38615ffe34eff0ea0b8bb76146ce9395.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Myers’ PSYCHOLOGY (6 th Ed) Chapter 10 Thinking and Language James A. Mc. Cubbin, Ph. D Clemson University Worth Publishers
Myers’ PSYCHOLOGY (6 th Ed) Chapter 10 Thinking and Language James A. Mc. Cubbin, Ph. D Clemson University Worth Publishers
 Thinking z. Cognition ymental activity associated with processing, understanding, and communicating information z. Cognitive Psychology ythe study of these mental activities xconcept formation xproblem solving xdecision making xjudgement formation ystudy of both logical and illogical thinking
Thinking z. Cognition ymental activity associated with processing, understanding, and communicating information z. Cognitive Psychology ythe study of these mental activities xconcept formation xproblem solving xdecision making xjudgement formation ystudy of both logical and illogical thinking
 Thinking z. Concept ymental grouping of similar objects, events, or people xaddress • country, city, street, house • zip codes z. Prototype ythe best example of a category xmatching new items to the prototype provides a quick and easy method for including items in a category (as when comparing feathered creatures to a prototypical bird, such as a robin. )
Thinking z. Concept ymental grouping of similar objects, events, or people xaddress • country, city, street, house • zip codes z. Prototype ythe best example of a category xmatching new items to the prototype provides a quick and easy method for including items in a category (as when comparing feathered creatures to a prototypical bird, such as a robin. )
 Thinking z. Algorithm ymethodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem ycontrasts with the usually speedier – but also more error-prone use of heuristics
Thinking z. Algorithm ymethodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem ycontrasts with the usually speedier – but also more error-prone use of heuristics
 Thinking z. Heuristic yrule-of-thumb strategy that often allows us to make judgements and solve problems efficiently yusually speedier than algorithms ymore error-prone than algorithms ysometimes we’re unaware of using heuristics
Thinking z. Heuristic yrule-of-thumb strategy that often allows us to make judgements and solve problems efficiently yusually speedier than algorithms ymore error-prone than algorithms ysometimes we’re unaware of using heuristics
 Thinking Unscramble SPLOYOCHYG z. Algorithm yall 907, 208 combinations z. Heuristic ythrow out all YY combinations yother heuristics?
Thinking Unscramble SPLOYOCHYG z. Algorithm yall 907, 208 combinations z. Heuristic ythrow out all YY combinations yother heuristics?
 Thinking z Insight ysudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem ycontrasts with strategy-based solutions z Confirmation Bias ytendency to search for information that confirms one’s preconceptions z Fixation yinability to see a problem from a new perspective yimpediment to problem solving
Thinking z Insight ysudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem ycontrasts with strategy-based solutions z Confirmation Bias ytendency to search for information that confirms one’s preconceptions z Fixation yinability to see a problem from a new perspective yimpediment to problem solving
 The Matchstick Problem z How would you arrange six matches to form four equilateral triangles?
The Matchstick Problem z How would you arrange six matches to form four equilateral triangles?
 The Candle-Mounting Problem z Using these materials, how would you mount the candle on a bulletin board?
The Candle-Mounting Problem z Using these materials, how would you mount the candle on a bulletin board?
