f93a1e2837ebdfb3ab73f0d757048877.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 NATIONAL CENTER FOR CASE STUDY TEACHING IN SCIENCE A Presentation to Accompany the Case Study: Living on the Edge A Day in the Life of a Hummingbird by Giovanni Casotti Department of Biology West Chester University, West Chester, PA
NATIONAL CENTER FOR CASE STUDY TEACHING IN SCIENCE A Presentation to Accompany the Case Study: Living on the Edge A Day in the Life of a Hummingbird by Giovanni Casotti Department of Biology West Chester University, West Chester, PA
 Extreme environments: Osmoregulation
Extreme environments: Osmoregulation
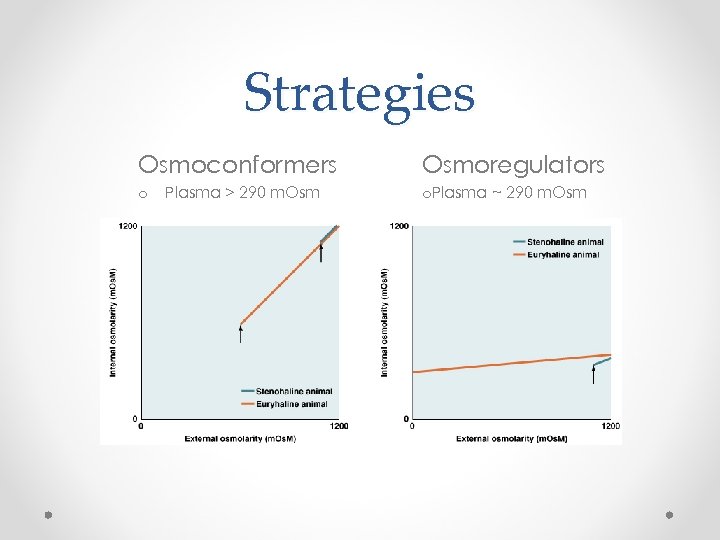 Strategies Osmoconformers o Plasma > 290 m. Osmoregulators o. Plasma ~ 290 m. Osm
Strategies Osmoconformers o Plasma > 290 m. Osmoregulators o. Plasma ~ 290 m. Osm
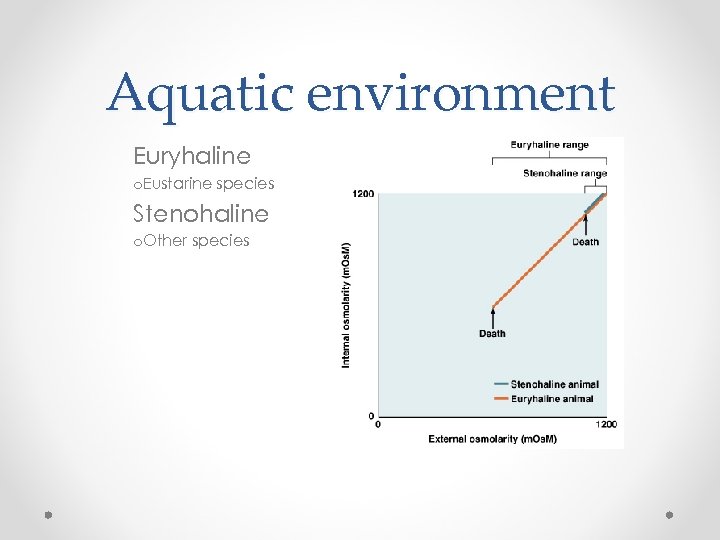 Aquatic environment Euryhaline o. Eustarine species Stenohaline o. Other species
