8e42790db0b43b2c94e9d131cd05b2a5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 My Introduction § Name : Kustanto § Address: Perum. Puri Malangjiwan 3. N 0. 12. Colomadu § Highest education: S 2 TE UGM § Concentration : Computer Systems Informatics
My Introduction § Name : Kustanto § Address: Perum. Puri Malangjiwan 3. N 0. 12. Colomadu § Highest education: S 2 TE UGM § Concentration : Computer Systems Informatics
 Final Assessment § § Presence Task Midterms Final Exams Chapter 1 Computer Systems = 5% = @15% = 30% = 35% 1 -2
Final Assessment § § Presence Task Midterms Final Exams Chapter 1 Computer Systems = 5% = @15% = 30% = 35% 1 -2
 § Delay Tolerance Attend College = 20 Minute § College Syllabus Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -3
§ Delay Tolerance Attend College = 20 Minute § College Syllabus Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -3
 Chaper 1. Computer Systems by Kustanto
Chaper 1. Computer Systems by Kustanto
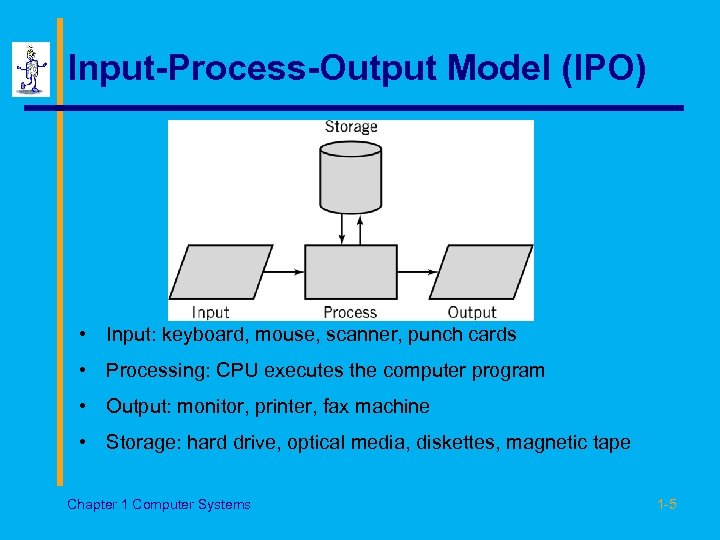 Input-Process-Output Model (IPO) • Input: keyboard, mouse, scanner, punch cards • Processing: CPU executes the computer program • Output: monitor, printer, fax machine • Storage: hard drive, optical media, diskettes, magnetic tape Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -5
Input-Process-Output Model (IPO) • Input: keyboard, mouse, scanner, punch cards • Processing: CPU executes the computer program • Output: monitor, printer, fax machine • Storage: hard drive, optical media, diskettes, magnetic tape Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -5
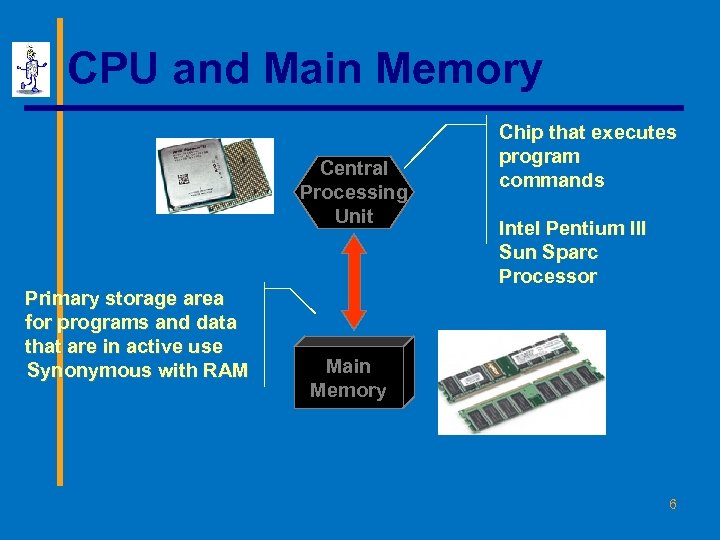 CPU and Main Memory Central Processing Unit Primary storage area for programs and data that are in active use Synonymous with RAM Chip that executes program commands Intel Pentium III Sun Sparc Processor Main Memory 6
CPU and Main Memory Central Processing Unit Primary storage area for programs and data that are in active use Synonymous with RAM Chip that executes program commands Intel Pentium III Sun Sparc Processor Main Memory 6
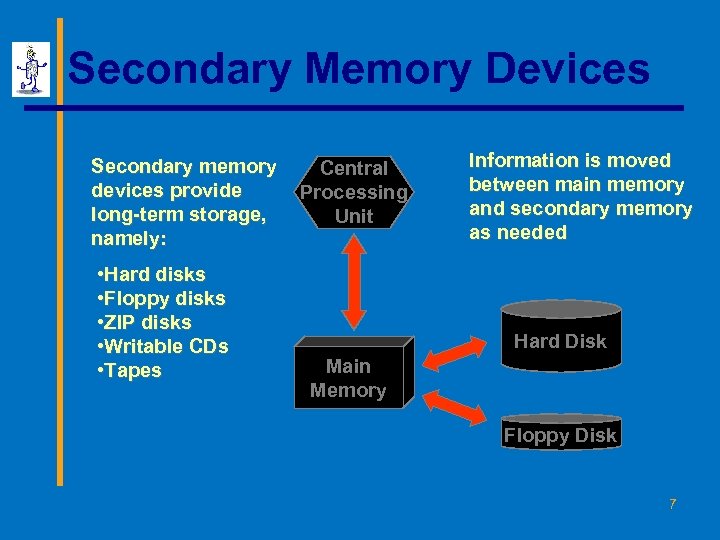 Secondary Memory Devices Secondary memory devices provide long-term storage, namely: • Hard disks • Floppy disks • ZIP disks • Writable CDs • Tapes Central Processing Unit Information is moved between main memory and secondary memory as needed Hard Disk Main Memory Floppy Disk 7
Secondary Memory Devices Secondary memory devices provide long-term storage, namely: • Hard disks • Floppy disks • ZIP disks • Writable CDs • Tapes Central Processing Unit Information is moved between main memory and secondary memory as needed Hard Disk Main Memory Floppy Disk 7
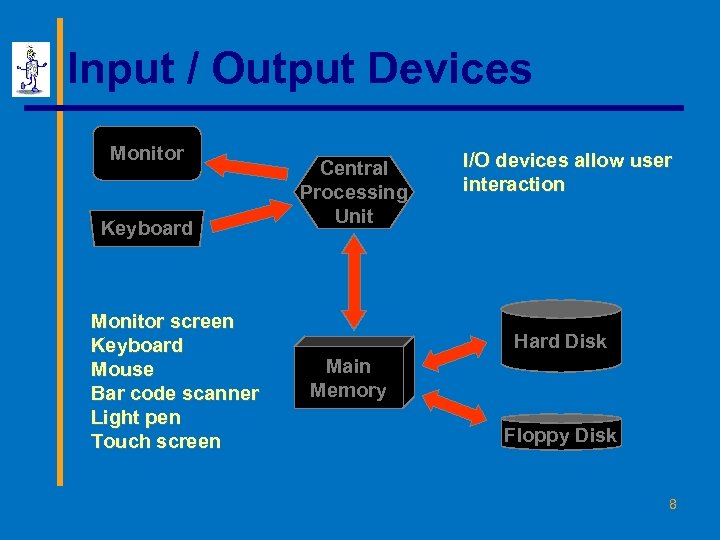 Input / Output Devices Monitor Keyboard Monitor screen Keyboard Mouse Bar code scanner Light pen Touch screen Central Processing Unit I/O devices allow user interaction Hard Disk Main Memory Floppy Disk 8
Input / Output Devices Monitor Keyboard Monitor screen Keyboard Mouse Bar code scanner Light pen Touch screen Central Processing Unit I/O devices allow user interaction Hard Disk Main Memory Floppy Disk 8
