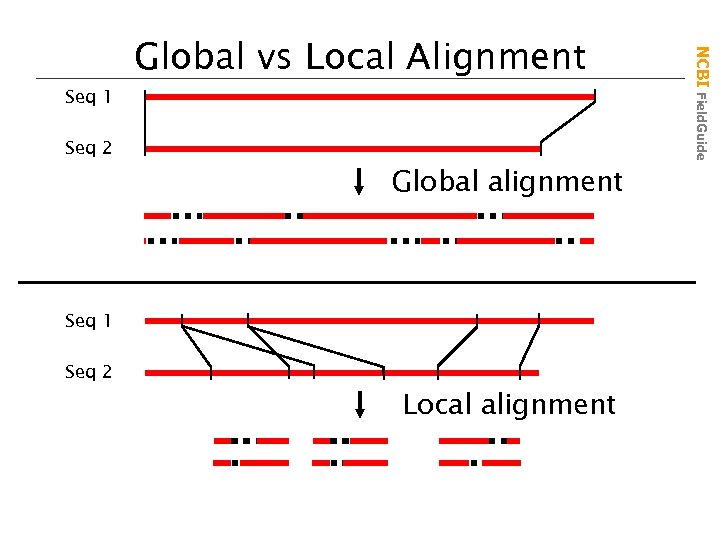
Seq 2 Global alignment Seq 1 Seq 2 Local alignment NCBI Field. Guide Seq 1 Global vs Local Alignment
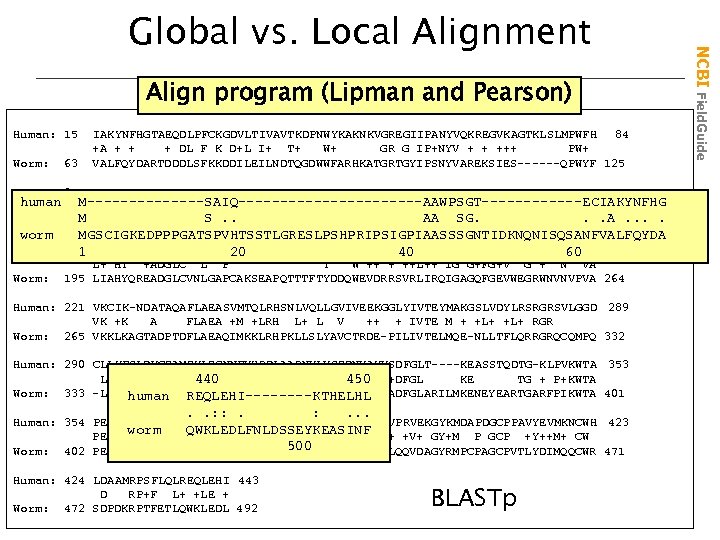
Align program (Lipman and Pearson) Human: 15 63 IAKYNFHGTAEQDLPFCKGDVLTIVAVTKDPNWYKAKNKVGREGIIPANYVQKREGVKAGTKLSLMPWFH 84 +A + + + DL F K D+L I+ T+ W+ GR G IP+NYV + + +++ PW+ VALFQYDARTDDDLSFKKDDILEILNDTQGDWWFARHKATGRTGYIPSNYVAREKSIES------QPWYF 125 Human: 85 GKITREQAERLLYPP--ETGLFLVRESTNYPGDYTLCVSCDGKVEHYRI-MYHASKLSIDEEVYFENLMQ 151 Worm: human M-------SAIQ-----------AAWPSGT------ECIAKYNFHG GK+ R AE+ L E G FLVR+S + D +L V + V+HYRI + H I F L M GKMRRIDAEKCLLHTLNEHGAFLVRDSESRQHDLSLSVRENDSVKHYRIQLDHGGYF-IARRRPFATLHD. A. . S. . AA SG. . 194 Worm: 126 worm MGSCIGKEDPPPGATSPVHTSSTLGRESLPSHPRIPSIGPIAASSSGNTIDKNQNISQSANFVALFQYDA Human: 152 LVEHYTSDADGLCTRLIKPKVMEGTVAAQDEFYRSGWALNMKELKLLQTIGKGEFGDVMLGDYRGN-KVA 220 1 20 40 60 Worm: L+ HY +ADGLC L P Y W ++ + ++L++ IG G+FG+V G + N VA 195 LIAHYQREADGLCVNLGAPCAKSEAPQTTTFTYDDQWEVDRRSVRLIRQIGAGQFGEVWEGRWNVNVPVA 264 Human: 221 VKCIK-NDATAQAFLAEASVMTQLRHSNLVQLLGVIVEEKGGLYIVTEYMAKGSLVDYLRSRGRSVLGGD 289 VK +K A FLAEA +M +LRH L+ L V ++ + IVTE M + +L+ RGR Worm: 265 VKKLKAGTADPTDFLAEAQIMKKLRHPKLLSLYAVCTRDE-PILIVTELMQE-NLLTFLQRRGRQCQMPQ 332 Human: 290 CLLKFSLDVCEAMEYLEGNNFVHRDLAARNVLVSEDNVAKVSDFGLT----KEASSTQDTG-KLPVKWTA 353 L++ S V M YLE NF+HRDLAARN+L++ 450 K++DFGL KE TG + P+KWTA 440 Worm: 333 -LVEISAQVAAGMAYLEEMNFIHRDLAARNILINNSLSVKIADFGLARILMKENEYEARTGARFPIKWTA 401 human REQLEHI----KTHELHL . . : : . . . Human: 354 PEALREKKFSTKSDVWSFGILLWEIYSFGRVPYPRIPLKDVVPRVEKGYKMDAPDGCPPAVYEVMKNCWH 423 worm QWKLEDLFNLDSSEYKEASINF +V+ GY+M P GCP +Y++M+ CW PEA +F+TKSDVWSFGILL EI +FGR+PYP + 500 Worm: 402 PEAANYNRFTTKSDVWSFGILLTEIVTFGRLPYPGMTNAEVLQQVDAGYRMPCPAGCPVTLYDIMQQCWR 471 Human: 424 LDAAMRPSFLQLREQLEHI 443 D RP+F L+ +LE + Worm: 472 SDPDKRPTFETLQWKLEDL 492 BLASTp NCBI Field. Guide Global vs. Local Alignment
