cbb3e3fd7fac8f6f5ad8e0fb73312c22.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

My. SQL and GRID Gabriele Carcassi STAR Collaboration 6 May 2002 - Proposal
Why? «STAR uses My. SQL to keep track of data files (file catalog) ¬ There already many projects concerning file catalogs ¬ MAGDA already uses My. SQL to store file catalog information ¬ We will not concentrate on this aspect
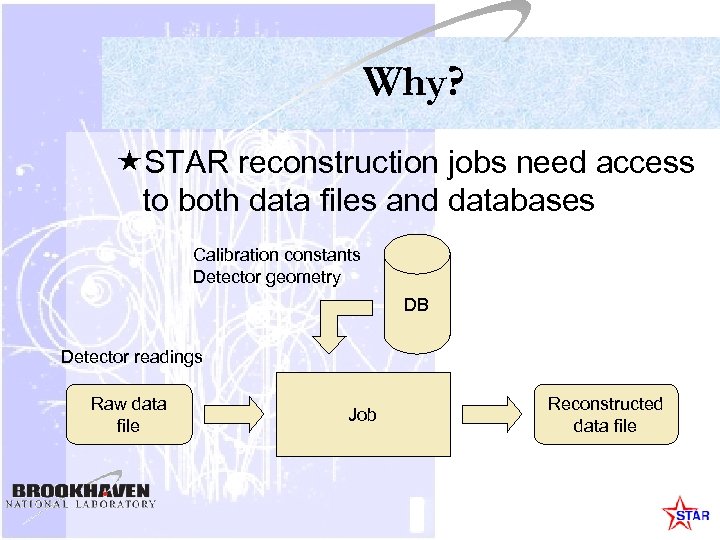
Why? «STAR reconstruction jobs need access to both data files and databases Calibration constants Detector geometry DB Detector readings Raw data file Job Reconstructed data file
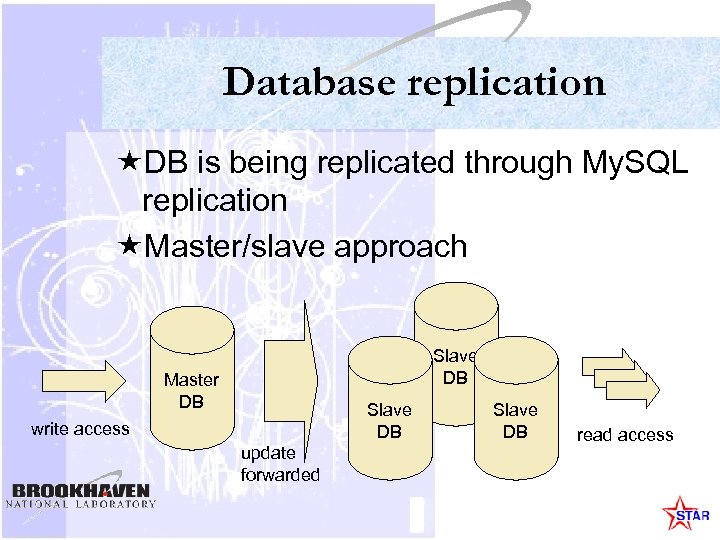
Database replication «DB is being replicated through My. SQL replication «Master/slave approach Slave DB Master DB Slave DB write access update forwarded Slave DB read access
GRID and DB replicas «Database replication is essential because: ¬ Increase data availability ¬ Allows locations to run jobs independently (in case of network congestion) ¬ Correction to the DB are available to all locations «In order to successfully execute jobs in a GRID environment, we need database replication to be somehow integrated
Steps 1. Aid DB administrator to manage complexity of database replication 2. Tools to install a mirror using GRID technology 3. Database catalogs and integration with file catalogs 4. Integrate GRID authentication
1. Manage complexity «The more server you have, the more complicated is to manage the system «Build a GUI that helps the database administrator (DBA) to have a general picture
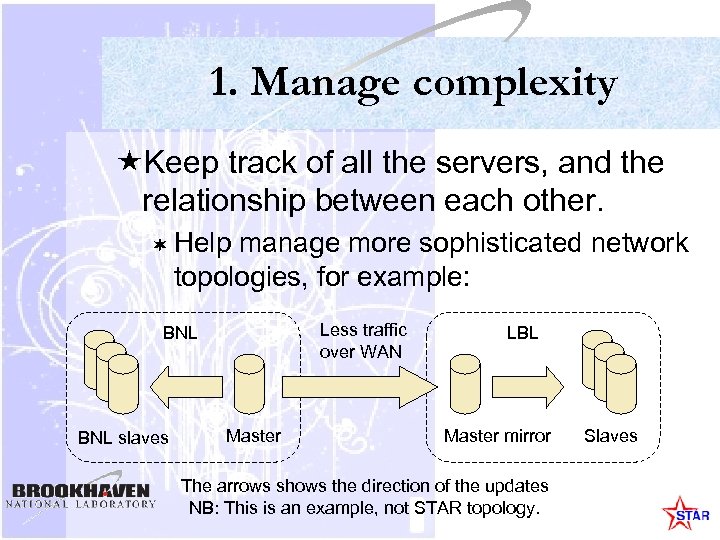
1. Manage complexity «Keep track of all the servers, and the relationship between each other. ¬ Help manage more sophisticated network topologies, for example: Less traffic over WAN BNL slaves Master LBL Master mirror The arrows shows the direction of the updates NB: This is an example, not STAR topology. Slaves
1. Manage complexity «Configurations ¬ Aid the comparison between server characteristics (i. e. OS version, My. SQL version) ¬ Aid the comparison of the settings of the different database servers «User management ¬ Create and delete users on a group of servers
1. Manage complexity «Consistency checks ¬ Compare row counts of different replicas ¬ Compare master log pointer with slaves ¬ Check slave connections to the master «Evaluate the replication ¬ Monitor CPU and network activity of the servers to help decide if the current number of servers is sufficient

