86495e598262b6c261dfcfdfe771e081.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS NEW TECHNIQUES Matilda A. Papathanasiou Assist. professor of Neuroradiology Dpt of Radiology University of Athens Medical School ’’ΑΤΤΙΚΟΝ’’ University Hospital .
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS NEW TECHNIQUES Matilda A. Papathanasiou Assist. professor of Neuroradiology Dpt of Radiology University of Athens Medical School ’’ΑΤΤΙΚΟΝ’’ University Hospital .
 OVERVIEW • Review indications for imaging-protocol • Review imaging findings in clinical setting • New imaging techniques – Findings – Implications – Limitations
OVERVIEW • Review indications for imaging-protocol • Review imaging findings in clinical setting • New imaging techniques – Findings – Implications – Limitations
 MRI WHO ? HOW ?
MRI WHO ? HOW ?
 MRI INDICATIONS Ι 1. Initial evaluation after a CIS or based on past history that is suspicious 2. Baseline imaging evaluation in MS 3. Spinal cord imaging a. Symptoms s. c. (+ brain) b. Findings in brain MR ? J. H. Simon, D. Li, et al Standardized MR Imaging Protocol for Multiple Sclerosis: Consortium of MS Centers Consensus Guidelines AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. , Feb 2006; 27: 455 - 461
MRI INDICATIONS Ι 1. Initial evaluation after a CIS or based on past history that is suspicious 2. Baseline imaging evaluation in MS 3. Spinal cord imaging a. Symptoms s. c. (+ brain) b. Findings in brain MR ? J. H. Simon, D. Li, et al Standardized MR Imaging Protocol for Multiple Sclerosis: Consortium of MS Centers Consensus Guidelines AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. , Feb 2006; 27: 455 - 461
 MRI INDICATIONS ΙΙ 4. Follow up 1. when clinical indications a. Unexpected worsening b. Reassess burden for initiation of Tx c. Suspicion of secondary Dx 2. routine periodically (yearly) optional 5. Contrast • • • initial baseline exam Periodic follow up J. H. Simon, D. Li, et al Standardized MR Imaging Protocol for Multiple Sclerosis: Consortium of MS Centers Consensus Guidelines AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. , Feb 2006; 27: 455 - 461
MRI INDICATIONS ΙΙ 4. Follow up 1. when clinical indications a. Unexpected worsening b. Reassess burden for initiation of Tx c. Suspicion of secondary Dx 2. routine periodically (yearly) optional 5. Contrast • • • initial baseline exam Periodic follow up J. H. Simon, D. Li, et al Standardized MR Imaging Protocol for Multiple Sclerosis: Consortium of MS Centers Consensus Guidelines AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. , Feb 2006; 27: 455 - 461