 Thinking z. Mental Set ytendency to approach a problem in a particular way yespecially a way that has been successful in the past but may or may not be helpful in solving a new problem
Thinking z. Mental Set ytendency to approach a problem in a particular way yespecially a way that has been successful in the past but may or may not be helpful in solving a new problem
 Thinking z. Functional Fixedness ytendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions yimpediment to problem solving
Thinking z. Functional Fixedness ytendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions yimpediment to problem solving
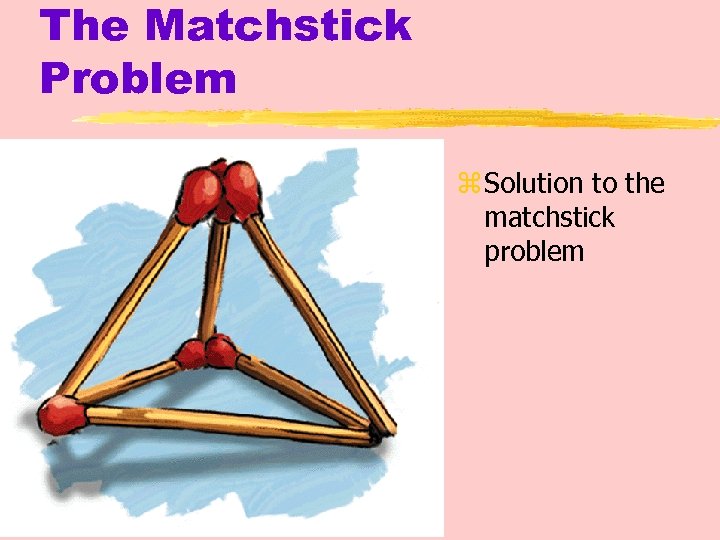 The Matchstick Problem z Solution to the matchstick problem
The Matchstick Problem z Solution to the matchstick problem
 The Three-Jugs Problem z Solution: a) All seven problems can be solved by the equation shown in (a): B-A-2 C= desired volume. z b) But simpler solutions exist for problems 6 and 7, such as A-C for problem 6.
The Three-Jugs Problem z Solution: a) All seven problems can be solved by the equation shown in (a): B-A-2 C= desired volume. z b) But simpler solutions exist for problems 6 and 7, such as A-C for problem 6.
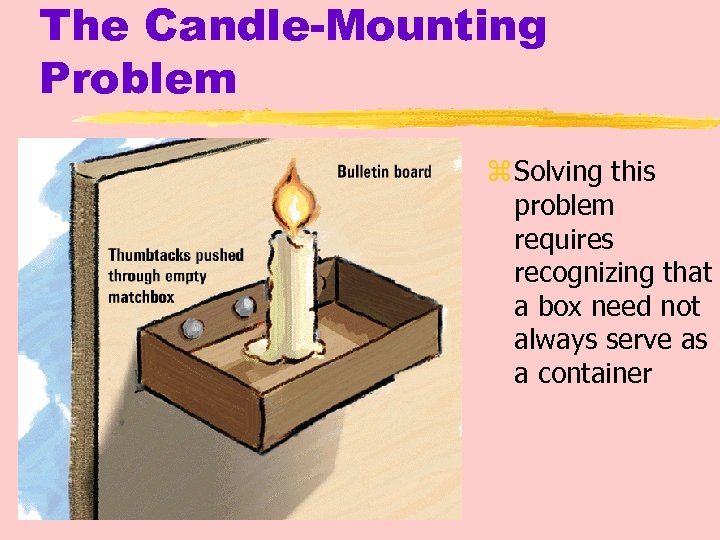 The Candle-Mounting Problem z Solving this problem requires recognizing that a box need not always serve as a container
The Candle-Mounting Problem z Solving this problem requires recognizing that a box need not always serve as a container
 Types of Heuristics z Availability- relying on info that is more easily recalled and overlook less prominent info y. Lottery winnings z Representativeness- assuming that if an item similar to members of a category, it probably is a member too y. Coin flipping z Anchoring- making decisions based on ideas that are important to us y. People who sleep in are lazy
Types of Heuristics z Availability- relying on info that is more easily recalled and overlook less prominent info y. Lottery winnings z Representativeness- assuming that if an item similar to members of a category, it probably is a member too y. Coin flipping z Anchoring- making decisions based on ideas that are important to us y. People who sleep in are lazy
 Thinking z. Overconfidence ytendency to be more confident than correct ytendency to overestimate the accuracy of one’s beliefs and judgements
Thinking z. Overconfidence ytendency to be more confident than correct ytendency to overestimate the accuracy of one’s beliefs and judgements
 Thinking z. Framing ythe way an issue is posed yhow an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgements y. Example: What is the best way to market ground beef- As 25% fat or 75% lean?
Thinking z. Framing ythe way an issue is posed yhow an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgements y. Example: What is the best way to market ground beef- As 25% fat or 75% lean?
