34d378064591a530658ebfcabfd72293.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 n Essential Question: –What early precedents in American government were established in Washington’s first 2 terms as president? n Warm-Up Question: –RQ 8 B (246 -263) –Take notes during the video on George Washington (12. 40)
n Essential Question: –What early precedents in American government were established in Washington’s first 2 terms as president? n Warm-Up Question: –RQ 8 B (246 -263) –Take notes during the video on George Washington (12. 40)
 The Young Republic, 1788 -1800 George Washington & America’s 1 st Political Parties
The Young Republic, 1788 -1800 George Washington & America’s 1 st Political Parties
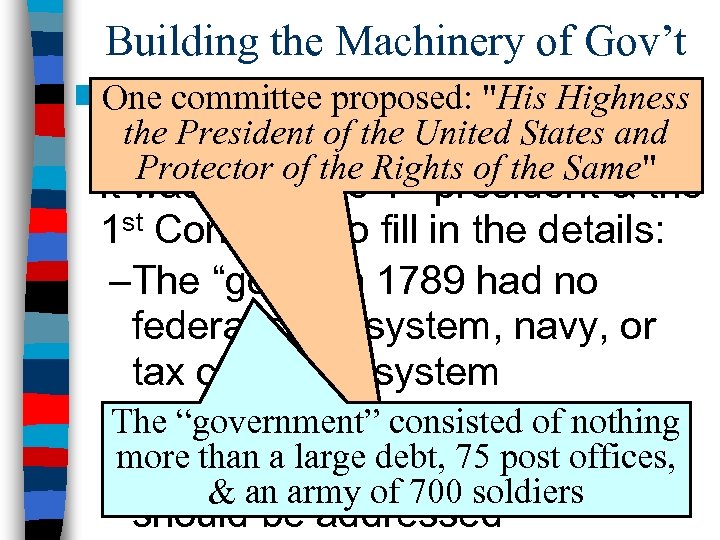 Building the Machinery of Gov’t n The committee proposed: "Hisa One Constitution created Highness the President of the United States and “general framework” of gov’t but Protector of the Rights of the Same" st it was up to the 1 president & the 1 st Congress to fill in the details: –The “gov’t” in 1789 had no federal court system, navy, or tax collection system The “government” consisted of nothing –The Senate spent 3 weeks more than a large debt, president 75 post offices, debating how the & an army of 700 soldiers should be addressed
Building the Machinery of Gov’t n The committee proposed: "Hisa One Constitution created Highness the President of the United States and “general framework” of gov’t but Protector of the Rights of the Same" st it was up to the 1 president & the 1 st Congress to fill in the details: –The “gov’t” in 1789 had no federal court system, navy, or tax collection system The “government” consisted of nothing –The Senate spent 3 weeks more than a large debt, president 75 post offices, debating how the & an army of 700 soldiers should be addressed
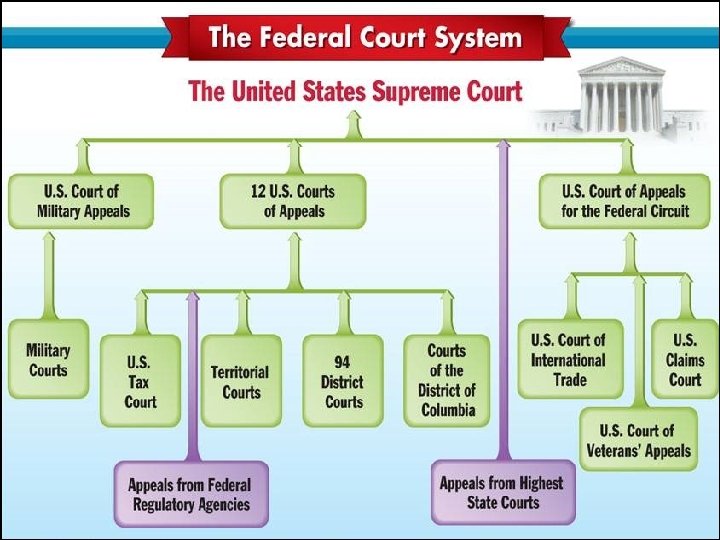
 Building the Machinery of Gov’t n With James Madison’s leadership, the House of Representatives: Consisted of a Supreme Court with –raised revenue by passingeach six justices, a district court in a state, and three a tax courts protective tariff &appeals on liquor –gave structure to the executive branch by creating the State, Treasury, Justice, & War Depts –organized a federal court system via the Judiciary Act of 1789
Building the Machinery of Gov’t n With James Madison’s leadership, the House of Representatives: Consisted of a Supreme Court with –raised revenue by passingeach six justices, a district court in a state, and three a tax courts protective tariff &appeals on liquor –gave structure to the executive branch by creating the State, Treasury, Justice, & War Depts –organized a federal court system via the Judiciary Act of 1789
 The Importance of James Madison “Father of the Constitution; ” leader of Congress who helped create the 1 st federal taxes, depts & courts; & will serve as the 4 th president
The Importance of James Madison “Father of the Constitution; ” leader of Congress who helped create the 1 st federal taxes, depts & courts; & will serve as the 4 th president
 Washington as President n The unanimous choice for the leader of the infant republic was George Washington n He established many precedents to make the presidency: –Created the 1 st cabinet –Delivering an inaugural address –The title “Mr. President”
Washington as President n The unanimous choice for the leader of the infant republic was George Washington n He established many precedents to make the presidency: –Created the 1 st cabinet –Delivering an inaugural address –The title “Mr. President”
