8847aa0b2c8dc07b49d9da75a9b95fd2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Natural Resources, the Environment and Agriculture Chapter 10
Natural Resources, the Environment and Agriculture Chapter 10
 Topics of Discussion üAgriculture and the environment üEconomics of resources in agriculture üGovernment policies for agriculture, natural resourcs, and the environment
Topics of Discussion üAgriculture and the environment üEconomics of resources in agriculture üGovernment policies for agriculture, natural resourcs, and the environment
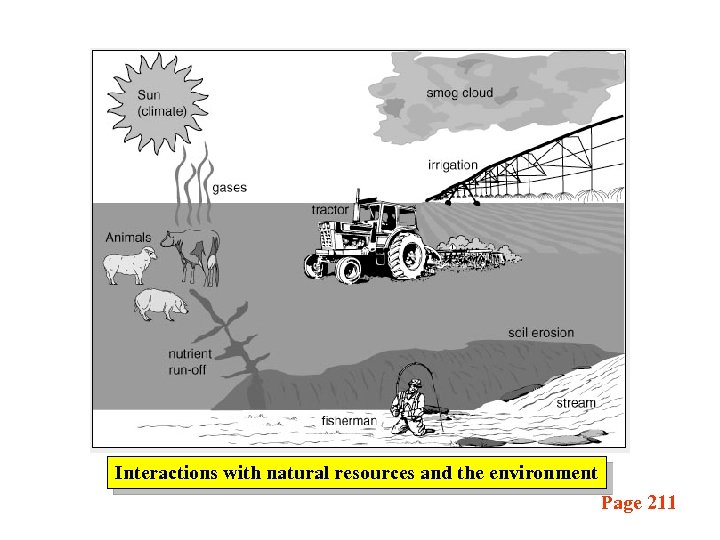 Interactions with natural resources and the environment Page 211
Interactions with natural resources and the environment Page 211
 Environmental and Natural Resources üNatural resources are part of the environment üEnvironment is a natural resource üEnvironmental Economics üRefers to the study of flows, such as pollution, that affect others üNatural Resource Economics üThe study of natural assets that are valued for their productive capacity Pages 211 -212
Environmental and Natural Resources üNatural resources are part of the environment üEnvironment is a natural resource üEnvironmental Economics üRefers to the study of flows, such as pollution, that affect others üNatural Resource Economics üThe study of natural assets that are valued for their productive capacity Pages 211 -212
 Agriculture and the Environment üWater pollution üAir pollution üGlobal warming üOther environmental impacts Pages 212 -216
Agriculture and the Environment üWater pollution üAir pollution üGlobal warming üOther environmental impacts Pages 212 -216
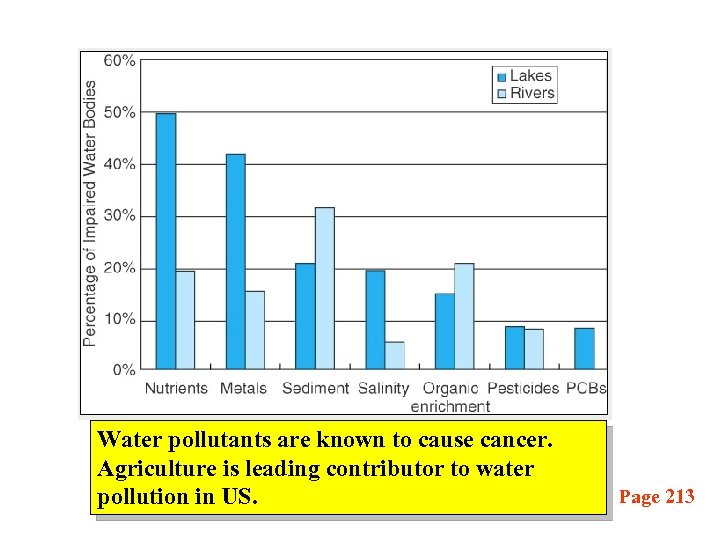 Water pollutants are known to cause cancer. Agriculture is leading contributor to water pollution in US. Page 213
Water pollutants are known to cause cancer. Agriculture is leading contributor to water pollution in US. Page 213
