4a3b0942e90d31cb7df5d57043dea3f6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 125
 National Nonstructural/ Flood Proofing Committee
National Nonstructural/ Flood Proofing Committee
 Nonstructural Measures for Flood Risk Management and Policy, Guidance, and Law Buffalo District Planning Conference 6 August 2009
Nonstructural Measures for Flood Risk Management and Policy, Guidance, and Law Buffalo District Planning Conference 6 August 2009
 v. Kenneth Zwickl, HQ v. Larry Buss, Omaha District v. Gene Barr, Huntington District v. Clark Frentzen, South Pacific Division v. Joseph Remondini, Tulsa District v. Stuart Davis, Institute for Water Research v. Randall Behm, Omaha District v. Mark Harberg, Fort Worth District v. Kim Gavigan, Los Angeles District v. Steve O’Leary, Huntington District v. Keven Lovetro, New Orleans District v. Carol Holloway, Institute for Water Research
v. Kenneth Zwickl, HQ v. Larry Buss, Omaha District v. Gene Barr, Huntington District v. Clark Frentzen, South Pacific Division v. Joseph Remondini, Tulsa District v. Stuart Davis, Institute for Water Research v. Randall Behm, Omaha District v. Mark Harberg, Fort Worth District v. Kim Gavigan, Los Angeles District v. Steve O’Leary, Huntington District v. Keven Lovetro, New Orleans District v. Carol Holloway, Institute for Water Research
 Mission v Flood Proofing v Nonstructural
Mission v Flood Proofing v Nonstructural
 Definitions Ø Nonstructural Ø Structural
Definitions Ø Nonstructural Ø Structural
 National Nonstructural Flood Proofing Committee Nonstructural Mitigation Measures
National Nonstructural Flood Proofing Committee Nonstructural Mitigation Measures
 Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees & Berms Ø Buyout/Acquisition Ø Dry Flood Proofing Ø Wet Flood Proofing Ø Flooding Warning/Preparedness Ø National Flood Insurance Program
Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees & Berms Ø Buyout/Acquisition Ø Dry Flood Proofing Ø Wet Flood Proofing Ø Flooding Warning/Preparedness Ø National Flood Insurance Program
 Elevating on Extended Walls Foundation
Elevating on Extended Walls Foundation
 Elevating on Extended Foundation Walls
Elevating on Extended Foundation Walls
 Elevating on Extended Foundation Walls
Elevating on Extended Foundation Walls
 Elevating on Fill
Elevating on Fill
 Elevating on Fill
Elevating on Fill
 Elevating on Piers, Posts, Piles. . . … or Columns
Elevating on Piers, Posts, Piles. . . … or Columns
 Elevation on Piers, Posts, Piles, or Columns Piers Piles Posts Columns
Elevation on Piers, Posts, Piles, or Columns Piers Piles Posts Columns
 Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Ø Buyout/Acquisition Ø Dry Flood Proofing Ø Wet Flood Proofing Ø Flooding Warning/Preparedness Ø National Flood Insurance Program
Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Ø Buyout/Acquisition Ø Dry Flood Proofing Ø Wet Flood Proofing Ø Flooding Warning/Preparedness Ø National Flood Insurance Program
 Relocation Process Moving the Structure Ø Evacuate temporary roadway Ø Attach structure to trailer Ø Transport structure to new site
Relocation Process Moving the Structure Ø Evacuate temporary roadway Ø Attach structure to trailer Ø Transport structure to new site
 Relocation Process Restoration of Old Site Ø Demolish and remove foundation and pavement Ø Disconnect and remove all utilities Ø Grading and site stabilization
Relocation Process Restoration of Old Site Ø Demolish and remove foundation and pavement Ø Disconnect and remove all utilities Ø Grading and site stabilization
 Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Ø Buyout/Acquisition Ø Dry Flood Proofing Ø Wet Flood Proofing Ø Flooding Warning/Preparedness Ø National Flood Insurance Program
Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Ø Buyout/Acquisition Ø Dry Flood Proofing Ø Wet Flood Proofing Ø Flooding Warning/Preparedness Ø National Flood Insurance Program
 Construction Barriers Berms, Levees and Floodwalls Floodwall Sump and pump for internal drainage Berm or Levee Sewer One-way valve
Construction Barriers Berms, Levees and Floodwalls Floodwall Sump and pump for internal drainage Berm or Levee Sewer One-way valve
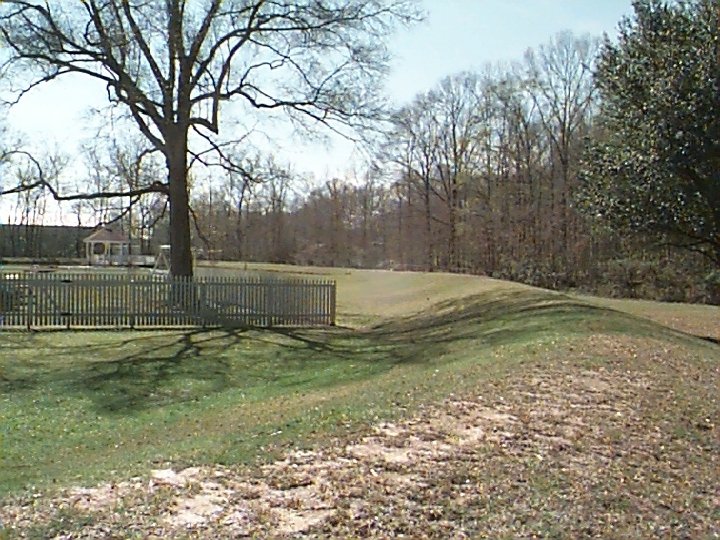


 Three Foot Earthen Levee
Three Foot Earthen Levee


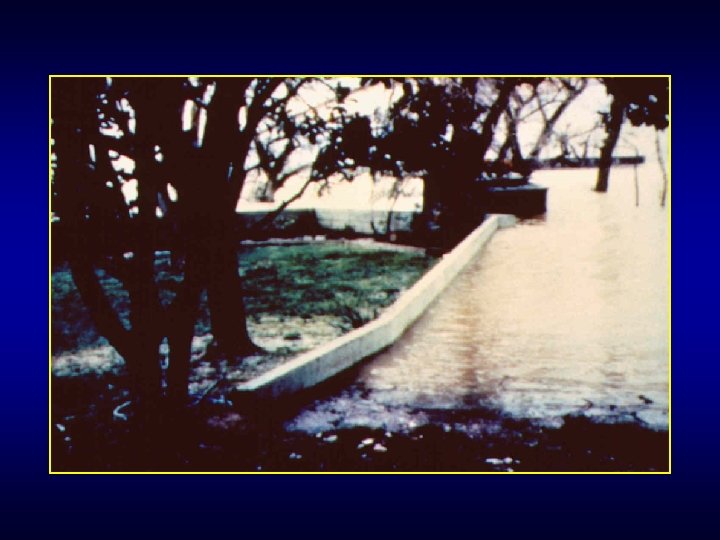
 Flood Protection with Floodwalls Floodwall
Flood Protection with Floodwalls Floodwall





 Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Ø Ø Ø Buyout/Acquisition Dry Flood Proofing Wet Flood Proofing Flooding Warning/Preparedness National Flood Insurance Program
Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Ø Ø Ø Buyout/Acquisition Dry Flood Proofing Wet Flood Proofing Flooding Warning/Preparedness National Flood Insurance Program
 Basic Acquisition Ø Acquire land structures Ø Demolish structures Ø Easiest type of acquisition
