feb1afaf2cfe7bc77186e352353769db.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Multilayer thin film technology enabling technology for solving high density interconnect and assembly problems Eric Beyne IMEC, Kapeldreef 75, B-3001 Leuven IWORID 2002 Amsterdam September 10, 2002 © imec 2002 First. Name Last. Name – Activity / Group

Outline n Introduction : Impact scaling trends microelectronic circuit technology on packaging & interconnection technology n n Multilayer thin film technology n Application examples n © imec 2002 Interconnect technology gap Conclusion E. Beyne 2
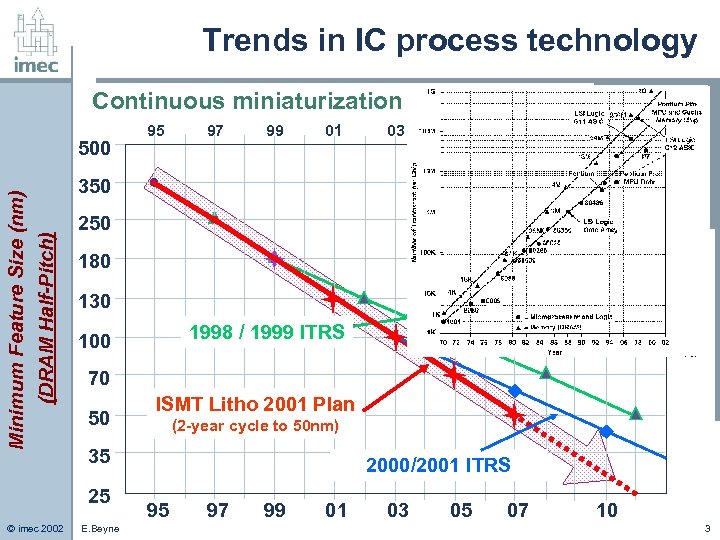
Trends in IC process technology Continuous miniaturization 97 99 01 03 05 07 10 350 (DRAM Half-Pitch) Minimum Feature Size (nm) 500 95 250 180 130 70 50 ISMT Litho 2001 Plan (2 -year cycle to 50 nm) 35 25 © imec 2002 1998 / 1999 ITRS 100 E. Beyne 2000/2001 ITRS 95 97 99 01 03 05 07 10 3
System-on-a-chip, SOC SIA Roadmaps : continuation of Moore’s Law n Decreasing transistor size : smaller die for same function n For the same functionality : higher I/O density