8df8b8b69c541657c49c73ef27ad4031.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Myers’ PSYCHOLOGY (7 th Ed) Chapter 11 Intelligence James A. Mc. Cubbin, Ph. D Clemson University Worth Publishers 1
Myers’ PSYCHOLOGY (7 th Ed) Chapter 11 Intelligence James A. Mc. Cubbin, Ph. D Clemson University Worth Publishers 1
 Origins of Intelligence Assessments/Inventories (“Testing”) § Plato: Saw & noted individual differences § Intelligence Test: *Binet (1905 +-) § method of assessing an individual’s mental aptitudes & comparing them to those of others, using numerical scores § Testing Paris school kids to ID those who were low & needed help 2
Origins of Intelligence Assessments/Inventories (“Testing”) § Plato: Saw & noted individual differences § Intelligence Test: *Binet (1905 +-) § method of assessing an individual’s mental aptitudes & comparing them to those of others, using numerical scores § Testing Paris school kids to ID those who were low & needed help 2
 § Mental Age § measure of intelligence test performance devised by Alfred Binet, Paris, late 1800’s § Why? to ID slower kids in Paris school system to help them do better § chronological age: actual age § mental age: if a child does as well as the average 8 -year-old is said to have a of 8 § Stanford-Binet: widely used American revision of Binet’s original intelligence test (1914 -15) § revised by Terman at Stanford University § Stern designed the intelligence quotient (IQ) 3
§ Mental Age § measure of intelligence test performance devised by Alfred Binet, Paris, late 1800’s § Why? to ID slower kids in Paris school system to help them do better § chronological age: actual age § mental age: if a child does as well as the average 8 -year-old is said to have a of 8 § Stanford-Binet: widely used American revision of Binet’s original intelligence test (1914 -15) § revised by Terman at Stanford University § Stern designed the intelligence quotient (IQ) 3
 § Intelligence Quotient (IQ) § Originally, ratio of mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca) multiplied by 100 § IQ = ma ÷ ca x 100 (ma/ca x 100) § on contemporary tests, the avg performance for a specific age is assigned a score of 100 § Most intellg. tests (including the Stanford-Binet) no longer compute an “IQ” score (reification: p. 422) § What IS Intelligence? § ability to learn from experience, solve problems, & use knowledge to adapt to new situations § Is determined by a social definition & varies from culture to culture, era to era 4
§ Intelligence Quotient (IQ) § Originally, ratio of mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca) multiplied by 100 § IQ = ma ÷ ca x 100 (ma/ca x 100) § on contemporary tests, the avg performance for a specific age is assigned a score of 100 § Most intellg. tests (including the Stanford-Binet) no longer compute an “IQ” score (reification: p. 422) § What IS Intelligence? § ability to learn from experience, solve problems, & use knowledge to adapt to new situations § Is determined by a social definition & varies from culture to culture, era to era 4
 What is Intelligence? § Factor Analysis § statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test § ID’s different performance dimensions that underlie our total score § These factors indicate a basic ability level § Eugenics: Terman & others belief that genetics was the predominate factor in IQ --was a “scientific” sort of racism…no major basis in modern psych…Basically said some races, etc. , were genetically better than others. Who used these ideas? 5
What is Intelligence? § Factor Analysis § statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test § ID’s different performance dimensions that underlie our total score § These factors indicate a basic ability level § Eugenics: Terman & others belief that genetics was the predominate factor in IQ --was a “scientific” sort of racism…no major basis in modern psych…Basically said some races, etc. , were genetically better than others. Who used these ideas? 5
 Spearman’s G Factor: § Spearman’s General Intelligence (g factor) § Spearman & others said one single factor (a general factor) underlies specific mental abilities § This factor is measured by every task on an intelligence test § g = general 6
Spearman’s G Factor: § Spearman’s General Intelligence (g factor) § Spearman & others said one single factor (a general factor) underlies specific mental abilities § This factor is measured by every task on an intelligence test § g = general 6
 Most commonly administered intelligence assessments: Ø WISC-IV: most commonly used IQ test for ages 6 -16 Ø WAIS -III is for adults. Ø WIPPSI-III is for preschoolers. Ø Others also use the Stanford-Binet, 5 th edition, or the Kaufman ABC-II battery for children. NOTE: Roman numerals reflect the multiple revisions of the tests since 7 their original versions.
Most commonly administered intelligence assessments: Ø WISC-IV: most commonly used IQ test for ages 6 -16 Ø WAIS -III is for adults. Ø WIPPSI-III is for preschoolers. Ø Others also use the Stanford-Binet, 5 th edition, or the Kaufman ABC-II battery for children. NOTE: Roman numerals reflect the multiple revisions of the tests since 7 their original versions.
