cb6769583fbe741260e05d329199f339.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

NATIONAL INITIATIVES FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT ZANZIBAR Zanzibar Planning Commission 21 st OCTOBER, 2013
ZANZIBAR 2 Unguja Island Pemba Island

Outline 3 § Country Profile § Planning & Development Framework in Zanzibar 2000 – 2020, The Vision § Implementation of Vision 2020 § 2012 at a glance, Zanzibar in figures § ZSGRP I (MKUZA I) § ZSGRP II (MKUZA II) § MKUZA II Implementation Plan § Government Objectives (True North for Zanzibar) § Challenges § Conclusion

Country Profile 4 Zanzibar consists of two main islands, Unguja and Pemba Located in the Western Indian Ocean, about 30 km off the East Coast of Africa between latitudes 5 and 7 degrees south of Equator Zanzibar has a total area of 2, 654 sq km , out of this, Unguja has an area of 1, 666 sq km and Pemba has an area of 988 sq km. Population of Zanzibar reach 1, 303, 568 according to 2012 Population and housing Census from 981, 754 2002

Country Profile 5 Constitutionally, Zanzibar is one of the two countries that united in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania Zanzibar has its own government; the Executive, Judicial System and Legislative Assembly Zanzibar has its own autonomy in its domestics affairs include Economic planning and Management Administratively the islands are divided into five regions (three in Unguja and two in Pemba) with ten districts (two each).

Planning & Development Framework in Zanzibar 2000 - 2020 6

The Overall Development Objective for Vision 2020 7 Transform Zanzibar into a middle income country and enable it to eradicate absolute poverty in the society through: Building a strong and competitive economy; Achieving high quality livelihoods for citizens Improve good governance and the rule of law without compromising Zanzibar’s rich culture. By 2020 Zanzibar should have gone through an unprecedented economic transformation and development to achieve middle income status characterized by: High levels of industrialization, Competitiveness, Quality livelihoods,
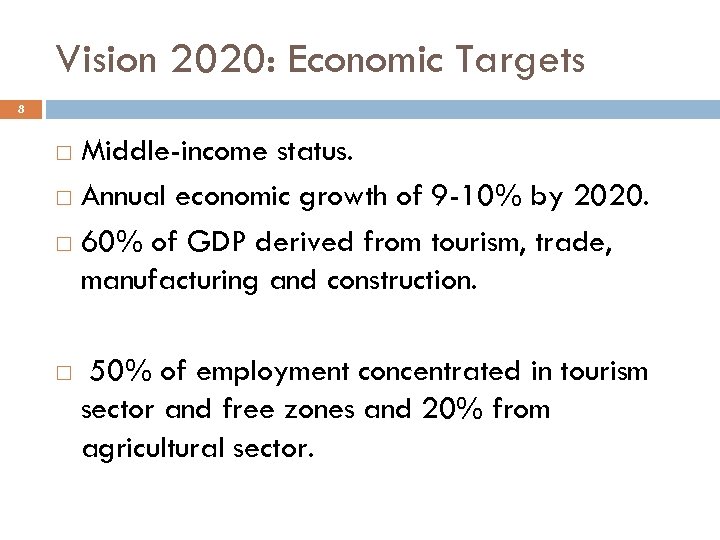
Vision 2020: Economic Targets 8 Middle-income status. Annual economic growth of 9 -10% by 2020. 60% of GDP derived from tourism, trade, manufacturing and construction. 50% of employment concentrated in tourism sector and free zones and 20% from agricultural sector.

VISION 2020 – SOCIAL TARGETS 9 Access to safe water. Access to basic, high-quality healthcare. Infant mortality rate of 20 per thousand. Life expectancy of 65 years. 100% enrolment in primary education (by 2005).

Implementation of the Vision 10 THROUGH MEDIUM-TERM STRATEGIES AND PLANS q Zanzibar Poverty Reduction Plan (ZPRP) 2002 -2005 The ZPRP involved a strategic selection of priority sectors deemed to have a more direct impact on poverty reduction. Hence these priority sectors (education, water, health, HIV/AIDS, good governance, infrastructure) were allocated more resources relative to other sectors

Implementation of the Vision, cont… 11 Zanzibar Strategy for Growth and Reduction of Poverty (ZSGRP I) 2007 -2010 The ZSGRP I, which is more popularly known in its Kiswahili acronym, MKUZA I, was adopted to retain and scale up achievements as well as addressing the challenges and weaknesses of the ZPRP. ü It was outcome-based and thus it clustered the strategies and interventions around linked goals and outcomes. ü

Implementation of the Vision, cont… 12 Cluster I Growth and Reduction of Income Poverty Primarily addresses Zanzibar’ s Growth Challenges Cluster II Social Services and Well Being Aims at improving wellbeing and social services Cluster III Good Governance and National Unity Aims at putting in place an improved governance systems

ZSGRP II (MKUZA II) 13 Zanzibar Strategy for Growth and Reduction of Poverty (ZSGRP II) 2010 -2015 The ZSGRP II or MKUZA II was adopted to maintain and scale up achievements as well as addressing the challenges and weaknesses of the ZSGRP I. ü Like ZSGRP, It is outcome-based and thus it clustered the strategies and interventions around linked goals and outcomes to MDG goals. ü Both ZSGRPs mainstreamed all crosscutting issues including HIV/AIDS, gender and environment. ü

The FOCUS includes 14 implementation of Growth Strategy by coordinating and linking with other sectors and scale up growthrelated interventions To harness and scale up the Public Private Partnership Implementation of Core Reforms

15 MKUZA II 5 years Implementation Plan Developed an actionable program/project plan which sequences interventions in a logical manner arising from MKUZA II outcomes, the flagship projects. Developed and costed the Investment Plan based on priority areas as stipulated in MKUZA II and the Growth Strategy Ensure actionable program/projects plan strengthen the credibility and consistency of MTEFs in accordance with MKUZA II outcomes

Priority areas……. . 16 Cluster I: Growth and Reduction of Income Poverty focus on: q Tourism, Trade, Agriculture, Services (particularly ICT), and manufacturing/value addition, q Energy, harbours, Roads network, land development (including land use planning) and Water for irrigation

Priority Areas ………. 17 Cluster II: Social Welfare and Well-being Focus on: q Provision of quality health, education and water q Skills development relevant to the planned activities of clusters I, II and III. Cluster III: Good Governance, the Rule of Law and National Unity focus on: q Filling the gaps in governance and leadership, particularly reform the way leaders and public servants act at all levels, such that they operate using result-based management approach.

