a7c408b30db64ac44a0ef456a4bc521c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Multimodal Monitoring in Head Injured Patients Management of CPP: Detection and Treatment of optimal CPP Jürgen Meixensberger Department of Neurosurgery
Multimodal Monitoring in Head Injured Patients Management of CPP: Detection and Treatment of optimal CPP Jürgen Meixensberger Department of Neurosurgery
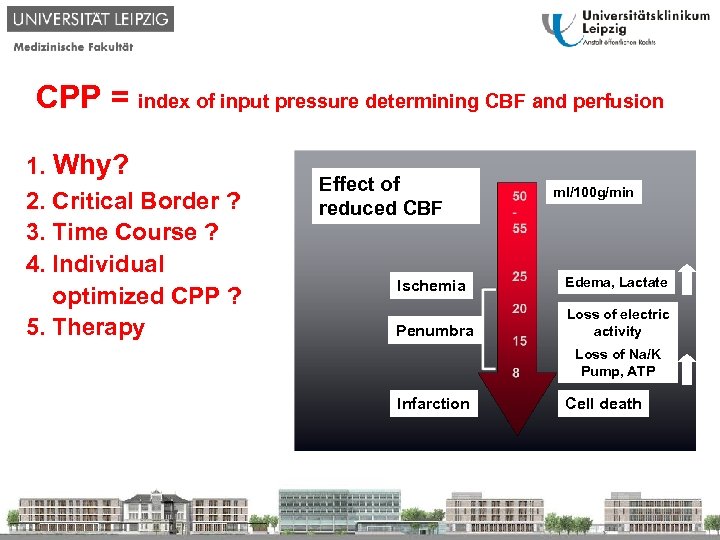 CPP = index of input pressure determining CBF and perfusion 1. Why? 2. Critical Border ? 3. Time Course ? 4. Individual optimized CPP ? 5. Therapy Effect of reduced CBF ml/100 g/min Ischemia Edema, Lactate Penumbra Loss of electric activity Loss of Na/K Pump, ATP Infarction Cell death
CPP = index of input pressure determining CBF and perfusion 1. Why? 2. Critical Border ? 3. Time Course ? 4. Individual optimized CPP ? 5. Therapy Effect of reduced CBF ml/100 g/min Ischemia Edema, Lactate Penumbra Loss of electric activity Loss of Na/K Pump, ATP Infarction Cell death
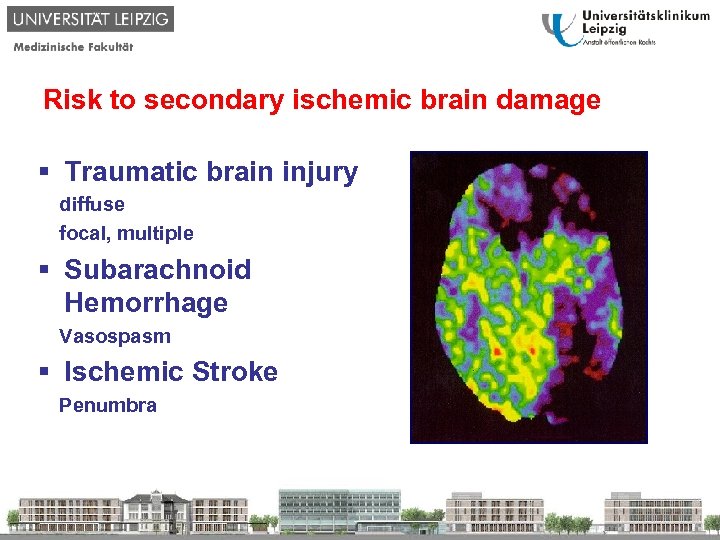 Risk to secondary ischemic brain damage § Traumatic brain injury diffuse focal, multiple § Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Vasospasm § Ischemic Stroke Penumbra
Risk to secondary ischemic brain damage § Traumatic brain injury diffuse focal, multiple § Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Vasospasm § Ischemic Stroke Penumbra
