d7920f8c17bffd47595043c15ed0f736.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 National Institute of Justice Standards and Testing Program Debra Stoe Physical Scientist Body Armor and Standards and Testing Program October 21, 2009
National Institute of Justice Standards and Testing Program Debra Stoe Physical Scientist Body Armor and Standards and Testing Program October 21, 2009
 Agenda • Introduction to the National Institute of Justice (NIJ) • NIJ Standard Development Process • Summary of Standards Under Development or Revision
Agenda • Introduction to the National Institute of Justice (NIJ) • NIJ Standard Development Process • Summary of Standards Under Development or Revision
 NIJ’s Mission • Research, development and evaluation arm of the Department of Justice • Advances scientific research, development, and evaluation – to enhance the criminal justice (CJ) system – to increase public safety • Emphasis on State and local practitioner needs • Committed to scientific process of open competition, peerreview, publication of reports and archiving data
NIJ’s Mission • Research, development and evaluation arm of the Department of Justice • Advances scientific research, development, and evaluation – to enhance the criminal justice (CJ) system – to increase public safety • Emphasis on State and local practitioner needs • Committed to scientific process of open competition, peerreview, publication of reports and archiving data
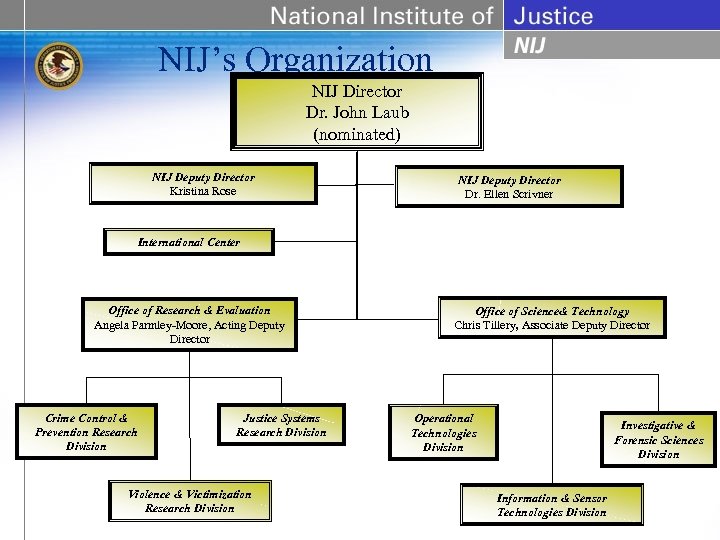 NIJ’s Organization NIJ Director Dr. John Laub (nominated) NIJ Deputy Director Kristina Rose NIJ Deputy Director Dr. Ellen Scrivner International Center Office of Research & Evaluation Angela Parmley-Moore, Acting Deputy Director Crime Control & Prevention Research Division Justice Systems Research Division Violence & Victimization Research Division Office of Science& Technology Chris Tillery, Associate Deputy Director Operational Technologies Division Investigative & Forensic Sciences Division Information & Sensor Technologies Division
NIJ’s Organization NIJ Director Dr. John Laub (nominated) NIJ Deputy Director Kristina Rose NIJ Deputy Director Dr. Ellen Scrivner International Center Office of Research & Evaluation Angela Parmley-Moore, Acting Deputy Director Crime Control & Prevention Research Division Justice Systems Research Division Violence & Victimization Research Division Office of Science& Technology Chris Tillery, Associate Deputy Director Operational Technologies Division Investigative & Forensic Sciences Division Information & Sensor Technologies Division
 NIJ Standards for Law Enforcement and Corrections Equipment Purpose: • Establish minimum design (weight / size) and performance requirements for equipment and define tests methods to measure performance Benefits: • Provides the end user with performance information on key equipment characteristics • Allows comparison of products based on common testing and minimum requirements • Provides a level of confidence in a product’s fitness for use
NIJ Standards for Law Enforcement and Corrections Equipment Purpose: • Establish minimum design (weight / size) and performance requirements for equipment and define tests methods to measure performance Benefits: • Provides the end user with performance information on key equipment characteristics • Allows comparison of products based on common testing and minimum requirements • Provides a level of confidence in a product’s fitness for use
 Why are NIJ Standards Used? • Manufacturers: Develop products that meet NIJ standards because of grant funding tied to standards and law enforcement procurement requirements specifying certified products • Purchasers: Specify and buy products that meet NIJ standards because of grant funding requirements and the need for confidence in performance Notes: • NIJ Standards are voluntary • No regulatory authority to compel conformity
Why are NIJ Standards Used? • Manufacturers: Develop products that meet NIJ standards because of grant funding tied to standards and law enforcement procurement requirements specifying certified products • Purchasers: Specify and buy products that meet NIJ standards because of grant funding requirements and the need for confidence in performance Notes: • NIJ Standards are voluntary • No regulatory authority to compel conformity
 NIJ Standard Development Process Previous Process: • NIJ funded technical partners to develop standard; practitioner involvement was limited. • Sometimes conformity assessment requirements were established. (Example: Body Armor Compliance Testing Program) • Sometimes users’ guides were developed. New Process: • Practitioners, technical experts, and stakeholder organizations collaborate. • Conformity assessment requirements always established. • Selection and Application Guides always developed. • Basic flow chart on next 2 slides.