 Washington as President n Washington’s 1 st term as president was defined by domestic policy: policy –He helped define a strong & active presidency –Appointed strong, able leaders to cabinet posts –Focused on the U. S. economy –Traveled to every state to “show the people” their national gov’t
Washington as President n Washington’s 1 st term as president was defined by domestic policy: policy –He helped define a strong & active presidency –Appointed strong, able leaders to cabinet posts –Focused on the U. S. economy –Traveled to every state to “show the people” their national gov’t
 Washington’s Cabinet Hamilton, Alexander Henry Knox, Secretary of Treasury Secretary of War George Washington, Washington acted as presidentto be his most Hamilton & Jefferson proved as he did as a President military general: members. Edmund Randolph, capable cabinet he surrounded himself with but were also the most. Thomas Jefferson, they had to theirdifferent capable subordinates, listened vastly General divisive because Attorney advice, Secretary role of gov’t for the new views on the made the final decision nation then of State
Washington’s Cabinet Hamilton, Alexander Henry Knox, Secretary of Treasury Secretary of War George Washington, Washington acted as presidentto be his most Hamilton & Jefferson proved as he did as a President military general: members. Edmund Randolph, capable cabinet he surrounded himself with but were also the most. Thomas Jefferson, they had to theirdifferent capable subordinates, listened vastly General divisive because Attorney advice, Secretary role of gov’t for the new views on the made the final decision nation then of State
 Alexander Hamilton n Hamilton believed a strong central gov’t was best for America: –He wanted the U. S. to grow as an industrial power with less dependency on Europe –He wanted the U. S. economy to mirror the English economy As Sec of Treasury, Hamilton shaped the economy of the new nation –He feared democracy would lead to anarchy; power should be in hands of wealthy citizens
Alexander Hamilton n Hamilton believed a strong central gov’t was best for America: –He wanted the U. S. to grow as an industrial power with less dependency on Europe –He wanted the U. S. economy to mirror the English economy As Sec of Treasury, Hamilton shaped the economy of the new nation –He feared democracy would lead to anarchy; power should be in hands of wealthy citizens
 Thomas Jefferson n Jefferson believed that a limited gov’t would preserve liberty: –He saw the U. S. as an agrarian nation with active foreign trade to buy manufactured goods –He trusted the common people over the elitist aristocracy –He favored close ties with France, especially when the French Revolution began
Thomas Jefferson n Jefferson believed that a limited gov’t would preserve liberty: –He saw the U. S. as an agrarian nation with active foreign trade to buy manufactured goods –He trusted the common people over the elitist aristocracy –He favored close ties with France, especially when the French Revolution began

 Hamilton’s Economic Plan for America
Hamilton’s Economic Plan for America
 $54 million in $25 Plan Hamilton's Economic million in national debt state debts n By 1789, one of America’s biggest challenges was its huge debt n Hamilton’s Report on Public Credit (1790) proposed: –“Funding” the national debt –“Assumption" of state debts –Creating a national bank –Gov’t aid to manufacturing
$54 million in $25 Plan Hamilton's Economic million in national debt state debts n By 1789, one of America’s biggest challenges was its huge debt n Hamilton’s Report on Public Credit (1790) proposed: –“Funding” the national debt –“Assumption" of state debts –Creating a national bank –Gov’t aid to manufacturing