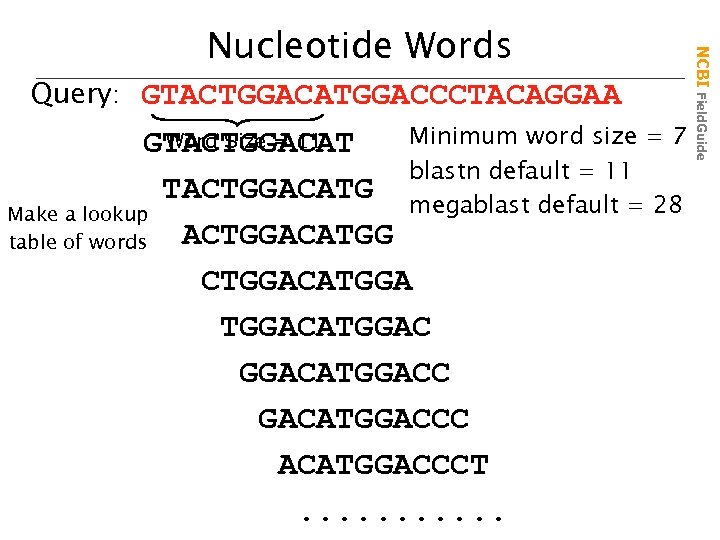
Query: GTACTGGACATGGACCCTACAGGAA Minimum word size = 7 Word Size = 11 GTACTGGACAT blastn default = 11 TACTGGACATG megablast default = 28 Make a lookup ACTGGACATGG table of words CTGGACATGGAC GGACATGGACCC ACATGGACCCT. . . NCBI Field. Guide Nucleotide Words
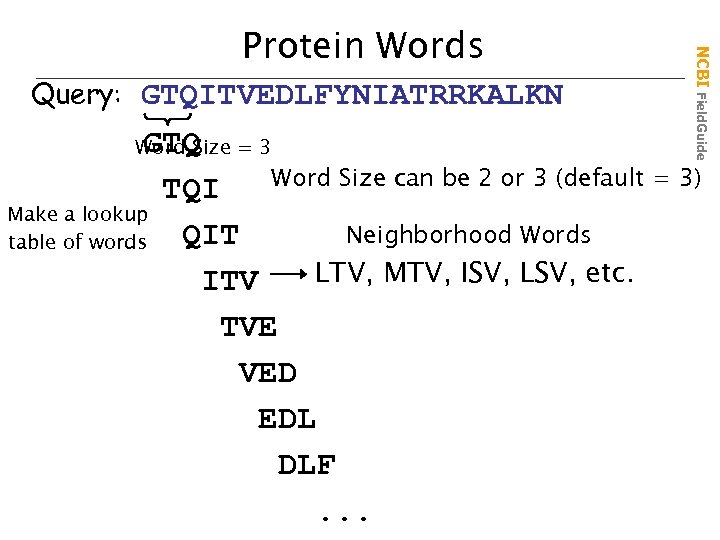
Query: GTQITVEDLFYNIATRRKALKN NCBI Field. Guide Protein Words GTQ Word Size can be 2 or 3 (default = 3) TQI Make a lookup Neighborhood Words QIT table of words LTV, MTV, ISV, LSV, etc. ITV TVE VED EDL DLF. . . Word Size = 3
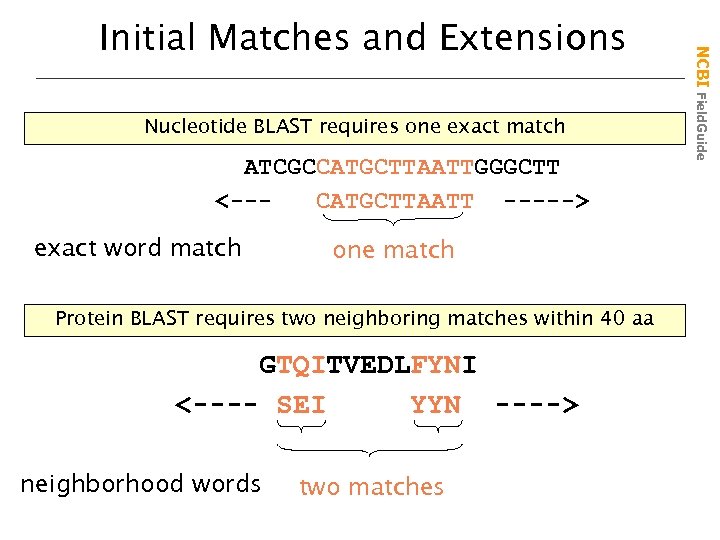
Nucleotide BLAST requires one exact match ATCGCCATGCTTAATTGGGCTT <--CATGCTTAATT -----> exact word match one match Protein BLAST requires two neighboring matches within 40 aa GTQITVEDLFYNI <---- SEI YYN ----> neighborhood words two matches NCBI Field. Guide Initial Matches and Extensions

1 GAATATATGAAGACCAAGATTGCAGTCCTGCTGGCCTGAACCACGCTATTCTTGCTGTTG || || || |||||| | | ||| | 1 GAGTGTACGATGAGCCCGAGTGTAGCAGTGAAGATCTGGACCACGGTGTACTCGTTGTCG 61 GTTACGGAACCGAGAATGGTAAAGACTACTGGATCATTAAGAACTCCTGGGGAGCCAGTT | || ||| ||||||| | | 61 GCTATGGTGTTAAGGGTGGGAAGAAGTACTGGCTCGTCAAGAACAGCTGGGCTGAATCCT 121 GGGGTGAACAAGGTTATTTCAGGCTTGCTCGTGGTAAAAAC |||| || || | | |||| || ||| 121 GGGGAGACCAAGGCTACATCCTTATGTCCCGTGACAACAAC NCBI Field. Guide An alignment that BLAST can’t find
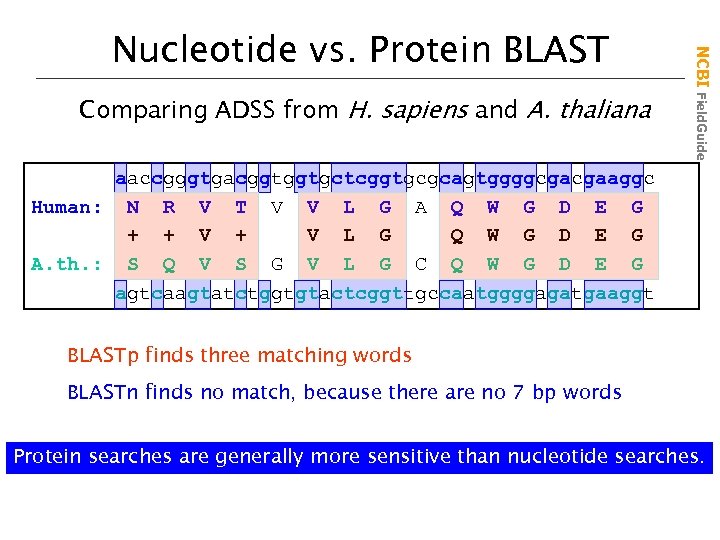
Comparing ADSS from H. sapiens and A. thaliana NCBI Field. Guide Nucleotide vs. Protein BLAST aaccgggtgacggtggtgctcggtgcgcagtggggcgacgaaggc Human: N R V T V V L G A Q W G D E G + + V L G Q W G D E G A. th. : S Q V S G V L G C Q W G D E G agtcaagtatctggtgtactcggttgccaatggggagatgaaggt BLASTp finds three matching words BLASTn finds no match, because there are no 7 bp words Protein searches are generally more sensitive than nucleotide searches.
