7ba7a5a930de18bcb34ade9ae6dac946.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 National Source Tracking System (NSTS) Overview Irene Wu U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission March 2017
National Source Tracking System (NSTS) Overview Irene Wu U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission March 2017
 Background • Energy Policy Act of 2005 contains a national source tracking provision, which required the NRC to issue regulations establishing a mandatory tracking system for radiation sources in the United States. • In response to that mandate, the NSTS was developed through close cooperation with other Federal and State agencies. • NSTS meets the U. S. Government's commitment to implement a national source registry, as described in the Code of Conduct on the Safety and Security of Radioactive Sources. 2 National Source Tracking System
Background • Energy Policy Act of 2005 contains a national source tracking provision, which required the NRC to issue regulations establishing a mandatory tracking system for radiation sources in the United States. • In response to that mandate, the NSTS was developed through close cooperation with other Federal and State agencies. • NSTS meets the U. S. Government's commitment to implement a national source registry, as described in the Code of Conduct on the Safety and Security of Radioactive Sources. 2 National Source Tracking System
 Establishing NSTS • Interim database created in 2005 as a precursor to the NSTS to collect an initial inventory of sources containing the materials of greatest concern. This inventory was developed to create a snapshot of licensees, facilities, and the sources they possess. This effort established contact with licensees who would later participate in implementing the NSTS. • NSTS Version 1 was deployed in December 2008. Licensees were required to begin reporting to the system by January 31, 2009. • Version 2 of NSTS became operational in May 2011. Version 2 includes functionality enhancements designed to broaden the system capabilities for all system users. Enhancements for licensees include event-triggered alerts and automated system interfaces. Enhancements for agency users include full reporting and query capabilities and the ability to download data to share with other Federal agencies. 3 National Source Tracking System
Establishing NSTS • Interim database created in 2005 as a precursor to the NSTS to collect an initial inventory of sources containing the materials of greatest concern. This inventory was developed to create a snapshot of licensees, facilities, and the sources they possess. This effort established contact with licensees who would later participate in implementing the NSTS. • NSTS Version 1 was deployed in December 2008. Licensees were required to begin reporting to the system by January 31, 2009. • Version 2 of NSTS became operational in May 2011. Version 2 includes functionality enhancements designed to broaden the system capabilities for all system users. Enhancements for licensees include event-triggered alerts and automated system interfaces. Enhancements for agency users include full reporting and query capabilities and the ability to download data to share with other Federal agencies. 3 National Source Tracking System
 Access to NSTS • In 2006 when the access level was first determined for NSTS, the highest level authentication assurance level (Level 4) was determined to be appropriate for all users of the system. Smart cards and card readers were used to access NSTS. • NRC had anticipated more licensees would apply for online access to NSTS but due to application challenges and transaction frequency, more users preferred to report to NSTS via fax/email. • In 2010, NRC enlisted help from a marketing contractor to improve the online use of NSTS and increase support of the online system from NSTS stakeholders. 4 National Source Tracking System