n Faster transistor operation Increasing system complexity n Up to today : faster growth than size reduction larger die sizes n Feasibility © imec 2002 E. Beyne of “System-on-a-Chip” SOC architectures 4
System-in-a-package, SIP Single Chip SOC systems ? n There is a divergence among Si-technologies : high density logic (CMOS), Memory, Analog, rf, MEMS, …. n Systems consist of many non-silicon components : Passives, Displays, sensors, antennas, connectors, … n SOC single component system “System-in-a-Package” SIP solution : = Multiple components on a high density interconnect substrate, realizing a (sub)-system function Contradiction SOC - SIP ? Because of SOC, (sub)systems may be miniaturised to the scale of a package © imec 2002 E. Beyne 5
Miniaturisation of Electronic Systems Enabling Technologies : n Si-integration : SOC n High Density Interconnection technologies SIP – “System-in-a-package” © imec 2002 E. Beyne 6
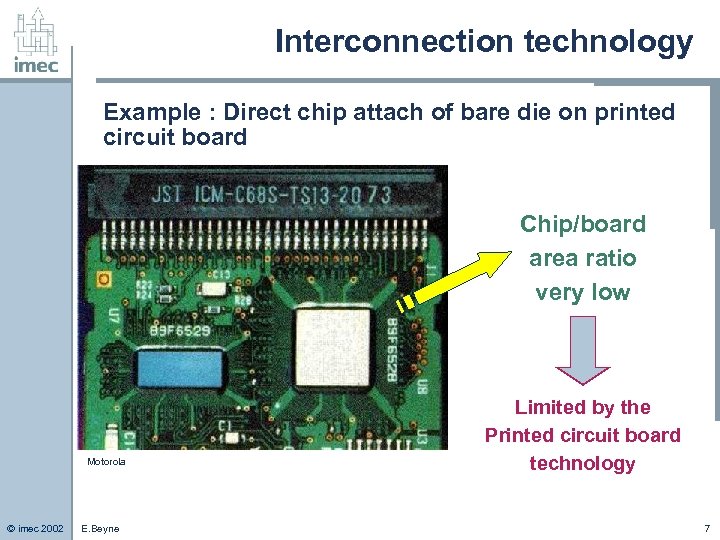
Interconnection technology Example : Direct chip attach of bare die on printed circuit board Chip/board area ratio very low Motorola © imec 2002 E. Beyne Limited by the Printed circuit board technology 7
