3db3ae69273444381a01ae3d2a427ecc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
NC State Government • 3 Branches and a Declaration of Rights

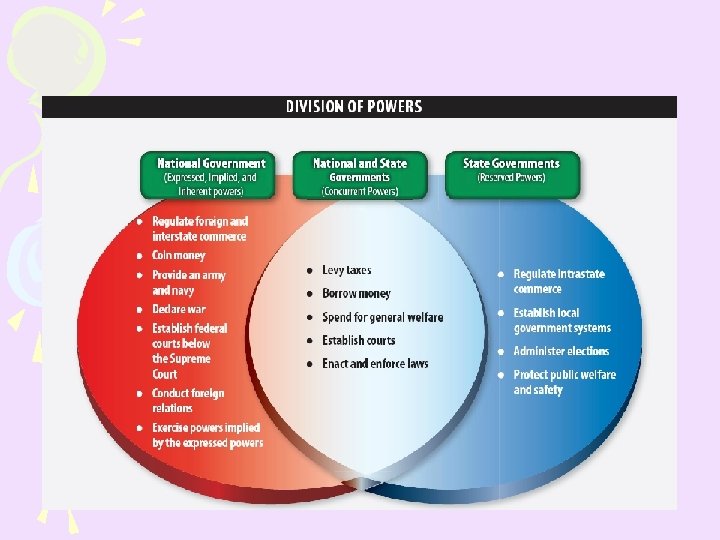
-Federalism- • Powers shared between the national and state governments • These powers are listed below: -ENumerated Powers: • National gov’t powers -Re. Served Powers- • State powers -CONcurrent Powers- shared by both. . . -Supremacy Clause-ntl law and st law conflict. . . National is supreme! -State Constitutions-yes, we have one -Federal-State Cooperation-must work together to have order and protection of citizens!
State Executive Branch -Governor– (P) • 4 year term • 2 consecutive term limit • at least 30 years old -Lieutenant Governor (VP) • must meet same requirements • In place to take over if need be • Few duties • ** preside over state senate • Some states the Lt. Governor and Gov run as a team
State Executive Branch -Same Roles as President • Executive • Most Important role • Responsible for carrying out laws of the state • Legislative • State’s chief legislator • Gets to play a part in the Legislative process • Suggest new bills • Try to persuade the Gen. Assembly to pass them • Power to veto • Commander in chief • In charge of National Guard (State militia) • Party • Leads the political party in the state • Judicial • Offers pardons, reprieves, grants paroles • State • Chief of State • Ceremonial • Greets important visitors • Represents the state

Examples: • Sec of State- manage elections • Attorney General- represents the state in lawsuits. Gives legal advice to governor, state agencies and L branch State Executive Branch -State Executive Departments and Agencies • Treasurer- collects taxes, invests state funds • Governors have a cabinet (like the pres) • Dept of Public Works- responsible for building and maintaining roads, bridges, public buildings. . . • Top officials in charge of executive departments for state • Some are elected/some are appointed -10 major Executive Departments(appointed) -8 Council of State Departments(elected)
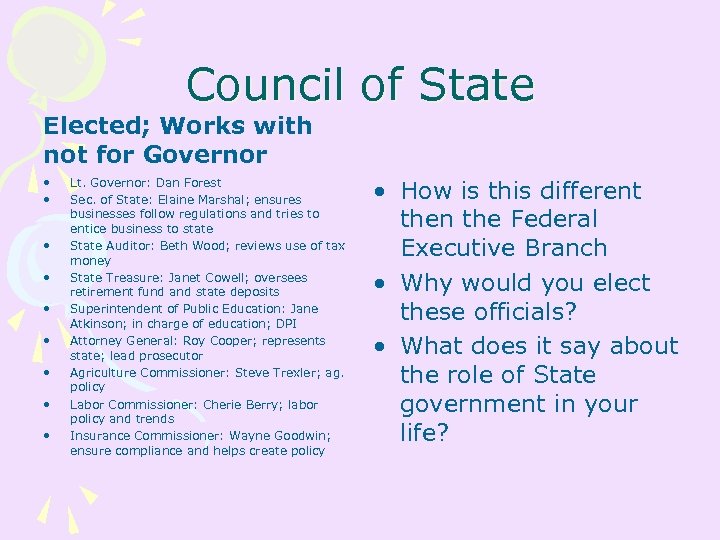
Council of State Elected; Works with not for Governor • • • Lt. Governor: Dan Forest Sec. of State: Elaine Marshal; ensures businesses follow regulations and tries to entice business to state State Auditor: Beth Wood; reviews use of tax money State Treasure: Janet Cowell; oversees retirement fund and state deposits Superintendent of Public Education: Jane Atkinson; in charge of education; DPI Attorney General: Roy Cooper; represents state; lead prosecutor Agriculture Commissioner: Steve Trexler; ag. policy Labor Commissioner: Cherie Berry; labor policy and trends Insurance Commissioner: Wayne Goodwin; ensure compliance and helps create policy • How is this different then the Federal Executive Branch • Why would you elect these officials? • What does it say about the role of State government in your life?
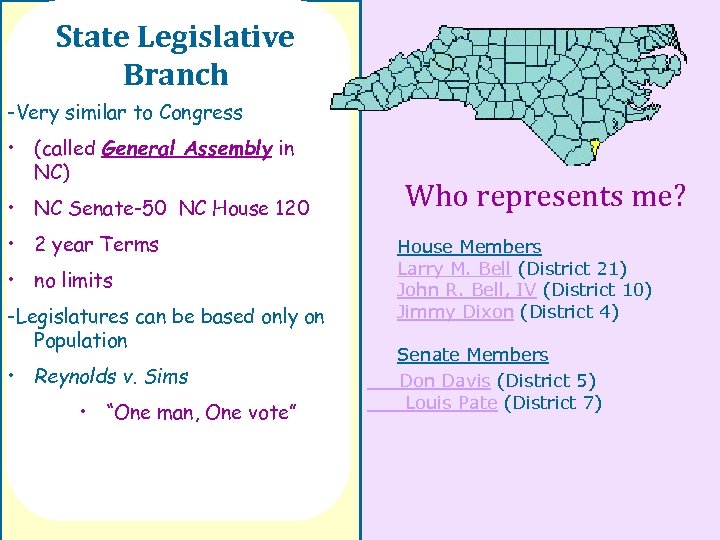
State Legislative Branch -Very similar to Congress • (called General Assembly in NC) • NC Senate-50 NC House 120 • 2 year Terms • no limits -Legislatures can be based only on Population • Reynolds v. Sims • “One man, One vote” Who represents me? House Members Larry M. Bell (District 21) John R. Bell, IV (District 10) Jimmy Dixon (District 4) Senate Members Don Davis (District 5) Louis Pate (District 7)