 Brain Teasers z 1) If there are 7 months that have 31 days in them and 11 months that have 30 days in them, how many months have 28 days in them? z 2) What is boiled then cooled, sweetened then soured? z 3) A woman gives a beggar 50 cents; the woman is the beggar’s sister, but the beggar is not the woman’s brother. Why? z 4) What is brought to the table and cut, but never eaten? z 5) What is neither inside a house nor outside a house, but no house would be complete without it? z 6) Two men play five games of checkers. Each man wins the same number of games. There are no ties. Explain this. z 7) What is pronounced like one letter, written with three letters, and belongs to all animals? z 8) What is the beginning of eternity, the end of time and space, the beginning of every end, and the end of every race? z 9) What is very light but can’t be lifted? z 10) What overpowers you without hurting you?
Brain Teasers z 1) If there are 7 months that have 31 days in them and 11 months that have 30 days in them, how many months have 28 days in them? z 2) What is boiled then cooled, sweetened then soured? z 3) A woman gives a beggar 50 cents; the woman is the beggar’s sister, but the beggar is not the woman’s brother. Why? z 4) What is brought to the table and cut, but never eaten? z 5) What is neither inside a house nor outside a house, but no house would be complete without it? z 6) Two men play five games of checkers. Each man wins the same number of games. There are no ties. Explain this. z 7) What is pronounced like one letter, written with three letters, and belongs to all animals? z 8) What is the beginning of eternity, the end of time and space, the beginning of every end, and the end of every race? z 9) What is very light but can’t be lifted? z 10) What overpowers you without hurting you?
 Brain Teasers z 11) What question can you never answer “yes” to? z 12) I have two U. S. coins totaling 55 cents. One is not a nickel. What are the coins? z 13) If you only have one match and you walked into a room where there was an oil burner, a kerosene lamp, and a wood burning stove, which one would you light first? z 14) Which two letters of the alphabet are nothing? z 15) How far can a dog run into the woods? z 16) With what vegetable to you throw away the outside, cook the inside, eat the outside, and throw away the inside? z 17) A clerk in the butcher shoe is 5’ 10” tall. What does he weigh? z 18) A man and a dog going down the street. The man rode; yet walked. What was the dog’s name? z 19) If the ruler of Russia was the Czar and his wife the Czarina, what were his children called? z 20) How can you make seven?
Brain Teasers z 11) What question can you never answer “yes” to? z 12) I have two U. S. coins totaling 55 cents. One is not a nickel. What are the coins? z 13) If you only have one match and you walked into a room where there was an oil burner, a kerosene lamp, and a wood burning stove, which one would you light first? z 14) Which two letters of the alphabet are nothing? z 15) How far can a dog run into the woods? z 16) With what vegetable to you throw away the outside, cook the inside, eat the outside, and throw away the inside? z 17) A clerk in the butcher shoe is 5’ 10” tall. What does he weigh? z 18) A man and a dog going down the street. The man rode; yet walked. What was the dog’s name? z 19) If the ruler of Russia was the Czar and his wife the Czarina, what were his children called? z 20) How can you make seven?
 Belief Bias z. Democrats support free speech. z. Dictators are not democrats. z. Dictators do not support free speech. z. Robins have feathers. z. Chickens are not robins. z. Therefore, chickens do not have feathers.
Belief Bias z. Democrats support free speech. z. Dictators are not democrats. z. Dictators do not support free speech. z. Robins have feathers. z. Chickens are not robins. z. Therefore, chickens do not have feathers.
 Thinking z. Belief Bias ythe tendency for one’s preexisting beliefs to distort logical reasoning ysometimes by making invalid conclusions seem valid, or valid conclusions seem invalid z. Belief Perseverance yclinging to one’s initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
Thinking z. Belief Bias ythe tendency for one’s preexisting beliefs to distort logical reasoning ysometimes by making invalid conclusions seem valid, or valid conclusions seem invalid z. Belief Perseverance yclinging to one’s initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
 Language z. Language your spoken, written, or gestured works and the way we combine them to communicate meaning z. Phoneme yin a spoken language, the smallest distinctive sound unit
Language z. Language your spoken, written, or gestured works and the way we combine them to communicate meaning z. Phoneme yin a spoken language, the smallest distinctive sound unit
 What Are Phonemes? PHONEME - shortest segment of speech, which, if changed, would change the meaning of a spoken word. /bit/ /bait/ /beet/ Only 60 phonemes necessary to account for all worlds’ languages! English requires 48 phonemes. Hawaiian requires only 11!
