acf319d9b6dec18f335aa898695d10bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 National Central University Department of Mathematics Numerical Electro. Magnetics & Semiconductor Industrial Applications 10 Summary: RC extractor & Electro. Magnetic (EM) field solver Ke-Ying Su Ph. D.
National Central University Department of Mathematics Numerical Electro. Magnetics & Semiconductor Industrial Applications 10 Summary: RC extractor & Electro. Magnetic (EM) field solver Ke-Ying Su Ph. D.
 Contents (1) Design flow & EDA tools • Methods in Raphael 2 D & 3 D, QRC, Peak. View, Momentum, & EMX. (2) Quasi-static-analyses (C extraction) • • • corss-section profile vs Green's function process variation vs method of moment 2 D & 3 D models in a RC techfile (3) PEEC (RLK extraction) • • Partial-Element-Equivalent-Circuit (PEEC) RLK relations in spiral inductors and interconnects (4) Full-wave analyses (S-parameter extraction) • • Maxwell's equations S-parameters from current waves (5) Double Patterning Technology & Solution P. 1 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
Contents (1) Design flow & EDA tools • Methods in Raphael 2 D & 3 D, QRC, Peak. View, Momentum, & EMX. (2) Quasi-static-analyses (C extraction) • • • corss-section profile vs Green's function process variation vs method of moment 2 D & 3 D models in a RC techfile (3) PEEC (RLK extraction) • • Partial-Element-Equivalent-Circuit (PEEC) RLK relations in spiral inductors and interconnects (4) Full-wave analyses (S-parameter extraction) • • Maxwell's equations S-parameters from current waves (5) Double Patterning Technology & Solution P. 1 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
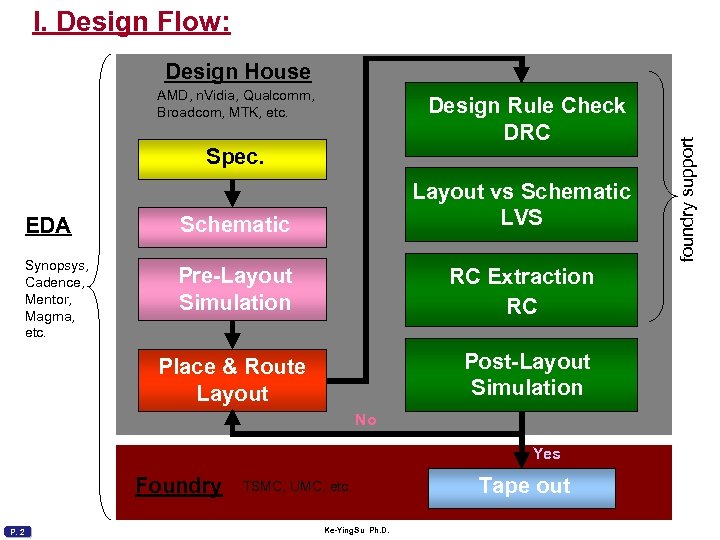 I. Design Flow: AMD, n. Vidia, Qualcomm, Broadcom, MTK, etc. Design Rule Check DRC Spec. EDA Schematic Layout vs Schematic LVS Synopsys, Cadence, Mentor, Magma, etc. Pre-Layout Simulation RC Extraction RC Place & Route Layout Post-Layout Simulation No Yes Foundry P. 2 TSMC, UMC, etc. Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. Tape out foundry support Design House
I. Design Flow: AMD, n. Vidia, Qualcomm, Broadcom, MTK, etc. Design Rule Check DRC Spec. EDA Schematic Layout vs Schematic LVS Synopsys, Cadence, Mentor, Magma, etc. Pre-Layout Simulation RC Extraction RC Place & Route Layout Post-Layout Simulation No Yes Foundry P. 2 TSMC, UMC, etc. Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. Tape out foundry support Design House
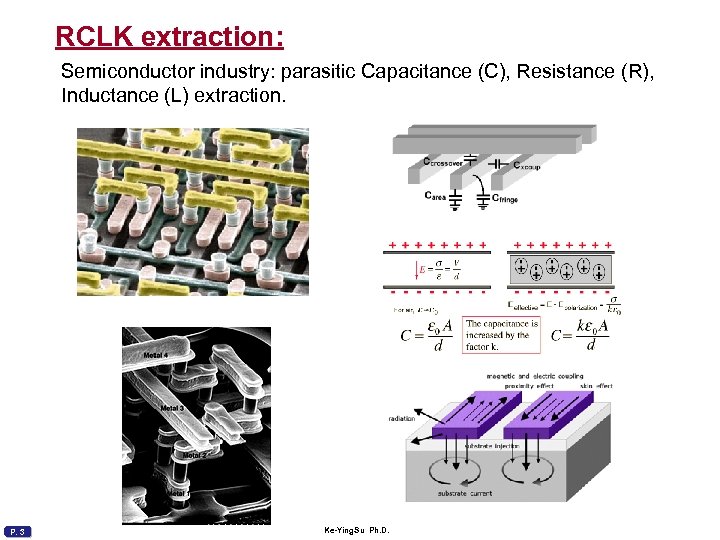 RCLK extraction: Semiconductor industry: parasitic Capacitance (C), Resistance (R), Inductance (L) extraction. P. 3 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