 What are PCBs? • Polychlorinated Biphenyl - a synthetic, organic chemical once widely used in electrical equipment, specialized hydraulic systems, heat transfer systems, and other industrial products. Highly toxic and a potent carcinogen • PCBs were a common industrial discharge up around the 1980 s and they are now a huge problem. • Some companies paying billions of dollars to deal with these nasties
What are PCBs? • Polychlorinated Biphenyl - a synthetic, organic chemical once widely used in electrical equipment, specialized hydraulic systems, heat transfer systems, and other industrial products. Highly toxic and a potent carcinogen • PCBs were a common industrial discharge up around the 1980 s and they are now a huge problem. • Some companies paying billions of dollars to deal with these nasties

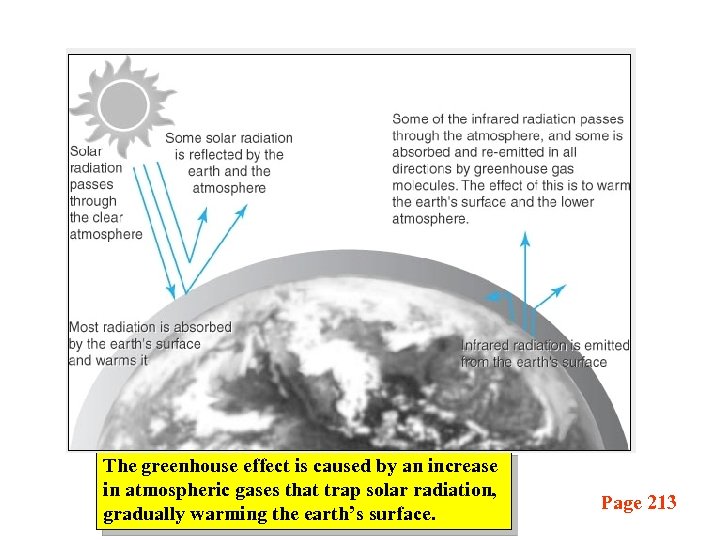 The greenhouse effect is caused by an increase in atmospheric gases that trap solar radiation, gradually warming the earth’s surface. Page 213
The greenhouse effect is caused by an increase in atmospheric gases that trap solar radiation, gradually warming the earth’s surface. Page 213
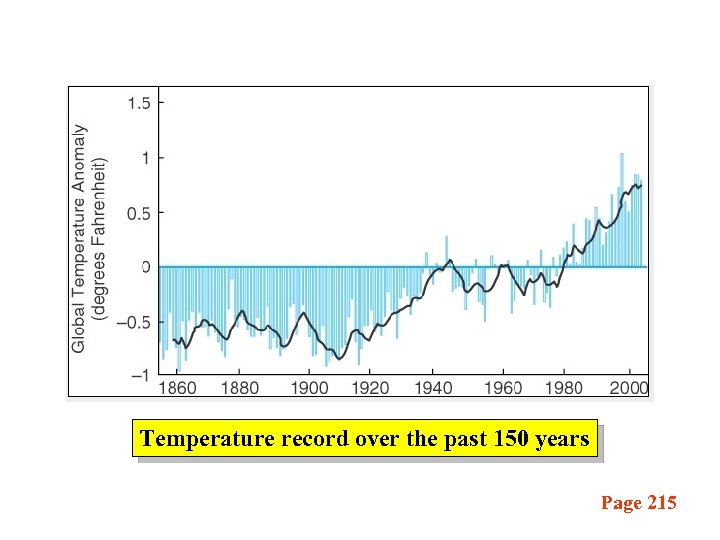 Temperature record over the past 150 years Page 215
Temperature record over the past 150 years Page 215
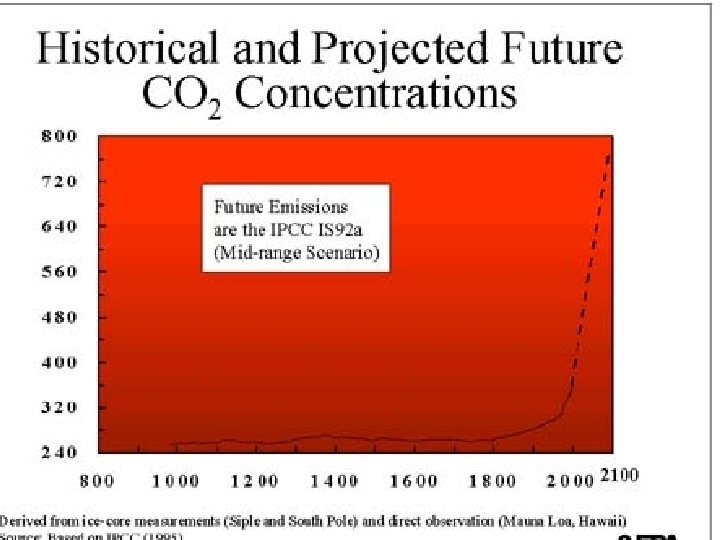
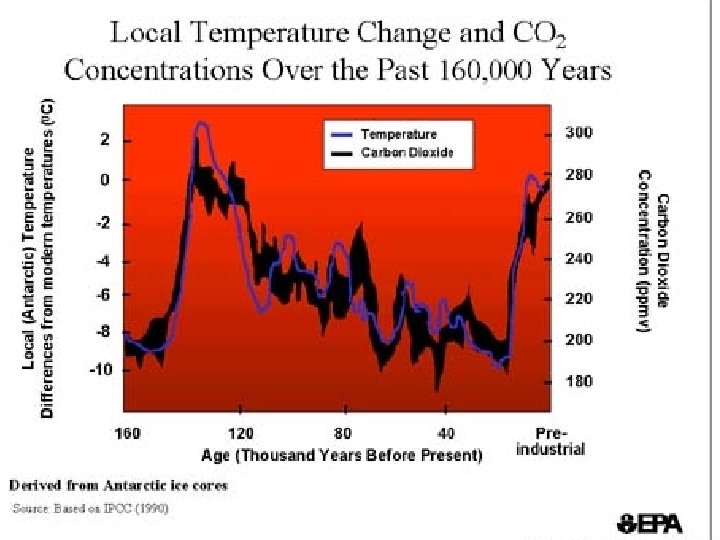
 The latest science • National Academy of Sciences, “the warming trend in the global mean surface temperature observations during the past 20 years is undoubtedly real and is substantially greater than the average rate of warming in the 20 th century. ”
The latest science • National Academy of Sciences, “the warming trend in the global mean surface temperature observations during the past 20 years is undoubtedly real and is substantially greater than the average rate of warming in the 20 th century. ”
 • August 17, 2000 • “ 10 Arctic scientists have reviewed nearly 40 years of polar research… Their new survey paints a picture broadly consistent with climate-model forecasts. • Mark Serreze, the survey's lead author: "Now, I'm definitely leaning very hard toward accepting the notion, although I haven't toppled yet. "