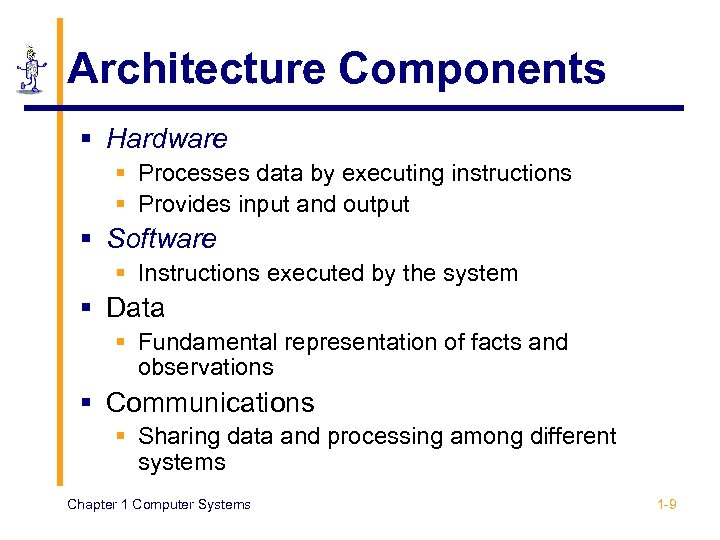 Architecture Components § Hardware § Processes data by executing instructions § Provides input and output § Software § Instructions executed by the system § Data § Fundamental representation of facts and observations § Communications § Sharing data and processing among different systems Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -9
Architecture Components § Hardware § Processes data by executing instructions § Provides input and output § Software § Instructions executed by the system § Data § Fundamental representation of facts and observations § Communications § Sharing data and processing among different systems Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -9
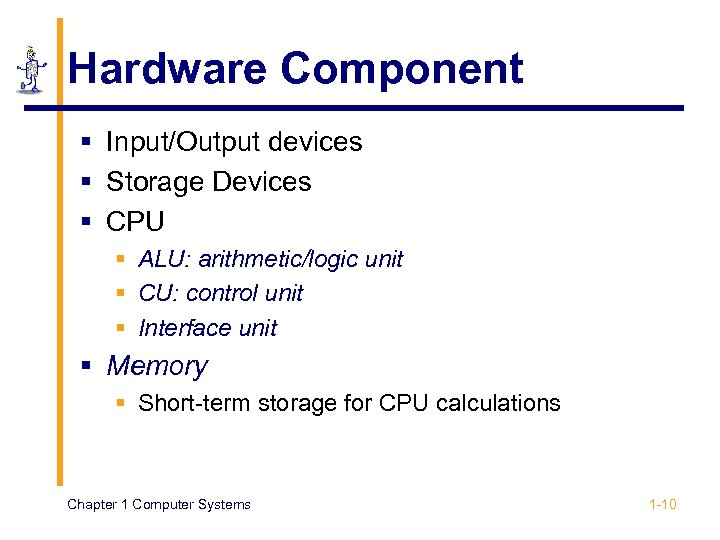 Hardware Component § Input/Output devices § Storage Devices § CPU § ALU: arithmetic/logic unit § CU: control unit § Interface unit § Memory § Short-term storage for CPU calculations Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -10
Hardware Component § Input/Output devices § Storage Devices § CPU § ALU: arithmetic/logic unit § CU: control unit § Interface unit § Memory § Short-term storage for CPU calculations Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -10
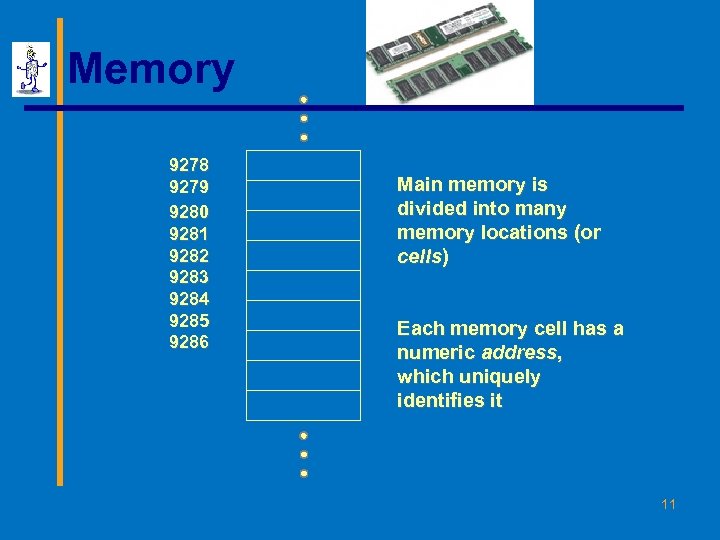 Memory 9278 9279 9280 9281 9282 9283 9284 9285 9286 Main memory is divided into many memory locations (or cells) Each memory cell has a numeric address, which uniquely identifies it 11
Memory 9278 9279 9280 9281 9282 9283 9284 9285 9286 Main memory is divided into many memory locations (or cells) Each memory cell has a numeric address, which uniquely identifies it 11
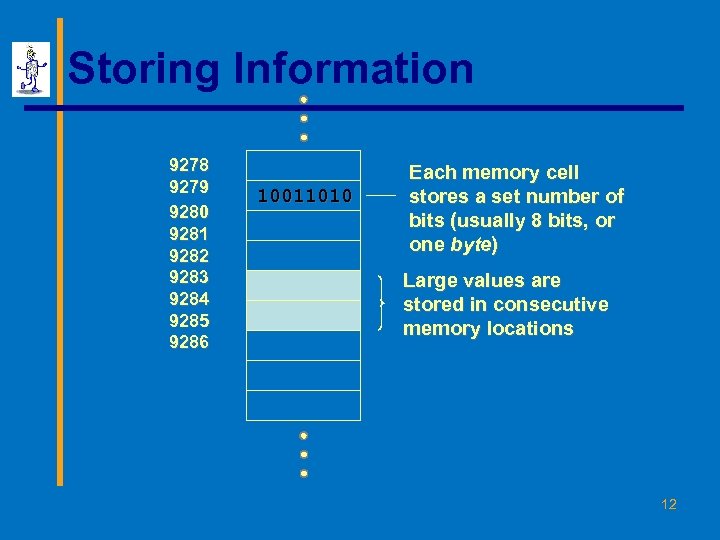 Storing Information 9278 9279 9280 9281 9282 9283 9284 9285 9286 10011010 Each memory cell stores a set number of bits (usually 8 bits, or one byte) Large values are stored in consecutive memory locations 12
Storing Information 9278 9279 9280 9281 9282 9283 9284 9285 9286 10011010 Each memory cell stores a set number of bits (usually 8 bits, or one byte) Large values are stored in consecutive memory locations 12
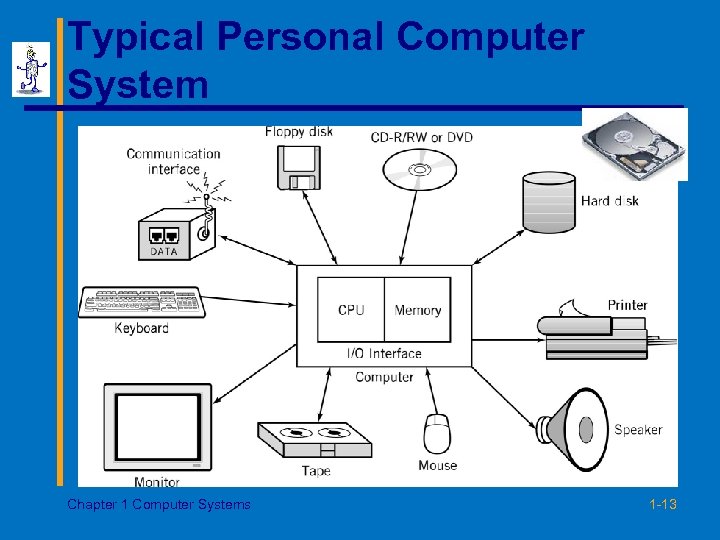 Typical Personal Computer System Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -13
Typical Personal Computer System Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -13
 CPU: Central Processing Unit § ALU: arithmetic/logic unit § Performs arithmetic and Boolean logical calculations § CU: control unit § Controls processing of instructions § Controls movement of data within the CPU § Interface unit § Moves instructions and data between the CPU and other hardware components § Bus: bundle of wires that carry signals and power between different components Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -14
CPU: Central Processing Unit § ALU: arithmetic/logic unit § Performs arithmetic and Boolean logical calculations § CU: control unit § Controls processing of instructions § Controls movement of data within the CPU § Interface unit § Moves instructions and data between the CPU and other hardware components § Bus: bundle of wires that carry signals and power between different components Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -14
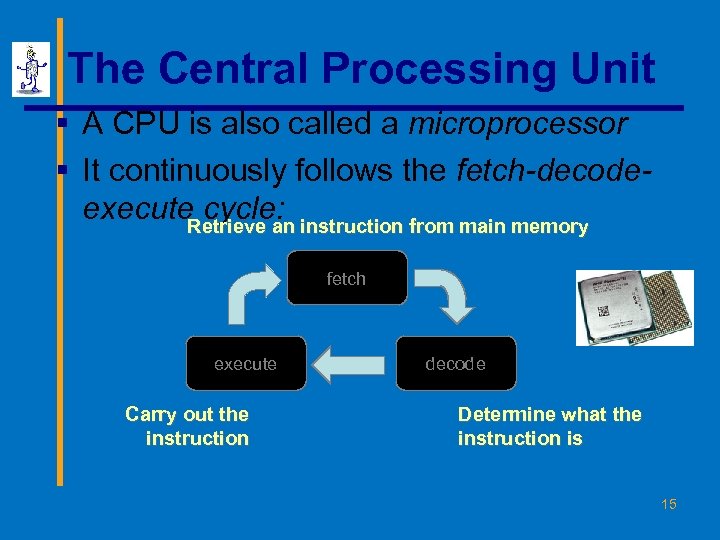 The Central Processing Unit § A CPU is also called a microprocessor § It continuously follows the fetch-decodeexecute cycle: instruction from main memory Retrieve an fetch execute Carry out the instruction decode Determine what the instruction is 15
