Multiple Gestation.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 MULTIPLE GESTATION ; u Dr Fahmi I EL-URI u MRCOG, FRCOG u ASS. PROFESSOR OB/GYN u Faculty of medicine u MUTAH UNIVERSITY
MULTIPLE GESTATION ; u Dr Fahmi I EL-URI u MRCOG, FRCOG u ASS. PROFESSOR OB/GYN u Faculty of medicine u MUTAH UNIVERSITY
 Multiple Gestation : u Definition : It is any pregnancy in which two or more embryos or fetuses exist simultaneously. u PNM & morbidity in multiple gestation exceed that of singleton gestation in a disproportionate manner.
Multiple Gestation : u Definition : It is any pregnancy in which two or more embryos or fetuses exist simultaneously. u PNM & morbidity in multiple gestation exceed that of singleton gestation in a disproportionate manner.
 Etiology & Classification of Twins : u Dizygotic ( fraternal ) twins : result from ‘ fertilization of more than one egg by more than one sperm. They will always have two amnions & two chorions , the placentas may be either separate or fused, & ‘ sexes may be different. u Monozygotic (identical ) twins. u Superfecundation.
Etiology & Classification of Twins : u Dizygotic ( fraternal ) twins : result from ‘ fertilization of more than one egg by more than one sperm. They will always have two amnions & two chorions , the placentas may be either separate or fused, & ‘ sexes may be different. u Monozygotic (identical ) twins. u Superfecundation.
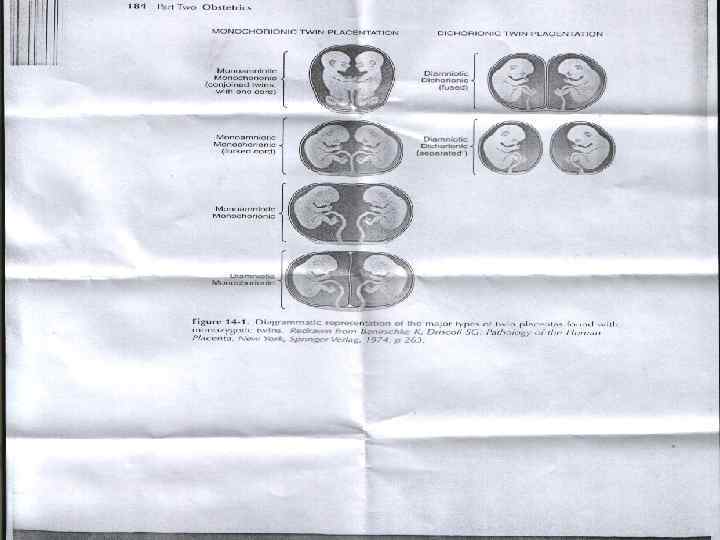
 Monozygotic ( identical ) Twins : This may arise from cleavage of a fertilized egg(embryonic mass) at various stages during embryogenesis, & ‘ relation of ‘ fetal membranes depends on ‘ time at which ‘ embryo divides : u 0 -72 hr = Diamniotic , dichorionic. u 4 -8 days = Diamniotic , monochorionic. u 9 -12 days =Monoamniotic , monochorionic 70% of monozygotic twins, are monochorionic , diamniotic. The 30% are diamniotic , dichorionic u
Monozygotic ( identical ) Twins : This may arise from cleavage of a fertilized egg(embryonic mass) at various stages during embryogenesis, & ‘ relation of ‘ fetal membranes depends on ‘ time at which ‘ embryo divides : u 0 -72 hr = Diamniotic , dichorionic. u 4 -8 days = Diamniotic , monochorionic. u 9 -12 days =Monoamniotic , monochorionic 70% of monozygotic twins, are monochorionic , diamniotic. The 30% are diamniotic , dichorionic u

 Superfecundation : This may occur , when two ova are fertilized within a short period of time but not at ‘ same coitus.
Superfecundation : This may occur , when two ova are fertilized within a short period of time but not at ‘ same coitus.