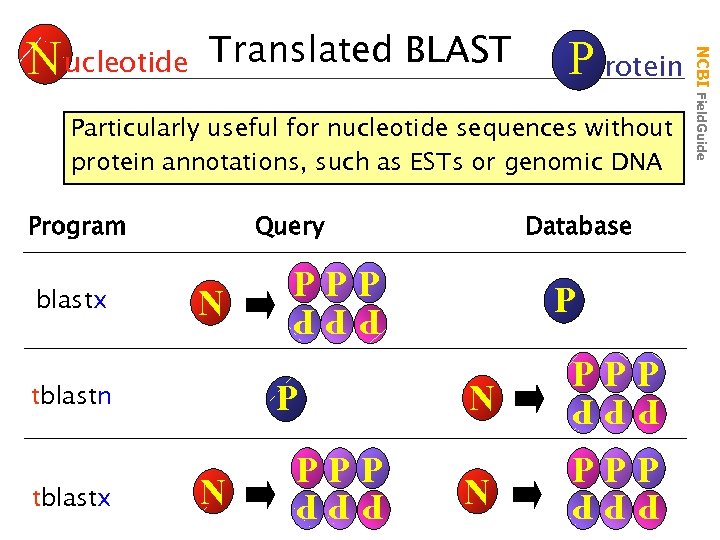
Translated BLAST P rotein Particularly useful for nucleotide sequences without protein annotations, such as ESTs or genomic DNA tblastn P N PPP tblastx PPP P N N PPP PPP N Database PPP blastx Query PPP Program NCBI Field. Guide N ucleotide
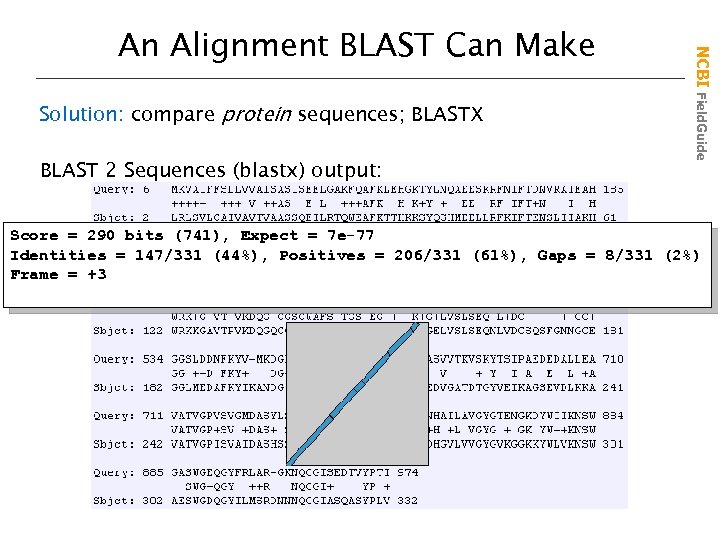
Solution: compare protein sequences; BLASTX BLAST 2 Sequences (blastx) output: NCBI Field. Guide An Alignment BLAST Can Make Score = 290 bits (741), Expect = 7 e-77 Identities = 147/331 (44%), Positives = 206/331 (61%), Gaps = 8/331 (2%) Frame = +3
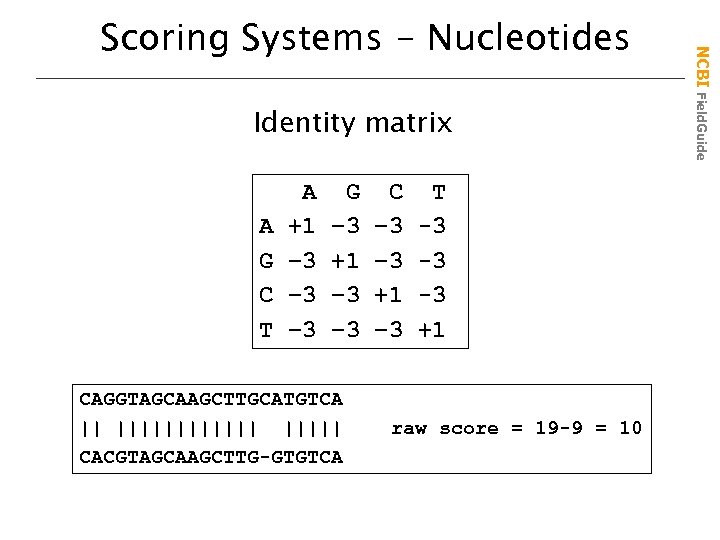
Identity matrix A G C T A +1 – 3 – 3 G – 3 +1 – 3 CAGGTAGCAAGCTTGCATGTCA || |||||| CACGTAGCAAGCTTG-GTGTCA C – 3 +1 – 3 T -3 -3 -3 +1 raw score = 19 -9 = 10 NCBI Field. Guide Scoring Systems - Nucleotides
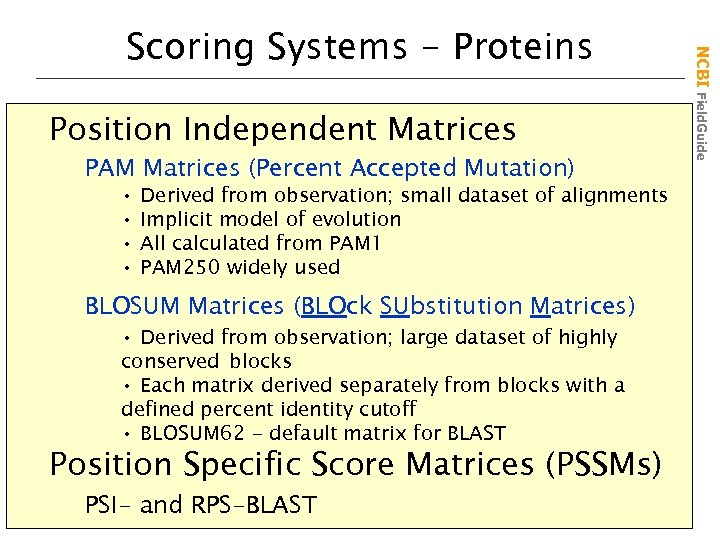
Position Independent Matrices PAM Matrices (Percent Accepted Mutation) • • Derived from observation; small dataset of alignments Implicit model of evolution All calculated from PAM 1 PAM 250 widely used BLOSUM Matrices (BLOck SUbstitution Matrices) • Derived from observation; large dataset of highly conserved blocks • Each matrix derived separately from blocks with a defined percent identity cutoff • BLOSUM 62 - default matrix for BLAST Position Specific Score Matrices (PSSMs) PSI- and RPS-BLAST NCBI Field. Guide Scoring Systems - Proteins
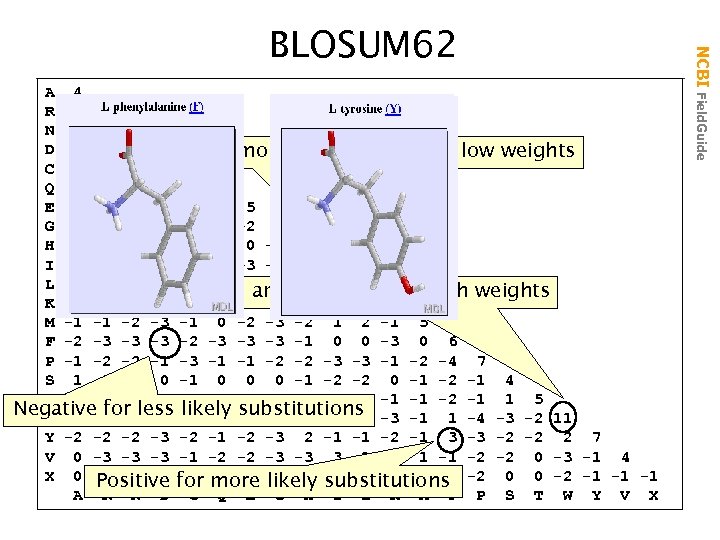
A 4 R -1 5 N -2 0 6 D -2 -2 1 6 Common amino acids have low weights C 0 -3 -3 -3 9 Q -1 1 0 0 -3 5 E -1 0 0 2 -4 2 5 G 0 -2 0 -1 -3 -2 -2 6 H -2 0 1 -1 -3 0 0 -2 8 I -1 -3 -3 -3 -1 -3 -3 -4 -3 4 L -1 -2 -3 -4 -3 2 4 Rare amino acids have high weights K -1 2 0 -1 -3 1 1 -2 -1 -3 -2 5 M -1 -1 -2 -3 -1 0 -2 -3 -2 1 2 -1 5 F -2 -3 -3 -3 -1 0 0 -3 0 6 P -1 -2 -2 -1 -3 -1 -1 -2 -2 -3 -3 -1 -2 -4 7 S 1 -1 1 0 -1 0 0 0 -1 -2 -2 0 -1 -2 -1 4 T 0 -1 -1 -2 -2 -1 -1 -2 -1 1 5 Negative for less -2 -2 -3 -1 1 -4 -3 -2 11 likely substitutions W -3 -3 -4 -4 Y -2 -2 -2 -3 -2 -1 -2 -3 2 -1 -1 -2 -1 3 -3 -2 -2 2 7 V 0 -3 -3 -3 -1 -2 -2 -3 -3 3 1 -2 1 -1 -2 -2 0 -3 -1 4 X 0 -1 -1 -1 for -1 -1 -1 -2 0 0 -2 -1 -1 -1 Positive -2 more likely substitutions A R N D C Q E G H I L K M F P S T W Y V X NCBI Field. Guide BLOSUM 62
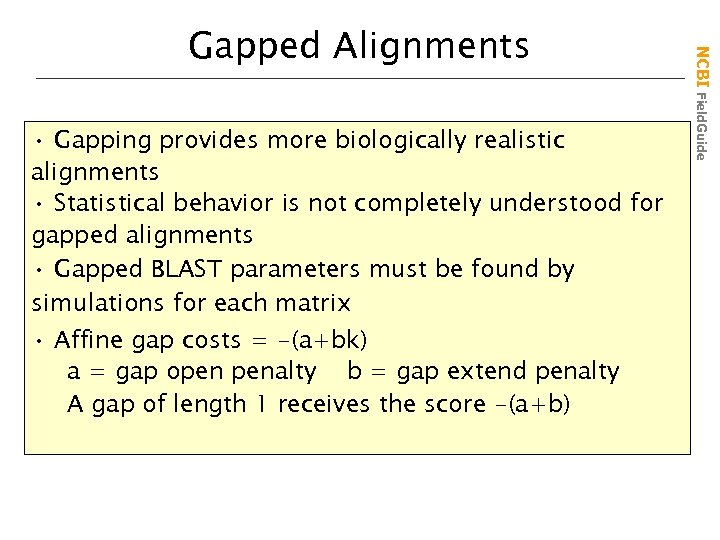
• Gapping provides more biologically realistic alignments • Statistical behavior is not completely understood for gapped alignments • Gapped BLAST parameters must be found by simulations for each matrix • Affine gap costs = -(a+bk) a = gap open penalty b = gap extend penalty A gap of length 1 receives the score -(a+b) NCBI Field. Guide Gapped Alignments
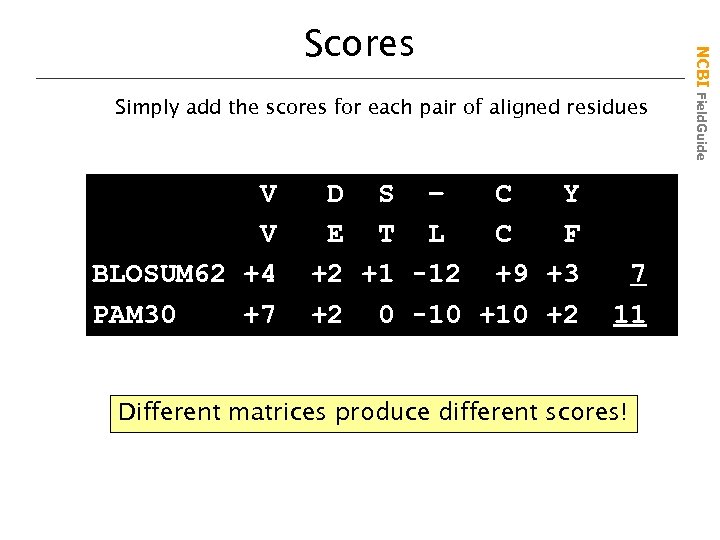
Simply add the scores for each pair of aligned residues V V BLOSUM 62 +4 PAM 30 +7 D S – C Y E T L C F +2 +1 -12 +9 +3 +2 0 -10 +2 7 11 Different matrices produce different scores! NCBI Field. Guide Scores
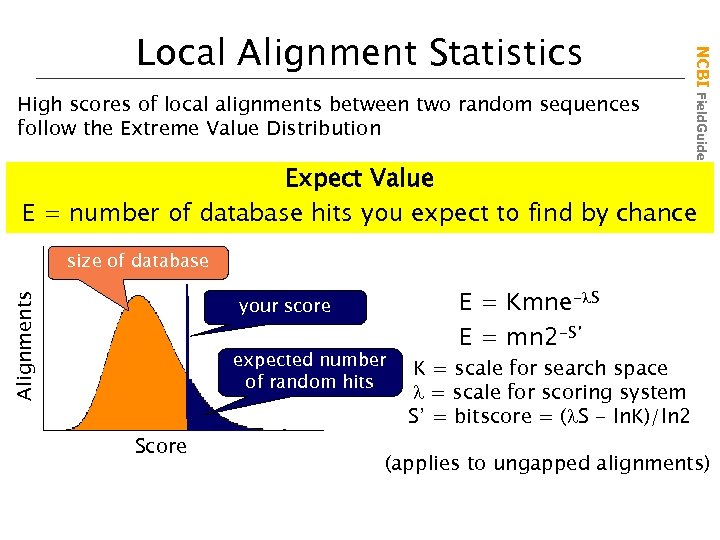
High scores of local alignments between two random sequences follow the Extreme Value Distribution NCBI Field. Guide Local Alignment Statistics Expect Value E = number of database hits you expect to find by chance Alignments size of database your score expected number of random hits Score E = Kmne- S E = mn 2 -S’ K = scale for search space = scale for scoring system S’ = bitscore = ( S - ln. K)/ln 2 (applies to ungapped alignments)
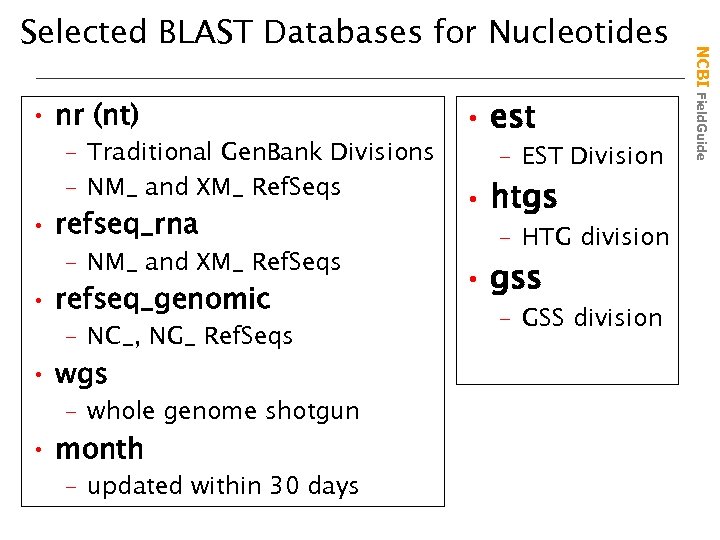
• nr (nt) – Traditional Gen. Bank Divisions – NM_ and XM_ Ref. Seqs • refseq_rna – NM_ and XM_ Ref. Seqs • refseq_genomic – NC_, NG_ Ref. Seqs • wgs – whole genome shotgun • month – updated within 30 days • est – EST Division • htgs – HTG division • gss – GSS division NCBI Field. Guide Selected BLAST Databases for Nucleotides