The Central Processing Unit § A CPU is also called a microprocessor § It continuously follows the fetch-decodeexecute cycle: instruction from main memory Retrieve an fetch execute Carry out the instruction decode Determine what the instruction is 15
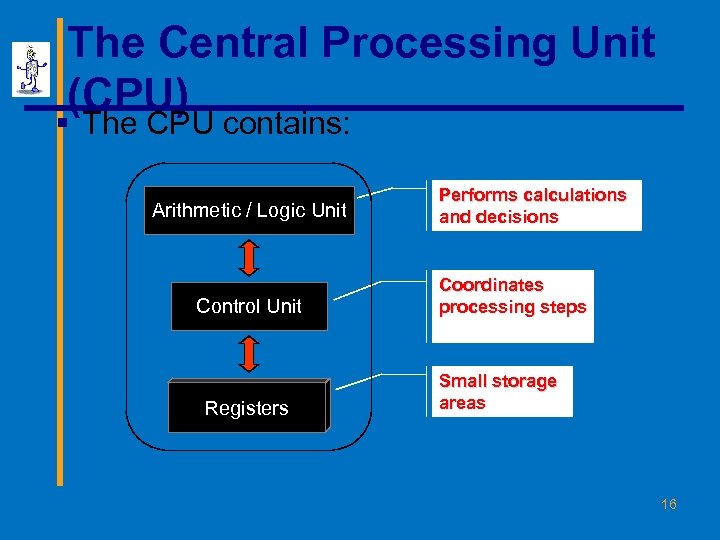 The Central Processing Unit (CPU) § The CPU contains: Arithmetic / Logic Unit Control Unit Registers Performs calculations and decisions Coordinates processing steps Small storage areas 16
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) § The CPU contains: Arithmetic / Logic Unit Control Unit Registers Performs calculations and decisions Coordinates processing steps Small storage areas 16
 The Central Processing Unit § The speed of a CPU is controlled by the system clock § The system clock generates an electronic pulse at regular intervals § The pulses coordinate the activities of the CPU § The speed is measured in megahertz (MHz) 17
The Central Processing Unit § The speed of a CPU is controlled by the system clock § The system clock generates an electronic pulse at regular intervals § The pulses coordinate the activities of the CPU § The speed is measured in megahertz (MHz) 17
 Memory § Also known as primary storage, working storage, and RAM (random access memory) § Consists of bits, each of which hold a value of either 0 or 1 (8 bits = 1 byte) § Holds both instructions and data of a computer program (stored program concept) Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -18
Memory § Also known as primary storage, working storage, and RAM (random access memory) § Consists of bits, each of which hold a value of either 0 or 1 (8 bits = 1 byte) § Holds both instructions and data of a computer program (stored program concept) Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -18
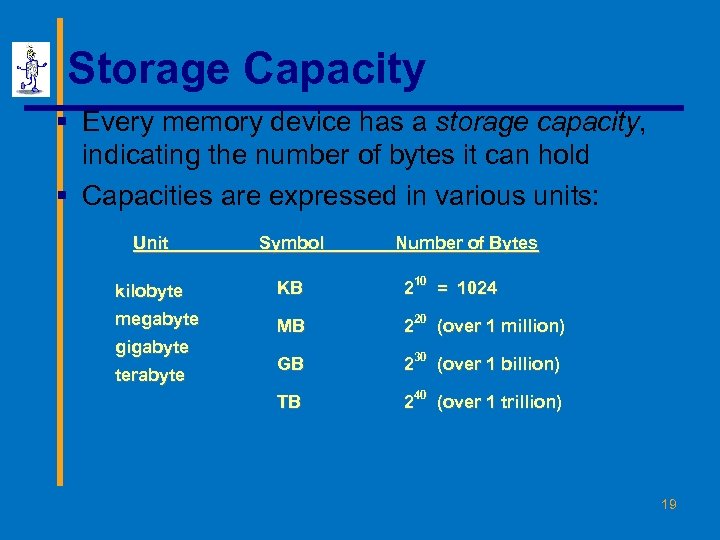 Storage Capacity § Every memory device has a storage capacity, indicating the number of bytes it can hold § Capacities are expressed in various units: Unit Symbol kilobyte KB 210 = 1024 megabyte MB 220 (over 1 million) GB 230 (over 1 billion) TB 240 (over 1 trillion) gigabyte terabyte Number of Bytes 19
Storage Capacity § Every memory device has a storage capacity, indicating the number of bytes it can hold § Capacities are expressed in various units: Unit Symbol kilobyte KB 210 = 1024 megabyte MB 220 (over 1 million) GB 230 (over 1 billion) TB 240 (over 1 trillion) gigabyte terabyte Number of Bytes 19
 Memory § Main memory is volatile - stored information is lost if the electric power is removed § Secondary memory devices are nonvolatile § Main memory and disks are direct access devices information can be reached directly § The terms direct access and random access are often used interchangeably § A magnetic tape is a sequential access device since its data is arranged in a linear order - you must get by the intervening data in order to access other information 20
Memory § Main memory is volatile - stored information is lost if the electric power is removed § Secondary memory devices are nonvolatile § Main memory and disks are direct access devices information can be reached directly § The terms direct access and random access are often used interchangeably § A magnetic tape is a sequential access device since its data is arranged in a linear order - you must get by the intervening data in order to access other information 20