 And Fundingtax on. Assumption an excise and distilled liquors (whiskey) n Funding: Congress to redeem U. S. Funding Was initially defeated but salvaged certificates of debt at face value to when northern VA was proposed as prove tocite for new U. S. capital the foreign investors that In 1790, Washington signed into U. S. would repayproposals on its debts law Hamilton’s n Assumption: &Foreign investment Assumption Federal government funding assumption would purchase states' debts to poured into the U. S. gain a better interest rate & create Was unsuccessfully opposed a “national” problem rather because most certificates were than currently held by problems individual statespeculators
And Fundingtax on. Assumption an excise and distilled liquors (whiskey) n Funding: Congress to redeem U. S. Funding Was initially defeated but salvaged certificates of debt at face value to when northern VA was proposed as prove tocite for new U. S. capital the foreign investors that In 1790, Washington signed into U. S. would repayproposals on its debts law Hamilton’s n Assumption: &Foreign investment Assumption Federal government funding assumption would purchase states' debts to poured into the U. S. gain a better interest rate & create Was unsuccessfully opposed a “national” problem rather because most certificates were than currently held by problems individual statespeculators
 The Bank Controversy n Hamilton proposed the creation of a National Bank that would be privately owned, but federally chartered to regulate finance This type of interpretation of the n Madison & Jefferson opposed the Constitution is called “strict construction” Bank of the U. S. (BUS) because: –It appeared to favor the rich –Its creation was not mentioned in the Constitution
The Bank Controversy n Hamilton proposed the creation of a National Bank that would be privately owned, but federally chartered to regulate finance This type of interpretation of the n Madison & Jefferson opposed the Constitution is called “strict construction” Bank of the U. S. (BUS) because: –It appeared to favor the rich –Its creation was not mentioned in the Constitution
 The Bank Controversy n Hamilton defended creating a BUS under Article 1, section 8: –The Necessary & Proper Clause gave Congress “implied powers” to interpret the Constitution –This “Elastic Clause” allowed Hamilton to make a successful “loose construction” argument –Congress chartered the Bank of the United States in 1791
The Bank Controversy n Hamilton defended creating a BUS under Article 1, section 8: –The Necessary & Proper Clause gave Congress “implied powers” to interpret the Constitution –This “Elastic Clause” allowed Hamilton to make a successful “loose construction” argument –Congress chartered the Bank of the United States in 1791
 Promoting Manufacturing n Report on Manufacturing sought to boost manufacturing & reduce U. S. dependency on Europe n Opposition to Hamilton’s plan: –Madison feared strengthening the federal gov’t would destroy state sovereignty –Jefferson feared that the rise of cities would destroy agriculture & agrarian civic virtue n This plan was soundly defeated
Promoting Manufacturing n Report on Manufacturing sought to boost manufacturing & reduce U. S. dependency on Europe n Opposition to Hamilton’s plan: –Madison feared strengthening the federal gov’t would destroy state sovereignty –Jefferson feared that the rise of cities would destroy agriculture & agrarian civic virtue n This plan was soundly defeated
 Foreign Affairs
Foreign Affairs
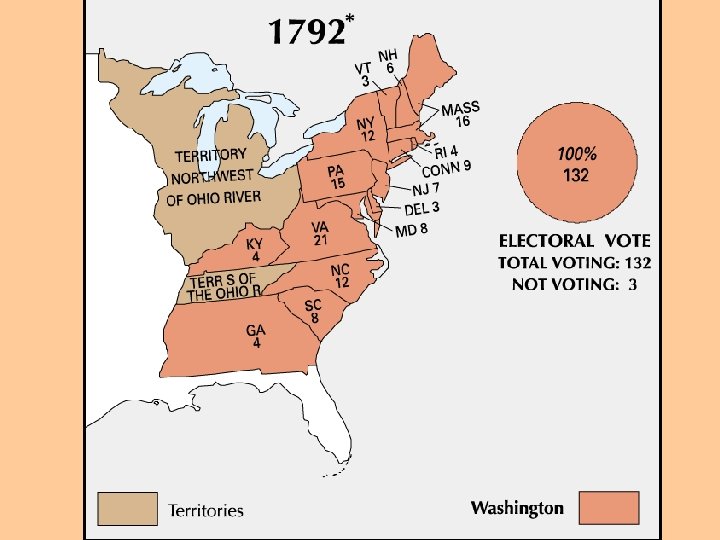
