Multiple choice question presented by Dr: ADNAN RADIImmunological


Multiple choice question presented by Dr: ADNAN RADI

Immunological disease with pregnancy

The initial maternal immunological response to primary rubella infection is Immunoglobulin M Immunoglobulin G Immunoglobulin A Immunoglobulin D

WOMEN WHO HAVE SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS SHOULD BE COUNSELED THAT ? Pregnancy is contraindicated If pregnant they should have a therapeutic abortion Their disease is likely to inhibit their fertility Their disease is likely to flare up after delivery

ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS CAN BE CAUSED BY MATERNAL INCOMPATIBILITY WITH THE FOLLOWING ANTIGENS EXCEPT Kell Kidd Duffy Lewis
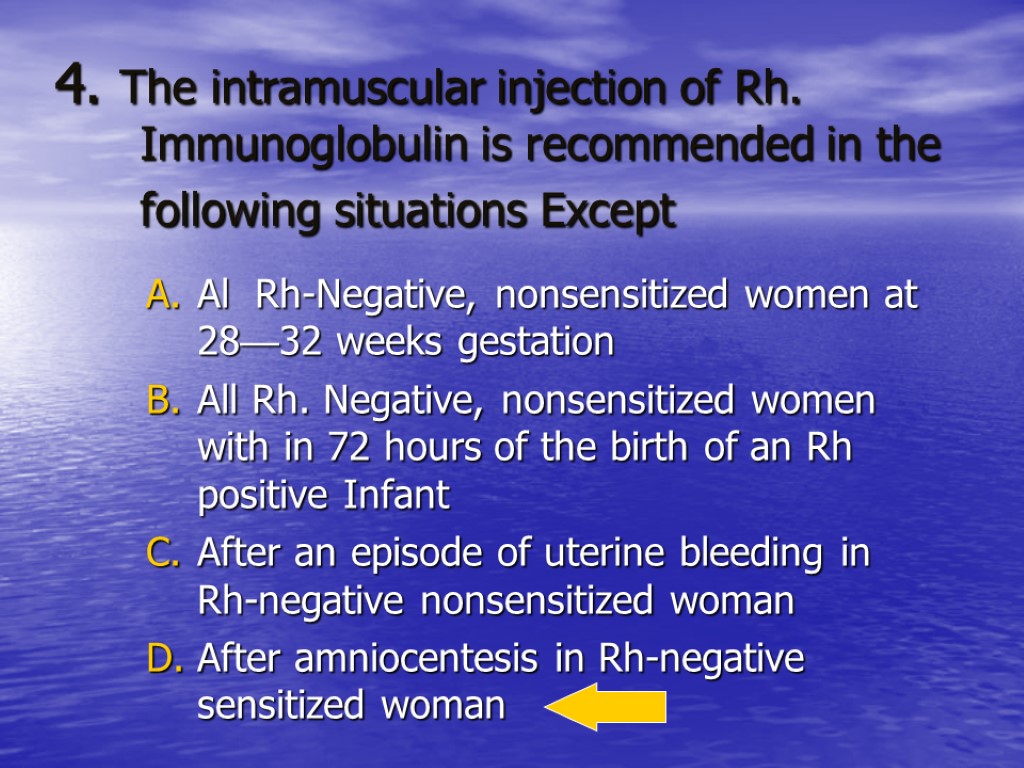
4. The intramuscular injection of Rh. Immunoglobulin is recommended in the following situations Except Al Rh-Negative, nonsensitized women at 28—32 weeks gestation All Rh. Negative, nonsensitized women with in 72 hours of the birth of an Rh positive Infant After an episode of uterine bleeding in Rh-negative nonsensitized woman After amniocentesis in Rh-negative sensitized woman

The neonatal risk of maternal immune thrombocytopenia purpura is Increased abortion rate Thrombocytopenia Necrotizing enterocolitis No risk

GENITAL PROLAPS

COMMON PROBLEM OCCURING AFTER VAGINAL HYSTRECTOMY INCLUDE ALL THE FOLLOWING EXCEPT Stress urinary incontinence Dyspareunia Non-fistulous fecal incontinence Vagina vault prolapse

UTRO- VAGINAL PROLAPSE Is termed procidentia when the cervix lies outside the introitus May be asymptomatic Is best treated by a ring pessary Is prevented by liberal use of episiotomy

RENAL DISEASE WITH PREGNANCY

HOW MUCH PROTEINURIA IS CONSIDERED ABNORMAL DURING PREGNANCY? 50 mgday 100mgday 200mgday 500mgday

