6dcf7e2ca3d02c6d6015a27c6e7c520f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Multistep microsatellite mutation in the maternally transmitted locus D 13 S 317: a case of maternal allele mismatch in the child Devinder Singh Negi. Mahfooz Alam. S. Annapurna Bhavani. Javaregowda Nagaraju Present by… Nonglak Sinkhan ID 51312307
Multistep microsatellite mutation in the maternally transmitted locus D 13 S 317: a case of maternal allele mismatch in the child Devinder Singh Negi. Mahfooz Alam. S. Annapurna Bhavani. Javaregowda Nagaraju Present by… Nonglak Sinkhan ID 51312307
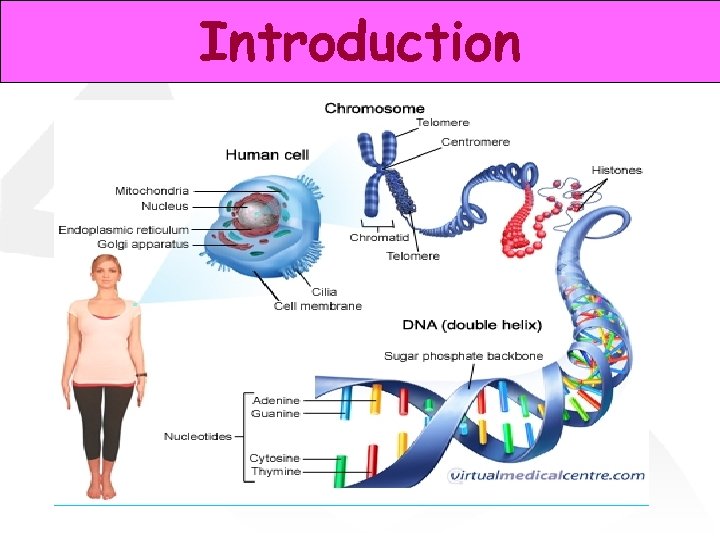 Introduction
Introduction
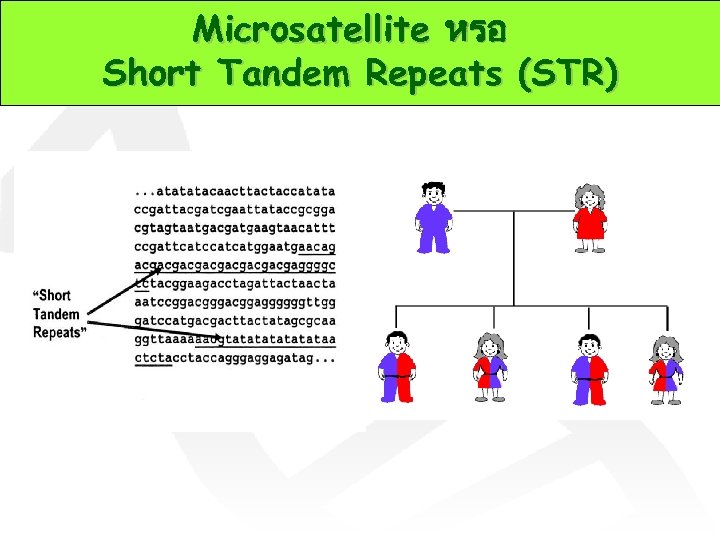 Microsatellite หรอ Short Tandem Repeats (STR)
Microsatellite หรอ Short Tandem Repeats (STR)
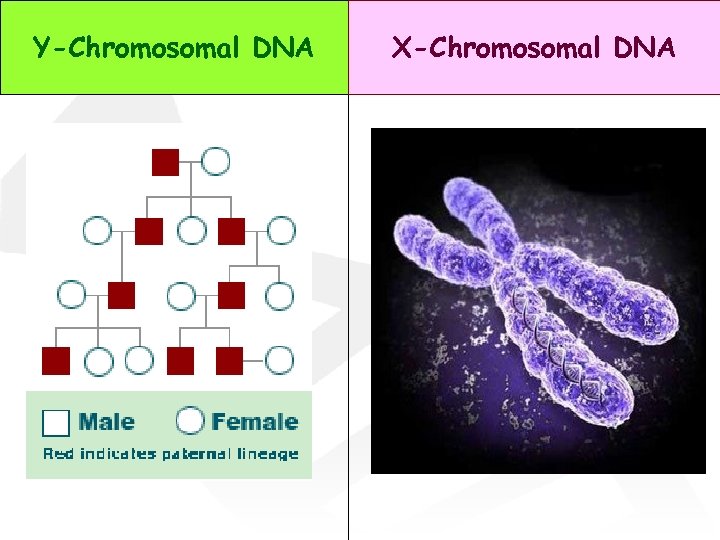 Y-Chromosomal DNA X-Chromosomal DNA
Y-Chromosomal DNA X-Chromosomal DNA
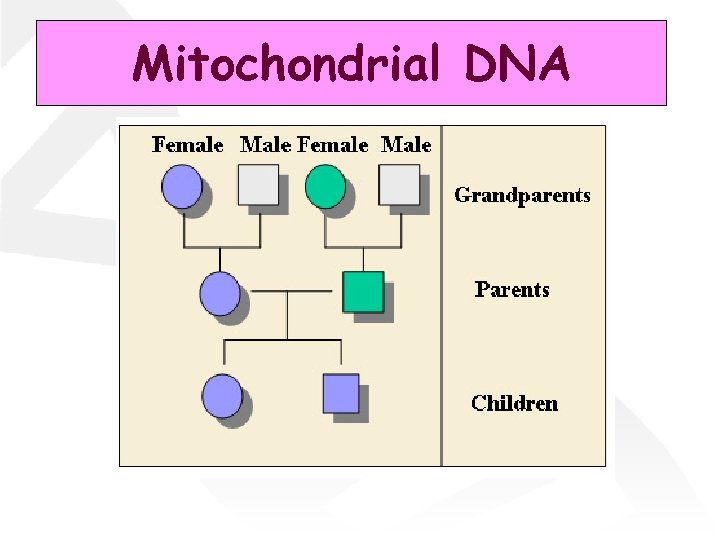 Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA
 Microsatellite mutation
Microsatellite mutation
 Purpose
Purpose
 Materials Ø Sample Blood samples at the Laboratory of DNA Fingerprinting Services of Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics, Hyderabad, India
Materials Ø Sample Blood samples at the Laboratory of DNA Fingerprinting Services of Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics, Hyderabad, India
 Method
Method
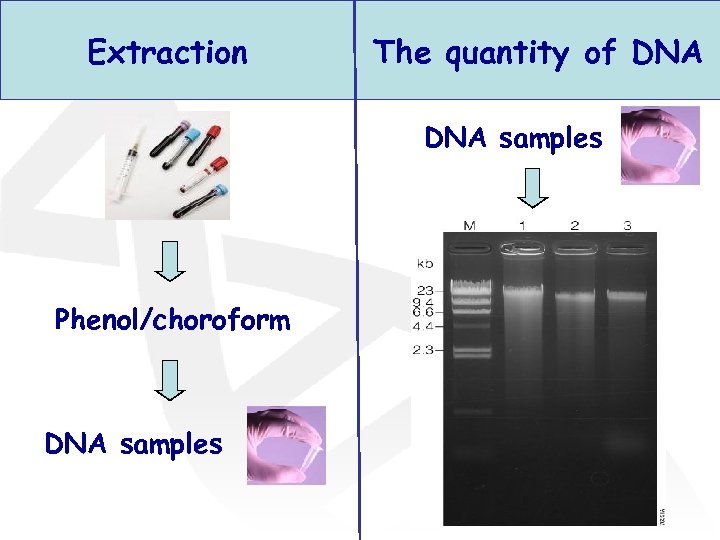 Extraction The quantity of DNA samples Phenol/choroform DNA samples
Extraction The quantity of DNA samples Phenol/choroform DNA samples
 Amplification Ø STR Amp. Fl. STR Profiler Plus, Identifiler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA) Power. Plex (Promega Corporation, Wisconsin, USA) Ø X chromosome published primer sequences Ø Mitochondrial DNA hypervariable regions HV 1 and. HV 2 published primer sequences