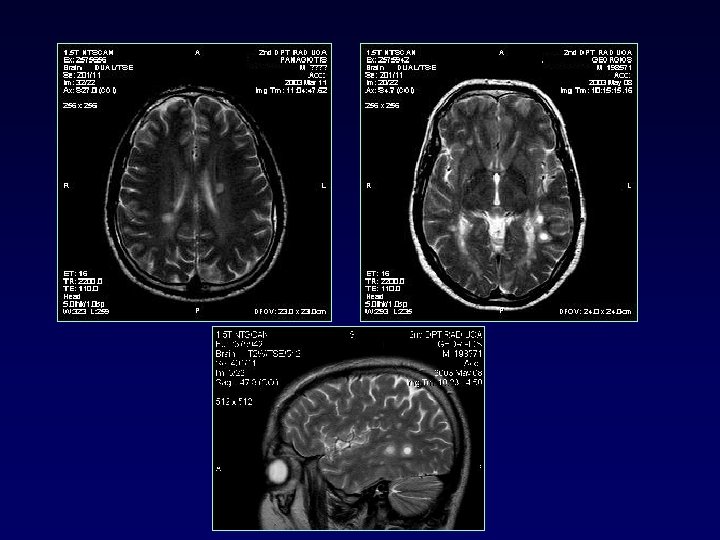
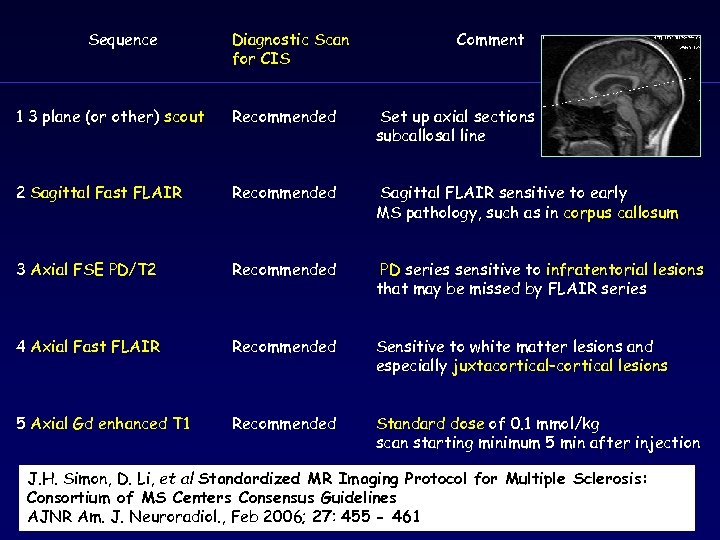 Sequence Diagnostic Scan for CIS Comment 1 3 plane (or other) scout Recommended Set up axial sections through subcallosal line 2 Sagittal Fast FLAIR Recommended Sagittal FLAIR sensitive to early MS pathology, such as in corpus callosum 3 Axial FSE PD/T 2 Recommended PD series sensitive to infratentorial lesions that may be missed by FLAIR series 4 Axial Fast FLAIR Recommended Sensitive to white matter lesions and especially juxtacortical–cortical lesions 5 Axial Gd enhanced T 1 Recommended Standard dose of 0. 1 mmol/kg scan starting minimum 5 min after injection J. H. Simon, D. Li, et al Standardized MR Imaging Protocol for Multiple Sclerosis: Consortium of MS Centers Consensus Guidelines AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. , Feb 2006; 27: 455 - 461
Sequence Diagnostic Scan for CIS Comment 1 3 plane (or other) scout Recommended Set up axial sections through subcallosal line 2 Sagittal Fast FLAIR Recommended Sagittal FLAIR sensitive to early MS pathology, such as in corpus callosum 3 Axial FSE PD/T 2 Recommended PD series sensitive to infratentorial lesions that may be missed by FLAIR series 4 Axial Fast FLAIR Recommended Sensitive to white matter lesions and especially juxtacortical–cortical lesions 5 Axial Gd enhanced T 1 Recommended Standard dose of 0. 1 mmol/kg scan starting minimum 5 min after injection J. H. Simon, D. Li, et al Standardized MR Imaging Protocol for Multiple Sclerosis: Consortium of MS Centers Consensus Guidelines AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. , Feb 2006; 27: 455 - 461
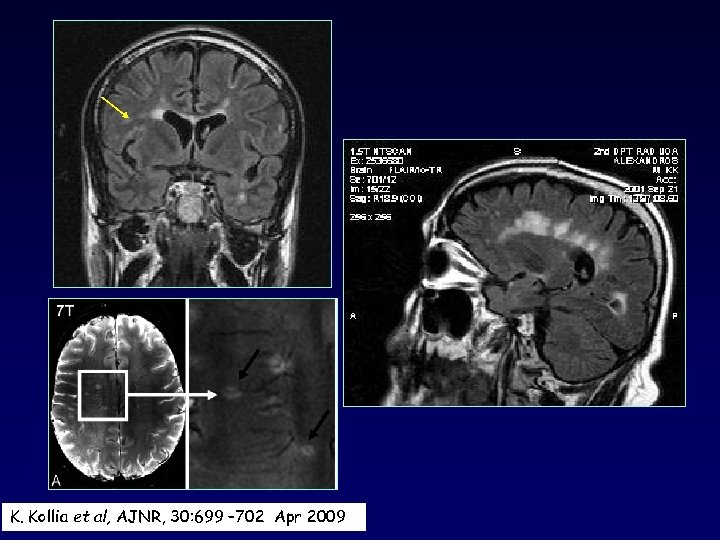 K. Kollia et al, AJNR, 30: 699 – 702 Apr 2009
K. Kollia et al, AJNR, 30: 699 – 702 Apr 2009
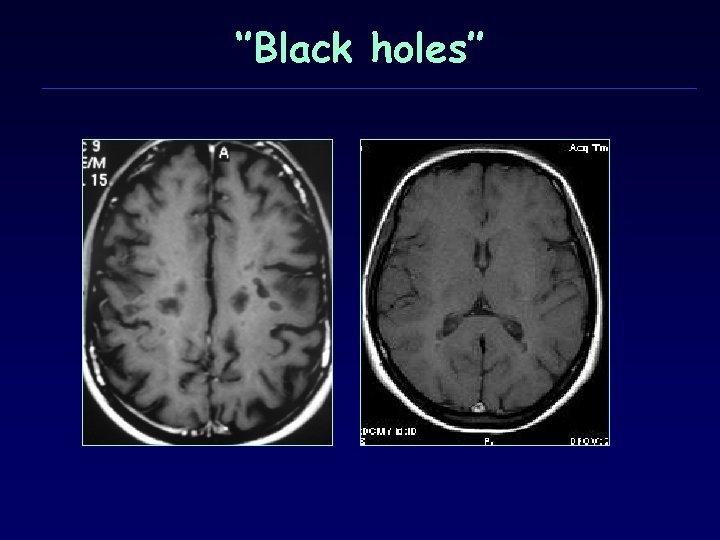 ‘’Black holes’’
‘’Black holes’’
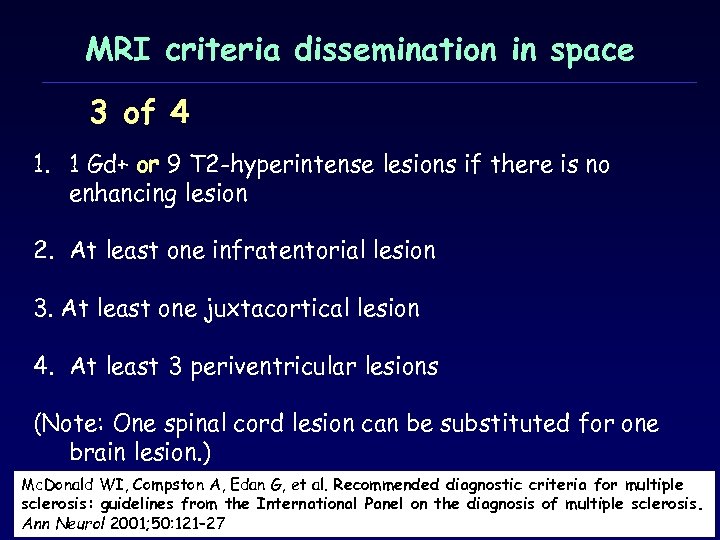 MRI criteria dissemination in space 3 of 4 1. 1 Gd+ or 9 T 2 -hyperintense lesions if there is no enhancing lesion 2. At least one infratentorial lesion 3. At least one juxtacortical lesion 4. At least 3 periventricular lesions (Note: One spinal cord lesion can be substituted for one brain lesion. ) Mc. Donald WI, Compston A, Edan G, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis οf multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2001; 50: 121– 27
