0d8609edfa2f5167d0555e1cb14186cd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Municipal Department for the Promotion and Coordination of Women‘ s Issues – MA 57 Ricarda Götz 1
Municipal Department for the Promotion and Coordination of Women‘ s Issues – MA 57 Ricarda Götz 1
 • City of Vienna Women‘s department – Fem. Cities – Gender Equality Monitoring Report – Campaigns • How does the City of Vienna support worklife balance? 2
• City of Vienna Women‘s department – Fem. Cities – Gender Equality Monitoring Report – Campaigns • How does the City of Vienna support worklife balance? 2
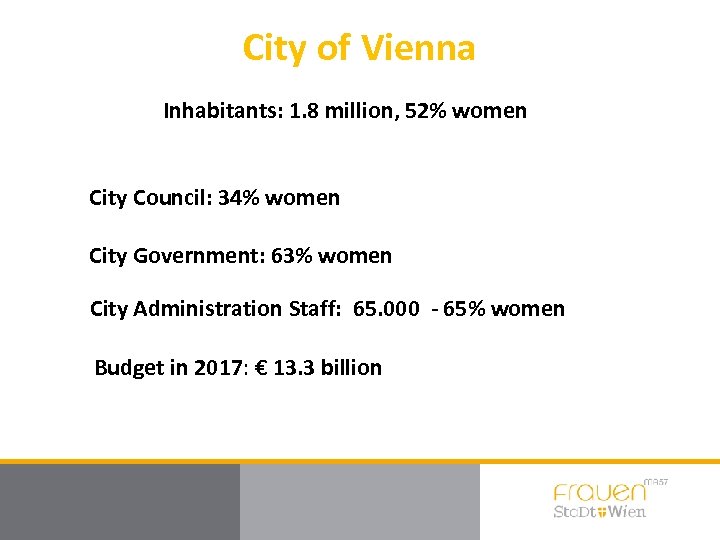 City of Vienna Inhabitants: 1. 8 million, 52% women City Council: 34% women City Government: 63% women City Administration Staff: 65. 000 - 65% women Budget in 2017: € 13. 3 billion
City of Vienna Inhabitants: 1. 8 million, 52% women City Council: 34% women City Government: 63% women City Administration Staff: 65. 000 - 65% women Budget in 2017: € 13. 3 billion
 Milestones: Gender in Vienna 1996 Vienna Equal Opportunities Act 2005 Gender Mainstreaming is established at the Chief Executive Office 2005 Gender Budgeting as integral part of the overall budgeting process 2006 Mayor Michael Häupl signs the European Charter for Equality of Women and Men in Local Life 2008 Laws and regulations have to be checked for conformity with equal opportunities 2010 pilot project: Public procurement must consider gender aspects and promotion of women
Milestones: Gender in Vienna 1996 Vienna Equal Opportunities Act 2005 Gender Mainstreaming is established at the Chief Executive Office 2005 Gender Budgeting as integral part of the overall budgeting process 2006 Mayor Michael Häupl signs the European Charter for Equality of Women and Men in Local Life 2008 Laws and regulations have to be checked for conformity with equal opportunities 2010 pilot project: Public procurement must consider gender aspects and promotion of women
 Goals of the Women‘s Department = Goals of the European Pillar of Social Rights Ø Empowerment of women and girls Ø Combatting gender-specific violence Ø Overcoming gender-specific stereotypes Ø Equal opportunities for women and men in society and on the labour market Ø Equal pay for women and men Ø MA 57: Sustained and secure funding for womenoriented projects and organisations 5
Goals of the Women‘s Department = Goals of the European Pillar of Social Rights Ø Empowerment of women and girls Ø Combatting gender-specific violence Ø Overcoming gender-specific stereotypes Ø Equal opportunities for women and men in society and on the labour market Ø Equal pay for women and men Ø MA 57: Sustained and secure funding for womenoriented projects and organisations 5
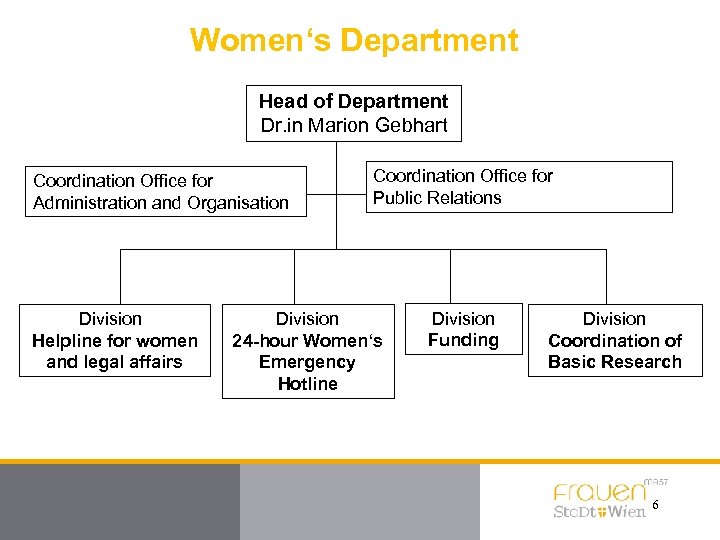 Women‘s Department Head of Department Dr. in Marion Gebhart Coordination Office for Administration and Organisation Division Helpline for women and legal affairs Coordination Office for Public Relations Division 24 -hour Women‘s Emergency Hotline Division Funding Division Coordination of Basic Research 6
