467de7e60968c7281e66ed53c223a219.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Multinational Companies Chapter 5. 2, pages 150 -156
Multinational Companies Chapter 5. 2, pages 150 -156
 Corporation n n A corporation or limited company is a legal entity created by law and established by a corporate charter. A corporation can enter agreements, own land property, and hold contracts just like an individual. The liability of business owners is limited to the amount they invest in the corporation. Corporations are often managed by a board of directors elected by shareholders. This board appoints a president and managers to take care of the everyday operation of the business. Ownership is divided into shares, and their can be one owner or thousands of owners.
Corporation n n A corporation or limited company is a legal entity created by law and established by a corporate charter. A corporation can enter agreements, own land property, and hold contracts just like an individual. The liability of business owners is limited to the amount they invest in the corporation. Corporations are often managed by a board of directors elected by shareholders. This board appoints a president and managers to take care of the everyday operation of the business. Ownership is divided into shares, and their can be one owner or thousands of owners.
 Multinational Company (MNC) n n n AKA transnational company A business enterprise that conducts business in several countries Must observe national regulations in countries where they operate Account for more than 70% of world trade Over 90% of parent companies are in the northern hemisphere
Multinational Company (MNC) n n n AKA transnational company A business enterprise that conducts business in several countries Must observe national regulations in countries where they operate Account for more than 70% of world trade Over 90% of parent companies are in the northern hemisphere
 MNC’s can be very economically powerful q q q extract, refine and distribute most of the world’s oil and gas build most of the world’s hydroelectric and nuclear plants manufacture most of the world’s communications equipment, chemicals and medicine (including H 1 N 1 vaccines and anti-viral medicines)
MNC’s can be very economically powerful q q q extract, refine and distribute most of the world’s oil and gas build most of the world’s hydroelectric and nuclear plants manufacture most of the world’s communications equipment, chemicals and medicine (including H 1 N 1 vaccines and anti-viral medicines)
 MNC’s usually have there HQ in a major city and operate in one of three ways n Ethnocentric MNC q n Polycentric MNC q n Operates internationally like it does at home, with tight controls over foreign operations (i. e. Coca Cola) Understands the differences in other countries and gives more autonomy to foreign operations (i. e. 3 -M) Geocentric MNC q global in the true meaning of the word, since there is no strategic base left in the home country; not traditionally bound to any particular place; looks at the world as one big market, therefore being located in the most suitable place in relation to its activities
MNC’s usually have there HQ in a major city and operate in one of three ways n Ethnocentric MNC q n Polycentric MNC q n Operates internationally like it does at home, with tight controls over foreign operations (i. e. Coca Cola) Understands the differences in other countries and gives more autonomy to foreign operations (i. e. 3 -M) Geocentric MNC q global in the true meaning of the word, since there is no strategic base left in the home country; not traditionally bound to any particular place; looks at the world as one big market, therefore being located in the most suitable place in relation to its activities
 Global Organizational Structure There are various organizational structure possibilities for MNC’s n Separate International Divisions – separate from company, own systems n Functional Divisions – by departments n Product Divisions – by product groupings n Geographic Divisions – by global regions n Matrix Organization – reporting flows through all departments
