4aabbb99036715b6a8c0e0e4fb74d2a2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62

 Name of era comes from Mark Twain society & economy appear strong government is weak and corrupt things were NOT as promising as they appeared Gilded Age
Name of era comes from Mark Twain society & economy appear strong government is weak and corrupt things were NOT as promising as they appeared Gilded Age
 Gilded Age
Gilded Age
 President Rutherford B. Hayes Elected 1872, received Demo. votes in exchange for ending Reconstruction. “Stolen Election” Does not use spoils system angers party
President Rutherford B. Hayes Elected 1872, received Demo. votes in exchange for ending Reconstruction. “Stolen Election” Does not use spoils system angers party
 James Garfield Republican Half breed Chester A. Arthur was his VP July 2, 1881 Garfield shot by Charles Guiteau Garfield dies from wounds Guiteau hung, thought to be insane
James Garfield Republican Half breed Chester A. Arthur was his VP July 2, 1881 Garfield shot by Charles Guiteau Garfield dies from wounds Guiteau hung, thought to be insane
 Chester A. Arthur Reformed civil service with the Pendleton Act Created a merit system commission gave exams for all seeking govt. jobs
Chester A. Arthur Reformed civil service with the Pendleton Act Created a merit system commission gave exams for all seeking govt. jobs
 Chester A. Arthur Reformed civil service with the Pendleton Act Created a merit system commission gave exams for all seeking govt. jobs
Chester A. Arthur Reformed civil service with the Pendleton Act Created a merit system commission gave exams for all seeking govt. jobs
 Political Machines controlled local politics in cities Helped immigrants for votes William “Boss” Tweed of NYC most famous for his Tammany Hall Cost NYC around $100 mill. Brought down by newspaper cartoonist, Thomas Nast
Political Machines controlled local politics in cities Helped immigrants for votes William “Boss” Tweed of NYC most famous for his Tammany Hall Cost NYC around $100 mill. Brought down by newspaper cartoonist, Thomas Nast
 Importance of immigrants Easily accessible/lots of them(votes) Needed jobs, services, housing Were loyal to the machines Immigrants Corruption Immigrants were hired to vote “early and often” Bosses took bribes, kickbacks, and payoffs.
Importance of immigrants Easily accessible/lots of them(votes) Needed jobs, services, housing Were loyal to the machines Immigrants Corruption Immigrants were hired to vote “early and often” Bosses took bribes, kickbacks, and payoffs.
 Thomas Nast Drew the political cartoon that introduced the donkey as Democrat and elephant as Republican.
Thomas Nast Drew the political cartoon that introduced the donkey as Democrat and elephant as Republican.
 Grover Cleveland Democratic reformer, helped put down Tweed ring Reps. split over nominee Cleveland & election wins NY
Grover Cleveland Democratic reformer, helped put down Tweed ring Reps. split over nominee Cleveland & election wins NY
 Cleveland Reforms Presidential Succession Act 1886 listed order of who would succeed fallen pres. and vice president Interstate Commerce Act 1887 rail rate should be “reasonable and just”
Cleveland Reforms Presidential Succession Act 1886 listed order of who would succeed fallen pres. and vice president Interstate Commerce Act 1887 rail rate should be “reasonable and just”
