9e736df62433536fdcd3a1cb9764d92a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

NASA STEP for Aerospace Workshop Jet Propulsion Lab Pasadena CA January 16 -20, 2001 An AP 210 -based Repository for Collaborative Electronics Engineering Russell S. Peak Senior Researcher & Co-Director Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu CALS Technology Center Georgia Institute of Technology January 18, 2000 Copyright © 2001 by Georgia Tech Research Corporation, Atlanta, Georgia 30332 -0415 USA. All Rights Reserved. Permission to distribute at no charge and without changes is hereby granted provided this notice is included.
Outline AP 210 -based Environment - JPL/NASA Phase 1 – – Ancillary Information Problem Phase 1 Scope (work-in-progress) Collaboration Expected Benefits Other Potential AP 210 Applications: Chip Package Design & Analysis - Shinko Phase 1, 2 – Phase 1 Accomplishments References & Nomenclature © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 2

Development of Advanced Collaborative Engineering Environments (CEEs) Phase 1: CEE-based PWB Stackup Design Tool This presentation overviews work-in-progress for Phase 1. © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 3
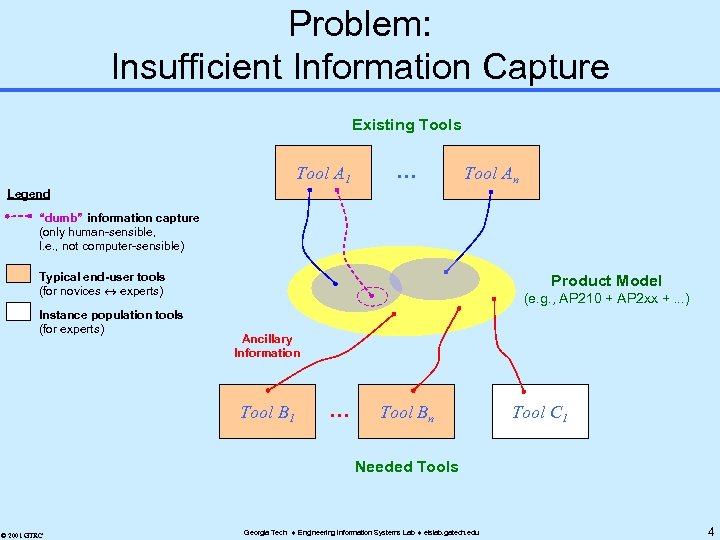
Problem: Insufficient Information Capture Existing Tools Tool A 1 . . . Tool An Legend “dumb” information capture (only human-sensible, I. e. , not computer-sensible) Typical end-user tools (for novices experts) Instance population tools (for experts) Product Model (e. g. , AP 210 + AP 2 xx +. . . ) Ancillary Information Tool B 1 . . . Tool Bn Tool C 1 Needed Tools © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 4
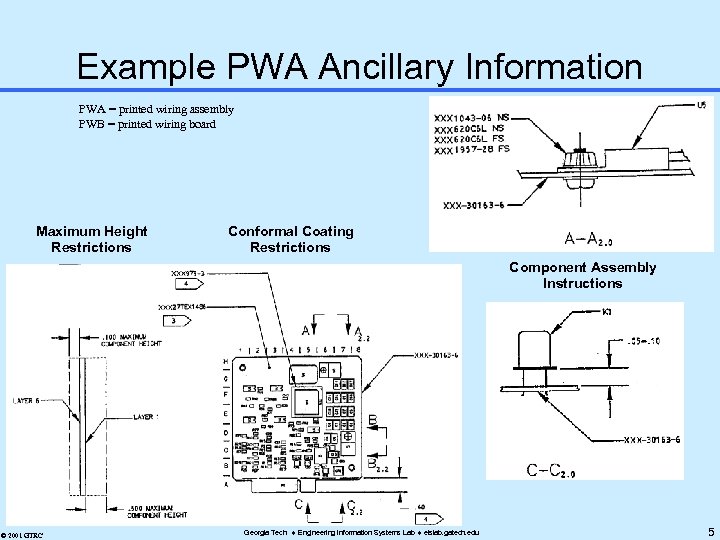