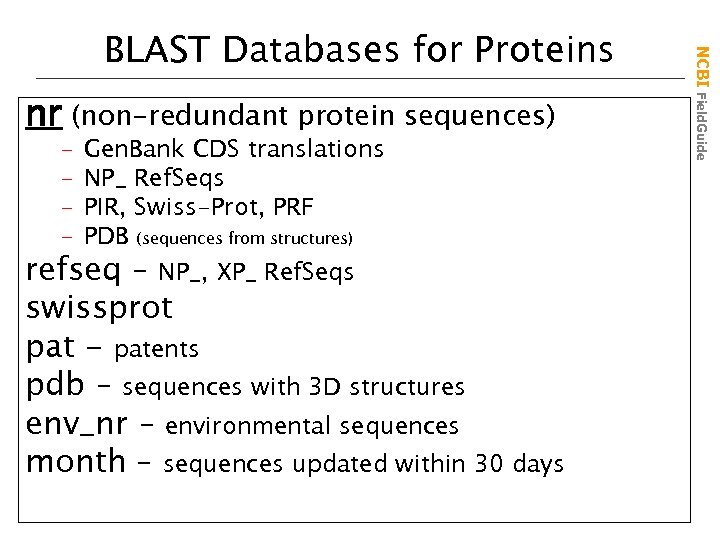
nr (non-redundant protein sequences) – – Gen. Bank CDS translations NP_ Ref. Seqs PIR, Swiss-Prot, PRF PDB (sequences from structures) refseq – NP_, XP_ Ref. Seqs swissprot pat - patents pdb – sequences with 3 D structures env_nr – environmental sequences month – sequences updated within 30 days NCBI Field. Guide BLAST Databases for Proteins
![Example Entrez Queries nucleotide all[Filter] NOT mammalia[Organism] green plants[Organism] biomol mrna[Properties] gbdiv est[Properties] AND Example Entrez Queries nucleotide all[Filter] NOT mammalia[Organism] green plants[Organism] biomol mrna[Properties] gbdiv est[Properties] AND](https://present5.com/presentation/81b022b0b5f70349412ed932c90be266/image-54.jpg)
Example Entrez Queries nucleotide all[Filter] NOT mammalia[Organism] green plants[Organism] biomol mrna[Properties] gbdiv est[Properties] AND rat[organism] Other Advanced –e 10000 expect value -v 2000 descriptions -b 2000 alignments NCBI Field. Guide Advanced BLAST Options
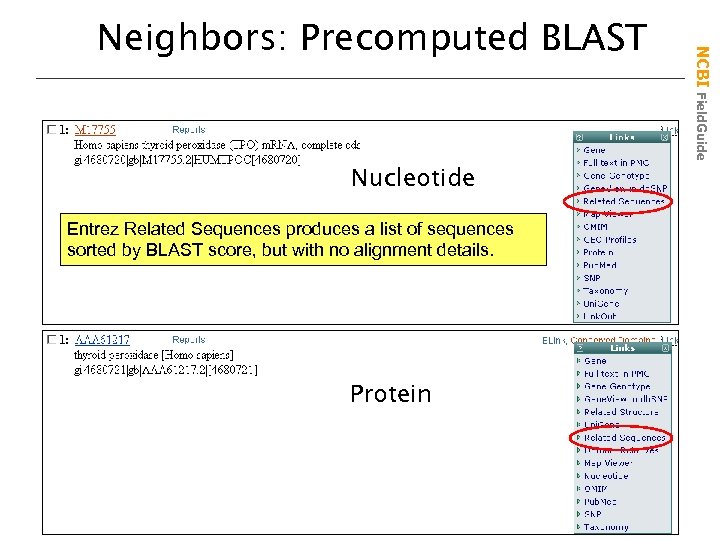
Nucleotide Entrez Related Sequences produces a list of sequences sorted by BLAST score, but with no alignment details. Protein NCBI Field. Guide Neighbors: Precomputed BLAST
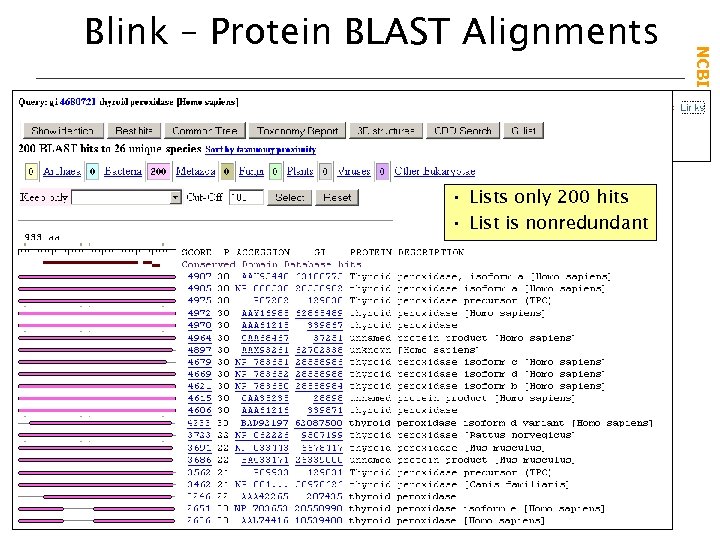
• Lists only 200 hits • List is nonredundant NCBI Field. Guide Blink – Protein BLAST Alignments
• Long alignments of similar DNA sequences • Default word size = 28 • Concatenation of query sequences • Faster than blastn; less sensitive NCBI Field. Guide Megablast: NCBI’s Genome Annotator