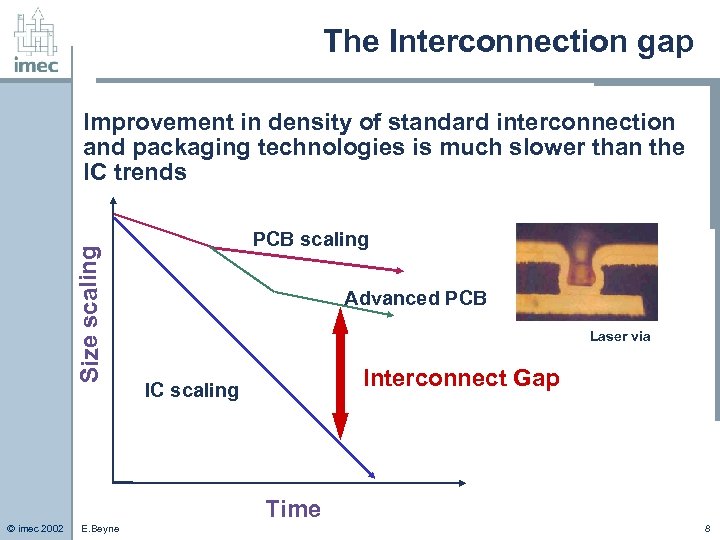
The Interconnection gap Size scaling Improvement in density of standard interconnection and packaging technologies is much slower than the IC trends PCB scaling Advanced PCB Laser via Interconnect Gap IC scaling Time © imec 2002 E. Beyne 8
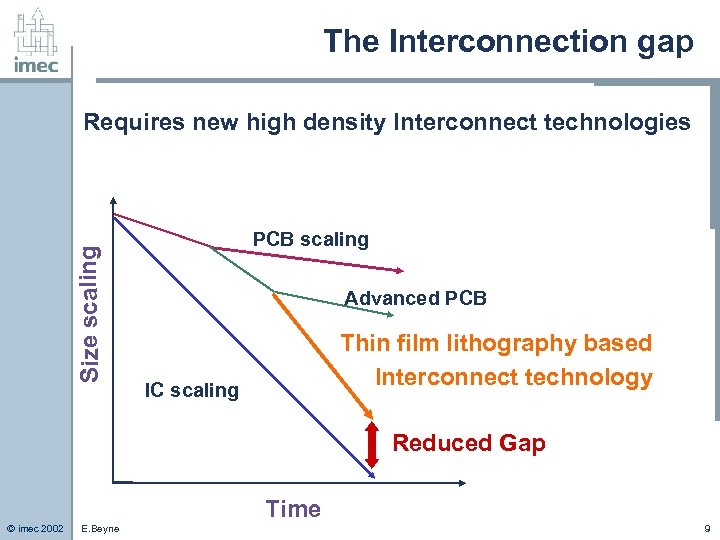
The Interconnection gap Size scaling Requires new high density Interconnect technologies PCB scaling Advanced PCB Thin film lithography based Interconnect technology IC scaling Reduced Gap Time © imec 2002 E. Beyne 9
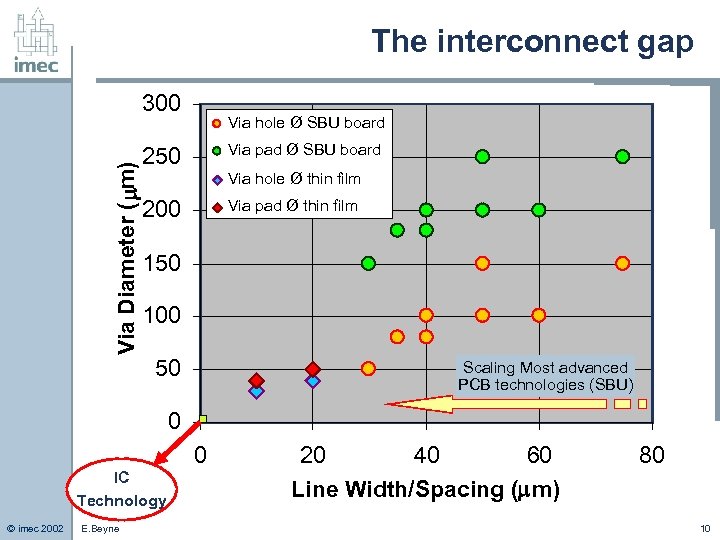
The interconnect gap Via Diameter ( m) 300 Via hole Ø SBU board Via pad Ø SBU board 250 Via hole Ø thin film 200 Via pad Ø thin film 150 100 50 Scaling Most advanced PCB technologies (SBU) 0 0 IC Technology © imec 2002 E. Beyne 20 40 60 Line Width/Spacing ( m) 80 10
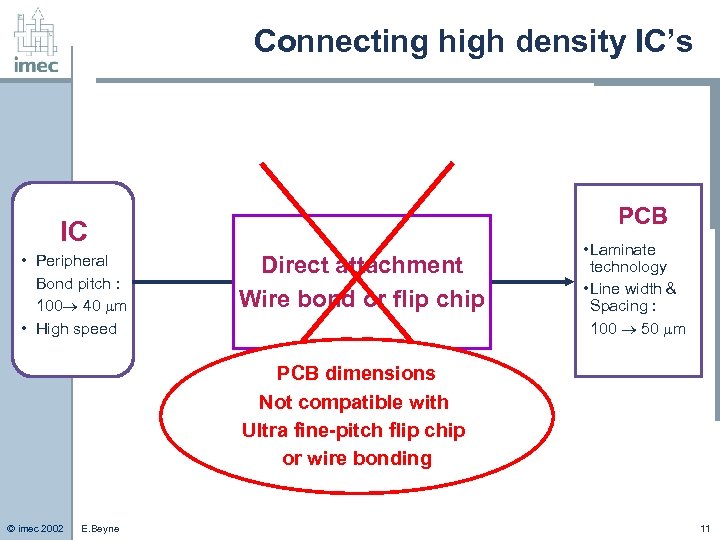