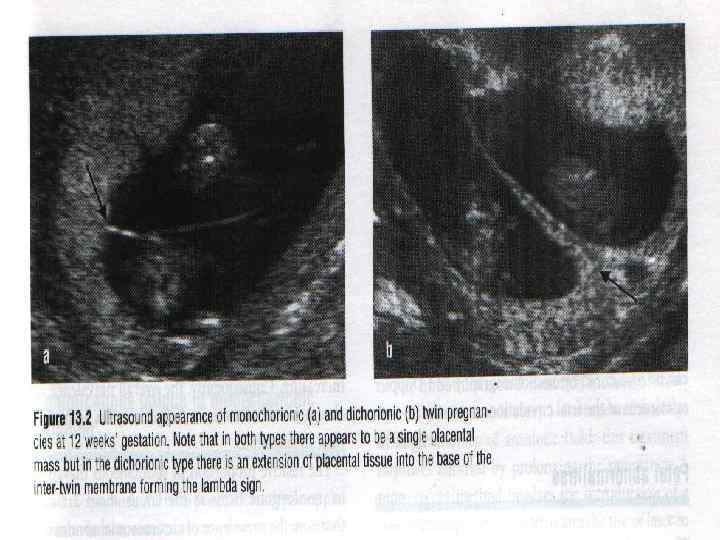
 Determination of Zygosity : Ultrasonography will allow for ‘ prenatal determination of zygosity. This is important because monochorionic twins are at increased risk for complications. After delivery of twins , an attempt should be made to confirm zygosity , in 80% of twins , this may be done easily by determining ‘ relationship of ‘ fetal membranes, sex, & blood groupings. The 20% will have ‘ same sex , dichorionic placentas , & identical blood groupings , DNA analysis is needed.
Determination of Zygosity : Ultrasonography will allow for ‘ prenatal determination of zygosity. This is important because monochorionic twins are at increased risk for complications. After delivery of twins , an attempt should be made to confirm zygosity , in 80% of twins , this may be done easily by determining ‘ relationship of ‘ fetal membranes, sex, & blood groupings. The 20% will have ‘ same sex , dichorionic placentas , & identical blood groupings , DNA analysis is needed.
 Incidence & Epidemiology : Twins occur in 1% of all pregnancies with 2/3 diazygotic & 1/3 monozygotic. The incidence varies with : u Ethnic group ( 5 times higher in certain parts of Africa & half as high in Asia ). u Materrnal age (2% at 35 years ). u Parity ( 2% after four pregnancies). u Method of conception (20% -ovulation induction) u Family history. u
Incidence & Epidemiology : Twins occur in 1% of all pregnancies with 2/3 diazygotic & 1/3 monozygotic. The incidence varies with : u Ethnic group ( 5 times higher in certain parts of Africa & half as high in Asia ). u Materrnal age (2% at 35 years ). u Parity ( 2% after four pregnancies). u Method of conception (20% -ovulation induction) u Family history. u
 Continue : u The incidence of monozygotic twins is similar in all ethinic groups & doesn’t vary with maternal age , parity , or method of conception. u Assisted reproduction techniques ART is an important causes of multiple gestations of about 20% of IVF pregnancies.
Continue : u The incidence of monozygotic twins is similar in all ethinic groups & doesn’t vary with maternal age , parity , or method of conception. u Assisted reproduction techniques ART is an important causes of multiple gestations of about 20% of IVF pregnancies.
 Abnormalities of the twinning process : u Conjoined Twins. u Placental Vascular Anastomosis. u Twin – Twin Transfusion Syndrome. u Fetal Malformations. u Umbilical Cord Abnormalities.
Abnormalities of the twinning process : u Conjoined Twins. u Placental Vascular Anastomosis. u Twin – Twin Transfusion Syndrome. u Fetal Malformations. u Umbilical Cord Abnormalities.
 Conjoined Twins : u If division of ‘ embryo occurs after ‘ embryonic disc has formed , i. e. 13 days after fertilization , cleavage of ‘ embryo is incomplete & results in Conjoined(Siamese). u The incidence is 1 in 70, 000 deliveries.
Conjoined Twins : u If division of ‘ embryo occurs after ‘ embryonic disc has formed , i. e. 13 days after fertilization , cleavage of ‘ embryo is incomplete & results in Conjoined(Siamese). u The incidence is 1 in 70, 000 deliveries.
 Placental Vascular Anastomosis: u It occurs almost exclusively in monochorionic twins. u The most common type is arterial – arterial followed by arterial-venous & then venous-venous. u This may give rise to a number of problems; abortion, hydramnios, twin transfusion syndrome & fetal malformations.
Placental Vascular Anastomosis: u It occurs almost exclusively in monochorionic twins. u The most common type is arterial – arterial followed by arterial-venous & then venous-venous. u This may give rise to a number of problems; abortion, hydramnios, twin transfusion syndrome & fetal malformations.
 Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome: u TTTS occurs due to ‘ presence of arterialvenous anastomosis in ‘ placenta. It is present in approximately 10 % of monochorionic twins. As a result of this chronic shunting , the donor twin develops; hypovolemia, hypotension, anaem -ia , oligohydramnios, & growth restriction. The recipient twin may develop hypervolemia, hyperviscosity, thrombosis, & hypertension, cardiomegaly, polycythemia, e dema congestive heat failure.
Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome: u TTTS occurs due to ‘ presence of arterialvenous anastomosis in ‘ placenta. It is present in approximately 10 % of monochorionic twins. As a result of this chronic shunting , the donor twin develops; hypovolemia, hypotension, anaem -ia , oligohydramnios, & growth restriction. The recipient twin may develop hypervolemia, hyperviscosity, thrombosis, & hypertension, cardiomegaly, polycythemia, e dema congestive heat failure.
 Fetal Malformations : u Arterial-arterial anastomosis may result in a number of fetal malformations.
Fetal Malformations : u Arterial-arterial anastomosis may result in a number of fetal malformations.
 Umbilical Cord Abnormalities : u Abnormalities of ‘ umbilical cord occur with a higher frequency in twins. Absence of one umbilical artery occurs in about 3 -4% of twins, as opposed to 0. 5 -1% of singletons, this may cause renal agenesis. u Marginal & velamentous umbilical cord insertions also occur more frequently in twins, occurring in about 5% of cases.
Umbilical Cord Abnormalities : u Abnormalities of ‘ umbilical cord occur with a higher frequency in twins. Absence of one umbilical artery occurs in about 3 -4% of twins, as opposed to 0. 5 -1% of singletons, this may cause renal agenesis. u Marginal & velamentous umbilical cord insertions also occur more frequently in twins, occurring in about 5% of cases.
 Diagnosis : Twins may be suspected if there is +ve maternal family history or maternal sensation of feeling larger & sensation of excessive fetal movements. u Physical signs : excessive wt gain , rapid uterine growth , abdominal palpation of an excessive number of fetal parts , auscultation of two separate fetal heart rates that differ by >10 beats/min. u Today ‘ routine sonar during ‘ 2 nd trimester makes ‘ undiagnosed twin is a rare occurrence. u
Diagnosis : Twins may be suspected if there is +ve maternal family history or maternal sensation of feeling larger & sensation of excessive fetal movements. u Physical signs : excessive wt gain , rapid uterine growth , abdominal palpation of an excessive number of fetal parts , auscultation of two separate fetal heart rates that differ by >10 beats/min. u Today ‘ routine sonar during ‘ 2 nd trimester makes ‘ undiagnosed twin is a rare occurrence. u
 Antepartum Management : u Intensive antepartum management serves to prolong gestation, increase birth wt, and decrease PNM & morbidity and decrease ‘ incidence of maternal complications. The following management is adviced : u 1 - The patient should be seen every 1 -2 wk beginning in ‘ mid-second trimester=20 wks
Antepartum Management : u Intensive antepartum management serves to prolong gestation, increase birth wt, and decrease PNM & morbidity and decrease ‘ incidence of maternal complications. The following management is adviced : u 1 - The patient should be seen every 1 -2 wk beginning in ‘ mid-second trimester=20 wks
 Continue ; u 2 -The cervix should be assessed frequently. u 3 -The patient should be examined for edema, urinalysis for protein , & BP. u 4 -Dietary considerations : there is an increased need for calories , iron, vitamins, and folate. Total wt gain at term for a woman with twins pregnancy should be 16 -20 kg.
Continue ; u 2 -The cervix should be assessed frequently. u 3 -The patient should be examined for edema, urinalysis for protein , & BP. u 4 -Dietary considerations : there is an increased need for calories , iron, vitamins, and folate. Total wt gain at term for a woman with twins pregnancy should be 16 -20 kg.
 Continue : u Prevention of prematurity by : bed rest, hospitalization, prophylatic betasympathomimetic (tocolytic) & cx cerclage u 6 - Routine sonography should be performed at monthly intervals to assess fetal growth. u 7 -NST should be performed weekly at 36 wks or earlier if there is any complication in pregnancy.