Basic Acquisition Ø Acquire land structures Ø Demolish structures Ø Easiest type of acquisition

 Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Ø Buyout/Acquisition Ø Dry Flood Proofing Ø Wet Flood Proofing Ø Flooding Warning/Preparedness Ø National Flood Insurance Program
Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Elevation Ø Relocation Ø Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Ø Buyout/Acquisition Ø Dry Flood Proofing Ø Wet Flood Proofing Ø Flooding Warning/Preparedness Ø National Flood Insurance Program
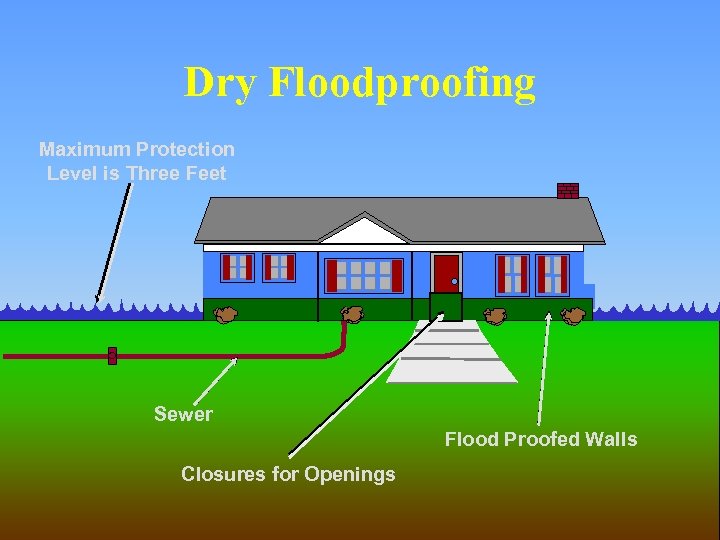 Dry Floodproofing Maximum Protection Level is Three Feet One-Way Valve Sewer Flood Proofed Walls Closures for Openings
Dry Floodproofing Maximum Protection Level is Three Feet One-Way Valve Sewer Flood Proofed Walls Closures for Openings
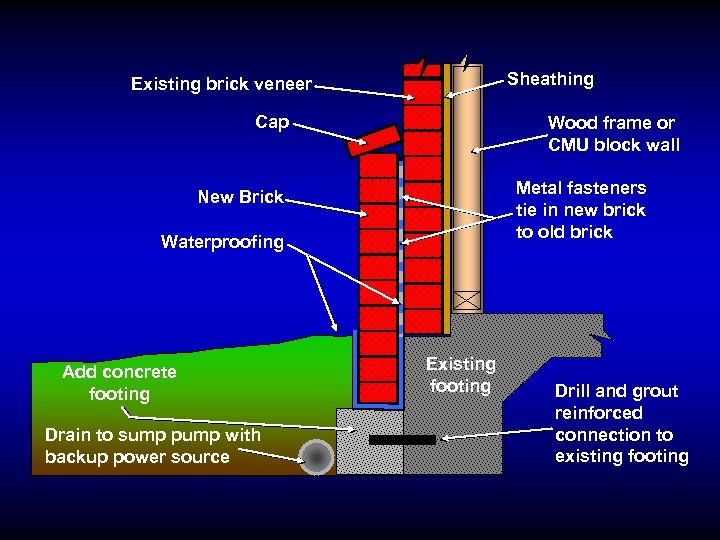 Sheathing Existing brick veneer Cap Wood frame or CMU block wall Metal fasteners tie in new brick to old brick New Brick Waterproofing Add concrete footing Drain to sump pump with backup power source Existing footing Drill and grout reinforced connection to existing footing
Sheathing Existing brick veneer Cap Wood frame or CMU block wall Metal fasteners tie in new brick to old brick New Brick Waterproofing Add concrete footing Drain to sump pump with backup power source Existing footing Drill and grout reinforced connection to existing footing
 Dry Flood Proofing Methods Waterproof Sealant
Dry Flood Proofing Methods Waterproof Sealant
 Dry Flood Proofing Methods Waterproof Sealant Veneer
Dry Flood Proofing Methods Waterproof Sealant Veneer
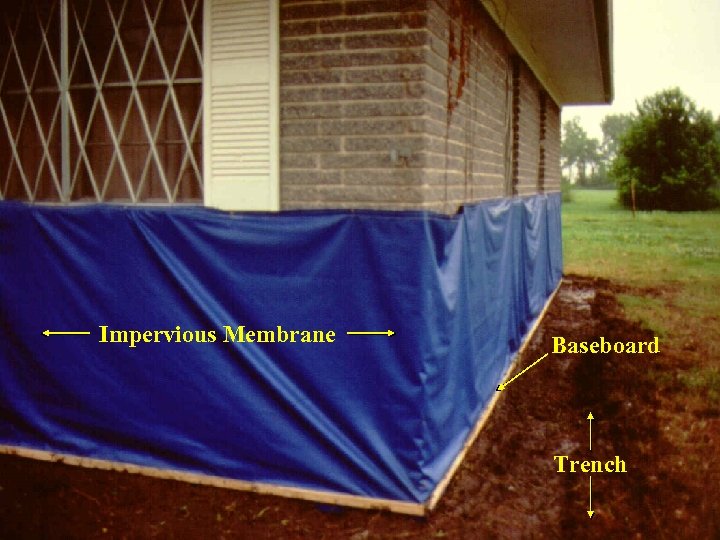 Impervious Membrane Baseboard Trench
Impervious Membrane Baseboard Trench
 2 feet of water in back of house
2 feet of water in back of house
 Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Ø Ø Ø Elevation Relocation Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Buyout/Acquisition Dry Flood Proofing Wet Flood Proofing Flooding Warning/Preparedness National Flood Insurance Program
Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Ø Ø Ø Elevation Relocation Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Buyout/Acquisition Dry Flood Proofing Wet Flood Proofing Flooding Warning/Preparedness National Flood Insurance Program
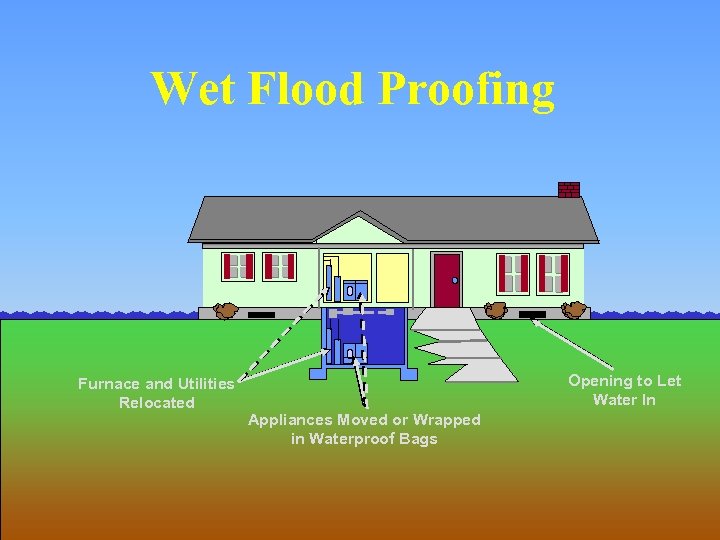 Wet Flood Proofing Furnace and Utilities Relocated Opening to Let Water In Appliances Moved or Wrapped in Waterproof Bags
Wet Flood Proofing Furnace and Utilities Relocated Opening to Let Water In Appliances Moved or Wrapped in Waterproof Bags
 Wet Flood Proofing Elevate Utilities
Wet Flood Proofing Elevate Utilities
 Wet Flood Proofing Elevate Utilities
Wet Flood Proofing Elevate Utilities
 Wet Flood Proofing Let Water In Louvre
Wet Flood Proofing Let Water In Louvre
 Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Ø Ø Ø Elevation Relocation Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Buyout/Acquisition Dry Flood Proofing Wet Flood Proofing Flooding Warning/Preparedness National Flood Insurance Program
Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Ø Ø Ø Elevation Relocation Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Buyout/Acquisition Dry Flood Proofing Wet Flood Proofing Flooding Warning/Preparedness National Flood Insurance Program
 Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Ø Flood Threat Recognition System Ø Warning Dissemination Ø Emergency Response Ø Post-Flood Recovery Ø Continued Plan Management
Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Ø Flood Threat Recognition System Ø Warning Dissemination Ø Emergency Response Ø Post-Flood Recovery Ø Continued Plan Management
 Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Flood Threat Recognition System Ø Ø Ø Collection of information Transmission of Information Receipt of information Organization/Display of information Prediction or timing and magnitude of flood event
Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Flood Threat Recognition System Ø Ø Ø Collection of information Transmission of Information Receipt of information Organization/Display of information Prediction or timing and magnitude of flood event
 Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Warning Dissemination Ø Determine affected areas Ø Identify affected parties Ø Prepare warning message Ø Distribute warning message
Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Warning Dissemination Ø Determine affected areas Ø Identify affected parties Ø Prepare warning message Ø Distribute warning message
 Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Emergency Response Ø Temporary evacuation Ø Search and rescue Ø Mass care Ø Ø Ø center operations Public property protection Flood fight Maintenance of vital services
Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Emergency Response Ø Temporary evacuation Ø Search and rescue Ø Mass care Ø Ø Ø center operations Public property protection Flood fight Maintenance of vital services
 Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Post-Flood Recovery Ø Ø Evacuee return Debris clearance Return of services Damage assessment Ø Provisions for assistance
Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Post-Flood Recovery Ø Ø Evacuee return Debris clearance Return of services Damage assessment Ø Provisions for assistance
 Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Continued Plan Management Ø Ø Public Awareness/Education Programs O&M equipment Periodic drills Update plan
Flood Warning/Preparedness Components Continued Plan Management Ø Ø Public Awareness/Education Programs O&M equipment Periodic drills Update plan
 Flood Warning System
Flood Warning System
 Alert Ø Ø Ø Remote rain and stage gages Transmit information Base station computer Process information Automated threatened area notification (most advance systems)
Alert Ø Ø Ø Remote rain and stage gages Transmit information Base station computer Process information Automated threatened area notification (most advance systems)
 Automated Stage Detection Ø Float switch/submersed electric circuit activated by rising water Ø Telephone automatic alarm dialers activated Ø Calls placed to emergency managers Ø Manual threatened area notification
Automated Stage Detection Ø Float switch/submersed electric circuit activated by rising water Ø Telephone automatic alarm dialers activated Ø Calls placed to emergency managers Ø Manual threatened area notification
 Manual Ø Observer read stage or rain gages. Ø Two way telephonic communication between observers and emergency managers Ø Manual threatened area notification
Manual Ø Observer read stage or rain gages. Ø Two way telephonic communication between observers and emergency managers Ø Manual threatened area notification
 Hybrid Ø Combination of Alert and USGS stream gaging methods and equipment Ø Remote rain and stage gages Ø Transmit information Ø Base station computer or two way telephonic communication with gages Ø Manual or automated threatened area notification
Hybrid Ø Combination of Alert and USGS stream gaging methods and equipment Ø Remote rain and stage gages Ø Transmit information Ø Base station computer or two way telephonic communication with gages Ø Manual or automated threatened area notification
 Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Ø Ø Ø Elevation Relocation Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Buyout/Acquisition Dry Flood Proofing Wet Flood Proofing Flooding Warning/Preparedness National Flood Insurance Program
Nonstructural Mitigation Measures Ø Ø Ø Ø Elevation Relocation Floodwalls, Levees and Berms Buyout/Acquisition Dry Flood Proofing Wet Flood Proofing Flooding Warning/Preparedness National Flood Insurance Program
 National Flood Insurance Program 44 CFR 59 -78 Ø Flood Plain Regulation Ø Flood Insurance Ø Flood Mitigation
National Flood Insurance Program 44 CFR 59 -78 Ø Flood Plain Regulation Ø Flood Insurance Ø Flood Mitigation
 Why Investigate Nonstructural Measures ? Ø Requirements Ø Opportunities
Why Investigate Nonstructural Measures ? Ø Requirements Ø Opportunities
 Requirements The Flood Control Act of 1938 – authorized the Corps “where the construction cost of levees or flood walls included in any authorized project can be substantially reduced by the evacuation of a portion or all of the area proposed to be protected” to expend funds “toward the evacuation of the locality eliminated from protection and the rehabilitation of the persons so evacuated”.
Requirements The Flood Control Act of 1938 – authorized the Corps “where the construction cost of levees or flood walls included in any authorized project can be substantially reduced by the evacuation of a portion or all of the area proposed to be protected” to expend funds “toward the evacuation of the locality eliminated from protection and the rehabilitation of the persons so evacuated”.
 Requirements The Flood Control Act of 1960 – authorized the Corps “to compile and disseminate information on floods and flood damages, including identification of areas subject to inundation by floods of various magnitudes and frequencies, and general criteria for guidance in the use of flood plain areas, and to provide engineering advice to local interests for their use in planning to ameliorate the flood hazard. : This is the Flood Plain Management Services Program.
Requirements The Flood Control Act of 1960 – authorized the Corps “to compile and disseminate information on floods and flood damages, including identification of areas subject to inundation by floods of various magnitudes and frequencies, and general criteria for guidance in the use of flood plain areas, and to provide engineering advice to local interests for their use in planning to ameliorate the flood hazard. : This is the Flood Plain Management Services Program.