RCLK extraction: Semiconductor industry: parasitic Capacitance (C), Resistance (R), Inductance (L) extraction. P. 3 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
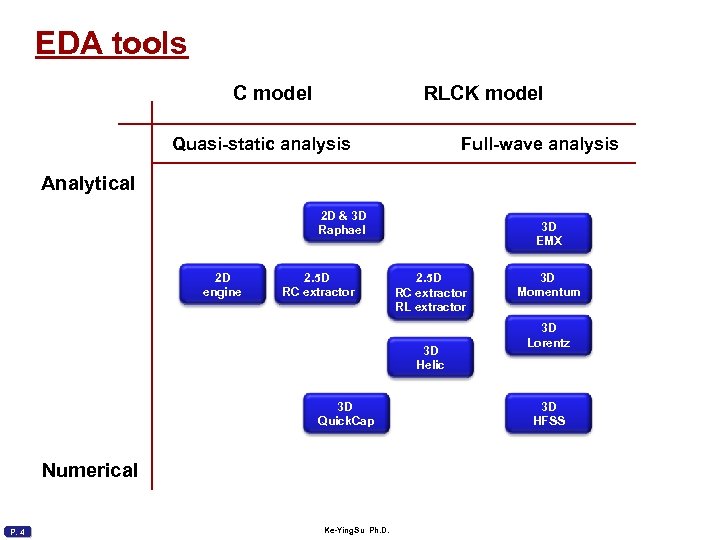 EDA tools C model RLCK model Quasi-static analysis Full-wave analysis Analytical 2 D & 3 D Raphael 2 D engine 2. 5 D RC extractor 3 D EMX 2. 5 D RC extractor RL extractor 3 D Helic 3 D Quick. Cap Numerical P. 4 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. 3 D Momentum 3 D Lorentz 3 D HFSS
EDA tools C model RLCK model Quasi-static analysis Full-wave analysis Analytical 2 D & 3 D Raphael 2 D engine 2. 5 D RC extractor 3 D EMX 2. 5 D RC extractor RL extractor 3 D Helic 3 D Quick. Cap Numerical P. 4 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. 3 D Momentum 3 D Lorentz 3 D HFSS
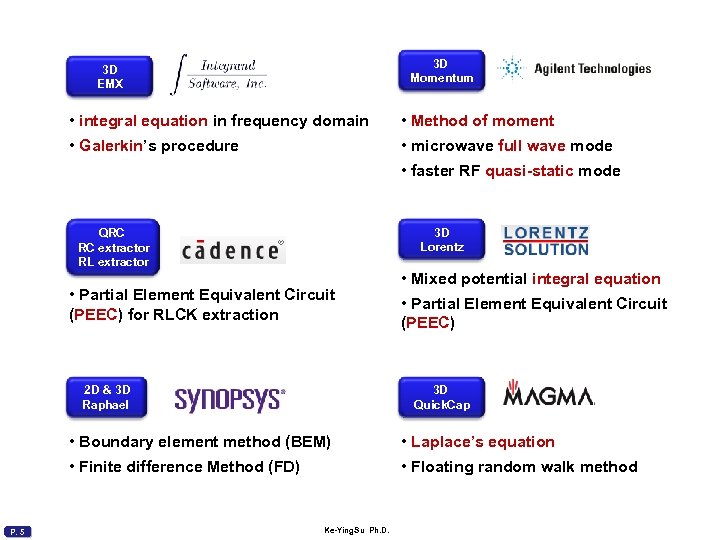 3 D Momentum 3 D EMX • integral equation in frequency domain • Method of moment • Galerkin’s procedure • microwave full wave mode • faster RF quasi-static mode 3 D Lorentz QRC RC extractor RL extractor • Partial Element Equivalent Circuit (PEEC) for RLCK extraction 2 D & 3 D Raphael • Mixed potential integral equation • Partial Element Equivalent Circuit (PEEC) 3 D Quick. Cap • Boundary element method (BEM) • Finite difference Method (FD) P. 5 • Laplace’s equation • Floating random walk method Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
3 D Momentum 3 D EMX • integral equation in frequency domain • Method of moment • Galerkin’s procedure • microwave full wave mode • faster RF quasi-static mode 3 D Lorentz QRC RC extractor RL extractor • Partial Element Equivalent Circuit (PEEC) for RLCK extraction 2 D & 3 D Raphael • Mixed potential integral equation • Partial Element Equivalent Circuit (PEEC) 3 D Quick. Cap • Boundary element method (BEM) • Finite difference Method (FD) P. 5 • Laplace’s equation • Floating random walk method Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
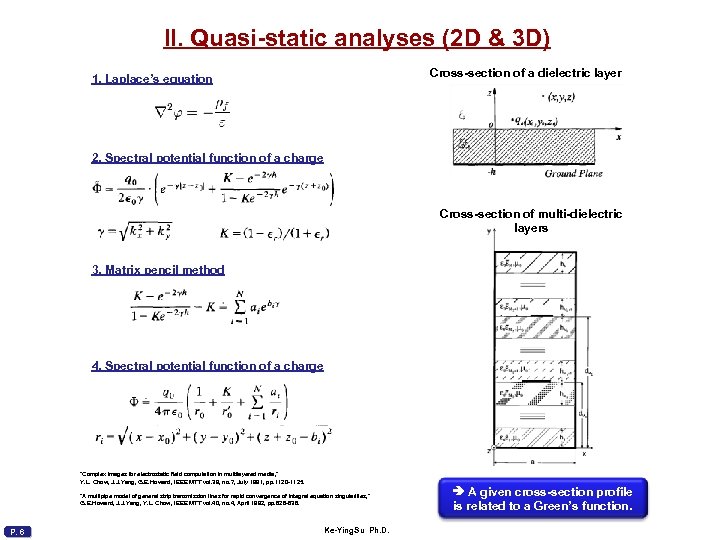 II. Quasi-static analyses (2 D & 3 D) Cross-section of a dielectric layer 1. Laplace’s equation 2. Spectral potential function of a charge Cross-section of multi-dielectric layers 3. Matrix pencil method 4. Spectral potential function of a charge “Complex images for electrostatic field computation in multilayered media, ” Y. L. Chow, J. J. Yang, G. E. Howard, IEEE MTT vol. 39, no. 7, July 1991, pp. 1120 -1125. “A multipipe model of general strip transmission lines for rapid convergence of integral equation singularities, ” G. E. Howard, J. J. Yang, Y. L. Chow, IEEE MTT vol. 40, no. 4, April 1992, pp. 628 -636. P. 6 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. A given cross-section profile is related to a Green’s function.