Global Organizational Structure There are various organizational structure possibilities for MNC’s n Separate International Divisions – separate from company, own systems n Functional Divisions – by departments n Product Divisions – by product groupings n Geographic Divisions – by global regions n Matrix Organization – reporting flows through all departments
 Separate International Division n See p. 154
Separate International Division n See p. 154
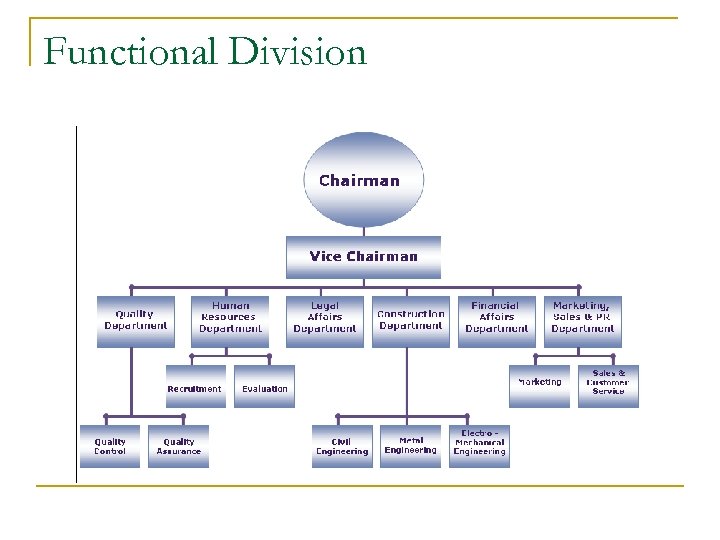 Functional Division
Functional Division
 Product Divisions n See p. 155
Product Divisions n See p. 155
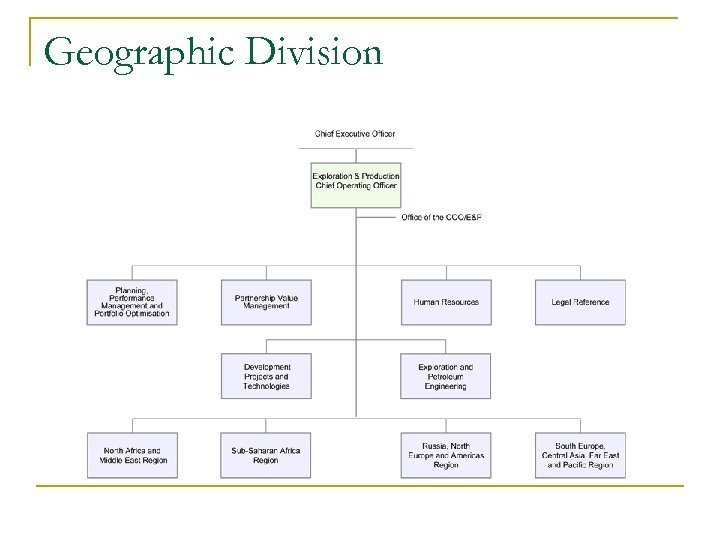 Geographic Division
Geographic Division
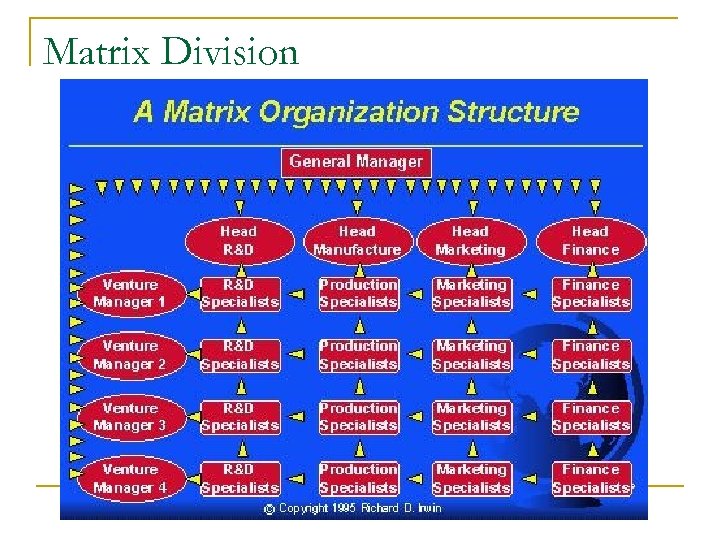 Matrix Division
Matrix Division
 Trading Stocks There are four basic ways to trade stocks: n Buy (BO) q When buying a stock, you are taking a “long position” with the hope that the price per share will increase. n Sell (SC) q When you sell a stock, you close that long position. n Short sell (SS) q Selling short is selling a stock that you don’t own (you actually borrow the stock from the broker) with the hope that you can later buy the stock back at a lower price. n Short cover (CO) q When you buy the stock to pay back what you borrowed, it is called “covering” your short position. q To buy or short sell a stock, specify how many shares you want, rather than how much money you have to spend.
Trading Stocks There are four basic ways to trade stocks: n Buy (BO) q When buying a stock, you are taking a “long position” with the hope that the price per share will increase. n Sell (SC) q When you sell a stock, you close that long position. n Short sell (SS) q Selling short is selling a stock that you don’t own (you actually borrow the stock from the broker) with the hope that you can later buy the stock back at a lower price. n Short cover (CO) q When you buy the stock to pay back what you borrowed, it is called “covering” your short position. q To buy or short sell a stock, specify how many shares you want, rather than how much money you have to spend.
 FUTURES CONTRACT A standardized, transferable legal agreement to make or take delivery of a specified amount of a certain commodity, currency, or an asset at the end of specified time frame. The price is determined when the agreement is made. Future contracts are always marked to market.
FUTURES CONTRACT A standardized, transferable legal agreement to make or take delivery of a specified amount of a certain commodity, currency, or an asset at the end of specified time frame. The price is determined when the agreement is made. Future contracts are always marked to market.
 OPTIONS CONTRACT n A contract where an investor buys a call or put option for Hunderd stocks for the stock option contract. On the other hand, the size of the future contract depends on the future, which is usually same as the size of futures contract.
OPTIONS CONTRACT n A contract where an investor buys a call or put option for Hunderd stocks for the stock option contract. On the other hand, the size of the future contract depends on the future, which is usually same as the size of futures contract.
 MUTUAL FUNDS n A mutual fund is a pooling of investor (shareholder) assets, which is professionally managed by an investment company for the benefit of the fund's shareholders. Each fund has specific investment objectives and associated risk. Mutual funds offer shareholders the advantage of diversification and professional management in exchange for a management fee.
MUTUAL FUNDS n A mutual fund is a pooling of investor (shareholder) assets, which is professionally managed by an investment company for the benefit of the fund's shareholders. Each fund has specific investment objectives and associated risk. Mutual funds offer shareholders the advantage of diversification and professional management in exchange for a management fee.


