4ba8e587b3f5ede1e698da0851df701f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Musculoskeletal Management Upper Body Mark Shoring Practice Principle and Owner – Master Healthcare Head of School (Bioscience and Oriental Medicine) ECNH Acupuncturist, Herbalist, Musculoskeletal Therapist, Naturopath, Nutritionist Registered Chinese Herbal Medicine Practitioner (CMRB 1695) §Master of Acupuncture UWS §Master of Applied Science (Chinese Herbal Medicine) RMIT §Master of Health Science (Nutrition Medicine) UNE §Master of Health Science (Herbal Medicine) UNE §Graduate Certificate of Health Science (Human Nutrition – Sports Nutrition) Deakin §Graduate Certificate of Education (Higher Education) UQ §Bachelor of Health Science (Naturopathy) ACNM §Bachelor of Health Science (Acupuncture) ACNM §Bachelor of Health Science (Musculoskeletal Therapy) Endeavour §Certificate IV(Oriental Massage) ACNM §Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Internship Guangxi TCM University §Cert. IV A&WT Russo ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 1

Session Aim § § Discuss the multi-faceted components (and underlying mechanisms) that should be considered within the management cervical conditions; Outline and demonstrate key treatment approaches and suggest potential mechanisms necessary for the successful management of cervical conditions. Treatment approaches include: § Acupuncture § Traditional Acupuncture Approaches § AHSI Point Therapy § Chinese Herbal Medicine § Musculoskeletal Therapy § Massage § Dry Needling § Naturopathy § Nutritional Medicine § Western Herbal Medicine ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 2

Releasing Trigger / ASHI Points § Direct Pressure and Massage § Fillaform Needling § Dry needling § Acupuncture § Wet Needling § Biomesotherapy § Biopuncture § Activator Methods § Ingestible methods § Nutrition § Herbal Medicine ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 3

Ming Dynasty Needle Technique ‘Shao Shan Huo’ | Volcanic Fire Lift and Thrust: Emphasize thrust (reinforcing) Twist and Rotate: Small rotations (less than 90 o) (reinforcing) Nine or Six: Rotate nine times (reinforcing) Rapid & Slow: Lift slowly & gently, thrust quickly & forcefully Open & Closed: Close the hole after withdrawal (reinforcing) ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 4
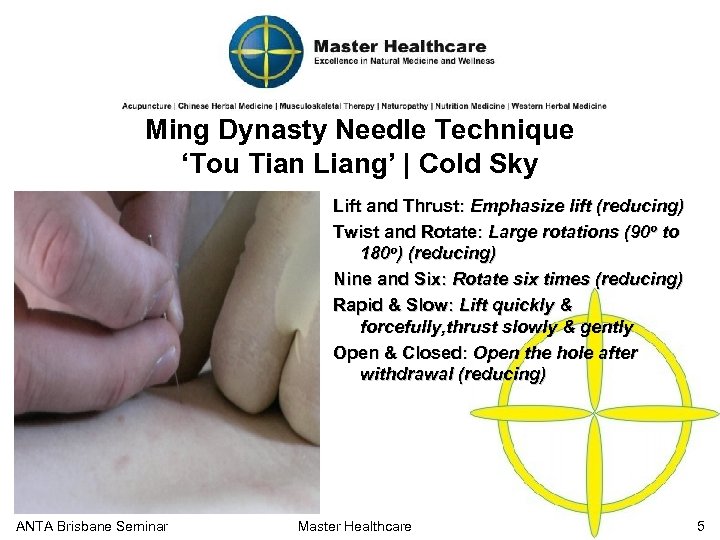
Ming Dynasty Needle Technique ‘Tou Tian Liang’ | Cold Sky Lift and Thrust: Emphasize lift (reducing) Twist and Rotate: Large rotations (90 o to 180 o) (reducing) Nine and Six: Rotate six times (reducing) Rapid & Slow: Lift quickly & forcefully, thrust slowly & gently Open & Closed: Open the hole after withdrawal (reducing) ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 5

Ming Dynasty Needle Technique “Green Dragon Wags His Tail” ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 6