Amplification Ø STR Amp. Fl. STR Profiler Plus, Identifiler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA) Power. Plex (Promega Corporation, Wisconsin, USA) Ø X chromosome published primer sequences Ø Mitochondrial DNA hypervariable regions HV 1 and. HV 2 published primer sequences
 Amplification 50 -ng DNA 200 -µM d. NTPs 6 pmol primer 2. 5 -U Ampli. Taq Gold 1 x. PCR buffer 1. 5 -m. MMg. Cl 2
Amplification 50 -ng DNA 200 -µM d. NTPs 6 pmol primer 2. 5 -U Ampli. Taq Gold 1 x. PCR buffer 1. 5 -m. MMg. Cl 2
 PCR Thermal cycling condition : Denaturation Annealing 50ºC ถง 55 ºC Extension ABI Gene. Amp PCR system 9700 ) Perkin 90ºC ถง 95ºC 70 °C ถง 75 ºC
PCR Thermal cycling condition : Denaturation Annealing 50ºC ถง 55 ºC Extension ABI Gene. Amp PCR system 9700 ) Perkin 90ºC ถง 95ºC 70 °C ถง 75 ºC
 Gene. Scan and genotyping ABI PRISM® 3100 Automated Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA)
Gene. Scan and genotyping ABI PRISM® 3100 Automated Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA)
 Sequencing of D 13 S 317 alleles DNA samples of the suspiciousfather, mother and questioned child PCR allelic product of D 13 S 317 locus purified 6% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) Eluted from the gel Elution buffer (0. 5 M ammonium acetate, 1 -m. MEDTA, p. H 8. 0) precipitated 100% ethanol
Sequencing of D 13 S 317 alleles DNA samples of the suspiciousfather, mother and questioned child PCR allelic product of D 13 S 317 locus purified 6% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) Eluted from the gel Elution buffer (0. 5 M ammonium acetate, 1 -m. MEDTA, p. H 8. 0) precipitated 100% ethanol