 Requirements National Flood Insurance Act of 1968 – authorized the National Flood Insurance Program, which has evolved to generally consist of flood insurance, flood plain regulation, and flood hazard mitigation through primarily nonstructural measures.
Requirements National Flood Insurance Act of 1968 – authorized the National Flood Insurance Program, which has evolved to generally consist of flood insurance, flood plain regulation, and flood hazard mitigation through primarily nonstructural measures.
 Requirements The Water Resources Development Act of 1974 – requires of the Corps that “consideration shall be given to nonstructural alternatives to prevent or reduce flood damages”.
Requirements The Water Resources Development Act of 1974 – requires of the Corps that “consideration shall be given to nonstructural alternatives to prevent or reduce flood damages”.
 Requirements Executive Order 11988 dated 24 May 1977 – requires the Corps to implement “action to reduce the risk of flood loss, to minimize the impact of floods on human safety, health and welfare, and to restore and preserve the natural and beneficial values served by floodplains. ”
Requirements Executive Order 11988 dated 24 May 1977 – requires the Corps to implement “action to reduce the risk of flood loss, to minimize the impact of floods on human safety, health and welfare, and to restore and preserve the natural and beneficial values served by floodplains. ”
 Requirements Economic and Environmental Principles and Guidelines for Water and Related Land Resources Implementation Studies dated March 1983 (P&G) – requires of the Corps that “nonstructural measures should be considered as means for addressing problems and opportunities” in water and related land resources implementation studies.
Requirements Economic and Environmental Principles and Guidelines for Water and Related Land Resources Implementation Studies dated March 1983 (P&G) – requires of the Corps that “nonstructural measures should be considered as means for addressing problems and opportunities” in water and related land resources implementation studies.
![Requirements Digest of Water Resources Policies and Authorities [EP 1165 -2 -1] – requires Requirements Digest of Water Resources Policies and Authorities [EP 1165 -2 -1] – requires](https://present5.com/presentation/4a3b0942e90d31cb7df5d57043dea3f6/image-67.jpg) Requirements Digest of Water Resources Policies and Authorities [EP 1165 -2 -1] – requires that “Consideration will be given both to measures intended to modify flood behavior [structural measures] and those intended to modify damage susceptibility by altering the ways in which people would otherwise occupy and use flood plain lands and waters [nonstructural measures]. ”
Requirements Digest of Water Resources Policies and Authorities [EP 1165 -2 -1] – requires that “Consideration will be given both to measures intended to modify flood behavior [structural measures] and those intended to modify damage susceptibility by altering the ways in which people would otherwise occupy and use flood plain lands and waters [nonstructural measures]. ”
![Requirements Planning Guidance Notebook [ER 1105 -2 -100] – requires nonstructural measure consideration by Requirements Planning Guidance Notebook [ER 1105 -2 -100] – requires nonstructural measure consideration by](https://present5.com/presentation/4a3b0942e90d31cb7df5d57043dea3f6/image-68.jpg) Requirements Planning Guidance Notebook [ER 1105 -2 -100] – requires nonstructural measure consideration by stating “Section 73 of the Water Resources Development Act of 1974 requires consideration of nonstructural alternatives in flood damage reduction studies.
Requirements Planning Guidance Notebook [ER 1105 -2 -100] – requires nonstructural measure consideration by stating “Section 73 of the Water Resources Development Act of 1974 requires consideration of nonstructural alternatives in flood damage reduction studies.
 Opportunities Ø Another set of tools Ø No Adverse Impacts Flood Plain ü Environmental Complies with E. O. 11988 Complies with NFIP Regulations ü HMGP acquired land ü Insurable structures/Fill in floodway ü Ø Ø
Opportunities Ø Another set of tools Ø No Adverse Impacts Flood Plain ü Environmental Complies with E. O. 11988 Complies with NFIP Regulations ü HMGP acquired land ü Insurable structures/Fill in floodway ü Ø Ø
 Opportunities (cont. ) Ø New Uses of the Evacuated Flood Plain Ecosystem Restoration ü Recreation ü Spillover Benefits Ø Water Quality Improvement Ø Recreation Costs - 50% versus 10% Ø Cost Sharing ü 35% / 65% Ø Lower Cost - Possible Ø Mitigation of Adverse Effects of Structural Projects ü
Opportunities (cont. ) Ø New Uses of the Evacuated Flood Plain Ecosystem Restoration ü Recreation ü Spillover Benefits Ø Water Quality Improvement Ø Recreation Costs - 50% versus 10% Ø Cost Sharing ü 35% / 65% Ø Lower Cost - Possible Ø Mitigation of Adverse Effects of Structural Projects ü
 Opportunities (cont. ) Ø Ø Ø Ø Achievement of Strategic Goals Achievement of the Environmental Operating Principles Achievement of Actions for Change Partnering Lower O&M Costs Supports both short term and long term flood risk reduction Ø Redundant flood risk reduction consequence focused.
Opportunities (cont. ) Ø Ø Ø Ø Achievement of Strategic Goals Achievement of the Environmental Operating Principles Achievement of Actions for Change Partnering Lower O&M Costs Supports both short term and long term flood risk reduction Ø Redundant flood risk reduction consequence focused.