Ming Dynasty Needle Technique “White Tiger Shakes his Head” ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 7
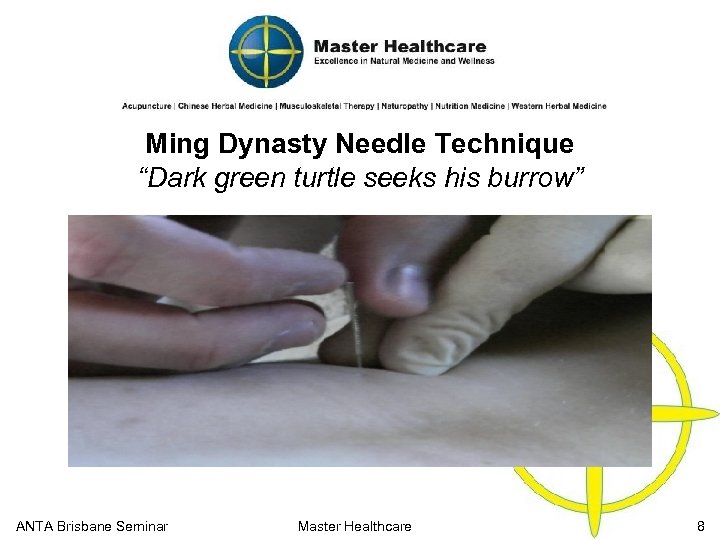
Ming Dynasty Needle Technique “Dark green turtle seeks his burrow” ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 8

Ming Dynasty Needle Technique “Red phoenix sores forth from the spring” ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 9

Review of Cervical Region Anatomy and Physiology (Tortora & Derrickson 2009) ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 10

Trigger Point Complex • The central trigger point (CTr. P) is found in the endplate zone and contains numerous electrically active loci, and contains numerous contraction knots (Simons et al 1998). • A taut band of muscle fibers extends from the trigger point to the attachment at each end of the involved fibers. The sustained tension that the taut band exerts on the attachment tissues can induce a localized enthesopathy that is identified as an attachment trigger point (ATr. P) (Simons et al 1998). • The local tenderness of the enthesopathy at the ATr. P is identified by a red circle with a black Master Healthcare border ANTA Brisbane Seminar 11

http: //www. univie. ac. at/cga/courses/be 522/emg/ Acetylcholine - Stored in vesicles in preparation for transmission Glucose Ca+ Sarcolemma P GLUT IV ATP ADP c. AMP + Coleus +Adenosine P Ca+ Channel Cholinerg ic Receptor Adenyl Cyclase - Mistletoe + Coleus, Mg Mg Protein Phosphodiesterase ATP IIII Kinase A ADP - Mistletoe +Mg Ca+ Mg Troponin C ATP ADP ANTA Brisbane Seminar Anaerobic Glycolysis P P Aerobic Calmodulin Phospholamban Glycolysis Sarcoplasmic Kinase II Reticulum +D, Mg ATP Master Healthcare 12

“Herbal Actions Commonly Utilized in MSK” Action Herbal Therapeutics (Bone 2003) Adaptogens Astralgalus, Siberian Ginseng, Gotu Kola, Korean Ginseng, Withania Analgesic Arnica (topically), Calfornia Poppy, Devil’s Claw, Kava, Pasque Flower Anti-Edematous Bilberry, Horsechestnut Anti-inflammatory Chamomile, Devil’s Claw, Prickely Ash Anti-Spasmodic Coleus, Cramp Bark, Kava Cardiotonic Astragalus. Coleus, Hawthorn, Korean Ginseng, Motherwort Circulatory Stimulant Ginkgo, Prickley Ash, Ginger Collagen Stabilizing Hawthorn ANTA Brisbane Seminar Hypotensive Master Healthcare Astragalus. Coleus, Hawthorn, Mistletoe, Motherwort, Olive 13

Lumbar Anatomy - Intervertebral Disc ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 14