 Guideline German Society of Neurosurgery Traumatic Brain Injury in Adults CPP „Adequate cerebral perfusion pressure is necessary to provide a sufficient cerebral blood flow. The question, whether to treat increased ICP or maintainance of CPP as first treatment goal, is still controversial in the literature. “ AWMF – Leitlinien – Register Nr. 008/001
Guideline German Society of Neurosurgery Traumatic Brain Injury in Adults CPP „Adequate cerebral perfusion pressure is necessary to provide a sufficient cerebral blood flow. The question, whether to treat increased ICP or maintainance of CPP as first treatment goal, is still controversial in the literature. “ AWMF – Leitlinien – Register Nr. 008/001
 Cerebral Perfusion Pressure CPP Definition Cerebral Perfusion Pressure* is a surrogate of cerebral blood flow CBF = CPP (MAP – ICP*)/CVR * Referenced to the Foramen of Monroi
Cerebral Perfusion Pressure CPP Definition Cerebral Perfusion Pressure* is a surrogate of cerebral blood flow CBF = CPP (MAP – ICP*)/CVR * Referenced to the Foramen of Monroi
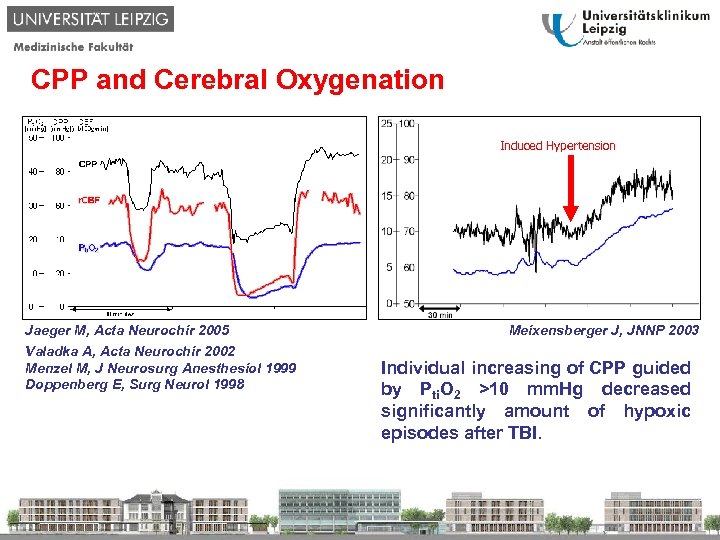 CPP and Cerebral Oxygenation Induced Hypertension Jaeger M, Acta Neurochir 2005 Valadka A, Acta Neurochir 2002 Menzel M, J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 1999 Doppenberg E, Surg Neurol 1998 Meixensberger J, JNNP 2003 Individual increasing of CPP guided by Pti. O 2 >10 mm. Hg decreased significantly amount of hypoxic episodes after TBI.
CPP and Cerebral Oxygenation Induced Hypertension Jaeger M, Acta Neurochir 2005 Valadka A, Acta Neurochir 2002 Menzel M, J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 1999 Doppenberg E, Surg Neurol 1998 Meixensberger J, JNNP 2003 Individual increasing of CPP guided by Pti. O 2 >10 mm. Hg decreased significantly amount of hypoxic episodes after TBI.
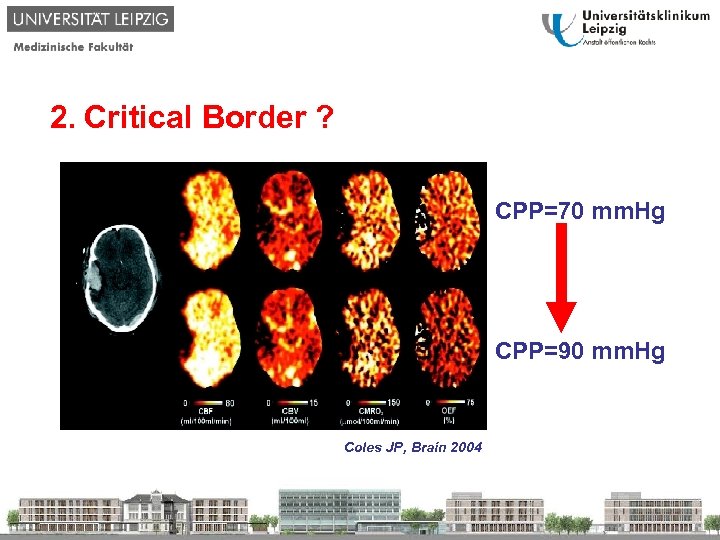 1. Why? 2. Critical Border ? 3. Time Course ? 4. Individual optimized CPP ? 5. Causes 6. Therapy CPP=70 mm. Hg CPP=90 mm. Hg Coles JP, Brain 2004
1. Why? 2. Critical Border ? 3. Time Course ? 4. Individual optimized CPP ? 5. Causes 6. Therapy CPP=70 mm. Hg CPP=90 mm. Hg Coles JP, Brain 2004
 § The optimal CPP in patients suffering from TBI is unclear. § Recommendations: From CPP>50, > 60 mm. Hg to CPP>90 mm. Hg § Reduced as well as high CPP influenced Outcome in a negative manner. Robertson et al. Crit Care Med 1999, Contant et al. J Neurosurg 2001 (n=189) Balestreri et al. Neurocrit Care 2006 (n=429)