What Are Phonemes? PHONEME - shortest segment of speech, which, if changed, would change the meaning of a spoken word. /bit/ /bait/ /beet/ Only 60 phonemes necessary to account for all worlds’ languages! English requires 48 phonemes. Hawaiian requires only 11!
 What Are Morphemes? Morpheme - the shortest unit of spoken or written language that carries meaning Some morphemes are phonemes (e. g. , “I” and “a”) Most are combos of 2 or more phonemes Some morphemes are words (e. g. , “bat”)
What Are Morphemes? Morpheme - the shortest unit of spoken or written language that carries meaning Some morphemes are phonemes (e. g. , “I” and “a”) Most are combos of 2 or more phonemes Some morphemes are words (e. g. , “bat”)
 Language z. Morpheme yin a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning ymay be a word or a part of a word (such as a prefix) z. Grammar ya system of rules in a language that enables us to communicate with and understand others
Language z. Morpheme yin a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning ymay be a word or a part of a word (such as a prefix) z. Grammar ya system of rules in a language that enables us to communicate with and understand others
 Language z. Semantics ythe set of rules by which we derive meaning from morphemes, words, and sentences in a given language yalso, the study of meaning z. Syntax ythe rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences in a given language
Language z. Semantics ythe set of rules by which we derive meaning from morphemes, words, and sentences in a given language yalso, the study of meaning z. Syntax ythe rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences in a given language
 Language Development How Many Words Do You Know? Average High School Grad Knows ~ 80, 000 words Schools teach approx 200 words per year BUT You learned approx 5, 000 words per year! How Did You Learn All Those Other Words? !?
Language Development How Many Words Do You Know? Average High School Grad Knows ~ 80, 000 words Schools teach approx 200 words per year BUT You learned approx 5, 000 words per year! How Did You Learn All Those Other Words? !?
 Language z We are all born to recognize speech sounds from all the world’s languages Percentage able 100 to discriminate 90 Hindi t’s 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Hindispeaking adults 6 -8 months 8 -10 months 10 -12 months Infants from English-speaking homes Englishspeaking adults
Language z We are all born to recognize speech sounds from all the world’s languages Percentage able 100 to discriminate 90 Hindi t’s 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Hindispeaking adults 6 -8 months 8 -10 months 10 -12 months Infants from English-speaking homes Englishspeaking adults
 Language z. Babbling Stage ybeginning at 3 to 4 months ythe stage of speech development in which the infant spontaneously utters various sounds at first unrelated to the household language z. One-Word Stage yfrom about age 1 to 2 ythe stage in speech development during which a child speaks mostly in single words
Language z. Babbling Stage ybeginning at 3 to 4 months ythe stage of speech development in which the infant spontaneously utters various sounds at first unrelated to the household language z. One-Word Stage yfrom about age 1 to 2 ythe stage in speech development during which a child speaks mostly in single words
 Language z. Two-Word Stage ybeginning about age 2 ythe stage in speech development during which a child speaks mostly two-word statements z. Telegraphic Speech yearly speech stage in which the child speaks like a telegram – “go car” – using mostly nouns and verbs and omitting “auxiliary” words
Language z. Two-Word Stage ybeginning about age 2 ythe stage in speech development during which a child speaks mostly two-word statements z. Telegraphic Speech yearly speech stage in which the child speaks like a telegram – “go car” – using mostly nouns and verbs and omitting “auxiliary” words
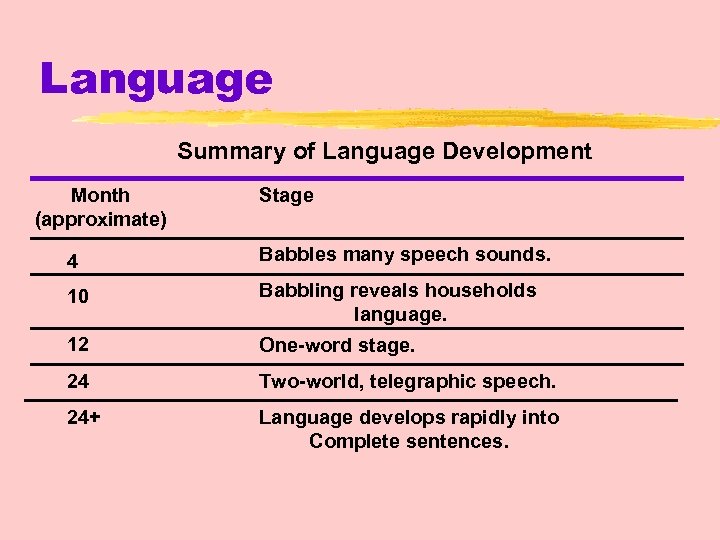 Language Summary of Language Development Month (approximate) Stage 4 Babbles many speech sounds. 10 Babbling reveals households language. 12 One-word stage. 24 Two-world, telegraphic speech. 24+ Language develops rapidly into Complete sentences.