 National Flood Insurance Program 44 CFR 59 -78 Flood Plain Regulation 44 CFR 60 Ø Definitions Base Flood ü Flood Plain ü Floodway ü Substantial Damage ü Substantial Improvement ü
National Flood Insurance Program 44 CFR 59 -78 Flood Plain Regulation 44 CFR 60 Ø Definitions Base Flood ü Flood Plain ü Floodway ü Substantial Damage ü Substantial Improvement ü
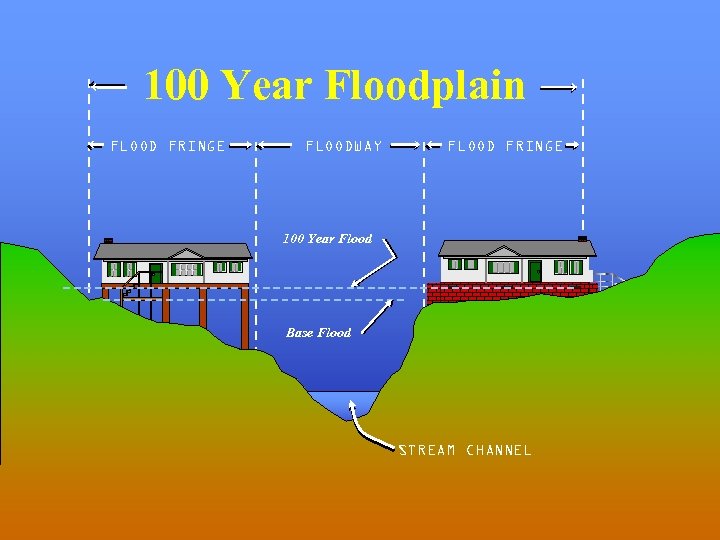 100 Year Floodplain FLOOD FRINGE FLOODWAY FLOOD FRINGE 100 Year Flood Base Flood STREAM CHANNEL
100 Year Floodplain FLOOD FRINGE FLOODWAY FLOOD FRINGE 100 Year Flood Base Flood STREAM CHANNEL
 Coastal Flood Plain • • V Zone Coastal A Zone X Zone
Coastal Flood Plain • • V Zone Coastal A Zone X Zone
 Ø Flood Plain Regulation Ø Flood Insurance Ø Flood Mitigation NFIP Floodplain Regulation Flood Insurance Flood Mitigation
Ø Flood Plain Regulation Ø Flood Insurance Ø Flood Mitigation NFIP Floodplain Regulation Flood Insurance Flood Mitigation
 Requirements - Riverine Ø All new construction and substantial improvements of : ü ü Residential structures have the lowest floor, including basement, elevated to or above the Base Flood Non-Residential structures have the lowest floor, including basement, flood proofed to or above the Base Flood
Requirements - Riverine Ø All new construction and substantial improvements of : ü ü Residential structures have the lowest floor, including basement, elevated to or above the Base Flood Non-Residential structures have the lowest floor, including basement, flood proofed to or above the Base Flood
 Requirements - Riverine ØProhibit encroachments within the floodway unless it has been demonstrated through hydrologic and hydraulic analysis that the proposed encroachment will not result in any increase in the Base Flood Elevation
Requirements - Riverine ØProhibit encroachments within the floodway unless it has been demonstrated through hydrologic and hydraulic analysis that the proposed encroachment will not result in any increase in the Base Flood Elevation
 Requirements - Coastal Ø All new construction and substantial improvements of : ü Residential structures have the lowest floor, including basement, elevated to or above the Base Flood ü Non-Residential structures have the lowest floor, including basement, flood proofed to or above the Base Flood
Requirements - Coastal Ø All new construction and substantial improvements of : ü Residential structures have the lowest floor, including basement, elevated to or above the Base Flood ü Non-Residential structures have the lowest floor, including basement, flood proofed to or above the Base Flood
 Requirements - Coastal Ø All new construction and substantial improvements within V zones : ü Be elevated on piles or columns so the bottom of the lowest horizontal structural member is Elevated to or above the Base Flood with the space below the lowest floor either free of obstruction or constructed with breakaway wall or open lattice ü Do not use Fill
Requirements - Coastal Ø All new construction and substantial improvements within V zones : ü Be elevated on piles or columns so the bottom of the lowest horizontal structural member is Elevated to or above the Base Flood with the space below the lowest floor either free of obstruction or constructed with breakaway wall or open lattice ü Do not use Fill
 ØFlood Plain Regulation ØFlood Insurance ØFlood Mitigation NFIP Floodplain Regulation Flood Insurance Flood Mitigation
ØFlood Plain Regulation ØFlood Insurance ØFlood Mitigation NFIP Floodplain Regulation Flood Insurance Flood Mitigation
 Flood Insurance Definitions Ø Ø Ø Basement Building Post FIRM building Pre FIRM building Walled and Roofed
Flood Insurance Definitions Ø Ø Ø Basement Building Post FIRM building Pre FIRM building Walled and Roofed
 Flood Insurance Definitions Ø Basement – any area of a building having its floor subgrade below ground level on all sides Ø Building – a walled and roofed structure that is principally above ground affixed to a permanent site Ø Post FIRM building – a building for which the start of construction or substantial improvement occurred on or after the effective date of the initial FIRM for the community
Flood Insurance Definitions Ø Basement – any area of a building having its floor subgrade below ground level on all sides Ø Building – a walled and roofed structure that is principally above ground affixed to a permanent site Ø Post FIRM building – a building for which the start of construction or substantial improvement occurred on or after the effective date of the initial FIRM for the community
 Flood Insurance Definitions Ø Pre FIRM building – a building for which the start of construction or substantial improvement occurred before the effective date of the initial FIRM for the community Ø Walled and Roofed – the building has in place two or more exterior rigid walls and the roof is fully secured so that the building will resist flotation, collapse, and lateral movement
Flood Insurance Definitions Ø Pre FIRM building – a building for which the start of construction or substantial improvement occurred before the effective date of the initial FIRM for the community Ø Walled and Roofed – the building has in place two or more exterior rigid walls and the roof is fully secured so that the building will resist flotation, collapse, and lateral movement
 Flood Insurance Ø General dwelling losses not covered ü ü ü Loss of insured property use Loss of access to insured property Loss of profits Losses resulting from additional living expenses while the insured property is being repaired Losses resulting from casualties other than as defined as a flood
Flood Insurance Ø General dwelling losses not covered ü ü ü Loss of insured property use Loss of access to insured property Loss of profits Losses resulting from additional living expenses while the insured property is being repaired Losses resulting from casualties other than as defined as a flood
 Flood Insurance Ø Dwelling Property covered: ü Building Property ü The building ü ü ü Additions and extensions to the building Materials and supplies to be used in constructing or altering the building Fixtures, machinery, and equipment within the building and owned by the insured such as: furnaces, permanently installed wall mirrors, cupboards, bookcases, paneling, wallpaper, blinds, dishwashers, carpet, and garbage disposals, pumps, plumbing, ranges, stoves, refrigerators, etc.
Flood Insurance Ø Dwelling Property covered: ü Building Property ü The building ü ü ü Additions and extensions to the building Materials and supplies to be used in constructing or altering the building Fixtures, machinery, and equipment within the building and owned by the insured such as: furnaces, permanently installed wall mirrors, cupboards, bookcases, paneling, wallpaper, blinds, dishwashers, carpet, and garbage disposals, pumps, plumbing, ranges, stoves, refrigerators, etc.