 Passed in 1887 due to public outrage of Supreme Court support of railroads Gave government right to monitor rail traffic and freight rates Interstate Commerce Commission created to enforce law Had little affect until the early 1900 s Interstate Commerce Act
Passed in 1887 due to public outrage of Supreme Court support of railroads Gave government right to monitor rail traffic and freight rates Interstate Commerce Commission created to enforce law Had little affect until the early 1900 s Interstate Commerce Act
 Election of 1888 D. Cleveland, R. Harrison Democrats push low tariffs, Republicans push high tariffs, pensions for union veterans. Harrison wins but not by majority of popular vote not a strong President but an important administration Benjamin Harrison
Election of 1888 D. Cleveland, R. Harrison Democrats push low tariffs, Republicans push high tariffs, pensions for union veterans. Harrison wins but not by majority of popular vote not a strong President but an important administration Benjamin Harrison
 Harrison Reforms Sherman Silver Purchase Act 1890 “free & unlimited” coinage of silver inflates currency aids farmers Mc. Kinley Tariff passed in cooperation with Sherman Act, raised tariff rates to protect Northern business
Harrison Reforms Sherman Silver Purchase Act 1890 “free & unlimited” coinage of silver inflates currency aids farmers Mc. Kinley Tariff passed in cooperation with Sherman Act, raised tariff rates to protect Northern business
 Reforms Continued Sherman Anti-Trust Act protect farmers & small business from trusts insure no monopolies and restrict trade law was too vague and no penalties for breaking law
Reforms Continued Sherman Anti-Trust Act protect farmers & small business from trusts insure no monopolies and restrict trade law was too vague and no penalties for breaking law
 Many states passed laws restricting mergers Congress passes Sherman Anti -trust Act in 1890 to protect from monopolies and restriction of trade Did little to curb big business Was however used to restrict labor Restricting Big Business
Many states passed laws restricting mergers Congress passes Sherman Anti -trust Act in 1890 to protect from monopolies and restriction of trade Did little to curb big business Was however used to restrict labor Restricting Big Business
 Homestead Strike ((Pennsylvania, 1892) at Carnegie’s steel plant Plant cuts pay to weaken union, hires scabs(people who cross picket lines Bloody confrontation between strikers & hired scabs Plant remains open with nonunion workers
Homestead Strike ((Pennsylvania, 1892) at Carnegie’s steel plant Plant cuts pay to weaken union, hires scabs(people who cross picket lines Bloody confrontation between strikers & hired scabs Plant remains open with nonunion workers
 Election of 1892 Harrison-R vs. Cleveland-D as well as Populist James Weaver Cleveland wins making him the only President to serve two non-consecutive terms Populist receive 22 electoral votes and will win many statewide elections and congress seats
Election of 1892 Harrison-R vs. Cleveland-D as well as Populist James Weaver Cleveland wins making him the only President to serve two non-consecutive terms Populist receive 22 electoral votes and will win many statewide elections and congress seats
