4a5e81a014946ecceb6cc9efcfdd9953.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

NBS State Status: The Transition from GOTS to a Collaboratively Developed Solution Session Moderator: Keith Higginbotham, BA - AL NBS IT Manager Presenter: Tina Pippin, RN - AL NBS Surveillance Manager Presenter: Doug Hamaker, MS - TX NBS Coordinator Presenter: Lesliann Helmus, MS - VA NBS Coordinator

Overview of Topics • “Setting the stage” – Define Collaboration – Partners in Collaboration – Maturation of the NBS • Ongoing Collaborative Efforts – – – Business Processes NEDSS Base System (NBS) Alerting Geographic Information System (GIS) Electronic Lab Reports (ELR) Reporting and Analysis

What is Collaboration? • Collaboration is defined as "a process through which parties who see different aspects of a problem [or issue] can constructively explore their differences and search for solutions that go beyond their own limited vision of what is possible" (Gray, 1989, p. 5).

NBS Partners in Collaboration • Bidirectional avenues for Collaboration – States to Federal – State to State – State to Local – Programmatic to Technology

NBS: Maturing from GOTs to a Collaboratively Developed Solution (a State’s Perspective) • Version 1. 0 (10/1/2002) – Version 1. 1. 3 (4/1/2004) – – – • Data collection was very CDC oriented Didn’t contain work process features LDFs/CDFs introduced in version 1. 1. 1 NND Messaging Foodborne PAM 10/27/2005 NEDSS User Group (NUG) formed – 16 NBS States – CDC – CSC (NBS Development Team) • 5/26/2006 Sitescape launched for NUG – Forum for the electronic exchange of information related to the NBS – Knowledge Base that can be searched before entering a Help Desk Ticket – Repository for up-to-date documentation and materials NBS Production Sites (16)

NBS: Maturing from GOTs to Collaboratively Developed Solution (a State’s Perspective) • Version 1. 1. 5 (9/15/2006) – – – Migration to JBoss Application Server Almost entirely focused on State requested enhancements New Data Marts for Reporting Usability enhancements Service packs 1 and 2 • • Version 1. 1. 6 (9/28/2007) – – • Rejected Notifications Queue Data Validation Report Cascading Transfer Ownership Enhancements to “work” queues Additional client-side data validations Enhanced reporting modules Integrated Geocoding for all address information within NBS Version 1. 1. 7 (12/31/2007) – Version 1. 2 (7/31/2008) – New Report Administration Module – Alerting triggered by receipt of Lab Reports NBS Production Sites (16)

Epidemiology Surveillance Then and Now Changes in Business Practice Transition from NETSS to NBS Tina Pippin Alabama Department Public Health August 25, 2008

Bureau of Communicable Disease • • • Tuberculosis (NBS TB PAM Jan 09) Sexually Transmitted Diseases HIV/AIDS Immunization (NBS) Epidemiology (NBS)

Division of Epidemiology • • • Infection Control Toxicology Zoonosis Surveillance Analysis and Reporting

Who’s involved? • Central Office Staff – – 2 Nurses 3 Epidemiologists 1 Public Health Research Analyst 1 Administrative Assistant • Field Staff- 11 Public Health Areas – 1 Public Health Physician – 3 Masters Public Health – 18 Nurses (most have 2 per Area) – 2 Disease Intervention Specialists

NBS-Qualitatively Different Approach to Disease Reporting • Paradigm shift from reporting system based on reportable diseases to a person -based system with features allowing extension of the reporting umbrella to laboratories, clinics, and primary care providers.
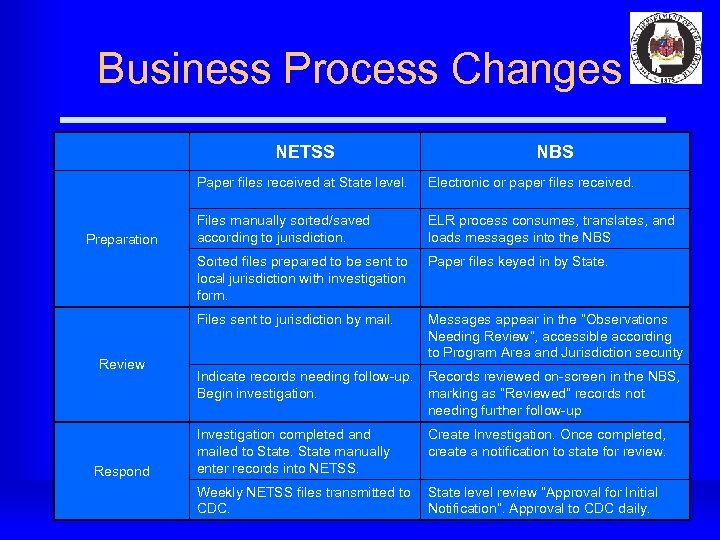
Business Process Changes NETSS NBS Paper files received at State level. Respond ELR process consumes, translates, and loads messages into the NBS Paper files keyed in by State. Files sent to jurisdiction by mail. Review Files manually sorted/saved according to jurisdiction. Sorted files prepared to be sent to local jurisdiction with investigation form. Preparation Electronic or paper files received. Messages appear in the “Observations Needing Review”, accessible according to Program Area and Jurisdiction security Indicate records needing follow-up. Begin investigation. Records reviewed on-screen in the NBS, marking as “Reviewed” records not needing further follow-up Investigation completed and mailed to State manually enter records into NETSS. Create Investigation. Once completed, create a notification to state for review. Weekly NETSS files transmitted to CDC. State level review “Approval for Initial Notification”. Approval to CDC daily.