> 1133045 gnl|UG|Hs#S 1133045 qd 43 b 11. x 1 Homo sapiens c. DNA, 3' AI 217550 CATGTAAGCCATTTATTGGTTTTAAAAATATGTATTTATACATGAAGTTTG AI 251192 GTGAGAAGTGCTCGATTAGTTCAGACAACATCTGGCACTTGATGTCCTTCCCTCCT TTTTCCTACTCTCTTCTCCCCTCCTGCTGGTCATTGTGCAGTTCTGGAAATTAAAAAGGT AI 254381 GACAGCCAGGCTAAAAGCTAAGGGTTGGGTCTAGCTCACCTCCCACCCCCAACCACACCG BE 645079 TCTGCAGCCCCAGGCACCTGTCTCAAAGCTCCCGGGCTGTCCACACAAAAAC CACAGTCTCCTTCCGGCCAGCTGGCAGCCCGACCTGC > 1141828 gnl|UG|Hs#S 1141828 qv 37 f 11. x 1 Homo sapiens c. DNA, 3' GAGAAGACGACAGAAGGGGAGAAGAGAGTAGGAAAAAGGAGGGAAGGACATCAAGT GCCAGATGTTGTCTGAACTAATCGAGCACTTCTCACCAAACTTCATGTATAAAATA CATATTTTTAAAACCAATAAATGGCTTACATCAAAAAAAAAAAA GTCGTATCGATGT > 1145899 gnl|UG|Hs#S 1145899 qv 33 c 06. x 1 Homo sapiens c. DNA, 3' GAGAAGACGACAGAAGGGGAGAAGAGAGTAGGAAAAAGGAGGGAAGGACATCAAGT GCCAGATGTTGTCTGAACTAATCGAGCACTTCTCACCAAACTTCATGTATAAAATA CATATTTTTAAAACCAATAAATGGCTTACATCAAAAAAAAAAAA GTCGTATCGATGT > 2291670 gnl|UG|Hs#S 2291670 7 e 65 f 04. x 1 Homo sapiens c. DNA, 3' TTTCATGTAAGCCATTTATTGGTTTTAAAAATATGTATTTATACATGAAGT TTGGTGAGAAGTGCTCGATTAGTTCAAACAACATCTGGCACTTGATGTCCTTCCCT CCTTTTTCCTACTCTCTTCTCCCCTCCTGCTGGTCATTGTGCAGTTCTGGAAATTAAAAA GGTGACAGCCAGGCTAAAAGCTAAGGGTTGGGTCTAGCTCACCTCCCACCCCCAACCACA CCGTCTGCAGCCCCAGGCACCTGTCTCAAAGCTCCCGGGCTGTCCACACAAA AACCACAGTCTCCTTCCGGCCAGCTGGCAGCCCGACCTGCCTCCCAACCGCATTC CTGCCTGTGTAGCAGGCGGTGAGCACCCAGAAGGGGCACATACCTCTCCAAGCCTTGAAA GCAAAGCATGGAGATCTACAAAAATAGGATTTCCACTTGGAGAAATGTCGCTGGGACAGT end C: seqhs. 4. fsa end NCBI Field. Guide Mega. BLAST
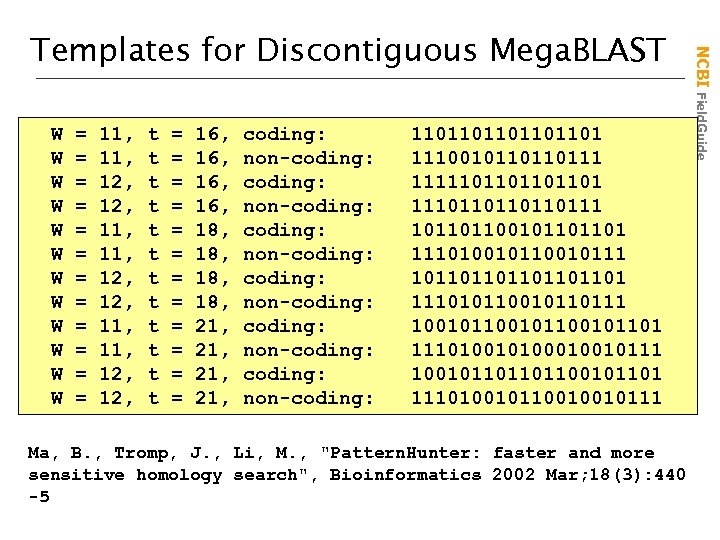
W W W = = = 11, 11, 12, 12, 11, 12, t t t = = = 16, 16, 18, 18, 21, 21, coding: non-coding: coding: non-coding: 1101101101 1110010110110111 111110110111 101101100101101101 111010010111 101101101 111010110111 100101100101101 1110100010010111 100101101101100101101 111010010110010010111 Ma, B. , Tromp, J. , Li, M. , "Pattern. Hunter: faster and more sensitive homology search", Bioinformatics 2002 Mar; 18(3): 440 -5 NCBI Field. Guide Templates for Discontiguous Mega. BLAST