 Cleveland term 2 Panic of 1893 caused by inflation, labor & agriculture. Problems, & over speculating stocks causes worst economic depression ever tries to repeal Sherman Silver Act & sends in troops to end Pullman strike, angers labor tries to pass Income Tax, unconstitutional according to courts sets up heated election of 1896
Cleveland term 2 Panic of 1893 caused by inflation, labor & agriculture. Problems, & over speculating stocks causes worst economic depression ever tries to repeal Sherman Silver Act & sends in troops to end Pullman strike, angers labor tries to pass Income Tax, unconstitutional according to courts sets up heated election of 1896
 Pullman Workers Strike employees strike in 1894 because of cut wages RR workers union refuses to handle Pullman cars so rail traffic is paralyzed Pullman files injunction to stop strike Union leader Eugene Debs jailed refusing to stop Pres. Cleveland uses federal troops to end strike
Pullman Workers Strike employees strike in 1894 because of cut wages RR workers union refuses to handle Pullman cars so rail traffic is paralyzed Pullman files injunction to stop strike Union leader Eugene Debs jailed refusing to stop Pres. Cleveland uses federal troops to end strike
 Attempt to make the government respond to farmer demands Farmers deep in debt, prices falling because of larger crops high costs of shipping, storage, and interest caused farmers to lose their land droughts, floods, insects did not help
Attempt to make the government respond to farmer demands Farmers deep in debt, prices falling because of larger crops high costs of shipping, storage, and interest caused farmers to lose their land droughts, floods, insects did not help
 Populist Platform Inflationary policy = unlimited silver coinage graduated income tax 8 hour work day govt. owned RR, telegram, telephone immigrant restrictions Political reforms: ◦ secret ballots ◦ initiative ◦ referendum ◦ recall ◦ direct election of US senators “equal rights for all & special privileges for none”
Populist Platform Inflationary policy = unlimited silver coinage graduated income tax 8 hour work day govt. owned RR, telegram, telephone immigrant restrictions Political reforms: ◦ secret ballots ◦ initiative ◦ referendum ◦ recall ◦ direct election of US senators “equal rights for all & special privileges for none”
 Election of 1896 Populist & Democrats nominate William Jennings Bryan Republicans nominate William Mc. Kinley Bryan gives famous “cross of gold” speech Mc. Kinley wins because of labor votes
Election of 1896 Populist & Democrats nominate William Jennings Bryan Republicans nominate William Mc. Kinley Bryan gives famous “cross of gold” speech Mc. Kinley wins because of labor votes
 Inventions fuel new industries and communication Industries create wealth and a working class Unions form to protect the worker Immigrants fuel growth of nation
Inventions fuel new industries and communication Industries create wealth and a working class Unions form to protect the worker Immigrants fuel growth of nation
 The Inventors and their Inventions
The Inventors and their Inventions
 Thomas Edison More than 1, 000 patents Created: light bulb, phonograph, projector, storage battery, and telephone transmitter nation’s first industrial research lab first electric power plant in NYC