Cervical Functional Anatomy: X-Ray ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 15
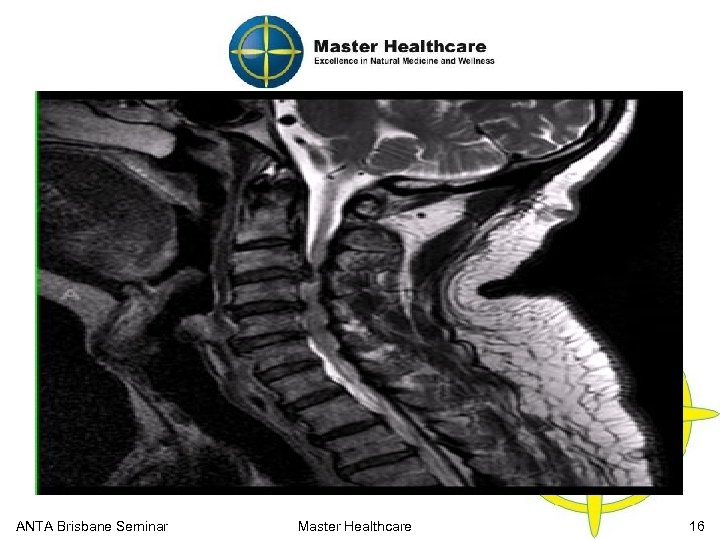
Cervical Functional Anatomy MRI Cervical Region (Disc Herniation) ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 16

Cervical Functional Anatomy X-Ray (Anterior View) ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 17
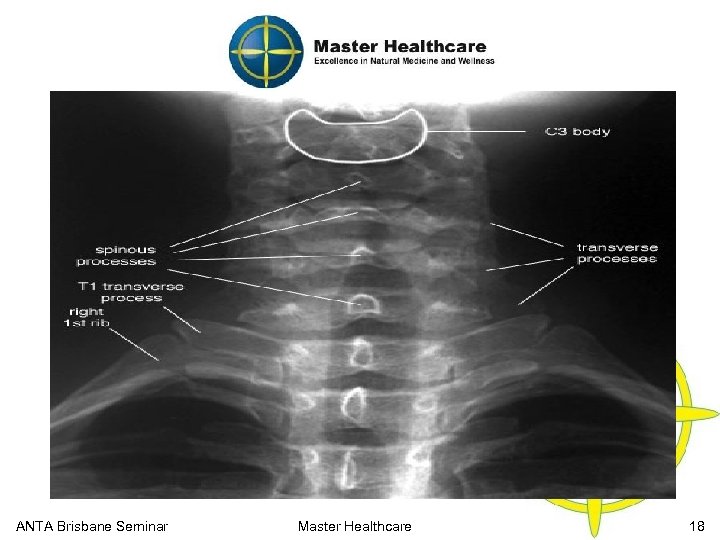
Cervical Functional Anatomy X-Ray (Posterior View) ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 18