Aquatic environment Euryhaline o. Eustarine species Stenohaline o. Other species
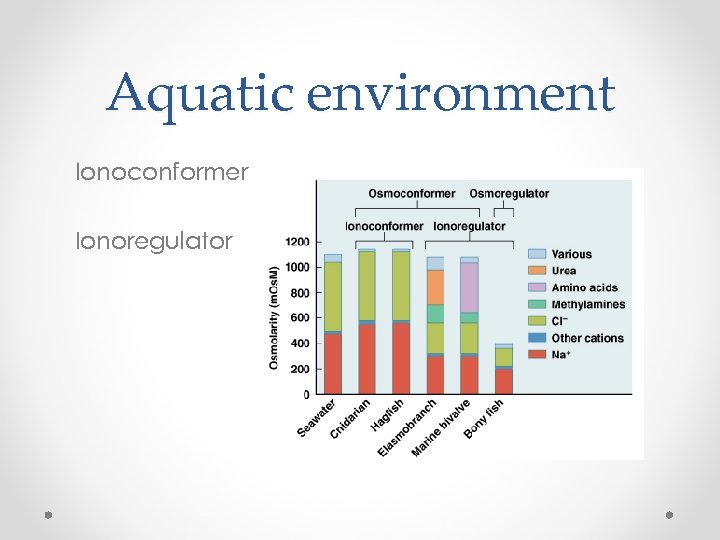 Aquatic environment Ionoconformer Ionoregulator
Aquatic environment Ionoconformer Ionoregulator
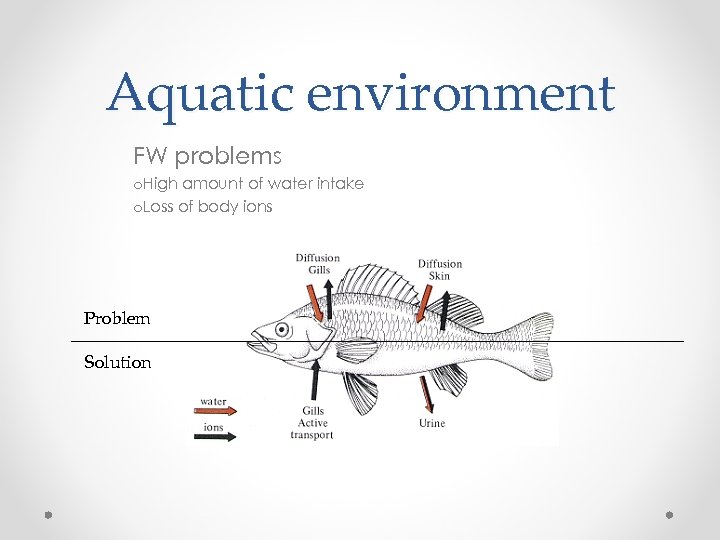 Aquatic environment FW problems o. High amount of water intake o. Loss of body ions Problem Solution
Aquatic environment FW problems o. High amount of water intake o. Loss of body ions Problem Solution
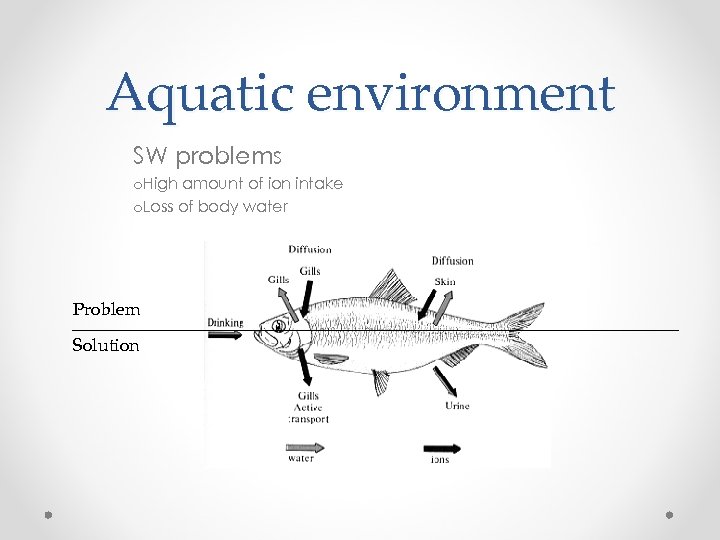 Aquatic environment SW problems o. High amount of ion intake o. Loss of body water Problem Solution
Aquatic environment SW problems o. High amount of ion intake o. Loss of body water Problem Solution
 Evolution onto land Problem - dehydration o. Evolve renal morphology (birds and mammals) thus altering function Birds o Role of the cloaca Mammals o Efficient kidneys