Connecting high density IC’s PCB IC • Peripheral Bond pitch : 100 40 m • High speed Direct attachment Wire bond or flip chip • Laminate technology • Line width & Spacing : 100 50 m PCB dimensions Not compatible with Ultra fine-pitch flip chip or wire bonding © imec 2002 E. Beyne 11
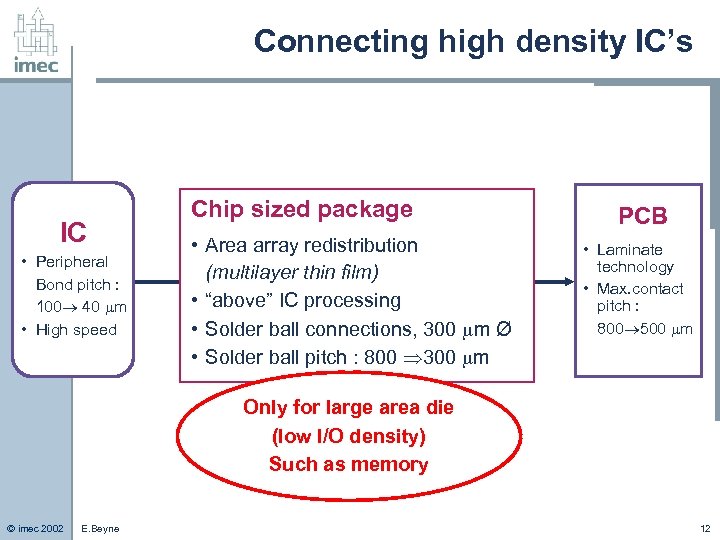
Connecting high density IC’s IC • Peripheral Bond pitch : 100 40 m • High speed Chip sized package • Area array redistribution (multilayer thin film) • “above” IC processing • Solder ball connections, 300 m Ø • Solder ball pitch : 800 300 m PCB • Laminate technology • Max. contact pitch : 800 500 m Only for large area die (low I/O density) Such as memory © imec 2002 E. Beyne 12
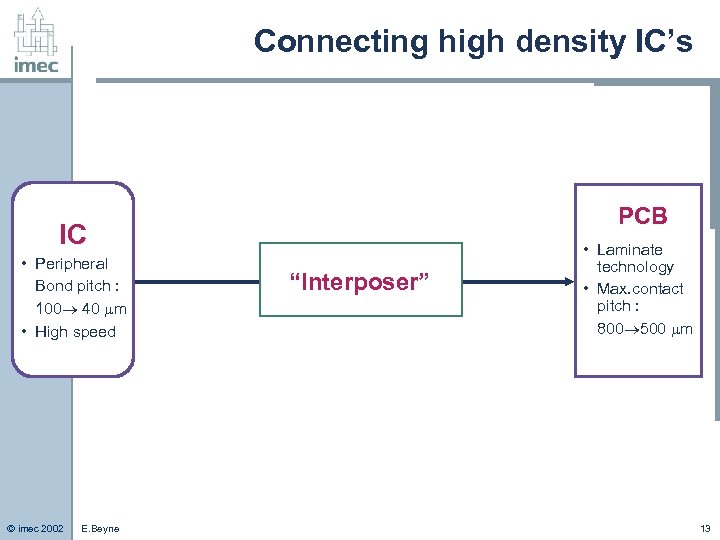
Connecting high density IC’s PCB IC • Peripheral Bond pitch : 100 40 m • High speed © imec 2002 E. Beyne “Interposer” • Laminate technology • Max. contact pitch : 800 500 m 13
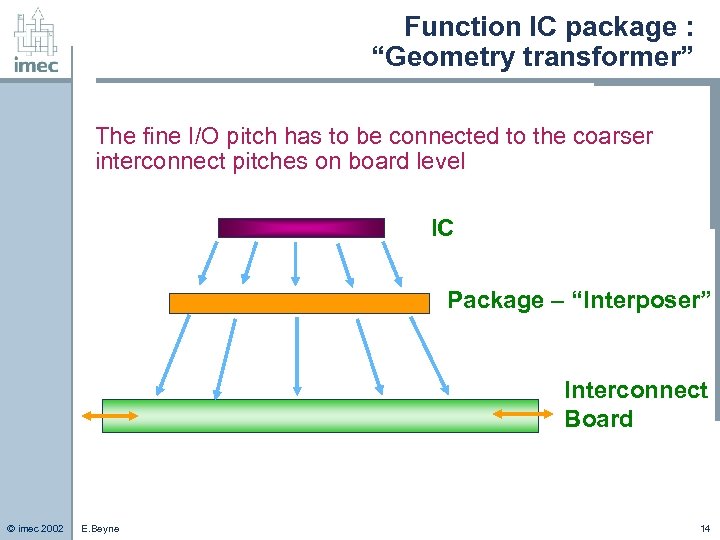
Function IC package : “Geometry transformer” The fine I/O pitch has to be connected to the coarser interconnect pitches on board level IC Package – “Interposer” Interconnect Board © imec 2002 E. Beyne 14
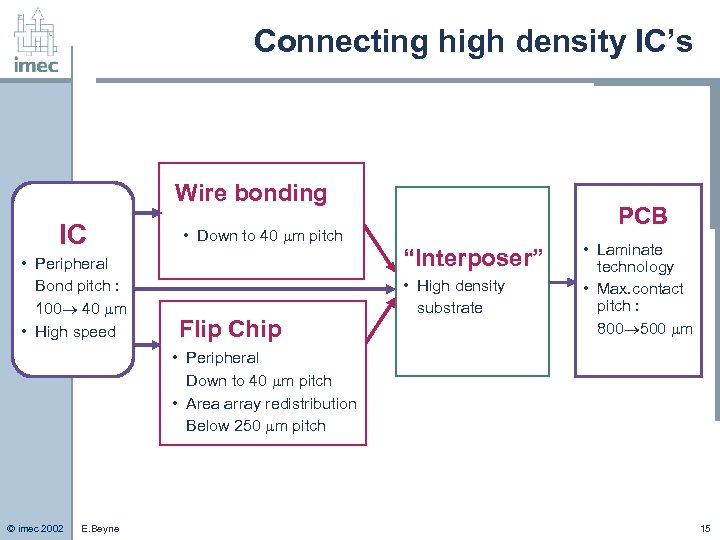