NIJ Standard Development Process Previous Process: • NIJ funded technical partners to develop standard; practitioner involvement was limited. • Sometimes conformity assessment requirements were established. (Example: Body Armor Compliance Testing Program) • Sometimes users’ guides were developed. New Process: • Practitioners, technical experts, and stakeholder organizations collaborate. • Conformity assessment requirements always established. • Selection and Application Guides always developed. • Basic flow chart on next 2 slides.
 NIJ Standards Development Process 1. Need identified through Technology Working Groups, stakeholder groups, or practitioners. 4. NIJ establishes a Special Technical Committee. 2. NIJ evaluates need and determines path forward. 5. Committee works to develop draft documents over ~ 6 months. 3. NIJ convenes practitioner group to develop operational needs and requirements. 6. Draft documents posted for public review and comment on www. justnet. org.
NIJ Standards Development Process 1. Need identified through Technology Working Groups, stakeholder groups, or practitioners. 4. NIJ establishes a Special Technical Committee. 2. NIJ evaluates need and determines path forward. 5. Committee works to develop draft documents over ~ 6 months. 3. NIJ convenes practitioner group to develop operational needs and requirements. 6. Draft documents posted for public review and comment on www. justnet. org.
 NIJ Standards Development Process (continued) 7. Committee addresses comments and refines documents. 8. NIJ has any necessary validation testing performed. 9. NIJ reviews and publishes documents. 10. Conformity assessment begins. Standards Technology Working Group: Assists NIJ in managing standards and revision cycles.
NIJ Standards Development Process (continued) 7. Committee addresses comments and refines documents. 8. NIJ has any necessary validation testing performed. 9. NIJ reviews and publishes documents. 10. Conformity assessment begins. Standards Technology Working Group: Assists NIJ in managing standards and revision cycles.
 Committees Involved Special Technical Committee (STC) Advisory Working Group (AWG) Steering Committee (SC)
Committees Involved Special Technical Committee (STC) Advisory Working Group (AWG) Steering Committee (SC)
 Special Technical Committee Membership: • Law enforcement and corrections practitioners with relevant experience and expertise • Stakeholder organizations represented may include: FBOP, DEA, FOP, IACP, NSA, NTOA, LAPD, NYPD. • Technical experts (engineers, scientists, test labs, conformity assessment bodies, standards development organizations) • No manufacturers allowed on the STC NIJ and other support: • Facilitator, NIJ PM and technical support, editors/note takers Timeframe: • ~ 12 months meeting once per month for 2 days
Special Technical Committee Membership: • Law enforcement and corrections practitioners with relevant experience and expertise • Stakeholder organizations represented may include: FBOP, DEA, FOP, IACP, NSA, NTOA, LAPD, NYPD. • Technical experts (engineers, scientists, test labs, conformity assessment bodies, standards development organizations) • No manufacturers allowed on the STC NIJ and other support: • Facilitator, NIJ PM and technical support, editors/note takers Timeframe: • ~ 12 months meeting once per month for 2 days
 Advisory Working Group (AWG) • Provides oversight/guidance to the STCs during standard development effort • Senior-level personnel representing major stakeholder organizations, such as: Ø National Institute of Justice Ø National Institute of Standards and Technology/Office of Law Enforcement Standards Ø Department of Homeland Security Ø Fraternal Order of Police Ø National Tactical Officers Association Ø International Association of Chiefs of Police Ø National Sheriffs’ Association Ø American Correctional Association