Naturopathic Nutritional Approach Disc Dimensions and Composition § Nucleus Pulposus Constitiution: § 70 -90% Water § Glycosaminoglycans § Proteoglycans § Collagen § Annulus Fibrosis consists of 10 -20 concentric circles of collagen. § Collagen (type I and II) § Proteoglycan (Pedrini-Mille et al 1987) § 5% Elastin (Yu 2002) ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 19
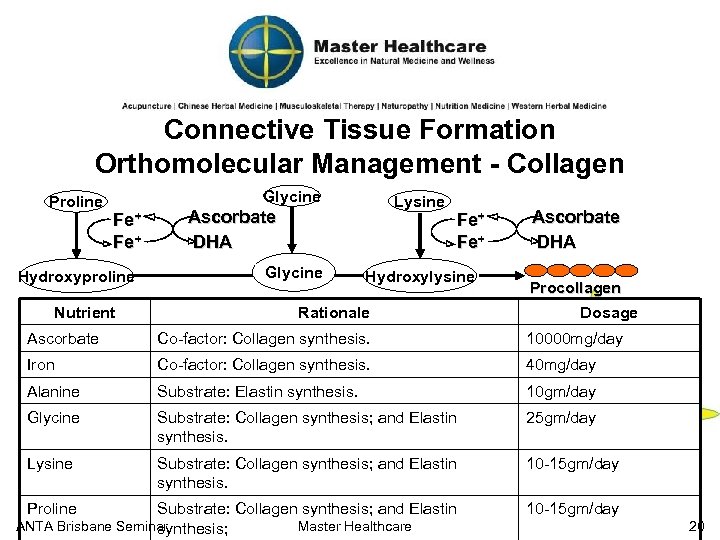
Connective Tissue Formation Orthomolecular Management - Collagen Proline Glycine Fe+ Hydroxyproline Nutrient Lysine Ascorbate DHA Glycine Fe+ Hydroxylysine Rationale Ascorbate DHA Procollagen Dosage Ascorbate Co-factor: Collagen synthesis. 10000 mg/day Iron Co-factor: Collagen synthesis. 40 mg/day Alanine Substrate: Elastin synthesis. 10 gm/day Glycine Substrate: Collagen synthesis; and Elastin synthesis. 25 gm/day Lysine Substrate: Collagen synthesis; and Elastin synthesis. 10 -15 gm/day Substrate: Collagen synthesis; and Elastin ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare synthesis; 10 -15 gm/day Proline 20
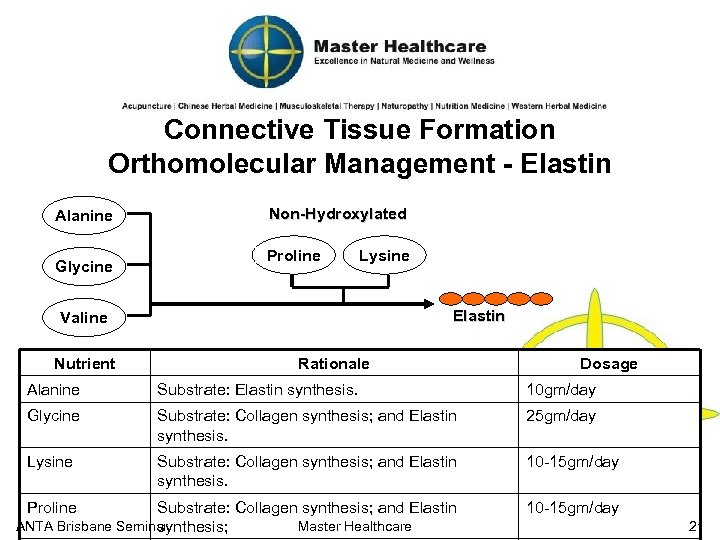
Connective Tissue Formation Orthomolecular Management - Elastin Alanine Glycine Non-Hydroxylated Proline Lysine Elastin Valine Nutrient Rationale Dosage Alanine Substrate: Elastin synthesis. 10 gm/day Glycine Substrate: Collagen synthesis; and Elastin synthesis. 25 gm/day Lysine Substrate: Collagen synthesis; and Elastin synthesis. 10 -15 gm/day Substrate: Collagen synthesis; and Elastin ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare synthesis; 10 -15 gm/day Proline 21

Bone Formation (Part I) § § Bone Constitution: § Minerals: Calcium (60 -66%), Magnesium (Gropper et al) § Water, Ground Substance & Protein (34 -40%) (Gropper et al 2005) K Bone-based Protein Constitution: Ca 2+ § Collagen (85 -90%) (Gropper et al 2005) Protein § Osteonectin (Gropper et al 2005) § Osteopontin (Gropper et al 2005) § Bone Sailoprotein (Gropper et al 2005) § Osteocalcin (Vitamin K Dependent) (Gropper et al 2005) § Matrix Gla protein (Vitamin K Master Healthcare ANTA Brisbane Seminar Bone 22
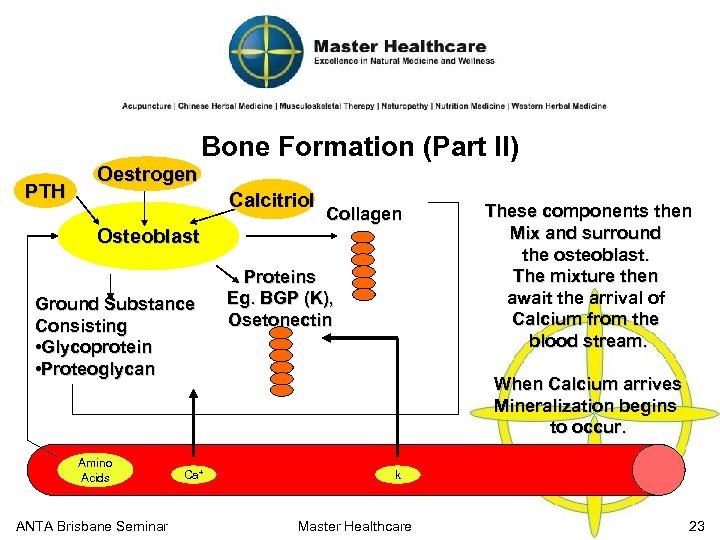
Bone Formation (Part II) PTH Oestrogen Calcitriol Collagen Osteoblast Ground Substance Consisting • Glycoprotein • Proteoglycan Amino Acids ANTA Brisbane Seminar Ca+ Proteins Eg. BGP (K), Osetonectin These components then Mix and surround the osteoblast. The mixture then await the arrival of Calcium from the blood stream. When Calcium arrives Mineralization begins to occur. k Master Healthcare 23