 Are There Multiple Intelligences? § Savant Syndrome § condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill… --often (NOT always. . ) related to autism § Computation § Drawing (EX below) § Social Intelligence § the know-how involved in comprehending social situations & managing oneself successfully § Emotional Intelligence p. 426 § ability to perceive, express, understand, & regulate emotions 8
Are There Multiple Intelligences? § Savant Syndrome § condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill… --often (NOT always. . ) related to autism § Computation § Drawing (EX below) § Social Intelligence § the know-how involved in comprehending social situations & managing oneself successfully § Emotional Intelligence p. 426 § ability to perceive, express, understand, & regulate emotions 8
 Intelligence & Creativity § Creativity: the ability to produce novel and valuable ideas… § Those = creative usually have at least avg. or above avg. g factor § Things that make this possible: § Expertise (have knowledge base) § imaginative thinking skills (outside the box) § venturesome personality (take chances) § intrinsic motivation § creative environment 9
Intelligence & Creativity § Creativity: the ability to produce novel and valuable ideas… § Those = creative usually have at least avg. or above avg. g factor § Things that make this possible: § Expertise (have knowledge base) § imaginative thinking skills (outside the box) § venturesome personality (take chances) § intrinsic motivation § creative environment 9
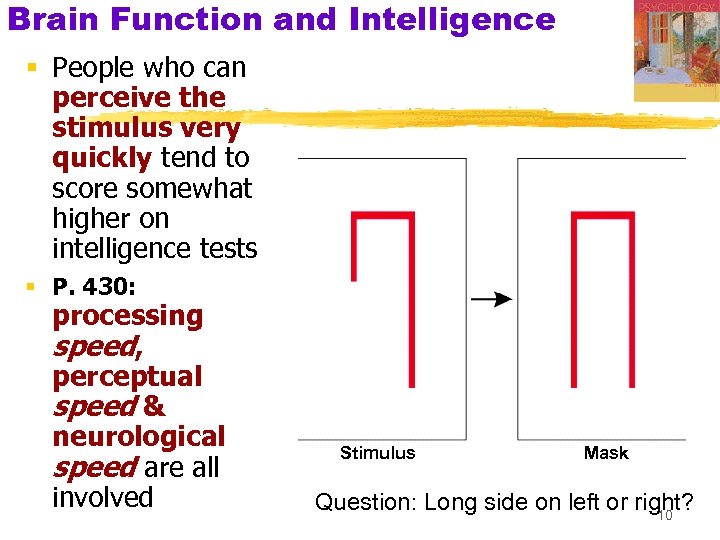 Brain Function and Intelligence § People who can perceive the stimulus very quickly tend to score somewhat higher on intelligence tests § P. 430: processing speed, perceptual speed & neurological speed are all involved Stimulus Mask Question: Long side on left or right? 10
Brain Function and Intelligence § People who can perceive the stimulus very quickly tend to score somewhat higher on intelligence tests § P. 430: processing speed, perceptual speed & neurological speed are all involved Stimulus Mask Question: Long side on left or right? 10
 Assessing (“Testing”!!) Intelligence § Aptitude Test: designed to predict a person’s future performance § looks at abilities…what you should be able to do § aptitude is the capacity to learn § Achievement Test § test designed to assess what person has learned § Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) § most widely used intelligence test (WWI) § 2 subtests 1) verbal 2) performance (nonverbal) § WAIS-R = revised adult test; § WISC-R = revised kids’ test 11