THE ADVERSE PREGNANCY OUTCOMES ASSOCIATED WITH ASYMPTOMATIC BACTURIURIA IS .. Low birthweight infant Acute pyelonephritis Antepartum hage Pregnancy induced hypertension

WHAT IS THE MOST COMMON SERIOUS MEDICAL COMPLICATION OF PREGNANCY IN.. Cystitis Pneumonia Pancreatitis Pyelonephritis

THE DIFFERNTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR PYELONEPHRITS INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING EXCEPT Chorioamnionitis Labour Pneumonia Abruption-placenta

THE FOLLOWING COMPLICATIONS IS ASSOCIATED WITH RENAL CORTICAL NECROSIS EXCEPT ECLAMPSIA ABRUPTIO- PLACENTA PLACENTA PRAEVIA ENDOTOXIN –INDUCED SHOCK

HEMATOLOGICAL DISEASE WITH PREGNANCY

ANAEMIA DURING PREGNANCY IS DEFINED AS Hemoglobin concentration <8 gm/dl Hemoglobin concentration <10.5 gm/dl Hemoglobin concentration <12 gm/dl Hemoglobin concentration <14 gm/dl

14.The MOST COMMON CAUSES OF ANAEMIA DURING PREGNANCY IS IRON DEFICIENCY ANAEMIA SICKLE CELL FOLATE DEFICIENCY THALASSEMIA
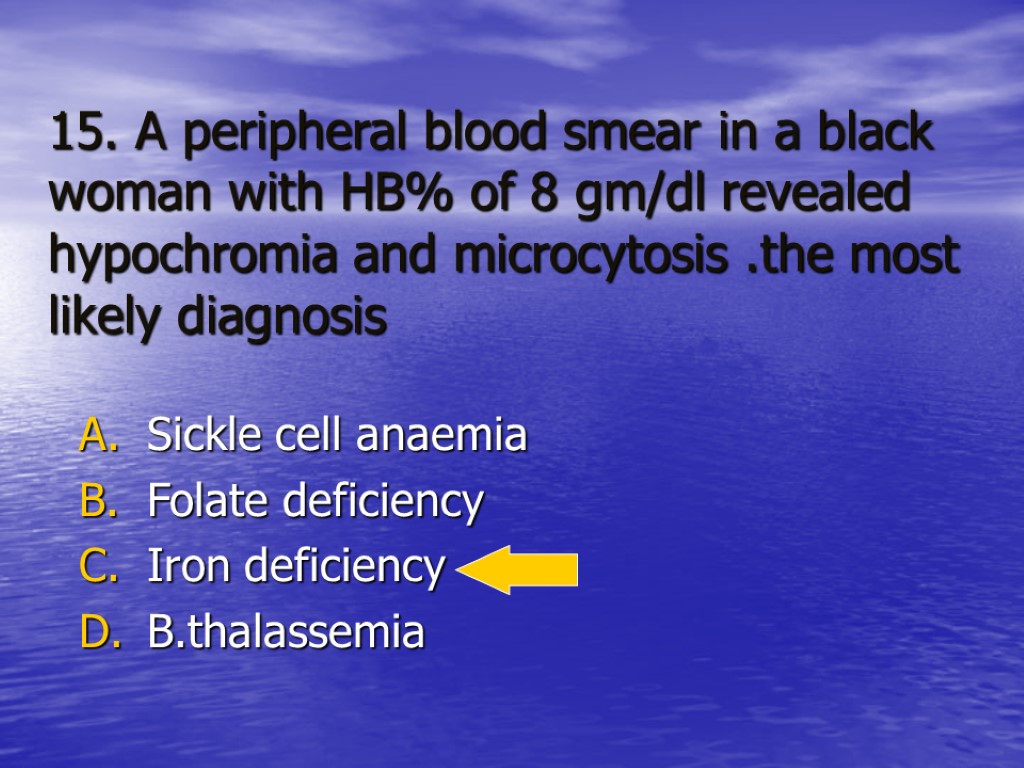
15. A peripheral blood smear in a black woman with HB% of 8 gm/dl revealed hypochromia and microcytosis .the most likely diagnosis Sickle cell anaemia Folate deficiency Iron deficiency B.thalassemia