What the heck is a Gift List? • This "No Gifts List" is maintained for Members who indicate their desire that no gift items be delivered to their offices located in the Legislative Building or Legislative Office Building. Currently gifts from lobbyist or lobbyist principals will now be covered in the new ethics law – • G. S. 138 A-32 (c) No public servant, legislator, or legislative employee shall knowingly accept a gift, directly or indirectly, from a lobbyist or lobbyist principal as defined in G. S. 120 C-100.

Committee System • Similar system • For Full list: http: //www. ncleg. net/gascripts/Committe es/Committees. asp • Speaker of House: Thom Thillis • Leadership system same as Fed.
State Legislative Branch -State Congressmen/women varying requirements, full time job NC House-21, NC Senate 25 -Law Passing Process very similar to Congress -Budget Problems are greatest concerns -Leandro case involving school funding(1995) Is there a baseline level of education to which all children in North Carolina are constitutionally entitled, and if so, what is it? Who is responsible for providing this baseline level of education? and Upon answering the former two questions, what are the parameters that the constitutionally responsible party must respect in providing the baseline level of education? • p. 652

Leandro v. State of NC • **The constitution does not require equal funding but requires that every child have an opportunity to receive a sound basic education.
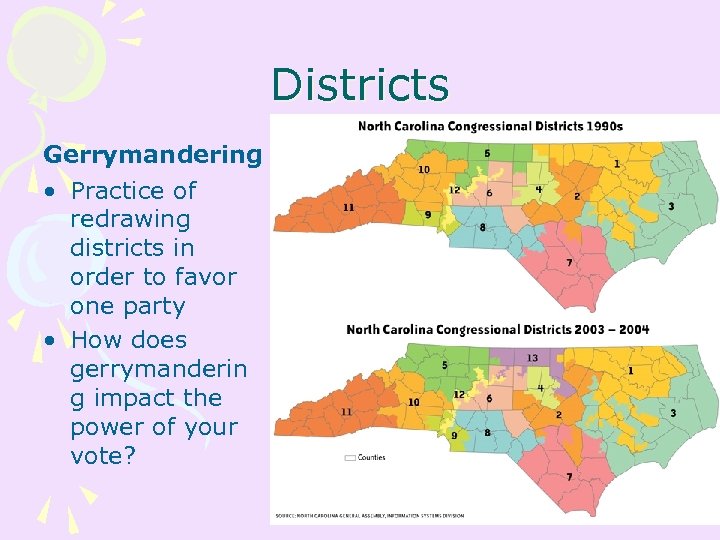
Districts Gerrymandering • Practice of redrawing districts in order to favor one party • How does gerrymanderin g impact the power of your vote?