Priority areas………. 18 q q Implementing major reforms like Zanzibar Public Service Reform, Zanzibar Local Government Reform, Zanzibar Legal Sector Reform, etc Enhancing the tracking of governance indicator. Building effective governance institutions. Undertaking institutional reforms in the public services by reforming the way bureaucracy operates and making it more responsive and efficient through nurturing, selection, training and retaining able and dedicated civil servants.

19 Structure of Prioritization of projects and programs On going Programs/projects b. New Programs/projects (Flagship) flagship projects consist three Categories characterized by: ü Their potential for achieving Vision 2020 aspirations; ü those that are strategic and/or important prerequisites for the implementation of other programmes/projects; ü readiness of their implementation; and ü financial availability and cost implications. a.

20 Structure of Prioritization of projects and programs. . Category I consists of programs and projects with the following attributes: feasibility Study is Completed, require less pre requisite from other programs/projects; it is critical for economic growth and employment generation and; have higher chances/potential for being financed. Category II is of those programs and projects with the following main attributes: they are dependent on the completion of programs/Projects from other Sectors feasibility Study is under Pre preparation. Category III are those programs and projects, which are on concept note stage.
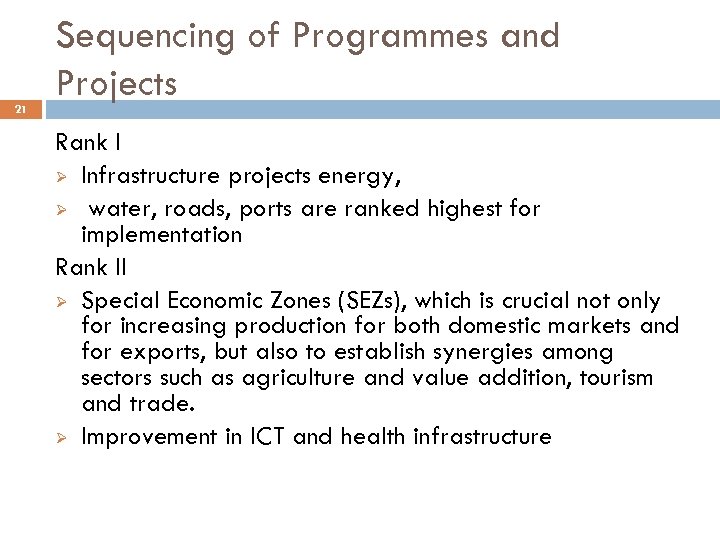
21 Sequencing of Programmes and Projects Rank I Ø Infrastructure projects energy, Ø water, roads, ports are ranked highest for implementation Rank II Ø Special Economic Zones (SEZs), which is crucial not only for increasing production for both domestic markets and for exports, but also to establish synergies among sectors such as agriculture and value addition, tourism and trade. Ø Improvement in ICT and health infrastructure

Sequencing of Programs and Projects 22 Rank III Ø Institutional reform, Ø capacity building, Ø environmental management; etc. Rank IV Ø Remaining programs and projects are found under all three clusters
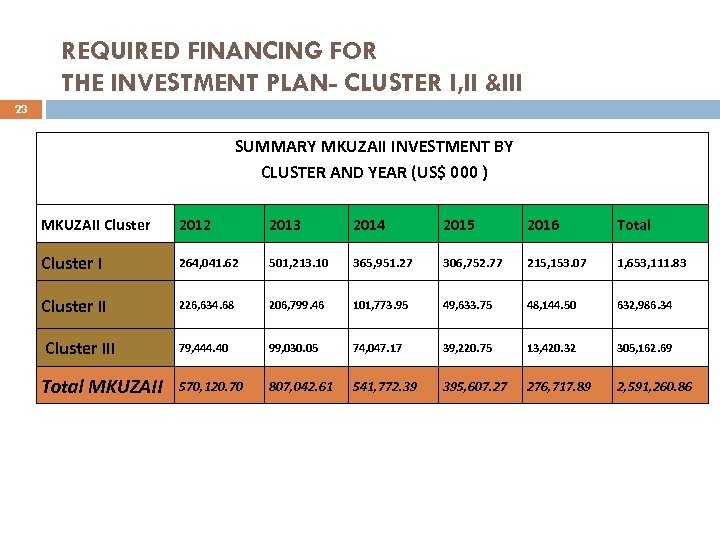
REQUIRED FINANCING FOR THE INVESTMENT PLAN- CLUSTER I, II &III 23 SUMMARY MKUZAII INVESTMENT BY CLUSTER AND YEAR (US$ 000 ) MKUZAII Cluster 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Total Cluster I 264, 041. 62 501, 213. 10 365, 951. 27 306, 752. 77 215, 153. 07 1, 653, 111. 83 Cluster II 226, 634. 68 206, 799. 46 101, 773. 95 49, 633. 75 48, 144. 50 632, 986. 34 79, 444. 40 99, 030. 05 74, 047. 17 39, 220. 75 13, 420. 32 305, 162. 69 570, 120. 70 807, 042. 61 541, 772. 39 395, 607. 27 276, 717. 89 2, 591, 260. 86 Cluster III Total MKUZAII

Source of financing A. § § § Conventional/Traditional Sources Tax collection Non tax collection Foreign Grants and Concessional Loans Climate Change Financing Mechanism Bolstering Skills Development Financing

