c43978aef14c78873487b3dd85b34c05.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 National Association of County Agricultural Agents Annual Meeting and Professional Improvement Conference 24 July 2006 Cincinnati, OH Soil Fertility Resources for Extension Agents Tom Bruulsema, Ph. D Northeast Director Potash & Phosphate Institute
National Association of County Agricultural Agents Annual Meeting and Professional Improvement Conference 24 July 2006 Cincinnati, OH Soil Fertility Resources for Extension Agents Tom Bruulsema, Ph. D Northeast Director Potash & Phosphate Institute
 PPI/PPIC Member Companies
PPI/PPIC Member Companies
 PPI’s Northeast Region
PPI’s Northeast Region
 Why Educate on Soil Fertility?
Why Educate on Soil Fertility?
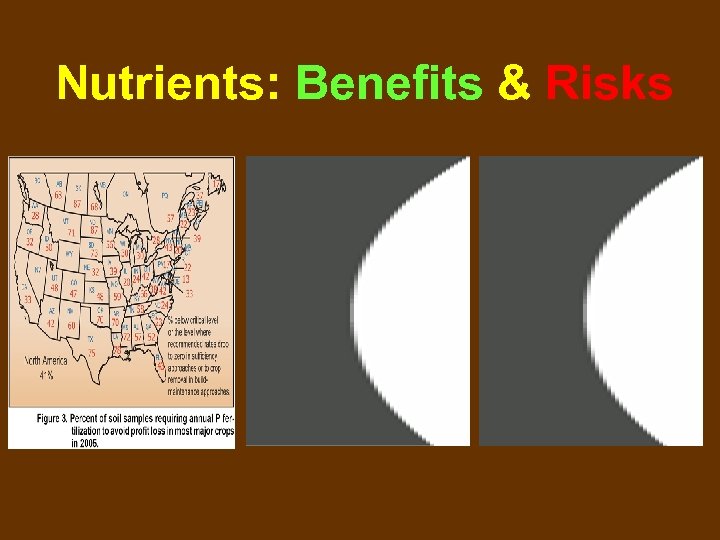 Nutrients: Benefits & Risks
Nutrients: Benefits & Risks
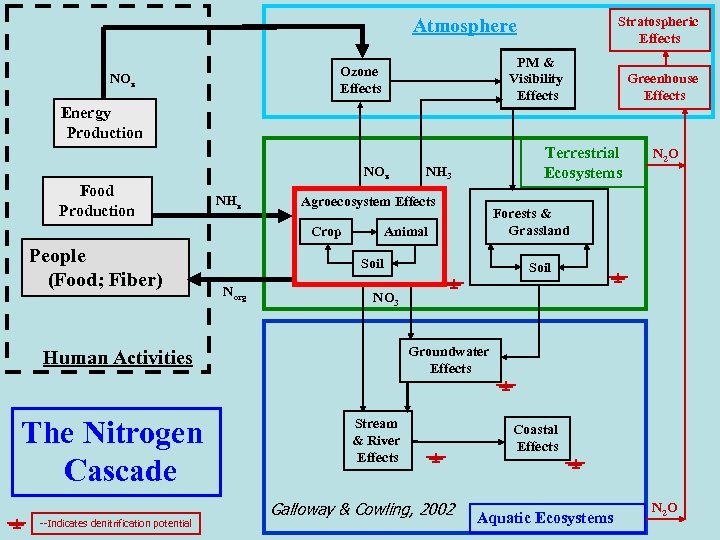 Stratospheric Effects Atmosphere PM & Visibility Effects Ozone Effects NOx Greenhouse Effects Energy Production NOx Food Production NHx Soil Norg --Indicates denitrification potential N 2 O Forests & Grassland Animal Soil NO 3 Groundwater Effects Human Activities The Nitrogen Cascade NH 3 Agroecosystem Effects Crop People (Food; Fiber) Terrestrial Ecosystems Stream & River Effects Galloway & Cowling, 2002 Coastal Effects Aquatic Ecosystems N 2 O
Stratospheric Effects Atmosphere PM & Visibility Effects Ozone Effects NOx Greenhouse Effects Energy Production NOx Food Production NHx Soil Norg --Indicates denitrification potential N 2 O Forests & Grassland Animal Soil NO 3 Groundwater Effects Human Activities The Nitrogen Cascade NH 3 Agroecosystem Effects Crop People (Food; Fiber) Terrestrial Ecosystems Stream & River Effects Galloway & Cowling, 2002 Coastal Effects Aquatic Ecosystems N 2 O
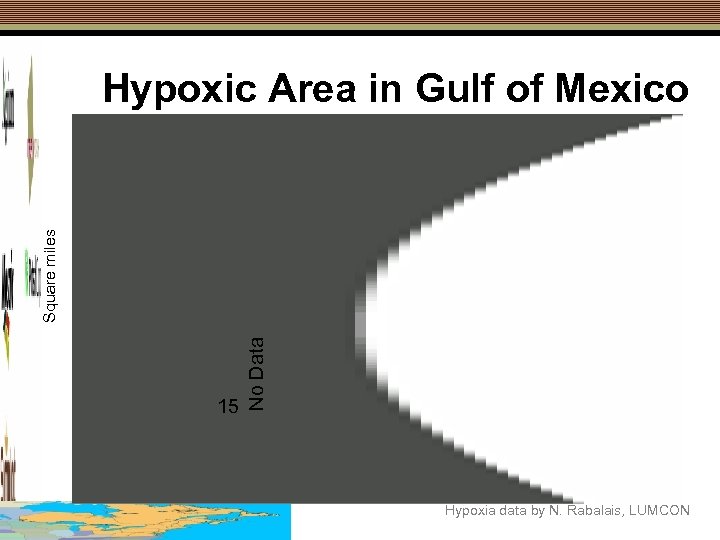 15 No Data Square miles Hypoxic Area in Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia data by N. Rabalais, LUMCON
15 No Data Square miles Hypoxic Area in Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia data by N. Rabalais, LUMCON