§ The optimal CPP in patients suffering from TBI is unclear. § Recommendations: From CPP>50, > 60 mm. Hg to CPP>90 mm. Hg § Reduced as well as high CPP influenced Outcome in a negative manner. Robertson et al. Crit Care Med 1999, Contant et al. J Neurosurg 2001 (n=189) Balestreri et al. Neurocrit Care 2006 (n=429)
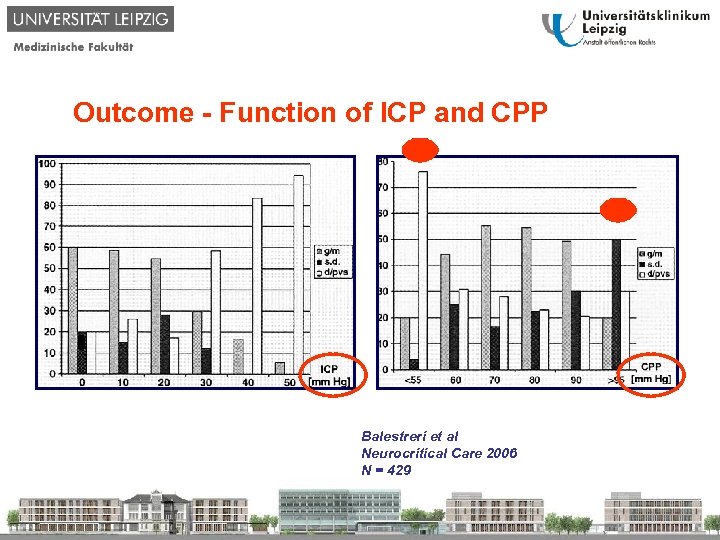 Outcome - Function of ICP and CPP Balestreri et al Neurocritical Care 2006 N = 429
Outcome - Function of ICP and CPP Balestreri et al Neurocritical Care 2006 N = 429
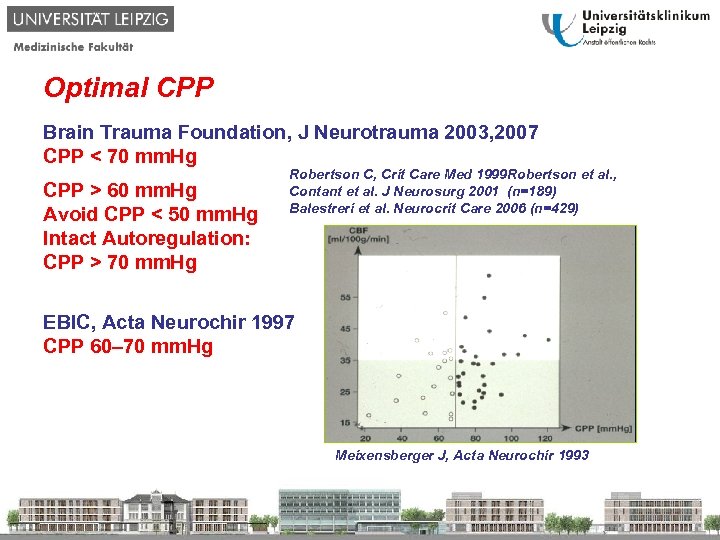 Optimal CPP Brain Trauma Foundation, J Neurotrauma 2003, 2007 CPP < 70 mm. Hg CPP > 60 mm. Hg Avoid CPP < 50 mm. Hg Intact Autoregulation: CPP > 70 mm. Hg Robertson C, Crit Care Med 1999 Robertson et al. , Contant et al. J Neurosurg 2001 (n=189) Balestreri et al. Neurocrit Care 2006 (n=429) EBIC, Acta Neurochir 1997 CPP 60– 70 mm. Hg Meixensberger J, Acta Neurochir 1993
Optimal CPP Brain Trauma Foundation, J Neurotrauma 2003, 2007 CPP < 70 mm. Hg CPP > 60 mm. Hg Avoid CPP < 50 mm. Hg Intact Autoregulation: CPP > 70 mm. Hg Robertson C, Crit Care Med 1999 Robertson et al. , Contant et al. J Neurosurg 2001 (n=189) Balestreri et al. Neurocrit Care 2006 (n=429) EBIC, Acta Neurochir 1997 CPP 60– 70 mm. Hg Meixensberger J, Acta Neurochir 1993
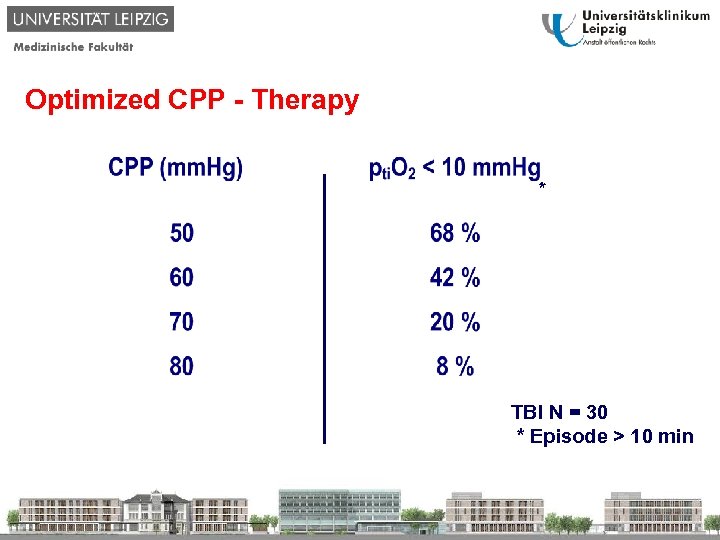 Optimized CPP - Therapy * TBI N = 30 * Episode > 10 min