 RAM vs. ROM § RAM - Random Access Memory (direct access) § ROM - Read-Only Memory § The terms RAM and main memory are basically interchangeable § ROM could be a set of memory chips, or a separate device, such as a CD ROM § Both RAM and ROM are random (direct) access devices! § RAM should probably be called Read-Write Memory ROM RAM 21
RAM vs. ROM § RAM - Random Access Memory (direct access) § ROM - Read-Only Memory § The terms RAM and main memory are basically interchangeable § ROM could be a set of memory chips, or a separate device, such as a CD ROM § Both RAM and ROM are random (direct) access devices! § RAM should probably be called Read-Write Memory ROM RAM 21
 Monitor § The size of a monitor (17") is measured diagonally, like a television screen § Most monitors these days have multimedia capabilities: text, graphics, video, etc. § A monitor has a certain maximum resolution , indicating the number of picture elements, called pixels, that it can display (such as 1280 by 1024) § High resolution (more pixels) produces sharper pictures 22
Monitor § The size of a monitor (17") is measured diagonally, like a television screen § Most monitors these days have multimedia capabilities: text, graphics, video, etc. § A monitor has a certain maximum resolution , indicating the number of picture elements, called pixels, that it can display (such as 1280 by 1024) § High resolution (more pixels) produces sharper pictures 22
 Modem § Data transfer devices allow information to be sent and received between computers § Many computers include a modem, which allows information to be moved across a telephone line § A data transfer device has a maximum data transfer rate § A modem, for instance, may have a data transfer rate of 56, 000 bits per second (bps) 23
Modem § Data transfer devices allow information to be sent and received between computers § Many computers include a modem, which allows information to be moved across a telephone line § A data transfer device has a maximum data transfer rate § A modem, for instance, may have a data transfer rate of 56, 000 bits per second (bps) 23
 Networks § A network is two or more computers that are connected so that data and resources can be shared § Most computers are connected to some kind of network § Each computer has its own network address, which uniquely identifies it among the others § A file server is a network computer dedicated to storing programs and data that are shared among network users 24
Networks § A network is two or more computers that are connected so that data and resources can be shared § Most computers are connected to some kind of network § Each computer has its own network address, which uniquely identifies it among the others § A file server is a network computer dedicated to storing programs and data that are shared among network users 24
 A Computer Specification § Consider the following specification for a personal computer: § § § 600 MHz Pentium III Processor 256 MB RAM 16 GB Hard Disk 24 x speed CD ROM Drive 17” Multimedia Video Display with 1280 x 1024 resolution § 56 KB Modem 25