Source of Financing cont…. B. Non-Conventional Approach § Sovereign Borrowing § Utilization of Diaspora § Regional Arrangement § Private Sectors and PPP
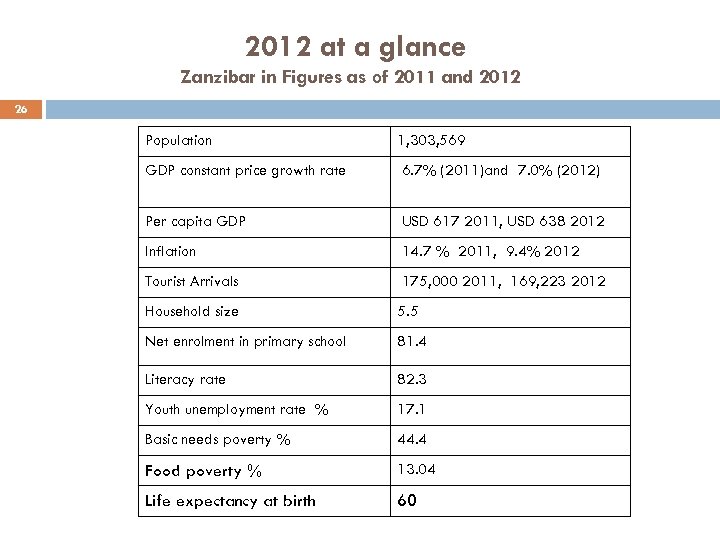
2012 at a glance Zanzibar in Figures as of 2011 and 2012 26 Population 1, 303, 569 GDP constant price growth rate 6. 7% (2011)and 7. 0% (2012) Per capita GDP USD 617 2011, USD 638 2012 Inflation 14. 7 % 2011, 9. 4% 2012 Tourist Arrivals 175, 000 2011, 169, 223 2012 Household size 5. 5 Net enrolment in primary school 81. 4 Literacy rate 82. 3 Youth unemployment rate % 17. 1 Basic needs poverty % 44. 4 Food poverty % 13. 04 Life expectancy at birth 60
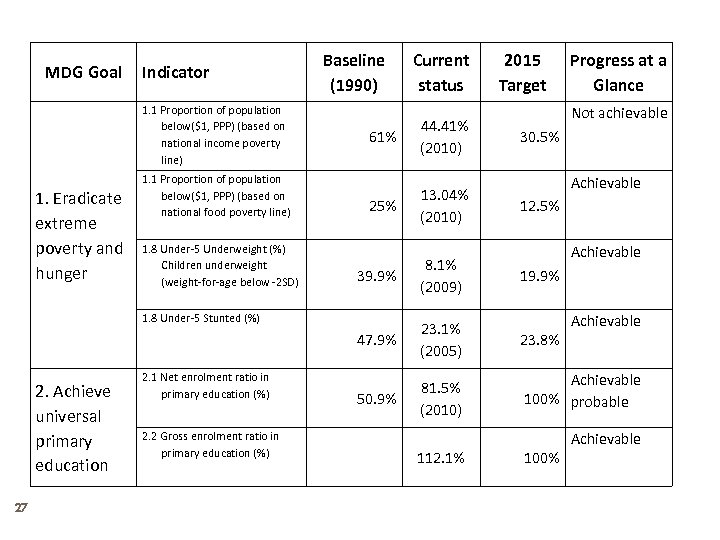
MDG Goal Indicator 1. 1 Proportion of population below($1, PPP) (based on national income poverty line) 1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger 1. 1 Proportion of population below($1, PPP) (based on national food poverty line) 1. 8 Under-5 Underweight (%) Children underweight (weight-for-age below -2 SD) Baseline (1990) 61% 25% Current status 44. 41% (2010) 13. 04% (2010) 2015 Target Progress at a Glance Not achievable 30. 5% Achievable 12. 5% Achievable 39. 9% 8. 1% (2009) 47. 9% 23. 1% (2005) 23. 8% 50. 9% 81. 5% (2010) Achievable 100% probable 1. 8 Under-5 Stunted (%) 2. Achieve universal primary education 27 2. 1 Net enrolment ratio in primary education (%) 2. 2 Gross enrolment ratio in primary education (%) 112. 1% 19. 9% 100% Achievable
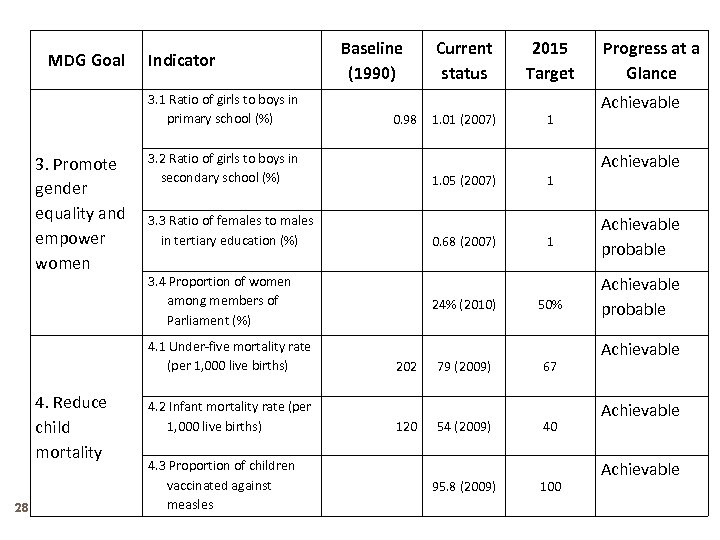
MDG Goal Indicator 3. 1 Ratio of girls to boys in primary school (%) 3. Promote gender equality and empower women 28 0. 98 3. 2 Ratio of girls to boys in secondary school (%) 4. 3 Proportion of children vaccinated against measles 2015 Target 1. 01 (2007) 1 0. 68 (2007) 3. 4 Proportion of women among members of Parliament (%) 4. 2 Infant mortality rate (per 1, 000 live births) Current status 1. 05 (2007) 3. 3 Ratio of females to males in tertiary education (%) 4. 1 Under-five mortality rate (per 1, 000 live births) 4. Reduce child mortality Baseline (1990) 24% (2010) 202 120 79 (2009) 54 (2009) 95. 8 (2009) 1 1 50% 67 40 100 Progress at a Glance Achievable probable Achievable
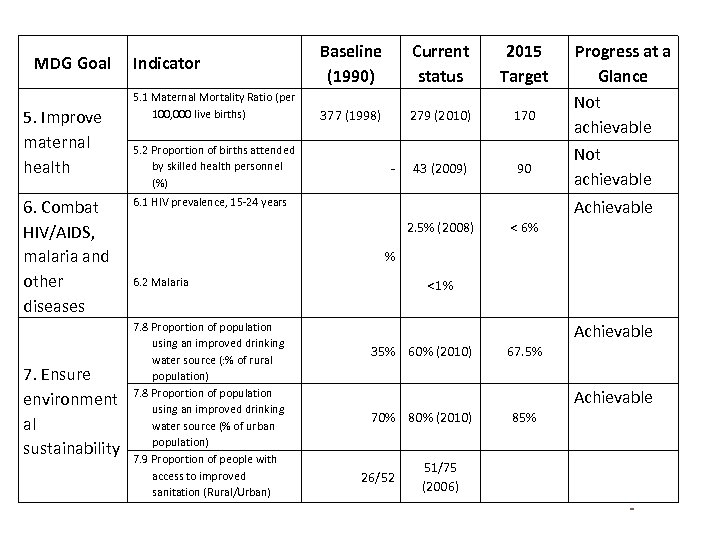
MDG Goal 5. Improve maternal health 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases 7. Ensure environment al sustainability Indicator 5. 1 Maternal Mortality Ratio (per 100, 000 live births) 5. 2 Proportion of births attended by skilled health personnel (%) Baseline (1990) Current status 2015 Target 377 (1998) 279 (2010) 170 43 (2009) 90 - 6. 1 HIV prevalence, 15 -24 years Progress at a Glance Not achievable Achievable 2. 5% (2008) < 6% % 6. 2 Malaria 7. 8 Proportion of population using an improved drinking water source (: % of rural population) 7. 8 Proportion of population using an improved drinking water source (% of urban population) 7. 9 Proportion of people with access to improved sanitation (Rural/Urban) <1% Achievable 35% 60% (2010) 67. 5% Achievable 70% 80% (2010) 26/52 85% 51/75 (2006) -