Assessing (“Testing”!!) Intelligence § Aptitude Test: designed to predict a person’s future performance § looks at abilities…what you should be able to do § aptitude is the capacity to learn § Achievement Test § test designed to assess what person has learned § Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) § most widely used intelligence test (WWI) § 2 subtests 1) verbal 2) performance (nonverbal) § WAIS-R = revised adult test; § WISC-R = revised kids’ test 11
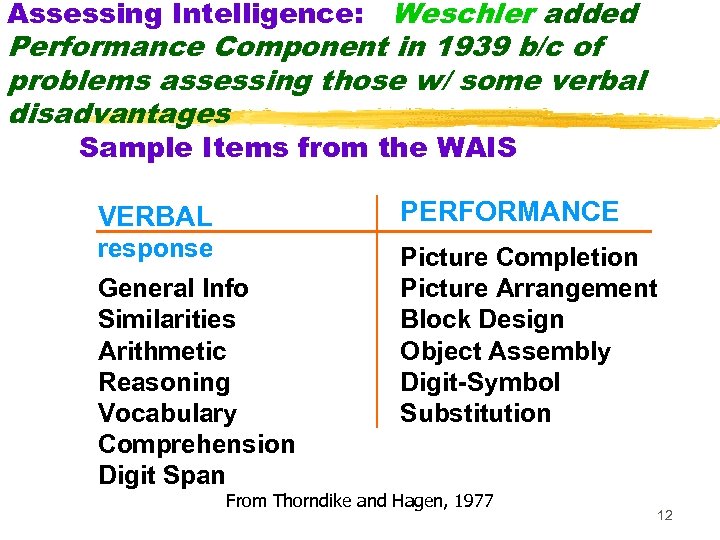 Weschler added Performance Component in 1939 b/c of problems assessing those w/ some verbal disadvantages Assessing Intelligence: Sample Items from the WAIS VERBAL PERFORMANCE response Picture Completion Picture Arrangement Block Design Object Assembly Digit-Symbol Substitution General Info Similarities Arithmetic Reasoning Vocabulary Comprehension Digit Span From Thorndike and Hagen, 1977 12
Weschler added Performance Component in 1939 b/c of problems assessing those w/ some verbal disadvantages Assessing Intelligence: Sample Items from the WAIS VERBAL PERFORMANCE response Picture Completion Picture Arrangement Block Design Object Assembly Digit-Symbol Substitution General Info Similarities Arithmetic Reasoning Vocabulary Comprehension Digit Span From Thorndike and Hagen, 1977 12
 WAIS-R EX’s: Visual Analogies…. . block design…. . pic sequencing…. . WAIS-R performance assessment kit 13
WAIS-R EX’s: Visual Analogies…. . block design…. . pic sequencing…. . WAIS-R performance assessment kit 13
 14
14
 Assessing Intelligence § Standardization § defining meaningful scores by comparison w/ the performance of a pre-tested standardization group to create a norm Normal Curve § symmetrical bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical & psych. attributes § most scores fall near the avg, & fewer scores lie near the extremes 15
Assessing Intelligence § Standardization § defining meaningful scores by comparison w/ the performance of a pre-tested standardization group to create a norm Normal Curve § symmetrical bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical & psych. attributes § most scores fall near the avg, & fewer scores lie near the extremes 15
 Study sessions for MARCH Sat. March 24 12: 00 – 1 : 30 AP Psy 1. 5 Thurs. March 29 3: 45 – 5 : 00 AP Psy 1. 5 Sun. April 1 2 : 00 – 4 : 00 AP Psy 2. 0 Wed. April 4 5: 30 – 7 : 00 AP Psy 1. 5 Sat. Apr. 7 11: 30 – 1: 30 AP Psy 2. 0 Sat. Apr. 14 1: 30 – 3: 30 (after ACT) AP Psy 2. 0 16
Study sessions for MARCH Sat. March 24 12: 00 – 1 : 30 AP Psy 1. 5 Thurs. March 29 3: 45 – 5 : 00 AP Psy 1. 5 Sun. April 1 2 : 00 – 4 : 00 AP Psy 2. 0 Wed. April 4 5: 30 – 7 : 00 AP Psy 1. 5 Sat. Apr. 7 11: 30 – 1: 30 AP Psy 2. 0 Sat. Apr. 14 1: 30 – 3: 30 (after ACT) AP Psy 2. 0 16
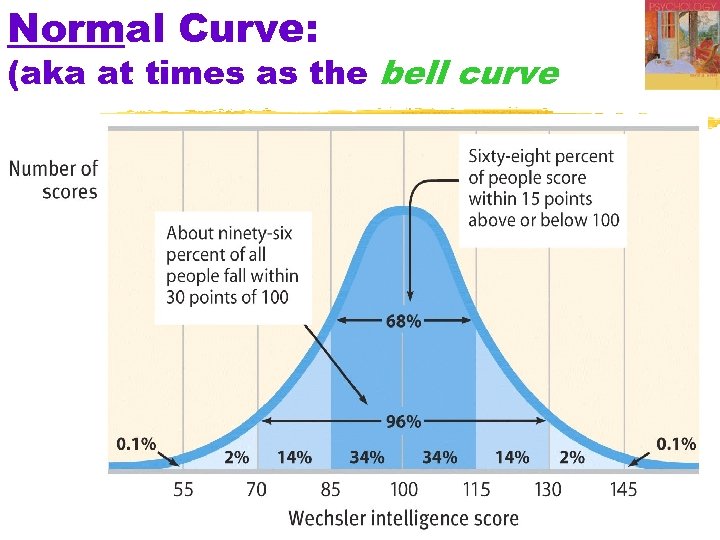 Normal Curve: (aka at times as the bell curve 17