Language Summary of Language Development Month (approximate) Stage 4 Babbles many speech sounds. 10 Babbling reveals households language. 12 One-word stage. 24 Two-world, telegraphic speech. 24+ Language develops rapidly into Complete sentences.
 Explaining Language Development z Skinner- Operant Conditioning y. Association, imitation, and reinforcement z Chomsky- Inborn Universal Grammar y. Acquire grammar and language without being taught y. Over-generalizing z Cognitive Neuroscientists- Statistical Learning y. Gradual changes in neural networks based on experience y. First few years are critical
Explaining Language Development z Skinner- Operant Conditioning y. Association, imitation, and reinforcement z Chomsky- Inborn Universal Grammar y. Acquire grammar and language without being taught y. Over-generalizing z Cognitive Neuroscientists- Statistical Learning y. Gradual changes in neural networks based on experience y. First few years are critical
 A B C D E F Suddenly Several Naked Giraffes Ran Into the room Slowly Six Hairy Martians Jumped Out of the box Without warning Those Bloody Students Slipped Between the houses Amazingly Some Blueblooded Dalmatians Fled Reluctantly The Laughing Duchesses Skipped Down the road Carefully A few Dark Boys Crawled Over the hill Fortunately A great many Bald Lawyers Darted Through the tunnel Cunningly Twenty- Unscrup- Octotwo ulous genarians Danced Across the bridge In due course Innumer Dirty able Limped Up the street Feminists From behind the trees
A B C D E F Suddenly Several Naked Giraffes Ran Into the room Slowly Six Hairy Martians Jumped Out of the box Without warning Those Bloody Students Slipped Between the houses Amazingly Some Blueblooded Dalmatians Fled Reluctantly The Laughing Duchesses Skipped Down the road Carefully A few Dark Boys Crawled Over the hill Fortunately A great many Bald Lawyers Darted Through the tunnel Cunningly Twenty- Unscrup- Octotwo ulous genarians Danced Across the bridge In due course Innumer Dirty able Limped Up the street Feminists From behind the trees