Access to NSTS • In 2006 when the access level was first determined for NSTS, the highest level authentication assurance level (Level 4) was determined to be appropriate for all users of the system. Smart cards and card readers were used to access NSTS. • NRC had anticipated more licensees would apply for online access to NSTS but due to application challenges and transaction frequency, more users preferred to report to NSTS via fax/email. • In 2010, NRC enlisted help from a marketing contractor to improve the online use of NSTS and increase support of the online system from NSTS stakeholders. 4 National Source Tracking System
 Access to NSTS (continued) • In 2011, the access level of NSTS was reduced for all users (Level 3). One Time Password devices were implemented in 2013. • Applicants have to go through a credentialing process. – Employment verification – Need-to-know determination – Identity proofing • Users have different roles to access NSTS. Licensees are only able to see their inventory information. Regulators are able to see their licensees’ information. 5 National Source Tracking System
Access to NSTS (continued) • In 2011, the access level of NSTS was reduced for all users (Level 3). One Time Password devices were implemented in 2013. • Applicants have to go through a credentialing process. – Employment verification – Need-to-know determination – Identity proofing • Users have different roles to access NSTS. Licensees are only able to see their inventory information. Regulators are able to see their licensees’ information. 5 National Source Tracking System
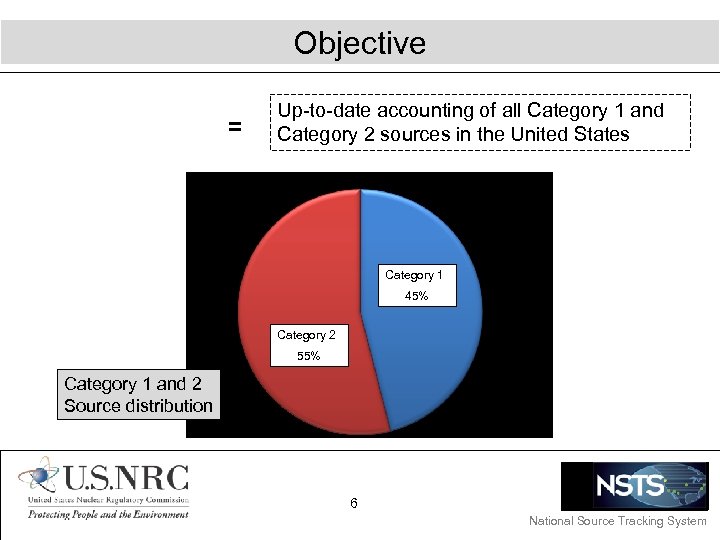 Objective = Up-to-date accounting of all Category 1 and Category 2 sources in the United States Category 1 45% Category 2 55% Category 1 and 2 Source distribution 6 National Source Tracking System
Objective = Up-to-date accounting of all Category 1 and Category 2 sources in the United States Category 1 45% Category 2 55% Category 1 and 2 Source distribution 6 National Source Tracking System
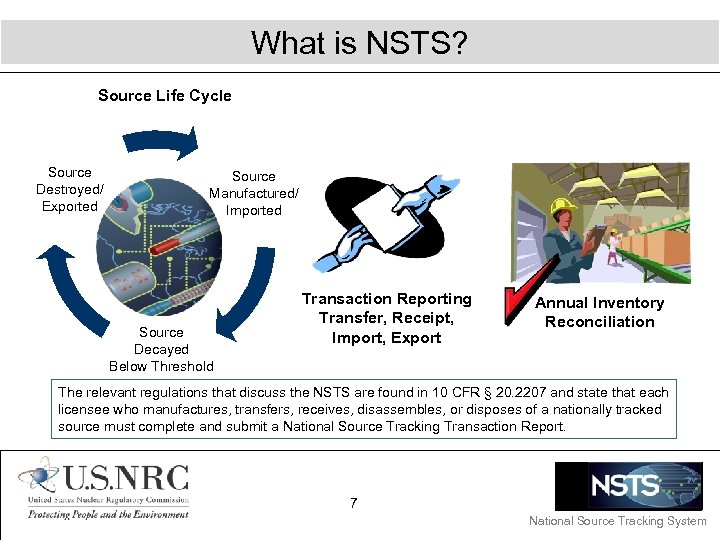 What is NSTS? Source Life Cycle Source Destroyed/ Exported Source Manufactured/ Imported Source Decayed Below Threshold Transaction Reporting Transfer, Receipt, Import, Export Annual Inventory Reconciliation The relevant regulations that discuss the NSTS are found in 10 CFR § 20. 2207 and state that each licensee who manufactures, transfers, receives, disassembles, or disposes of a nationally tracked source must complete and submit a National Source Tracking Transaction Report. 7 National Source Tracking System
What is NSTS? Source Life Cycle Source Destroyed/ Exported Source Manufactured/ Imported Source Decayed Below Threshold Transaction Reporting Transfer, Receipt, Import, Export Annual Inventory Reconciliation The relevant regulations that discuss the NSTS are found in 10 CFR § 20. 2207 and state that each licensee who manufactures, transfers, receives, disassembles, or disposes of a nationally tracked source must complete and submit a National Source Tracking Transaction Report. 7 National Source Tracking System