Example PWA Ancillary Information PWA = printed wiring assembly PWB = printed wiring board Maximum Height Restrictions Conformal Coating Restrictions Component Assembly Instructions Stackup Notes © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 5
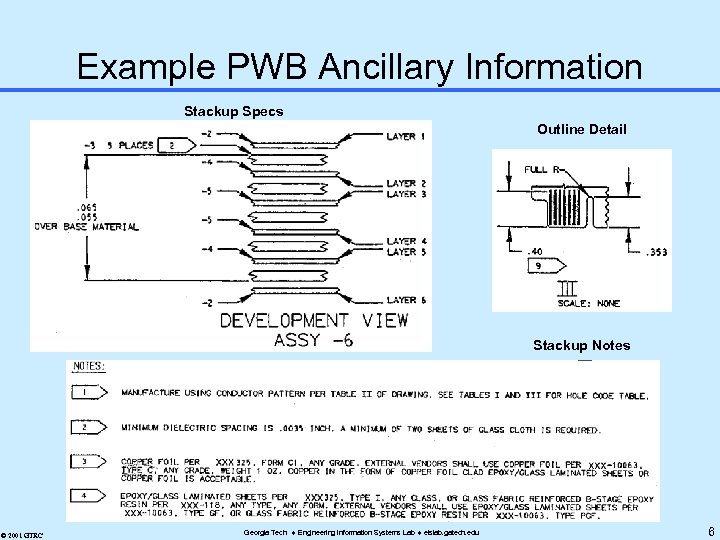
Example PWB Ancillary Information Stackup Specs Outline Detail Stackup Notes © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 6

Current Situation (typical) u u u CAx tools of diverse disciplines Each focuses on information subset (some overlap) Much ancillary information – Some captured as “dumb” notes & sketches in CAD » Human-oriented, not computer-sensible – Much not captured at all – Lack of fine-grain explicit associativity u Problems – Manually intensive transformations – Error-prone transcription / re-creation downstream – Little knowledge capture © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 7
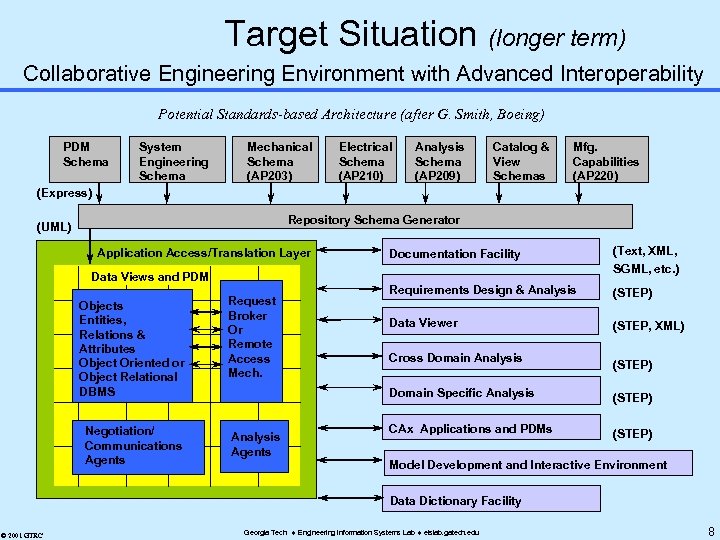
Target Situation (longer term) Collaborative Engineering Environment with Advanced Interoperability Potential Standards-based Architecture (after G. Smith, Boeing) PDM Schema System Engineering Schema Mechanical Schema (AP 203) Electrical Schema (AP 210) Analysis Schema (AP 209) Catalog & View Schemas Mfg. Capabilities (AP 220) (Express) Repository Schema Generator (UML) Application Access/Translation Layer Data Views and PDM Objects Entities, Relations & Attributes Object Oriented or Object Relational DBMS Negotiation/ Communications Agents Request Broker Or Remote Access Mech. Documentation Facility (Text, XML, SGML, etc. ) Requirements Design & Analysis (STEP) Data Viewer (STEP, XML) Cross Domain Analysis (STEP) Domain Specific Analysis Agents (STEP) CAx Applications and PDMs (STEP) Model Development and Interactive Environment Data Dictionary Facility © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 8