MRI criteria dissemination in space 3 of 4 1. 1 Gd+ or 9 T 2 -hyperintense lesions if there is no enhancing lesion 2. At least one infratentorial lesion 3. At least one juxtacortical lesion 4. At least 3 periventricular lesions (Note: One spinal cord lesion can be substituted for one brain lesion. ) Mc. Donald WI, Compston A, Edan G, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis οf multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2001; 50: 121– 27
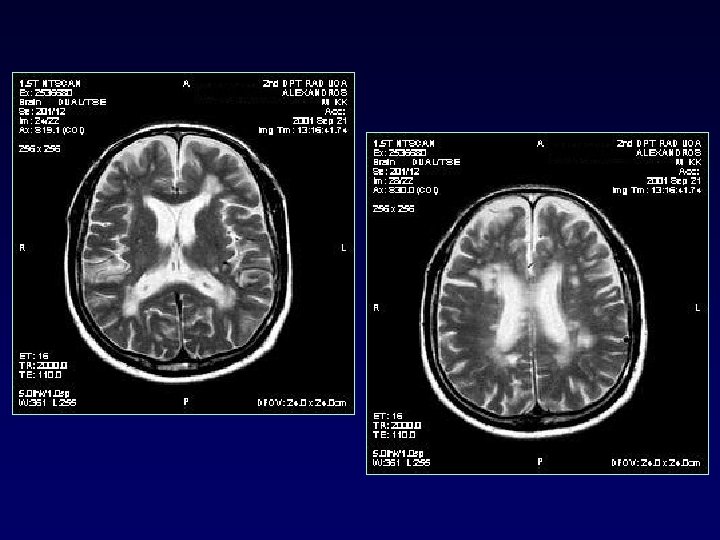
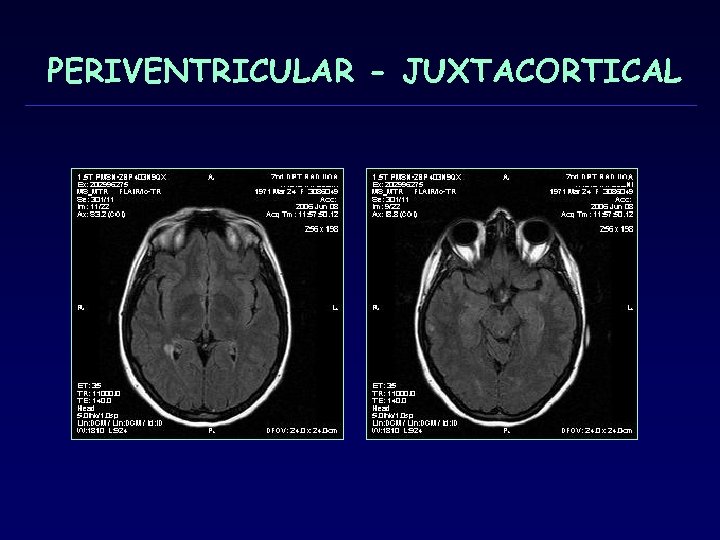 PERIVENTRICULAR - JUXTACORTICAL
PERIVENTRICULAR - JUXTACORTICAL
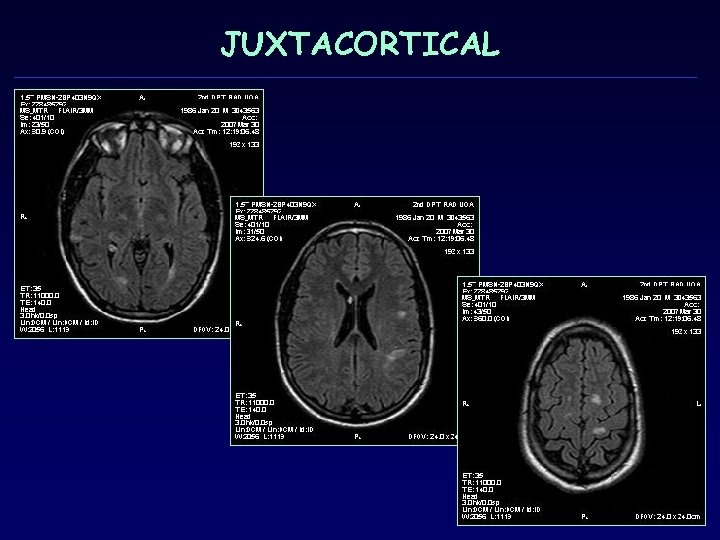 JUXTACORTICAL
JUXTACORTICAL
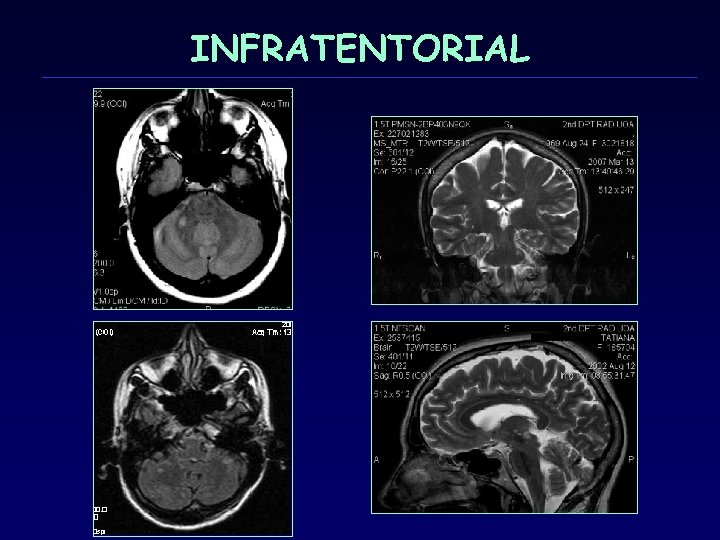 INFRATENTORIAL
INFRATENTORIAL
 MRI criteria dissemination in time • 1. MRI > 3 mo after clinical event, Gd+ site # original • 2. MRI > 3 mo after clinical event, Gdrepeat MRI in additional 3 mo new Τ 2 or new Gd+ Mc. Donald WI, Compston A, Edan G, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis οf multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2001; 50: 121– 27
MRI criteria dissemination in time • 1. MRI > 3 mo after clinical event, Gd+ site # original • 2. MRI > 3 mo after clinical event, Gdrepeat MRI in additional 3 mo new Τ 2 or new Gd+ Mc. Donald WI, Compston A, Edan G, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis οf multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2001; 50: 121– 27
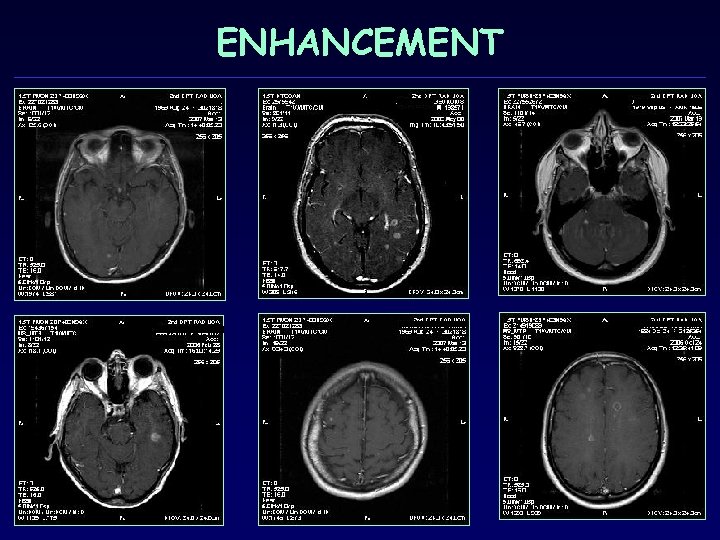 ENHANCEMENT
ENHANCEMENT
 SPINAL CORD • • 50 -90% MS up to 25% only site involved cervical dorsolateral, < 2 vertebral bodies < half transverse diameter Multifocal Cord atrophy
SPINAL CORD • • 50 -90% MS up to 25% only site involved cervical dorsolateral, < 2 vertebral bodies < half transverse diameter Multifocal Cord atrophy
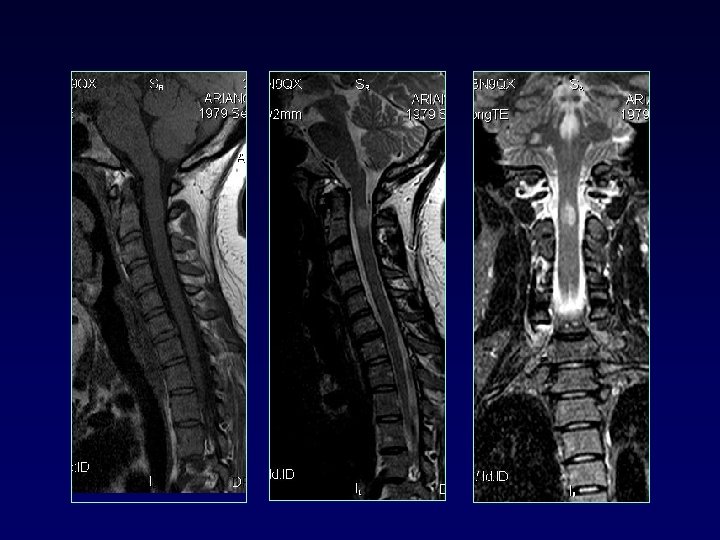
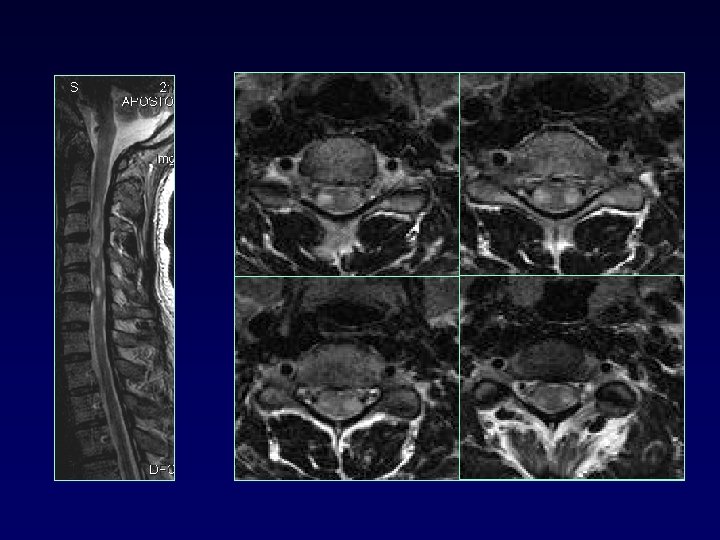
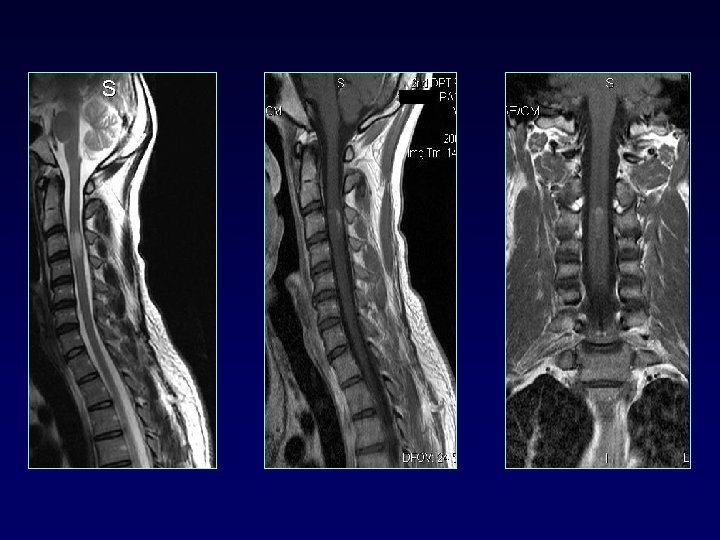
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS § § § § § Ischemic lesions (small vessel disease) Migraine Vasculitis collagen v d Encephalitis (ADEM, SSPE) Trauma Mets Sarcoid Dilated perivascular spaces VR UBO (20%) tumor (solitary lesions)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS § § § § § Ischemic lesions (small vessel disease) Migraine Vasculitis collagen v d Encephalitis (ADEM, SSPE) Trauma Mets Sarcoid Dilated perivascular spaces VR UBO (20%) tumor (solitary lesions)