 The engulfed in the French Affairs France was. Battle over Foreign. Revolution; The U. S. supported the revolution, but feared n In the radical election, nature its 1792 & bloody Washington was unanimously chosen again U. S. neutrality seemed to be the best option n Foreign policy became the focus of Washington’s 2 nd term: –War between England & France broke out in 1793 which divided Americans over who to support –England refused to obey the Treaty of Paris (1783) & barred the U. S. from West Indian trade
The engulfed in the French Affairs France was. Battle over Foreign. Revolution; The U. S. supported the revolution, but feared n In the radical election, nature its 1792 & bloody Washington was unanimously chosen again U. S. neutrality seemed to be the best option n Foreign policy became the focus of Washington’s 2 nd term: –War between England & France broke out in 1793 which divided Americans over who to support –England refused to obey the Treaty of Paris (1783) & barred the U. S. from West Indian trade
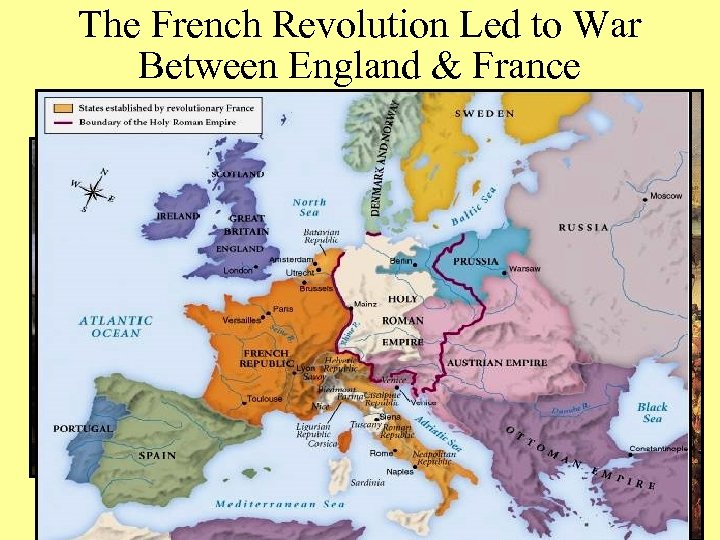 The French Revolution Led to War Between England & France
The French Revolution Led to War Between England & France
 Americans seemed to favor. Neutrality to France due The Peril of. American Rev French assistance in the n Hamilton & Jefferson wanted neutrality but disagreed how: –Jefferson: punish England (due Jefferson to impressment) by cutting off impressment trade & reward France –Hamilton: England needed to be Hamilton appeased, not coerced n. At least until the Genet Affair: French Washington signed Proclamation diplomat Edmond Genet challenged of Neutrality (1793) to keep American neutrality repeatedly in public America out of foreign wars
Americans seemed to favor. Neutrality to France due The Peril of. American Rev French assistance in the n Hamilton & Jefferson wanted neutrality but disagreed how: –Jefferson: punish England (due Jefferson to impressment) by cutting off impressment trade & reward France –Hamilton: England needed to be Hamilton appeased, not coerced n. At least until the Genet Affair: French Washington signed Proclamation diplomat Edmond Genet challenged of Neutrality (1793) to keep American neutrality repeatedly in public America out of foreign wars
 The treaty avoided war with England but did Jay's Treaty with England not get the British to pay Southerners for lost n John Jay demanded from England slaves or merchants for impressed ships –The removal of British soldiers Jay was hung in The House challenged the from western forts in America effigy throughout Senate’s Constitutional America authority to ratify the treaty –payment for impressed ships –acceptance of U. S. neutrality n Jay’s Treaty (1794) –British vacated western forts –U. S. gained trade in West Indies –But, England did not recognize neutrality or end impressment
The treaty avoided war with England but did Jay's Treaty with England not get the British to pay Southerners for lost n John Jay demanded from England slaves or merchants for impressed ships –The removal of British soldiers Jay was hung in The House challenged the from western forts in America effigy throughout Senate’s Constitutional America authority to ratify the treaty –payment for impressed ships –acceptance of U. S. neutrality n Jay’s Treaty (1794) –British vacated western forts –U. S. gained trade in West Indies –But, England did not recognize neutrality or end impressment
 Pinckney’s Treaty with Spain n Prior to 1795, Spain closed U. S. access to the Mississippi River & encouraged Indian attacks n But, Spain interpreted Jay's Treaty as Anglo-American alliance against Spain & signed the Treaty of San Lorenzo (Pinckney’s Treaty): –Spain reopened the Mississippi –Settled the disputed border between Florida & U. S.