Thomas Edison More than 1, 000 patents Created: light bulb, phonograph, projector, storage battery, and telephone transmitter nation’s first industrial research lab first electric power plant in NYC
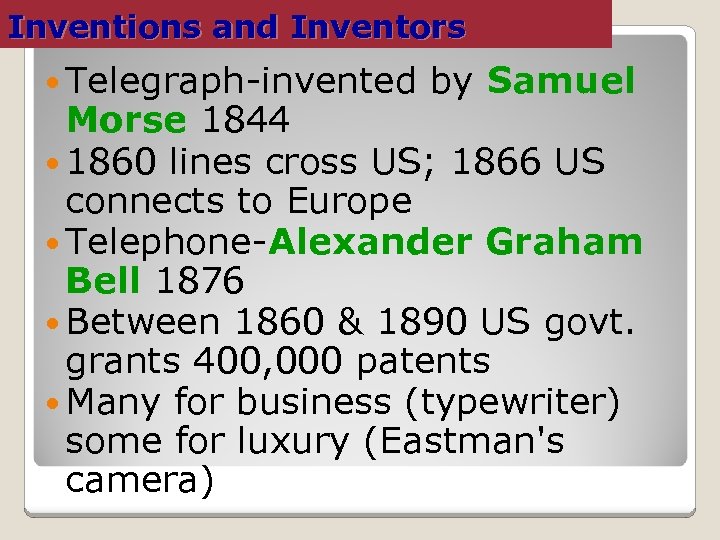 Inventions and Inventors Telegraph-invented by Samuel Morse 1844 1860 lines cross US; 1866 US connects to Europe Telephone-Alexander Graham Bell 1876 Between 1860 & 1890 US govt. grants 400, 000 patents Many for business (typewriter) some for luxury (Eastman's camera)
Inventions and Inventors Telegraph-invented by Samuel Morse 1844 1860 lines cross US; 1866 US connects to Europe Telephone-Alexander Graham Bell 1876 Between 1860 & 1890 US govt. grants 400, 000 patents Many for business (typewriter) some for luxury (Eastman's camera)
 First to mass produce an automobile first car was the model T Cars were more affordable because of a process called the assembly line Henry Ford
First to mass produce an automobile first car was the model T Cars were more affordable because of a process called the assembly line Henry Ford
 Wright Brothers First successful flight plane had 12 hp motor flew 120 feet Orville piloted, Wilbur watched Flew at Kitty hawk, NC
Wright Brothers First successful flight plane had 12 hp motor flew 120 feet Orville piloted, Wilbur watched Flew at Kitty hawk, NC
 Captains of Industry
Captains of Industry
 Railroads lead the way in industry by 1900 there are five transcontinental lines large RR’s are consolidating smaller RR’s Cornelius Vanderbilt one of the RR barons, owns lines from NYC to the Great Lakes
Railroads lead the way in industry by 1900 there are five transcontinental lines large RR’s are consolidating smaller RR’s Cornelius Vanderbilt one of the RR barons, owns lines from NYC to the Great Lakes
 RR Growth Iron and steel needed for track and locomotives; Lumber for rails, coal for fuel - Industry must grow to meet these demands - RR’s change to a standard gauge track: all lines use the same rails = faster shipping -
RR Growth Iron and steel needed for track and locomotives; Lumber for rails, coal for fuel - Industry must grow to meet these demands - RR’s change to a standard gauge track: all lines use the same rails = faster shipping -
 RR Improvements -Air brakes, refrigerated cars, Pullmans sleeper cars along with dining cars make RR better -RR’s compete using rebates to keep and attract customers -Some RR’s form pools = agreements of no competition allowing them to set higher prices
RR Improvements -Air brakes, refrigerated cars, Pullmans sleeper cars along with dining cars make RR better -RR’s compete using rebates to keep and attract customers -Some RR’s form pools = agreements of no competition allowing them to set higher prices
 Large mills open in Pittsburgh, PN (steel Steel Industry capital) Andrew Carnegie opens his first mill here vertical integration = bought mines, ships, warehouses, and RR’s Sold out to J. P. Morgan; creates first billion $ corporation
Large mills open in Pittsburgh, PN (steel Steel Industry capital) Andrew Carnegie opens his first mill here vertical integration = bought mines, ships, warehouses, and RR’s Sold out to J. P. Morgan; creates first billion $ corporation
 John Rockefeller creates a refinery for oil in Cleveland, OH Standard Oil begins buying out other refineries low prices, customer pressure, RR rebates to destroy competition creates 1 st trust has a monopoly on oil in the USA