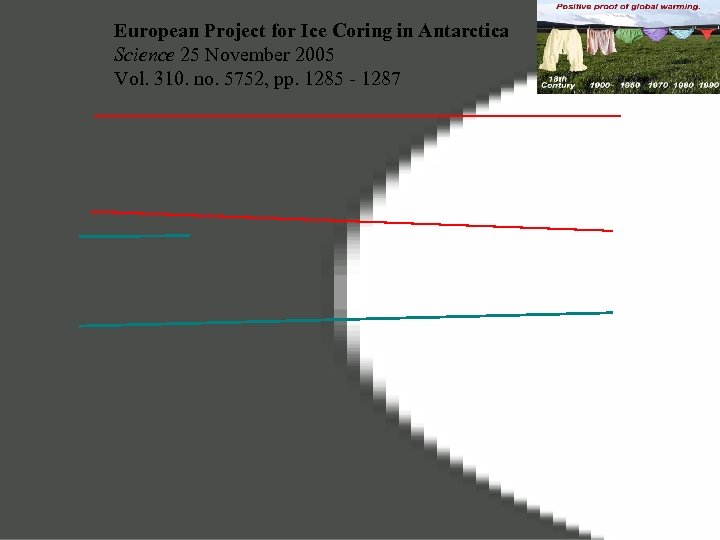 European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica Science 25 November 2005 Vol. 310. no. 5752, pp. 1285 - 1287
European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica Science 25 November 2005 Vol. 310. no. 5752, pp. 1285 - 1287
 Greenhouse Gases N 2 O
Greenhouse Gases N 2 O
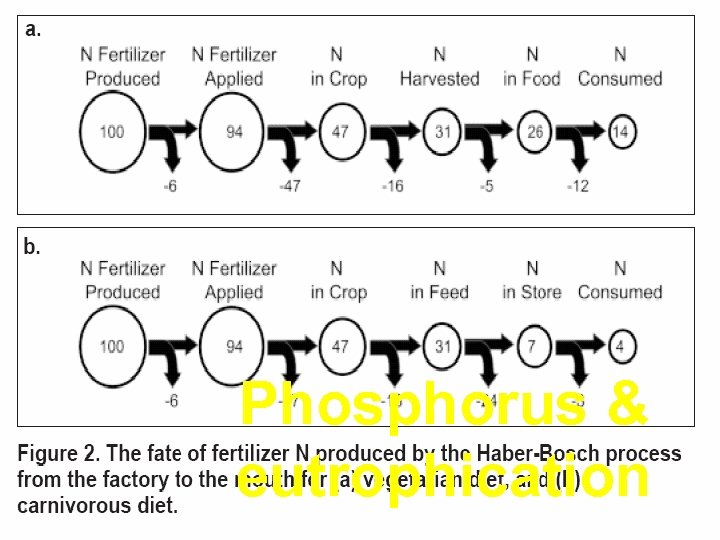 Phosphorus & eutrophication
Phosphorus & eutrophication
 Improving Nutrient Use Efficiency
Improving Nutrient Use Efficiency
 Improvement: % P: 108% N: 43% K: 90% Source: USDA-NASS; PPI Corn Yield: 55%
Improvement: % P: 108% N: 43% K: 90% Source: USDA-NASS; PPI Corn Yield: 55%
 85 28 Galloway and Cowling, 2002
85 28 Galloway and Cowling, 2002
 Ending Poverty Requires Fertilizer…
Ending Poverty Requires Fertilizer…
 Best Management Practices Right rate Right time Right place
Best Management Practices Right rate Right time Right place


 Who Needs to Know? • • • Everyone! Soil Fertility Specialists Producers Policymakers and Regulators Public – young & old
Who Needs to Know? • • • Everyone! Soil Fertility Specialists Producers Policymakers and Regulators Public – young & old
 PPI Publications
PPI Publications
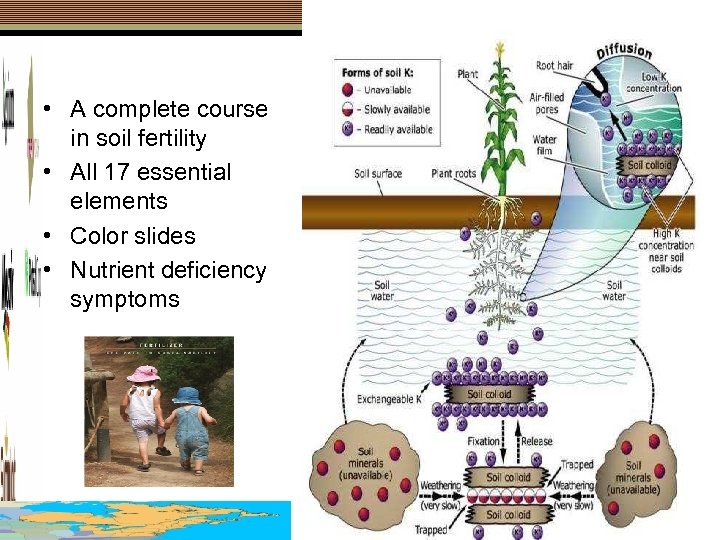 • A complete course in soil fertility • All 17 essential elements • Color slides • Nutrient deficiency symptoms
• A complete course in soil fertility • All 17 essential elements • Color slides • Nutrient deficiency symptoms
 How Potassium Moves in Soil
How Potassium Moves in Soil

 Elementary Education
Elementary Education


 Powerpoint Presentations • Phosphorus Nutrition – – – Alfalfa Canola Corn Cotton Wheat • Potassium Nutrition – Alfalfa – Cotton – Northern Great Plains
Powerpoint Presentations • Phosphorus Nutrition – – – Alfalfa Canola Corn Cotton Wheat • Potassium Nutrition – Alfalfa – Cotton – Northern Great Plains

 Quality for Health • Agriculture’s connection to food – Take a Closer Look – Fertilizer and Tofu – Functional Foods research – Fertilizer Impacts on Quality