Optimized CPP - Therapy * TBI N = 30 * Episode > 10 min
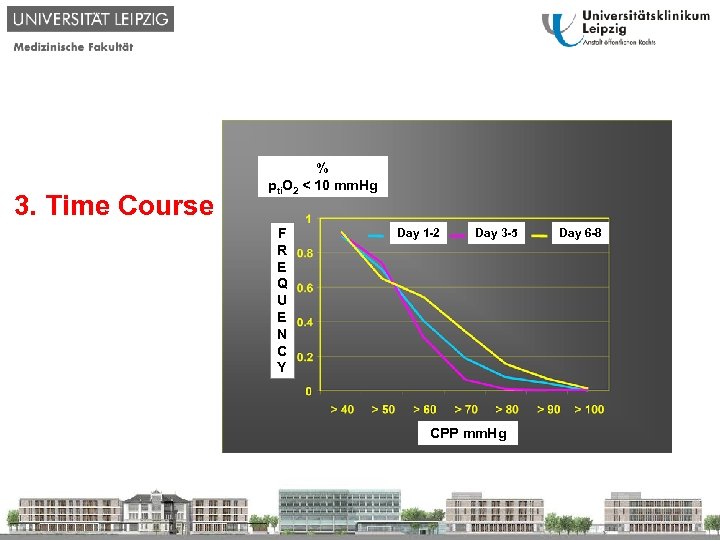 1. Why? 2. Critical Border ? 3. Time Course ? 4. Individual optimized CPP ? 5. Causes 6. Therapy % % ppti. O 2 < 10 mm. Hg F R E Q U E N C Y Day 1 -2 Day 3 -5 CPP mm. Hg Day 6 -8
1. Why? 2. Critical Border ? 3. Time Course ? 4. Individual optimized CPP ? 5. Causes 6. Therapy % % ppti. O 2 < 10 mm. Hg F R E Q U E N C Y Day 1 -2 Day 3 -5 CPP mm. Hg Day 6 -8
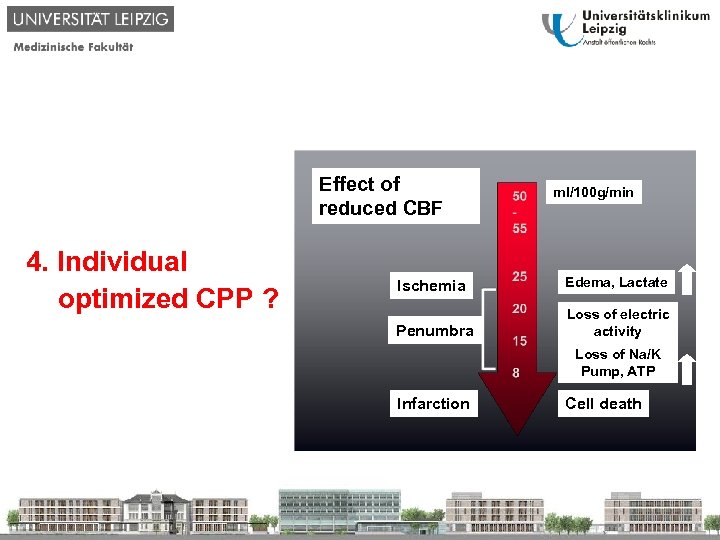 1. Why? 2. Critical Border ? 3. Time Course ? 4. Individual optimized CPP ? 5. Causes Effect of reduced CBF ml/100 g/min Ischemia Edema, Lactate Penumbra Loss of electric activity Loss of Na/K Pump, ATP 6. Therapy Infarction Cell death
1. Why? 2. Critical Border ? 3. Time Course ? 4. Individual optimized CPP ? 5. Causes Effect of reduced CBF ml/100 g/min Ischemia Edema, Lactate Penumbra Loss of electric activity Loss of Na/K Pump, ATP 6. Therapy Infarction Cell death
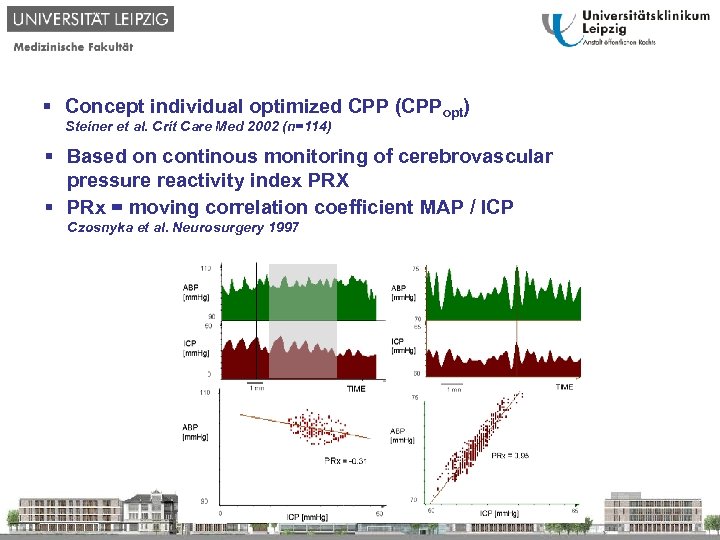 § Concept individual optimized CPP (CPPopt) Steiner et al. Crit Care Med 2002 (n=114) § Based on continous monitoring of cerebrovascular pressure reactivity index PRX § PRx = moving correlation coefficient MAP / ICP Czosnyka et al. Neurosurgery 1997