16. The earliest morphological evidence of folic acid deficiency is Hyper segmentation of neutrophils Microcytosis Macrocytic erythrocytes Nucleated red blood cells
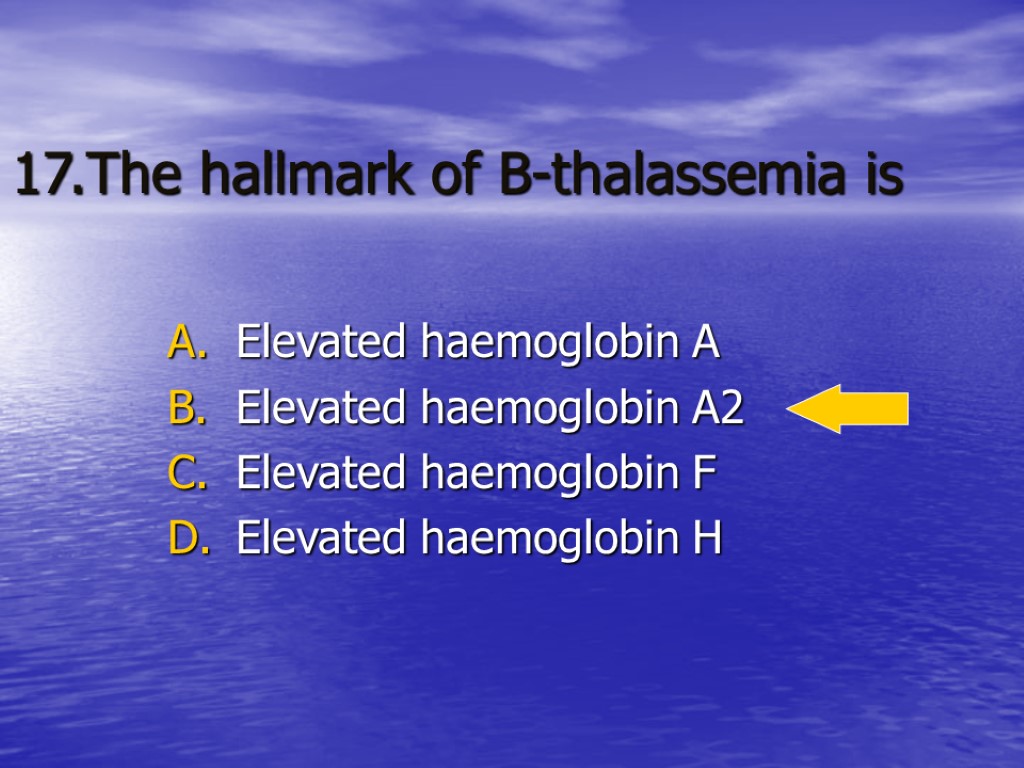
17.The hallmark of B-thalassemia is Elevated haemoglobin A Elevated haemoglobin A2 Elevated haemoglobin F Elevated haemoglobin H
Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy

18. The infant of diabetic mother is at risk for all of the following except Increased perinatal death rate Neural tube defects Hyperglycaemia macrosomia

19.Diagnosis of diabetes during pregnancy is suspected in women who have:- Strong family history of diabetes Previous history of macrosomic baby Persistent glycosurea All of the above

20.Effect of diabetes on pregnant mother Increase incidence of pre-eclampsia Infection Hydramnibs All of the above

21.The fetus of a diabetic mother is at increased risk of:- Congenital abnormalities Increased perinatal mortality &morbidity Neonatal hypoglycemia All of the above

Positive family history of diabetes History of deliver of macrosomic babies Normtensive mothers History of congenital anomaly 22. Risk factors requiring diabetic screening include all of the followings EXCEPT :-

23. The objective of treatment of pregnant diabetic mother is to maintain :- The fasting blood suger under 150 mg/dl The fasting blood suger under 180 mg/d The fasting blood suger under 105 mg/dl The fasting blood suger under 70 mg/dl

Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy

24. Pre-eclampsia is hypertension with protein urea induced by pregnancy after twentieth week unless is :- Molar pregnancy Multiple pregnancy Hydrops fetalis Renal disease

25. Management of pre eclamptic patient include all of the following EXCEPT Bed rest Contraction stress test Diuretics Hospitalization

26. Pre eclampsia in the multiparous pregnant patient is associated with all of the following condition EXCEPT Multiple gestation Diabetes Hyperthyroidism Chronic hypertension

27.Characters of severs pre eclapsia include all of the following EXCEPT Diastolic blood pressure of 110 mm Hg. Or more 2+ protein urea Thrombocytopenia Low creatinine level

28. Indications for delivery of pre-eclamplic patient include Worsening hypertension Increasing protein urea Compromise in fetal well –being All of the above