Outline AP 210 -based Environment - JPL/NASA Phase 1 – Ancillary Information Problem – Phase 1 Scope (work-in-progress) » Background: Pro. AM/TIGER Projects, XAI » Phase 1 Architectures – Collaboration – Expected Benefits Other Potential AP 210 Applications: Chip Package Design & Analysis - Shinko Phase 1, 2 – Phase 1 Accomplishments References & Nomenclature © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 9
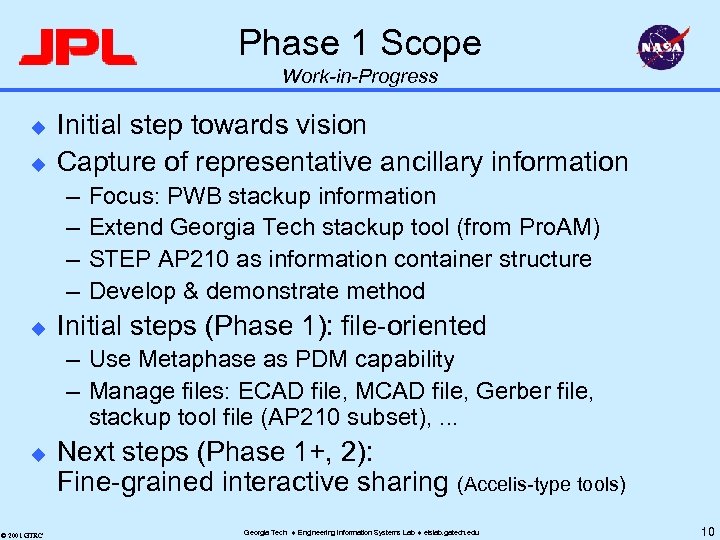
Phase 1 Scope Work-in-Progress u u Initial step towards vision Capture of representative ancillary information – – u Focus: PWB stackup information Extend Georgia Tech stackup tool (from Pro. AM) STEP AP 210 as information container structure Develop & demonstrate method Initial steps (Phase 1): file-oriented – Use Metaphase as PDM capability – Manage files: ECAD file, MCAD file, Gerber file, stackup tool file (AP 210 subset), . . . u © 2001 GTRC Next steps (Phase 1+, 2): Fine-grained interactive sharing (Accelis-type tools) Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 10
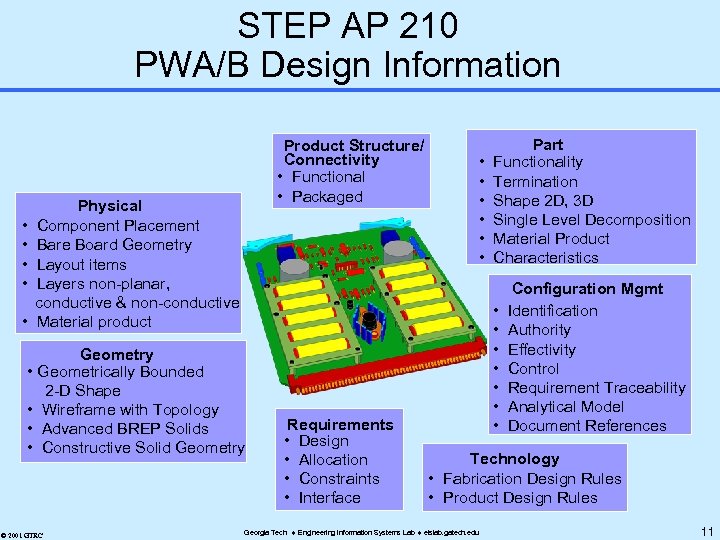
STEP AP 210 PWA/B Design Information • • • Product Structure/ Connectivity • Functional • Packaged Physical Component Placement Bare Board Geometry Layout items Layers non-planar, conductive & non-conductive Material product Geometry • Geometrically Bounded 2 -D Shape • Wireframe with Topology • Advanced BREP Solids • Constructive Solid Geometry © 2001 GTRC Requirements • Design • Allocation • Constraints • Interface • • • Part Functionality Termination Shape 2 D, 3 D Single Level Decomposition Material Product Characteristics • • Configuration Mgmt Identification Authority Effectivity Control Requirement Traceability Analytical Model Document References Technology • Fabrication Design Rules • Product Design Rules Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 11