Normal Curve: (aka at times as the bell curve 17
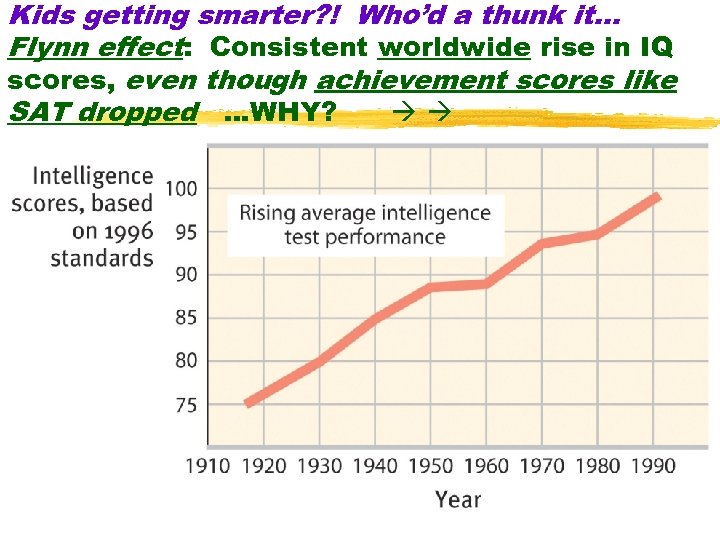 Kids getting smarter? ! Who’d a thunk it… Flynn effect: Consistent worldwide rise in IQ scores, even though achievement scores like SAT dropped …WHY? 18
Kids getting smarter? ! Who’d a thunk it… Flynn effect: Consistent worldwide rise in IQ scores, even though achievement scores like SAT dropped …WHY? 18
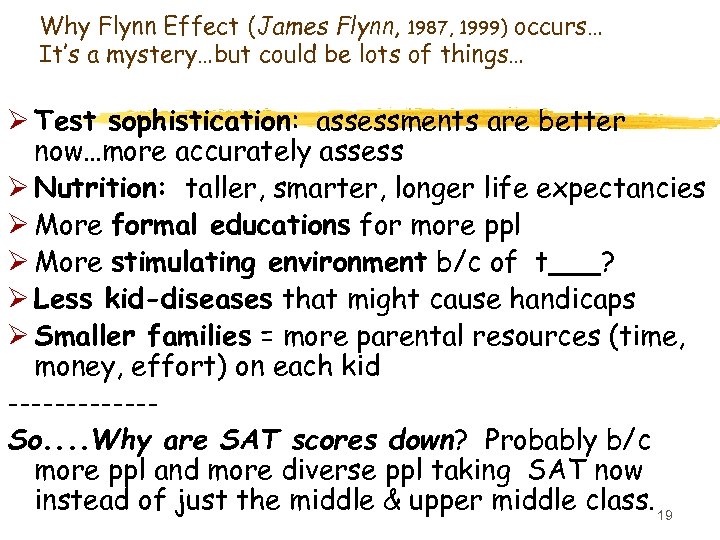 Why Flynn Effect (James Flynn, 1987, 1999) occurs… It’s a mystery…but could be lots of things… Ø Test sophistication: assessments are better now…more accurately assess Ø Nutrition: taller, smarter, longer life expectancies Ø More formal educations for more ppl Ø More stimulating environment b/c of t___? Ø Less kid-diseases that might cause handicaps Ø Smaller families = more parental resources (time, money, effort) on each kid ------So. . Why are SAT scores down? Probably b/c more ppl and more diverse ppl taking SAT now instead of just the middle & upper middle class. 19
Why Flynn Effect (James Flynn, 1987, 1999) occurs… It’s a mystery…but could be lots of things… Ø Test sophistication: assessments are better now…more accurately assess Ø Nutrition: taller, smarter, longer life expectancies Ø More formal educations for more ppl Ø More stimulating environment b/c of t___? Ø Less kid-diseases that might cause handicaps Ø Smaller families = more parental resources (time, money, effort) on each kid ------So. . Why are SAT scores down? Probably b/c more ppl and more diverse ppl taking SAT now instead of just the middle & upper middle class. 19
 Assessments of Intelligence (aka Testing) Reliability & Validity § Reliability: extent to which a test yields consistent results assessed by consistency of scores in 3 ways: § two halves of the test § alternate forms of the test § retesting § Validity: How well a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to EX: Does SAT predict success in the 1 st year of college? 3 aspects to validity… Content validity Predictive validity Criterion validity 20
Assessments of Intelligence (aka Testing) Reliability & Validity § Reliability: extent to which a test yields consistent results assessed by consistency of scores in 3 ways: § two halves of the test § alternate forms of the test § retesting § Validity: How well a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to EX: Does SAT predict success in the 1 st year of college? 3 aspects to validity… Content validity Predictive validity Criterion validity 20