Pinckney’s Treaty with Spain n Prior to 1795, Spain closed U. S. access to the Mississippi River & encouraged Indian attacks n But, Spain interpreted Jay's Treaty as Anglo-American alliance against Spain & signed the Treaty of San Lorenzo (Pinckney’s Treaty): –Spain reopened the Mississippi –Settled the disputed border between Florida & U. S.
 Treaty of Greenville with Indians n To end Indian attacks against white settlers in the West, the U. S. fought an Ohio Indian alliance led by the Shawnee. Georgia, Kentucky, Settlers rushed to at Battle of Fallen Tennessee, Ohio, Timbers (1794)& western New York n Led to the Treaty of Greenville: Greenville –Indians ceded lands in Ohio –The U. S. promised “fair” dealings with Indian nations
Treaty of Greenville with Indians n To end Indian attacks against white settlers in the West, the U. S. fought an Ohio Indian alliance led by the Shawnee. Georgia, Kentucky, Settlers rushed to at Battle of Fallen Tennessee, Ohio, Timbers (1794)& western New York n Led to the Treaty of Greenville: Greenville –Indians ceded lands in Ohio –The U. S. promised “fair” dealings with Indian nations
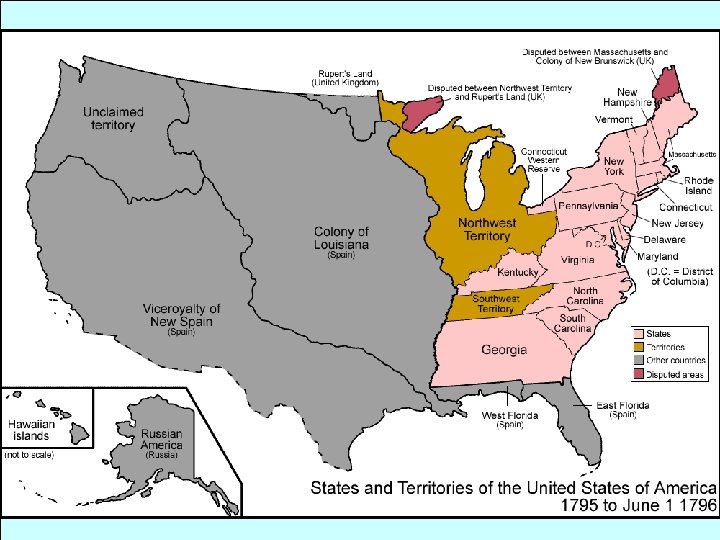
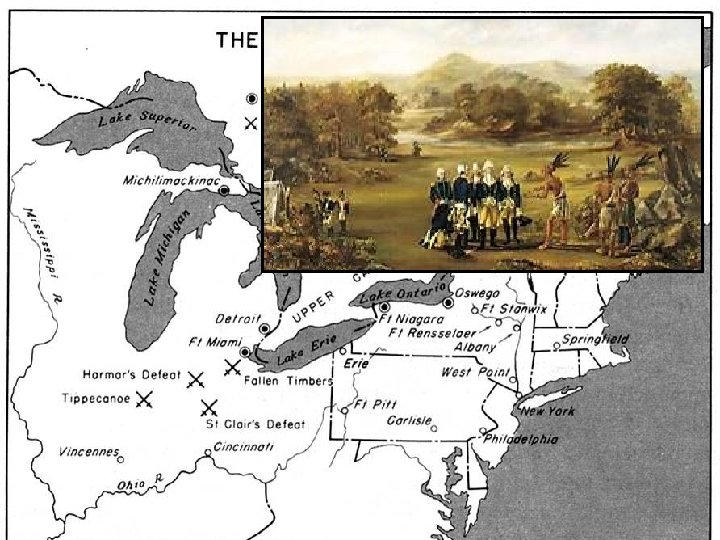 Conquest of the West (Notice the British forts in the West!)
Conquest of the West (Notice the British forts in the West!)