§ Concept individual optimized CPP (CPPopt) Steiner et al. Crit Care Med 2002 (n=114) § Based on continous monitoring of cerebrovascular pressure reactivity index PRX § PRx = moving correlation coefficient MAP / ICP Czosnyka et al. Neurosurgery 1997
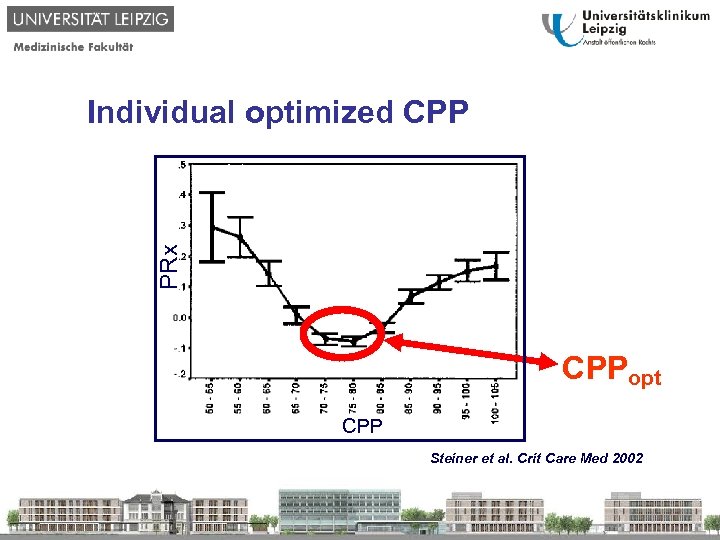 PRx Individual optimized CPPopt CPP Steiner et al. Crit Care Med 2002
PRx Individual optimized CPPopt CPP Steiner et al. Crit Care Med 2002
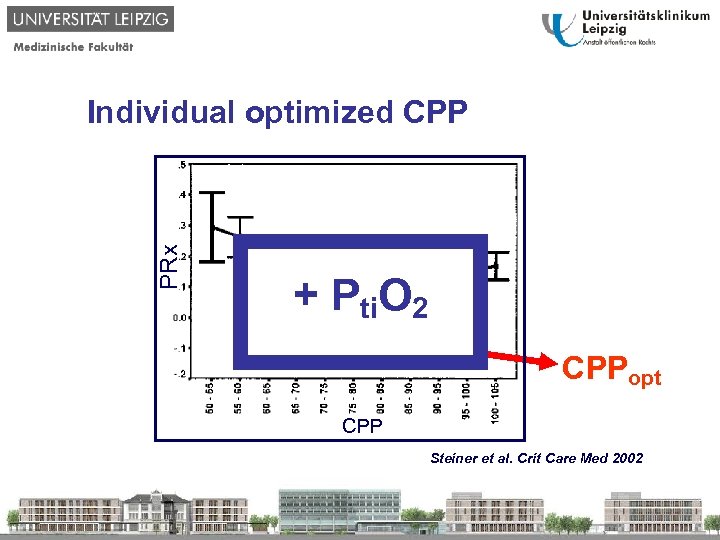 PRx Individual optimized CPP + Pti. O 2 CPPopt CPP Steiner et al. Crit Care Med 2002
PRx Individual optimized CPP + Pti. O 2 CPPopt CPP Steiner et al. Crit Care Med 2002
![§ TBI n=33 § Continous Monitoring (ICM-plus Software) MAP ICP [Codman] CPP Pti. O § TBI n=33 § Continous Monitoring (ICM-plus Software) MAP ICP [Codman] CPP Pti. O](https://present5.com/presentation/a7c408b30db64ac44a0ef456a4bc521c/image-17.jpg) § TBI n=33 § Continous Monitoring (ICM-plus Software) MAP ICP [Codman] CPP Pti. O 2 [Licox] § PRx = moving correlationcoefficient MAP / ICP §Czosnyka et al. Neurosurgey 1997 § Data analysis CPP vs. PRx CPP vs. Pti. O 2 CPP-class of 5 mm. Hg
§ TBI n=33 § Continous Monitoring (ICM-plus Software) MAP ICP [Codman] CPP Pti. O 2 [Licox] § PRx = moving correlationcoefficient MAP / ICP §Czosnyka et al. Neurosurgey 1997 § Data analysis CPP vs. PRx CPP vs. Pti. O 2 CPP-class of 5 mm. Hg