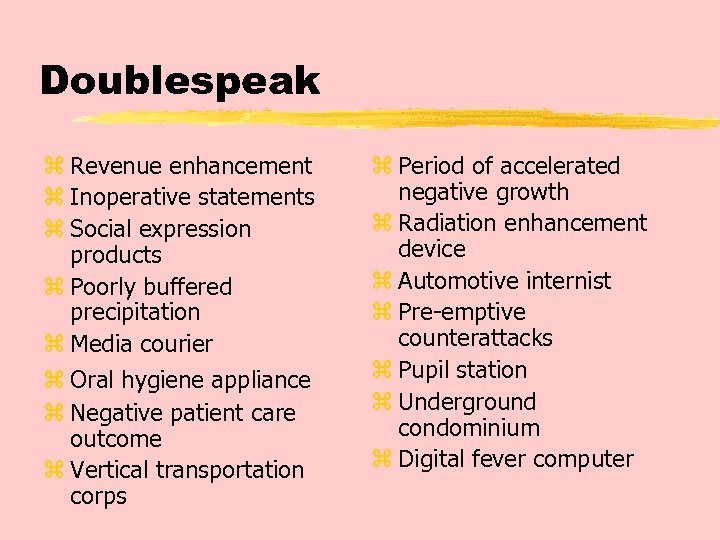 Doublespeak z Revenue enhancement z Inoperative statements z Social expression products z Poorly buffered precipitation z Media courier z Oral hygiene appliance z Negative patient care outcome z Vertical transportation corps z Period of accelerated negative growth z Radiation enhancement device z Automotive internist z Pre-emptive counterattacks z Pupil station z Underground condominium z Digital fever computer
Doublespeak z Revenue enhancement z Inoperative statements z Social expression products z Poorly buffered precipitation z Media courier z Oral hygiene appliance z Negative patient care outcome z Vertical transportation corps z Period of accelerated negative growth z Radiation enhancement device z Automotive internist z Pre-emptive counterattacks z Pupil station z Underground condominium z Digital fever computer
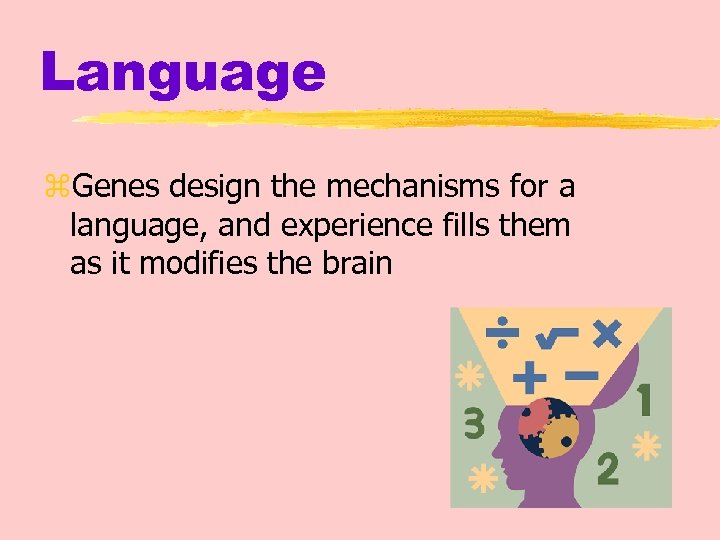 Language z. Genes design the mechanisms for a language, and experience fills them as it modifies the brain
Language z. Genes design the mechanisms for a language, and experience fills them as it modifies the brain
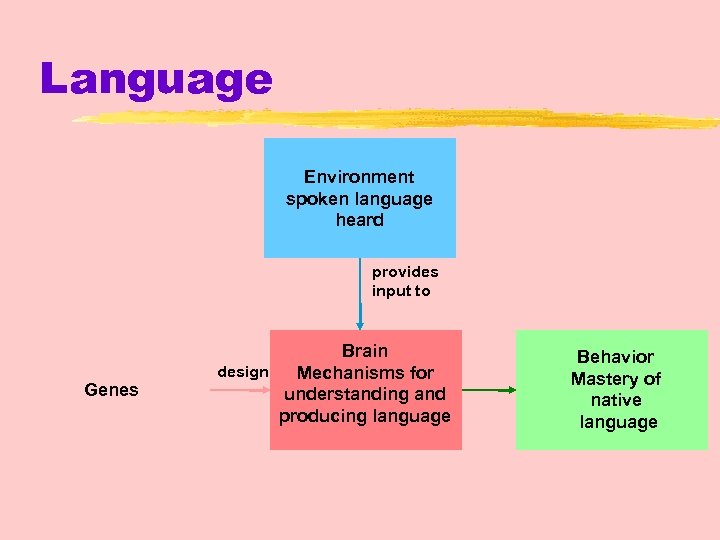 Language Environment spoken language heard provides input to Genes Brain design Mechanisms for understanding and producing language Behavior Mastery of native language
Language Environment spoken language heard provides input to Genes Brain design Mechanisms for understanding and producing language Behavior Mastery of native language
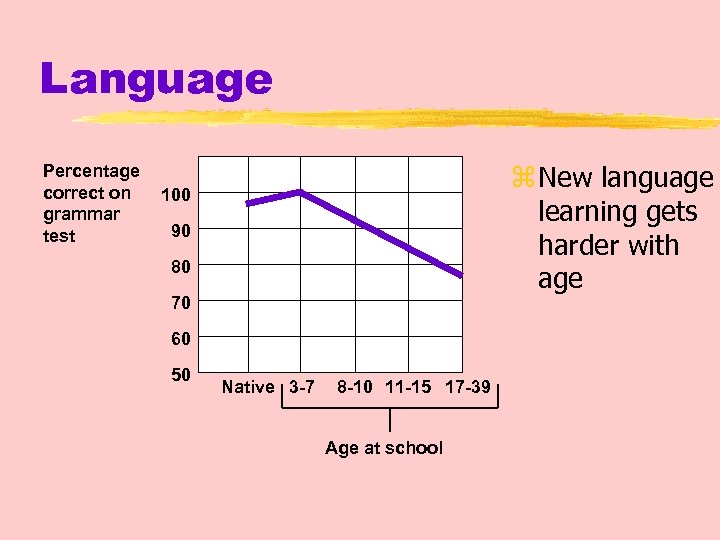 Language Percentage correct on grammar test z New language learning gets harder with age 100 90 80 70 60 50 Native 3 -7 8 -10 11 -15 17 -39 Age at school