 Assessing Intelligence: 3 major considerations: 1. Content Validity: extent to which a test samples a behavior that is of interest EX: Driving test that samples driving tasks… DOES it evaluate the content you want to look at? 2. Criterion validity § Some behavior that a test is designed to predict EX: Are college grades being predicted by SAT performance? …or. . . In driving, do 3 pt. turns, parking, handling the car in tight spaces, etc. , represent things you will need to do while driving? § the measure (part of the operational definition) used in defining whether the test does have predictive validity § Criterion is what they are shooting for, trying to 21 do
Assessing Intelligence: 3 major considerations: 1. Content Validity: extent to which a test samples a behavior that is of interest EX: Driving test that samples driving tasks… DOES it evaluate the content you want to look at? 2. Criterion validity § Some behavior that a test is designed to predict EX: Are college grades being predicted by SAT performance? …or. . . In driving, do 3 pt. turns, parking, handling the car in tight spaces, etc. , represent things you will need to do while driving? § the measure (part of the operational definition) used in defining whether the test does have predictive validity § Criterion is what they are shooting for, trying to 21 do
 3. Predictive Validity § success w/ which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict § assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior (behav. you’re interested in) § aka criterion-related validity § This is whether it can give good predictions RE: the behavior looked at… or not EX: DOES the SAT predict success in college? Generally, yes. BUT…GRE (graduate record exam)…not as much b/c all are higher performing… 22
3. Predictive Validity § success w/ which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict § assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior (behav. you’re interested in) § aka criterion-related validity § This is whether it can give good predictions RE: the behavior looked at… or not EX: DOES the SAT predict success in college? Generally, yes. BUT…GRE (graduate record exam)…not as much b/c all are higher performing… 22
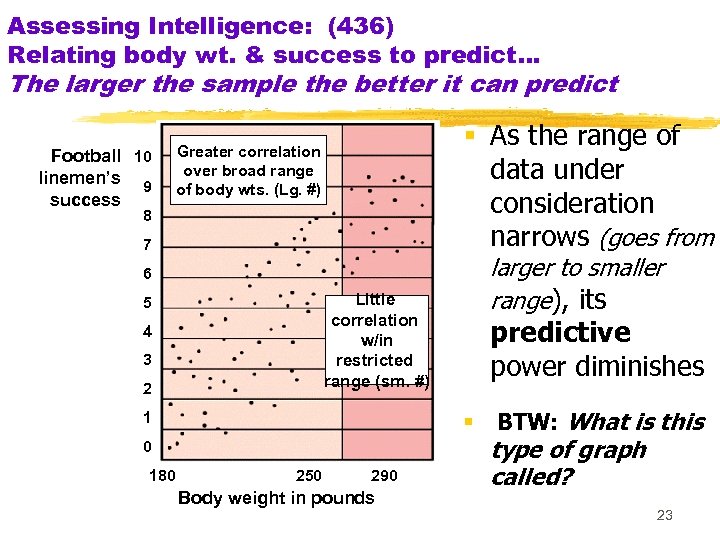 Assessing Intelligence: (436) Relating body wt. & success to predict… The larger the sample the better it can predict Football 10 linemen’s 9 success § As the range of data under consideration narrows (goes from Greater correlation over broad range of body wts. (Lg. #) 8 7 6 Little correlation w/in restricted range (sm. #) 5 4 3 2 1 0 180 250 290 Body weight in pounds larger to smaller range), its predictive power diminishes § BTW: What is this type of graph called? 23