A Computer Specification § Consider the following specification for a personal computer: § § § 600 MHz Pentium III Processor 256 MB RAM 16 GB Hard Disk 24 x speed CD ROM Drive 17” Multimedia Video Display with 1280 x 1024 resolution § 56 KB Modem 25
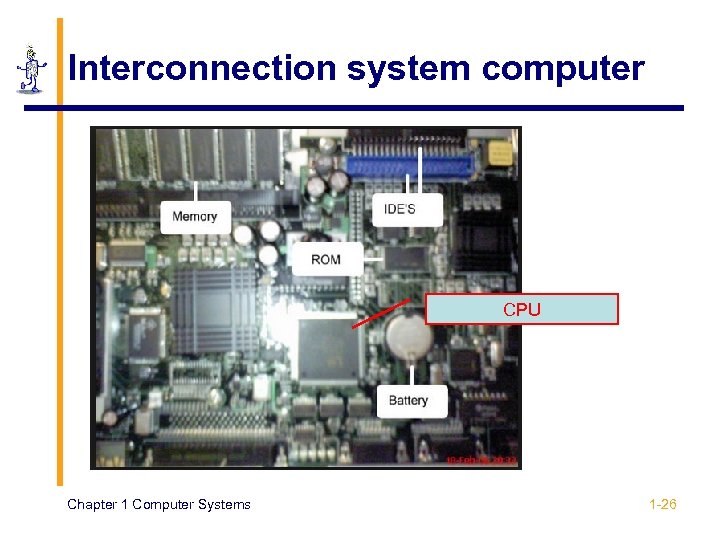 Interconnection system computer CPU Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -26
Interconnection system computer CPU Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -26
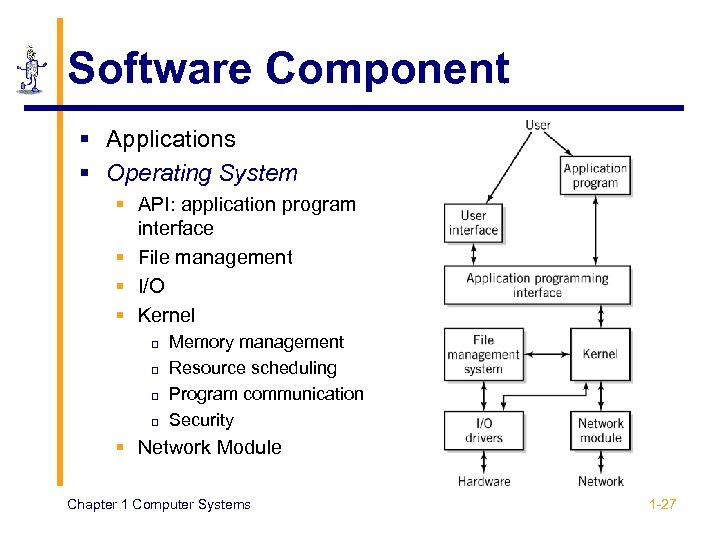 Software Component § Applications § Operating System § API: application program interface § File management § I/O § Kernel p p Memory management Resource scheduling Program communication Security § Network Module Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -27
Software Component § Applications § Operating System § API: application program interface § File management § I/O § Kernel p p Memory management Resource scheduling Program communication Security § Network Module Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -27
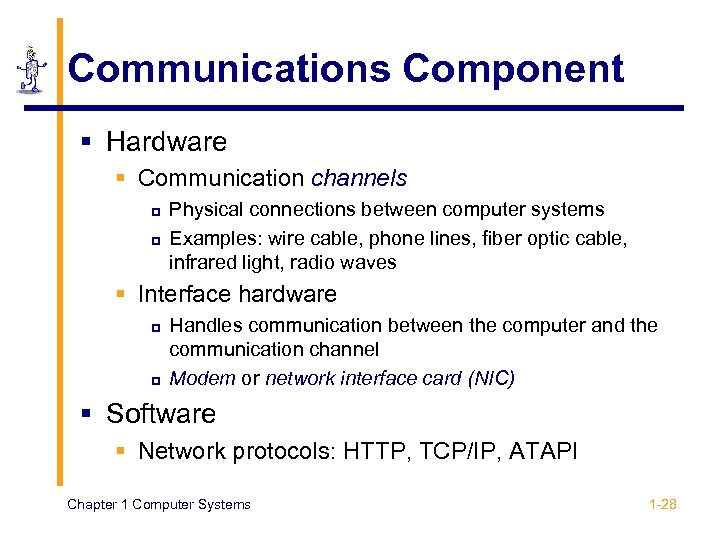 Communications Component § Hardware § Communication channels p p Physical connections between computer systems Examples: wire cable, phone lines, fiber optic cable, infrared light, radio waves § Interface hardware p p Handles communication between the computer and the communication channel Modem or network interface card (NIC) § Software § Network protocols: HTTP, TCP/IP, ATAPI Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -28
Communications Component § Hardware § Communication channels p p Physical connections between computer systems Examples: wire cable, phone lines, fiber optic cable, infrared light, radio waves § Interface hardware p p Handles communication between the computer and the communication channel Modem or network interface card (NIC) § Software § Network protocols: HTTP, TCP/IP, ATAPI Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -28
 Computer Systems All computer systems, consists of the following: § At least one CPU § Memory to hold programs and data § I/O devices § Long-term storage Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -29
Computer Systems All computer systems, consists of the following: § At least one CPU § Memory to hold programs and data § I/O devices § Long-term storage Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -29
 Protocols § Common ground rules of communication between computers, I/O devices, and many software programs § Examples § HTTP: between Web servers and Web browsers § TCP/IP: between computers on the Internet and local area networks § ATAPI: between a CPU and CD-ROMs Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -30
Protocols § Common ground rules of communication between computers, I/O devices, and many software programs § Examples § HTTP: between Web servers and Web browsers § TCP/IP: between computers on the Internet and local area networks § ATAPI: between a CPU and CD-ROMs Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -30
 Standards § Created to ensure universal compatibility of data formats and protocols § May be created by committee or may become a de facto standard through popular use § Examples: § § Computer languages: Java, SQL, C, Java. Script Display standards: Postscript, MPEG-2, JPEG, GIF Character set standards: ASCII, Unicode, EBCDIC Video standards: VGA, XGA, RGB Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -31