Women‘s Department Head of Department Dr. in Marion Gebhart Coordination Office for Administration and Organisation Division Helpline for women and legal affairs Coordination Office for Public Relations Division 24 -hour Women‘s Emergency Hotline Division Funding Division Coordination of Basic Research 6
 Division: Basic Research • to develop concepts for gender equality within the city and for the public • to promote and implement projects in the field of research into women‘s issues and to commission studies • to process data for policy makers (statistics, information from NGOs) • to assess draft laws and make statements • to implement a gender-specific viewpoint as experts within the city administration and in working groups and networks • (international) networking and lobbying; Fem. Cities 7
Division: Basic Research • to develop concepts for gender equality within the city and for the public • to promote and implement projects in the field of research into women‘s issues and to commission studies • to process data for policy makers (statistics, information from NGOs) • to assess draft laws and make statements • to implement a gender-specific viewpoint as experts within the city administration and in working groups and networks • (international) networking and lobbying; Fem. Cities 7
 Current Projects • Fem. Cities • Gender Equality Monitoring Report • Sexist Advertisement Watch Group • Network against Antifeminism • Workshops for girls and young women • Campaigns, Manuals 8
Current Projects • Fem. Cities • Gender Equality Monitoring Report • Sexist Advertisement Watch Group • Network against Antifeminism • Workshops for girls and young women • Campaigns, Manuals 8
 9
9
 – networking for gender equality Foundation: in 1997 as MILENA network, from 2005: Fem. Cities = (informal) network of administrations in European cities and municipalities that aims to promote women and gender equality and share best practice examples www. femcities. at 10
– networking for gender equality Foundation: in 1997 as MILENA network, from 2005: Fem. Cities = (informal) network of administrations in European cities and municipalities that aims to promote women and gender equality and share best practice examples www. femcities. at 10
 – networking for gender equality Network partners = specialist departments in European cities and municipalities (in the field of gender equality/equal opportunities/women) Basel Stuttgart Graz Baden-Baden Frankfurt Bern Linz Baglar Zagreb Offenburg Marburg Sarajevo Klagenfurt Belgrade Vienna St. Pölten 11
– networking for gender equality Network partners = specialist departments in European cities and municipalities (in the field of gender equality/equal opportunities/women) Basel Stuttgart Graz Baden-Baden Frankfurt Bern Linz Baglar Zagreb Offenburg Marburg Sarajevo Klagenfurt Belgrade Vienna St. Pölten 11
 – networking for gender equality Fem. Cities activities: • Regular exchange of information and best practices • Publications • Annual international Fem. Cities conference – Latest in Vienna with the topic: Refugee Women • Periodic network meetings on gender equality issues • Implementation of the project „Fem. Cities Danube Region“ • Contact: femcities@femcities. at 12