Advisory Working Group (AWG) • Provides oversight/guidance to the STCs during standard development effort • Senior-level personnel representing major stakeholder organizations, such as: Ø National Institute of Justice Ø National Institute of Standards and Technology/Office of Law Enforcement Standards Ø Department of Homeland Security Ø Fraternal Order of Police Ø National Tactical Officers Association Ø International Association of Chiefs of Police Ø National Sheriffs’ Association Ø American Correctional Association
 Steering Committee • Purpose is to provide overall direction of the effort and approve the completed standard and related documents • Consists of the following senior advisors: Ø NIJ Deputy Director for Science and Technology Ø Standards Executive, Department of Homeland Security Science & Technology Ø Director, National Institute of Standards and Technology/Office of Law Enforcement Standards
Steering Committee • Purpose is to provide overall direction of the effort and approve the completed standard and related documents • Consists of the following senior advisors: Ø NIJ Deputy Director for Science and Technology Ø Standards Executive, Department of Homeland Security Science & Technology Ø Director, National Institute of Standards and Technology/Office of Law Enforcement Standards
 NIJ Standards: 3 Related Documents 1. Standard - Defines minimum design and performance requirements and test methods to assess performance 2. Conformity Assessment Requirements – Details the requirements for demonstrating that products conform to the standard 3. Selection and Application Guide - Provides information to assist law enforcement and corrections agency decision-makers, procurement officials, and end users; directly tied to 1 and 2
NIJ Standards: 3 Related Documents 1. Standard - Defines minimum design and performance requirements and test methods to assess performance 2. Conformity Assessment Requirements – Details the requirements for demonstrating that products conform to the standard 3. Selection and Application Guide - Provides information to assist law enforcement and corrections agency decision-makers, procurement officials, and end users; directly tied to 1 and 2
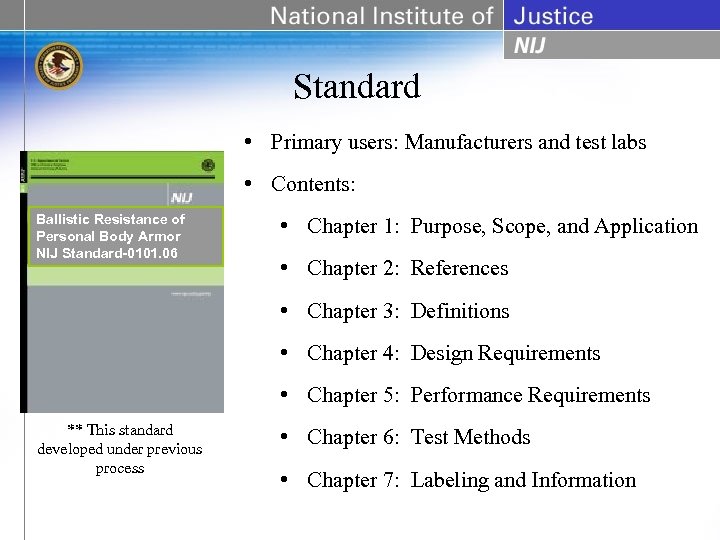 Standard • Primary users: Manufacturers and test labs • Contents: Ballistic Resistance of Personal Body Armor NIJ Standard-0101. 06 • Chapter 1: Purpose, Scope, and Application • Chapter 2: References • Chapter 3: Definitions • Chapter 4: Design Requirements • Chapter 5: Performance Requirements ** This standard developed under previous process • Chapter 6: Test Methods • Chapter 7: Labeling and Information
Standard • Primary users: Manufacturers and test labs • Contents: Ballistic Resistance of Personal Body Armor NIJ Standard-0101. 06 • Chapter 1: Purpose, Scope, and Application • Chapter 2: References • Chapter 3: Definitions • Chapter 4: Design Requirements • Chapter 5: Performance Requirements ** This standard developed under previous process • Chapter 6: Test Methods • Chapter 7: Labeling and Information
 Conformity Assessment Requirements NIJ Restraints Conformity Assessment Requirements Independent, Third-Party Certification or Compliance Testing Program • Ensures products are tested and meet the requirements of the standard • Requires ‘type testing’ in which samples are initially 2010 tested for conformity to the standard • Includes additional requirements for ongoing factory Independent Oversight: Trust but Verify surveillance and periodic follow-up testing • Manufacturer’s Declaration of Conformity not typically an NIJ option due to safety issues