Chinese Herbal Formulae – Cervical Region § Gui Zhi Tang – Wry Neck | Neck Stiffness § 9 gm Gui Zhi (Cinnamon Twig) – Release exterior / warming / harmonize ying and wei § 9 gm Bai Shao (Paeonia lactifolia radix) – Harmonize ying and wei, stops spasms and pain § 9 gm Sheng Jiang (Ginger) – Release exterior / warming / harmonize ying and wei § 12 pcs Da Zao (Chinese Date) – Qi and Chinese Spleen (Digestive) Building § 6 gm Gan Cao (Licorice) – Harmonizing formulae, stops spasms and pain, reinforce qi and blood § Tao Hong Su Wu Tang – Acute Injury § 9 gm Tao Ren (Prunus persica – peach kernal) – IBC and stop pain § 7 gm Hong Hua (Carthamus flos – Safflower) – IBC and stop pain § 7 gm Shu Di (Rehmannia glutinosa root) – Tonify yin and blood § 7 gm Bai Shao (Paeonia lactiolia radix) – Harmonize ying and wei, stops spasms and pain ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 24

Chinese Herbal Formulae – Cervical Region § Shao Yao Gan Cao Tang - Nerve root pain § 20 gm Bai Shao (Paeonia lactifolia radix) – Harmonize ying and wei, stops spasms and pain § 10 gm Ge Gen (Puerariae radix) – Release exterior, muscle and clear heat, vent rash § 10 gm Xu Duan (Dipsaci radix) – Strengths sinews/bone, tonifies liver/kidney, regulates blood § 10 gm Ru Xiang (Olibanum gummi - Frankinscence) – IBC, moves qi, healing / inflammation § 10 gm Mo Yao (Myrrha commiphora – Myrrh) – IBC, reduces inflammation, reinforces healing § 6 gm Gan Cao (Licorice) – Harmonizing formulae, stops spasms and pain, reinforce qi and blood ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 25

Western Herbal Formulae – Cervical Region § 100 m. L Liquid Tincture – General neck pain and muscular tension Dosage: 10 -15 m. L BID § 40 m. L Devil’s Claw § 30 m. L Withania § 30 m. L Coleus § Herbal Cream Applied topically two times per day (Vitamin E Cream Base) § 10 m. L Cayenne § 15 m. L Mistletoe § 15 m. L Devil’s Claw ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 26

Treatment Approach Proposed 1. Determine the patients diagnosis; 1. Question patient (onset, pain type and duration, quality of life, agg, imp, etc); 2. Assess clinical findings (eg. x-ray, MRI, CT scans, etc) 3. Assess ROM (Range of Movement); 4. Determine the presence of ASHI / Trigger points (points to be needled/pressed/etc); 5. Consider potential mechanisms at play in the patient (biomechanics, pathology mechanisms, etc); 2. Provide hands on treatment; 3. Reassess clinical findings (eg. ROM and palpation post treatment); and 4. Provide further medications to manage condition. ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 27