II. Quasi-static analyses (2 D & 3 D) Cross-section of a dielectric layer 1. Laplace’s equation 2. Spectral potential function of a charge Cross-section of multi-dielectric layers 3. Matrix pencil method 4. Spectral potential function of a charge “Complex images for electrostatic field computation in multilayered media, ” Y. L. Chow, J. J. Yang, G. E. Howard, IEEE MTT vol. 39, no. 7, July 1991, pp. 1120 -1125. “A multipipe model of general strip transmission lines for rapid convergence of integral equation singularities, ” G. E. Howard, J. J. Yang, Y. L. Chow, IEEE MTT vol. 40, no. 4, April 1992, pp. 628 -636. P. 6 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. A given cross-section profile is related to a Green’s function.
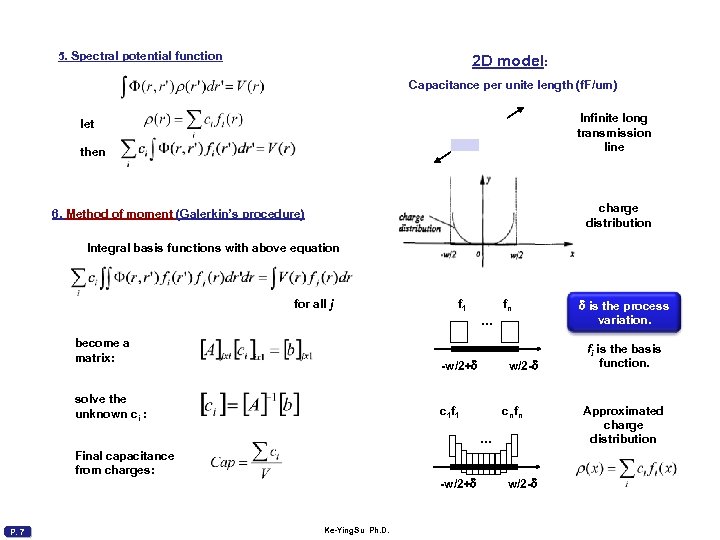 5. Spectral potential function 2 D model: Capacitance per unite length (f. F/um) Infinite long transmission line let then charge distribution 6. Method of moment (Galerkin’s procedure) Integral basis functions with above equation for all j f 1 fn … become a matrix: -w/2+d solve the unknown ci : w/2 -d c 1 f 1 cnfn … Final capacitance from charges: -w/2+d P. 7 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. w/2 -d d is the process variation. fi is the basis function. Approximated charge distribution
5. Spectral potential function 2 D model: Capacitance per unite length (f. F/um) Infinite long transmission line let then charge distribution 6. Method of moment (Galerkin’s procedure) Integral basis functions with above equation for all j f 1 fn … become a matrix: -w/2+d solve the unknown ci : w/2 -d c 1 f 1 cnfn … Final capacitance from charges: -w/2+d P. 7 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. w/2 -d d is the process variation. fi is the basis function. Approximated charge distribution
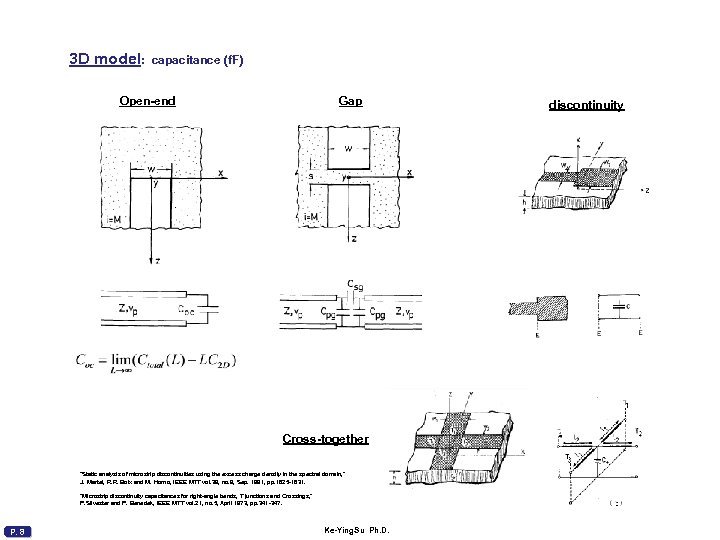 3 D model: capacitance (f. F) Open-end Gap Cross-together “Static analysis of microstrip discontinuities using the excess charge density in the spectral domain, ” J. Martel, R. R. Boix and M. Horno, IEEE MTT vol. 39, no. 9, Sep. 1991, pp. 1625 -1631. “Microstrip discontinuity capacitances for right-angle bends, T junctions and Crossings, ” P. Silvester and P. Benedek, IEEE MTT vol. 21, no. 5, April 1973, pp. 341 -347. P. 8 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. discontinuity