Continue : u Prevention of prematurity by : bed rest, hospitalization, prophylatic betasympathomimetic (tocolytic) & cx cerclage u 6 - Routine sonography should be performed at monthly intervals to assess fetal growth. u 7 -NST should be performed weekly at 36 wks or earlier if there is any complication in pregnancy.
 Complications of Multiple Gestation: A- Maternal Complications as follows ; u Anemia u Hydramnios u Hypertension u Premature labor u Postpartum uterine atony & PPH u PET u C. S. u +Obstructive Uropathy & renal failure. u
Complications of Multiple Gestation: A- Maternal Complications as follows ; u Anemia u Hydramnios u Hypertension u Premature labor u Postpartum uterine atony & PPH u PET u C. S. u +Obstructive Uropathy & renal failure. u
 Fetal Complications : u Placenta previa u Abrupto placentae u Umbilical cord prolapse u Malpresentation u PROM u Prematurity u IUGR u Congenital anomalies u Increased PNM & Morbidity.
Fetal Complications : u Placenta previa u Abrupto placentae u Umbilical cord prolapse u Malpresentation u PROM u Prematurity u IUGR u Congenital anomalies u Increased PNM & Morbidity.
 Intrapartum Management : u Should preterm labor develop prior to 34 wks , aggressive management must be considered : tocolytic agents to arrest labor, administration of glucocorticoids to accelerate fetal lung maturity & to avoid fluid ovreload.
Intrapartum Management : u Should preterm labor develop prior to 34 wks , aggressive management must be considered : tocolytic agents to arrest labor, administration of glucocorticoids to accelerate fetal lung maturity & to avoid fluid ovreload.
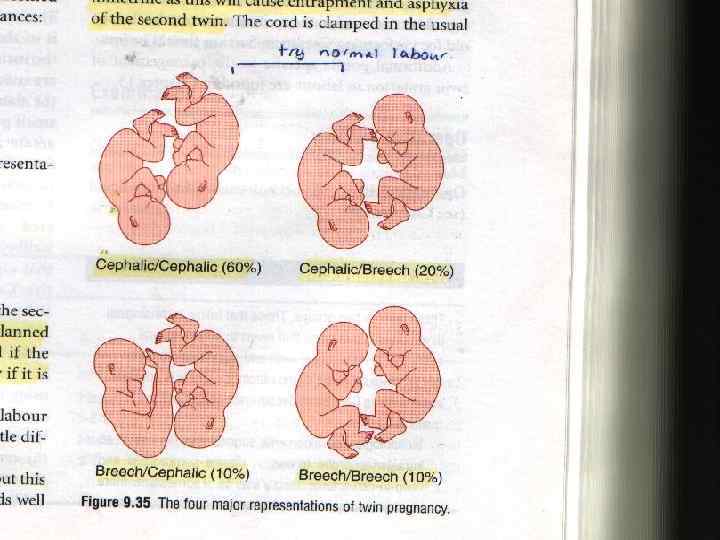
 Methods of delivery : u Vertex-Vertex Presentations : The presentations of ‘ fetuses must be accurately known to determine ‘ best method of delivery. The presenting twin is called twin A & ‘ second twin , twin B. u Vertex-Vertex most common (50%) , followed by Vertex-Breech, Breech. Vertex & finally Breech-Breech.
Methods of delivery : u Vertex-Vertex Presentations : The presentations of ‘ fetuses must be accurately known to determine ‘ best method of delivery. The presenting twin is called twin A & ‘ second twin , twin B. u Vertex-Vertex most common (50%) , followed by Vertex-Breech, Breech. Vertex & finally Breech-Breech.