 Sequencing of D 13 S 317 alleles The purified products Run on ABI 3100 Automated Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA)
Sequencing of D 13 S 317 alleles The purified products Run on ABI 3100 Automated Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA)
 Sequencing with HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria PCR product of HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria purified 1 U of shrimp alkaline phosphatase (MBI Fermentas, USA) 37ºC for 15 min 2 U of exonuclease I (NEB, USA) 80ºC for 15 min The purified products quantified electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel
Sequencing with HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria PCR product of HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria purified 1 U of shrimp alkaline phosphatase (MBI Fermentas, USA) 37ºC for 15 min 2 U of exonuclease I (NEB, USA) 80ºC for 15 min The purified products quantified electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel
 Sequencing with HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria 50 -ng DNA of each of the purified products Big-Dye Terminator )Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA) kit forward primers of HV 1 and HV 2 mitochondrial regions PCR products precipitated 100% ethanol wash 70% ethanol
Sequencing with HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria 50 -ng DNA of each of the purified products Big-Dye Terminator )Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA) kit forward primers of HV 1 and HV 2 mitochondrial regions PCR products precipitated 100% ethanol wash 70% ethanol
 Sequencing with HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria The purified products Run on ABI 3100 Automated Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA)
Sequencing with HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria The purified products Run on ABI 3100 Automated Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA)
 Results
Results
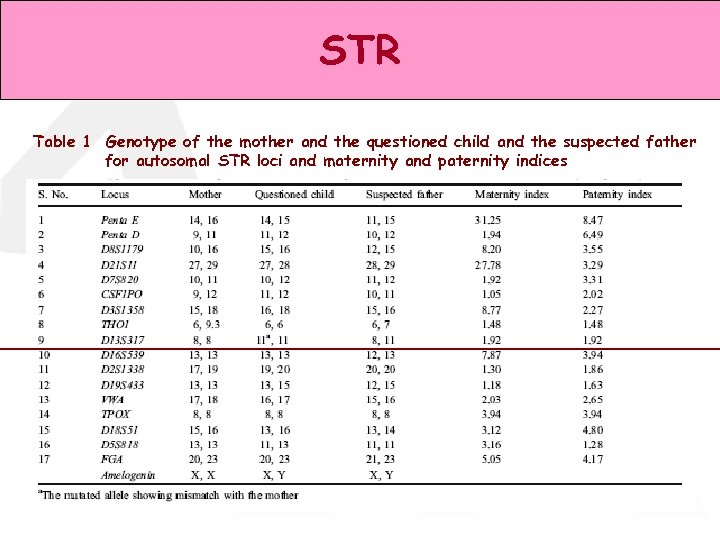 STR Table 1 Genotype of the mother and the questioned child and the suspected father for autosomal STR loci and maternity and paternity indices
STR Table 1 Genotype of the mother and the questioned child and the suspected father for autosomal STR loci and maternity and paternity indices
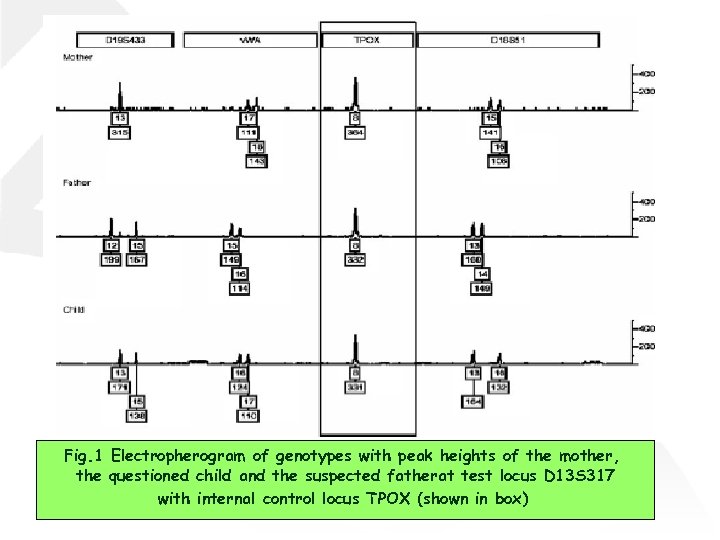 Fig. 1 Electropherogram of genotypes with peak heights of the mother, the questioned child and the suspected fatherat test locus D 13 S 317 with internal control locus TPOX (shown in box)
Fig. 1 Electropherogram of genotypes with peak heights of the mother, the questioned child and the suspected fatherat test locus D 13 S 317 with internal control locus TPOX (shown in box)
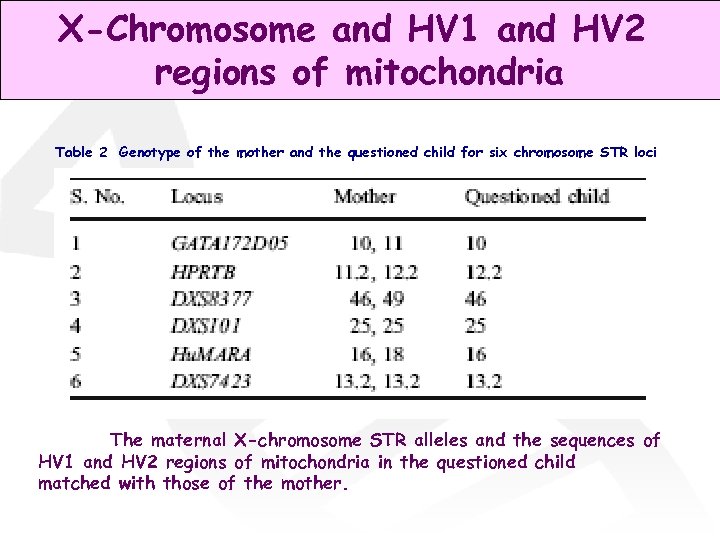 X-Chromosome and HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria Table 2 Genotype of the mother and the questioned child for six chromosome STR loci The maternal X-chromosome STR alleles and the sequences of HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria in the questioned child matched with those of the mother.
X-Chromosome and HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria Table 2 Genotype of the mother and the questioned child for six chromosome STR loci The maternal X-chromosome STR alleles and the sequences of HV 1 and HV 2 regions of mitochondria in the questioned child matched with those of the mother.