 America’s First Political Parties
America’s First Political Parties
 st Political Parties Represented the “Spirit of 1776” Also called Jeffersonian Republicans America’s 1 & thesimply, Republicans or fight against tyranny n Disagreements over Hamilton’s Represented the “Spirit of 1787” & financial plans & Anglo-French the fight for a the 1 st political gov’t stronger national parties: Wars led to –Democratic-Republicans: Democratic-Republicans led by Jefferson, favored states’ rights, “strict construction, ” ties to France, & liberty –Federalists: led by Hamilton, favored a strong national gov’t, “loose construction”, ties to England, & public order
st Political Parties Represented the “Spirit of 1776” Also called Jeffersonian Republicans America’s 1 & thesimply, Republicans or fight against tyranny n Disagreements over Hamilton’s Represented the “Spirit of 1787” & financial plans & Anglo-French the fight for a the 1 st political gov’t stronger national parties: Wars led to –Democratic-Republicans: Democratic-Republicans led by Jefferson, favored states’ rights, “strict construction, ” ties to France, & liberty –Federalists: led by Hamilton, favored a strong national gov’t, “loose construction”, ties to England, & public order

 America’s st 1 Political Parties n Political parties were seen as a conspiracy against liberty –Federalists & Dem-Republicans thought it was their duty to destroy the other party –In the Washington & Adams Commoners in the U. S. were highly literate eras, the Federalists dominated Newspapers transformed political culture politics, but Jefferson’s election in the U. S. ; they were widely read, highly in 1800 killed the partisan influential, & totally Federalists
America’s st 1 Political Parties n Political parties were seen as a conspiracy against liberty –Federalists & Dem-Republicans thought it was their duty to destroy the other party –In the Washington & Adams Commoners in the U. S. were highly literate eras, the Federalists dominated Newspapers transformed political culture politics, but Jefferson’s election in the U. S. ; they were widely read, highly in 1800 killed the partisan influential, & totally Federalists
 Whiskey Rebellion Hamilton interpreted Jefferson saw it as an n rebellion as a the. The whiskey tax led yeomen in to excuse by Federalists western Pennsylvania an army to Jefferson-inspired raise to start a conspiracy intimidate Republicans Whiskey Rebellion in 1794 –When the governor of PA refused to act, Federalists saw Rioted with the same fervor as the revolt as thethreat to safety those against a Stamp Act –Washington himself led the U. S. army to suppress the rebellion –Both parties used the event to attack each other
Whiskey Rebellion Hamilton interpreted Jefferson saw it as an n rebellion as a the. The whiskey tax led yeomen in to excuse by Federalists western Pennsylvania an army to Jefferson-inspired raise to start a conspiracy intimidate Republicans Whiskey Rebellion in 1794 –When the governor of PA refused to act, Federalists saw Rioted with the same fervor as the revolt as thethreat to safety those against a Stamp Act –Washington himself led the U. S. army to suppress the rebellion –Both parties used the event to attack each other
 His mere presence. Rebellion, 1794 Whiskey (and the 15, 000 soldiers he brought with him) was enough to end the Whiskey Rebellion President Washington is one of two presidents (Madison is the other) who participated in combat while serving as president
His mere presence. Rebellion, 1794 Whiskey (and the 15, 000 soldiers he brought with him) was enough to end the Whiskey Rebellion President Washington is one of two presidents (Madison is the other) who participated in combat while serving as president
 Washington's Farewell Address Washington never acknowledged the n faction in his cabinet, not tended to by the Washington was he limited side with the Federalist 2 terms, but in 1796 Constitution to perspective of gov’t he announced his decision to retire n Washington’s Farewell Address: Address Washington’s decision to retire –Warned against political parties established the precedent of 2 terms against “entangling –Warnedin office for presidents alliances” with foreign nations (led to the precedent of nonintervention in foreign affairs)
Washington's Farewell Address Washington never acknowledged the n faction in his cabinet, not tended to by the Washington was he limited side with the Federalist 2 terms, but in 1796 Constitution to perspective of gov’t he announced his decision to retire n Washington’s Farewell Address: Address Washington’s decision to retire –Warned against political parties established the precedent of 2 terms against “entangling –Warnedin office for presidents alliances” with foreign nations (led to the precedent of nonintervention in foreign affairs)
 Discussion Question: n George Washington is universally agreed to be the most significant of America’s Founding Fathers… n But, who is the 2 nd most important of these early political leaders: – James Madison? – Alexander Hamilton? – Thomas Jefferson? – Someone else? n Make an argument for each & then rank order them with a clear justification for your #1 choice
Discussion Question: n George Washington is universally agreed to be the most significant of America’s Founding Fathers… n But, who is the 2 nd most important of these early political leaders: – James Madison? – Alexander Hamilton? – Thomas Jefferson? – Someone else? n Make an argument for each & then rank order them with a clear justification for your #1 choice