John Rockefeller creates a refinery for oil in Cleveland, OH Standard Oil begins buying out other refineries low prices, customer pressure, RR rebates to destroy competition creates 1 st trust has a monopoly on oil in the USA
 Owned largest banking chain in US Grew wealthy through investment Purchased many industries using strength and financial backing of his bank J. P. Morgan
Owned largest banking chain in US Grew wealthy through investment Purchased many industries using strength and financial backing of his bank J. P. Morgan
 Growing Corporations begin to merge economic power controlled by few corporations 1900 one-third of ALL manufacturing controlled by 1% of country’s corporations many states encouraged the practice
Growing Corporations begin to merge economic power controlled by few corporations 1900 one-third of ALL manufacturing controlled by 1% of country’s corporations many states encouraged the practice
 Labor
Labor
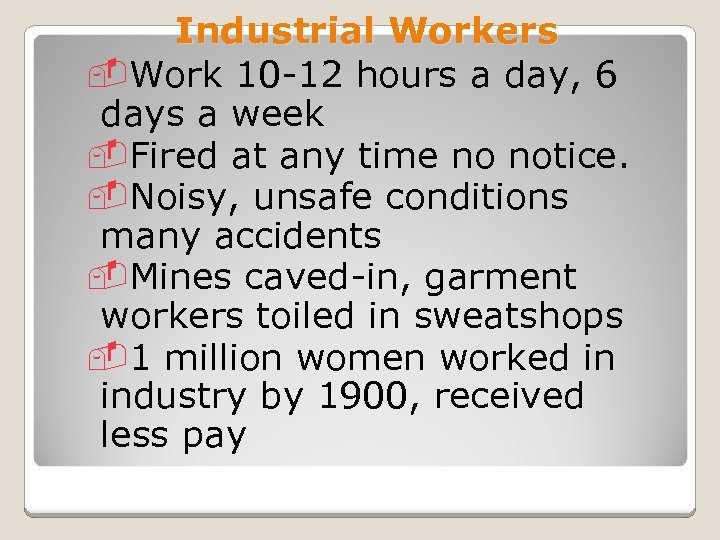 Industrial Workers -Work 10 -12 hours a day, 6 days a week -Fired at any time no notice. -Noisy, unsafe conditions many accidents -Mines caved-in, garment workers toiled in sweatshops -1 million women worked in industry by 1900, received less pay
Industrial Workers -Work 10 -12 hours a day, 6 days a week -Fired at any time no notice. -Noisy, unsafe conditions many accidents -Mines caved-in, garment workers toiled in sweatshops -1 million women worked in industry by 1900, received less pay
 Child Labor Children worked in mines & factories as well as farms First child labor law said no child under 12 & kids could only work 10 hours per day. Widely ignored law especially on farms
Child Labor Children worked in mines & factories as well as farms First child labor law said no child under 12 & kids could only work 10 hours per day. Widely ignored law especially on farms
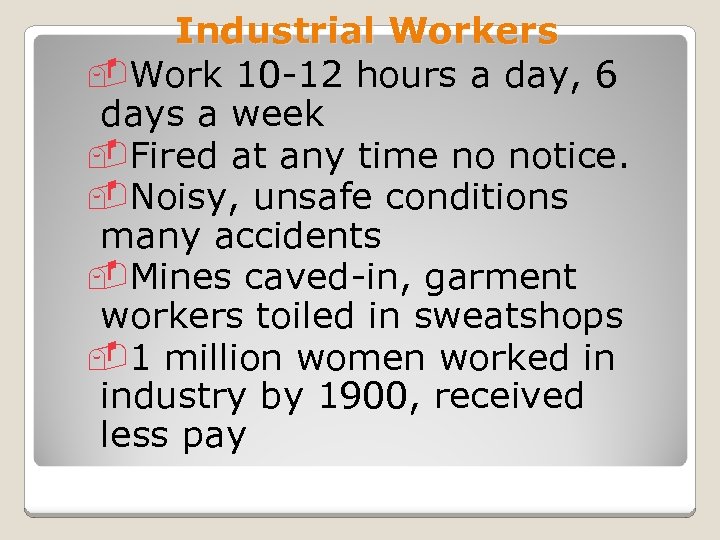 Industrial Workers -Work 10 -12 hours a day, 6 days a week -Fired at any time no notice. -Noisy, unsafe conditions many accidents -Mines caved-in, garment workers toiled in sweatshops -1 million women worked in industry by 1900, received less pay
Industrial Workers -Work 10 -12 hours a day, 6 days a week -Fired at any time no notice. -Noisy, unsafe conditions many accidents -Mines caved-in, garment workers toiled in sweatshops -1 million women worked in industry by 1900, received less pay
 Unions form from angry workers (Knights of Labor founded by garment workers in Philly met secretly. ( Became a national society in 1880 included women, African Americans, immigrants ( Strikes and poor public opinion in 1890’s ended its power
Unions form from angry workers (Knights of Labor founded by garment workers in Philly met secretly. ( Became a national society in 1880 included women, African Americans, immigrants ( Strikes and poor public opinion in 1890’s ended its power
 American Federation of Labor (AFL) 1886 ◦ Represented skilled labor led by Samuel Gompers ◦ pressed for higher wages, shorter hours, and better working conditions. ◦ wanted union to represent worker in meeting with management (collective bargaining) ◦ AFL survives strikes and by 1904 they have 1. 6 million members.