– networking for gender equality Fem. Cities activities: • Regular exchange of information and best practices • Publications • Annual international Fem. Cities conference – Latest in Vienna with the topic: Refugee Women • Periodic network meetings on gender equality issues • Implementation of the project „Fem. Cities Danube Region“ • Contact: femcities@femcities. at 12
 Gender Equality Monitoring Report 13
Gender Equality Monitoring Report 13
 Gender Equality Monitoring Report Vienna • first published in 2014, then periodically after 3 years • makes the degree of equality between women and men in Vienna measurable and visible • based on (periodically) available empirical data è development of the monitor in a cross-departmental, multistage process è Communicating of results: within municipal departments and in public workshops (“Dialogforen”) with different target groups http: //www. gleichstellungsmonitor. at/ 14
Gender Equality Monitoring Report Vienna • first published in 2014, then periodically after 3 years • makes the degree of equality between women and men in Vienna measurable and visible • based on (periodically) available empirical data è development of the monitor in a cross-departmental, multistage process è Communicating of results: within municipal departments and in public workshops (“Dialogforen”) with different target groups http: //www. gleichstellungsmonitor. at/ 14
 - 12 Topics women and men in Vienna health political participation education and training paid and unpaid work leisure time and sports art and media income poverty and social security housing and public space environment and mobility violence Based on previously defined equality objectives, a set of 123 equality indicators was developed in a discursive process. They are arranged into 12 topics Based on existing data Focus 2016: women with migration background 15
- 12 Topics women and men in Vienna health political participation education and training paid and unpaid work leisure time and sports art and media income poverty and social security housing and public space environment and mobility violence Based on previously defined equality objectives, a set of 123 equality indicators was developed in a discursive process. They are arranged into 12 topics Based on existing data Focus 2016: women with migration background 15
 Question What is the percentage of children between 3 -5 years old who are in child care? 38 % 67 % 93 % 16
Question What is the percentage of children between 3 -5 years old who are in child care? 38 % 67 % 93 % 16
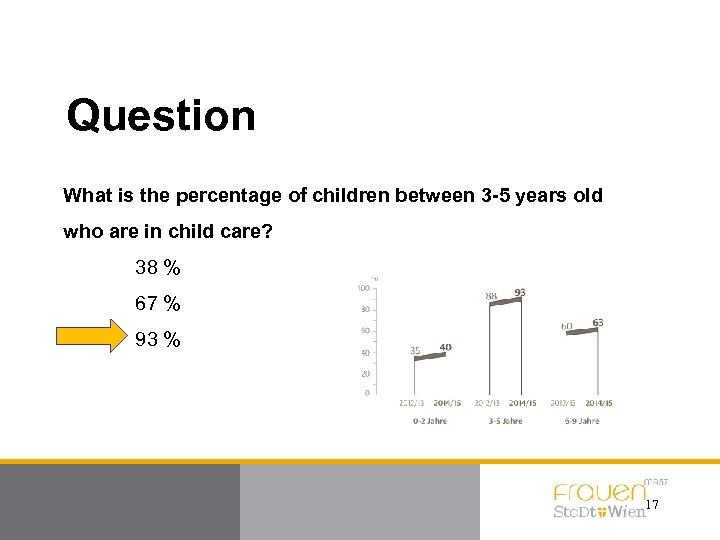 Question What is the percentage of children between 3 -5 years old who are in child care? 38 % 67 % 93 % 17
Question What is the percentage of children between 3 -5 years old who are in child care? 38 % 67 % 93 % 17
 Question How much time do women use (on average) for unpaid work (house- and family work) ? 5 -6 hours 3 -4 hours 1 -2 hours 18
Question How much time do women use (on average) for unpaid work (house- and family work) ? 5 -6 hours 3 -4 hours 1 -2 hours 18