3 D model: capacitance (f. F) Open-end Gap Cross-together “Static analysis of microstrip discontinuities using the excess charge density in the spectral domain, ” J. Martel, R. R. Boix and M. Horno, IEEE MTT vol. 39, no. 9, Sep. 1991, pp. 1625 -1631. “Microstrip discontinuity capacitances for right-angle bends, T junctions and Crossings, ” P. Silvester and P. Benedek, IEEE MTT vol. 21, no. 5, April 1973, pp. 341 -347. P. 8 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. discontinuity
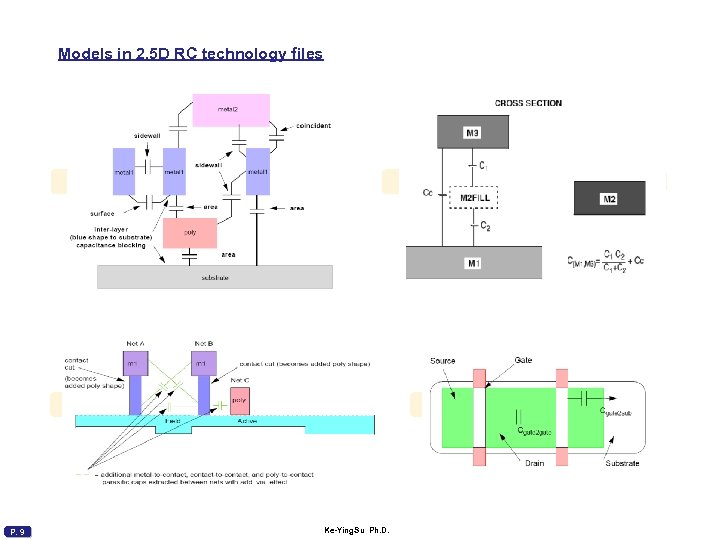 Models in 2. 5 D RC technology files P. 9 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
Models in 2. 5 D RC technology files P. 9 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
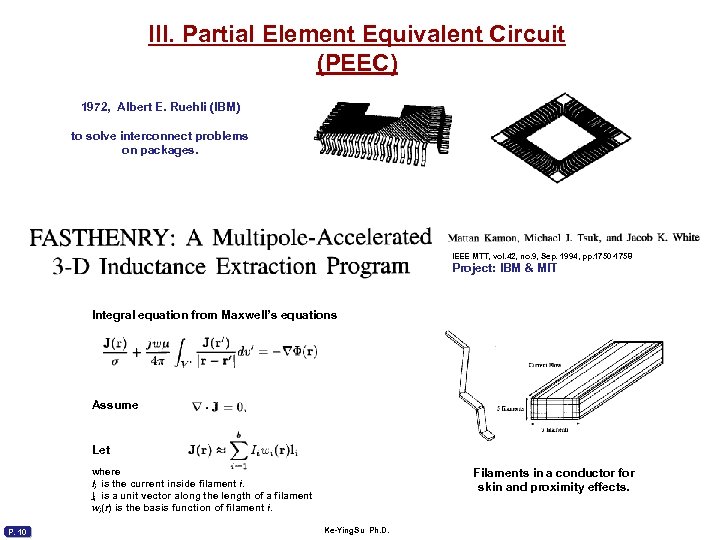 III. Partial Element Equivalent Circuit (PEEC) 1972, Albert E. Ruehli (IBM) to solve interconnect problems on packages. IEEE MTT, vol. 42, no. 9, Sep. 1994, pp. 1750 -1758 Project: IBM & MIT Integral equation from Maxwell’s equations Assume Let where Ii is the current inside filament i. Ii is a unit vector along the length of a filament wi(r) is the basis function of filament i. P. 10 Filaments in a conductor for skin and proximity effects. Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
III. Partial Element Equivalent Circuit (PEEC) 1972, Albert E. Ruehli (IBM) to solve interconnect problems on packages. IEEE MTT, vol. 42, no. 9, Sep. 1994, pp. 1750 -1758 Project: IBM & MIT Integral equation from Maxwell’s equations Assume Let where Ii is the current inside filament i. Ii is a unit vector along the length of a filament wi(r) is the basis function of filament i. P. 10 Filaments in a conductor for skin and proximity effects. Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
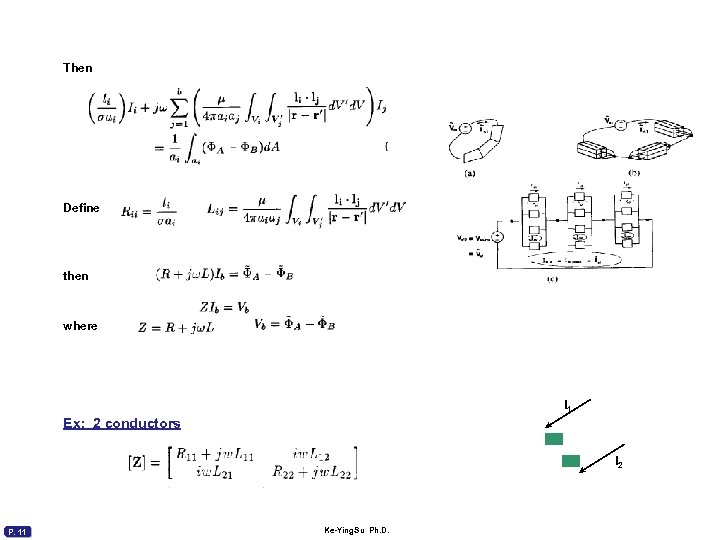 Then Define then where l 1 Ex: 2 conductors l 2 P. 11 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