Quality for Health • Agriculture’s connection to food – Take a Closer Look – Fertilizer and Tofu – Functional Foods research – Fertilizer Impacts on Quality
 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 PPI/PPIC/FAR Technical Bulletin 2005 -1 Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 PPI/PPIC/FAR Technical Bulletin 2005 -1 Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Private Laboratories A&L Analytical Labs, Inc. – Memphis, TN A&L Great Lakes Labs, Inc. – Fort Wayne, IN A&L Canada Laboratories, Inc. – London, ON A&L Plains, Ag Lab – Lubbock, TX Agri Analysis, Inc. – Leola, PA Agri-Food Laboratories – Guelph, ON AGVISE Laboratories – Northwood, ND Agri. Quanta – St-Ours, QC Agro-Enviro-Sol – La Pocatière, QC Alvey Lab – Belleville, IL Bradford Agri Lab – Yazoo City, MS Brookside Lab, Inc. – New Knoxville, OH Cooperative Federee de Quebec – Longueuil, QC Dairyland Laboratories, Inc. – Arcadia, WI Dellavalle Lab, Inc. – Fresno, CA Enviro-Test Labs – Calgary, AB LGI – Ellsworth, IA Litchfield Analytical Services – Litchfield, MI MDS Harris – Lincoln, NE Midwest Laboratories, Inc. – Omaha, NE Mowers Soil Testing Plus, Inc. – Toulon, IL Norwest Labs – Edmonton, AB Olsen’s Ag Lab – Mc. Cook, NE Precision Agri-lab – Madera, CA Rock River Lab – Watertown, WI Servi-Tech, Inc. – Amarillo, TX Servi-Tech, Inc. – Dodge City, KS Servi-Tech, Inc. – Hastings, NE Spectrum Analytic, Inc. – Washington Court House, OH Stratford Agri Analysis – Stratford, ON Stukenholtz Laboratory – Twin Falls, ID Syn. Agri – St-Hilaire, QC United Soils, Inc. – Fairbury, IL Ward Laboratories, Inc. – Kearney, NE Waters Agricultural Labs – Camilla, GA William Houde, Ltd. – St-Simon, QC Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Private Laboratories A&L Analytical Labs, Inc. – Memphis, TN A&L Great Lakes Labs, Inc. – Fort Wayne, IN A&L Canada Laboratories, Inc. – London, ON A&L Plains, Ag Lab – Lubbock, TX Agri Analysis, Inc. – Leola, PA Agri-Food Laboratories – Guelph, ON AGVISE