 DIAGNOSIS • MS is a clinical Dx • MRI supports or provides alternative dx
DIAGNOSIS • MS is a clinical Dx • MRI supports or provides alternative dx
 ? Findings with increased specificity for MS
? Findings with increased specificity for MS
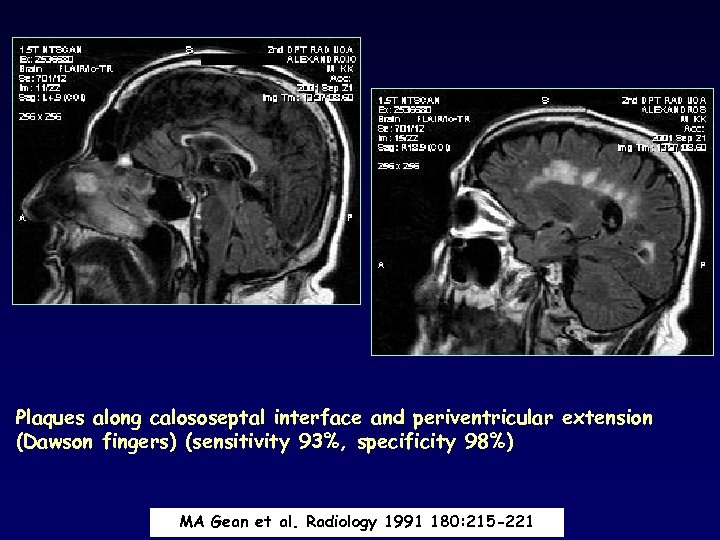 Plaques along calososeptal interface and periventricular extension (Dawson fingers) (sensitivity 93%, specificity 98%) MA Gean et al. Radiology 1991 180: 215 -221
Plaques along calososeptal interface and periventricular extension (Dawson fingers) (sensitivity 93%, specificity 98%) MA Gean et al. Radiology 1991 180: 215 -221
 Lesions indicative MS • Brain stem, subcortical, spinal cord • Posterolateral pons, cerebelar peduncles • Enhancement MS vs small vessel
Lesions indicative MS • Brain stem, subcortical, spinal cord • Posterolateral pons, cerebelar peduncles • Enhancement MS vs small vessel
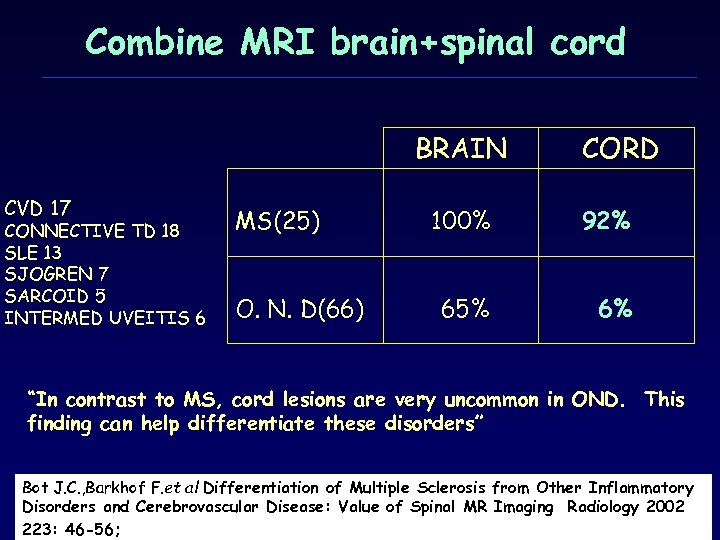 Combine MRI brain+spinal cord BRAIN CVD 17 CONNECTIVE TD 18 SLE 13 SJOGREN 7 SARCOID 5 INTERMED UVEITIS 6 MS(25) O. Ν. D(66) CORD 100% 92% 65% 6% “In contrast to MS, cord lesions are very uncommon in OND. This finding can help differentiate these disorders” Bot J. C. , Barkhof F. et al Differentiation of Multiple Sclerosis from Other Inflammatory Disorders and Cerebrovascular Disease: Value of Spinal MR Imaging Radiology 2002 223: 46 -56;
Combine MRI brain+spinal cord BRAIN CVD 17 CONNECTIVE TD 18 SLE 13 SJOGREN 7 SARCOID 5 INTERMED UVEITIS 6 MS(25) O. Ν. D(66) CORD 100% 92% 65% 6% “In contrast to MS, cord lesions are very uncommon in OND. This finding can help differentiate these disorders” Bot J. C. , Barkhof F. et al Differentiation of Multiple Sclerosis from Other Inflammatory Disorders and Cerebrovascular Disease: Value of Spinal MR Imaging Radiology 2002 223: 46 -56;
 CLINICORADIOLOGIC PARADOX • Poor correlation of conventional imaging/clinical • MRI 4 -10 x more sensitive in detecting lesions /clinical • Gd enhancement 5 -10 x /clinical
CLINICORADIOLOGIC PARADOX • Poor correlation of conventional imaging/clinical • MRI 4 -10 x more sensitive in detecting lesions /clinical • Gd enhancement 5 -10 x /clinical
 NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric MRI ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric MRI ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
 NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric MRI ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric MRI ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
 VOLUMETRIC MRI – LESION LOAD • • total lesion volume Τ 2, T 1 total lesion activity enhanced Τ 1 – BRAIN ATROPHY
VOLUMETRIC MRI – LESION LOAD • • total lesion volume Τ 2, T 1 total lesion activity enhanced Τ 1 – BRAIN ATROPHY
 VOLUMETRIC MRI LESION LOAD (T 2 lesion) • T 2 lesion volume increases 10%/year in early RRMS • T 2 lesion load SPMS > RRMS • Clinical trial studies however • Τ 2 lesions heterogenous • Τ 2 load does not include NAWM
VOLUMETRIC MRI LESION LOAD (T 2 lesion) • T 2 lesion volume increases 10%/year in early RRMS • T 2 lesion load SPMS > RRMS • Clinical trial studies however • Τ 2 lesions heterogenous • Τ 2 load does not include NAWM
 VOLUMETRIC MRI LESION LOAD (Τ 1 lesion) • Τ 1 Gd lesion load RRMS > SPMS • Τ 1 lesion load (Gd or black holes) correlate clinical outcome (EDSS) better than Τ 2 • Clinical trial studies
VOLUMETRIC MRI LESION LOAD (Τ 1 lesion) • Τ 1 Gd lesion load RRMS > SPMS • Τ 1 lesion load (Gd or black holes) correlate clinical outcome (EDSS) better than Τ 2 • Clinical trial studies
 LESION LOAD CONCLUSIONS • Lesion load does not account for patient’s functional state • Information monitoring natural history • Information monitoring treatment effects
LESION LOAD CONCLUSIONS • Lesion load does not account for patient’s functional state • Information monitoring natural history • Information monitoring treatment effects
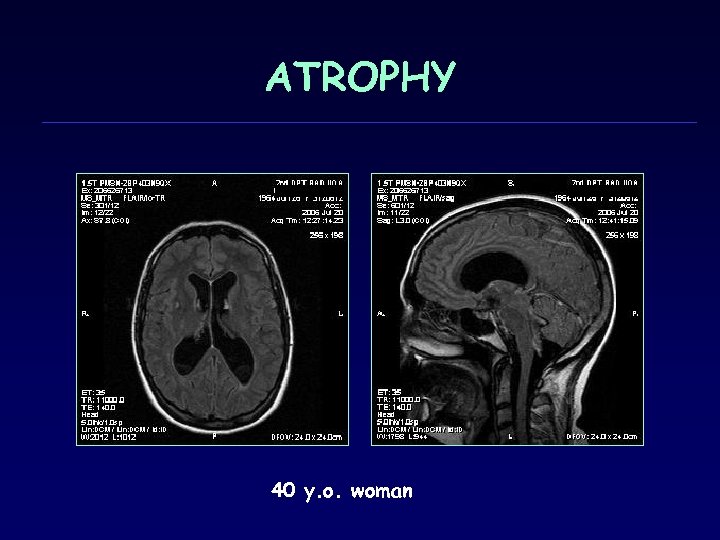 ATROPHY 40 y. o. woman
ATROPHY 40 y. o. woman
 VOLUMETRIC MRI ATROPHY – Global 0. 6 -1. 0% yearly MS ( 0. 1 -0. 3% nl) – Not reversible – Early prognosis – all MS subtypes, even early and CIS – Cortex / WM – GM volume loss affects different regions
VOLUMETRIC MRI ATROPHY – Global 0. 6 -1. 0% yearly MS ( 0. 1 -0. 3% nl) – Not reversible – Early prognosis – all MS subtypes, even early and CIS – Cortex / WM – GM volume loss affects different regions
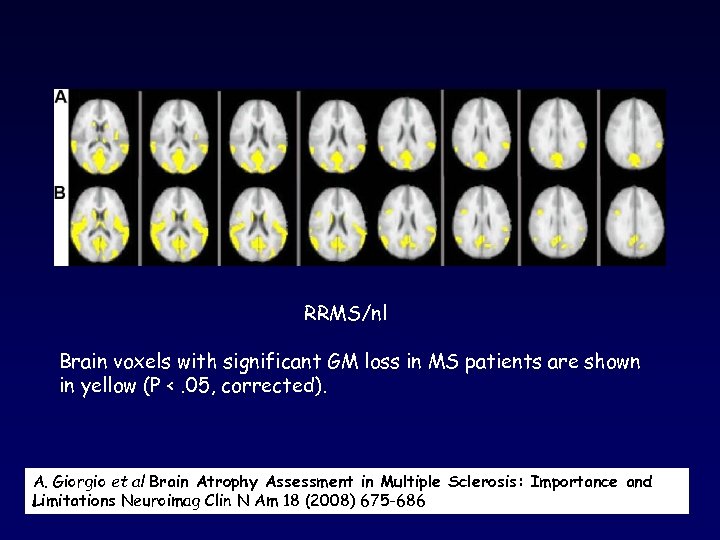 RRMS/nl Brain voxels with significant GM loss in MS patients are shown in yellow (P <. 05, corrected). A. Giorgio et al Brain Atrophy Assessment in Multiple Sclerosis: Importance and Limitations Neuroimag Clin N Am 18 (2008) 675 -686
RRMS/nl Brain voxels with significant GM loss in MS patients are shown in yellow (P <. 05, corrected). A. Giorgio et al Brain Atrophy Assessment in Multiple Sclerosis: Importance and Limitations Neuroimag Clin N Am 18 (2008) 675 -686