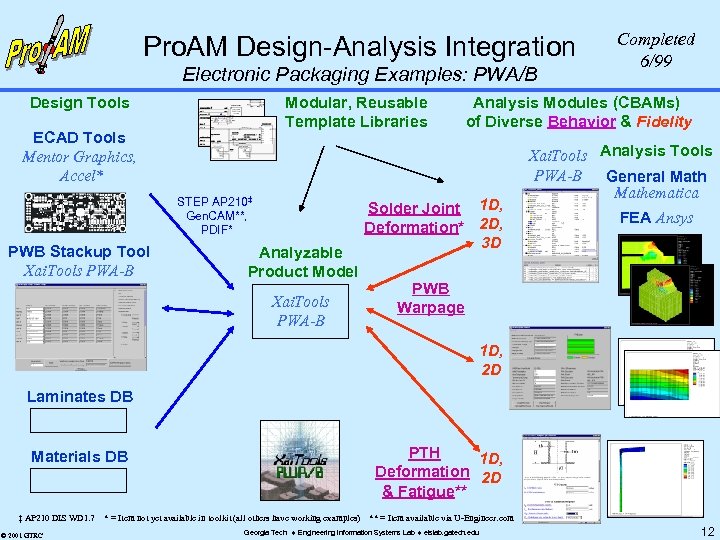
Pro. AM Design-Analysis Integration Electronic Packaging Examples: PWA/B Design Tools Modular, Reusable Template Libraries ECAD Tools Mentor Graphics, Accel* STEP AP 210‡ Gen. CAM**, PDIF* PWB Stackup Tool Xai. Tools PWA-B Analyzable Product Model Xai. Tools PWA-B Completed 6/99 Analysis Modules (CBAMs) of Diverse Behavior & Fidelity Solder Joint 1 D, Deformation* 2 D, 3 D Xai. Tools Analysis Tools PWA-B General Mathematica FEA Ansys PWB Warpage 1 D, 2 D Laminates DB PTH 1 D, Deformation 2 D & Fatigue** Materials DB ‡ AP 210 DIS WD 1. 7 © 2001 GTRC * = Item not yet available in toolkit (all others have working examples) ** = Item available via U-Engineer. com Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 12
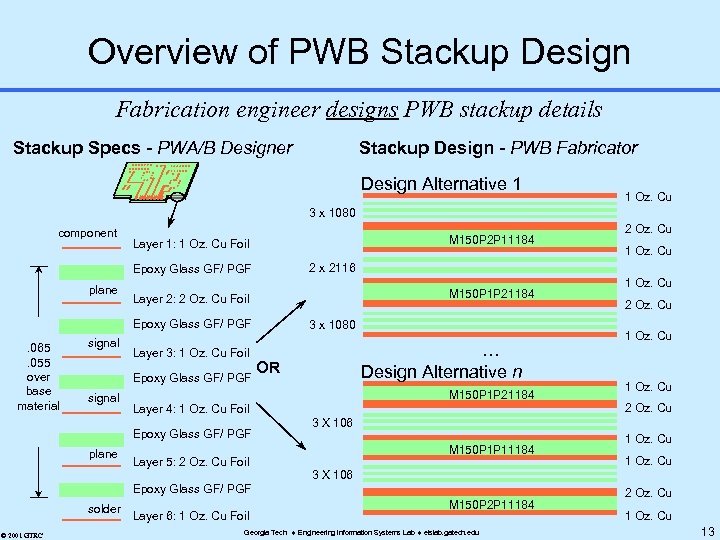
Overview of PWB Stackup Design Fabrication engineer designs PWB stackup details Stackup Specs - PWA/B Designer Stackup Design - PWB Fabricator Design Alternative 1 1 Oz. Cu 3 x 1080 component M 150 P 2 P 11184 Layer 1: 1 Oz. Cu Foil M 150 P 1 P 21184 Layer 2: 2 Oz. Cu Foil Epoxy Glass GF/ PGF . 065. 055 over base material signal Layer 3: 1 Oz. Cu Foil Epoxy Glass GF/ PGF signal plane 3 x 1080 … Design Alternative n OR M 150 P 1 P 21184 Layer 4: 1 Oz. Cu Foil Epoxy Glass GF/ PGF Layer 5: 2 Oz. Cu Foil © 2001 GTRC Layer 6: 1 Oz. Cu Foil 1 Oz. Cu 2 Oz. Cu 3 X 106 M 150 P 1 P 11184 1 Oz. Cu 3 X 106 Epoxy Glass GF/ PGF solder 1 Oz. Cu 2 x 2116 Epoxy Glass GF/ PGF plane 2 Oz. Cu M 150 P 2 P 11184 Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 2 Oz. Cu 13
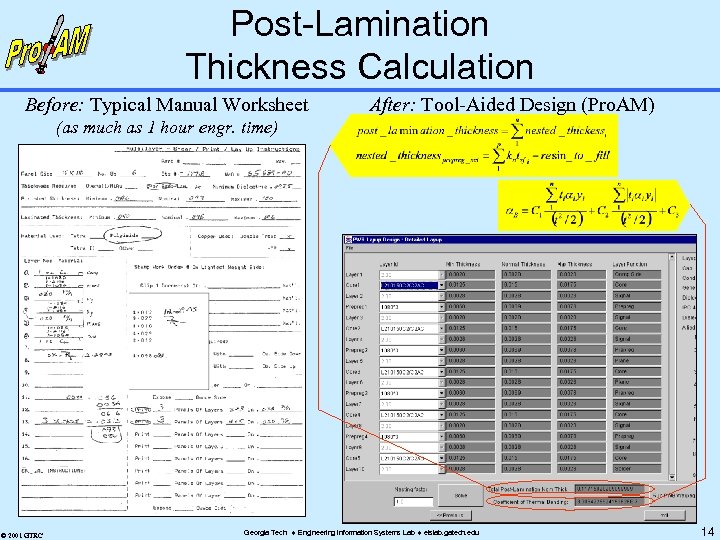
Post-Lamination Thickness Calculation Before: Typical Manual Worksheet After: Tool-Aided Design (Pro. AM) (as much as 1 hour engr. time) © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 14
