Natural hazards, Generalova A..pptx
- Количество слайдов: 27

Natural hazards Generalova A. , EPb - 131
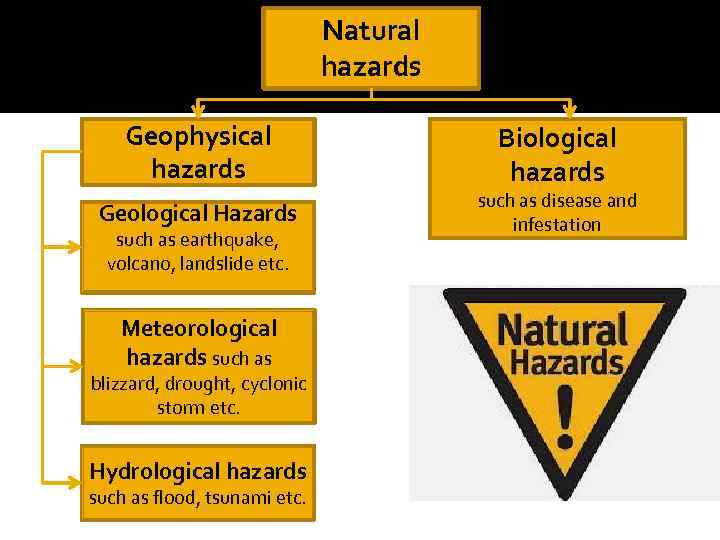
Natural hazards Geophysical hazards Geological Hazards such as earthquake, volcano, landslide etc. Meteorological hazards such as blizzard, drought, cyclonic storm etc. Hydrological hazards such as flood, tsunami etc. Biological hazards such as disease and infestation
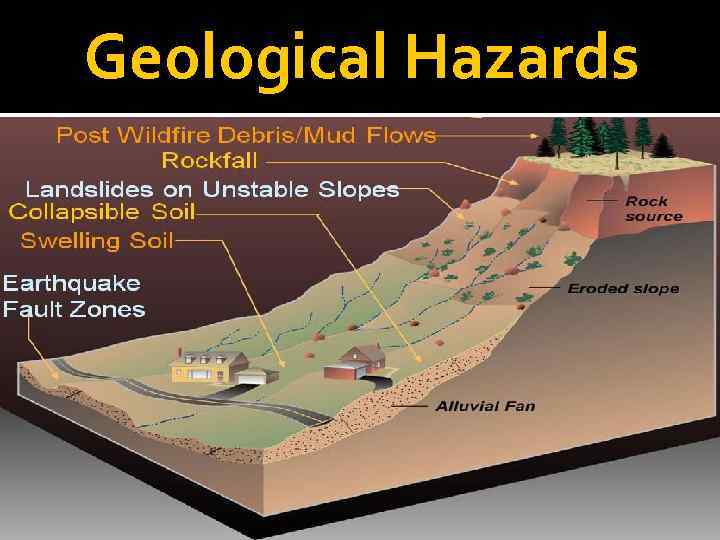
Geological Hazards

Avalanche An avalanche occurs when a large snow (or rock) mass slides down a mountainside.

Earthquake An earthquake is a phenomenon that results from a sudden release of stored energy that radiates seismic waves.

Landslide A landslide is a type of avalanche consisting of materials such as rock, slag or coal.

Volcanic eruption Volcanoes happen where the earth’s crust is thin - lava, dust and gases burst out (erupt) from beneath the earth.

Mudslide A mudslide — also called mudflow — is a flow of dirt and debris that occurs after intense rainfall or snow melt, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and severe wildfires.

Coastal Erosion Coastal erosion is a physical process by which shorelines in coastal areas around the world shift and change, primarily in response to waves and currents that can be influenced by tides and storm surge.

Meteorological hazards

Blizzard A blizzard is a severe winter storm icy and windy conditions characterized by low temperature, strong wind and heavy snow.

Drought Scientists warn that global warming and climate change may result in more extensive droughts in coming years.

Hailstorm A hailstorm is a natural hazard where a thunderstorm produces numerous hailstones which damage the location in which they fall.

Heat wave A heat wave is a hazard characterized by heat which is considered extreme and unusual in the area in which it occurs.

Cyclonic storm Hurricane, tropical cyclone, and typhoon are different names for the same phenomenon: a cyclonic storm system that forms over the oceans.


Ice storm An ice storm is a particular weather event in which precipitation falls as ice, due to atmosphere conditions.

Tornado A tornado is a natural disaster resulting from a thunderstorm.

Climate change is a long-term hazard which can increase or decrease the risk of other weather hazards, and also directly endangers property due to sea level rise and biological organisms due to habitat destruction.

Hydrological hazards

Flood is a natural disaster that often occurs as the result of prolonged rainfall in a location.

Maelstrom A maelstrom is a very powerful whirlpool. It is a large, swirling body of water with considerable downdraft.

Tsunami A tsunami also known as a seismic sea wave, is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, generally an ocean or a large lake.

Wildfires Other natural hazards such as wildfires can result from a combination of geological, hydrological, and climatic factors. Wildfire is a fire that burns in an uncontrolled and unplanned manner.

Biological hazards, also known as biohazards, refer to biological substances that pose a threat to the health of living organisms, primarily that of humans.


International campaigns In 2000, the United Nations launched the International Early Warning Programme to address the underlying causes of vulnerability and to build disaster-resilient communities by promoting increased awareness of the importance of Disaster Risk Reduction as an integral component of sustainable development, with the goal of reducing human, economic and environmental losses due to hazards of all kinds. But Natural disasters are often very unpredictable.
Natural hazards, Generalova A..pptx