 ATROPHY CONCLUSIONS – Correlates with clinical disability > lesion load – Correlates with cognitive impairment – Evident before clinical disability – Multicenter trials – Is the distribution of atrophy clinically significant? – programs ’’in-house’’
ATROPHY CONCLUSIONS – Correlates with clinical disability > lesion load – Correlates with cognitive impairment – Evident before clinical disability – Multicenter trials – Is the distribution of atrophy clinically significant? – programs ’’in-house’’
 NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric MRI ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric MRI ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
![MAGNETIZATION TRANSFER So Ss MTR = [ (So–Ss) / So] x 100% proportional to MAGNETIZATION TRANSFER So Ss MTR = [ (So–Ss) / So] x 100% proportional to](https://present5.com/presentation/86495e598262b6c261dfcfdfe771e081/image-39.jpg) MAGNETIZATION TRANSFER So Ss MTR = [ (So–Ss) / So] x 100% proportional to concentration of myelin
MAGNETIZATION TRANSFER So Ss MTR = [ (So–Ss) / So] x 100% proportional to concentration of myelin
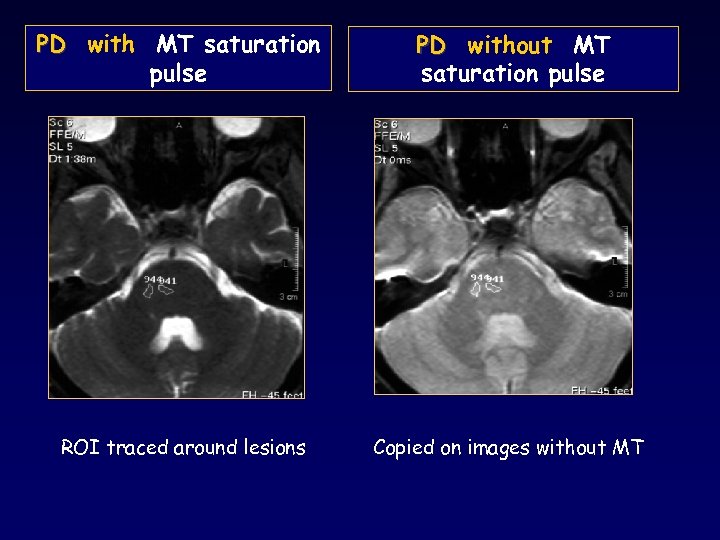 PD with MT saturation pulse PD without MT saturation pulse ROI traced around lesions Copied on images without MT
PD with MT saturation pulse PD without MT saturation pulse ROI traced around lesions Copied on images without MT
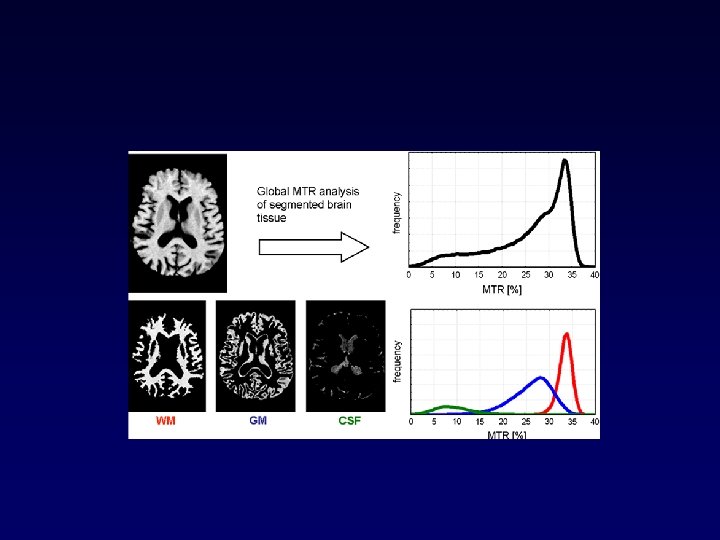
 MTR lesions, ΝAWM • MTR the first measurable abnormality not seen on conventional MRI ΝΑWM • T 1 black hole <Τ 1 isointense < perilesional < remote < ΝΑWM < nl • progressive • ΜΤR till a new lesion on Τ 2 ΜΤR on follow-up 1 -4 yrs
MTR lesions, ΝAWM • MTR the first measurable abnormality not seen on conventional MRI ΝΑWM • T 1 black hole <Τ 1 isointense < perilesional < remote < ΝΑWM < nl • progressive • ΜΤR till a new lesion on Τ 2 ΜΤR on follow-up 1 -4 yrs
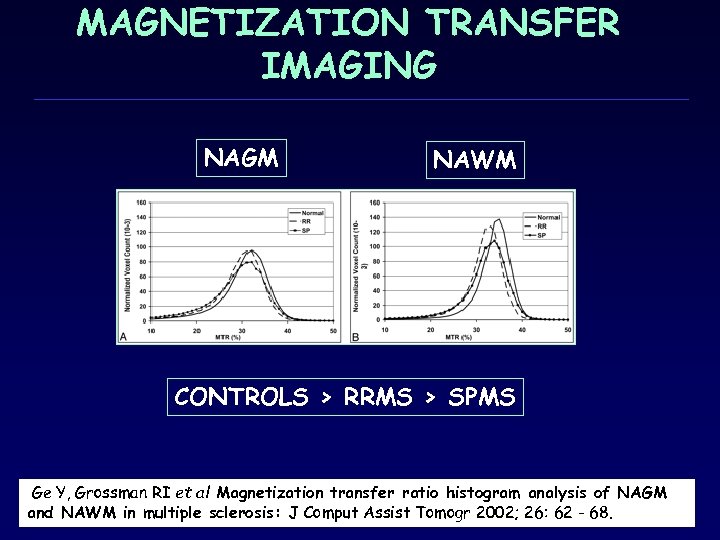 MAGNETIZATION TRANSFER IMAGING NAGM NAWM CONTROLS > RRMS > SPMS Ge Y, Grossman RI et al Magnetization transfer ratio histogram analysis of NAGM and NAWM in multiple sclerosis: J Comput Assist Tomogr 2002; 26: 62 - 68.
MAGNETIZATION TRANSFER IMAGING NAGM NAWM CONTROLS > RRMS > SPMS Ge Y, Grossman RI et al Magnetization transfer ratio histogram analysis of NAGM and NAWM in multiple sclerosis: J Comput Assist Tomogr 2002; 26: 62 - 68.