Laboratories – Northwood, ND Agri. Quanta – St-Ours, QC Agro-Enviro-Sol – La Pocatière, QC Alvey Lab – Belleville, IL Bradford Agri Lab – Yazoo City, MS Brookside Lab, Inc. – New Knoxville, OH Cooperative Federee de Quebec – Longueuil, QC Dairyland Laboratories, Inc. – Arcadia, WI Dellavalle Lab, Inc. – Fresno, CA Enviro-Test Labs – Calgary, AB LGI – Ellsworth, IA Litchfield Analytical Services – Litchfield, MI MDS Harris – Lincoln, NE Midwest Laboratories, Inc. – Omaha, NE Mowers Soil Testing Plus, Inc. – Toulon, IL Norwest Labs – Edmonton, AB Olsen’s Ag Lab – Mc. Cook, NE Precision Agri-lab – Madera, CA Rock River Lab – Watertown, WI Servi-Tech, Inc. – Amarillo, TX Servi-Tech, Inc. – Dodge City, KS Servi-Tech, Inc. – Hastings, NE Spectrum Analytic, Inc. – Washington Court House, OH Stratford Agri Analysis – Stratford, ON Stukenholtz Laboratory – Twin Falls, ID Syn. Agri – St-Hilaire, QC United Soils, Inc. – Fairbury, IL Ward Laboratories, Inc. – Kearney, NE Waters Agricultural Labs – Camilla, GA William Houde, Ltd. – St-Simon, QC Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Public Laboratories Auburn University Clemson University Colorado State University Cornell University Department of Natural Resources – Corner Brook, NL Iowa State University Kansas State University Kentucky Division of Regulatory Services Louisiana State University Mississippi State University New Brunswick Department of Agriculture and Rural Development New Mexico State University North Carolina Department of Ag North Dakota State University Oklahoma State University PEI Soil & Feed Testing Laboratory Rutgers University South Dakota State University Texas A&M University The Pennsylvania State University of Arkansas University of Connecticut University of Delaware University of Florida University of Georgia University of Guelph University of Maine University of Missouri University of Nebraska University of Tennessee University of Vermont University of West Virginia University of Wisconsin, Madison University of