Defining the True North for Zanzibar 30 Transforming Zanzibar. . . through an unprecedented socio-economic transformation and development to achieve middle income status; characterized by increasing levels of industrialization, competitiveness, quality livelihoods and good governance and rule of law; and having in place an educated and pro-learning society with distinct culture and values (ZDV 2020) q Zanzibar true north is to attain high GDP growth rate q anticipated to be 7. 5%

GOVERNMENT OBJECTIVES 31 Economic Transformation Programme Enablers Human Capital Development Government Transformation Programme Crosscutting issues
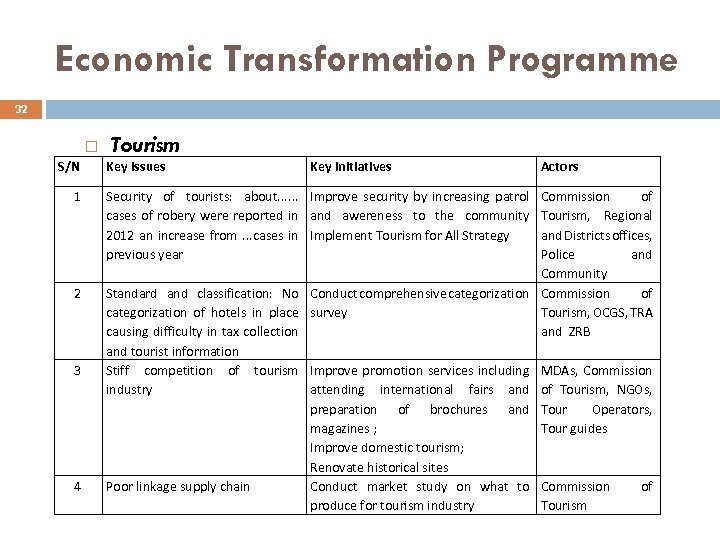
Economic Transformation Programme 32 S/N 1 2 3 4 Tourism Key Issues Key Initiatives Security of tourists: about. . . Improve security by increasing patrol cases of robery were reported in and awereness to the community 2012 an increase from. . . cases in Implement Tourism for All Strategy previous year Actors Commission of Tourism, Regional and Districts offices, Police and Community Standard and classification: No Conduct comprehensive categorization Commission of categorization of hotels in place survey Tourism, OCGS, TRA causing difficulty in tax collection and ZRB and tourist information Stiff competition of tourism Improve promotion services including MDAs, Commission industry attending international fairs and of Tourism, NGOs, preparation of brochures and Tour Operators, magazines ; Tour guides Improve domestic tourism; Renovate historical sites Poor linkage supply chain Conduct market study on what to Commission of produce for tourism industry Tourism
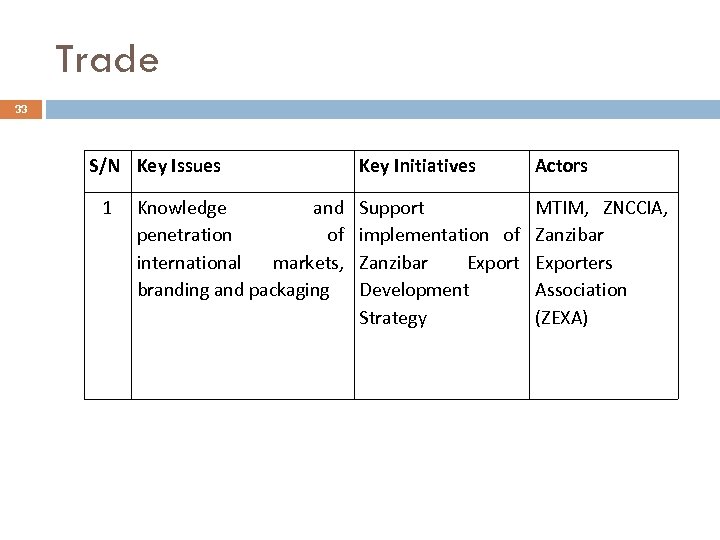
Trade 33 S/N Key Issues 1 Knowledge and penetration of international markets, branding and packaging Key Initiatives Actors Support implementation of Zanzibar Export Development Strategy MTIM, ZNCCIA, Zanzibar Exporters Association (ZEXA)