Then Define then where l 1 Ex: 2 conductors l 2 P. 11 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
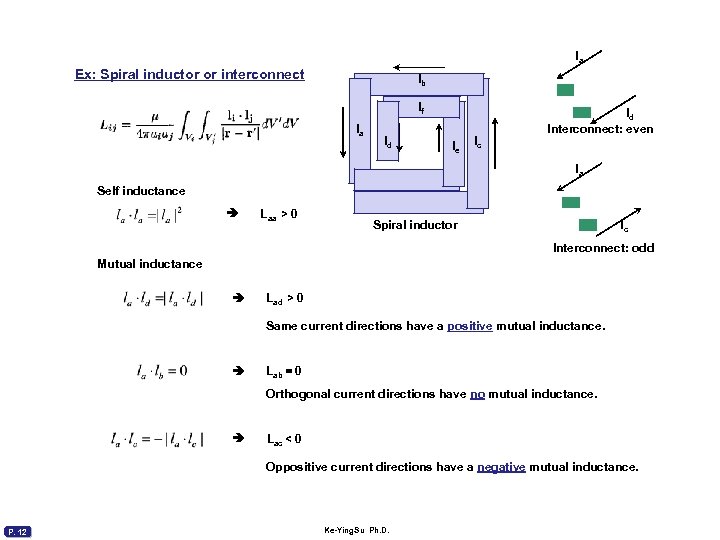 la Ex: Spiral inductor or interconnect lb lf la ld le lc ld Interconnect: even la Self inductance Laa > 0 Spiral inductor lc Interconnect: odd Mutual inductance Lad > 0 Same current directions have a positive mutual inductance. Lab = 0 Orthogonal current directions have no mutual inductance. Lac < 0 Oppositive current directions have a negative mutual inductance. P. 12 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
la Ex: Spiral inductor or interconnect lb lf la ld le lc ld Interconnect: even la Self inductance Laa > 0 Spiral inductor lc Interconnect: odd Mutual inductance Lad > 0 Same current directions have a positive mutual inductance. Lab = 0 Orthogonal current directions have no mutual inductance. Lac < 0 Oppositive current directions have a negative mutual inductance. P. 12 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
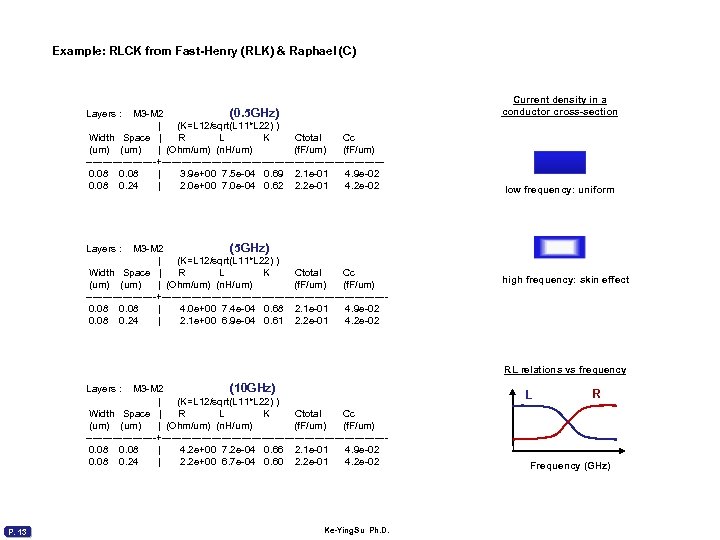 Example: RLCK from Fast-Henry (RLK) & Raphael (C) M 3 -M 2 (0. 5 GHz) | (K=L 12/sqrt(L 11*L 22) ) Width Space | R L K Ctotal Cc (um) | (Ohm/um) (n. H/um) (f. F/um) -----------+---------------------------------0. 08 | 3. 9 e+00 7. 5 e-04 0. 69 2. 1 e-01 4. 9 e-02 0. 08 0. 24 | 2. 0 e+00 7. 0 e-04 0. 62 2. 2 e-01 4. 2 e-02 Layers : M 3 -M 2 (5 GHz) | (K=L 12/sqrt(L 11*L 22) ) Width Space | R L K Ctotal Cc (um) | (Ohm/um) (n. H/um) (f. F/um) -----------+----------------------------------0. 08 | 4. 0 e+00 7. 4 e-04 0. 68 2. 1 e-01 4. 9 e-02 0. 08 0. 24 | 2. 1 e+00 6. 9 e-04 0. 61 2. 2 e-01 4. 2 e-02 Current density in a conductor cross-section low frequency: uniform Layers : high frequency: skin effect RL relations vs frequency M 3 -M 2 (10 GHz) | (K=L 12/sqrt(L 11*L 22) ) Width Space | R L K Ctotal Cc (um) | (Ohm/um) (n. H/um) (f. F/um) -----------+----------------------------------0. 08 | 4. 2 e+00 7. 2 e-04 0. 66 2. 1 e-01 4. 9 e-02 0. 08 0. 24 | 2. 2 e+00 6. 7 e-04 0. 60 2. 2 e-01 4. 2 e-02 Layers : P. 13 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. L R Frequency (GHz)