Wisconsin, Marshfield Utah State University Virginia Tech Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Public Laboratories Auburn University Clemson University Colorado State University Cornell University Department of Natural Resources – Corner Brook, NL Iowa State University Kansas State University Kentucky Division of Regulatory Services Louisiana State University Mississippi State University New Brunswick Department of Agriculture and Rural Development New Mexico State University North Carolina Department of Ag North Dakota State University Oklahoma State University PEI Soil & Feed Testing Laboratory Rutgers University South Dakota State University Texas A&M University The Pennsylvania State University of Arkansas University of Connecticut University of Delaware University of Florida University of Georgia University of Guelph University of Maine University of Missouri University of Nebraska University of Tennessee University of Vermont University of West Virginia University of Wisconsin, Madison University of Wisconsin, Marshfield Utah State University Virginia Tech Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
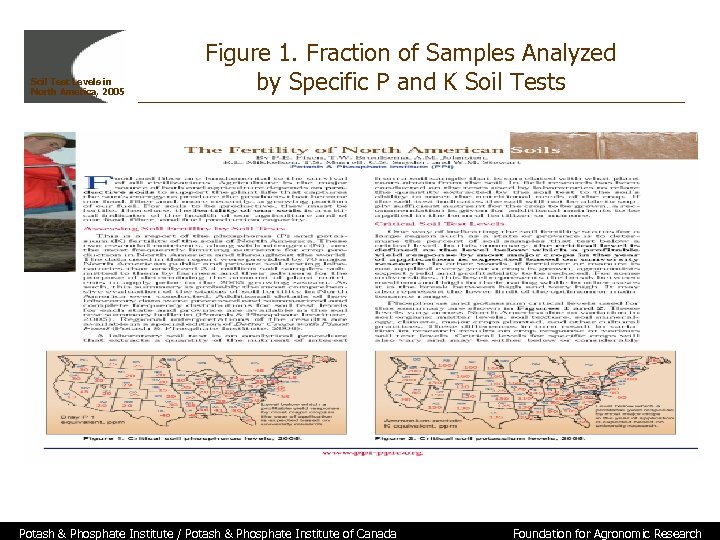 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 1. Fraction of Samples Analyzed by Specific P and K Soil Tests Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 1. Fraction of Samples Analyzed by Specific P and K Soil Tests Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
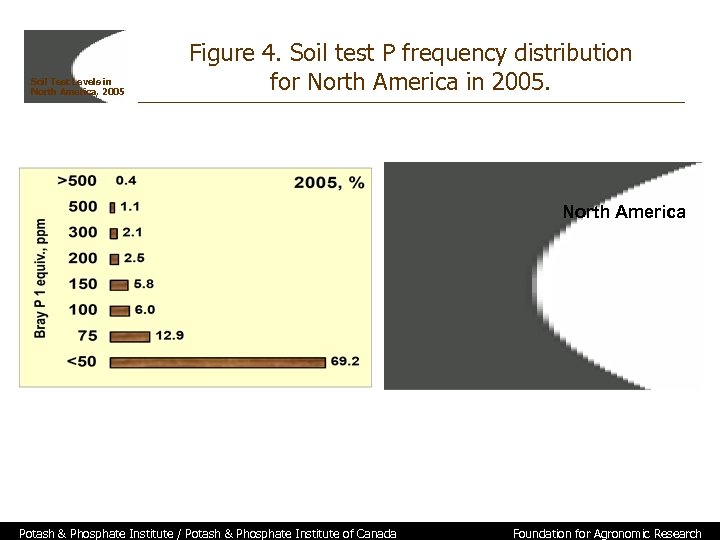 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 4. Soil test P frequency distribution for North America in 2005. North America Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 4. Soil test P frequency distribution for North America in 2005. North America Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
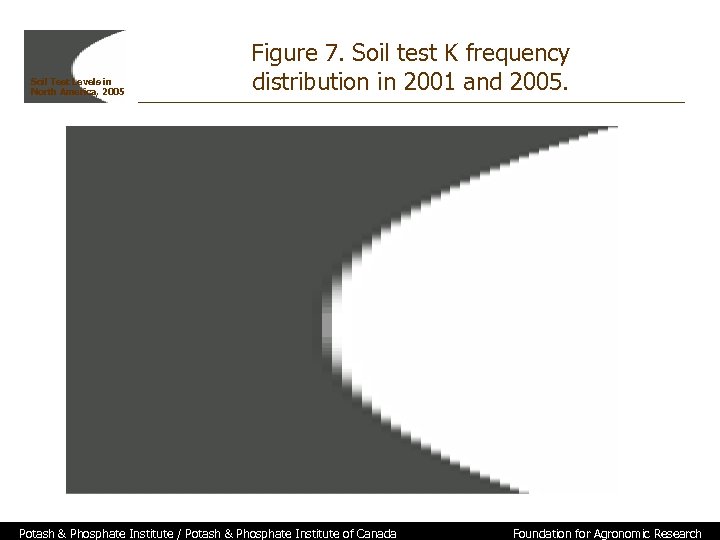 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 7. Soil test K frequency distribution in 2001 and 2005. Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 7. Soil test K frequency distribution in 2001 and 2005. Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research