Conformity Assessment Requirements NIJ Restraints Conformity Assessment Requirements Independent, Third-Party Certification or Compliance Testing Program • Ensures products are tested and meet the requirements of the standard • Requires ‘type testing’ in which samples are initially 2010 tested for conformity to the standard • Includes additional requirements for ongoing factory Independent Oversight: Trust but Verify surveillance and periodic follow-up testing • Manufacturer’s Declaration of Conformity not typically an NIJ option due to safety issues
 Conformity Assessment Example Body Armor Compliance Testing Program • Administered by NLECTC National the CT Program now follows requirements of ISO/IEC Guide 65 – General requirements for operating a product compliance system • Compliance Testing Program Document Series: – Posted on www. justnet. org/CTP – Body Armor CTP Administrative Manual – Ballistic Body Armor Applicant Instructions and Applicant Forms – Ballistics Test Laboratory Instructions, Application and Agreement – BA 9000: NIJ Body Armor Quality Management Requirements • Laboratory Accreditation and NIJ Approval • Conformity Assessment Follow-up Testing
Conformity Assessment Example Body Armor Compliance Testing Program • Administered by NLECTC National the CT Program now follows requirements of ISO/IEC Guide 65 – General requirements for operating a product compliance system • Compliance Testing Program Document Series: – Posted on www. justnet. org/CTP – Body Armor CTP Administrative Manual – Ballistic Body Armor Applicant Instructions and Applicant Forms – Ballistics Test Laboratory Instructions, Application and Agreement – BA 9000: NIJ Body Armor Quality Management Requirements • Laboratory Accreditation and NIJ Approval • Conformity Assessment Follow-up Testing
 Laboratory Accreditation and NIJ Approval • Test Laboratories must be accredited by the National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP) – Verifies that laboratories meet minimum quality requirements and are capable of performing test methods consistently and accurately – Reduces inter-laboratory variability • Laboratories must meet additional requirements to become NIJ-approved – Ensures independent laboratory testing with no conflicts of interest – Ensures all approved laboratories meet reporting requirements
Laboratory Accreditation and NIJ Approval • Test Laboratories must be accredited by the National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP) – Verifies that laboratories meet minimum quality requirements and are capable of performing test methods consistently and accurately – Reduces inter-laboratory variability • Laboratories must meet additional requirements to become NIJ-approved – Ensures independent laboratory testing with no conflicts of interest – Ensures all approved laboratories meet reporting requirements
 Conformity Assessment Follow-up Testing • Purpose is to ensure continued conformity of subsequent production compliant armor. • Involves periodic announced and unannounced sampling and re-testing of production armor. • Frequency of sampling and testing depends on the manufacturing location’s having or not having a registered quality management system – ISO 9001 and BA 9000 registration.
Conformity Assessment Follow-up Testing • Purpose is to ensure continued conformity of subsequent production compliant armor. • Involves periodic announced and unannounced sampling and re-testing of production armor. • Frequency of sampling and testing depends on the manufacturing location’s having or not having a registered quality management system – ISO 9001 and BA 9000 registration.
 QMS Options Impacting Frequency • Option 1: Manufacturing location does not have a registered QMS based on ISO 9001 in conjunction with BA 9000. ü Frequency: Sampling will be conducted 6 times within a 5 year listing cycle for each manufacturing location on each model. • Option 2: Manufacturing location have a registered QMS based on ISO 9001 in conjunction BA 9000. ü Frequency: Sampling will be conducted 3 times within a 5 year listing cycle for each manufacturing location on each model.