• August 17, 2000 • “ 10 Arctic scientists have reviewed nearly 40 years of polar research… Their new survey paints a picture broadly consistent with climate-model forecasts. • Mark Serreze, the survey's lead author: "Now, I'm definitely leaning very hard toward accepting the notion, although I haven't toppled yet. "
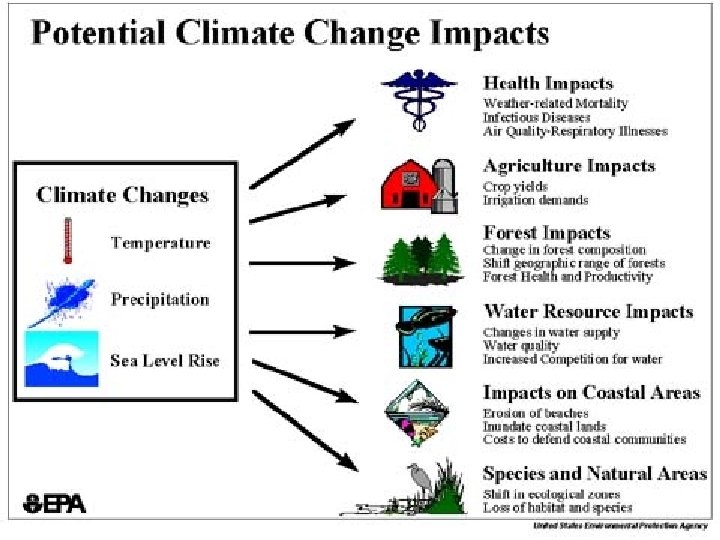
 Other Environmental Issues • Odor – Can be a health hazard – Can depress nearby property values • Endangering plant and animal species – Endangered Species Act (ESA) – Agriculture is one of many forces that can threaten species by encroaching on or contaminating their habitat • Open spaces and traditional landscape – Other people move to these areas and pay premium prices for lots surrounded by farms and/or open spaces
Other Environmental Issues • Odor – Can be a health hazard – Can depress nearby property values • Endangering plant and animal species – Endangered Species Act (ESA) – Agriculture is one of many forces that can threaten species by encroaching on or contaminating their habitat • Open spaces and traditional landscape – Other people move to these areas and pay premium prices for lots surrounded by farms and/or open spaces
 Economics of the Environment • Does the environment has value? • Demand supply for environmental improvements • WTP – willingness to pay to decrease or abate pollution
Economics of the Environment • Does the environment has value? • Demand supply for environmental improvements • WTP – willingness to pay to decrease or abate pollution
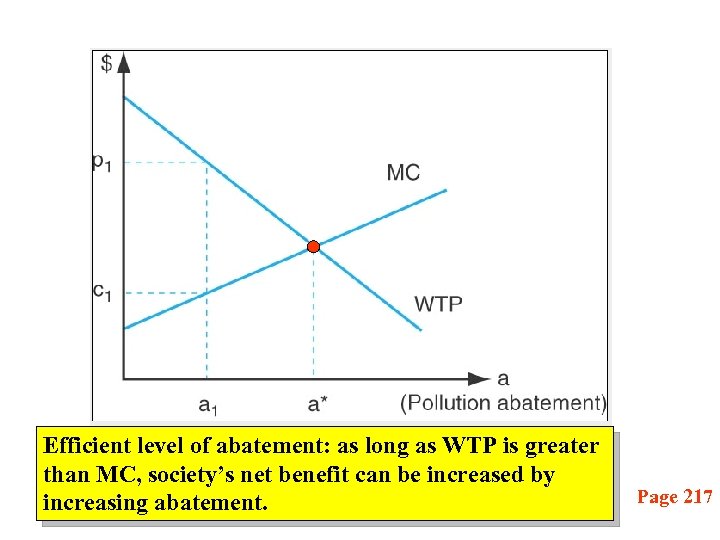 Efficient level of abatement: as long as WTP is greater than MC, society’s net benefit can be increased by increasing abatement. Page 217
Efficient level of abatement: as long as WTP is greater than MC, society’s net benefit can be increased by increasing abatement. Page 217