Assessing Intelligence: (436) Relating body wt. & success to predict… The larger the sample the better it can predict Football 10 linemen’s 9 success § As the range of data under consideration narrows (goes from Greater correlation over broad range of body wts. (Lg. #) 8 7 6 Little correlation w/in restricted range (sm. #) 5 4 3 2 1 0 180 250 290 Body weight in pounds larger to smaller range), its predictive power diminishes § BTW: What is this type of graph called? 23
 The Dynamics of Intelligence: The Low extreme of Intelligence: § Mental Challenged (formerly retardation) § a condition of limited mental ability § indicated by an intelligence score below 70 § produces difficulty in adapting to the demands of life § varies from mild to profound § Down Syndrome § retardation and associated physical disorders caused by an extra chromosome in one’s genetic makeup…mom’s age… 24
The Dynamics of Intelligence: The Low extreme of Intelligence: § Mental Challenged (formerly retardation) § a condition of limited mental ability § indicated by an intelligence score below 70 § produces difficulty in adapting to the demands of life § varies from mild to profound § Down Syndrome § retardation and associated physical disorders caused by an extra chromosome in one’s genetic makeup…mom’s age… 24
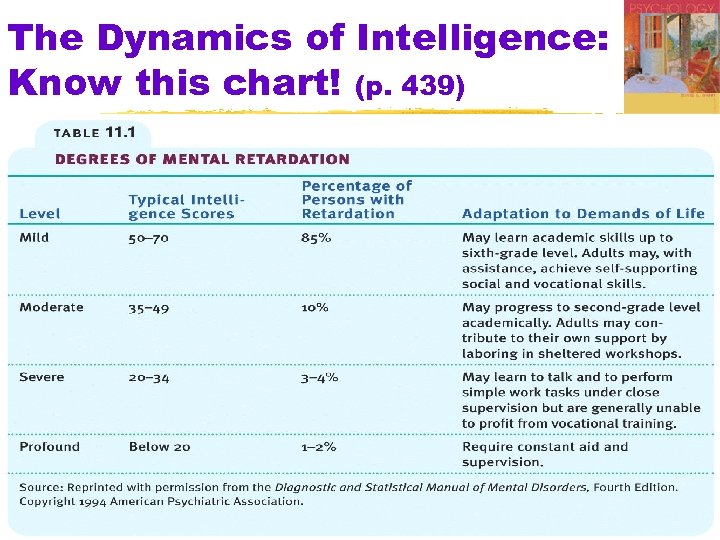 The Dynamics of Intelligence: Know this chart! (p. 439) 25
The Dynamics of Intelligence: Know this chart! (p. 439) 25
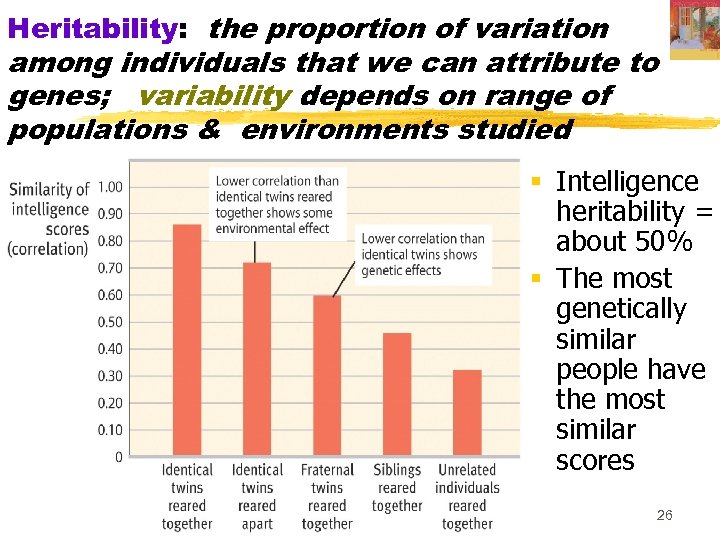 Heritability: the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes; variability depends on range of populations & environments studied § Intelligence heritability = about 50% § The most genetically similar people have the most similar scores 26
Heritability: the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes; variability depends on range of populations & environments studied § Intelligence heritability = about 50% § The most genetically similar people have the most similar scores 26
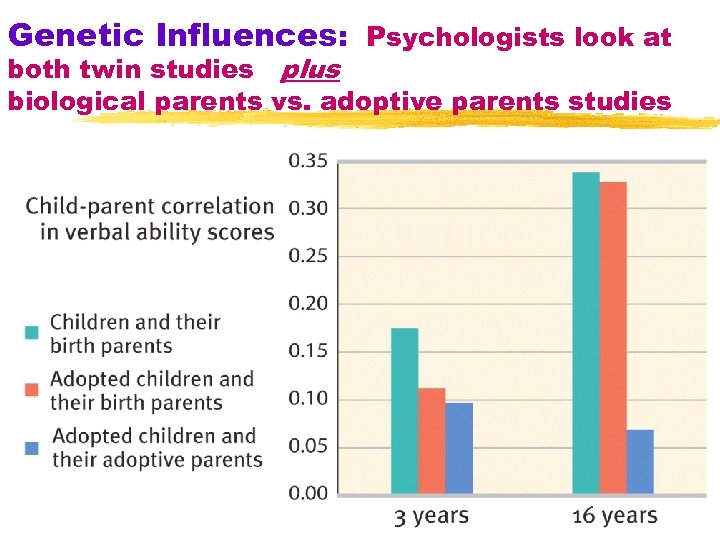 Genetic Influences: Psychologists look at both twin studies plus biological parents vs. adoptive parents studies 27
Genetic Influences: Psychologists look at both twin studies plus biological parents vs. adoptive parents studies 27
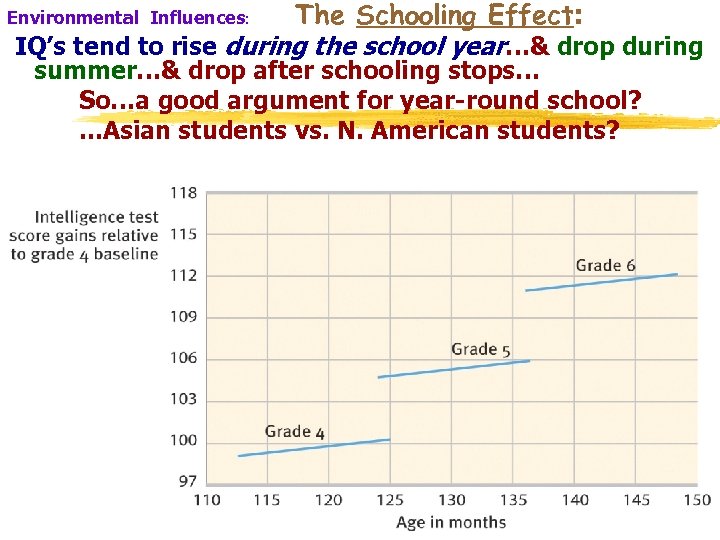 The Schooling Effect: IQ’s tend to rise during the school year…& drop during Environmental Influences: summer…& drop after schooling stops… So…a good argument for year-round school? . . . Asian students vs. N. American students? 28
The Schooling Effect: IQ’s tend to rise during the school year…& drop during Environmental Influences: summer…& drop after schooling stops… So…a good argument for year-round school? . . . Asian students vs. N. American students? 28
 What’s wrong with this picture? ? ? 29
What’s wrong with this picture? ? ? 29