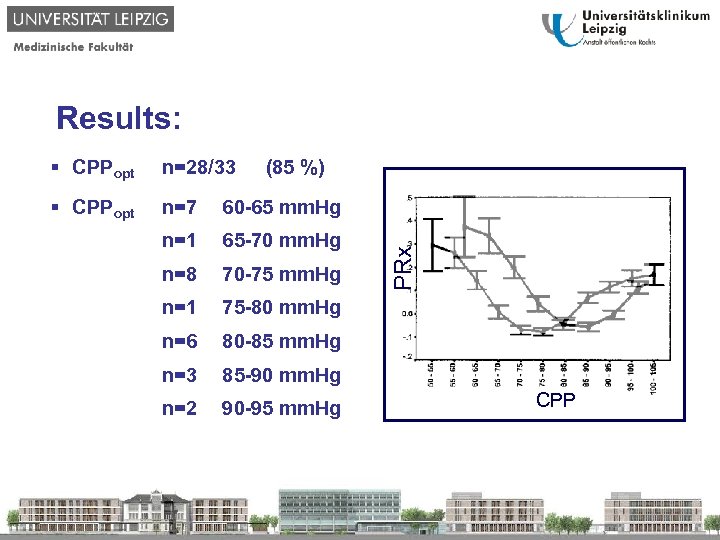 Results: § CPPopt n=28/33 § CPPopt n=7 60 -65 mm. Hg n=1 65 -70 mm. Hg n=8 70 -75 mm. Hg n=1 75 -80 mm. Hg n=6 80 -85 mm. Hg n=3 85 -90 mm. Hg n=2 90 -95 mm. Hg PRx (85 %) CPP
Results: § CPPopt n=28/33 § CPPopt n=7 60 -65 mm. Hg n=1 65 -70 mm. Hg n=8 70 -75 mm. Hg n=1 75 -80 mm. Hg n=6 80 -85 mm. Hg n=3 85 -90 mm. Hg n=2 90 -95 mm. Hg PRx (85 %) CPP
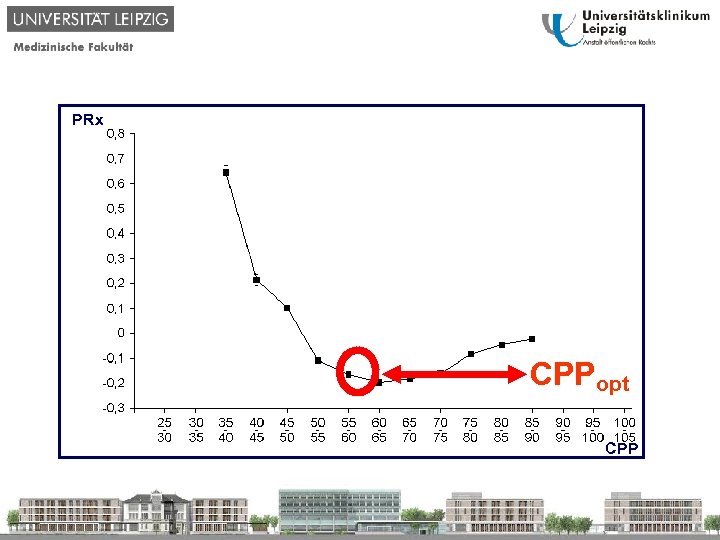 PRx CPPopt CPP
PRx CPPopt CPP
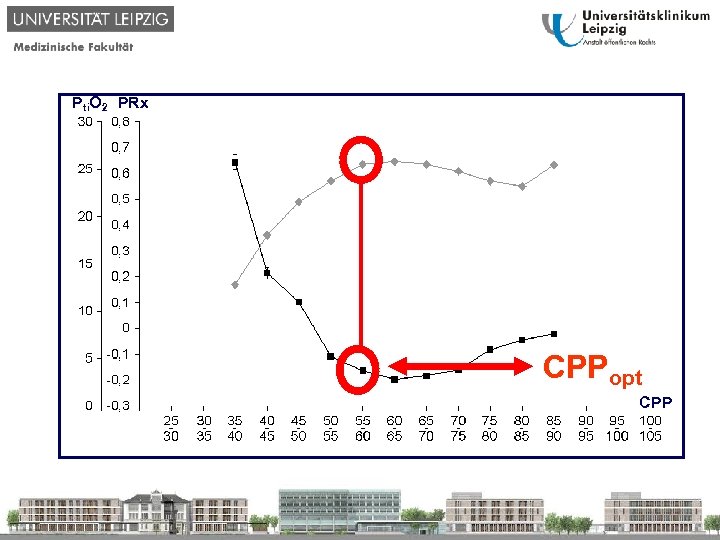 Pti. O 2 PRx CPPopt CPP
Pti. O 2 PRx CPPopt CPP
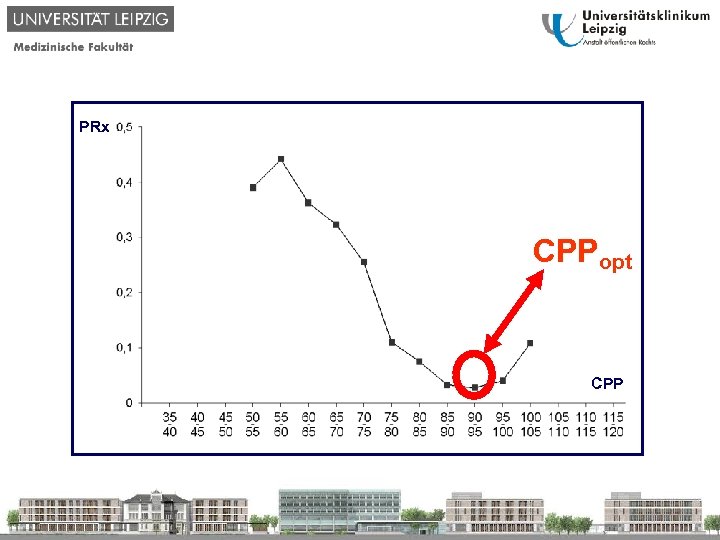 PRx CPPopt CPP
PRx CPPopt CPP
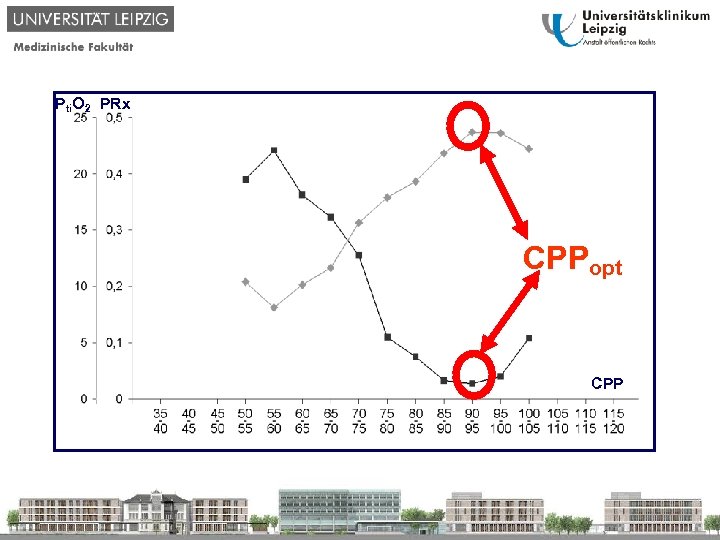 Pti. O 2 PRx CPPopt CPP
Pti. O 2 PRx CPPopt CPP
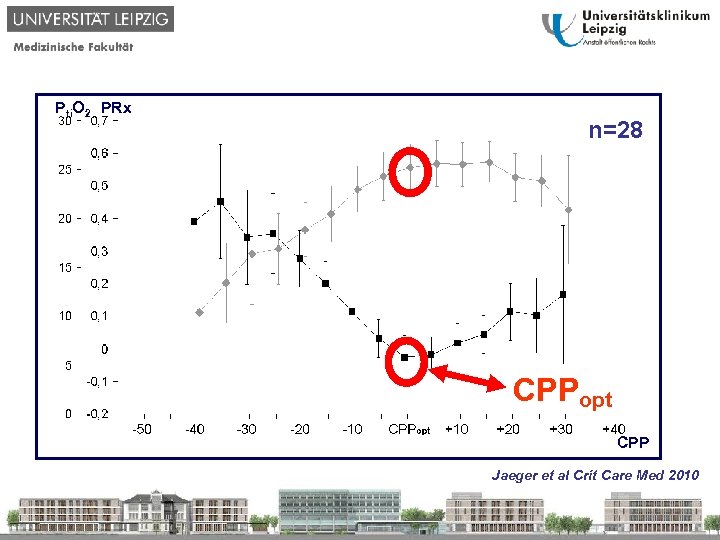 Pti. O 2 PRx n=28 CPPopt CPP Jaeger et al Crit Care Med 2010
Pti. O 2 PRx n=28 CPPopt CPP Jaeger et al Crit Care Med 2010
 Therapeutic Options: CPP > 60, < 70 mm. Hg * § Induced hypervolemia with cristalloids Cave: heart insufficience § No body/head – elevation 0° § Inotropica – infusion Cave: acute coronary syndrome, arrhythmia § Diuretics – Reduction of centralvenous pressure § Ventilation - „best PEEP“ - concept * Option; Prognostic value only given by case reports;