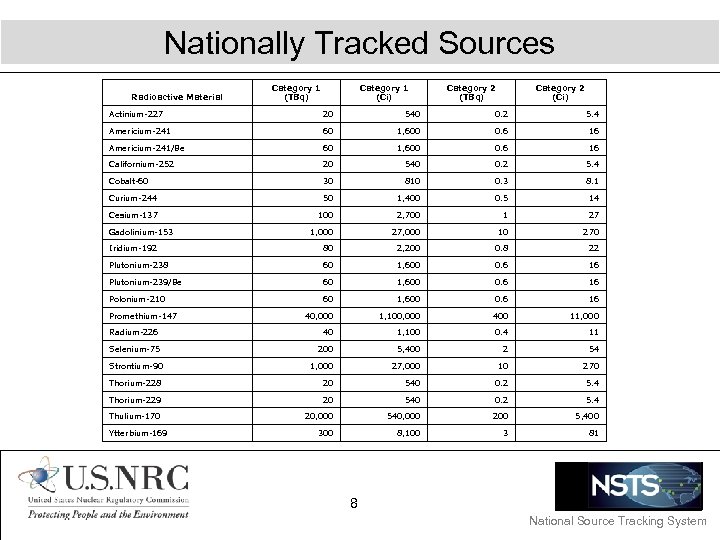 Nationally Tracked Sources Radioactive Material Category 1 (TBq) Category 1 (Ci) Category 2 (TBq) Category 2 (Ci) Actinium-227 20 540 0. 2 5. 4 Americium-241 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 Americium-241/Be 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 Californium-252 20 540 0. 2 5. 4 Cobalt-60 30 810 0. 3 8. 1 Curium-244 50 1, 400 0. 5 14 Cesium-137 100 2, 700 1 27 1, 000 27, 000 10 270 Iridium-192 80 2, 200 0. 8 22 Plutonium-238 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 Plutonium-239/Be 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 Polonium-210 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 40, 000 1, 100, 000 400 11, 000 Radium-226 40 1, 100 0. 4 11 Selenium-75 200 5, 400 2 54 Strontium-90 1, 000 27, 000 10 270 Thorium-228 20 540 0. 2 5. 4 Thorium-229 20 540 0. 2 5. 4 Thulium-170 20, 000 540, 000 200 5, 400 300 8, 100 3 81 Gadolinium-153 Promethium-147 Ytterbium-169 8 National Source Tracking System
Nationally Tracked Sources Radioactive Material Category 1 (TBq) Category 1 (Ci) Category 2 (TBq) Category 2 (Ci) Actinium-227 20 540 0. 2 5. 4 Americium-241 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 Americium-241/Be 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 Californium-252 20 540 0. 2 5. 4 Cobalt-60 30 810 0. 3 8. 1 Curium-244 50 1, 400 0. 5 14 Cesium-137 100 2, 700 1 27 1, 000 27, 000 10 270 Iridium-192 80 2, 200 0. 8 22 Plutonium-238 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 Plutonium-239/Be 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 Polonium-210 60 1, 600 0. 6 16 40, 000 1, 100, 000 400 11, 000 Radium-226 40 1, 100 0. 4 11 Selenium-75 200 5, 400 2 54 Strontium-90 1, 000 27, 000 10 270 Thorium-228 20 540 0. 2 5. 4 Thorium-229 20 540 0. 2 5. 4 Thulium-170 20, 000 540, 000 200 5, 400 300 8, 100 3 81 Gadolinium-153 Promethium-147 Ytterbium-169 8 National Source Tracking System
 NSTS Reporting Methods • Online access to NSTS • Batch upload • Email/fax National Source Tracking Transaction Report (NRC Form 748) • Phone Help Desk with follow-up by email/fax/mail • Resources: • Help Desk • Website with computerbased training modules and frequently asked questions 9 National Source Tracking System
NSTS Reporting Methods • Online access to NSTS • Batch upload • Email/fax National Source Tracking Transaction Report (NRC Form 748) • Phone Help Desk with follow-up by email/fax/mail • Resources: • Help Desk • Website with computerbased training modules and frequently asked questions 9 National Source Tracking System
 Annual Inventory Reconciliation • Every January • Streamlined process • Require each licensee to verify that NSTS inventory matches what they possess • Improves data integrity captures missing transactions, incorrect source information 10 National Source Tracking System
Annual Inventory Reconciliation • Every January • Streamlined process • Require each licensee to verify that NSTS inventory matches what they possess • Improves data integrity captures missing transactions, incorrect source information 10 National Source Tracking System
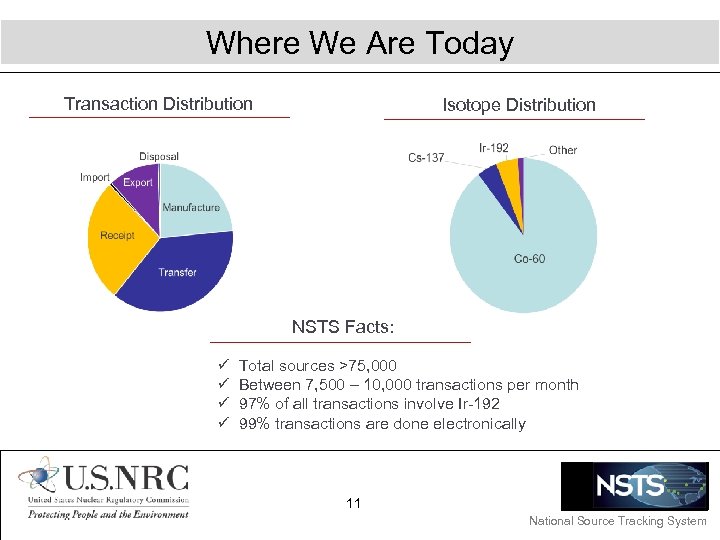 Where We Are Today Transaction Distribution 45% Cat 1 Isotope Distribution NSTS Facts: ü ü Total sources >75, 000 Between 7, 500 – 10, 000 transactions per month 97% of all transactions involve Ir-192 99% transactions are done electronically 11 National Source Tracking System
Where We Are Today Transaction Distribution 45% Cat 1 Isotope Distribution NSTS Facts: ü ü Total sources >75, 000 Between 7, 500 – 10, 000 transactions per month 97% of all transactions involve Ir-192 99% transactions are done electronically 11 National Source Tracking System
 Maintaining and Updating NSTS • NRC has a contractor that operates and maintains NSTS, processes data submitted by licensee for entry into NSTS, and runs the Help Desk. • NSTS Data – Licensees are responsible to report their transactions to NSTS by close of the next business day. Licensees must correct any errors within 5 business days of discovery of the error or missed transaction. – Regulators can see the source history and perform queries. – NSTS has automated alerts for when transactions are missing, when an unrecorded source gets reported, when a source goes below threshold, etc. • Improvements/Fixes to NSTS – Change requests are logged by stakeholders. – Change Control Board votes on the next maintenance release. – Change Control Board includes licensee representation. 12 National Source Tracking System