Evolution onto land Problem - dehydration o. Evolve renal morphology (birds and mammals) thus altering function Birds o Role of the cloaca Mammals o Efficient kidneys
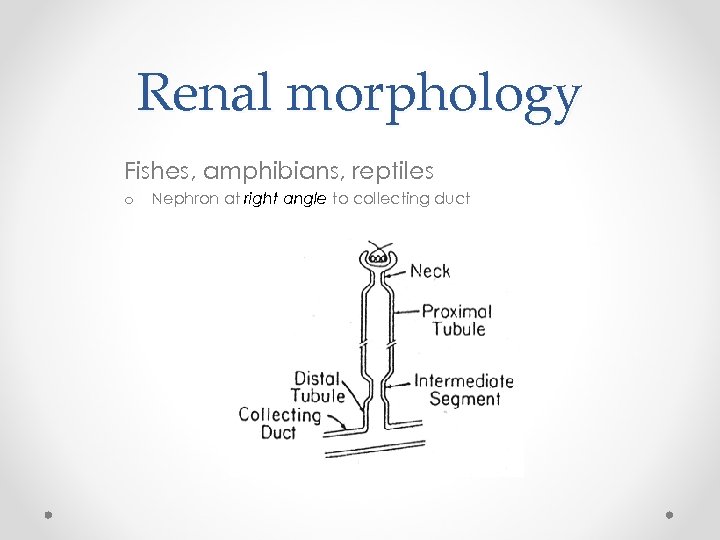 Renal morphology Fishes, amphibians, reptiles o Nephron at right angle to collecting duct
Renal morphology Fishes, amphibians, reptiles o Nephron at right angle to collecting duct
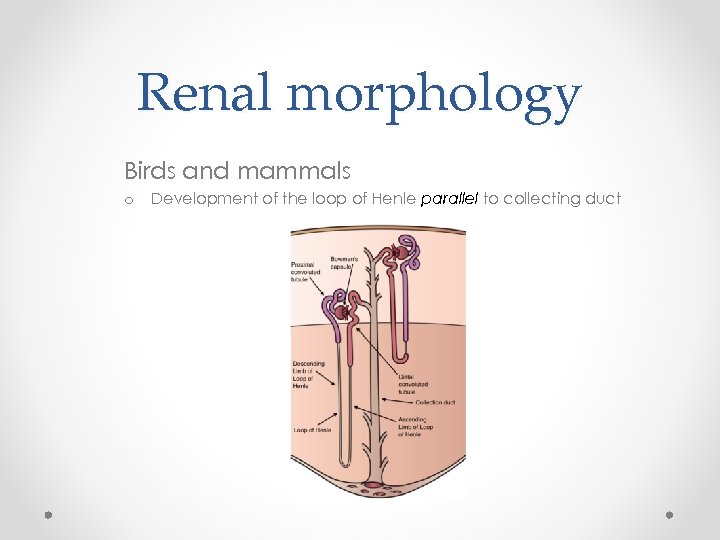 Renal morphology Birds and mammals o Development of the loop of Henle parallel to collecting duct
Renal morphology Birds and mammals o Development of the loop of Henle parallel to collecting duct
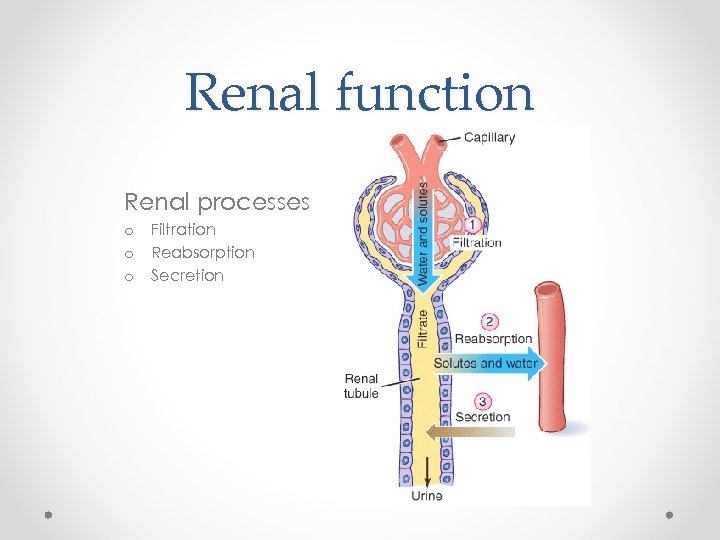 Renal function Renal processes o o o Filtration Reabsorption Secretion
Renal function Renal processes o o o Filtration Reabsorption Secretion
 Countercurrent multiplier Important points • Water movement if passive – osmosis • Water movement depends on ion gradient • Development of a concentration gradient in the medulla • The role of antidiuretic hormone • The role of the vasa recta