• These pages provide customized nucleotide and protein databases for each genome • If a Map Viewer is available, the BLAST hits can be viewed on the maps NCBI Field. Guide Genomic BLAST
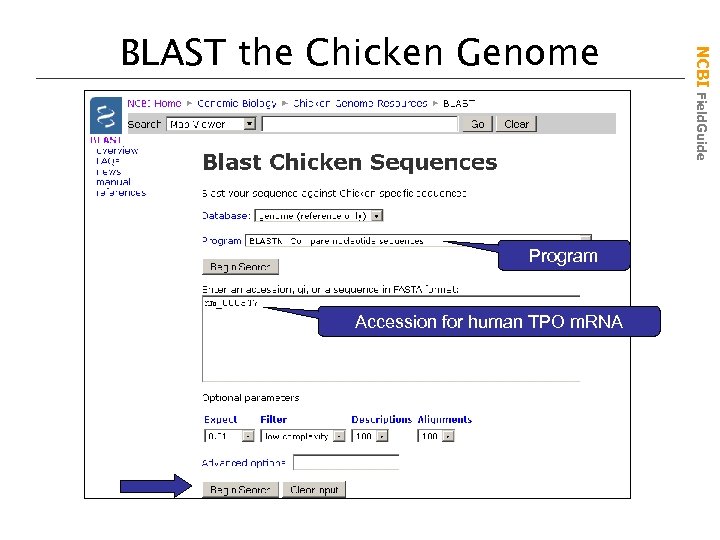
Program Accession for human TPO m. RNA NCBI Field. Guide BLAST the Chicken Genome
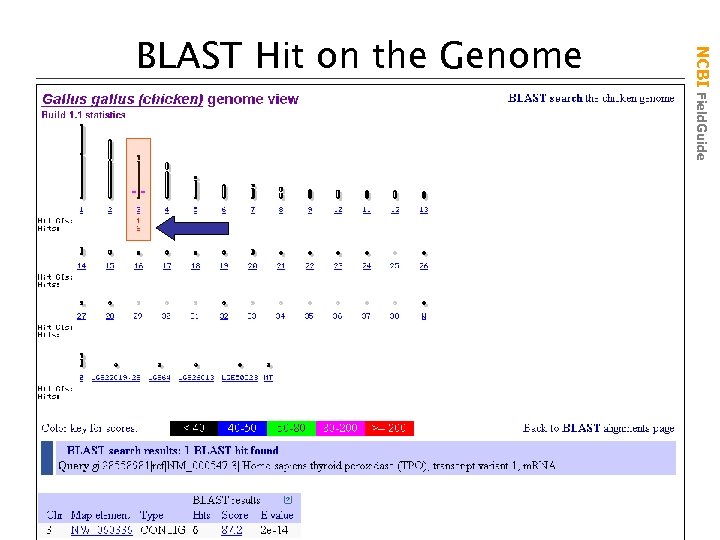
NCBI Field. Guide BLAST Hit on the Genome
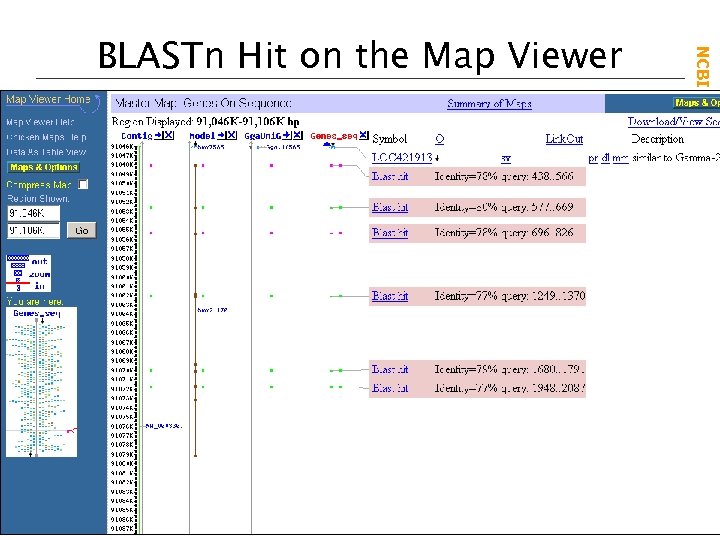
NCBI Field. Guide BLASTn Hit on the Map Viewer
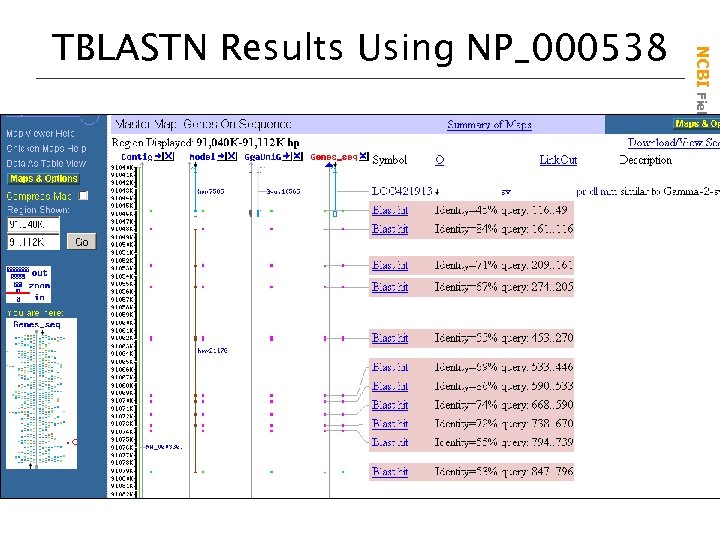
NCBI Field. Guide TBLASTN Results Using NP_000538
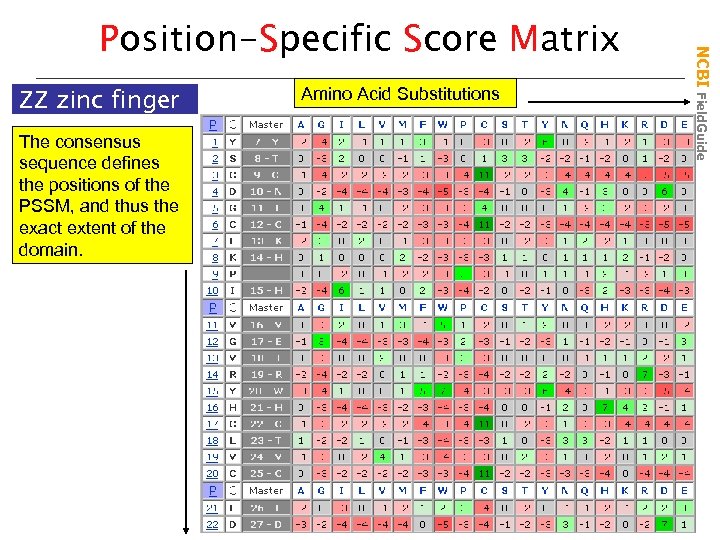
ZZ zinc finger The consensus sequence defines the positions of the PSSM, and thus the exact extent of the domain. Amino Acid Substitutions NCBI Field. Guide Position-Specific Score Matrix
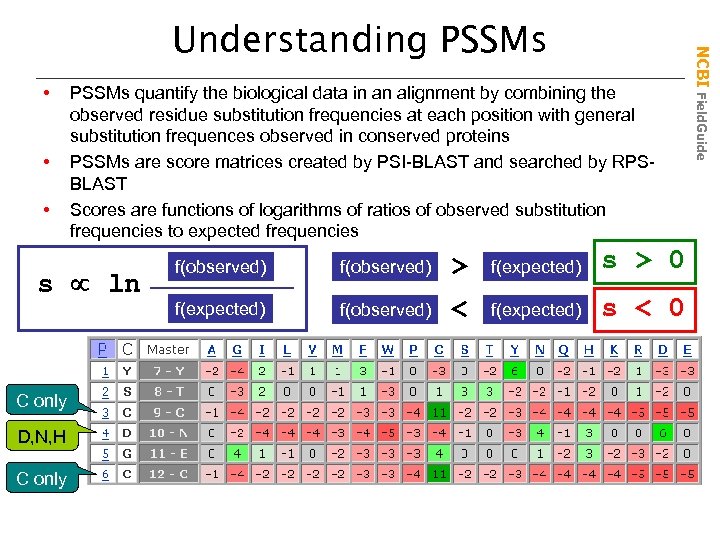
• • • PSSMs quantify the biological data in an alignment by combining the observed residue substitution frequencies at each position with general substitution frequences observed in conserved proteins PSSMs are score matrices created by PSI-BLAST and searched by RPSBLAST Scores are functions of logarithms of ratios of observed substitution frequencies to expected frequencies s ln C only D, N, H C only f(observed) > f(expected) s > 0 f(expected) f(observed) < f(expected) s < 0 NCBI Field. Guide Understanding PSSMs
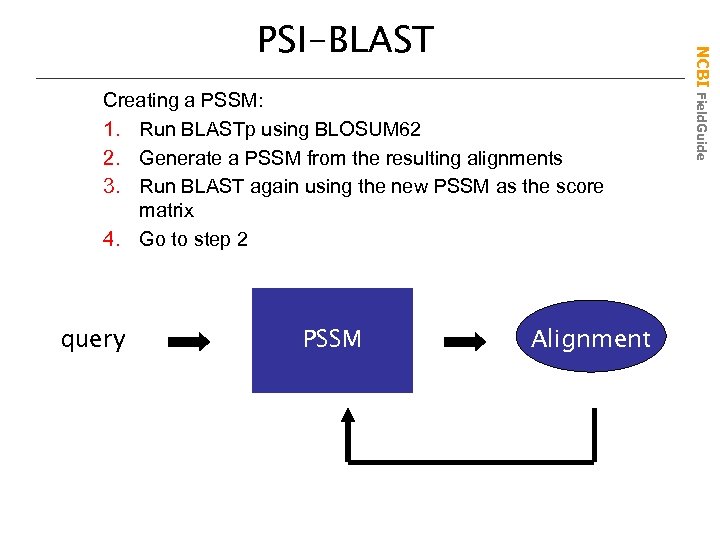
Creating a PSSM: 1. Run BLASTp using BLOSUM 62 2. Generate a PSSM from the resulting alignments 3. Run BLAST again using the new PSSM as the score matrix 4. Go to step 2 query PSSM BLOSUM 62 Alignment NCBI Field. Guide PSI-BLAST
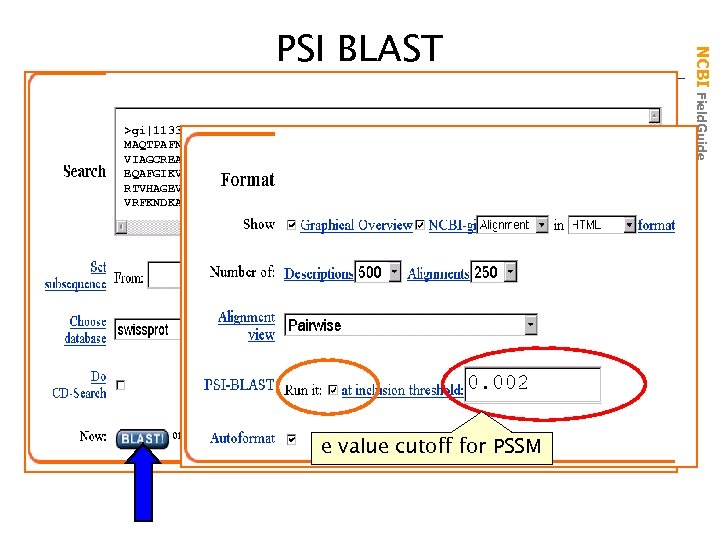