Cervical Region Deadman et al 2007 ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 28
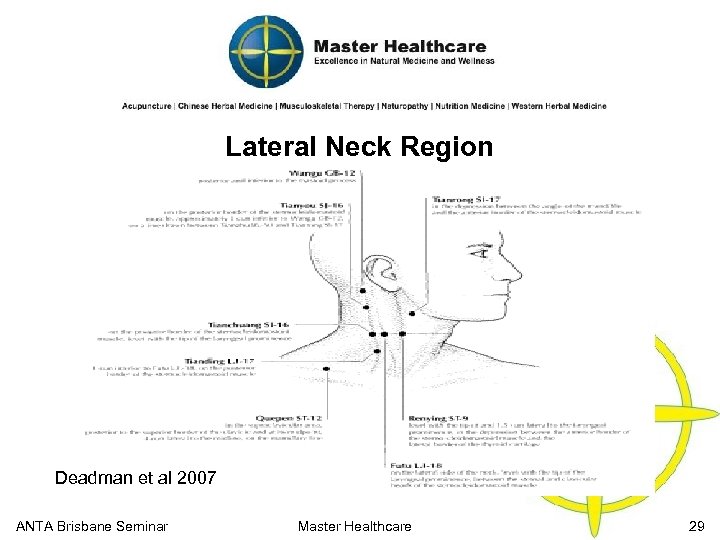
Lateral Neck Region Deadman et al 2007 ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 29
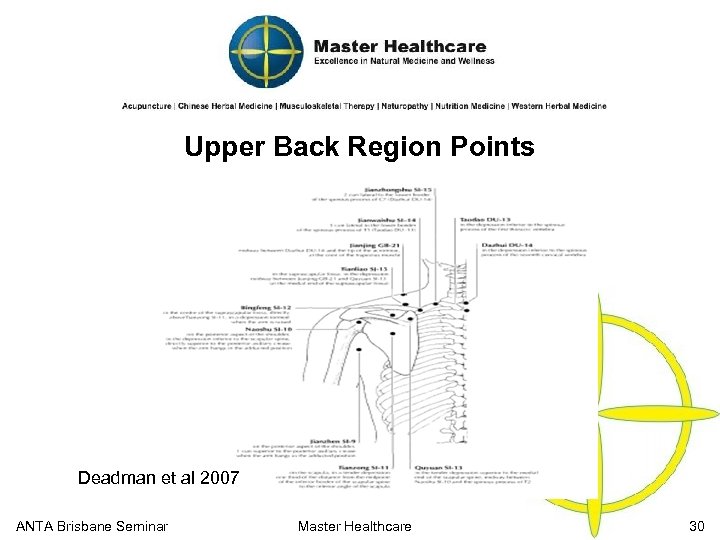
Upper Back Region Points Deadman et al 2007 ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 30

Back Region Deadman et al 2007 ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 31

Hua Tuo Jia Ji (extra points) ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 32