Countercurrent multiplier Important points • Water movement if passive – osmosis • Water movement depends on ion gradient • Development of a concentration gradient in the medulla • The role of antidiuretic hormone • The role of the vasa recta
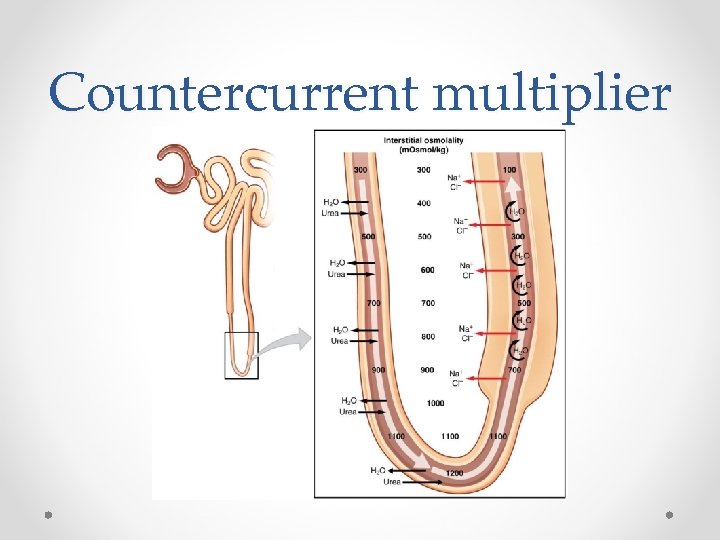 Countercurrent multiplier
Countercurrent multiplier
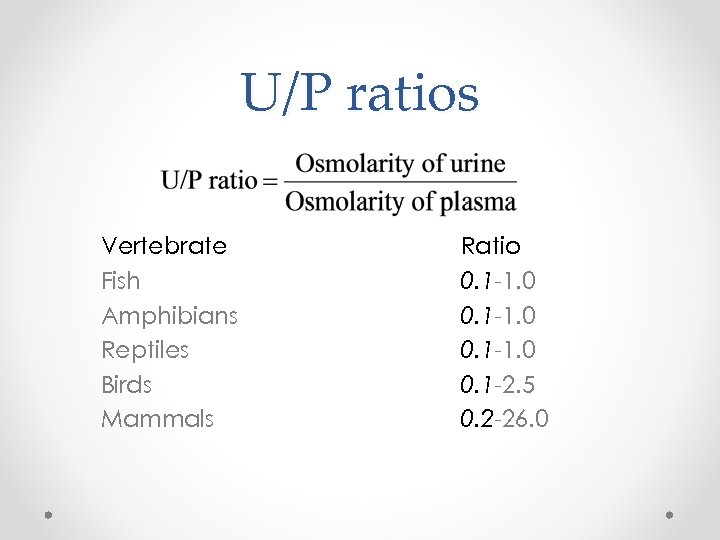 U/P ratios Vertebrate Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Ratio 0. 1 -1. 0 0. 1 -2. 5 0. 2 -26. 0
U/P ratios Vertebrate Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Ratio 0. 1 -1. 0 0. 1 -2. 5 0. 2 -26. 0
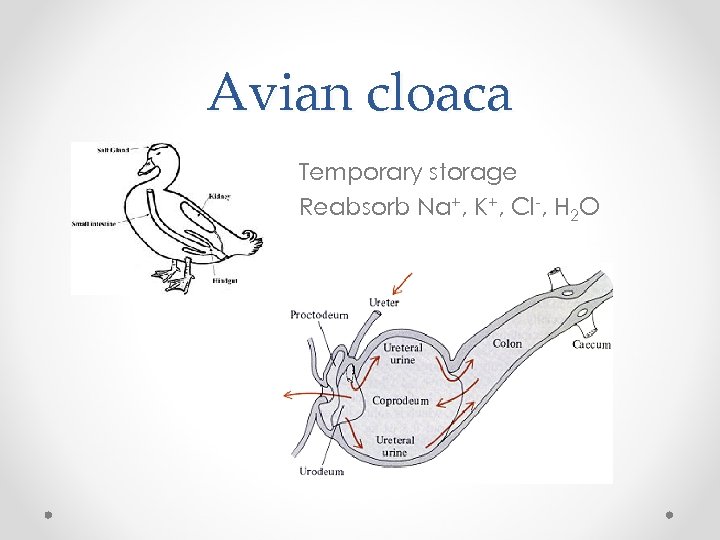 Avian cloaca Temporary storage Reabsorb Na+, K+, Cl-, H 2 O
Avian cloaca Temporary storage Reabsorb Na+, K+, Cl-, H 2 O
 Case study Hummingbirds/Sunbirds o. A unique animal on the edge of survival o. Watch the hummingbird video