 Flood Insurance ØDwelling Property covered: ü Personal Property * ü Owned by the insured or members within the insured’s household if stored within the building and secured to prevent flotation out of the building during flooding Debris Removal * Expense of debris removal if directly caused by a flood
Flood Insurance ØDwelling Property covered: ü Personal Property * ü Owned by the insured or members within the insured’s household if stored within the building and secured to prevent flotation out of the building during flooding Debris Removal * Expense of debris removal if directly caused by a flood
 Flood Insurance Ø Dwelling Property not covered: Personal property in the open Ø Fences, retaining walls, docks, etc. ü Indoor and outdoor pools ü Underground structures and equipment * Land, lawns, trees, etc. * Animals * Aircraft, watercraft * Manufactured homes that are not anchored ü Post FIRM basements in SFHA’s * Personal property * Fixtures/components attached to the building but not needed for building support or utilities * Finished walls ü
Flood Insurance Ø Dwelling Property not covered: Personal property in the open Ø Fences, retaining walls, docks, etc. ü Indoor and outdoor pools ü Underground structures and equipment * Land, lawns, trees, etc. * Animals * Aircraft, watercraft * Manufactured homes that are not anchored ü Post FIRM basements in SFHA’s * Personal property * Fixtures/components attached to the building but not needed for building support or utilities * Finished walls ü
 Ø Flood Plain Regulation Ø Flood Insurance Ø Flood Mitigation
Ø Flood Plain Regulation Ø Flood Insurance Ø Flood Mitigation
 Hazard Mitigation Grant Program Ø Project criteria ü ü ü Conform with hazard mitigation plan Be cost effective Conform with flood plain management criteria Have a beneficial impact on the designated disaster area 75/25 cost share Generally funded at 15% of total disaster grants
Hazard Mitigation Grant Program Ø Project criteria ü ü ü Conform with hazard mitigation plan Be cost effective Conform with flood plain management criteria Have a beneficial impact on the designated disaster area 75/25 cost share Generally funded at 15% of total disaster grants
 Hazard Mitigation Grant Program Types of Projects Ø Structural Ø Ø Ø Nonstructural Acquisition/relocation Develop state and local mitigation standards Develop comprehensive hazard mitigation programs with implementation as an essential component Develop or improve warning systems
Hazard Mitigation Grant Program Types of Projects Ø Structural Ø Ø Ø Nonstructural Acquisition/relocation Develop state and local mitigation standards Develop comprehensive hazard mitigation programs with implementation as an essential component Develop or improve warning systems
 Flood Mitigation Assistance Program ØPlanning grants Develop flood hazard mitigation plans ü 75/25 cost share ØProject grants ü Implement flood mitigation projects contained in the flood hazard mitigation plan ü 75/25 cost share ØTechnical assistance grants ü To aid applicants in applying for the FMA Program ü 100/0 cost share Ø$31 Million ü
Flood Mitigation Assistance Program ØPlanning grants Develop flood hazard mitigation plans ü 75/25 cost share ØProject grants ü Implement flood mitigation projects contained in the flood hazard mitigation plan ü 75/25 cost share ØTechnical assistance grants ü To aid applicants in applying for the FMA Program ü 100/0 cost share Ø$31 Million ü
 Pre-Disaster Mitigation Program Ø Mitigates all natural disasters – just flood Ø Must have approved mitigation for project funds Ø 75/25 cost share Ø Be cost effective Ø Eligible projects ü Mitigation planning ü Mitigation projects ü Information dissemination Ø $100 Million not plan
Pre-Disaster Mitigation Program Ø Mitigates all natural disasters – just flood Ø Must have approved mitigation for project funds Ø 75/25 cost share Ø Be cost effective Ø Eligible projects ü Mitigation planning ü Mitigation projects ü Information dissemination Ø $100 Million not plan
 Repetitive Flood Claims Grant Program Ø One or more claims to NFIP Ø Relocation/Buyout/ Ø Ø Ø Open Space Use Possible 100% Federal Up to $10 Million 75/25 Cost Share Standard
Repetitive Flood Claims Grant Program Ø One or more claims to NFIP Ø Relocation/Buyout/ Ø Ø Ø Open Space Use Possible 100% Federal Up to $10 Million 75/25 Cost Share Standard
 Repetitive Loss Ø Four or more paid losses of $1, 000 or more Ø Two paid losses within a 10 -year period Ø Three or more paid losses since 1978
Repetitive Loss Ø Four or more paid losses of $1, 000 or more Ø Two paid losses within a 10 -year period Ø Three or more paid losses since 1978
 Severe Repetitive Loss Program Ø Severe Repetitive Loss Properties üResidential üFour NFIP claims over $5, 000 each üAt least two claims within any 10 year period üAt least two claims that cumulatively Ø Ø Ø exceed the value of the property Possible 90% Federal 75/25 Cost Share Standard Up to $40 Million
Severe Repetitive Loss Program Ø Severe Repetitive Loss Properties üResidential üFour NFIP claims over $5, 000 each üAt least two claims within any 10 year period üAt least two claims that cumulatively Ø Ø Ø exceed the value of the property Possible 90% Federal 75/25 Cost Share Standard Up to $40 Million
 Community Rating System ØCredible activities ü Public Information * Elevation certificates * Map information * Outreach programs * Hazard Disclosure * Flood protection library * Flood protection assistance
Community Rating System ØCredible activities ü Public Information * Elevation certificates * Map information * Outreach programs * Hazard Disclosure * Flood protection library * Flood protection assistance
 Mapping and Regulatory Ø Ø Open space preservation Higher regulatory standards Flood data maintenance Stormwater management
Mapping and Regulatory Ø Ø Open space preservation Higher regulatory standards Flood data maintenance Stormwater management
 Flood Damage Reduction Activities Ø Flood plain management plans Ø Acquisition and relocation Ø Retrofitting Ø Drainage
Flood Damage Reduction Activities Ø Flood plain management plans Ø Acquisition and relocation Ø Retrofitting Ø Drainage
 Flood Preparedness Activities ØFlood Warning Program ØLevee Safety ØDam Safety Maximum flood insurance premium reduction is 45%
Flood Preparedness Activities ØFlood Warning Program ØLevee Safety ØDam Safety Maximum flood insurance premium reduction is 45%
 Flood Plain Management Criteria Relative to Structural Flood Damage Reduction Projects National Flood Insurance Program Ø Basic requirements of the structural flood damage reduction project ü No adopted regulatory floodway ü The project will not increase the Base Flood Elevation (BFE) more than a foot at any location
Flood Plain Management Criteria Relative to Structural Flood Damage Reduction Projects National Flood Insurance Program Ø Basic requirements of the structural flood damage reduction project ü No adopted regulatory floodway ü The project will not increase the Base Flood Elevation (BFE) more than a foot at any location
 Flood Plain Management Criteria Relative to Structural Flood Damage Reduction Projects National Flood Insurance Program ØAdopted regulatory floodway üThe project will not place fill material or new construction within the regulatory floodway unless it is demonstrated that no increase in the BFE will occur
Flood Plain Management Criteria Relative to Structural Flood Damage Reduction Projects National Flood Insurance Program ØAdopted regulatory floodway üThe project will not place fill material or new construction within the regulatory floodway unless it is demonstrated that no increase in the BFE will occur
 Ø Conditional Letter of Map Revision (CLOMR). Basic requirements of the CLOMR are as follows: üRequest for conditional approval of the FIRM change. üEvaluate alternatives which would not result in an increase in BFE üDocument that individual legal notice has been made to all increased BFE üGain concurrence of other impacted communities.
Ø Conditional Letter of Map Revision (CLOMR). Basic requirements of the CLOMR are as follows: üRequest for conditional approval of the FIRM change. üEvaluate alternatives which would not result in an increase in BFE üDocument that individual legal notice has been made to all increased BFE üGain concurrence of other impacted communities.
 Ø Conditional Letter of Map Revision (CLOMR). Basic requirements of the CLOMR are as follows: ü Certify that no structures are located in areas impacted by the increased BFE ü Provide documentation of hydrologic and hydraulic analysis reflecting the increase in BFE and change in floodway ü Provide a plan to mitigate the increased BFE and change in floodway. Ø A Letter of Map Revision (LOMR) submittal is required upon project completion.