American Federation of Labor (AFL) 1886 ◦ Represented skilled labor led by Samuel Gompers ◦ pressed for higher wages, shorter hours, and better working conditions. ◦ wanted union to represent worker in meeting with management (collective bargaining) ◦ AFL survives strikes and by 1904 they have 1. 6 million members.
 Wobblies Chicago 1905 by 43 groups who left AFL International Workers of the World formed Includes unskilled laborers Radical union included Socialists
Wobblies Chicago 1905 by 43 groups who left AFL International Workers of the World formed Includes unskilled laborers Radical union included Socialists
 (RR strike of 1877 happens when wages cut Workers destroy rail yards, track Strikebreakers hired to replace workers Federal troops must restore order Union Action through strikes!
(RR strike of 1877 happens when wages cut Workers destroy rail yards, track Strikebreakers hired to replace workers Federal troops must restore order Union Action through strikes!
 Trouble in Chicago Haymarket Riot Workers from Mc. Cormick Harvester are members of Knights of Labor Wages cut so they go on strike Workers & police clash 11 killed Public turns against Knights
Trouble in Chicago Haymarket Riot Workers from Mc. Cormick Harvester are members of Knights of Labor Wages cut so they go on strike Workers & police clash 11 killed Public turns against Knights
 Two movement patterns: Rural to urban (migration) Immigration to the United States Reasons cities grew: Transportation-trains, trolleys, subways made travel from the suburbs possible. The invention of the steel girder(Bessemer process) made skyscrapers possible(extended cities up) Challenge of Cities
Two movement patterns: Rural to urban (migration) Immigration to the United States Reasons cities grew: Transportation-trains, trolleys, subways made travel from the suburbs possible. The invention of the steel girder(Bessemer process) made skyscrapers possible(extended cities up) Challenge of Cities

 When the upper class moved to suburbs their houses were made into multifamily dwellings. Banks, businesses and government offices were located in central places within cities. Living conditions for city dwellers: Open sewers, rats and crowding caused diseases to travel quickly
When the upper class moved to suburbs their houses were made into multifamily dwellings. Banks, businesses and government offices were located in central places within cities. Living conditions for city dwellers: Open sewers, rats and crowding caused diseases to travel quickly
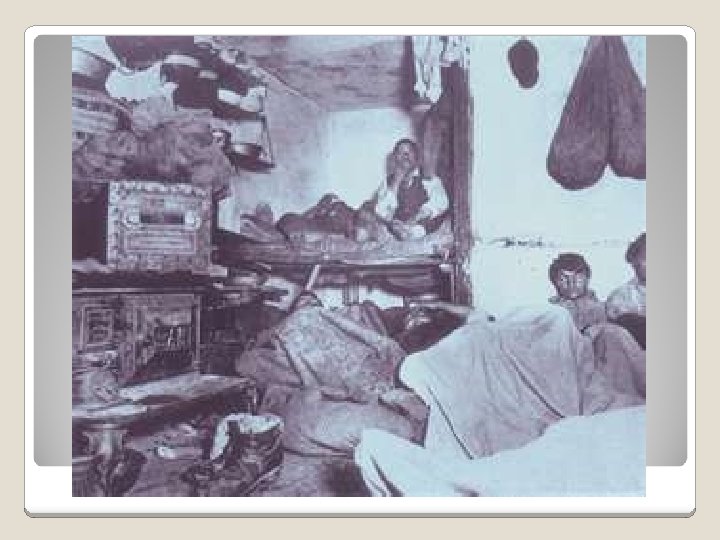

 Tenements were cheaply built and so close together that fires spread quickly. (slums) Ghettos formed for two reasons because of persecution and because of similarities in culture Rapid urban growth put pressure on city officials to make improvements on city services (police, fire, transportation, etc. )
Tenements were cheaply built and so close together that fires spread quickly. (slums) Ghettos formed for two reasons because of persecution and because of similarities in culture Rapid urban growth put pressure on city officials to make improvements on city services (police, fire, transportation, etc. )
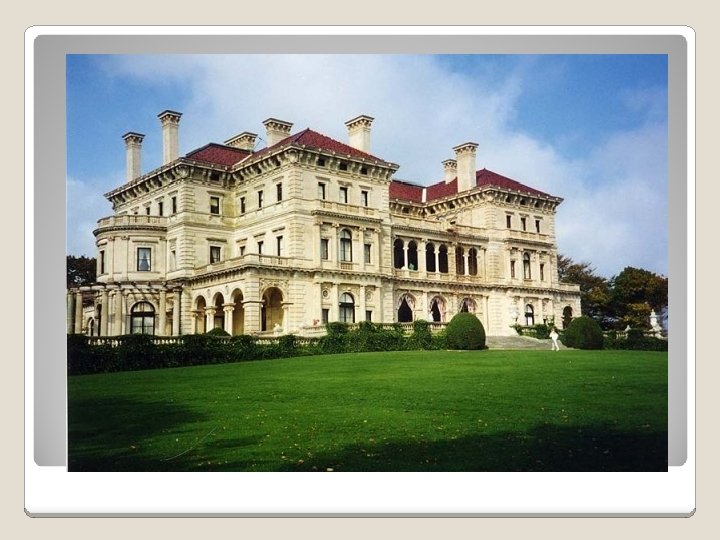