State Judicial Branch -State Courts handle all cases not given to federal jurisdiction, which is most all cases -Most state judges are elected officials -elected in non-partisan elections -debate over election process • Some people feel that judges who must run campaigns may be too concerned about the effect of their rulings on the public. • More people pleasing than administering the law impartially! Judges can be removed from office by impeachment or committee votes or state supreme court can suspend or remove judge!
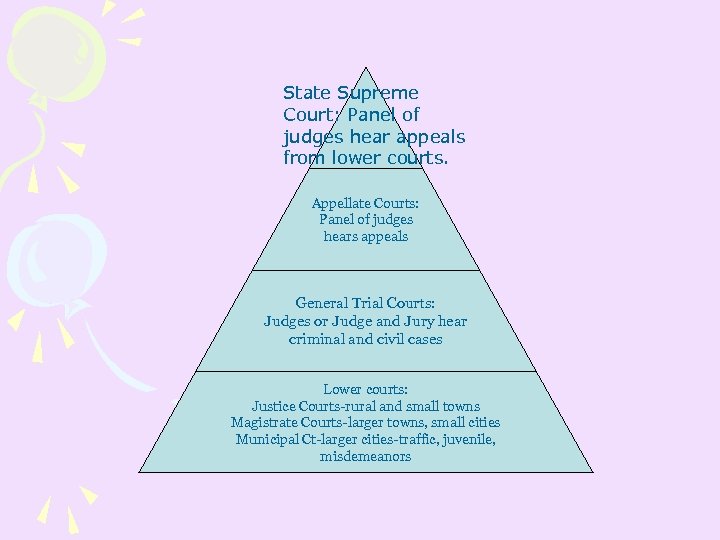
State Supreme Court: Panel of judges hear appeals from lower courts. Appellate Courts: Panel of judges hears appeals General Trial Courts: Judges or Judge and Jury hear criminal and civil cases Lower courts: Justice Courts-rural and small towns Magistrate Courts-larger towns, small cities Municipal Ct-larger cities-traffic, juvenile, misdemeanors

http: //www. nccourts. org/ State Judicial Branch -Lower State Courts– misdemeanor cases, family law and small civil suits—judge only -Higher State Courts– felony cases, large civil suits—jury trials -trial courts, county court, district court -Appellate Courts -State Supreme Courts
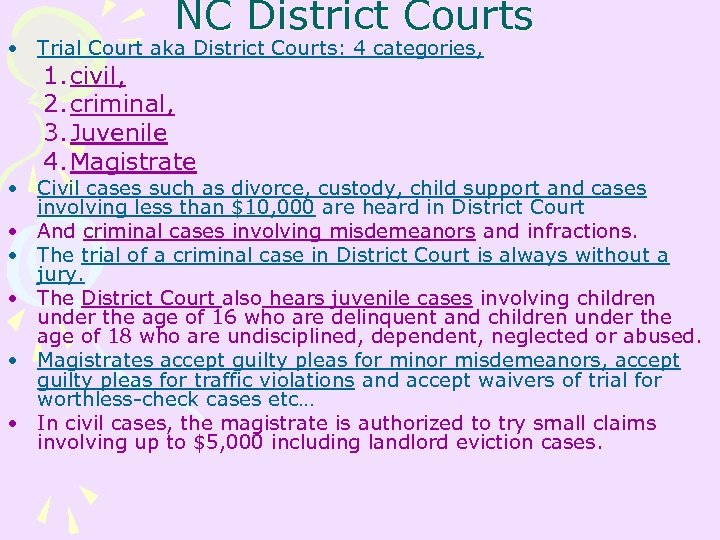
NC District Courts • Trial Court aka District Courts: 4 categories, 1. civil, 2. criminal, 3. Juvenile 4. Magistrate • Civil cases such as divorce, custody, child support and cases involving less than $10, 000 are heard in District Court • And criminal cases involving misdemeanors and infractions. • The trial of a criminal case in District Court is always without a jury. • The District Court also hears juvenile cases involving children under the age of 16 who are delinquent and children under the age of 18 who are undisciplined, dependent, neglected or abused. • Magistrates accept guilty pleas for minor misdemeanors, accept guilty pleas for traffic violations and accept waivers of trial for worthless-check cases etc… • In civil cases, the magistrate is authorized to try small claims involving up to $5, 000 including landlord eviction cases.

Court of Appeals of NC • The Court of Appeals is this state’s only intermediate appellate court. • 15 judges sit in rotating panels of 3, deciding only questions of law on every case appealed from the Superior and District courts except death penalty cases. • Appeals can range from a parking ticket case to murder case. • In fiscal year 2003 -2004, more than 1, 750 cases were filed with the Court of Appeals. • Cases in which there is a dissent in the Court of Appeals go to the Supreme Court as well as to those that the Supreme Court accepts for review through petition. • Court of Appeals judges serve eight-year terms

Supreme Court of NC • The Supreme Court of North Carolina is the state's highest court • There is no further appeal in the state from their decisions. • This court has a chief justice and six associate justices who sit together as a panel in Raleigh. • The Supreme Court has no jury, and it makes no determination of fact • What does it do? – It considers error in legal procedures or in judicial interpretation of the law.

Questions • Should judges be elected? Why or Why Not. • How are you impacted by state government?
3db3ae69273444381a01ae3d2a427ecc.ppt