Example: RLCK from Fast-Henry (RLK) & Raphael (C) M 3 -M 2 (0. 5 GHz) | (K=L 12/sqrt(L 11*L 22) ) Width Space | R L K Ctotal Cc (um) | (Ohm/um) (n. H/um) (f. F/um) -----------+---------------------------------0. 08 | 3. 9 e+00 7. 5 e-04 0. 69 2. 1 e-01 4. 9 e-02 0. 08 0. 24 | 2. 0 e+00 7. 0 e-04 0. 62 2. 2 e-01 4. 2 e-02 Layers : M 3 -M 2 (5 GHz) | (K=L 12/sqrt(L 11*L 22) ) Width Space | R L K Ctotal Cc (um) | (Ohm/um) (n. H/um) (f. F/um) -----------+----------------------------------0. 08 | 4. 0 e+00 7. 4 e-04 0. 68 2. 1 e-01 4. 9 e-02 0. 08 0. 24 | 2. 1 e+00 6. 9 e-04 0. 61 2. 2 e-01 4. 2 e-02 Current density in a conductor cross-section low frequency: uniform Layers : high frequency: skin effect RL relations vs frequency M 3 -M 2 (10 GHz) | (K=L 12/sqrt(L 11*L 22) ) Width Space | R L K Ctotal Cc (um) | (Ohm/um) (n. H/um) (f. F/um) -----------+----------------------------------0. 08 | 4. 2 e+00 7. 2 e-04 0. 66 2. 1 e-01 4. 9 e-02 0. 08 0. 24 | 2. 2 e+00 6. 7 e-04 0. 60 2. 2 e-01 4. 2 e-02 Layers : P. 13 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. L R Frequency (GHz)
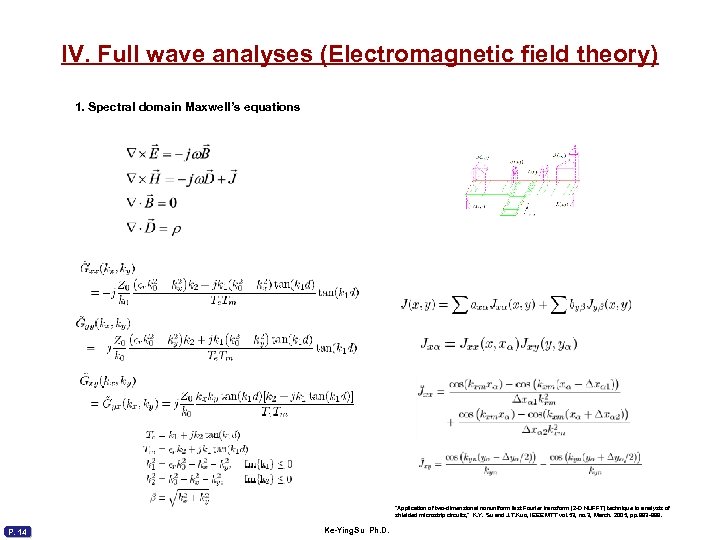 IV. Full wave analyses (Electromagnetic field theory) 1. Spectral domain Maxwell’s equations “Application of two-dimensional nonuniform fast Fourier transform (2 -D NUFFT) technique to analysis of shielded microstrip circuits, ” K. Y. Su and J. T. Kuo, IEEE MTT vol. 53, no. 3, March. 2005, pp. 993 -999. P. 14 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
IV. Full wave analyses (Electromagnetic field theory) 1. Spectral domain Maxwell’s equations “Application of two-dimensional nonuniform fast Fourier transform (2 -D NUFFT) technique to analysis of shielded microstrip circuits, ” K. Y. Su and J. T. Kuo, IEEE MTT vol. 53, no. 3, March. 2005, pp. 993 -999. P. 14 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
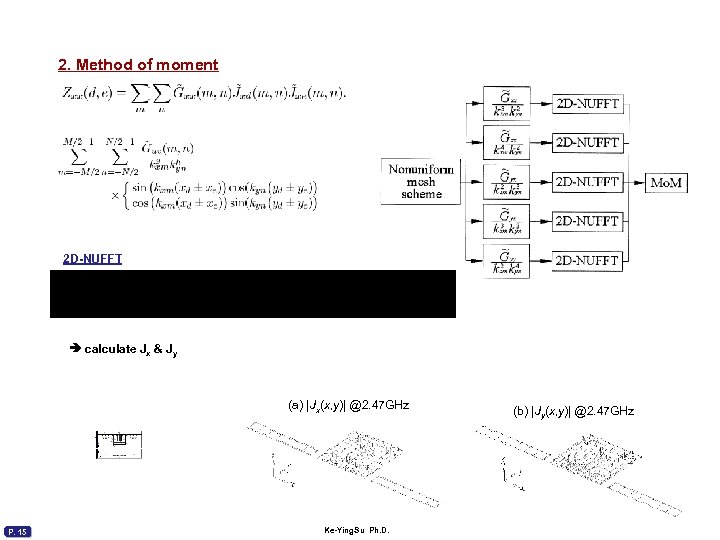 2. Method of moment 2 D-NUFFT calculate Jx & Jy (a) |Jx(x, y)| @2. 47 GHz P. 15 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. (b) |Jy(x, y)| @2. 47 GHz