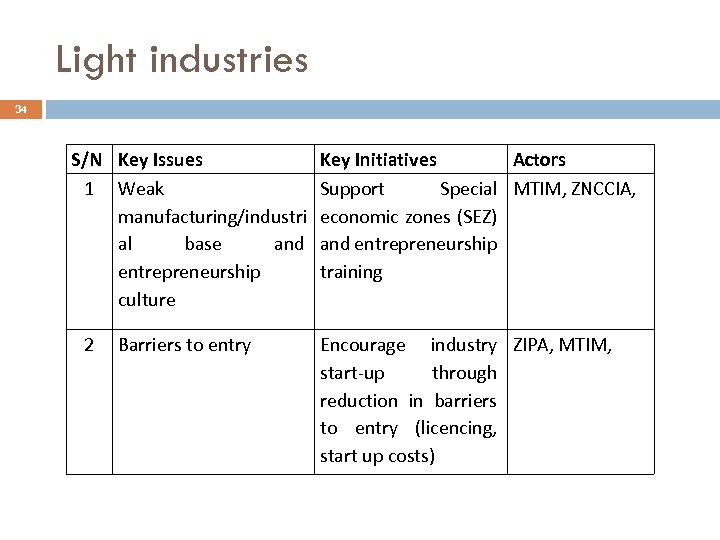
Light industries 34 S/N Key Issues 1 Weak manufacturing/industri al base and entrepreneurship culture 2 Barriers to entry Key Initiatives Actors Support Special MTIM, ZNCCIA, economic zones (SEZ) and entrepreneurship training Encourage industry ZIPA, MTIM, start-up through reduction in barriers to entry (licencing, start up costs)
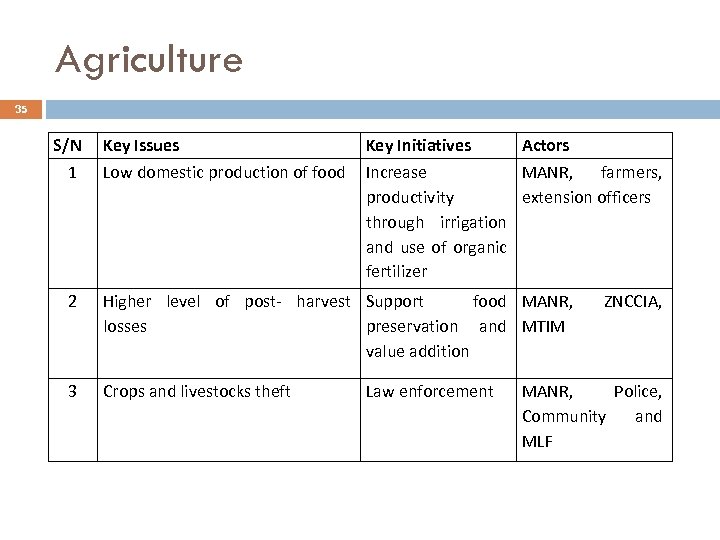
Agriculture 35 S/N 1 Key Issues Low domestic production of food Key Initiatives Actors Increase MANR, farmers, productivity extension officers through irrigation and use of organic fertilizer 2 Higher level of post- harvest Support food MANR, losses preservation and MTIM value addition 3 Crops and livestocks theft Law enforcement ZNCCIA, MANR, Police, Community and MLF
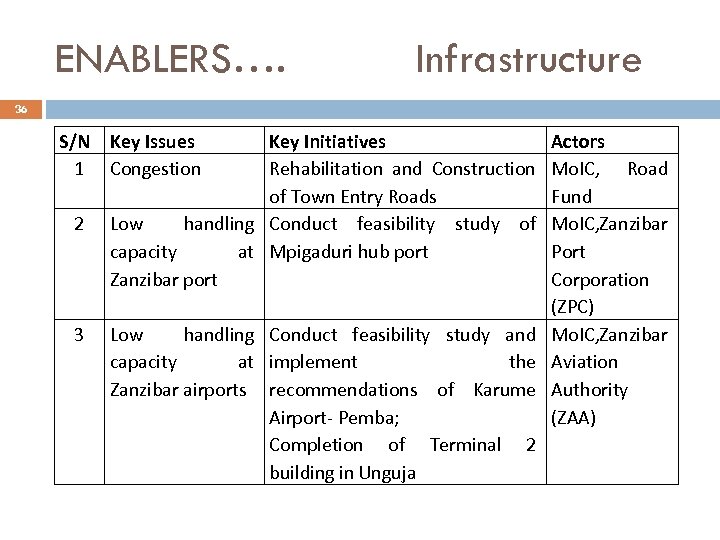
ENABLERS…. Infrastructure 36 S/N Key Issues 1 Congestion 2 3 Key Initiatives Rehabilitation and Construction of Town Entry Roads Low handling Conduct feasibility study of capacity at Mpigaduri hub port Zanzibar port Actors Mo. IC, Road Fund Mo. IC, Zanzibar Port Corporation (ZPC) Low handling Conduct feasibility study and Mo. IC, Zanzibar capacity at implement the Aviation Zanzibar airports recommendations of Karume Authority Airport- Pemba; (ZAA) Completion of Terminal 2 building in Unguja
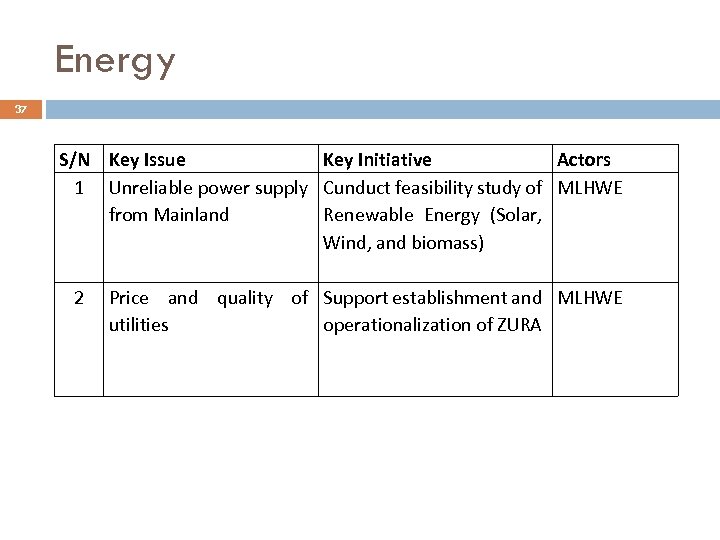
Energy 37 S/N Key Issue Key Initiative Actors 1 Unreliable power supply Cunduct feasibility study of MLHWE from Mainland Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind, and biomass) 2 Price and quality of Support establishment and MLHWE utilities operationalization of ZURA
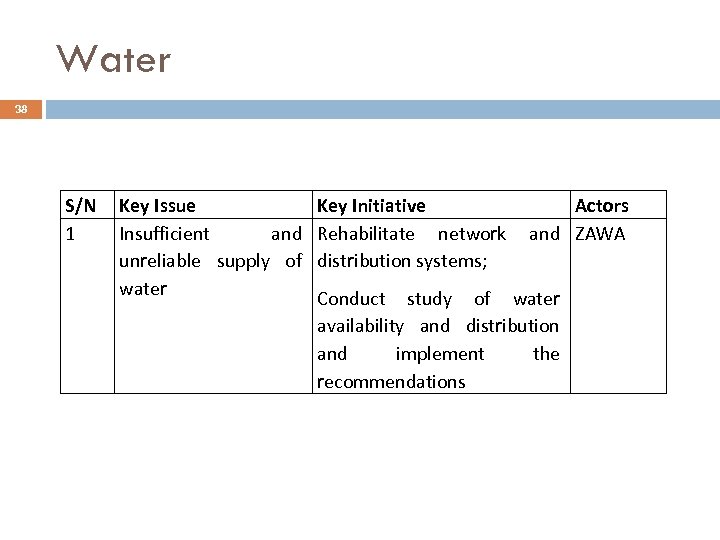