29. Which of the following is not diagnostic of severe pre-eclampsia pulmonary oedema 1 + protein urea thrombocytopenia levated liver enzymes

30. low dose aspirin given to pregnant women decrease thromboxane increase prostacycline increase prostaglandin E2 all of the above

31. Excretion of magnesium is via the Brain Liver Kidney Gastro intestinal tract

32. Management of cardiac failure during labour includes Oxygen Digitalis Diuretics All of the above

33.Management of pregnant cardiac patients include all of the followings except :- Hospitalization Adequate analgesia Delivery should be accomplished vaginally unless there is an obstetric indication for c.s No need to guard against post – partum infection and hemorrhage

34.The majority of heart disease in pregnacy is due to Idiopathic cardiomyopathy Constrictive pericarditis Hypertension Congenital heart lesions

35. The first warning sign of cardiac failure is Persistent rales at lung base Dyspnea Hemoptysis Progressive edema

Postdate and multiple pregnancy

36.Postterm pregnancy is defined as Beyond 37 wks Beyond 40 wks Beyond 42 wks Beyond 44 wks

37.The most common cause of oligohydramnious is:- Renal anomalies Fetal growth restriction Twin to twin transfusion Premature rupture of membranes

38. At 30 weeks one twin noticed to have died in the uterus , management includes :- Immediate delivery with oxytoain Immediate delivery with c.s Observation Heparin injection to avoid coagulopathy

39. The mean duration for gestation in twins pregnancy is .. 32 wks 34 wks 37 wks 40 wks

40. Twins pregnancy cause increased risk of all the following EXCEPT Cord entanglement Post partum haemorrhage Diabetes mellitus Pre eclampsia

41. Infant risks from postdate pregnancy include Abruptio- placenta Respiratory distress Precipitat delivery Cord compression

42. Monitoring the postdate pregnancy should include the following EXCEPT α –feto protein level Ultrasound exam Vaginal exam Maternal blood pressure

43.The fetus in postdate pregnancy can have the following EXCEPT Macrosomia Polycystic kidneys Oligohydramniose Placental insufficiency

Physiological changes during pregnancy

44. The following describe the physiological changes of the stomach during pregnancy EXCEPT Tone decrease Emptying time increase Motility decrease Gastro –oesphageal sphincter tone increase

45. Which of the following is the characters of hydronephrosis in pregnancy Common physiological findings Begins in the third trimester More prominent in the left than the right More prominent below the pelvic brim

46. All of the following are normal finding in the pregnancy EXCEPT Leg odema Systolic murmur Diastolic murmur Third heart sound
47. Increased cardiac output immediately post partum is due to Increase heart rate Release of obstruction of venous return Reduced motilization of extracellular fluid Reduced stroke volume

Disorders of uterine corpus ovaries and cervix

48. Often the most symptoms of cervical cancer is Leg pain Pain with intercourse Vaginal bleeding Vulvar pruritus

49.The most cervical cancers arise At the internal os At the external os In the endocervix At the squamo-columnar junction

50. The most common uterine tumour is Sarcoma Adenocarcinoma Adenomyosis leiomyoma

51.The most common symptoms of endometrial carcinoma is Vaginal discharge Vaginal bleeding Uterine enlargement pain

52. Which of the following symptoms most commonly accompanies early ovarian cancer Pelvic pain Dysuria Constipation Non of the above

53. Ovarian neoplasia most commonly arise from Ovarian epithylium Ovarian stroma Ovarian germ cells Ovarian sex cord
54. Which of the following HPV is not associated with lesions of the human genital tract HPV 6 HPV 10 HPV 16 HPV 18

55. Radical hysterectomy is commonly utilized for which of the following stages of cervical cancer Stage II A Stage II B Stage III A stage III B

56. The most accepted screening test for endometrial adenocarcinoma is pap .smear Endometrial biopsy Vaginal ultra sound None of the above

57.All of the following are characteristic of the functional ovarian cysts EXCEPT Thin wall Unilocular 10 cm. in diameter Resolves with 6-8 weeks

58. All of the following are characteristic of polycystic ovarian syndrome EXCEPT Amenorrhea Infertility Anvulation Pituitary adenoma

59. The largest benign neoplasms of the ovary have which of the following histology Serous cyst adenoma Mucinous cyst adenoma Teratoma fibrothecoma

60. The best therapy for post menopausal women with 3 cm unilocular adnexial cyst is Urgent laparotomy with cystectomy Laparoscopic excision Close monotoring Radiation therapy
dr_adnan_radi.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70