Ø Conditional Letter of Map Revision (CLOMR). Basic requirements of the CLOMR are as follows: ü Certify that no structures are located in areas impacted by the increased BFE ü Provide documentation of hydrologic and hydraulic analysis reflecting the increase in BFE and change in floodway ü Provide a plan to mitigate the increased BFE and change in floodway. Ø A Letter of Map Revision (LOMR) submittal is required upon project completion.
 Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø Basic Objectives ü Provide leadership in flood plain management ü Avoid long and short term adverse flood plain impacts associated with projects. ü Avoid direct and indirect support of development in the flood plain. ü Reduce the risk of flood loss. ü Minimize the impact of floods on health, safety, and welfare. Restore and preserve the natural and beneficial values of flood plains. ü Involve the public throughout the flood plain management decision process.
Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø Basic Objectives ü Provide leadership in flood plain management ü Avoid long and short term adverse flood plain impacts associated with projects. ü Avoid direct and indirect support of development in the flood plain. ü Reduce the risk of flood loss. ü Minimize the impact of floods on health, safety, and welfare. Restore and preserve the natural and beneficial values of flood plains. ü Involve the public throughout the flood plain management decision process.
 Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø Basic Steps ü ü Determine whether the project is in 100 -year or 500 -year flood plain. Notify the public early of a project that is proposed to be 100 -year or 500 -year flood plain to involve local decision makers in the decision process. Identify and evaluate practicable alternatives to locating the project in the flood plain. Identify the potential direct and indirect impacts with the project in the flood plain.
Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø Basic Steps ü ü Determine whether the project is in 100 -year or 500 -year flood plain. Notify the public early of a project that is proposed to be 100 -year or 500 -year flood plain to involve local decision makers in the decision process. Identify and evaluate practicable alternatives to locating the project in the flood plain. Identify the potential direct and indirect impacts with the project in the flood plain.
 Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø Basic Steps ü Minimize the potential adverse impacts to or within the flood plain. ü Reevaluate the project to see if it is still practicable in light of the impact to others ü Provide the public with the findings and explanation that the project in the flood plain is the only practicable alternative. ü Provide for mitigation of adverse affects of the project.
Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø Basic Steps ü Minimize the potential adverse impacts to or within the flood plain. ü Reevaluate the project to see if it is still practicable in light of the impact to others ü Provide the public with the findings and explanation that the project in the flood plain is the only practicable alternative. ü Provide for mitigation of adverse affects of the project.
 Basic Steps • NFIP standards are minimum • If locating "new construction" in a flood plain, flood proofing should be applied
Basic Steps • NFIP standards are minimum • If locating "new construction" in a flood plain, flood proofing should be applied
 Critical Actions • A slight chance of flooding is too great • If flooded, would the flood effects be worsened • Risk to public safety and increased hazard to life • 500 year flood standard minimum
Critical Actions • A slight chance of flooding is too great • If flooded, would the flood effects be worsened • Risk to public safety and increased hazard to life • 500 year flood standard minimum
 Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø Basic Mitigation Requirements ü Land * * Land that is within the regulatory floodway post-project that was not within the regulatory floodway pre-project. Land that is within the 100 -year flood boundary post-project that was not within the 100 -year flood boundary pre-project. Land that is in the pre-project floodway that has a floodway elevation post-project that is higher than the pre-project floodway elevation. Mitigation.
Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø Basic Mitigation Requirements ü Land * * Land that is within the regulatory floodway post-project that was not within the regulatory floodway pre-project. Land that is within the 100 -year flood boundary post-project that was not within the 100 -year flood boundary pre-project. Land that is in the pre-project floodway that has a floodway elevation post-project that is higher than the pre-project floodway elevation. Mitigation.
 Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) Insurable Structures ü Structures that are within the regulatory floodway post project that were not within the regulatory floodway pre-project. ü Structures that are within the 100 -year flood boundary post-project that were not in the 100 -year flood boundary pre-project. ü Structures that are subject to a 100 -year flood water surface elevation post-project that is higher than the 100 -year flood water surface elevation pre-project. ü Mitigation
Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management Ø National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) Insurable Structures ü Structures that are within the regulatory floodway post project that were not within the regulatory floodway pre-project. ü Structures that are within the 100 -year flood boundary post-project that were not in the 100 -year flood boundary pre-project. ü Structures that are subject to a 100 -year flood water surface elevation post-project that is higher than the 100 -year flood water surface elevation pre-project. ü Mitigation
 Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management ØState Minimum Standards for Flood Plain Management üVaries from State to State üAre always equal to or more restrictive than that of the NFIP in terms of: * Flood plain regulation • Elevation above the BFE. • Allowable rise due to fill or new construction in the flood plain * Mitigation of adverse impacts of projects.
Executive Order 11988 – Flood Plain Management ØState Minimum Standards for Flood Plain Management üVaries from State to State üAre always equal to or more restrictive than that of the NFIP in terms of: * Flood plain regulation • Elevation above the BFE. • Allowable rise due to fill or new construction in the flood plain * Mitigation of adverse impacts of projects.
 Section 202 of WRDA 1996 Flood Plain Management Plans • Applies to any flood damage reduction project which had the PPA signed after 12 October 1996. • Non Federal interests must prepare a flood plain management plan designed to reduce impacts of future floods in the project area • Develop within one year of PPA execution • Implement within one year after project completion • Primarily non structural measures are used
Section 202 of WRDA 1996 Flood Plain Management Plans • Applies to any flood damage reduction project which had the PPA signed after 12 October 1996. • Non Federal interests must prepare a flood plain management plan designed to reduce impacts of future floods in the project area • Develop within one year of PPA execution • Implement within one year after project completion • Primarily non structural measures are used
 Section 402 of WRDA 1986 • Applies to all flood damage reduction • projects Non Federal interests shall comply with applicable Federal flood plain management and flood insurance programs.
Section 402 of WRDA 1986 • Applies to all flood damage reduction • projects Non Federal interests shall comply with applicable Federal flood plain management and flood insurance programs.
 Section 219 of WRDA 1999 • Applies to the analysis of nonstructural buyout and • • • relocations measures All projects Benefit Calculation Use both externalized and internalized portions of flood damages prevented • Valued new use of evaluated flood plain • Reduction in damages to public property • Reduction in emergency costs • Reduction in admin costs of NFIP and disaster relief • Damages prevented
Section 219 of WRDA 1999 • Applies to the analysis of nonstructural buyout and • • • relocations measures All projects Benefit Calculation Use both externalized and internalized portions of flood damages prevented • Valued new use of evaluated flood plain • Reduction in damages to public property • Reduction in emergency costs • Reduction in admin costs of NFIP and disaster relief • Damages prevented
 Section 219 of WRDA 1999 (cont. ) • For real estate costs use comparable • flood free land building cost Betterments to gain DSS and housing costs of last resort are not included in flood free property cost.
Section 219 of WRDA 1999 (cont. ) • For real estate costs use comparable • flood free land building cost Betterments to gain DSS and housing costs of last resort are not included in flood free property cost.