2. Creating a new mirror «My. SQL keeps the slave synchronized, but you have to manually copy the db files during slave initialization «When the DB is already in place, you might have to copy each file by itself, since the total might exceed 2 GB «GRID technologies can be used to transfer the first copy of the database from site to site

2. Creating a new mirror « New mirror ¬ Steps for mirror creation 1. 2. 3. Install My. SQL (manual? ) Copy database files (through GRIDFtp) Configure master and slave « Creating/deleting a database on an existing mirror

2. Creating a new mirror «Ease of use ¬ Integration with the previous GUI ¬ Hide as much details as possible and encourage good configuration policies (i. e. create a user with suitable permissions to be used by the slave connection)
3. Catalogs «Jobs need to know to which database server to connect (for now, this is done by XML files) «In a GRID environment, jobs will contact a file catalog to determine the location of the files to be used «The scheme for the database catalog shouldn’t be different, and it should be as connected as possible to the file catalog
3. Catalogs «Database catalog ¬A job should query the catalog to know to which database server to connect ¬ If possible, file catalogs could be used directly. For example, instead of a physical file location, the catalog could return the parameters for the database connection (i. e. “mydb. star. bnl. gov: 3301”) ¬ If no connection can be established, the job might ask the catalog for an alternative server

3. Catalogs « Administration ¬ The DBA should be able to establish the policies that decide to which server a given job should connect (i. e. IP address, user groups) « Integration with the GUI The GUI would use the catalog to keep track of the different servers ¬ The GUI would help the DBA to assign policies, and check that the catalog information is not corrupted ¬
4. Authentication «GRID authentication should be integrated to the whole scheme ¬ Connection between database servers ¬ Connection to the catalog ¬ Connection job-database server

4. Authentication « My. SQL 4. 0 will integrate SSL for both user connections and between server connections ¬ My. SQL can be instructed to accept only certificate authentication « My. SQL 4. 0 is still in alpha and SSL is not GSI, but: Some issues should be already addressed ¬ A patch to enable GSI on SSH is available and might provide further insights ¬

4. Authentication «Integration with the GUI ¬ Just one authentication at the beginning of the application ¬ Same authentication used to authenticate to the servers ¬ User management
cbb3e3fd7fac8f6f5ad8e0fb73312c22.ppt