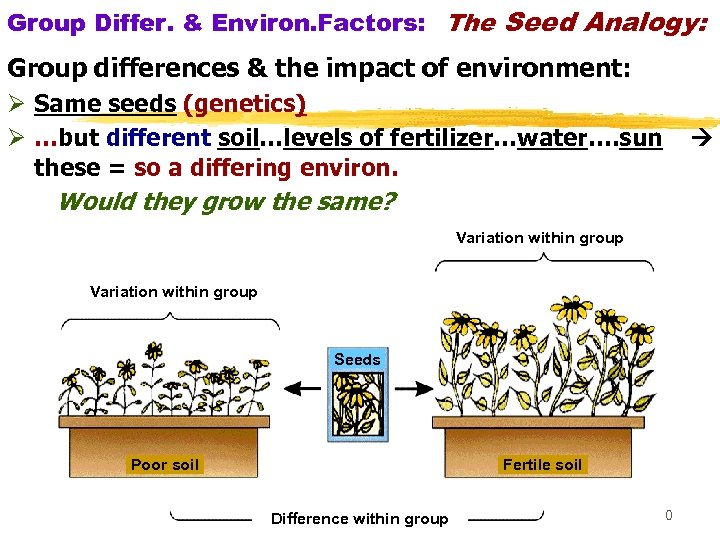 Group Differ. & Environ. Factors: The Seed Analogy: Group differences & the impact of environment: Ø Same seeds (genetics) Ø …but different soil…levels of fertilizer…water…. sun these = so a differing environ. Would they grow the same? Variation within group Seeds Poor soil Fertile soil Difference within group 30
Group Differ. & Environ. Factors: The Seed Analogy: Group differences & the impact of environment: Ø Same seeds (genetics) Ø …but different soil…levels of fertilizer…water…. sun these = so a differing environ. Would they grow the same? Variation within group Seeds Poor soil Fertile soil Difference within group 30
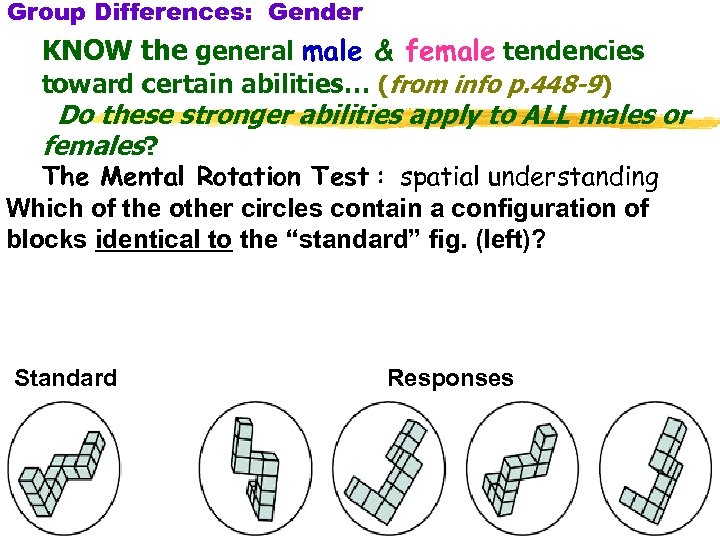 Group Differences: Gender KNOW the general male & female tendencies toward certain abilities… (from info p. 448 -9) Do these stronger abilities apply to ALL males or females? The Mental Rotation Test : spatial understanding Which of the other circles contain a configuration of blocks identical to the “standard” fig. (left)? Standard Responses 31
Group Differences: Gender KNOW the general male & female tendencies toward certain abilities… (from info p. 448 -9) Do these stronger abilities apply to ALL males or females? The Mental Rotation Test : spatial understanding Which of the other circles contain a configuration of blocks identical to the “standard” fig. (left)? Standard Responses 31
 Stereotype Threat § Self-confirming concern/belief: negative stereotypes give us “true” evaluation § Relates to “self-fulfilling prophecy” & placebo effect: believing something IS true increase chance it happens: “I will probably score low” = scoring lower Students told they are at a disadvantage on a test tend to do worse than those who are told the test should be one they do well on… EX’s: “You are not likely to do as well on this as usual…” …OR “You should do very well on this b/c it is written in a way that will show your strengths…” Also Afri. -Amer. or females taking test w/ only that group perform better than in mixed groups Summary: What you think & believe about YOU affect how you 32 perform!
Stereotype Threat § Self-confirming concern/belief: negative stereotypes give us “true” evaluation § Relates to “self-fulfilling prophecy” & placebo effect: believing something IS true increase chance it happens: “I will probably score low” = scoring lower Students told they are at a disadvantage on a test tend to do worse than those who are told the test should be one they do well on… EX’s: “You are not likely to do as well on this as usual…” …OR “You should do very well on this b/c it is written in a way that will show your strengths…” Also Afri. -Amer. or females taking test w/ only that group perform better than in mixed groups Summary: What you think & believe about YOU affect how you 32 perform!