 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Soil Test Interpretation • Why not one recommendation for a given soil test level? Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Soil Test Interpretation • Why not one recommendation for a given soil test level? Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
 96 site-years Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
96 site-years Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
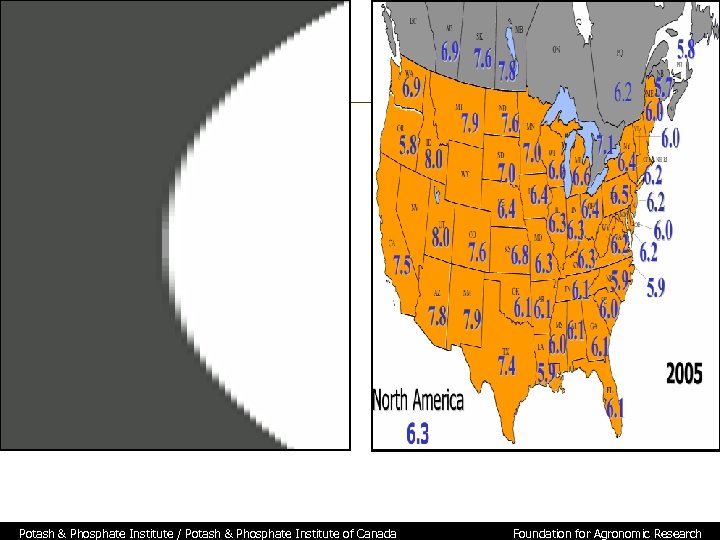
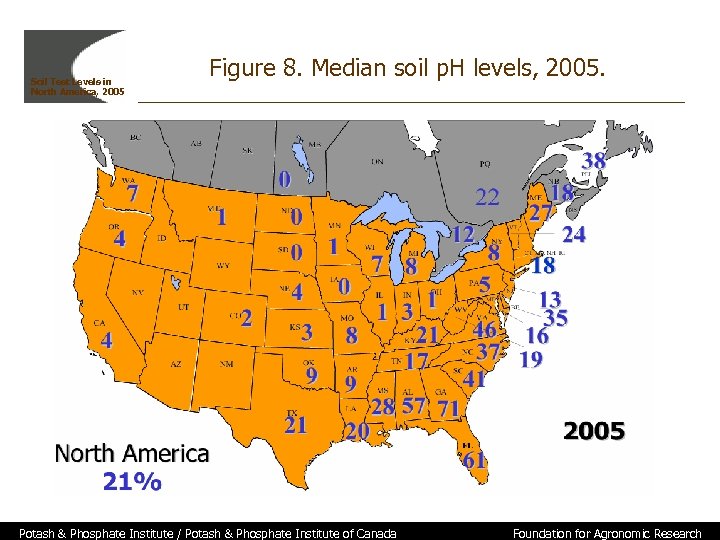 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 8. Median soil p. H levels, 2005. Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 8. Median soil p. H levels, 2005. Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
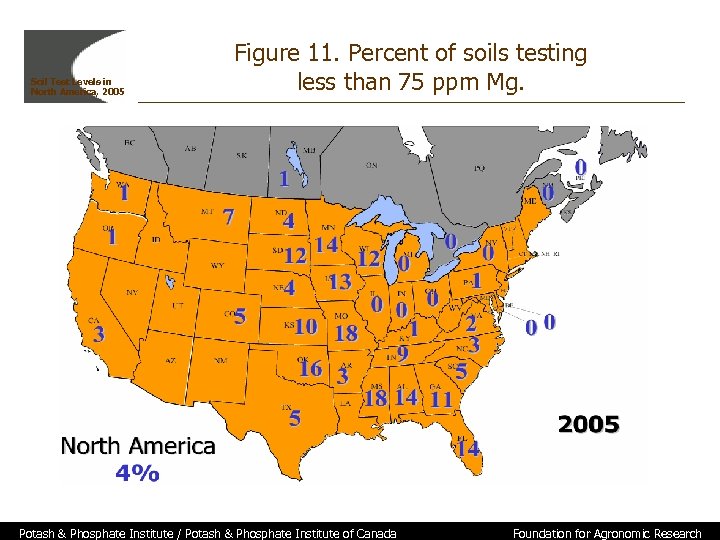 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 11. Percent of soils testing less than 75 ppm Mg. Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 11. Percent of soils testing less than 75 ppm Mg. Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 12. Percent of soils testing less than 3 ppm S. Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Figure 12. Percent of soils testing less than 3 ppm S. Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
 Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Summary • Approximately 3. 4 million samples from 70 laboratories are included in the summary • Results indicate the importance of regular soil testing because a large number of samples test in or near critical soil test ranges where nutrient recommendations vary greatly • Median P level is 31 ppm, with 41% of samples for 2005 crop year testing less than 25 ppm • Median K level is 154 ppm, with 33% of samples testing less than 120 ppm, and 53% less than 160 ppm • Median p. H for U. S. and Canada is 6. 3, with 31% of samples testing < 6. 0 • Need for soil testing is important to determine fertility status of specific fields Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
