6b474f0055cd8b19ba5e210f043b709a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9
 National Interests l Relatively enduring general issues of great importance to the “nation” or country – Survival as a nation, sovereignty – Welfare, especially economic – Widely shared (although not universally) values and broad aspirations – Leaders staying in power? l l Who says what they are? Which interests are vital & how do we know?
National Interests l Relatively enduring general issues of great importance to the “nation” or country – Survival as a nation, sovereignty – Welfare, especially economic – Widely shared (although not universally) values and broad aspirations – Leaders staying in power? l l Who says what they are? Which interests are vital & how do we know?
 National Objectives l l May be short, medium or long term specific goals or actions the state might take to further its national interests May be modified by: – Threats to national interests – Opportunities that arise to advance the nation’s interests – Capabilities available (or can be made so) to carry out objectives
National Objectives l l May be short, medium or long term specific goals or actions the state might take to further its national interests May be modified by: – Threats to national interests – Opportunities that arise to advance the nation’s interests – Capabilities available (or can be made so) to carry out objectives
 Objectives: Hard to Agree On l Competing interests can lead to incompatible objectives – Domestic vs Foreign issues – Human rights vs Trade – Democracy vs Alliance partners, Freedom vs Security l Hard to prioritize – Groups within the state have competing interests Executive vs Legislature vs opposing interest groups vs public opinion? l What do they need to stay in power or gain success? l
Objectives: Hard to Agree On l Competing interests can lead to incompatible objectives – Domestic vs Foreign issues – Human rights vs Trade – Democracy vs Alliance partners, Freedom vs Security l Hard to prioritize – Groups within the state have competing interests Executive vs Legislature vs opposing interest groups vs public opinion? l What do they need to stay in power or gain success? l
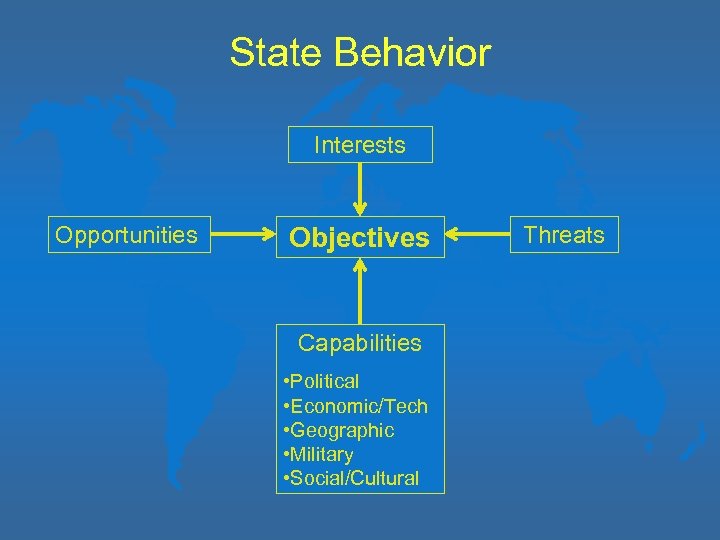 State Behavior Interests Opportunities Objectives Capabilities • Political • Economic/Tech • Geographic • Military • Social/Cultural Threats
State Behavior Interests Opportunities Objectives Capabilities • Political • Economic/Tech • Geographic • Military • Social/Cultural Threats
 Capabilities & Power l Power: Ability to influence others – Need those “others” to perceive capability and willingness to use it (credibility) – Power is relative to actors (and interests) involved l Capabilities that may give a state power: – Political – Economic/Technological – Geographic – Military – Social/Cultural/Religious
Capabilities & Power l Power: Ability to influence others – Need those “others” to perceive capability and willingness to use it (credibility) – Power is relative to actors (and interests) involved l Capabilities that may give a state power: – Political – Economic/Technological – Geographic – Military – Social/Cultural/Religious
 US/IRAQ War Timeline • • President Bush Speech to UN 12 Sep 02 US Congressional vote to authorize use of force 10 Oct 02 • Senate: 77 to 23, House: 296 to 133 • • US begins military buildup in Gulf, mainly in Kuwait and Qatar UN Security Council Resolution 1441 8 Nov 02 (Unanimous) • Iraq must divulge ALL information on WMD and allow inspectors free access to people and places or face “serious consequences” • Dec 02: Iraq maintains it has no WMD. Provides volumes of information, all previously known. US and British military buildup continues (passes 200, 000).