Benefits of NBS • Timely investigations and interventions • Field Staff able to view patient’s history (chronic hepatitis) • Timely reporting to CDC • Qualitative review of process • Increased involvement of staff

Successful Surveillance Models • Data entry occurring at/near case detection • Change from passive to an active data-use paradigm Requirement 1 Requirement 2 Recommendation 1 Minimum Data Set Reporting Required Fields Case Investigation Fields Data Required For Notification Approval Data Required To Complete Case Forms Complete Case Investigation closure • Supports bi-directional communication opportunities • Timely “Just in Time Training” regarding case definition provided during notification review

Collaboration Projects • • • NEDSS Steering Committee NEDSS Training Additional Layer of Approval Reports for use by field staff Qualitative Review of Business Practices

NEDSS Steering Committee • Collaboration with IT and Epi staff (other staff if indicated) • Met weekly in early phases • Open discussion • Agenda driven

Sample Agenda

NEDSS Training • • Organized by Epi in collaboration with IT Quarterly 2 day training in Central Office Assists IT to learn more regarding field practices • Videos available on NBS for anytime viewing

ALNBS Training Videos

Additional Layer of Approval • Largest volume of cases per county • Need for review process in field • Collaboration Field staff-Epi-IT

Reports for use by field staff • Assists staff in monitoring their data – Laboratory reports marked as reviewed – Potential duplicate investigations – Closed cases without notifications – Open cases without notifications – Disease Incidence Data

Qualitative Review of Business Practices • • • Average Days to Start and Complete Average Days to Mark Lab as Reviewed Data Validation Quick Reference Guide Case Investigation with Rejected Notifications

NEDSS Alerting • • Purpose: To decrease time appropriate public health staff receive notification of an immediately reportable disease and initiate investigation and improve the timeliness of any necessary interventions or public health responses. CDC’s Scope of Work: Develop an automated process to monitor the incoming lab results and morbidity reports in the NBS for specific alertable conditions and generate an automated ALERT to predefined appropriate public health personnel based on condition and jurisdiction. Alabama’s Scope of Work: Develop an interface to integrate our Health Alert Network as the alert delivery tool with the out of the box alerting functionality that the NBS will provide. Future Enhancements • Alerting triggered by receipt of Morbidity Reports • Aberration-based alerting

NBS - HAN Alerting Interface Conceptual Process Model ELR Labcorp Mayo State Lab Medtox Local Surveillance Nurse Text to speech Conversion of ALERT via Phone State EPI PHINMS & s. FTP Internet Authenticated ALNBS Data Entry NBS Event Identification (CDC) ALERT via Email Hospital Staff Mobidity Report (Clinical Diagnosis) Manual Lab Report Alerting (ADPH) Alert Contains: Condition Date Received Jurisdiction Identifier Instructions ALERT – HAN Global Secure’s Response Manager Alerting Web Service API Predefined Alerting Role. Grops Receipt Confirmation Secure Alerting

NBS - HAN Alerting Interface Demonstration

Alabama Public Health GIS Spatial Pattern of Disease Project • • Purpose: to provide spatial and other pertinent information to public health staff, health care providers, and community on disease incidence. This project will provide data helpful in the areas of surveillance, analysis, and response and will serve as a useful tool in our decision making process. Scope: Develop a tool to enable EPI to map reportable disease (investigation) surveillance data from the NEDSS Base System. Technologies Utilized • Google Maps API • Custom AJAX and. NET application • NBS Investigation data (including LDFs) • Centrus Geo. Stan Future Enhancements • Time Progression Modeling • County Rate Maps • Data Export
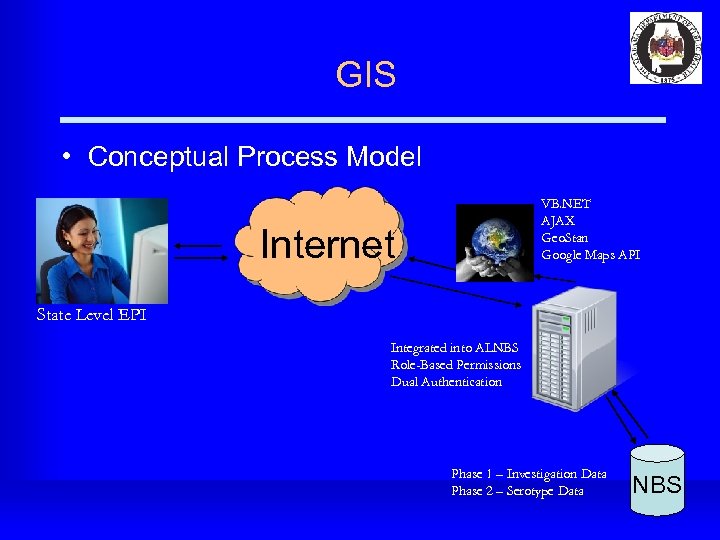
GIS • Conceptual Process Model VB. NET AJAX Geo. Stan Google Maps API Internet State Level EPI Integrated into ALNBS Role-Based Permissions Dual Authentication Phase 1 – Investigation Data Phase 2 – Serotype Data NBS

GIS Demonstration

Opportunities for continued Collaboration • • • NEDSS User Group NBS Consortium Rhapsody – ELR Reports/Data Marts Geo. Stan - GIS
4a5e81a014946ecceb6cc9efcfdd9953.ppt