 The upper class had made their money in the new industries or by investing in new inventions. They were known as “noveau rich” and spent their money so that everyone would know exactly how rich they were. They also gave their money to charity(philanthropy). Culturally, they followed strict Victorian society (behavior). UPPER CLASS
The upper class had made their money in the new industries or by investing in new inventions. They were known as “noveau rich” and spent their money so that everyone would know exactly how rich they were. They also gave their money to charity(philanthropy). Culturally, they followed strict Victorian society (behavior). UPPER CLASS

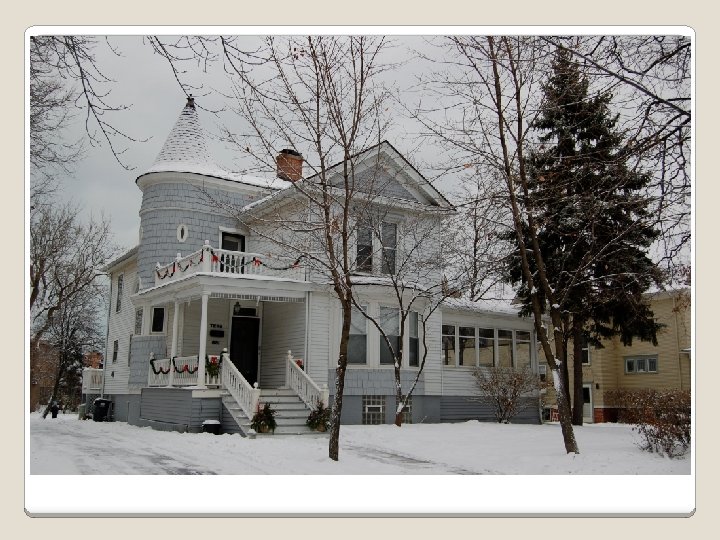
 The growth of new industries created more jobs for educated workers. They also were concerned with social behavior as well and some became reformers that led the Progressive movement. MIDDLE CLASS
The growth of new industries created more jobs for educated workers. They also were concerned with social behavior as well and some became reformers that led the Progressive movement. MIDDLE CLASS

 Mostly made of farmers/immigrants that lived in tenements that were poorly built. Often faced widespread discrimination and low pay. Mostly lived in parts of the city where other members of their culture lived. POOR CLASS
Mostly made of farmers/immigrants that lived in tenements that were poorly built. Often faced widespread discrimination and low pay. Mostly lived in parts of the city where other members of their culture lived. POOR CLASS
 LITTLE ITALY, NEW YORK
LITTLE ITALY, NEW YORK
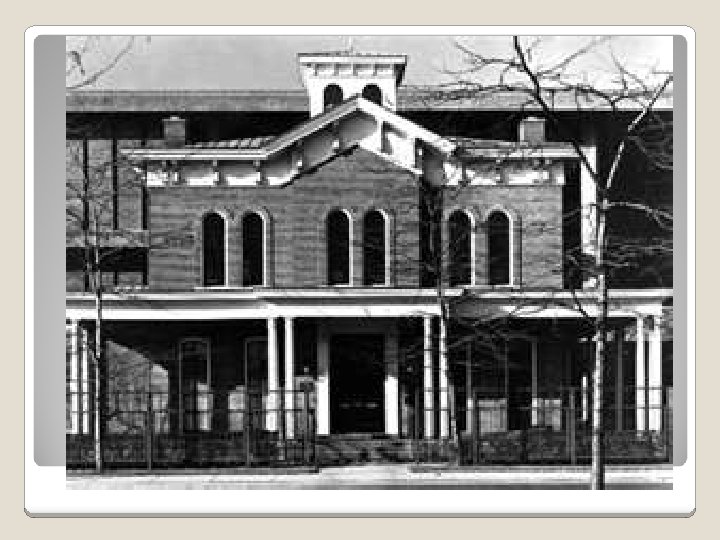
 Some reformers used the homes left by the wealthy to make multifamily dwellings. These were used as settlement homes for the new immigrants. They taught them English offered a daycare system and eventually added a kindergarten to help immigrants with language/skills. She won the Nobel Peace Prize for her work. Jane Addams/Hull House
Some reformers used the homes left by the wealthy to make multifamily dwellings. These were used as settlement homes for the new immigrants. They taught them English offered a daycare system and eventually added a kindergarten to help immigrants with language/skills. She won the Nobel Peace Prize for her work. Jane Addams/Hull House

 Prohibition-was a ban on the manufacture and sale of alcoholic beverages. Purity Crusaders-wanted to rid the communities of unwholesome and illegal activities. (Drugs, gambling, prostitution and the political machine) Charity Organization Movement-wanted immigrants to adopt American culture and customs. REFORM MOVEMENTS
Prohibition-was a ban on the manufacture and sale of alcoholic beverages. Purity Crusaders-wanted to rid the communities of unwholesome and illegal activities. (Drugs, gambling, prostitution and the political machine) Charity Organization Movement-wanted immigrants to adopt American culture and customs. REFORM MOVEMENTS
 The Social Gospel Movement-sought to apply the teachings of Jesus directly to society focused on charity, justice, and labor reforms. The Salvation Army-Settlement houses and Red Cross provided social services to communities. This was the most successful. More Reforms
The Social Gospel Movement-sought to apply the teachings of Jesus directly to society focused on charity, justice, and labor reforms. The Salvation Army-Settlement houses and Red Cross provided social services to communities. This was the most successful. More Reforms