Case study Hummingbirds/Sunbirds o. A unique animal on the edge of survival o. Watch the hummingbird video
 Hummingbirds Unique challenges o. Dilute (up to 3 - 6 times body mass/day) or a concentrated diet. Can they dehydrate?
Hummingbirds Unique challenges o. Dilute (up to 3 - 6 times body mass/day) or a concentrated diet. Can they dehydrate?
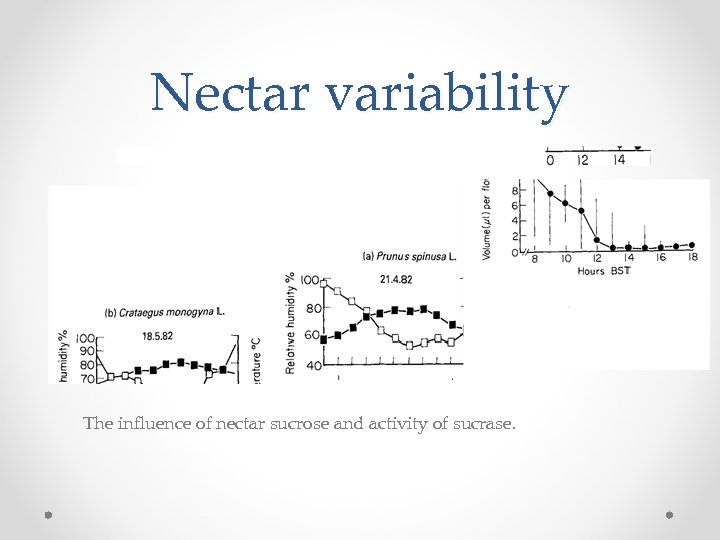 Nectar variability The influence of nectar sucrose and activity of sucrase.
Nectar variability The influence of nectar sucrose and activity of sucrase.
 Case Study Questions • 1. Do floral nectar concentrations vary throughout the day. Why do you think that hummingbirds are active feeders first thing in the morning? • 2. What are some of the daily osmotic challenges faced by sunbirds? How do they cope physiologically with low and high concentrations of nectar? • 3. Why don’t you see hummingbirds feed during the hottest part of the day?