>gi|113340|sp|P 03958|ADA_MOUSE ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (ADENOSINE AMINOH MAQTPAFNKPKVELHVHLDGAIKPETILYFGKKRGIALPADTVEELRNIIGMDKPLSLPGFLAKFDYY VIAGCREAIKRIAYEFVEMKAKEGVVYVEVRYSPHLLANSKVDPMPWNQTEGDVTPDDVVDLVNQGLQ EQAFGIKVRSILCCMRHQPSWSLEVLELCKKYNQKTVVAMDLAGDETIEGSSLFPGHVEAYEGAVKNG RTVHAGEVGSPEVVREAVDILKTERVGHGYHTIEDEALYNRLLKENMHFEVCPWSSYLTGAWDPKTTH VRFKNDKANYSLNTDDPLIFKSTLDTDYQMTKKDMGFTEEEFKRLNINAAKSSFLPEEEKKELLERLY e value cutoff for PSSM NCBI Field. Guide PSI BLAST
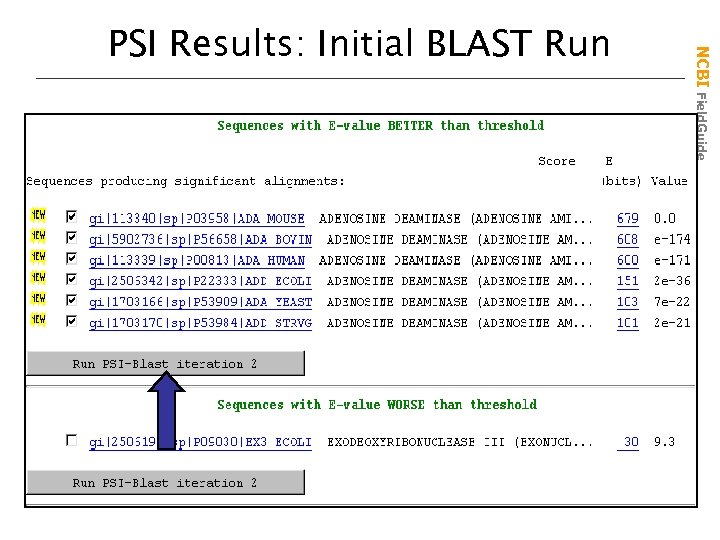
NCBI Field. Guide PSI Results: Initial BLAST Run
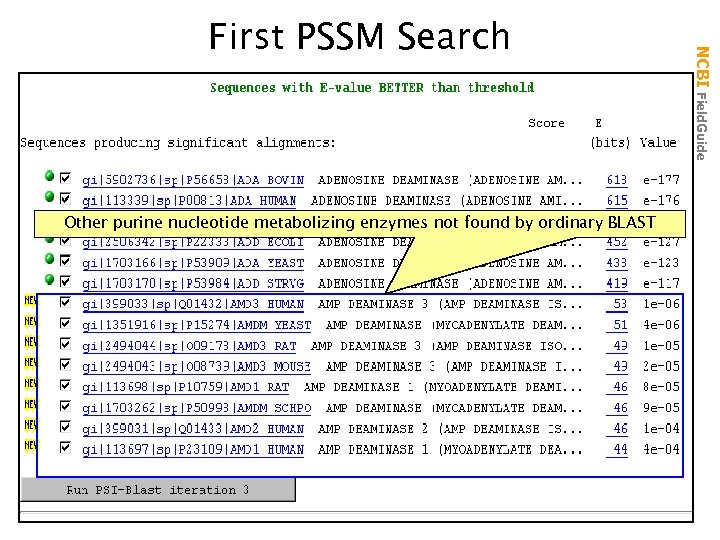
Other purine nucleotide metabolizing enzymes not found by ordinary BLAST NCBI Field. Guide First PSSM Search
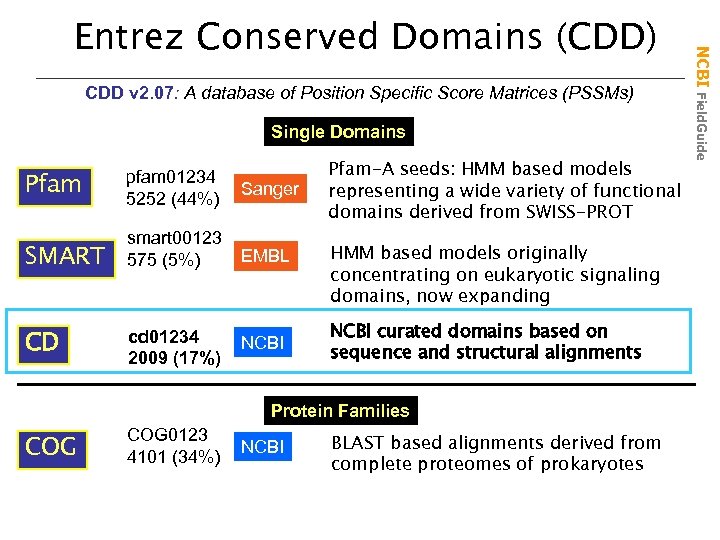
CDD v 2. 07: A database of Position Specific Score Matrices (PSSMs) Single Domains Pfam pfam 01234 5252 (44%) Sanger SMART smart 00123 575 (5%) EMBL CD cd 01234 2009 (17%) NCBI Pfam-A seeds: HMM based models representing a wide variety of functional domains derived from SWISS-PROT HMM based models originally concentrating on eukaryotic signaling domains, now expanding NCBI curated domains based on sequence and structural alignments Protein Families COG 0123 4101 (34%) NCBI BLAST based alignments derived from complete proteomes of prokaryotes NCBI Field. Guide Entrez Conserved Domains (CDD)
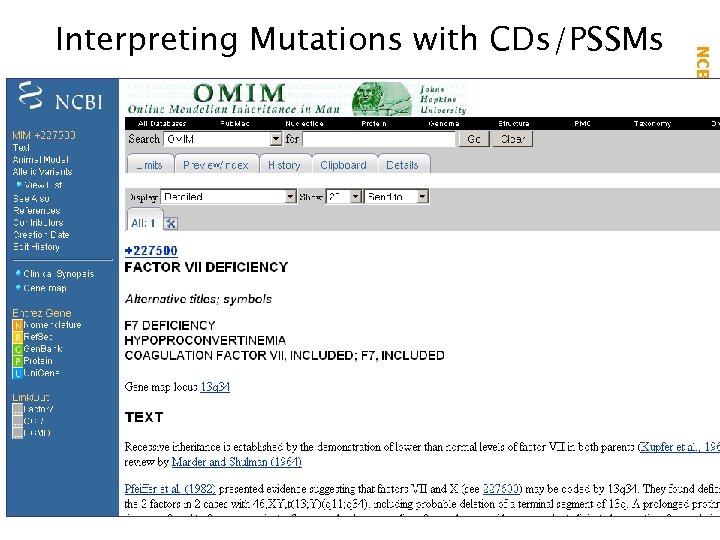
NCBI Field. Guide Interpreting Mutations with CDs/PSSMs

NCBI Field. Guide Allelic Variants in F 7
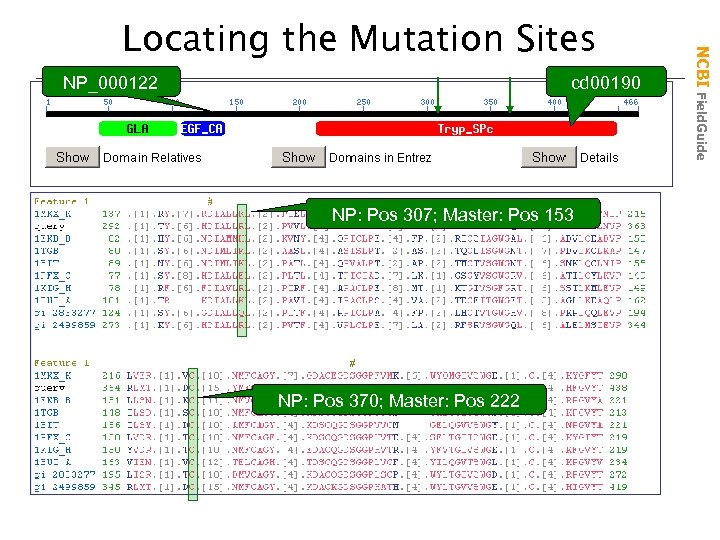
NP_000122 cd 00190 NP: Pos 307; Master: Pos 153 NP: Pos 370; Master: Pos 222 NCBI Field. Guide Locating the Mutation Sites
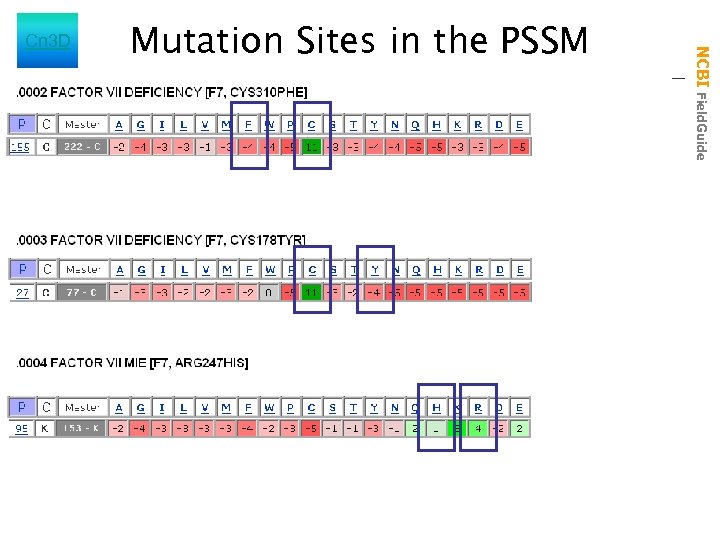
Mutation Sites in the PSSM NCBI Field. Guide Cn 3 D
81b022b0b5f70349412ed932c90be266.ppt