2. Method of moment 2 D-NUFFT calculate Jx & Jy (a) |Jx(x, y)| @2. 47 GHz P. 15 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. (b) |Jy(x, y)| @2. 47 GHz
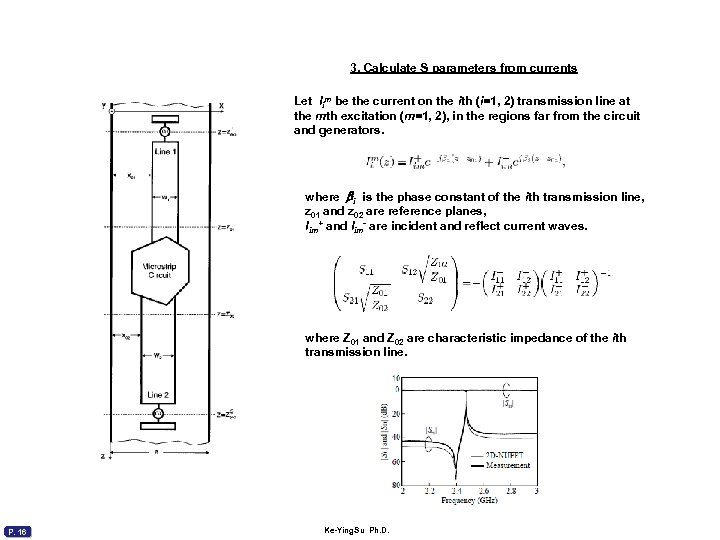 3. Calculate S parameters from currents Let Iim be the current on the ith (i=1, 2) transmission line at the mth excitation (m=1, 2), in the regions far from the circuit and generators. where bi is the phase constant of the ith transmission line, z 01 and z 02 are reference planes, Iim+ and Iim- are incident and reflect current waves. where Z 01 and Z 02 are characteristic impedance of the ith transmission line. P. 16 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
3. Calculate S parameters from currents Let Iim be the current on the ith (i=1, 2) transmission line at the mth excitation (m=1, 2), in the regions far from the circuit and generators. where bi is the phase constant of the ith transmission line, z 01 and z 02 are reference planes, Iim+ and Iim- are incident and reflect current waves. where Z 01 and Z 02 are characteristic impedance of the ith transmission line. P. 16 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
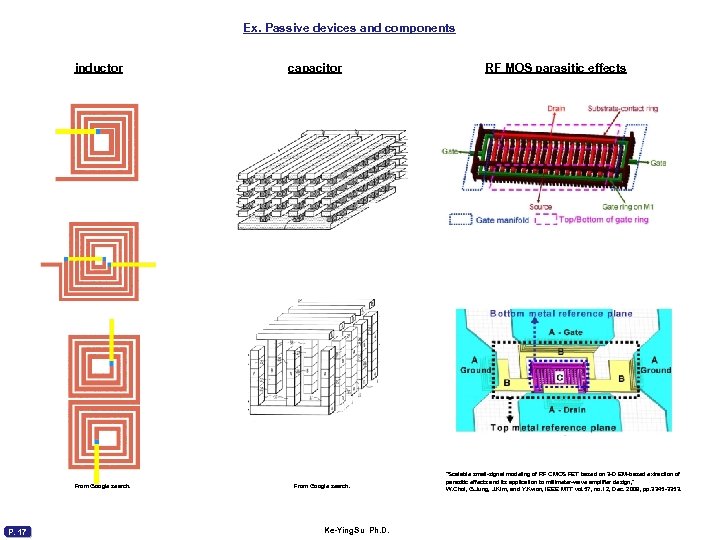 Ex. Passive devices and components inductor From Google search. P. 17 capacitor From Google search. Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. RF MOS parasitic effects “Scalable small-signal modeling of RF CMOS FET based on 3 -D EM-based extraction of parasitic effects and its application to millimeter-wave amplifier design, ” W. Choi, G. Jung, J. Kim, and Y. Kwon, IEEE MTT vol. 57, no. 12, Dec. 2009, pp. 3345 -3353.
Ex. Passive devices and components inductor From Google search. P. 17 capacitor From Google search. Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. RF MOS parasitic effects “Scalable small-signal modeling of RF CMOS FET based on 3 -D EM-based extraction of parasitic effects and its application to millimeter-wave amplifier design, ” W. Choi, G. Jung, J. Kim, and Y. Kwon, IEEE MTT vol. 57, no. 12, Dec. 2009, pp. 3345 -3353.