 Uniform Relocation Assistance and Real Property Policies Act of 1970 and the Uniform Relocation Act Amendments of 1987 Ø Purpose ü To ensure that persons displaced as a direct result of Federal and federally-assisted projects are treated fairly, consistently, and equitably so that such persons will not suffer disproportionate injuries as a result of projects designed for the benefit of the public as a whole.
Uniform Relocation Assistance and Real Property Policies Act of 1970 and the Uniform Relocation Act Amendments of 1987 Ø Purpose ü To ensure that persons displaced as a direct result of Federal and federally-assisted projects are treated fairly, consistently, and equitably so that such persons will not suffer disproportionate injuries as a result of projects designed for the benefit of the public as a whole.
 Ø Applicability The requirements apply to any acquisition of real property for a federal project or project, and to programs and projects where there is Federal financial assistance in any part of project costs except for: ü Voluntary transactions that meet all of the following conditions: * No specific site or property needs to be acquired * The property to be acquired is not part of an intended, planned, or designated project area where all or substantially all of the property within the area is to be acquired within specific time limits * The Agency will not acquire the property in the event negotiations fail to result in an amicable agreement, and the owner is so informed in writing. * The Agency will inform the owner of what it believes to be fair market value of the property. ü
Ø Applicability The requirements apply to any acquisition of real property for a federal project or project, and to programs and projects where there is Federal financial assistance in any part of project costs except for: ü Voluntary transactions that meet all of the following conditions: * No specific site or property needs to be acquired * The property to be acquired is not part of an intended, planned, or designated project area where all or substantially all of the property within the area is to be acquired within specific time limits * The Agency will not acquire the property in the event negotiations fail to result in an amicable agreement, and the owner is so informed in writing. * The Agency will inform the owner of what it believes to be fair market value of the property. ü
 Comparable Replacement Dwelling Ø Decent, Safe, and Sanitary Ø Functionally Equivalent to the present dwelling Ø Located in an area not less desirable than the present location Ø Currently available in the private market Ø Within the financial means of the displaced person
Comparable Replacement Dwelling Ø Decent, Safe, and Sanitary Ø Functionally Equivalent to the present dwelling Ø Located in an area not less desirable than the present location Ø Currently available in the private market Ø Within the financial means of the displaced person
 Uniform Relocation Assistance and Real Property Policies Act of 1970 and the Uniform Relocation Act Amendments of 1987 ØThe term “decent, safe, and sanitary” means a dwelling which: üIs structurally sound, weathertight, and in good repair. üContains a safe electrical wiring system adequate for lighting and other devices. üContains a heating system capable of sustaining a healthful temperature (of approximately 70 degrees) for a displaced person, except in those areas where local climatic conditions do not require such a system. üIs adequate in size with respect to the number of rooms and area of living space needed to accommodate the displaced person. üHas üIs proper ingress and egress properly connected to an appropriate water source and an appropriate sewage system.
Uniform Relocation Assistance and Real Property Policies Act of 1970 and the Uniform Relocation Act Amendments of 1987 ØThe term “decent, safe, and sanitary” means a dwelling which: üIs structurally sound, weathertight, and in good repair. üContains a safe electrical wiring system adequate for lighting and other devices. üContains a heating system capable of sustaining a healthful temperature (of approximately 70 degrees) for a displaced person, except in those areas where local climatic conditions do not require such a system. üIs adequate in size with respect to the number of rooms and area of living space needed to accommodate the displaced person. üHas üIs proper ingress and egress properly connected to an appropriate water source and an appropriate sewage system.
 Uniform Relocation Assistance and Real Property Policies Act of 1970 and the Uniform Relocation Act Amendments of 1987 Ø Replacement Housing Payments: üOwners Ø who were in occupancy 180 days or more prior to the initiation of negotiations may be eligible for a purchase supplement up to $22, 500 or rental assistance payment up to $5, 250. üTenants who were in occupancy for 90 days or more prior to initiation of negotiation man be eligible for a rental assistance payment up to $5, 250. Housing of Last Resort
Uniform Relocation Assistance and Real Property Policies Act of 1970 and the Uniform Relocation Act Amendments of 1987 Ø Replacement Housing Payments: üOwners Ø who were in occupancy 180 days or more prior to the initiation of negotiations may be eligible for a purchase supplement up to $22, 500 or rental assistance payment up to $5, 250. üTenants who were in occupancy for 90 days or more prior to initiation of negotiation man be eligible for a rental assistance payment up to $5, 250. Housing of Last Resort
 Engineering Regulation 1105 -2 -100
Engineering Regulation 1105 -2 -100
 Engineering Regulation 1105 -2 -100 Ø Nonstructural measures shall receive equal Ø consideration in the Planning process New uses of evacuated flood plain ü Recreation ü Ecosystem restoration ü Recreation cost may not exceed 50% of the total project costs ü Recreation benefits may exceed 50% of the benefits needed for project justification
Engineering Regulation 1105 -2 -100 Ø Nonstructural measures shall receive equal Ø consideration in the Planning process New uses of evacuated flood plain ü Recreation ü Ecosystem restoration ü Recreation cost may not exceed 50% of the total project costs ü Recreation benefits may exceed 50% of the benefits needed for project justification
 Engineering Regulation 1105 -2 -100 ØNew uses of evacuated flood plain (continued) ü Benefits from ecosystem restoration and recreation that are new uses of the evacuated flood plain are considered flood damage reduction ü Land costs applicable to ecosystem restoration should not exceed 25% of total project costs ü Recreation and ecosystem restoration, if considered incidental to the primary purpose of flood damage reduction, can be cost shared on the basis of flood damage reduction
Engineering Regulation 1105 -2 -100 ØNew uses of evacuated flood plain (continued) ü Benefits from ecosystem restoration and recreation that are new uses of the evacuated flood plain are considered flood damage reduction ü Land costs applicable to ecosystem restoration should not exceed 25% of total project costs ü Recreation and ecosystem restoration, if considered incidental to the primary purpose of flood damage reduction, can be cost shared on the basis of flood damage reduction
 Engineering Regulation 1105 -2 -100 Ø Relocation/buyout is justified by: Value of the new use of the evacuated flood plain ü Reduction in damage to public property ü Reduction in emergency costs ü Reduction in administrative costs of the NFIP and disaster relief ü Total flood damage reduced ü Spillover benefits Ø Two or more structures are needed unless single property protection is part of a larger plan benefiting multiple owners Ø 65%/35% cost share ü
Engineering Regulation 1105 -2 -100 Ø Relocation/buyout is justified by: Value of the new use of the evacuated flood plain ü Reduction in damage to public property ü Reduction in emergency costs ü Reduction in administrative costs of the NFIP and disaster relief ü Total flood damage reduced ü Spillover benefits Ø Two or more structures are needed unless single property protection is part of a larger plan benefiting multiple owners Ø 65%/35% cost share ü
 U. S. Army Corps of Engineers National Nonstructural Flood Proofing Committee
U. S. Army Corps of Engineers National Nonstructural Flood Proofing Committee