Maintaining and Updating NSTS • NRC has a contractor that operates and maintains NSTS, processes data submitted by licensee for entry into NSTS, and runs the Help Desk. • NSTS Data – Licensees are responsible to report their transactions to NSTS by close of the next business day. Licensees must correct any errors within 5 business days of discovery of the error or missed transaction. – Regulators can see the source history and perform queries. – NSTS has automated alerts for when transactions are missing, when an unrecorded source gets reported, when a source goes below threshold, etc. • Improvements/Fixes to NSTS – Change requests are logged by stakeholders. – Change Control Board votes on the next maintenance release. – Change Control Board includes licensee representation. 12 National Source Tracking System
 NSTS Challenges Initial challenges – Initial data integrity – NRC established a data integrity team dedicated to the function of correcting reported device information to replace it with source information. – Credentialing – NRC had not anticipated the challenges with getting people through the credentialing process (e. g. , going to a notary). – Accessibility – NRC had not anticipated how many licensees would opt to use alternative reporting methods. NRC also hadn’t anticipated the challenges experienced by users with the smart cards (i. e. , firewall issues). 13 National Source Tracking System
NSTS Challenges Initial challenges – Initial data integrity – NRC established a data integrity team dedicated to the function of correcting reported device information to replace it with source information. – Credentialing – NRC had not anticipated the challenges with getting people through the credentialing process (e. g. , going to a notary). – Accessibility – NRC had not anticipated how many licensees would opt to use alternative reporting methods. NRC also hadn’t anticipated the challenges experienced by users with the smart cards (i. e. , firewall issues). 13 National Source Tracking System
 NSTS Challenges Current challenges – Scope/limitations of NSTS • Not real time tracking – NSTS provides a relatively up-todate accounting system for risk-significant sources. • Category 3 sources – NRC is currently re-evaluating whether it is necessary to revise our regulations or processes governing source protection and accountability, including whether Category 3 sources should be included in NSTS. • Interest in capturing other source-related information in NSTS (transportation information, advance shipment notifications, import/export notifications) – Planning for lifecycle costs 14 National Source Tracking System
NSTS Challenges Current challenges – Scope/limitations of NSTS • Not real time tracking – NSTS provides a relatively up-todate accounting system for risk-significant sources. • Category 3 sources – NRC is currently re-evaluating whether it is necessary to revise our regulations or processes governing source protection and accountability, including whether Category 3 sources should be included in NSTS. • Interest in capturing other source-related information in NSTS (transportation information, advance shipment notifications, import/export notifications) – Planning for lifecycle costs 14 National Source Tracking System
 Questions Contact: Irene Wu Email: Irene. Wu@nrc. gov Phone: +1 301 415 1951 15 National Source Tracking System
Questions Contact: Irene Wu Email: Irene. Wu@nrc. gov Phone: +1 301 415 1951 15 National Source Tracking System