Key Trigger Points – Cervical Region § § § § § Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Scalene Muscle Trapezius Muscle Levator Scapulae Rhomboid Muscle Erector Spinae (group of muscles) Multifidus muscles Spinalis muscles Infraspinalis muscle Teres minor and major ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 33
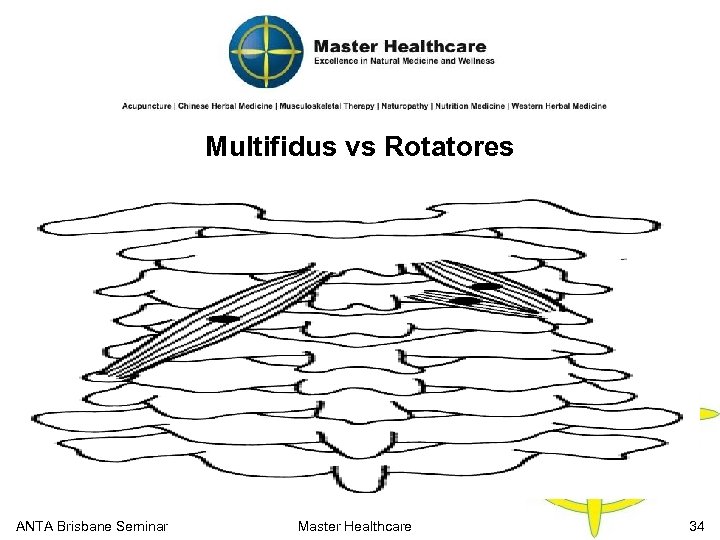
Multifidus vs Rotatores ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 34
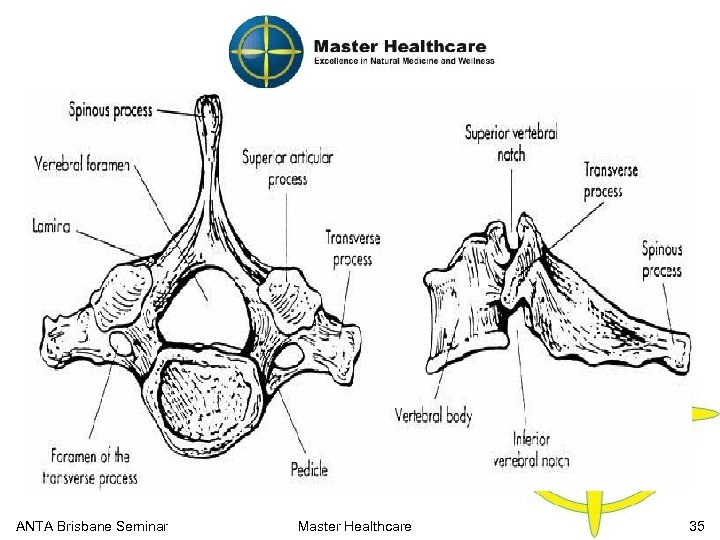
Cervical Spine Anatomy Vertebra ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 35
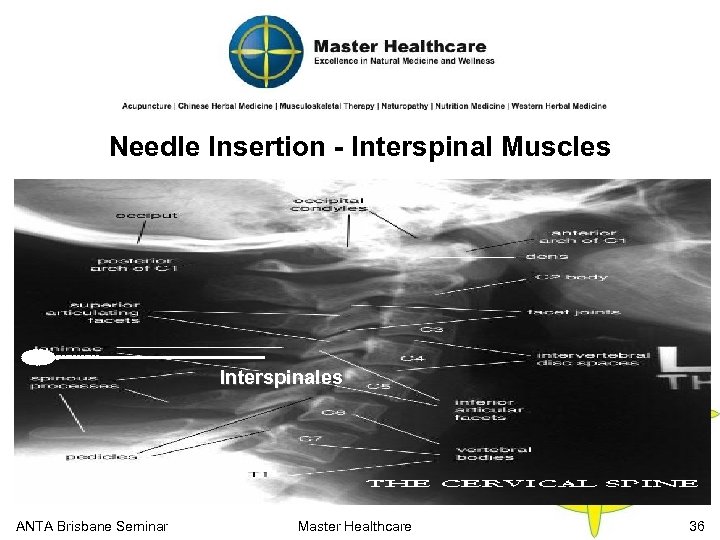
Needle Insertion - Interspinal Muscles Interspinales ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 36