 Question How much time do women use (on average) for unpaid work (house- and family work) ? 5 -6 hours 3 -4 hours 1 -2 hours Gender equality goal: improved reconciliation of private and professional life, redistribution of unpaid work (section paid and unpaid work) 19
Question How much time do women use (on average) for unpaid work (house- and family work) ? 5 -6 hours 3 -4 hours 1 -2 hours Gender equality goal: improved reconciliation of private and professional life, redistribution of unpaid work (section paid and unpaid work) 19
 Campaigns, Manuals etc. • Campaigns to increase - the amount of male day care teachers - the share of fathers taking paternal leave - Distributional justice (4 hands, 4 walls) 92% women and 74% men do unpaid work • Manuals for - The promotion of Women in Enterprises - Flexible Work Arrangements - Avoiding Sexual Harassment at the Workplace - Tipps for salary negotiations 20
Campaigns, Manuals etc. • Campaigns to increase - the amount of male day care teachers - the share of fathers taking paternal leave - Distributional justice (4 hands, 4 walls) 92% women and 74% men do unpaid work • Manuals for - The promotion of Women in Enterprises - Flexible Work Arrangements - Avoiding Sexual Harassment at the Workplace - Tipps for salary negotiations 20
 How does Vienna support work-life balance? • Care facilities – „Free Kindergarten“ – Older people and/or with special needs • • Sensitive public planning High level of Safety Safe work environment Implementation of Gender Budgeting 21
How does Vienna support work-life balance? • Care facilities – „Free Kindergarten“ – Older people and/or with special needs • • Sensitive public planning High level of Safety Safe work environment Implementation of Gender Budgeting 21
 Free Child Care/ Kindergarten • The organisation of public day care facilities falls under the jurisdiction of the individual provinces in Austria. The degree of care, hours of operation, and costs can therefore vary accordingly • Childcare in Vienna is free of charge for children up to 6 years of age (20 hours a week without lunch) • Afterschool care fees for pupils are graded according to family income • Children’s daycare centres in Vienna provide a vast offer and family-friendly opening hours (6: 30 – 18: 00) 22
Free Child Care/ Kindergarten • The organisation of public day care facilities falls under the jurisdiction of the individual provinces in Austria. The degree of care, hours of operation, and costs can therefore vary accordingly • Childcare in Vienna is free of charge for children up to 6 years of age (20 hours a week without lunch) • Afterschool care fees for pupils are graded according to family income • Children’s daycare centres in Vienna provide a vast offer and family-friendly opening hours (6: 30 – 18: 00) 22
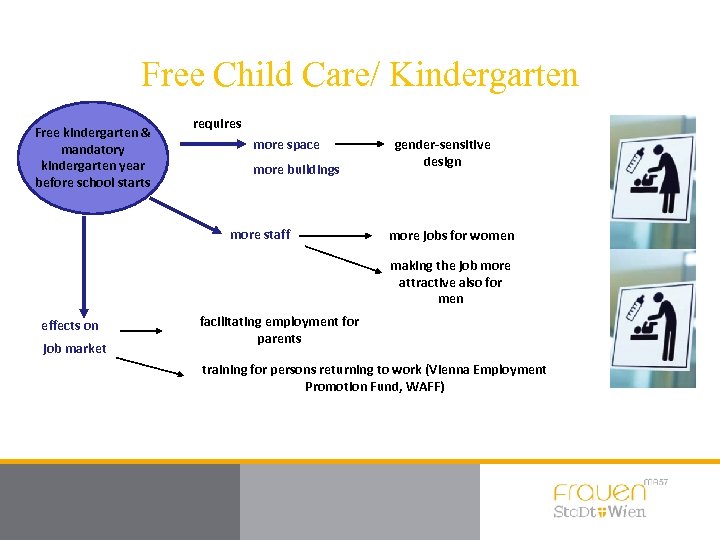 Free Child Care/ Kindergarten Free kindergarten & mandatory kindergarten year before school starts requires more space more buildings more staff gender-sensitive design more jobs for women making the job more attractive also for men effects on job market facilitating employment for parents training for persons returning to work (Vienna Employment Promotion Fund, WAFF)