Therapeutic Options: CPP > 60, < 70 mm. Hg * § Induced hypervolemia with cristalloids Cave: heart insufficience § No body/head – elevation 0° § Inotropica – infusion Cave: acute coronary syndrome, arrhythmia § Diuretics – Reduction of centralvenous pressure § Ventilation - „best PEEP“ - concept * Option; Prognostic value only given by case reports;
 Management of CPP after TBI Recommendations: Avoid CPP < 50 mm. Hg – to minimize edema formation CPP > 70 – 80 mm. Hg – can improve perfusion if autoregulation is intact Class II evidence CPP of 60 mm. Hg – sufficient CBF and cerebral perfusion in most cases Ancillary monitoring is helpful to target CPP
Management of CPP after TBI Recommendations: Avoid CPP < 50 mm. Hg – to minimize edema formation CPP > 70 – 80 mm. Hg – can improve perfusion if autoregulation is intact Class II evidence CPP of 60 mm. Hg – sufficient CBF and cerebral perfusion in most cases Ancillary monitoring is helpful to target CPP
 Management of CPP after TBI Recommendations: Need for more data § Individualized optimal CPP based on hemodynamic monitoring/ pressure autoregulation indices § Randomized outcome studies
Management of CPP after TBI Recommendations: Need for more data § Individualized optimal CPP based on hemodynamic monitoring/ pressure autoregulation indices § Randomized outcome studies
 Thank You for Your Attention !
Thank You for Your Attention !