Connecting high density IC’s Wire bonding IC • Peripheral Bond pitch : 100 40 m • High speed PCB • Down to 40 m pitch “Interposer” Flip Chip • High density substrate • Laminate technology • Max. contact pitch : 800 500 m • Peripheral Down to 40 m pitch • Area array redistribution Below 250 m pitch © imec 2002 E. Beyne 15
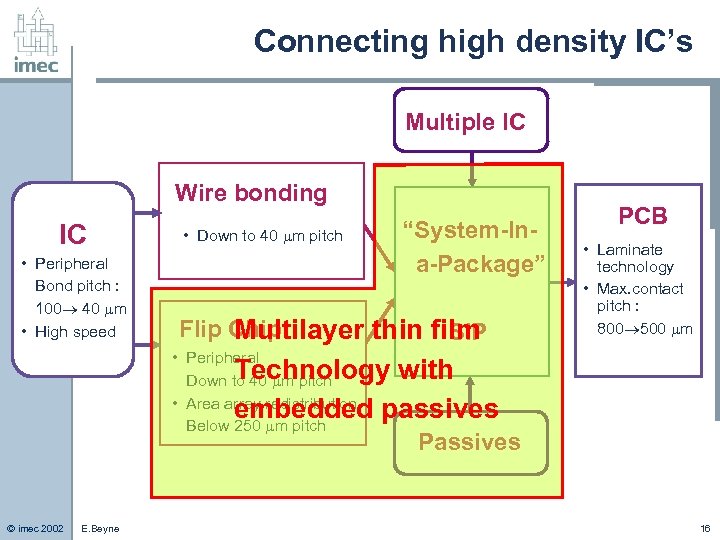
Connecting high density IC’s Multiple IC Wire bonding IC • Peripheral Bond pitch : 100 40 m • High speed • Down to 40 m pitch “System-In“Interposer” a-Package” • High density substrate Flip Chip Multilayer thin film SIP • Peripheral Down to 40 m pitch • Area array redistribution Below 250 m pitch PCB • Laminate technology • Max. contact pitch : 800 500 m Technology with embedded passives © imec 2002 E. Beyne Passives 16
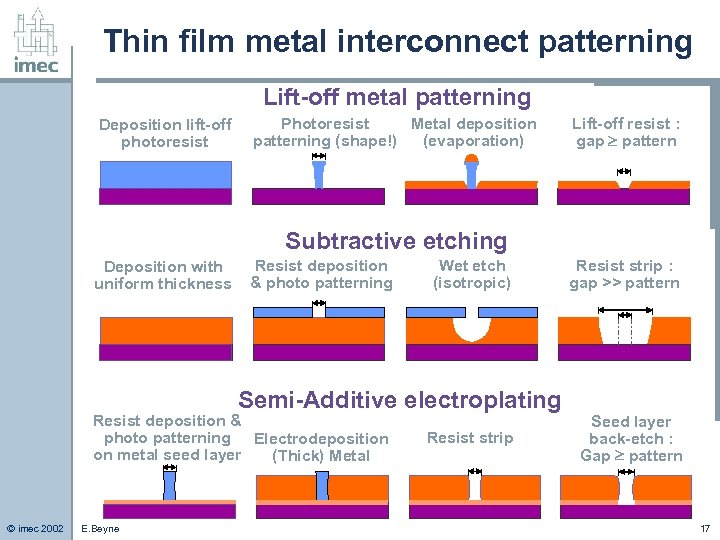
Thin film metal interconnect patterning Lift-off metal patterning Deposition lift-off photoresist Photoresist Metal deposition patterning (shape!) (evaporation) Lift-off resist : gap pattern Subtractive etching Deposition with uniform thickness Resist