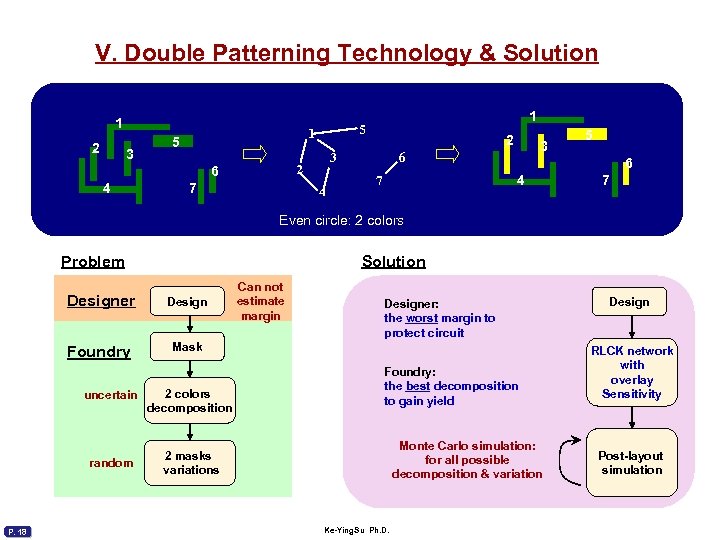 V. Double Patterning Technology & Solution 1 2 3 1 5 4 7 2 3 2 6 1 5 4 3 6 7 5 6 4 7 Even circle: 2 colors Problem Solution Designer Design Foundry Mask uncertain random P. 18 Can not estimate margin 2 colors decomposition Designer: the worst margin to protect circuit Foundry: the best decomposition to gain yield Monte Carlo simulation: for all possible decomposition & variation 2 masks variations Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. Design RLCK network with overlay Sensitivity Post-layout simulation
V. Double Patterning Technology & Solution 1 2 3 1 5 4 7 2 3 2 6 1 5 4 3 6 7 5 6 4 7 Even circle: 2 colors Problem Solution Designer Design Foundry Mask uncertain random P. 18 Can not estimate margin 2 colors decomposition Designer: the worst margin to protect circuit Foundry: the best decomposition to gain yield Monte Carlo simulation: for all possible decomposition & variation 2 masks variations Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. Design RLCK network with overlay Sensitivity Post-layout simulation
 Backup P. 19 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
Backup P. 19 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
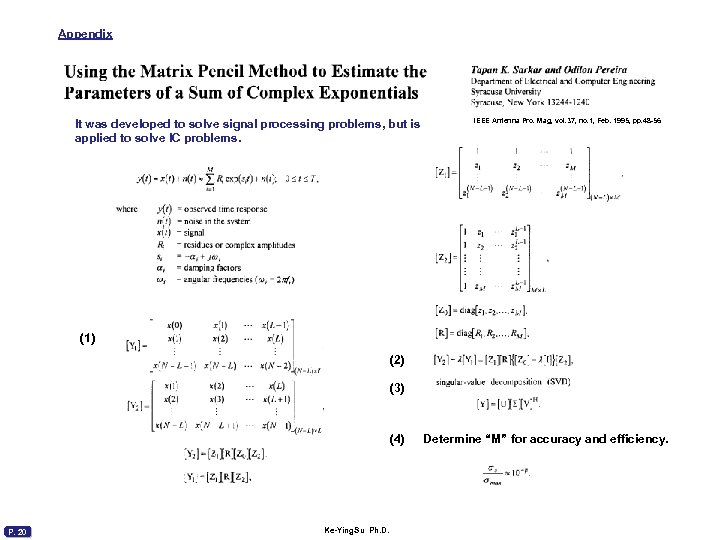 Appendix It was developed to solve signal processing problems, but is applied to solve IC problems. IEEE Antenna Pro. Mag, vol. 37, no. 1, Feb. 1995, pp. 48 -56 (1) (2) (3) (4) P. 20 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. Determine “M” for accuracy and efficiency.
Appendix It was developed to solve signal processing problems, but is applied to solve IC problems. IEEE Antenna Pro. Mag, vol. 37, no. 1, Feb. 1995, pp. 48 -56 (1) (2) (3) (4) P. 20 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D. Determine “M” for accuracy and efficiency.
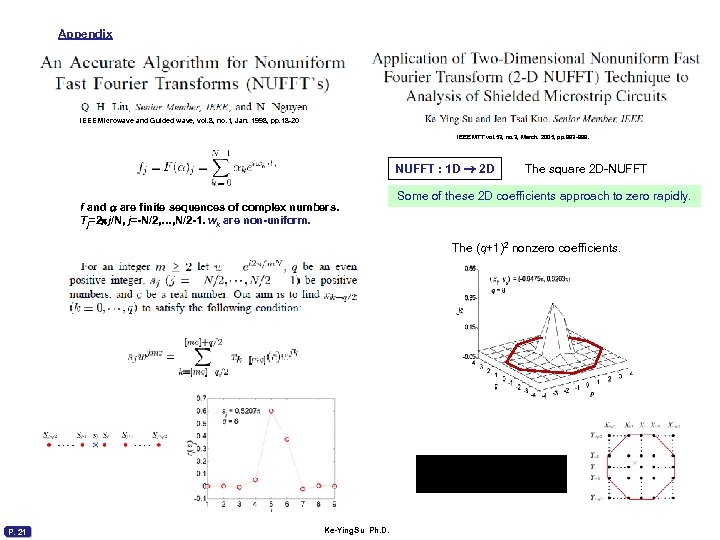 Appendix IEEE Microwave and Guided wave, vol. 8, no. 1, Jan. 1998, pp. 18 -20 IEEE MTT vol. 53, no. 3, March. 2005, pp. 993 -999. NUFFT : 1 D 2 D f and a are finite sequences of complex numbers. Tj=2 pj/N, j=-N/2, …, N/2 -1. wk are non-uniform. The square 2 D-NUFFT Some of these 2 D coefficients approach to zero rapidly. The (q+1)2 nonzero coefficients. P. 21 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.
Appendix IEEE Microwave and Guided wave, vol. 8, no. 1, Jan. 1998, pp. 18 -20 IEEE MTT vol. 53, no. 3, March. 2005, pp. 993 -999. NUFFT : 1 D 2 D f and a are finite sequences of complex numbers. Tj=2 pj/N, j=-N/2, …, N/2 -1. wk are non-uniform. The square 2 D-NUFFT Some of these 2 D coefficients approach to zero rapidly. The (q+1)2 nonzero coefficients. P. 21 Ke-Ying. Su Ph. D.