Free Child Care/ Kindergarten Free kindergarten & mandatory kindergarten year before school starts requires more space more buildings more staff gender-sensitive design more jobs for women making the job more attractive also for men effects on job market facilitating employment for parents training for persons returning to work (Vienna Employment Promotion Fund, WAFF)
 • • • You have the choice between: Public Day Care Private Day Care for Employees’ children Day Care at Universities + • Afternoon Care of School-Age Children 24
• • • You have the choice between: Public Day Care Private Day Care for Employees’ children Day Care at Universities + • Afternoon Care of School-Age Children 24
 Sensitive city/public planning 25
Sensitive city/public planning 25
 Gender Mainstreaming = a schoolyard of opportunities for all 26
Gender Mainstreaming = a schoolyard of opportunities for all 26
 Public lighting – Gender Mainstreaming Example: Resselpark at Karlsplatz 27
Public lighting – Gender Mainstreaming Example: Resselpark at Karlsplatz 27
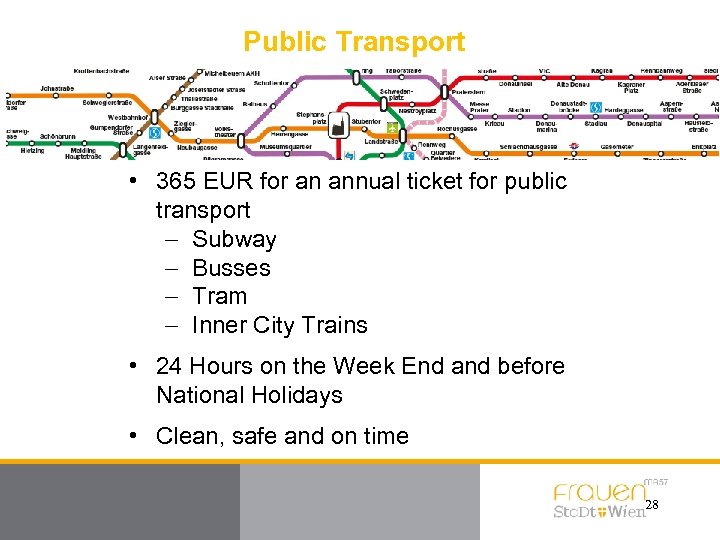 Public Transport • 365 EUR for an annual ticket for public transport - Subway - Busses - Tram - Inner City Trains • 24 Hours on the Week End and before National Holidays • Clean, safe and on time 28
Public Transport • 365 EUR for an annual ticket for public transport - Subway - Busses - Tram - Inner City Trains • 24 Hours on the Week End and before National Holidays • Clean, safe and on time 28
 The City´s Gender Network Municipal Department for the Promotion and Coordination of Women’s Issues Municipal Department for Economic Affairs, Labour and Statistics, expert on Gender Statistics Vienna Business Agency Chief Executive Office; Section Gender Mainstreaming Vienna Employment Promotion Fund Municipal Department for Health Care and Social Welfare Planning, Women‘s Health Group Equal Opportunities Advisors Municipal Departement for Financial Affairs, Division Gender Budgeting Executive Group for Construction and Technology Expertise for gender-sensitive Planning and Engineering
The City´s Gender Network Municipal Department for the Promotion and Coordination of Women’s Issues Municipal Department for Economic Affairs, Labour and Statistics, expert on Gender Statistics Vienna Business Agency Chief Executive Office; Section Gender Mainstreaming Vienna Employment Promotion Fund Municipal Department for Health Care and Social Welfare Planning, Women‘s Health Group Equal Opportunities Advisors Municipal Departement for Financial Affairs, Division Gender Budgeting Executive Group for Construction and Technology Expertise for gender-sensitive Planning and Engineering
 Gender Budgeting 30
Gender Budgeting 30
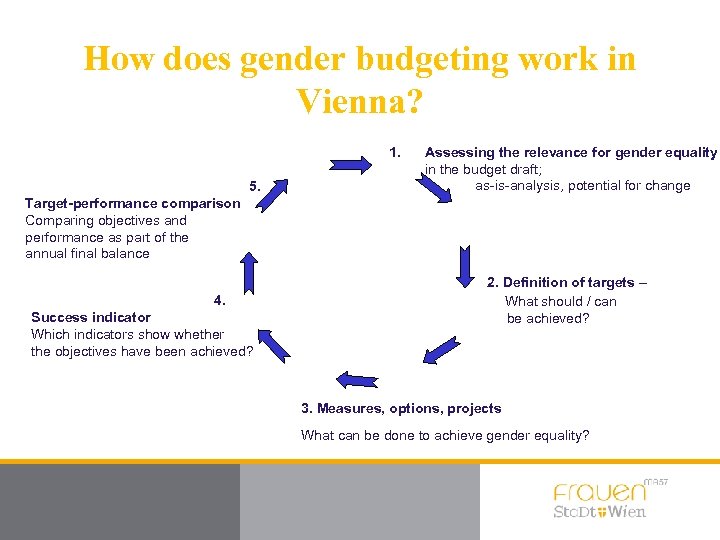 How does gender budgeting work in Vienna? 1. 5. Assessing the relevance for gender equality in the budget draft; as-is-analysis, potential for change Target-performance comparison Comparing objectives and performance as part of the annual final balance 4. Success indicator Which indicators show whether the objectives have been achieved? 2. Definition of targets – What should / can be achieved? 3. Measures, options, projects What can be done to achieve gender equality?