Standards § Created to ensure universal compatibility of data formats and protocols § May be created by committee or may become a de facto standard through popular use § Examples: § § Computer languages: Java, SQL, C, Java. Script Display standards: Postscript, MPEG-2, JPEG, GIF Character set standards: ASCII, Unicode, EBCDIC Video standards: VGA, XGA, RGB Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -31
 Chapter 5 Telecommunications System
Chapter 5 Telecommunications System
 Telecommunication model O’Brien 125 § Terminals § office equipment , telephones , . . . § Telecommunications processors § modems, multiplexers, front-end processors, . . . § Telecommunications channels and media § copper wires, coaxial cables, fiber optic cables, satellites, . . . § Computers § host computers, network servers, . . . § Telecommunications control software § telecommunication monitors, network operating systems, . . .
Telecommunication model O’Brien 125 § Terminals § office equipment , telephones , . . . § Telecommunications processors § modems, multiplexers, front-end processors, . . . § Telecommunications channels and media § copper wires, coaxial cables, fiber optic cables, satellites, . . . § Computers § host computers, network servers, . . . § Telecommunications control software § telecommunication monitors, network operating systems, . . .
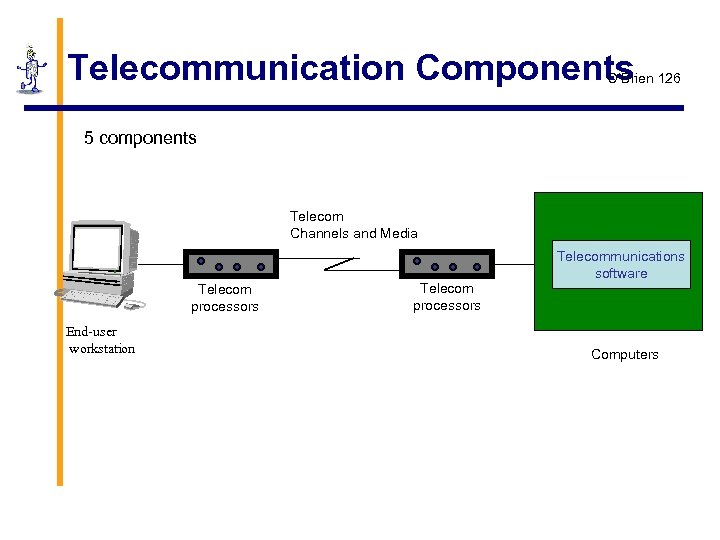 Telecommunication Components O’Brien 126 5 components Telecom Channels and Media Telecom processors End-user workstation Telecom processors Telecommunications software Computers
Telecommunication Components O’Brien 126 5 components Telecom Channels and Media Telecom processors End-user workstation Telecom processors Telecommunications software Computers
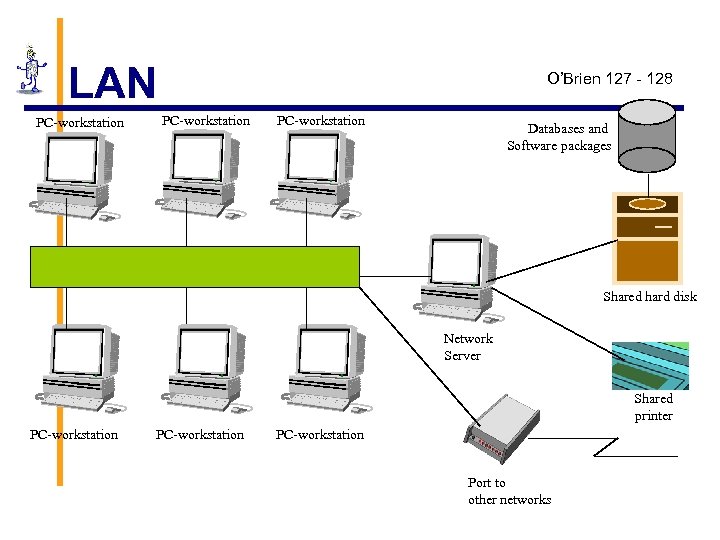 LAN PC-workstation O’Brien 127 - 128 PC-workstation Databases and Software packages Shared hard disk Network Server Shared printer PC-workstation Port to other networks
LAN PC-workstation O’Brien 127 - 128 PC-workstation Databases and Software packages Shared hard disk Network Server Shared printer PC-workstation Port to other networks
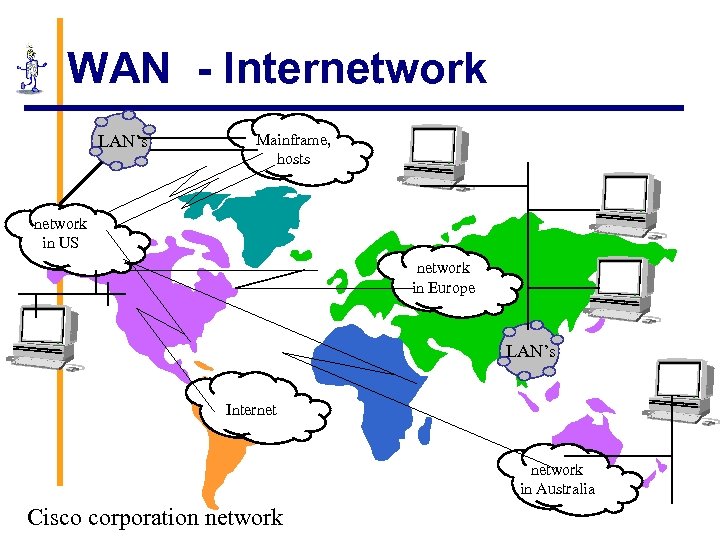 WAN - Internetwork LAN’s Mainframe, hosts network in US network in Europe LAN’s Internet network in Australia Cisco corporation network
WAN - Internetwork LAN’s Mainframe, hosts network in US network in Europe LAN’s Internet network in Australia Cisco corporation network
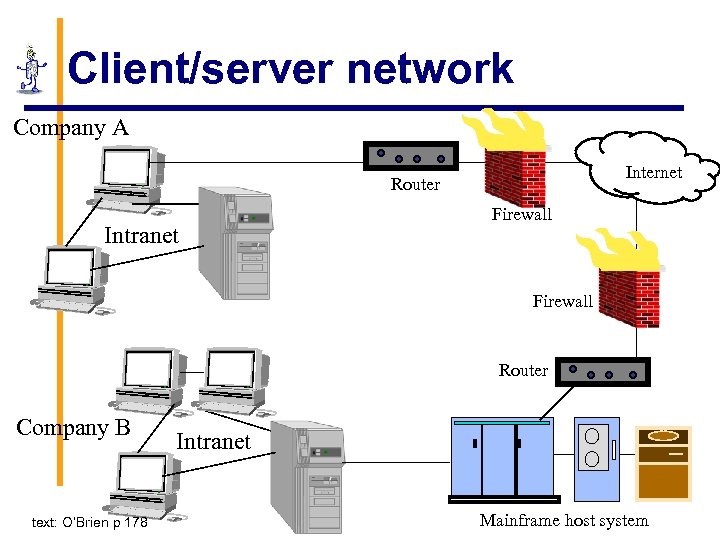 Client/server network Company A Internet Router Intranet Firewall Router Company B text: O’Brien p 178 Intranet Mainframe host system
Client/server network Company A Internet Router Intranet Firewall Router Company B text: O’Brien p 178 Intranet Mainframe host system
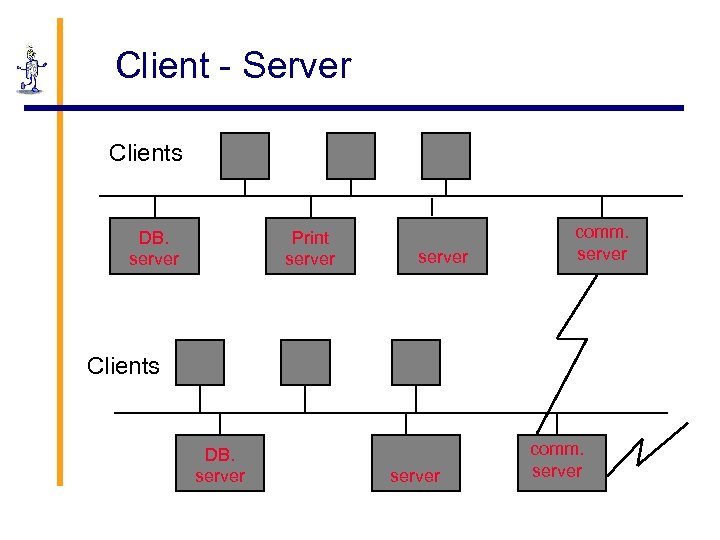 Client - Server Clients DB. server Print server comm. server Clients DB. server comm. server
Client - Server Clients DB. server Print server comm. server Clients DB. server comm. server
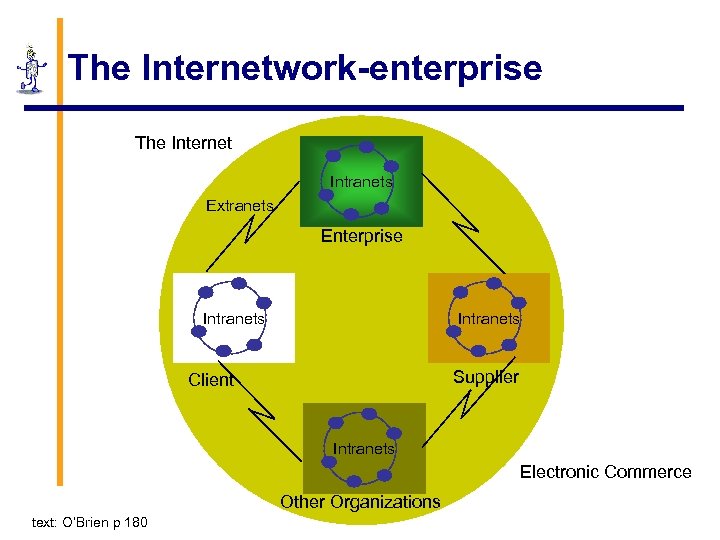 The Internetwork-enterprise The Internet Intranets Extranets Enterprise Intranets Supplier Client Intranets Electronic Commerce Other Organizations text: O’Brien p 180
The Internetwork-enterprise The Internet Intranets Extranets Enterprise Intranets Supplier Client Intranets Electronic Commerce Other Organizations text: O’Brien p 180
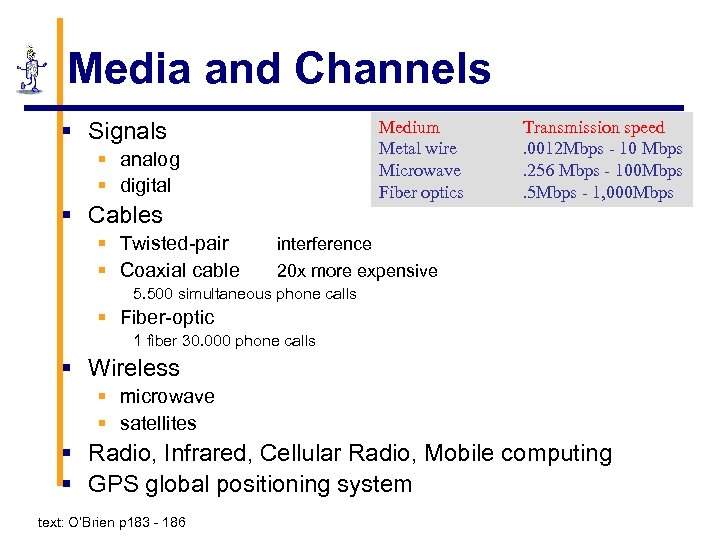 Media and Channels § Signals Medium Metal wire Microwave Fiber optics § analog § digital § Cables § Twisted-pair § Coaxial cable Transmission speed. 0012 Mbps - 10 Mbps. 256 Mbps - 100 Mbps. 5 Mbps - 1, 000 Mbps interference 20 x more expensive 5. 500 simultaneous phone calls § Fiber-optic 1 fiber 30. 000 phone calls § Wireless § microwave § satellites § Radio, Infrared, Cellular Radio, Mobile computing § GPS global positioning system text: O’Brien p 183 - 186
Media and Channels § Signals Medium Metal wire Microwave Fiber optics § analog § digital § Cables § Twisted-pair § Coaxial cable Transmission speed. 0012 Mbps - 10 Mbps. 256 Mbps - 100 Mbps. 5 Mbps - 1, 000 Mbps interference 20 x more expensive 5. 500 simultaneous phone calls § Fiber-optic 1 fiber 30. 000 phone calls § Wireless § microwave § satellites § Radio, Infrared, Cellular Radio, Mobile computing § GPS global positioning system text: O’Brien p 183 - 186
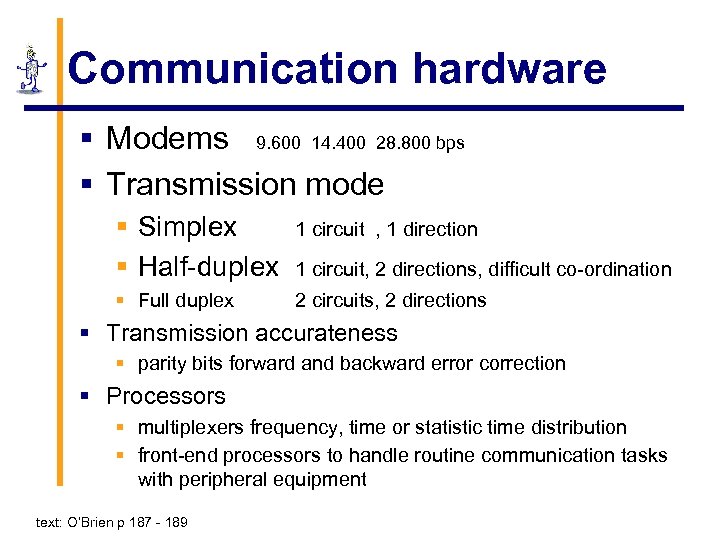 Communication hardware § Modems 9. 600 14. 400 28. 800 bps § Transmission mode § Simplex § Half-duplex 1 circuit , 1 direction § Full duplex 2 circuits, 2 directions 1 circuit, 2 directions, difficult co-ordination § Transmission accurateness § parity bits forward and backward error correction § Processors § multiplexers frequency, time or statistic time distribution § front-end processors to handle routine communication tasks with peripheral equipment text: O’Brien p 187 - 189
Communication hardware § Modems 9. 600 14. 400 28. 800 bps § Transmission mode § Simplex § Half-duplex 1 circuit , 1 direction § Full duplex 2 circuits, 2 directions 1 circuit, 2 directions, difficult co-ordination § Transmission accurateness § parity bits forward and backward error correction § Processors § multiplexers frequency, time or statistic time distribution § front-end processors to handle routine communication tasks with peripheral equipment text: O’Brien p 187 - 189
 Network Topology § Star § all communications go via the central system § Bus § can easily be extended at the ends § Ring § more secure
Network Topology § Star § all communications go via the central system § Bus § can easily be extended at the ends § Ring § more secure
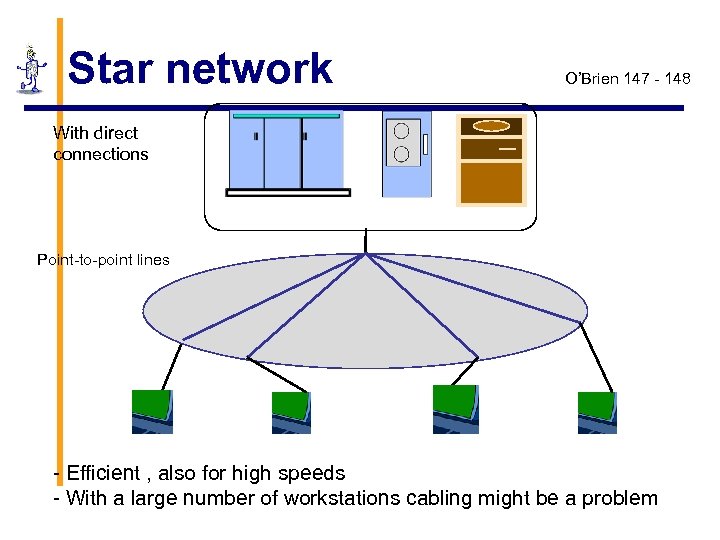 Star network O’Brien 147 - 148 With direct connections Point-to-point lines - Efficient , also for high speeds - With a large number of workstations cabling might be a problem
Star network O’Brien 147 - 148 With direct connections Point-to-point lines - Efficient , also for high speeds - With a large number of workstations cabling might be a problem
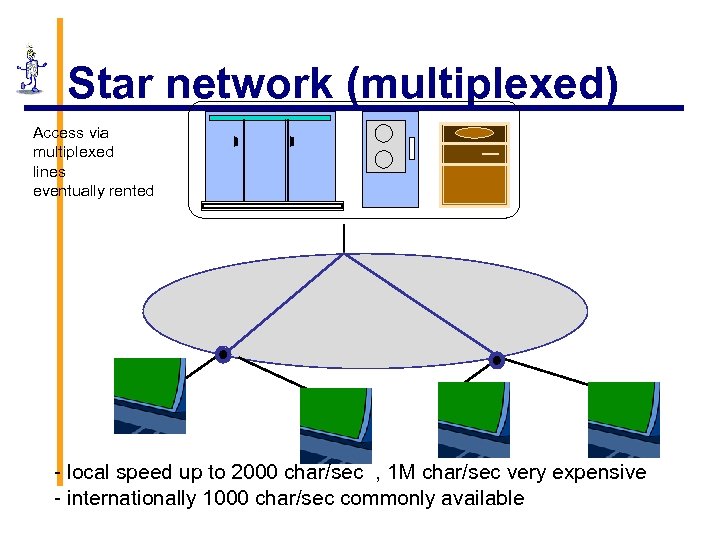 Star network (multiplexed) Access via multiplexed lines eventually rented - local speed up to 2000 char/sec , 1 M char/sec very expensive - internationally 1000 char/sec commonly available
Star network (multiplexed) Access via multiplexed lines eventually rented - local speed up to 2000 char/sec , 1 M char/sec very expensive - internationally 1000 char/sec commonly available