 MTR CONCLUSIONS • • • Measurable marker MS # nl Diffuse pathology ΝΑWM, NAGM ** Monitoring disease - treatment Histograms differ in clinical subtypes Gray matter MTR reductions correlate with cognitive tests • NOT • Individual patient management • Clinical practice • Need standardize (sequence, RF pulse, coils) • Multicenter trials
MTR CONCLUSIONS • • • Measurable marker MS # nl Diffuse pathology ΝΑWM, NAGM ** Monitoring disease - treatment Histograms differ in clinical subtypes Gray matter MTR reductions correlate with cognitive tests • NOT • Individual patient management • Clinical practice • Need standardize (sequence, RF pulse, coils) • Multicenter trials
 NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
 Diffusion ADC quantification
Diffusion ADC quantification
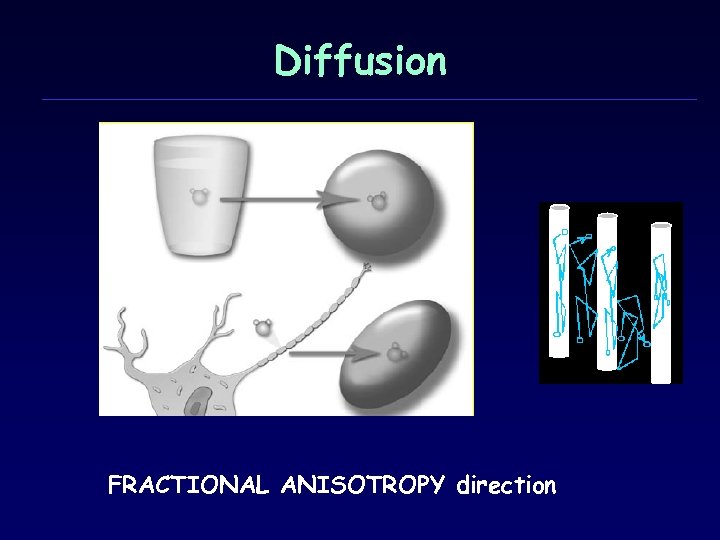 Diffusion FRACTIONAL ANISOTROPY direction
Diffusion FRACTIONAL ANISOTROPY direction
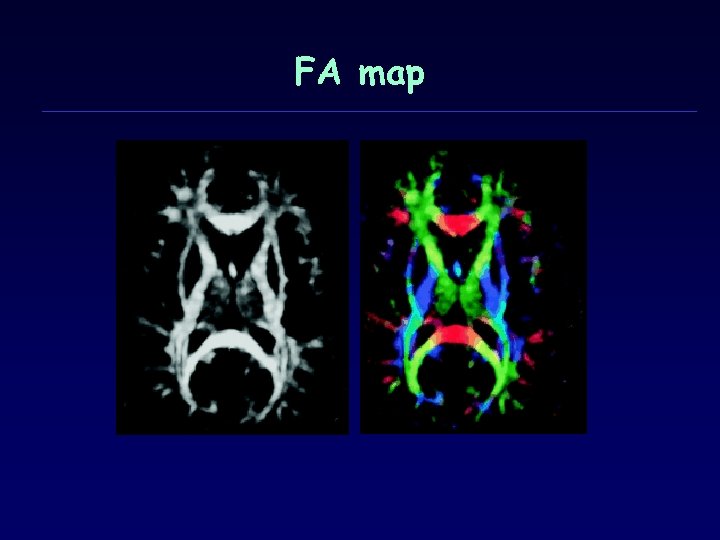 FA map
FA map
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging • Information – Tissue microstructure and architecture including size, shape and organization – Quantitative method for evaluating tissue integrity – FA info basis for fiber tractography i. e. anatomic pathways of white matter connectivity
Diffusion Tensor Imaging • Information – Tissue microstructure and architecture including size, shape and organization – Quantitative method for evaluating tissue integrity – FA info basis for fiber tractography i. e. anatomic pathways of white matter connectivity
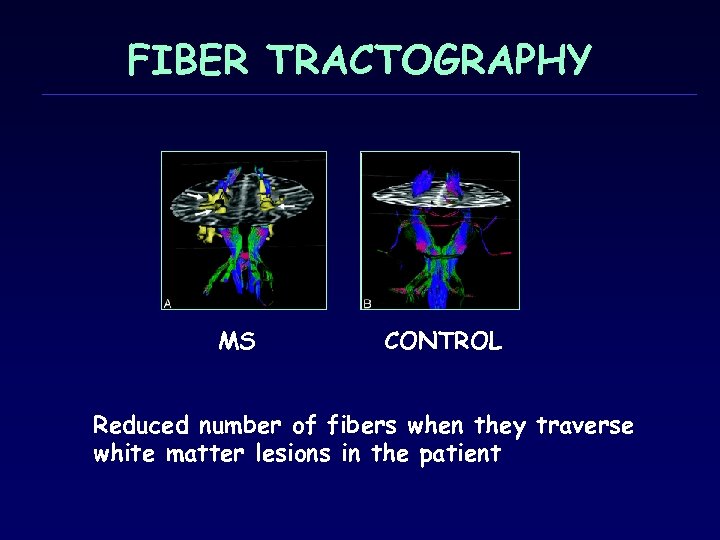 FIBER TRACTOGRAPHY MS CONTROL Reduced number of fibers when they traverse white matter lesions in the patient
FIBER TRACTOGRAPHY MS CONTROL Reduced number of fibers when they traverse white matter lesions in the patient
 DTI lesions • Lesions ADC and FA which indicates disruption of myelin and axonal structures that leads to disorganization and increase in extracellular space • Highest ADC in black holes • SPMS > RRMS
DTI lesions • Lesions ADC and FA which indicates disruption of myelin and axonal structures that leads to disorganization and increase in extracellular space • Highest ADC in black holes • SPMS > RRMS
 DTI NAWM • Lesion > NAWM perilesional > remote > nl • Corpus callosum > NAWM wallerian • Histogram for global DTI
DTI NAWM • Lesion > NAWM perilesional > remote > nl • Corpus callosum > NAWM wallerian • Histogram for global DTI
 Diffusion Imaging CONCLUSIONS • Measurable marker MS # nl • Generalized pathology • Need standardize • Multicenter trials
Diffusion Imaging CONCLUSIONS • Measurable marker MS # nl • Generalized pathology • Need standardize • Multicenter trials
 NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
 SPECTROSCOPY • NAA in chronic plaques, ‘’black holes’’ • in acute plaque NAA is partially reversible – Cho, Lac, MI • NAWM, progress to new lesion • The regional changes in all the metabolites are dynamic and variable over time and should be interpreted with caution
SPECTROSCOPY • NAA in chronic plaques, ‘’black holes’’ • in acute plaque NAA is partially reversible – Cho, Lac, MI • NAWM, progress to new lesion • The regional changes in all the metabolites are dynamic and variable over time and should be interpreted with caution
 SPECTROSCOPY WBNAA • Quantification whole brain ΝΑΑ • RRMS < controls • Loss ΝΑΑ 3, 6 x faster than atrophy precedes? ?
SPECTROSCOPY WBNAA • Quantification whole brain ΝΑΑ • RRMS < controls • Loss ΝΑΑ 3, 6 x faster than atrophy precedes? ?