Water 38 S/N 1 Key Issue Insufficient and unreliable supply of water Key Initiative Rehabilitate network distribution systems; Actors and ZAWA Conduct study of water availability and distribution and implement the recommendations
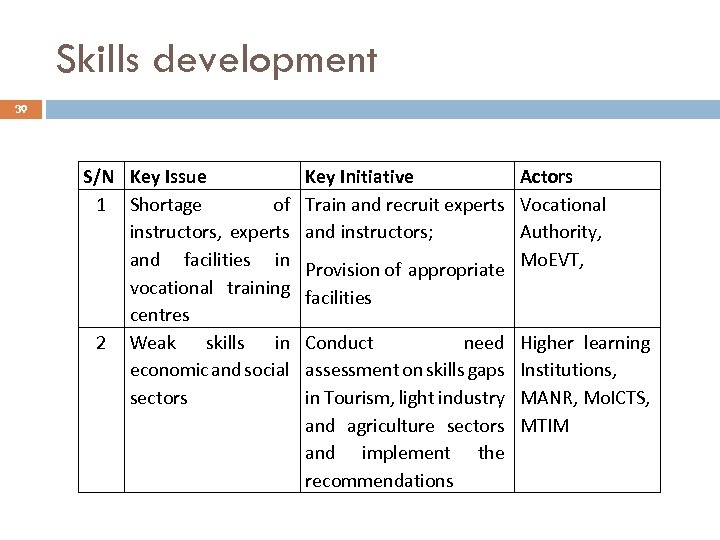
Skills development 39 S/N Key Issue 1 Shortage of instructors, experts and facilities in vocational training centres 2 Weak skills in economic and social sectors Key Initiative Actors Train and recruit experts Vocational and instructors; Authority, Provision of appropriate Mo. EVT, facilities Conduct need assessment on skills gaps in Tourism, light industry and agriculture sectors and implement the recommendations Higher learning Institutions, MANR, Mo. ICTS, MTIM
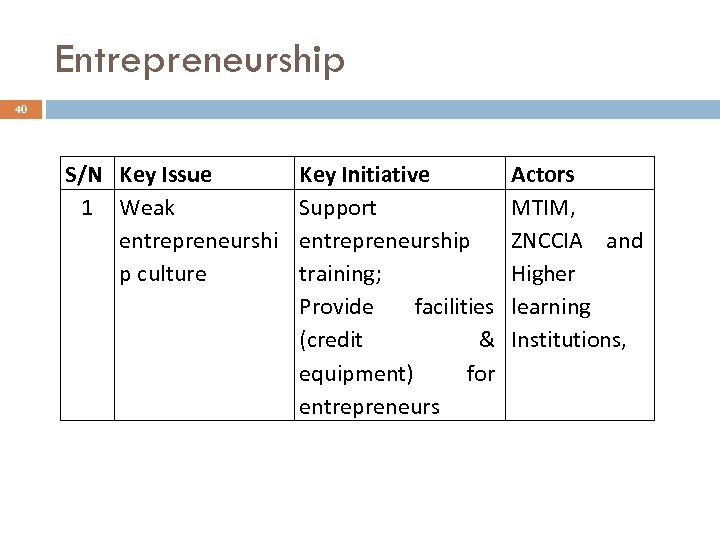
Entrepreneurship 40 S/N Key Issue 1 Weak entrepreneurshi p culture Key Initiative Support entrepreneurship training; Provide facilities (credit & equipment) for entrepreneurs Actors MTIM, ZNCCIA and Higher learning Institutions,
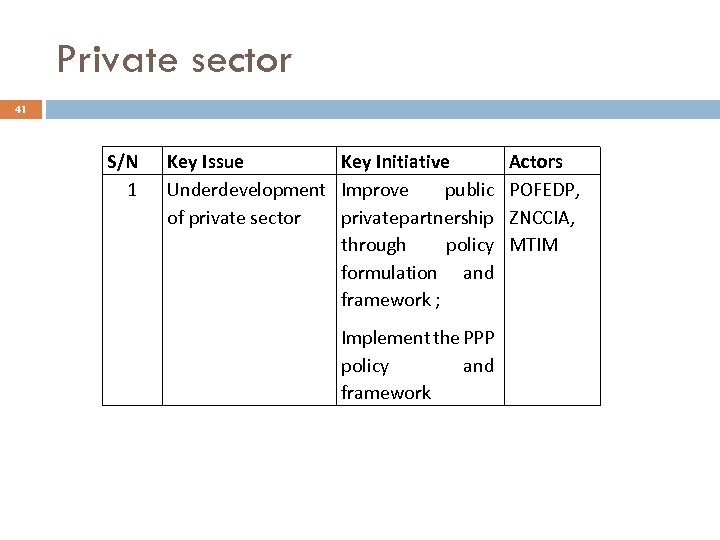
Private sector 41 S/N 1 Key Issue Key Initiative Underdevelopment Improve public of private sector private partnership through policy formulation and framework ; Implement the PPP policy and framework Actors POFEDP, ZNCCIA, MTIM
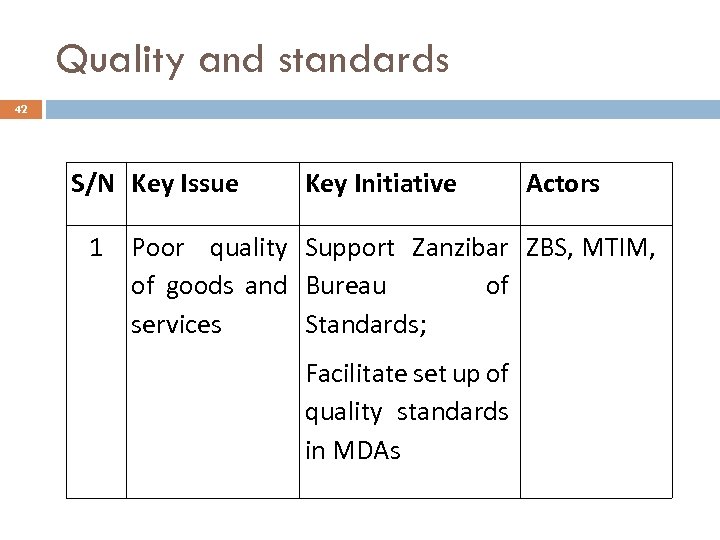
Quality and standards 42 S/N Key Issue 1 Key Initiative Actors Poor quality Support Zanzibar ZBS, MTIM, of goods and Bureau of services Standards; Facilitate set up of quality standards in MDAs
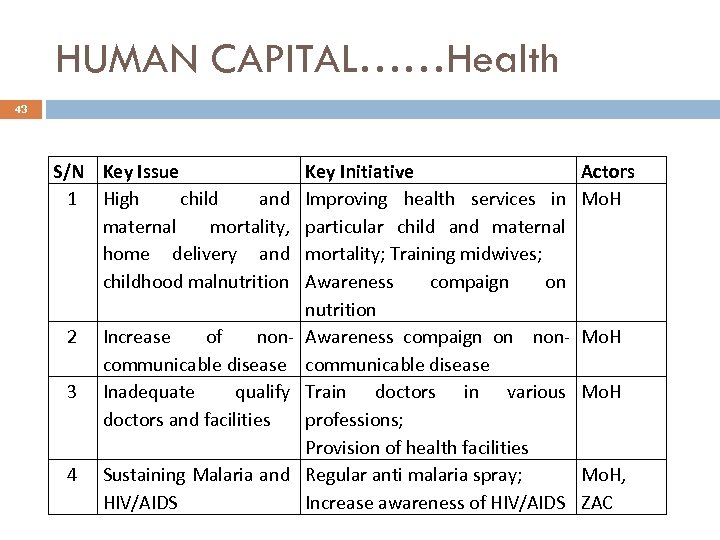
HUMAN CAPITAL……Health 43 S/N Key Issue 1 High child and maternal mortality, home delivery and childhood malnutrition 2 3 4 Increase of noncommunicable disease Inadequate qualify doctors and facilities Sustaining Malaria and HIV/AIDS Key Initiative Improving health services in particular child and maternal mortality; Training midwives; Awareness compaign on nutrition Awareness compaign on noncommunicable disease Train doctors in various professions; Provision of health facilities Regular anti malaria spray; Increase awareness of HIV/AIDS Actors Mo. H, ZAC