 High vs. low extremes of intelligence: Ø Myth: High IQ kids are mal-adjusted, weird, socially inept…. this is NOT TRUE -There is a high correlation for high IQ & healthy, well-adjusted, academically successful adults… Most thrive, though some are isolated more as kids b/c they don’t fit in w/ immature other kids Ø Remember: “giftedness” is a socially defined trait & not a “naturally occurring trait” like eye color or height (what is this called? ) Ø Brain size (relative to body size) IS slightly positively correlated to intelligence 33
High vs. low extremes of intelligence: Ø Myth: High IQ kids are mal-adjusted, weird, socially inept…. this is NOT TRUE -There is a high correlation for high IQ & healthy, well-adjusted, academically successful adults… Most thrive, though some are isolated more as kids b/c they don’t fit in w/ immature other kids Ø Remember: “giftedness” is a socially defined trait & not a “naturally occurring trait” like eye color or height (what is this called? ) Ø Brain size (relative to body size) IS slightly positively correlated to intelligence 33
 Big debate: tracking (segregating by ability level): Ø Often = low income & minority put into low levels, which encourages the stereotype threat… which. . . tends to widen, not shrink, the gap betwn. lo & hi especially in elementary school Best idea may be, like China & Japan: Avoid tracking thru elementary 34
Big debate: tracking (segregating by ability level): Ø Often = low income & minority put into low levels, which encourages the stereotype threat… which. . . tends to widen, not shrink, the gap betwn. lo & hi especially in elementary school Best idea may be, like China & Japan: Avoid tracking thru elementary 34
 Theories of Multiple Intelligences (pp. 424 -426) Is there 1 kind? …or 2? …or 3? . . or 8? Spearman: 1 basic general intel. (g factor) Gardner: said there are 8: -verbal -movement (kinesthetic) -math -understanding ourselves (emot. ) -music -understanding others (emot. ) -spatial analysis/visual -understanding our physical (art) environment (“street smarts”) Sternberg’s Big 3: -analytical: academic problem solving— 1 right answer -creative intell. : react to novel situations & use novel ideas -practical intel. : deal w/ everyday problems, come up w/ multiple solutions 35
Theories of Multiple Intelligences (pp. 424 -426) Is there 1 kind? …or 2? …or 3? . . or 8? Spearman: 1 basic general intel. (g factor) Gardner: said there are 8: -verbal -movement (kinesthetic) -math -understanding ourselves (emot. ) -music -understanding others (emot. ) -spatial analysis/visual -understanding our physical (art) environment (“street smarts”) Sternberg’s Big 3: -analytical: academic problem solving— 1 right answer -creative intell. : react to novel situations & use novel ideas -practical intel. : deal w/ everyday problems, come up w/ multiple solutions 35
 “Hey, I don’t have time to exercise!!” 36
“Hey, I don’t have time to exercise!!” 36
 Some review ? ’s How does head size correlate with intelligence? (p. 429) Can you assess an infant’s possible intelligence? 37
Some review ? ’s How does head size correlate with intelligence? (p. 429) Can you assess an infant’s possible intelligence? 37
 § Artificial Intelligence (AI) § designing & programming computer systems to… § …do intelligent things § …simulate human thought processes (parallel) § intuitive reasoning § learning § understanding language (272 Baron’s) § Computer Neural Networks § computer circuits that mimic brain’s interconnected neural cells & perform tasks much like humans… § learning to recognize visual patterns § learning to recognize smells 38
§ Artificial Intelligence (AI) § designing & programming computer systems to… § …do intelligent things § …simulate human thought processes (parallel) § intuitive reasoning § learning § understanding language (272 Baron’s) § Computer Neural Networks § computer circuits that mimic brain’s interconnected neural cells & perform tasks much like humans… § learning to recognize visual patterns § learning to recognize smells 38
 PPL to know RE: Intelligence & intelligence assessments: Binet Flynn Gardner Spearman Sternberg Terman Wechsler 39
PPL to know RE: Intelligence & intelligence assessments: Binet Flynn Gardner Spearman Sternberg Terman Wechsler 39
 Scoring Assessments Emotional Intelligence Assess. : On Items 5 28 33 (If put 1, change to 5 2 = 4 3 stays 3 4 =2 5 = 1 Then ADD all together…those #’s you changed + #’s you had at beginning for those NOT changed ----------------1. Friday 11. JANE 2. PY (silver anniversary) 12. 9: 00 PM 3. 25 13. b (both grow in ground) 4. anniversary 14. a. Alternate #’s go up by 2 & down 1 (from 1 – 10) 5. MENSA 15. e: only on not man-made art 6. b 16. PARACHUTE 7. b 17. 5 8. b 18. c 9. TOM 19. LAND 10. HOUSE 20. # of lines goes down opposite w/ stick & stick alternates lo L/top R 40
Scoring Assessments Emotional Intelligence Assess. : On Items 5 28 33 (If put 1, change to 5 2 = 4 3 stays 3 4 =2 5 = 1 Then ADD all together…those #’s you changed + #’s you had at beginning for those NOT changed ----------------1. Friday 11. JANE 2. PY (silver anniversary) 12. 9: 00 PM 3. 25 13. b (both grow in ground) 4. anniversary 14. a. Alternate #’s go up by 2 & down 1 (from 1 – 10) 5. MENSA 15. e: only on not man-made art 6. b 16. PARACHUTE 7. b 17. 5 8. b 18. c 9. TOM 19. LAND 10. HOUSE 20. # of lines goes down opposite w/ stick & stick alternates lo L/top R 40