QMS Options Impacting Frequency • Option 1: Manufacturing location does not have a registered QMS based on ISO 9001 in conjunction with BA 9000. ü Frequency: Sampling will be conducted 6 times within a 5 year listing cycle for each manufacturing location on each model. • Option 2: Manufacturing location have a registered QMS based on ISO 9001 in conjunction BA 9000. ü Frequency: Sampling will be conducted 3 times within a 5 year listing cycle for each manufacturing location on each model.
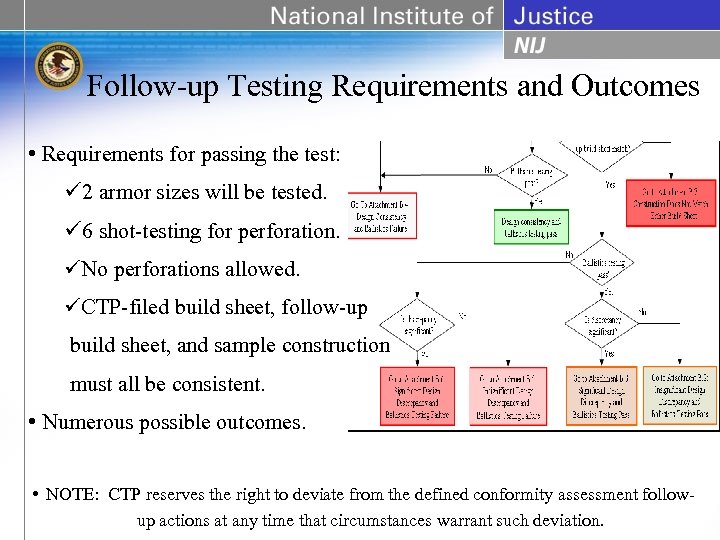 Follow-up Testing Requirements and Outcomes • Requirements for passing the test: ü 2 armor sizes will be tested. ü 6 shot-testing for perforation. üNo perforations allowed. üCTP-filed build sheet, follow-up build sheet, and sample construction must all be consistent. • Numerous possible outcomes. • NOTE: CTP reserves the right to deviate from the defined conformity assessment followup actions at any time that circumstances warrant such deviation.
Follow-up Testing Requirements and Outcomes • Requirements for passing the test: ü 2 armor sizes will be tested. ü 6 shot-testing for perforation. üNo perforations allowed. üCTP-filed build sheet, follow-up build sheet, and sample construction must all be consistent. • Numerous possible outcomes. • NOTE: CTP reserves the right to deviate from the defined conformity assessment followup actions at any time that circumstances warrant such deviation.
 NIJ Compliant Products List Current Numbers Manufacturer www. justnet. org
NIJ Compliant Products List Current Numbers Manufacturer www. justnet. org
 Selection and Application Guide Purpose: • Provides information to assist law enforcement and corrections agency decision-makers, procurement officials, and end users • Directly linked to the standard and conformity assessment requirements Contents may include: NIJ Restraints Selection and Application Guide Non-technical description of the NIJ standard and conformity assessment process • Types/Categories of equipment • Example scenarios for use of the equipment • 2010 • Guidance on procurement, selection, use, maintenance, care and disposal of equipment • Recommended Training
Selection and Application Guide Purpose: • Provides information to assist law enforcement and corrections agency decision-makers, procurement officials, and end users • Directly linked to the standard and conformity assessment requirements Contents may include: NIJ Restraints Selection and Application Guide Non-technical description of the NIJ standard and conformity assessment process • Types/Categories of equipment • Example scenarios for use of the equipment • 2010 • Guidance on procurement, selection, use, maintenance, care and disposal of equipment • Recommended Training
 Other Standards in Progress CBRN Protective Ensemble Standard Restraints Standard Hand Held and Walk Through Metal Detectors Standards Bomb Suit Standard Holster Standard Electronic Monitoring Standard
Other Standards in Progress CBRN Protective Ensemble Standard Restraints Standard Hand Held and Walk Through Metal Detectors Standards Bomb Suit Standard Holster Standard Electronic Monitoring Standard
 Questions? NIJ Standards and Testing Program Manager NIJ Body Armor Program Manager Debra Stoe debra. stoe@usdoj. gov
Questions? NIJ Standards and Testing Program Manager NIJ Body Armor Program Manager Debra Stoe debra. stoe@usdoj. gov