 Continue ; u For vertex-vertex presentations, labor is similar as singleton vertex. Both FHR should be monitored continuously in labor, in addition uterine contractions should be monitored as well using intrauterine pressure catheter. After delivery of twin A, the cord is clamped & cut. Vaginal exam, is performed to assess presentation & station of ‘
Continue ; u For vertex-vertex presentations, labor is similar as singleton vertex. Both FHR should be monitored continuously in labor, in addition uterine contractions should be monitored as well using intrauterine pressure catheter. After delivery of twin A, the cord is clamped & cut. Vaginal exam, is performed to assess presentation & station of ‘
 Continue ; If second twin still vertex , allow labor to contnue. Once ‘ vertex becomes fixed in ‘ pelvis, ARM done & a fetal scalp electrode applied. Labour will end in spontaneous or forceps if needed. u Optimal time between delivery of ‘ 1 st &2 nd twin is controversial ( < 20 minutes ). u After delivery of 2 nd twin, placenta delivered & blood samples obtained. u Measures to prevent PPH are taken. u
Continue ; If second twin still vertex , allow labor to contnue. Once ‘ vertex becomes fixed in ‘ pelvis, ARM done & a fetal scalp electrode applied. Labour will end in spontaneous or forceps if needed. u Optimal time between delivery of ‘ 1 st &2 nd twin is controversial ( < 20 minutes ). u After delivery of 2 nd twin, placenta delivered & blood samples obtained. u Measures to prevent PPH are taken. u
 Management of Other Presentations : Vertex-Breech or Vertex- transverse ; in inexperienced hands , C. S. performed. But with experienced obstetrician , safe delivery of 2 nd twin is achieved by breech extraction vaginally. u Breech-Vertex , C. S. is recommended to avoid interlocking twins as well as ‘ potential complications of a vaginal breech delivery. u Breech-Breech C. S. is indicated. u PS. <25 wks , C. S. is avoided because fetal survival is poor. u
Management of Other Presentations : Vertex-Breech or Vertex- transverse ; in inexperienced hands , C. S. performed. But with experienced obstetrician , safe delivery of 2 nd twin is achieved by breech extraction vaginally. u Breech-Vertex , C. S. is recommended to avoid interlocking twins as well as ‘ potential complications of a vaginal breech delivery. u Breech-Breech C. S. is indicated. u PS. <25 wks , C. S. is avoided because fetal survival is poor. u
 Perinatal Outcome : u PNM & Morbidity in twins greatly exceed those of singleton birth. It is 30 -50/1000 births i. e. 5 times ‘ singleton. RDS & Prematurity , account for half of ‘ PNM. u PNM for monochorionic twins (120/1000 live birth), is about 3 times that for dichorionic twins.
Perinatal Outcome : u PNM & Morbidity in twins greatly exceed those of singleton birth. It is 30 -50/1000 births i. e. 5 times ‘ singleton. RDS & Prematurity , account for half of ‘ PNM. u PNM for monochorionic twins (120/1000 live birth), is about 3 times that for dichorionic twins.
 Retained Dead Fetus Syndrome : u Disseminated Intravascular coagulopathy may develop in either ‘ live fetus or ‘ mother as a result of transfer of nonviable fetal material with thromboplastin-like activity in ‘ circulation of ‘ remaining twin or ‘ mother , leading to DIC. In this situation , check maternal platelet count & fibrinogen once weekly. Prior to 12 wks ‘ fetus is absorbed. Beyond this time ( fetus papyraceus or fetus compressus ).
Retained Dead Fetus Syndrome : u Disseminated Intravascular coagulopathy may develop in either ‘ live fetus or ‘ mother as a result of transfer of nonviable fetal material with thromboplastin-like activity in ‘ circulation of ‘ remaining twin or ‘ mother , leading to DIC. In this situation , check maternal platelet count & fibrinogen once weekly. Prior to 12 wks ‘ fetus is absorbed. Beyond this time ( fetus papyraceus or fetus compressus ).
 Multiple Gestation >Two Fetuses : u The incidence of spontaneous triplets is 1 in 8000 & that of spontaneous quadruplets is 1 in 700, 000 births. In IVF the incidence is 1 in 3000 births. Prematurity increases as ‘ number of fetuses increases. The average length of gestation is 33 wks for triplets & 29 wks for quadriplets. Many authorities believe that mutiple gestation more than 2 fetuses , C. S. is routinely done to avoid birth trauma, asphyxia, & cord prolapse.
Multiple Gestation >Two Fetuses : u The incidence of spontaneous triplets is 1 in 8000 & that of spontaneous quadruplets is 1 in 700, 000 births. In IVF the incidence is 1 in 3000 births. Prematurity increases as ‘ number of fetuses increases. The average length of gestation is 33 wks for triplets & 29 wks for quadriplets. Many authorities believe that mutiple gestation more than 2 fetuses , C. S. is routinely done to avoid birth trauma, asphyxia, & cord prolapse.
 Continue ; u The PNM rate for triplets & quadruplets is 50 to 100 per 1000 births , a rate that is twice that of twins.
Continue ; u The PNM rate for triplets & quadruplets is 50 to 100 per 1000 births , a rate that is twice that of twins.