References § § § § § § Bone, K. 2003. A Clinical Guide to Blending Liquid Herbs. Churchill Livingstone. London Borges, AC. Feres, T. Vianna, LM. Paiva, TB. 1999. Recovery of impaired K+ channels in mesenteric arteries from spontaneously hypertensive rats by prolonged treatment with cholecalciferol. British Journal of Pharmacology. 127(3): 772 -8 Burgos, RA. Aguila, MJ. Santiesteban, ET. Sanchez, NS. Hancke, JL. 2001. Andrographis paniculata (Ness) induces relaxation of uterus by blocking voltage operated calcium channels and inhibits Ca(+2) influx. Phytotherapy Research. 15(3): 235 -239 Cherif, S. Rahal, N. Haouala, M. Hizaoui, B. Dargoth, F. Gueddiche, M. Kallel, Z. Balansard, G. Boukef, K. 1996. A clinical trial of a titrated Olea extract in the treatment of essential arterial hypertension. Journal de pharmacie de Belgique. 51(2): 69 -71 Deliorman, D. Calis, I. Ergun, F. Dogan, BS. Buharalioglu, CK. Kanzik, I. 2000. Studies on the vascular effects of the fractions and phenolic compounds isolated from Viscum album ssp. album. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 72(1 -2): 323 -9 Dubey, MP. Srimal, RC. Nityanand, S. Dhawan, BN. 1981. Pharmacological Studies on Coleonol, a Hypotensive Diterpene from Coleus forskohlii. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 3(1): 113 Gropper, SS. Smith, JL. Groff, JL. 2005. Advanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism 4 th Edition. Wadsworth. Belmont Khayyal, MT. el-Ghazaly, MA. Abdullah, DM. Nassar, NN. Okpanyi, SN. Kreuter, MH. 2002. Blood pressure lowering effect of an olive leaf extract (Olea europaea) in L-NAME induced hypertension in rats. Arzneimittel-Forschung. 52(11): 797 -802 Kim, SH. Kang, KW. Kim, ND. 2000. Procyanidins in crataegus extract evoke endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in rat aorta. Life Science. 67(2): 121 -31 Militante, JD. Lombardini, JB. 2002. Treatment of hypertension with oral taurine: experimental and clinical studies. Amino Acids. 23(4): 381 -93 Nicholson, JA. Darby, TD. Jarboe, CH. 1972. Viopudial, a hypotensive and smooth muscle antispasmodic from Viburnum opulus. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 140(2): 457 -61 Shimosawa, T. Takano, K. Ando, K. Fujita, T. 2004. Magnesium inhibits noradrenaline release by blocking N—type Calcium Channels at peripheral sympathetic nerve endings. Hypertension. 44: 897 -902 Somova, LI. Shode, FO. Mipando, M. 2004. Cardiotonic and antidysrhythmic effects of oleanolic and ursolic acids, methyl maslinate and uvaol. Phytomedicine. 11(2 -3): 121 -9 Somova, LI. Shode, FO. Ramnanan, P. Nadar, A. 2003. Antihypertensive, antiatherosclerotic and antioxidant activity of triterpenoids isolated from Olea europaea, subspecies africana leaves. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 84(2 -3): 299 -305 Tenorio, FA. Del Valle, L. Gonzalez, A. Pastelin, G. 2005. Vasodilator activity of the aqueous extract of Viscum album. Fitoterapia. 76(2): 204 -9 Tenorio Lopez, FA. Del Valle Mondragon, L. Zarco Olvera, G. Torres Narvaez, JC. Pastelin Hernandez, G. 2006. Viscum album aqueous extract induces inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthases expression in isolated and perfused guinea pig heart. Evidence of the coronary vasodilation mechanism. Archivos de cardiología de México. 76(2): 130 -9 Venes, D. 2006. Taber’s Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary 20 th Edition. FA Davis Company. USA Walker, AF. Marakis, G. Morris, AP. Robinson, PA. 2002. Promising hypotensive effects of hawthorn extract: a randomized double blind pilot study of mild, essential hypertension. Phytotherapy Research. 16(1): 48 -54 Walker, AF. Marakis, G. Simpson, E. Hope, JL. Robinson, PA. Hassanein, M. Simpson, HC. 2006. Hypotensive effect of hawthorn for patients with diabetes taking prescription drugs: a randomized controlled trial. British journal of general practice. 56(527): 437 -43 Yamamoto, M. Jin, JJ. Wu, Z. Abe, M. Tabara, Y. Nagai, T. Yamasaki, E. Igase, M. Kohara, K. Miki, T. Nakura, J. 2006. Interaction between serotonin 2 A receptor and endothelin-1 variants in association with hypertension in Japanese. Hypertension Research. 29(4): 227 -32 Zhang, CY. Tan, BK. 1996. Hypotensive activity of aqueous extract of Andrographis paniculata in rats. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology. Zhang, CY. Kuroyangi, M. Tan, BK. 1998. Cardiovascular activity of 14 -deoxy-11, 12 -didehydroandrographolide in the anaesthetised rat and isolated right atria. Pharmacology Research. 38(6): 413 -7 Zhang, WD. Chen, H, Zhang, C. Liu, RH. Li, HL. Chen, HZ. 2006. Astragaloside IV from Astragalus membranaceus shows cardioprotection during myocardial ischemia in vivo and in vitro. Planta Medica. 72(1): 4 -8 Zhang, WD. Zhang, C. Wang, XH. Gao, PJ. Zhu, DL. Chen, H. Liu, RH. Li, HL. 2006. Astragaloside IV dilates aortic vessels from normal and spontaneously hypertensive rats through endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent ways. Planta Medica. 72(7): 621 -6 ANTA Brisbane Seminar Master Healthcare 37
4ba8e587b3f5ede1e698da0851df701f.ppt