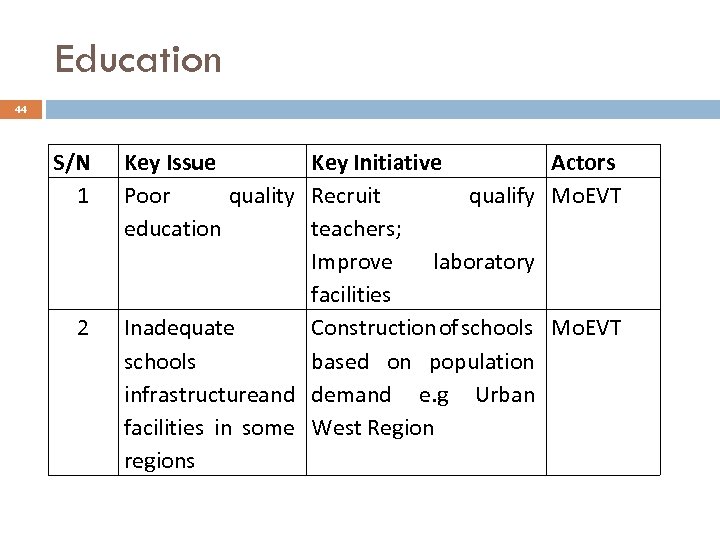
Education 44 S/N 1 2 Key Issue Key Initiative Actors Poor quality Recruit qualify Mo. EVT education teachers; Improve laboratory facilities Inadequate Construction of schools Mo. EVT schools based on population infrastructureand demand e. g Urban facilities in some West Region regions
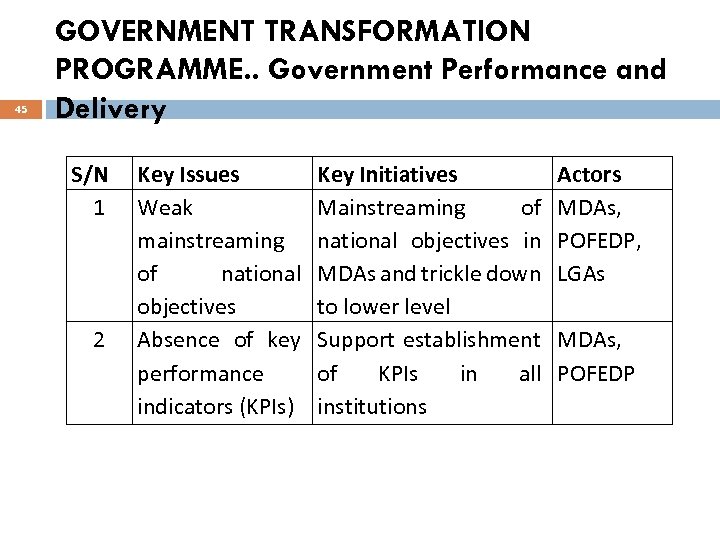
45 GOVERNMENT TRANSFORMATION PROGRAMME. . Government Performance and Delivery S/N 1 2 Key Issues Weak mainstreaming of national objectives Absence of key performance indicators (KPIs) Key Initiatives Mainstreaming of national objectives in MDAs and trickle down to lower level Support establishment of KPIs in all institutions Actors MDAs, POFEDP, LGAs MDAs, POFEDP
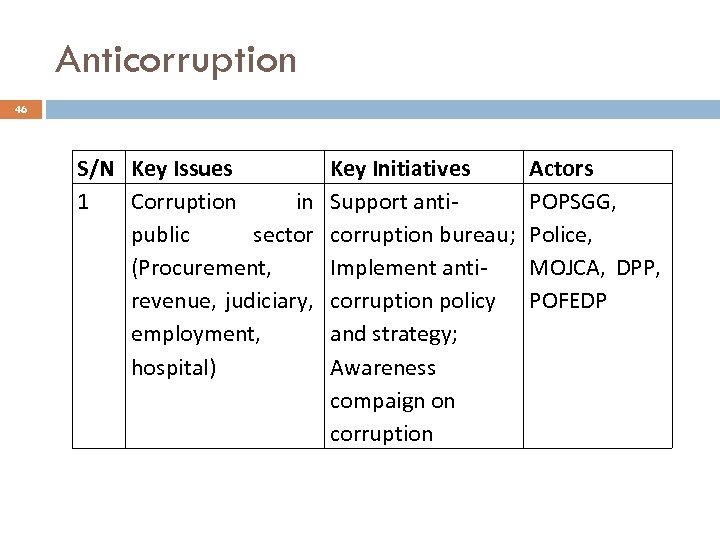
Anticorruption 46 S/N Key Issues 1 Corruption in public sector (Procurement, revenue, judiciary, employment, hospital) Key Initiatives Support anticorruption bureau; Implement anticorruption policy and strategy; Awareness compaign on corruption Actors POPSGG, Police, MOJCA, DPP, POFEDP
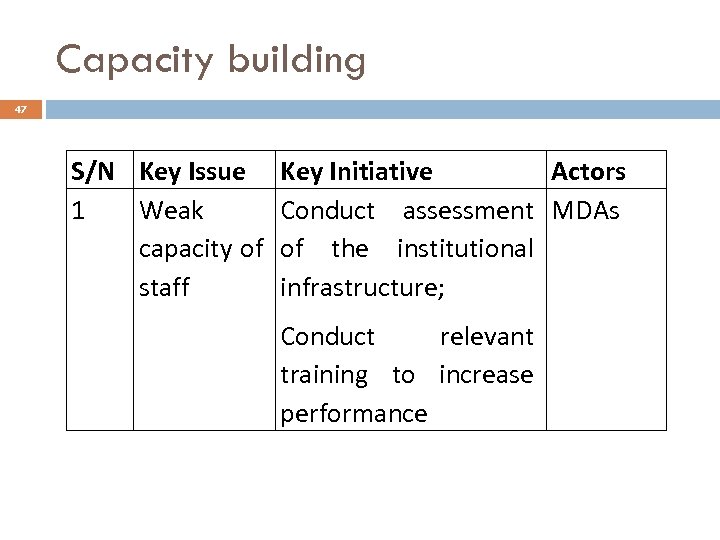
Capacity building 47 S/N Key Issue 1 Weak capacity of staff Key Initiative Actors Conduct assessment MDAs of the institutional infrastructure; Conduct relevant training to increase performance
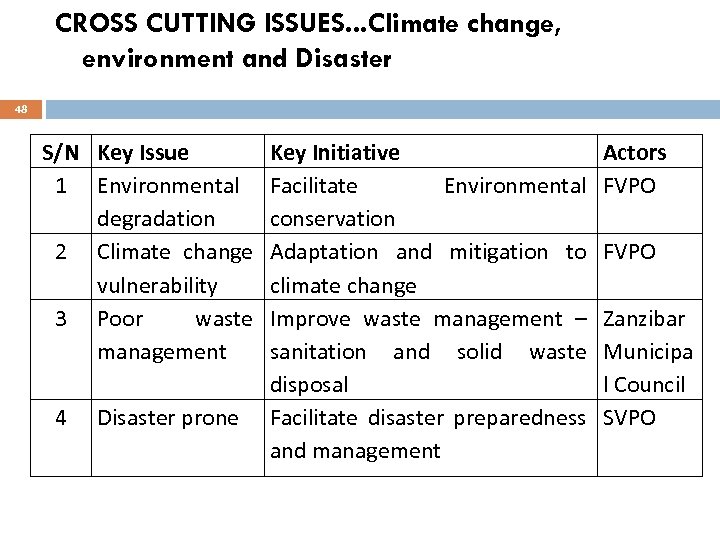
CROSS CUTTING ISSUES. . . Climate change, environment and Disaster 48 S/N Key Issue 1 Environmental degradation 2 Climate change vulnerability 3 Poor waste management 4 Disaster prone Key Initiative Facilitate Environmental conservation Adaptation and mitigation to climate change Improve waste management – sanitation and solid waste disposal Facilitate disaster preparedness and management Actors FVPO Zanzibar Municipa l Council SVPO