 So will a market actually arise for environmental improvements leading to a socially optimal outcome? Unfortunately, the answer is no since the characteristics of efficient property rights usually are not satisfied for environmental goods. Property Rights – privileges and limitations that are associated with the ownership of a resource.
So will a market actually arise for environmental improvements leading to a socially optimal outcome? Unfortunately, the answer is no since the characteristics of efficient property rights usually are not satisfied for environmental goods. Property Rights – privileges and limitations that are associated with the ownership of a resource.
 Efficient Property Rights ü Enforceability: security of individual rights üWithout this, no one would buy a good because it can taken away from them without permission. ü Transferability: can be transferred from one individual to another üWithout this, no market can arise because their sale is not allowed. ü Exclusivity: all associated benefits and costs are received by only the owner of the asset üExternalities – consequences of the use or ownership of a resource that befall someone other than the owner üE. g. , farmers do not pay the cost that might be imposed on downstream anglers due to declining water quality.
Efficient Property Rights ü Enforceability: security of individual rights üWithout this, no one would buy a good because it can taken away from them without permission. ü Transferability: can be transferred from one individual to another üWithout this, no market can arise because their sale is not allowed. ü Exclusivity: all associated benefits and costs are received by only the owner of the asset üExternalities – consequences of the use or ownership of a resource that befall someone other than the owner üE. g. , farmers do not pay the cost that might be imposed on downstream anglers due to declining water quality.