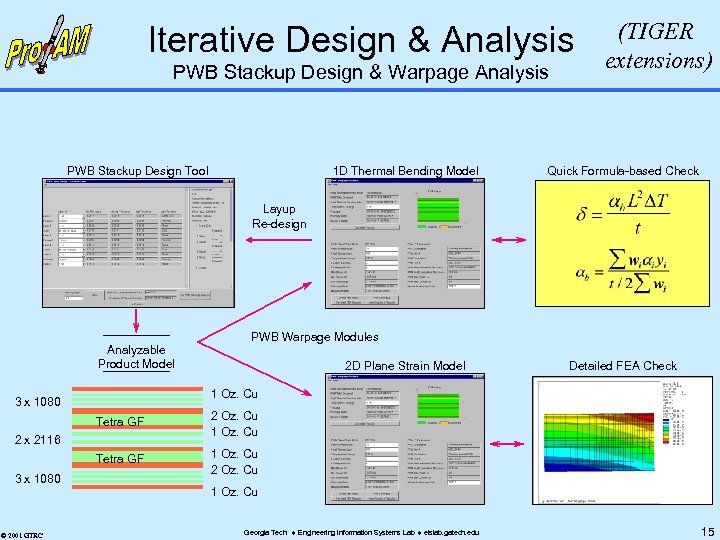
Iterative Design & Analysis PWB Stackup Design & Warpage Analysis PWB Stackup Design Tool 1 D Thermal Bending Model (TIGER extensions) Quick Formula-based Check Layup Re-design Analyzable Product Model PWB Warpage Modules 2 D Plane Strain Model 1 Oz. Cu 3 x 1080 Tetra GF 2 Oz. Cu 1 Oz. Cu Tetra GF 1 Oz. Cu 2 x 2116 3 x 1080 © 2001 GTRC Detailed FEA Check 1 Oz. Cu Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 15
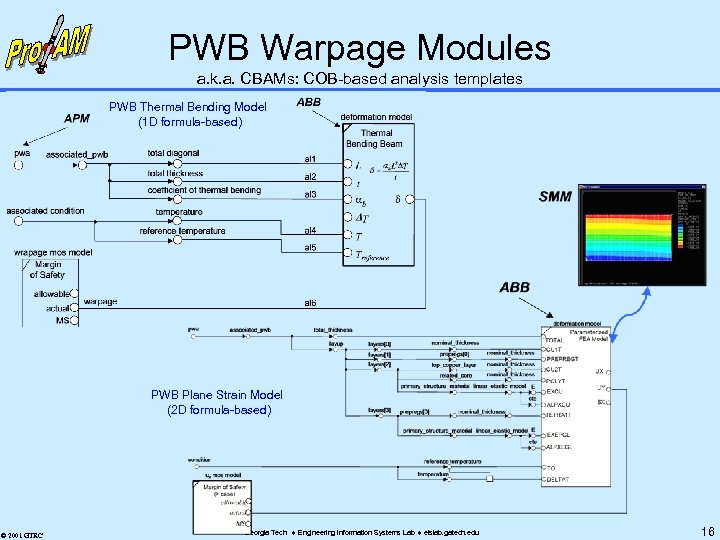
PWB Warpage Modules a. k. a. CBAMs: COB-based analysis templates PWB Thermal Bending Model (1 D formula-based) PWB Plane Strain Model (2 D formula-based) © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 16
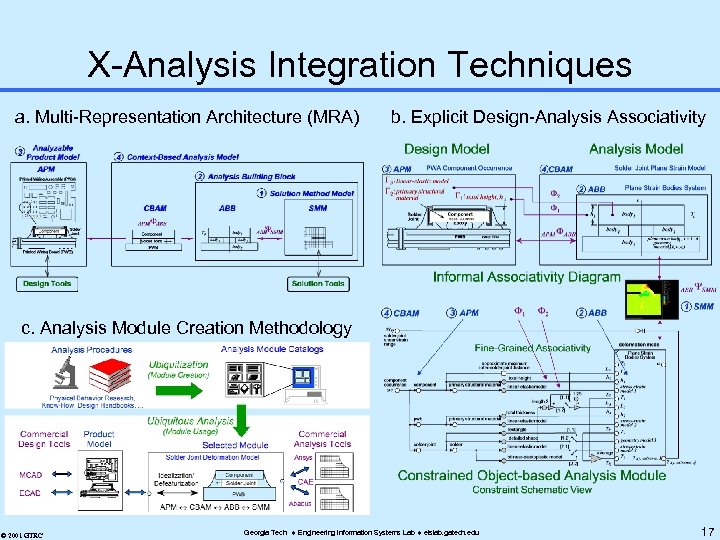
X-Analysis Integration Techniques a. Multi-Representation Architecture (MRA) b. Explicit Design-Analysis Associativity c. Analysis Module Creation Methodology © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 17
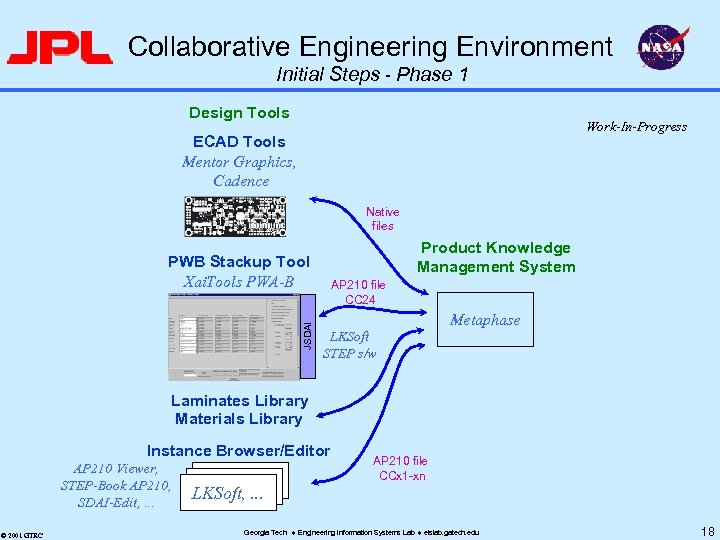
Collaborative Engineering Environment Initial Steps - Phase 1 Design Tools Work-In-Progress ECAD Tools Mentor Graphics, Cadence Native files Product Knowledge Management System JSDAI PWB Stackup Tool Xai. Tools PWA-B AP 210 file CC 24 Metaphase LKSoft STEP s/w Laminates Library Materials Library Instance Browser/Editor AP 210 Viewer, STEP-Book AP 210, SDAI-Edit, . . . © 2001 GTRC LKSoft, . . . AP 210 file CCx 1 -xn Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 18
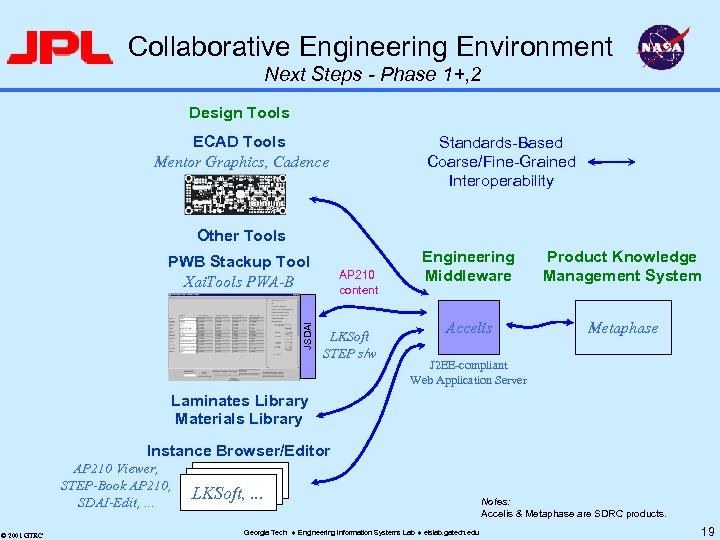
Collaborative Engineering Environment Next Steps - Phase 1+, 2 Design Tools ECAD Tools Mentor Graphics, Cadence Standards-Based Coarse/Fine-Grained Interoperability Other Tools JSDAI PWB Stackup Tool Xai. Tools PWA-B AP 210 content LKSoft STEP s/w Engineering Middleware Product Knowledge Management System Accelis Metaphase J 2 EE-compliant Web Application Server Laminates Library Materials Library Instance Browser/Editor AP 210 Viewer, STEP-Book AP 210, SDAI-Edit, . . . © 2001 GTRC LKSoft, . . . Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu Notes: Accelis & Metaphase are SDRC products. 19
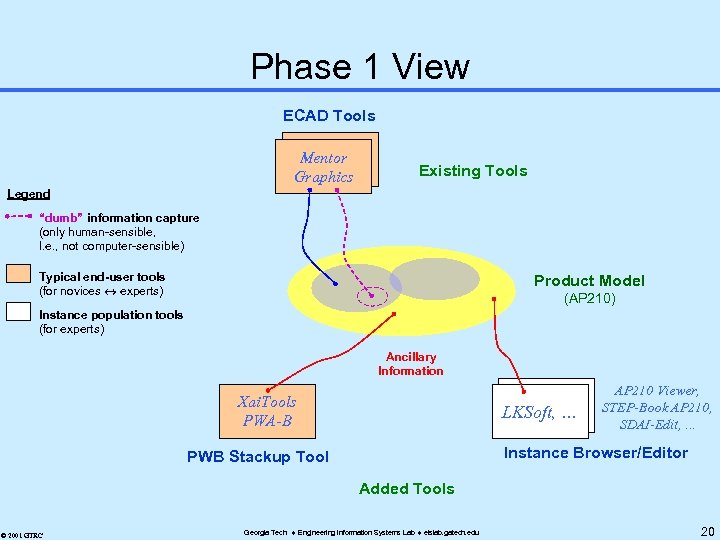
Phase 1 View ECAD Tools Mentor Graphics Existing Tools Legend “dumb” information capture (only human-sensible, I. e. , not computer-sensible) Typical end-user tools (for novices experts) Product Model (AP 210) Instance population tools (for experts) Ancillary Information Xai. Tools PWA-B LKSoft, … AP 210 Viewer, STEP-Book AP 210, SDAI-Edit, . . . Instance Browser/Editor PWB Stackup Tool Added Tools © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 20

Collaboration u JPL/NASA – Primary stakeholder, end users, tool experts u Georgia Tech – Architecture/method, PWB stackup tool, XAI methods u AP 210 Implementers Forum – Common interests & techniques – Cooperative exchanges u JPL/NASA suppliers – Software vendors © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 21
Expected Benefits: Phase 1 u STEP AP 210 -based method » Depth, extendibility u Capture of ancillary information – Representative tool: PWB stackup design » Graphics, automation » Tangible end user benefits » Technique illustration – “Better, faster, cheaper” » Increased product model completeness » Reduced downstream errors » Increased automation » Increased knowledge retention © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 22
Outline AP 210 -based Environment - JPL/NASA Phase 1 – – Ancillary Information Problem Phase 1 Scope (work-in-progress) Collaboration Expected Benefits Other Potential AP 210 Applications: Chip Package Design & Analysis - Shinko Phase 1, 2 – Phase 1 Accomplishments References & Nomenclature © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 23