Case Study Questions • 1. Do floral nectar concentrations vary throughout the day. Why do you think that hummingbirds are active feeders first thing in the morning? • 2. What are some of the daily osmotic challenges faced by sunbirds? How do they cope physiologically with low and high concentrations of nectar? • 3. Why don’t you see hummingbirds feed during the hottest part of the day?
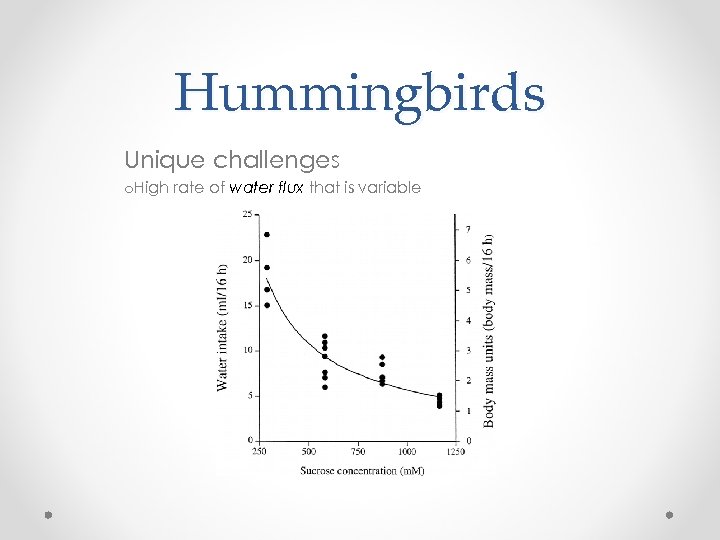 Hummingbirds Unique challenges o. High rate of water flux that is variable
Hummingbirds Unique challenges o. High rate of water flux that is variable
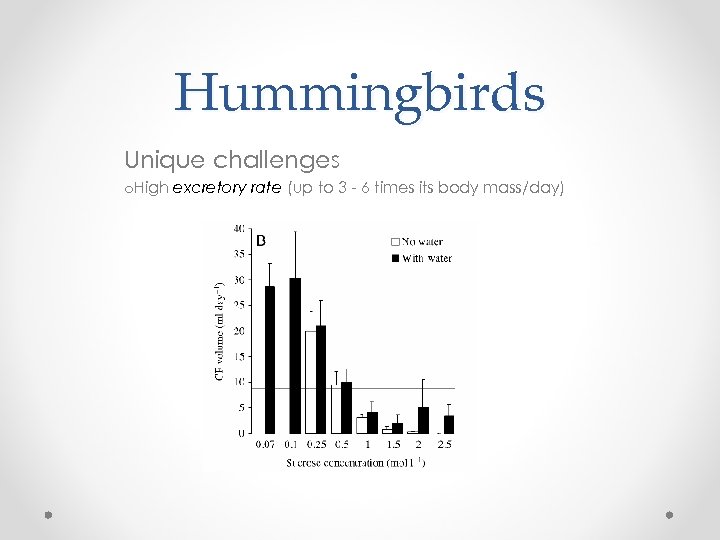 Hummingbirds Unique challenges o. High excretory rate (up to 3 - 6 times its body mass/day)
Hummingbirds Unique challenges o. High excretory rate (up to 3 - 6 times its body mass/day)
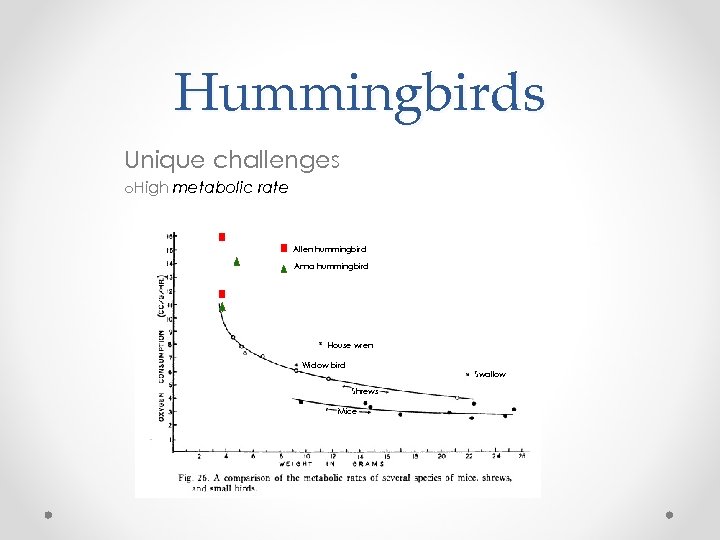 Hummingbirds Unique challenges o. High metabolic rate Allen hummingbird Anna hummingbird House wren Widow bird Swallow Shrews Mice
Hummingbirds Unique challenges o. High metabolic rate Allen hummingbird Anna hummingbird House wren Widow bird Swallow Shrews Mice
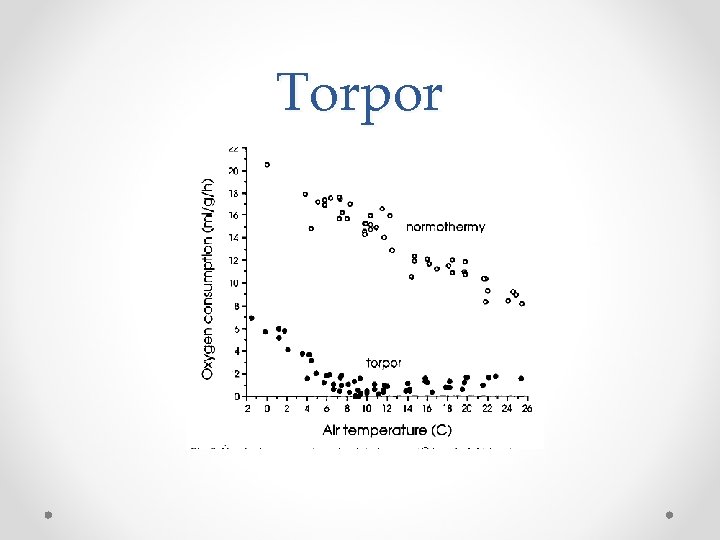
 Hummingbirds Unique solutions o. Modified kidneys with virtually no medulla o. Undergo Torpor
Hummingbirds Unique solutions o. Modified kidneys with virtually no medulla o. Undergo Torpor
 Case Study Question • 4. From the material presented in this lecture, explain how the mammal nephron produces a concentrated urine. In your answer explain how the countercurrent multiplier mechanism operates, the importance of the design of the thin descending and thick ascending limb of Henle, and the length of the loop of Henle.
Case Study Question • 4. From the material presented in this lecture, explain how the mammal nephron produces a concentrated urine. In your answer explain how the countercurrent multiplier mechanism operates, the importance of the design of the thin descending and thick ascending limb of Henle, and the length of the loop of Henle.
 Case Study Read the paper on hummingbird renal morphology Question • 5. Casotti et al. (1998) discusses 3 renal adaptations that enable Anna’s hummingbird to survive on a high water flux, low ion diet. What are they and how do they operate?
Case Study Read the paper on hummingbird renal morphology Question • 5. Casotti et al. (1998) discusses 3 renal adaptations that enable Anna’s hummingbird to survive on a high water flux, low ion diet. What are they and how do they operate?
 Torpor
Torpor
 Torpor
Torpor
 Case Study Reading the article on torpor in the Rufous hummingbird Questions • 6. What is torpor and why is it an important physiological adaptation for survival? • 7. How much of a decrease is there in O 2 consumption between normothermy and torpor? How long does torpor typically last?
Case Study Reading the article on torpor in the Rufous hummingbird Questions • 6. What is torpor and why is it an important physiological adaptation for survival? • 7. How much of a decrease is there in O 2 consumption between normothermy and torpor? How long does torpor typically last?