Language Percentage correct on grammar test z New language learning gets harder with age 100 90 80 70 60 50 Native 3 -7 8 -10 11 -15 17 -39 Age at school
 Language z. Linguistic Relativity y. Whorfs hypothesis that language determines the way we think
Language z. Linguistic Relativity y. Whorfs hypothesis that language determines the way we think
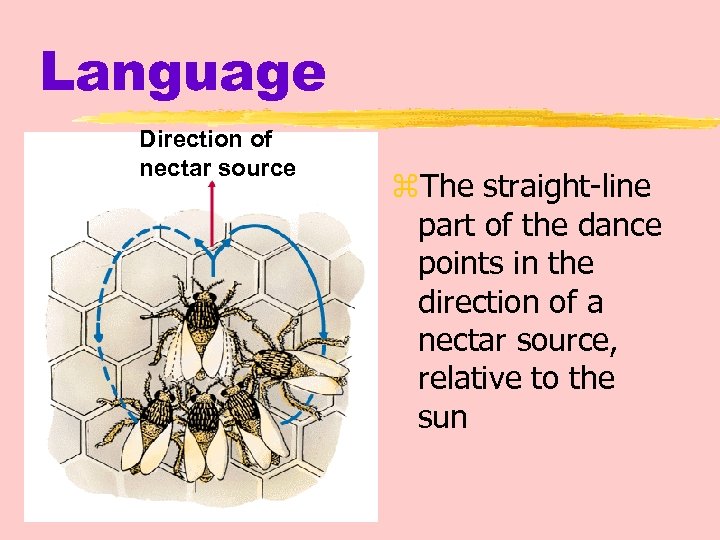 Language Direction of nectar source z. The straight-line part of the dance points in the direction of a nectar source, relative to the sun
Language Direction of nectar source z. The straight-line part of the dance points in the direction of a nectar source, relative to the sun
 Are We Alone? Can apes be taught “language”? Washoe learned 132 signs by age 4 and 240 signs by age 27 Evidence of creative sentence construction Vocabularies and sentences are simple (2 yr old child) But are apes really using “language”?
Are We Alone? Can apes be taught “language”? Washoe learned 132 signs by age 4 and 240 signs by age 27 Evidence of creative sentence construction Vocabularies and sentences are simple (2 yr old child) But are apes really using “language”?
 Animal Use of Language z. Beatrice Gardner- raised a baby chimp named Washoe and taught ASL y. Knew 87 signs by 3 ½ y. Knew 160 signs by 5 y. Can also use keyboards z. Cannot apply grammatical rules or arrange symbols to create new meanings (grammar)
Animal Use of Language z. Beatrice Gardner- raised a baby chimp named Washoe and taught ASL y. Knew 87 signs by 3 ½ y. Knew 160 signs by 5 y. Can also use keyboards z. Cannot apply grammatical rules or arrange symbols to create new meanings (grammar)
 So…Can Apes Possess Language? It depends. . . Verbal or signed expression of complex grammar? No. Communication through a meaningful sequence of symbols? Yes.
So…Can Apes Possess Language? It depends. . . Verbal or signed expression of complex grammar? No. Communication through a meaningful sequence of symbols? Yes.