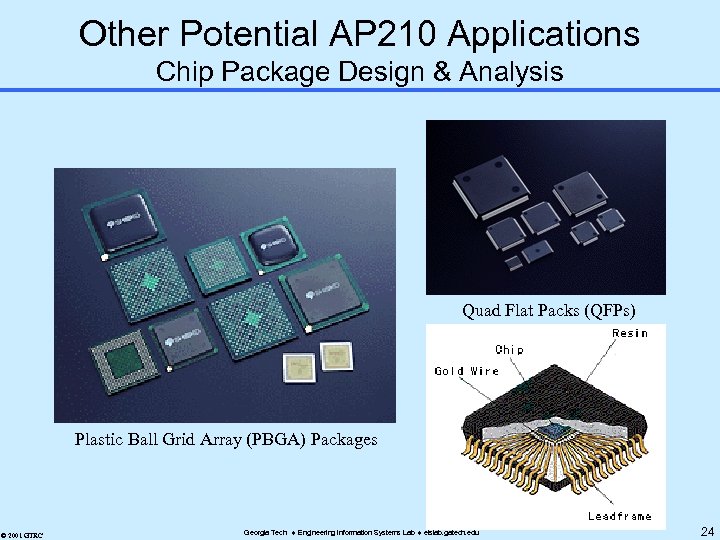
Other Potential AP 210 Applications Chip Package Design & Analysis Quad Flat Packs (QFPs) Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA) Packages © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 24
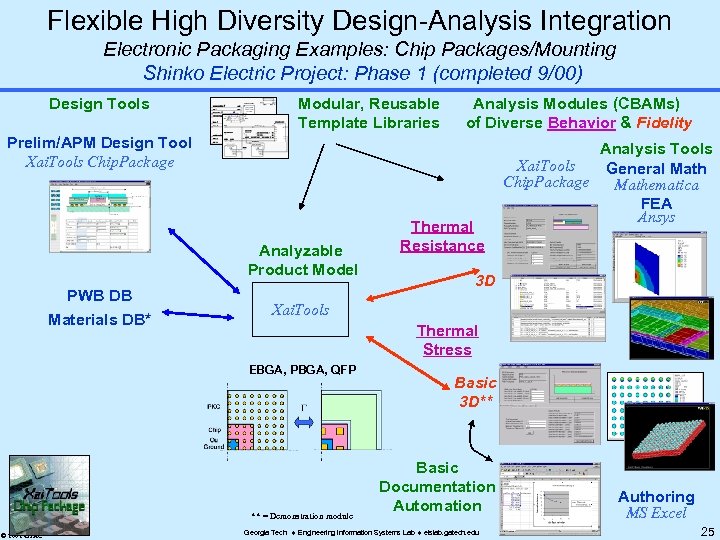
Flexible High Diversity Design-Analysis Integration Electronic Packaging Examples: Chip Packages/Mounting Shinko Electric Project: Phase 1 (completed 9/00) Design Tools Modular, Reusable Template Libraries Analysis Modules (CBAMs) of Diverse Behavior & Fidelity Prelim/APM Design Tool Xai. Tools Chip. Package Analyzable Product Model PWB DB Materials DB* 3 D Xai. Tools Thermal Stress EBGA, PBGA, QFP ** = Demonstration module © 2001 GTRC Thermal Resistance Analysis Tools Xai. Tools General Math Chip. Package Mathematica FEA Ansys Basic 3 D** Basic Documentation Automation Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu Authoring MS Excel 25
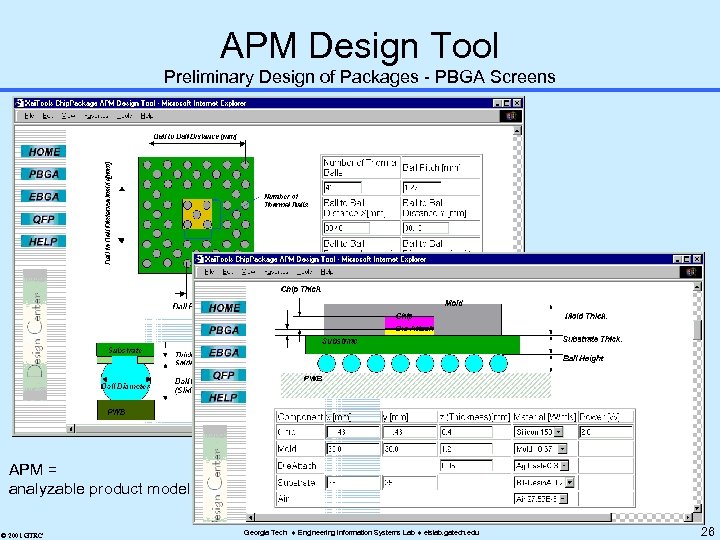
APM Design Tool Preliminary Design of Packages - PBGA Screens APM = analyzable product model © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 26
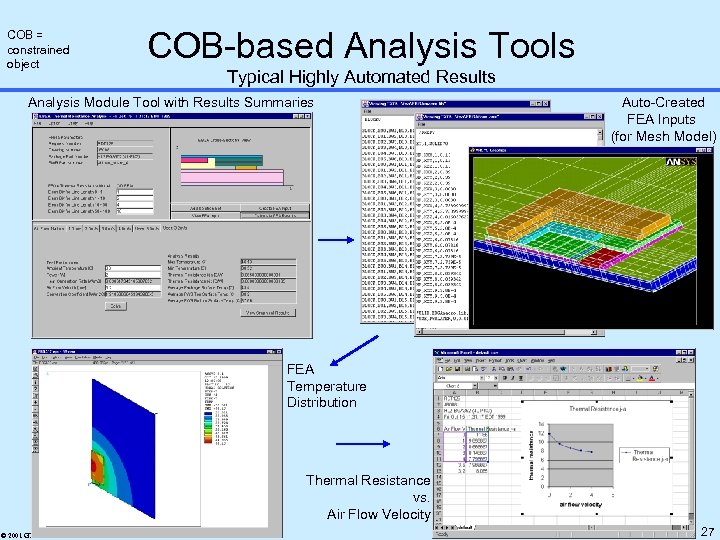
COB = constrained object COB-based Analysis Tools Typical Highly Automated Results Analysis Module Tool with Results Summaries Auto-Created FEA Inputs (for Mesh Model) FEA Temperature Distribution Thermal Resistance vs. Air Flow Velocity © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 27
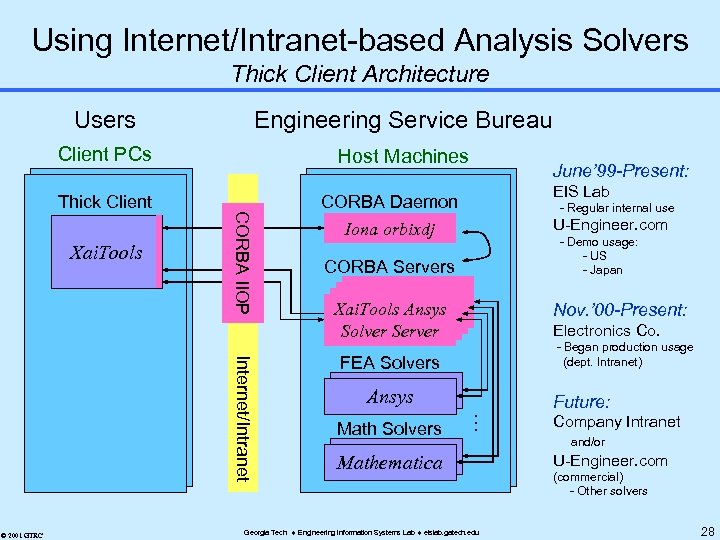