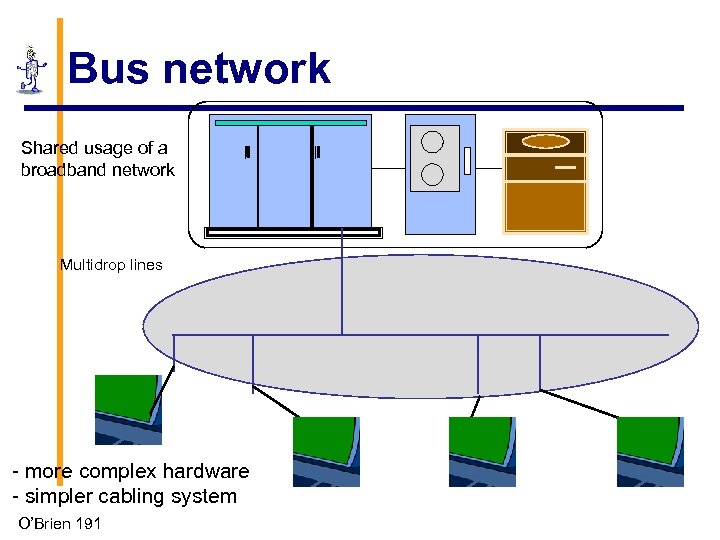 Bus network Shared usage of a broadband network Multidrop lines - more complex hardware - simpler cabling system O’Brien 191
Bus network Shared usage of a broadband network Multidrop lines - more complex hardware - simpler cabling system O’Brien 191
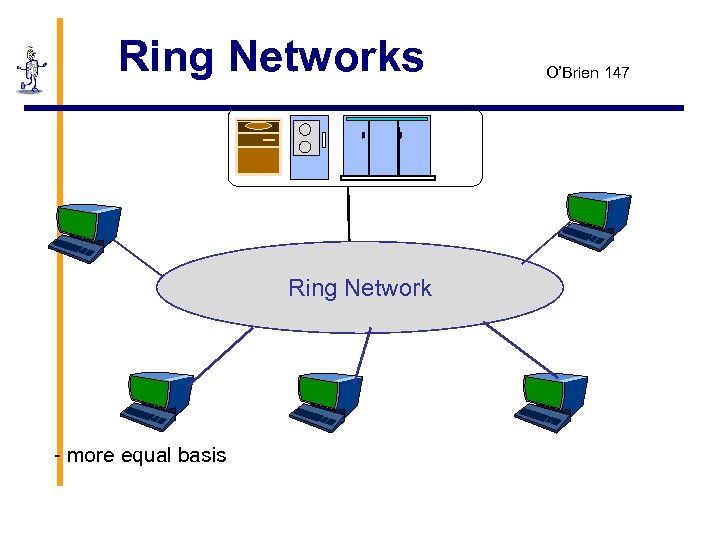 Ring Networks Ring Network - more equal basis O’Brien 147
Ring Networks Ring Network - more equal basis O’Brien 147
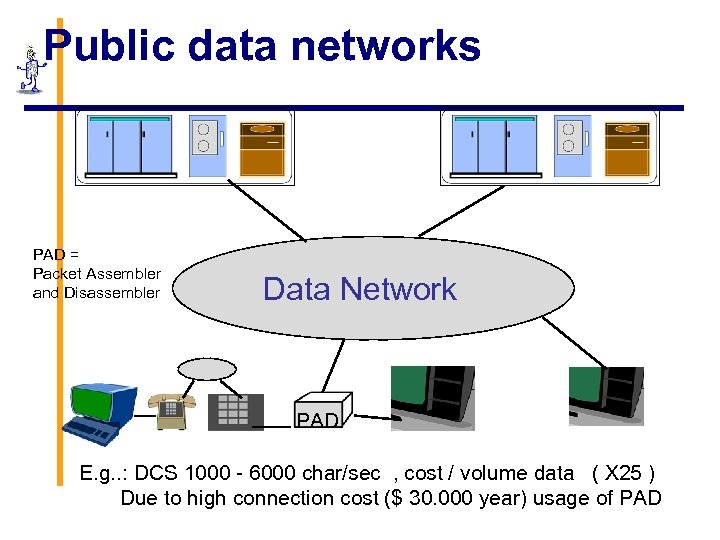 Public data networks PAD = Packet Assembler and Disassembler Data Network PAD E. g. . : DCS 1000 - 6000 char/sec , cost / volume data ( X 25 ) Due to high connection cost ($ 30. 000 year) usage of PAD
Public data networks PAD = Packet Assembler and Disassembler Data Network PAD E. g. . : DCS 1000 - 6000 char/sec , cost / volume data ( X 25 ) Due to high connection cost ($ 30. 000 year) usage of PAD
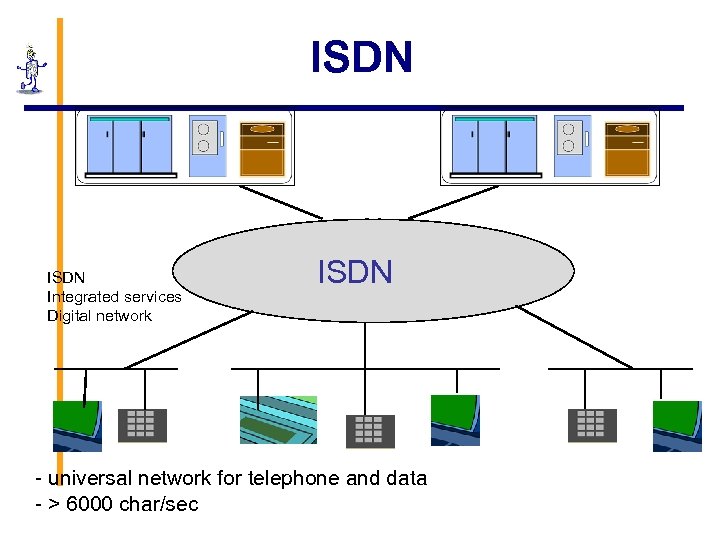 ISDN Integrated services Digital network ISDN - universal network for telephone and data - > 6000 char/sec
ISDN Integrated services Digital network ISDN - universal network for telephone and data - > 6000 char/sec
 Communication Systems th 13 lecture Chair of Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2008 49 | 51
Communication Systems th 13 lecture Chair of Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2008 49 | 51
 Textbook Overview § Web site: http: //www. wiley. com/college/englander § Part 1 (Chapter 1) § Computer system overview § Part 2 (Chapters 2 -5) § Number systems and data formats § Part 3 (Chapters 6 -12) § Computer architecture and hardware operation § Part 4 (Chapters 13 -18) § Software – operating systems, applications, development environments § Part 5 (Supplementary Chapters 1 -3) § Digital logic, addressing modes, and communication channel technology Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -50
Textbook Overview § Web site: http: //www. wiley. com/college/englander § Part 1 (Chapter 1) § Computer system overview § Part 2 (Chapters 2 -5) § Number systems and data formats § Part 3 (Chapters 6 -12) § Computer architecture and hardware operation § Part 4 (Chapters 13 -18) § Software – operating systems, applications, development environments § Part 5 (Supplementary Chapters 1 -3) § Digital logic, addressing modes, and communication channel technology Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -50
 § Text books (german): § Jochen Schiller, Mobilkommunikation § Bernhard Walke, Mobilfunknetze und ihre Protokolle, Grundlagen GSM, Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS), . . . § Link (see seminar slides and papers): § http: //www. ks. unifreiburg. de/download/papers/telsem. WS 05/ UMTS-next. Generation/UMTSSeminararbeit-Stefan%20 Nagy. pdf Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -51
§ Text books (german): § Jochen Schiller, Mobilkommunikation § Bernhard Walke, Mobilfunknetze und ihre Protokolle, Grundlagen GSM, Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS), . . . § Link (see seminar slides and papers): § http: //www. ks. unifreiburg. de/download/papers/telsem. WS 05/ UMTS-next. Generation/UMTSSeminararbeit-Stefan%20 Nagy. pdf Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -51
 §End Of Sessions Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -52
§End Of Sessions Chapter 1 Computer Systems 1 -52