Soil Test Levels in North America, 2005 Summary • Approximately 3. 4 million samples from 70 laboratories are included in the summary • Results indicate the importance of regular soil testing because a large number of samples test in or near critical soil test ranges where nutrient recommendations vary greatly • Median P level is 31 ppm, with 41% of samples for 2005 crop year testing less than 25 ppm • Median K level is 154 ppm, with 33% of samples testing less than 120 ppm, and 53% less than 160 ppm • Median p. H for U. S. and Canada is 6. 3, with 31% of samples testing < 6. 0 • Need for soil testing is important to determine fertility status of specific fields Potash & Phosphate Institute / Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada Foundation for Agronomic Research
 BMPs for Efficient Fertilizer Use 12 basic tips
BMPs for Efficient Fertilizer Use 12 basic tips
 Fertilizer BMPs 1. Measure what the soil can provide 2. Consider crop removal 3. Set realistic yield goals 4. Use all nutrient sources available
Fertilizer BMPs 1. Measure what the soil can provide 2. Consider crop removal 3. Set realistic yield goals 4. Use all nutrient sources available
 Fertilizer BMPs 5. Keep the proper balance of nutrients 6. Manage soil p. H 7. Manage for maximum economic yield 8. Time applications
Fertilizer BMPs 5. Keep the proper balance of nutrients 6. Manage soil p. H 7. Manage for maximum economic yield 8. Time applications
 Fertilizer BMPs 9. Control release 10. Band in the right place 11. Test on-farm 12. Consult a credible adviser
Fertilizer BMPs 9. Control release 10. Band in the right place 11. Test on-farm 12. Consult a credible adviser
 PPI Tools on the Web • • • www. ppi-ppic. org Crop Nutrient Response Tool PKalc Hybrid Maize Fertilizer Chooser
PPI Tools on the Web • • • www. ppi-ppic. org Crop Nutrient Response Tool PKalc Hybrid Maize Fertilizer Chooser
 3 6 7 4 1 5 2
3 6 7 4 1 5 2
 Thank You
Thank You