Using Internet/Intranet-based Analysis Solvers Thick Client Architecture Users Engineering Service Bureau Client PCs Host Machines Internet/Intranet © 2001 GTRC CORBA Daemon Iona orbixdj CORBA Servers Xai. Tools. Ansys Xai. Tools. Math. Xai. Tools. Ansys Xai. Tools Server Solver FEA Solvers Ansys Math Solvers EIS Lab - Regular internal use U-Engineer. com - Demo usage: - US - Japan Nov. ’ 00 -Present: Electronics Co. - Began production usage (dept. Intranet) Future: . . . Xai. Tools CORBA IIOP Internet Thick Client June’ 99 -Present: Mathematica Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu Company Intranet and/or U-Engineer. com (commercial) - Other solvers 28
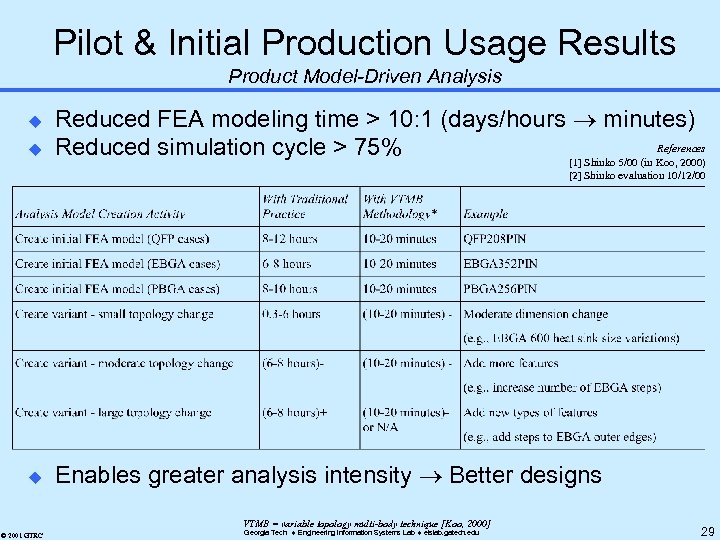
Pilot & Initial Production Usage Results Product Model-Driven Analysis u u Reduced FEA modeling time > 10: 1 (days/hours minutes) References Reduced simulation cycle > 75% [1] Shinko 5/00 (in Koo, 2000) [2] Shinko evaluation 10/12/00 u Enables greater analysis intensity Better designs VTMB = variable topology multi-body technique [Koo, 2000] © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 29

Phase 1 Summary - Shinko Project (Phase 2 is underway and evaluating usage of AP 210) © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 30

For Further Information. . . u EIS Lab web site: http: //eislab. gatech. edu/ – Publications, project overviews, tools, etc. – See: Publications DAI/XAI Suggested Starting Points X-Analysis Integration (XAI) Technology http: //eislab. gatech. edu/pubs/reports/EL 002/ u u © 2001 GTRC Xai. Tools home page: http: //eislab. gatech. edu/tools/Xai. Tools/ ™ Pilot commercial ESB: http: //www. u-engineer. com/ – Internet-based self-serve analysis – Analysis module catalog for electronic packaging – Highly automated front-ends to general FEA & math tools Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 31
Nomenclature © 2001 GTRC Georgia Tech Engineering Information Systems Lab eislab. gatech. edu 32
9e736df62433536fdcd3a1cb9764d92a.ppt