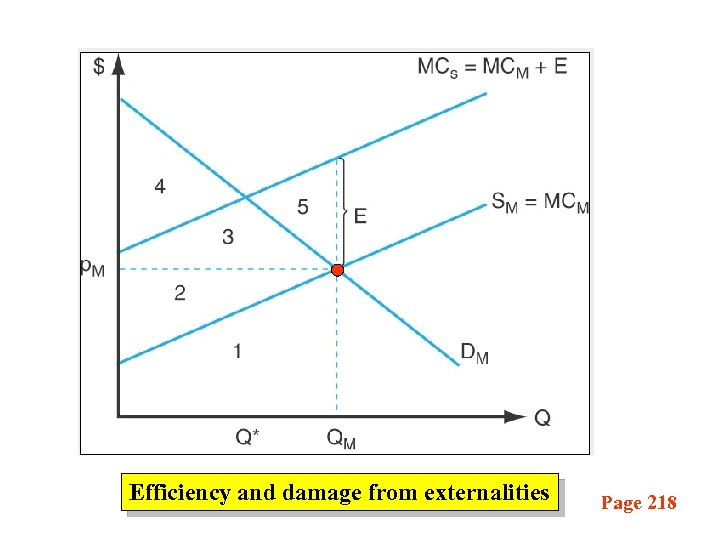 Efficiency and damage from externalities Page 218
Efficiency and damage from externalities Page 218
 Figure Explanation • Assume producing at Qm also causes pollution • Neither producers nor consumers of good take these into account – external to the market • Social MC = MCs = MCm+E • additional cost at Qm= Qm x E = 2+3+5 • Net social benefits = (2+3+4) – (2+3+5) = 4 -5 • So net social benefits could be increased by supplying less of Q • So with presence of externality - the free market will not achieve the socially efficient level of production
Figure Explanation • Assume producing at Qm also causes pollution • Neither producers nor consumers of good take these into account – external to the market • Social MC = MCs = MCm+E • additional cost at Qm= Qm x E = 2+3+5 • Net social benefits = (2+3+4) – (2+3+5) = 4 -5 • So net social benefits could be increased by supplying less of Q • So with presence of externality - the free market will not achieve the socially efficient level of production
 Cost Effective Environmental Policies • When negative externality exists, the free market will not lead to a socially efficient outcome. • The issue of free-riding (e. g. , fishermen could be organized and pay E to convince farmers to reduce their production; farmers required to pay the fishermen for the right to pollute) • As a result, government is frequently involved when externality problems arise. • Due to difficulty of getting WTP and MC estimates, environmental govt standards are rarely set at socially efficient levels.
Cost Effective Environmental Policies • When negative externality exists, the free market will not lead to a socially efficient outcome. • The issue of free-riding (e. g. , fishermen could be organized and pay E to convince farmers to reduce their production; farmers required to pay the fishermen for the right to pollute) • As a result, government is frequently involved when externality problems arise. • Due to difficulty of getting WTP and MC estimates, environmental govt standards are rarely set at socially efficient levels.
 Cost Effective Policies üCommand-Control policies üRegulations on technology or restrictions on practices üDoes not take into account heterogeneity of polluters üTaxes and subsidies üTax on pollution or subsidy for abatement üTransferable rights üRights to pollute can be bought and sold by polluters, moving the permits to pollute to those firms for which abatement is most expensive üGovernment can control overall level of pollution and leave the allocation up to the market
Cost Effective Policies üCommand-Control policies üRegulations on technology or restrictions on practices üDoes not take into account heterogeneity of polluters üTaxes and subsidies üTax on pollution or subsidy for abatement üTransferable rights üRights to pollute can be bought and sold by polluters, moving the permits to pollute to those firms for which abatement is most expensive üGovernment can control overall level of pollution and leave the allocation up to the market
 Summary ü Economists play a role in designing policies that affect the environment and natural resources. ü Incentives matter when designing policies to achieve desired objectives. ü Agriculture impacts the environment through water pollution, air pollution, global warming among other ways. ü Government plays an active role in guiding and regulating the use of resources and impact on environment.
Summary ü Economists play a role in designing policies that affect the environment and natural resources. ü Incentives matter when designing policies to achieve desired objectives. ü Agriculture impacts the environment through water pollution, air pollution, global warming among other ways. ü Government plays an active role in guiding and regulating the use of resources and impact on environment.
 Chapter 11 discusses other forms of governmental intervention, including price and income supports…
Chapter 11 discusses other forms of governmental intervention, including price and income supports…