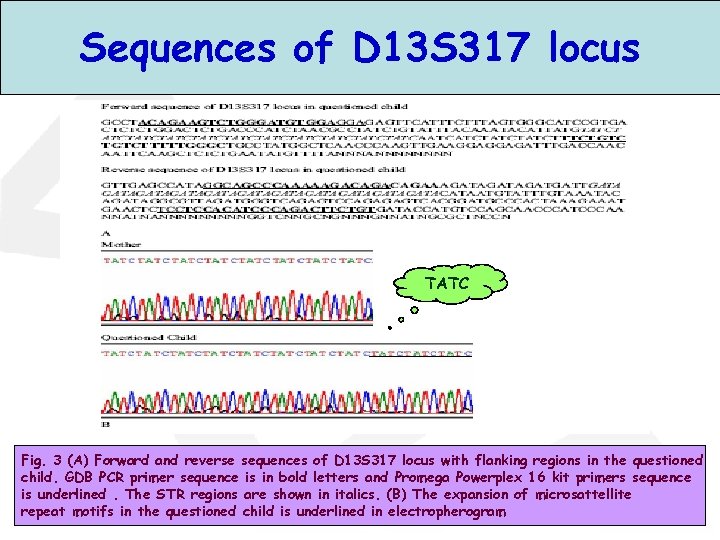 Sequences of D 13 S 317 locus TATC Fig. 3 (A) Forward and reverse sequences of D 13 S 317 locus with flanking regions in the questioned child. GDB PCR primer sequence is in bold letters and Promega Powerplex 16 kit primers sequence is underlined. The STR regions are shown in italics. (B) The expansion of microsattellite repeat motifs in the questioned child is underlined in electropherogram
Sequences of D 13 S 317 locus TATC Fig. 3 (A) Forward and reverse sequences of D 13 S 317 locus with flanking regions in the questioned child. GDB PCR primer sequence is in bold letters and Promega Powerplex 16 kit primers sequence is underlined. The STR regions are shown in italics. (B) The expansion of microsattellite repeat motifs in the questioned child is underlined in electropherogram
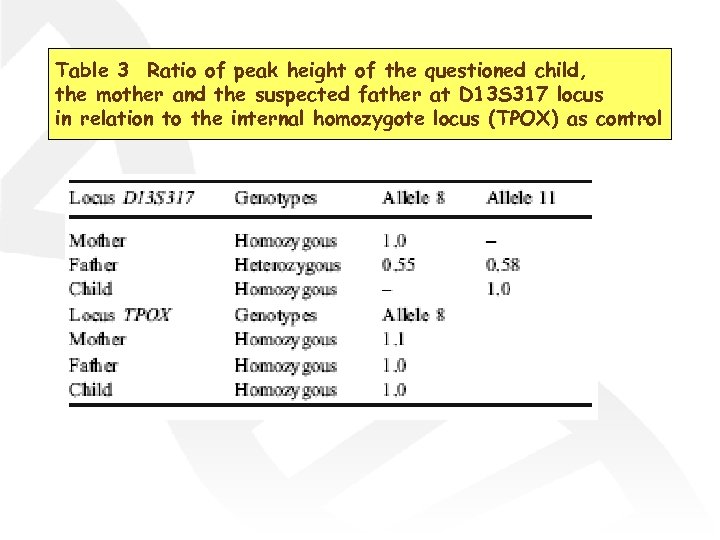 Table 3 Ratio of peak height of the questioned child, the mother and the suspected father at D 13 S 317 locus in relation to the internal homozygote locus (TPOX) as control
Table 3 Ratio of peak height of the questioned child, the mother and the suspected father at D 13 S 317 locus in relation to the internal homozygote locus (TPOX) as control