How does gender budgeting work in Vienna? 1. 5. Assessing the relevance for gender equality in the budget draft; as-is-analysis, potential for change Target-performance comparison Comparing objectives and performance as part of the annual final balance 4. Success indicator Which indicators show whether the objectives have been achieved? 2. Definition of targets – What should / can be achieved? 3. Measures, options, projects What can be done to achieve gender equality?
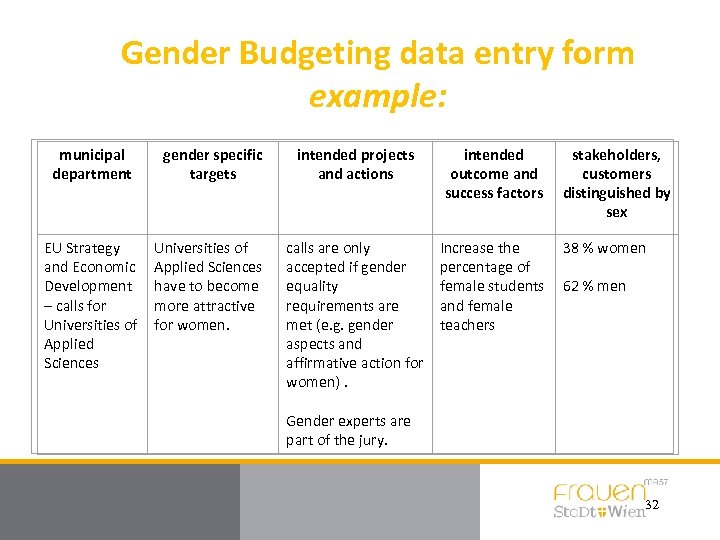 Gender Budgeting data entry form example: municipal department gender specific targets intended projects and actions intended outcome and success factors EU Strategy and Economic Development – calls for Universities of Applied Sciences have to become more attractive for women. calls are only accepted if gender equality requirements are met (e. g. gender aspects and affirmative action for women). Increase the percentage of female students and female teachers stakeholders, customers distinguished by sex 38 % women 62 % men Gender experts are part of the jury. 32
Gender Budgeting data entry form example: municipal department gender specific targets intended projects and actions intended outcome and success factors EU Strategy and Economic Development – calls for Universities of Applied Sciences have to become more attractive for women. calls are only accepted if gender equality requirements are met (e. g. gender aspects and affirmative action for women). Increase the percentage of female students and female teachers stakeholders, customers distinguished by sex 38 % women 62 % men Gender experts are part of the jury. 32
 How can we all proceed? 1. Clear political will lobbying and campaigns, gender trainings 2. Making gender differences visible: research and information, gender senstitive data 3. Implementing an equality support structure 4. Setting up an efficient reporting and controlling system: gender budgeting, quality management, gender check for legislation 5. Taking action setting up pilot projects and mainstream results and experience
How can we all proceed? 1. Clear political will lobbying and campaigns, gender trainings 2. Making gender differences visible: research and information, gender senstitive data 3. Implementing an equality support structure 4. Setting up an efficient reporting and controlling system: gender budgeting, quality management, gender check for legislation 5. Taking action setting up pilot projects and mainstream results and experience
 Ricarda Götz, MA Division for the Coordination of Basic Research Deputy coordinator Fem. Cities Coordinator Gender Equality Monitoring Report City of Vienna, Department for the Promotion and Coordination of Women´s Issues Friedrich-Schmidt-Platz 3 1082 Vienna Phone: +43 1 4000 83531 Ricarda. goetz@wien. gv. at 34
Ricarda Götz, MA Division for the Coordination of Basic Research Deputy coordinator Fem. Cities Coordinator Gender Equality Monitoring Report City of Vienna, Department for the Promotion and Coordination of Women´s Issues Friedrich-Schmidt-Platz 3 1082 Vienna Phone: +43 1 4000 83531 Ricarda. goetz@wien. gv. at 34