 SPECTROSCOPY CONCLUSIONS • Measurable marker MS # nl • Reversible • Generalized pathology WBNAA • Need standardize • Multicenter trials
SPECTROSCOPY CONCLUSIONS • Measurable marker MS # nl • Reversible • Generalized pathology WBNAA • Need standardize • Multicenter trials
 NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion. Tensor. Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion. Tensor. Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
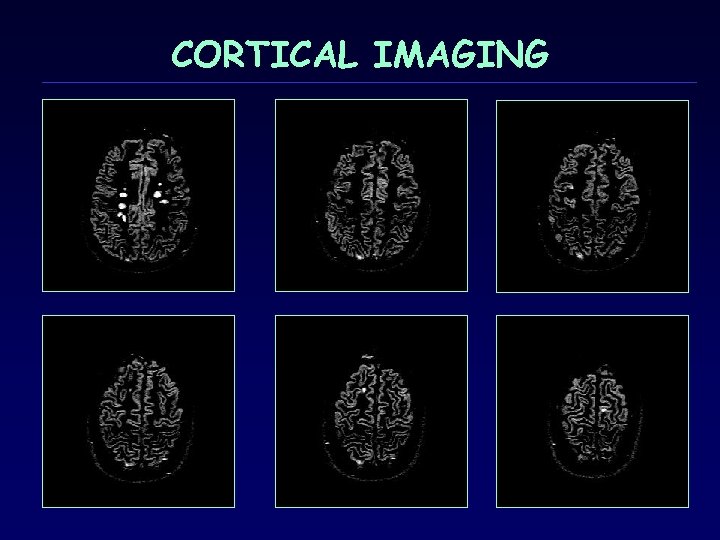 CORTICAL IMAGING
CORTICAL IMAGING
 CORTEX • DIR demonstrates cortical lesions • >1. 5 T • volumetry atrophy cortex • MTR, DTI, NAA measurable markers in cortex MS # nl • f-MRI plasticity
CORTEX • DIR demonstrates cortical lesions • >1. 5 T • volumetry atrophy cortex • MTR, DTI, NAA measurable markers in cortex MS # nl • f-MRI plasticity
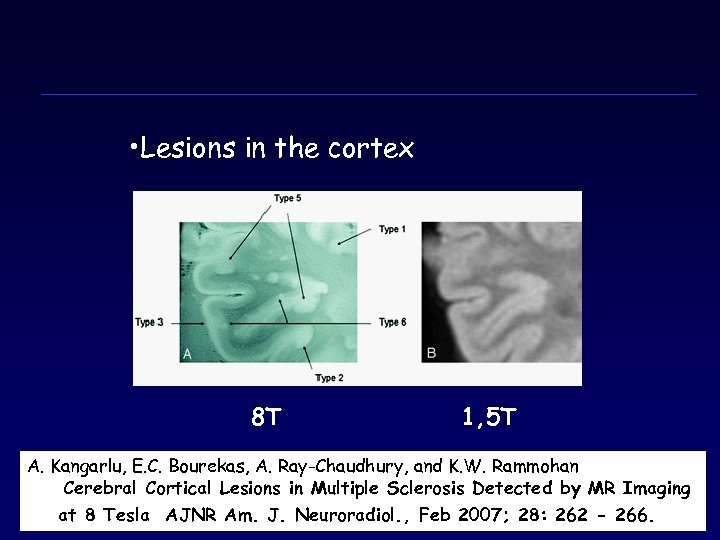 • Lesions in the cortex 8Τ 1, 5Τ A. Kangarlu, E. C. Bourekas, A. Ray-Chaudhury, and K. W. Rammohan Cerebral Cortical Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis Detected by MR Imaging at 8 Tesla AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. , Feb 2007; 28: 262 - 266.
• Lesions in the cortex 8Τ 1, 5Τ A. Kangarlu, E. C. Bourekas, A. Ray-Chaudhury, and K. W. Rammohan Cerebral Cortical Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis Detected by MR Imaging at 8 Tesla AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. , Feb 2007; 28: 262 - 266.
 NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
NEW TECHNIQUES ü Volumetric ü Magnetization transfer ü Diffusion Tensor Imaging ü MR Spectroscopy ü Cortical imaging ü Functional MRI
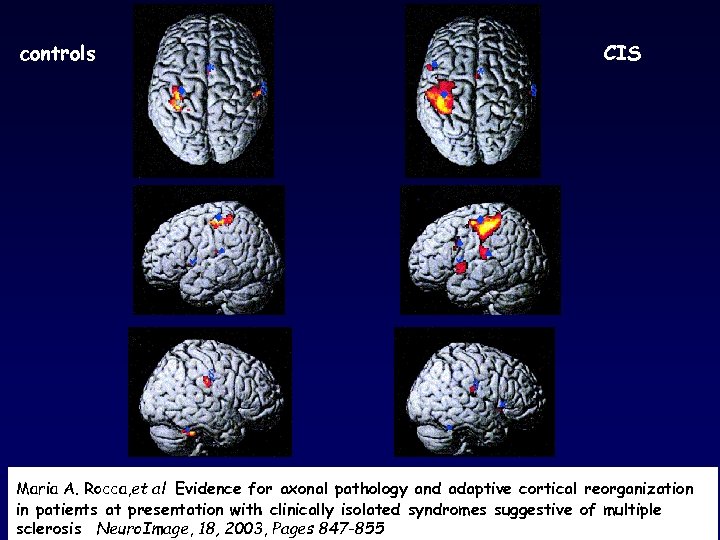 controls CIS Maria A. Rocca, et al Evidence for axonal pathology and adaptive cortical reorganization in patients at presentation with clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis Neuro. Image, 18, 2003, Pages 847 -855
controls CIS Maria A. Rocca, et al Evidence for axonal pathology and adaptive cortical reorganization in patients at presentation with clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis Neuro. Image, 18, 2003, Pages 847 -855
 f-MRI • visual, motor cognitive tasks • Cortical reorganization does occur CIS, RR, PPMS • Extent of activation correlates with degree of structural damage • more activation bilateral complex tasks
f-MRI • visual, motor cognitive tasks • Cortical reorganization does occur CIS, RR, PPMS • Extent of activation correlates with degree of structural damage • more activation bilateral complex tasks
 Role of functional cortical reorganization • Adaptive role compensation recovery, • Failure or exhaustion with increasing disease duration or burden irreversible disability
Role of functional cortical reorganization • Adaptive role compensation recovery, • Failure or exhaustion with increasing disease duration or burden irreversible disability
 CONCLUSIONS Ι CLINICAL APPLICATION • MS is a clinical diagnosis • MRI supports the diagnosis or provides alternative dx • Conventional sequences – reproducible positioning, protocol
CONCLUSIONS Ι CLINICAL APPLICATION • MS is a clinical diagnosis • MRI supports the diagnosis or provides alternative dx • Conventional sequences – reproducible positioning, protocol
 CONCLUSIONS ΙΙ NEW TECHNIQUES • Lesion load, ΝΑWM, MTR , WBNAA • • • Volumetry MT DTI Spectroscopy Gray matter f-MRI 8 T f-MRI SPEC MRI DTI MTR
CONCLUSIONS ΙΙ NEW TECHNIQUES • Lesion load, ΝΑWM, MTR , WBNAA • • • Volumetry MT DTI Spectroscopy Gray matter f-MRI 8 T f-MRI SPEC MRI DTI MTR
 8 T MRI f-MRI SPEC DTI MTR THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION
8 T MRI f-MRI SPEC DTI MTR THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION



