ce7a8525ca8978624d2b84798b957c81.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

NAZI PROPAGANDA

What is Propaganda • Biased information designed to shape public opinion and behavior • True, partially true, or blatantly false • Selectively omits information • Simplifies complex issues and ideas for mass consumption • Plays on emotions (hopes and dreams) • If your campaigning for office you will not give a whole speech, just a slogan • Not all propaganda works – If you have a radio show, but no one has a radio – you will fail • DOES NOT transform people into mindless robots – Might not agree with Hitler on the Jews, but like his other ideas • All started in World War I

Do Now: Analyze this picture

Analysis • Make him look like a leader • Simple – not a lot to remember • Eye contact • “I” lower case • Out of the darkness comes a new leader • Celebrity Endorsement • Hitler lost, but got 13 million votes (Not bad for someone who just became a citizen and never held political office)
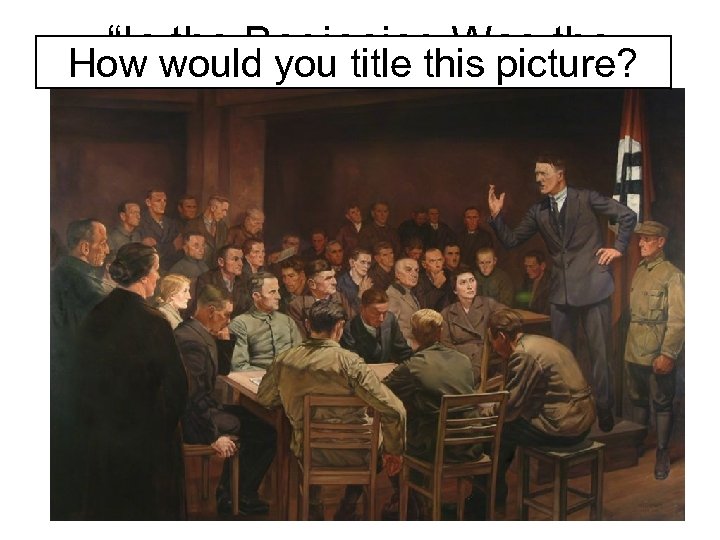

“In the Beginning Was the How would you title this picture? World”

• In the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God. • The same was in the beginning with God. • All things were made by him; and without him was not any thing made that was made • In him was life; and the life was the light of men

What is different about Hitler’s Face? What do you see in the Audience? What does this say about Hitler? Nazi MOVEMENT (Not party) Talk is cheap – but you know its working

Thoughts on Propaganda • “Propaganda must be limited to a very few points and must harp on these in slogans until the last member of the public understands what you want him to understand by your slogan” -Adolf Hitler

The Nazi government was the first to exploit the new technology of radio

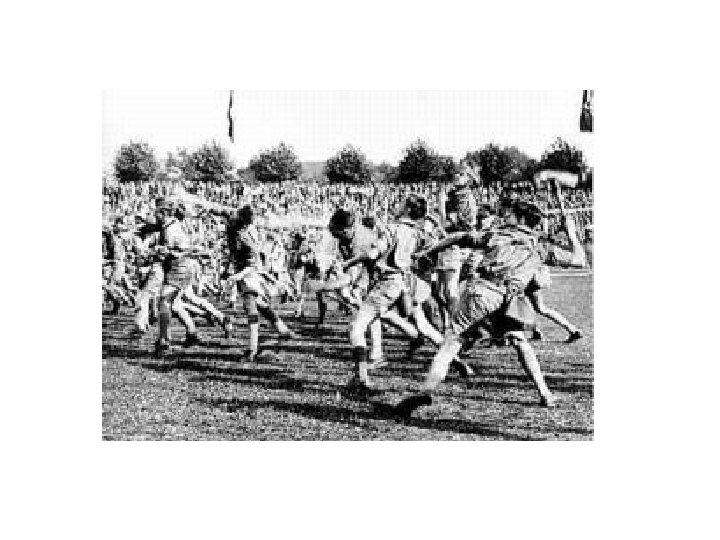
Hitler was a powerful and spellbinding orator! • The Nazis systematically created the cult of the Fuhrer, the great charismatic leader. • At public rallies, Hitler worked himself up to a pitch of near hysteria, and carried his audience with him.

Hitler’s audiences were caught up in emotion that took on the quality of a religious experience Demonstrations were held at night in a sports stadium. Thousands of men carried banners. Torch lights illuminated the stadium, making it seem like a cathedral of light, or a tribal ceremony

Dr. Joseph Goebbels Minister of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda • Ph. D. in Literature and Philosophy – University of Heidelberg. • Controlled the flow of public information through the press, radio and film. • Censored all newspapers.

Nazi propaganda was designed to shape a folk community bonded to its leader. Allegiance to Hitler was direct, personal and absolute; it superseded all other loyalties.

Nazi Propaganda Activity • Get into groups of 3 • Each group will receive 3 pieces of Nazi Propaganda • In your groups analyze each piece and fill out the chart • Be prepared to present your poster (if we have time)

Nazi Propaganda Continued • Julius Streicher was originally a Nazi lawyer who later became one of Germanys chief propagandists. His weekly newspaper, “Der Sturmer”, became the worlds most outspoken anti-Semitic publication. He also wrote children's books, such as the “Poisonous Mushroom”, for use in German schools. His literature was considered so vile that after the war he was convicted of crimes against humanity and sentenced to death. • We will now take a look at his “work” so you can know what type of person Julius Streicher was.

• The following cartoons are taken from “Der Sturmer”. • Analyze the following and answer the questions. – 1. What is the image intended to portray? – 2. How might this increase or reinforce anti. Semitism? The Golden Calf: All the world is in misery and the Jew only knows one thing, money.

“Buy from the Jews, betray your people. ” How are these Jewish men physically portrayed? “Our people crucified their Christ on the cross, and we do a great business on his birthday. ”
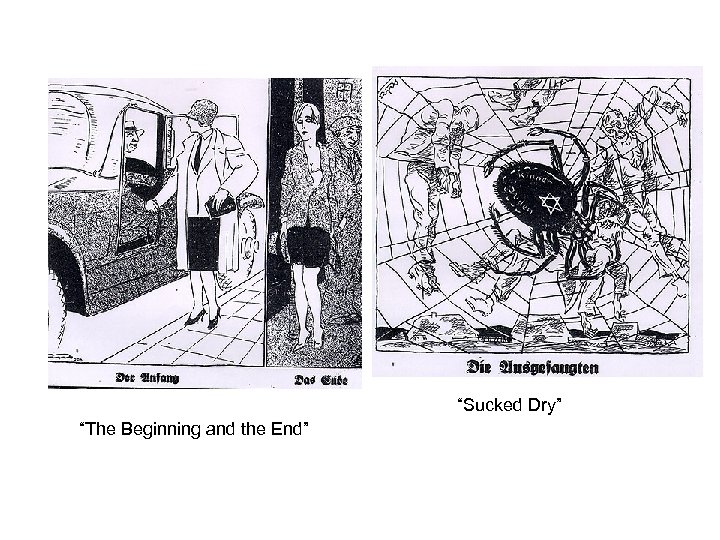
“Sucked Dry” “The Beginning and the End”

The Poisonous Mushroom • • Children’s Book Published by Julius Streicher in 1938 Der Giftpliz for “the toadstool” or “poison mushroom) Text by Ernst Hiemer Illustrated by Philipp Rupprecht

How to tell a Jew

What is a Talmud

The experience of Hans and Else with a strange man

Inge’s Visit to a Jewish Doctor

Propaganda Questions • Critical Thinking: You are an educated person living in Germany who doesn’t believe a word of Nazi propaganda. What effects might this daily bombardment in literature, radio, and film have on you? Do you think you would become a victim of this propaganda over time? • If you could ask the following men one question, what would it be? – Joseph Goebbels – Julius Streicher


The Nazi Olympics and the Jews • The Summer Olympic Games were held in Berlin during 1936. • Hitler wanted to use the games in order to promote both Nazism and his racial philosophy. • Originally Germany wanted to ban both Jewish and African athletes. After many nations threatened to boycott the Olympics over this policy, • Hitler changed his mind allowed them to compete. The Nazis even allowed 1 half Jewish athlete to join the German team.

1936 BERLIN OLYMPICS • Berlin was cleaned up. – Antisemitic billboards and posters were taken down. – The pace of persecution slowed. – Rhetoric of Nazi leaders toned down. – Jesse Owens, 4 Gold Medals, spoiled Hitler’s plans for an “Aryan” triumph. – Reports to FDR, “the synagogues were crowded and apparently there is nothing very wrong. ”

• At first the US Olympic team thought of boycotting the games, but decided to go after most Jewish and African-American athletes were in favor of attending. • The star of the games was US track star Jesse Owens. He won 4 gold medals including the 100 meter dash, beating the German favorite, much to Hitler’s chagrin. • In the end 13 Jewish and 14 African athletes won medals at the games. This includes Helene Mayer the sole Jewish member of the German team.

1938 Man of the Year

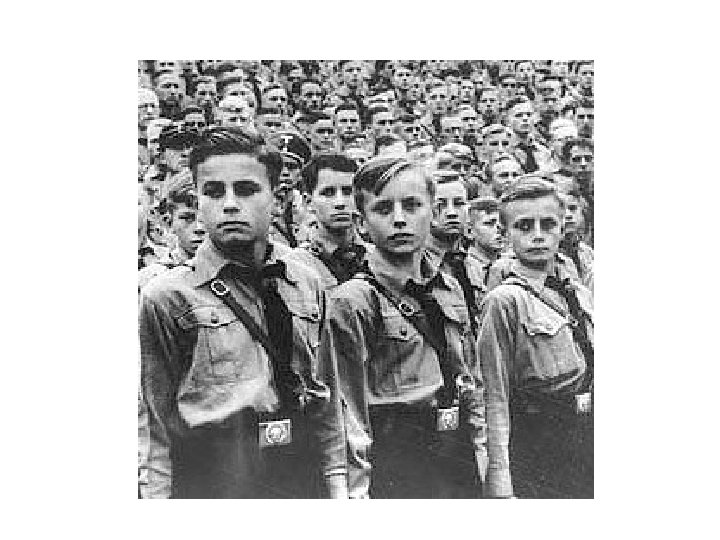
Hitler Youth

“We must develop organizations in which an individual’s entire life can take place. Then every activity and every individual will be regulated by the collectivity represented by the party. There is no longer any arbitrary will, there are no longer any free realms in which the individual belongs to himself … The time of personal happiness is over. ” -Hitler

- Hitler knew the minds of children could be shaped like clay. "If an adult says 'I will not come over to your side' I will calmly answer 'your child belongs to us already. ' What are you? You will pass on!"

- The “Big Father” - He took over their upbringing, education and leisure time - He warned parents that interference or failure to cooperate would result in imprisonment or having their children sent to other Nazi homes to be reared.

Hitler Youth • • As important as school High expectations: – “The weak must be chiselled away. I want young men and women who can suffer pain. A young German must be as swift as a greyhound, as tough as leather, and as hard as Krupp's steel. ” Method of Control A Preparation – Boys: Military – Girls: Motherhood



Modeled what German Girls must be



A Typical School Scene in Nazi Germany - At the front of the class, a picture of Hitler. - Salute the picture at least 10 times a day - Lunch: Prayer to the “Fueher” thanking him for the food - Teachers had to swear to make students into Nazis (under oath). “MEIN KAMPF”

Youth Groups Hitler Youth – boys 6 – 18 - After 1936, all boys had to be a part of the organization. - They attended military camps trained to be soldiers, studied the Nazi philosophy and swore an oath to Hitler. - "Blood and Honour" upon graduation and a diploma from the Hitler youth - Breeding ground for future SS members

League of German Maidens - girls 10 -18 - They wore uniforms, went backpacking on long marches and learned survival techniques. -“Proper Nazi mothers” “It is your duty to bear children for the fatherlands! The Fueher wills it! Marriage is unimportant'“ - As a result many young teenagers became mothers
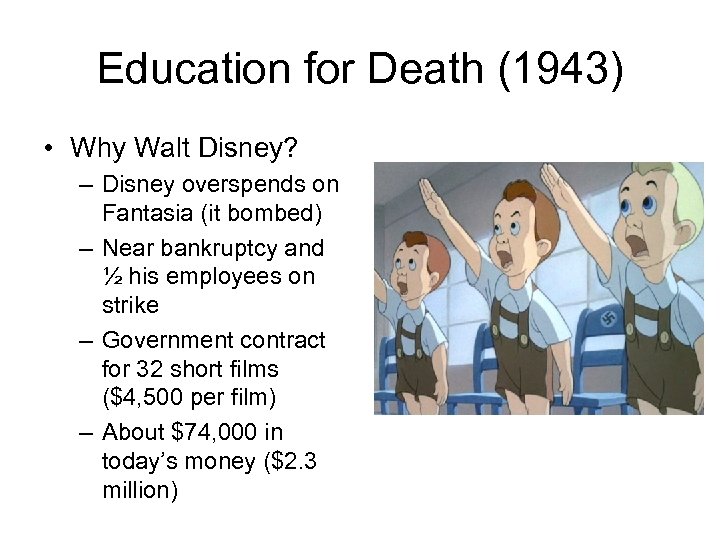
Education for Death (1943) • Why Walt Disney? – Disney overspends on Fantasia (it bombed) – Near bankruptcy and ½ his employees on strike – Government contract for 32 short films ($4, 500 per film) – About $74, 000 in today’s money ($2. 3 million)
ce7a8525ca8978624d2b84798b957c81.ppt