US/IRAQ War Timeline • • President Bush Speech to UN 12 Sep 02 US Congressional vote to authorize use of force 10 Oct 02 • Senate: 77 to 23, House: 296 to 133 • • US begins military buildup in Gulf, mainly in Kuwait and Qatar UN Security Council Resolution 1441 8 Nov 02 (Unanimous) • Iraq must divulge ALL information on WMD and allow inspectors free access to people and places or face “serious consequences” • Dec 02: Iraq maintains it has no WMD. Provides volumes of information, all previously known. US and British military buildup continues (passes 200, 000).
 US/IRAQ War Timeline (cont) • • • Jan – Mar 03: UN Inspectors go in, begin slow process of inspections, interviews. Get relatively free access to facilities, little cooperation on interviews. Find missiles with illegal range. US and British military buildup continues (exceeds 250, 000). Feb- Mar 03: US & BR work to get new UN Sec Council Resolution to more explicitly authorize use of force, claiming Iraq not complying with UN Res. 1441. Powell speech to UN Security Council. Actively opposed by French, somewhat by Germany, Russia. Mar 03: Votes do not appear to be there for US/BR resolution, so it is withdrawn. US and Britain, with other minor allies, invade Iraq.
US/IRAQ War Timeline (cont) • • • Jan – Mar 03: UN Inspectors go in, begin slow process of inspections, interviews. Get relatively free access to facilities, little cooperation on interviews. Find missiles with illegal range. US and British military buildup continues (exceeds 250, 000). Feb- Mar 03: US & BR work to get new UN Sec Council Resolution to more explicitly authorize use of force, claiming Iraq not complying with UN Res. 1441. Powell speech to UN Security Council. Actively opposed by French, somewhat by Germany, Russia. Mar 03: Votes do not appear to be there for US/BR resolution, so it is withdrawn. US and Britain, with other minor allies, invade Iraq.
 Invasion of Iraq: Potential US Loss • • Iraqi WMD or serious urban fighting kills many Coalition soldiers – Does not happen Significant Iraqi civilian refugee problem – Does not happen Anti-US riots in friendly Arab nations destabilize region, oil prices go way up - Does not happen Ethnic/religious civil war tear Iraq into separate pieces – Does not happen (yet) Coalition forces become focus for popular insurgency, Iraq becomes ungovernable; possible source of terrorists – Maybe International contention strains US alliances – Yes Distracts US from other threats: Korea, Al Queda – Maybe Other ?
Invasion of Iraq: Potential US Loss • • Iraqi WMD or serious urban fighting kills many Coalition soldiers – Does not happen Significant Iraqi civilian refugee problem – Does not happen Anti-US riots in friendly Arab nations destabilize region, oil prices go way up - Does not happen Ethnic/religious civil war tear Iraq into separate pieces – Does not happen (yet) Coalition forces become focus for popular insurgency, Iraq becomes ungovernable; possible source of terrorists – Maybe International contention strains US alliances – Yes Distracts US from other threats: Korea, Al Queda – Maybe Other ?
 Invasion of Iraq: Potential US Gains • • Increase in Israeli security, helps peace with Palestinians - Maybe Removes Saddam as unpredictable/dangerous regional actor- Yes • Human rights benefits • • Removes/verifies no WMD or threat of future WMD - Yes Arab democracy as example to other authoritarian Arab regimes as one answer to Islamic terrorism - Maybe Sanctions on Iraq can be dropped, US bases in Saudi Arabia no longer needed – Yes Iraqi oil production greatly increased – Not Yet • Greater supply makes for cheaper oil, boost to world economy • Alternative to Saudi oil can be developed: World economy not so dependent on future Saudi political stability • Other?
Invasion of Iraq: Potential US Gains • • Increase in Israeli security, helps peace with Palestinians - Maybe Removes Saddam as unpredictable/dangerous regional actor- Yes • Human rights benefits • • Removes/verifies no WMD or threat of future WMD - Yes Arab democracy as example to other authoritarian Arab regimes as one answer to Islamic terrorism - Maybe Sanctions on Iraq can be dropped, US bases in Saudi Arabia no longer needed – Yes Iraqi oil production greatly increased – Not Yet • Greater supply makes for cheaper oil, boost to world economy • Alternative to Saudi oil can be developed: World economy not so dependent on future Saudi political stability • Other?