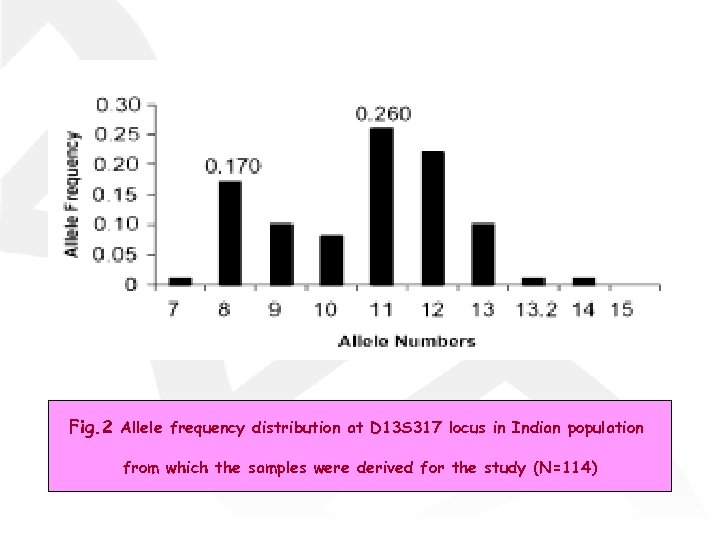 Fig. 2 Allele frequency distribution at D 13 S 317 locus in Indian population from which the samples were derived for the study (N=114)
Fig. 2 Allele frequency distribution at D 13 S 317 locus in Indian population from which the samples were derived for the study (N=114)
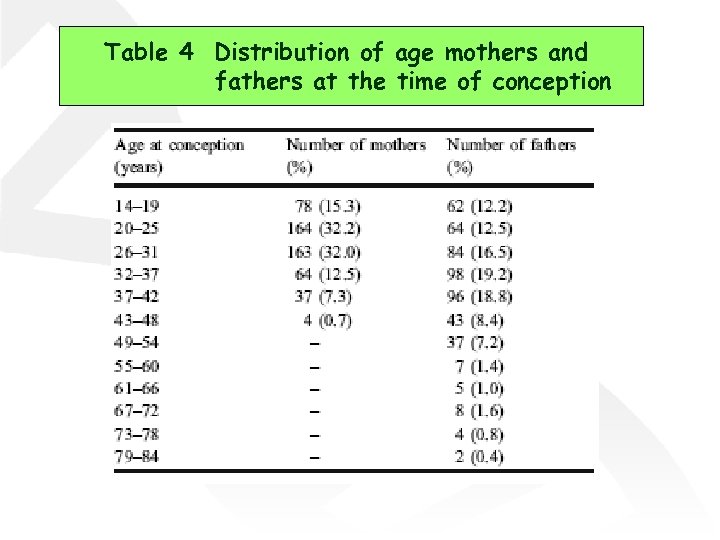 Table 4 Distribution of age mothers and fathers at the time of conception
Table 4 Distribution of age mothers and fathers at the time of conception
 Conclusion The mother and the suspected father are the biological parents of the child.
Conclusion The mother and the suspected father are the biological parents of the child.
 Thank you for attention…
Thank you for attention…
 Question? ? ?
Question? ? ?
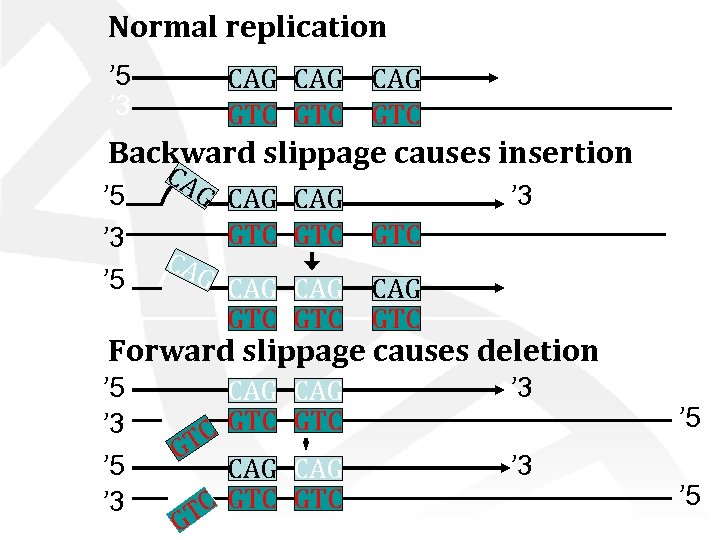 Normal replication ’ 5 ’ 3 CAG CAG GTC GTC ’ 3 ’ 5 Backward slippage causes insertion ’ 5 ’ 3 CA G CAG GTC ’ 3 ’ 5 GTC CAG GTC ’ 3 Forward slippage causes deletion ’ 5 ’ 3 CAG C GTC GT CAG GTC TC G ’ 3 ’ 5 ’ 5
Normal replication ’ 5 ’ 3 CAG CAG GTC GTC ’ 3 ’ 5 Backward slippage causes insertion ’ 5 ’ 3 CA G CAG GTC ’ 3 ’ 5 GTC CAG GTC ’ 3 Forward slippage causes deletion ’ 5 ’ 3 CAG C GTC GT CAG GTC TC G ’ 3 ’ 5 ’ 5