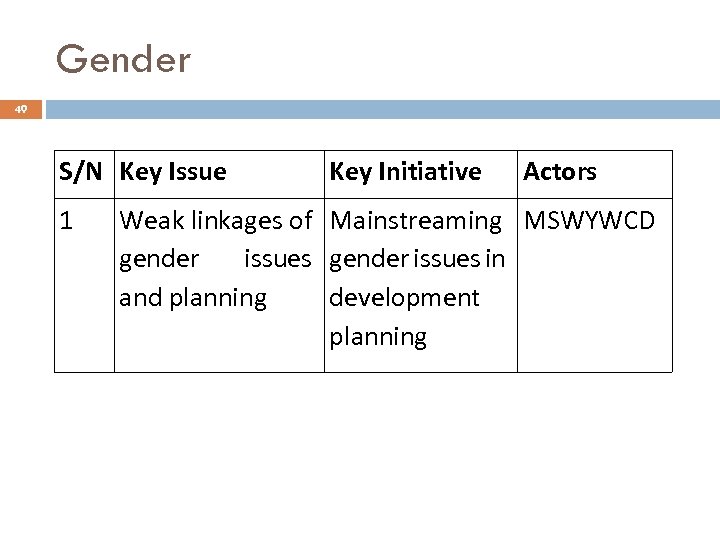
Gender 49 S/N Key Issue 1 Key Initiative Actors Weak linkages of Mainstreaming MSWYWCD gender issues in and planning development planning
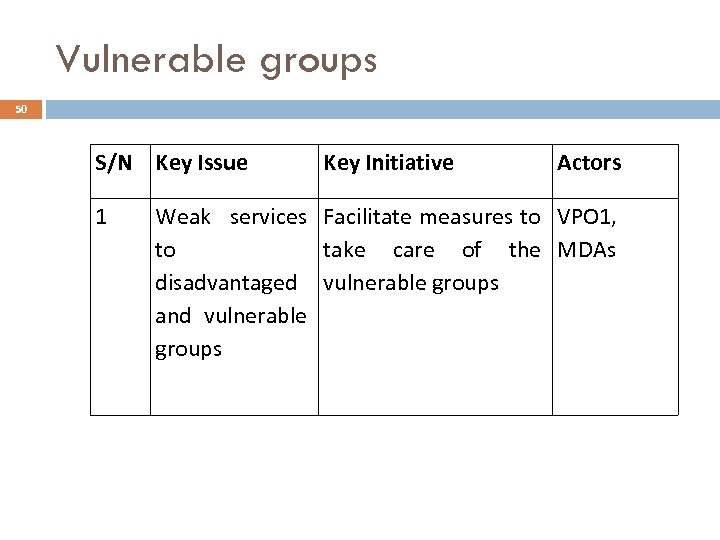
Vulnerable groups 50 S/N Key Issue 1 Key Initiative Actors Weak services Facilitate measures to VPO 1, to take care of the MDAs disadvantaged vulnerable groups and vulnerable groups

Challenges 51 • • • Balancing economic growth and protecting socio-cultural values of the people of Zanzibar Building a strong domestic Private sector capable of transforming the productive sectors of Zanzibar Establishing a prosperous society with an economy that is fully competitive, dynamic, robust and resilient Ensuring an economically just society, in which there is a fair and equitable distribution of the wealth of the nation Shortage of skills in priority areas like manufacturing and value addition in general

Challenges, cont… 52 • • Weak capacity in planning, policy analysis and monitoring and evaluation Absence of planning practices and framework at local level. Inadequate mobilization both domestic and external resources Weak capacity in the development of district plans and integration district plans into national plan

Conclusion 53 Second half of Vision 2020 is underway, effective implementation of MKUZA II is crucial Economic Transformation is key to achieve sustainable growth Capacity and Resources are main challenges, special efforts needed. Integration of District Plans into National plan We bank on all stakeholders and friends of Zanzibar in achieving the desired results We can attain middle income status by 2020 if everybody stay on course.

Ahsanteni 54
cb6769583fbe741260e05d329199f339.ppt