deposition & photo patterning Wet etch (isotropic) Semi-Additive electroplating Resist deposition & photo patterning Electrodeposition on metal seed layer (Thick) Metal © imec 2002 E. Beyne Resist strip : gap >> pattern Seed layer back-etch : Gap pattern 17
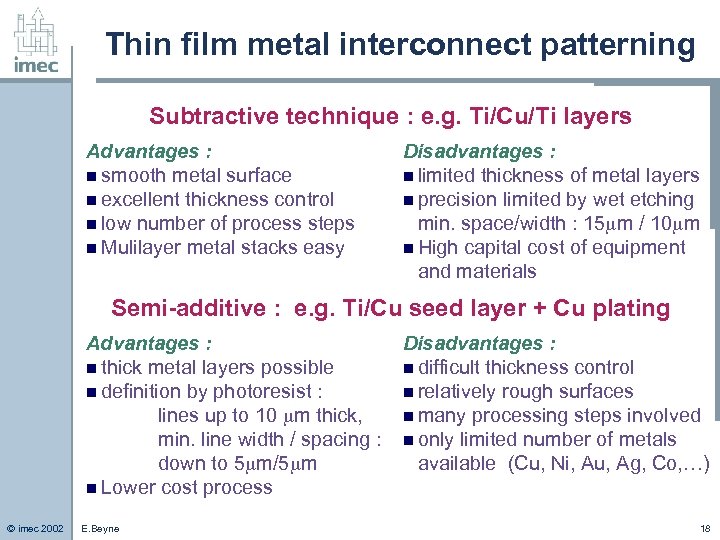
Thin film metal interconnect patterning Subtractive technique : e. g. Ti/Cu/Ti layers Advantages : n smooth metal surface n excellent thickness control n low number of process steps n Mulilayer metal stacks easy Disadvantages : n limited thickness of metal layers n precision limited by wet etching min. space/width : 15 m / 10 m n High capital cost of equipment and materials Semi-additive : e. g. Ti/Cu seed layer + Cu plating Advantages : n thick metal layers possible n definition by photoresist : lines up to 10 m thick, min. line width / spacing : down to 5 m/5 m n Lower cost process © imec 2002 E. Beyne Disadvantages : n difficult thickness control n relatively rough surfaces n many processing steps involved n only limited number of metals available (Cu, Ni, Au, Ag, Co, …) 18
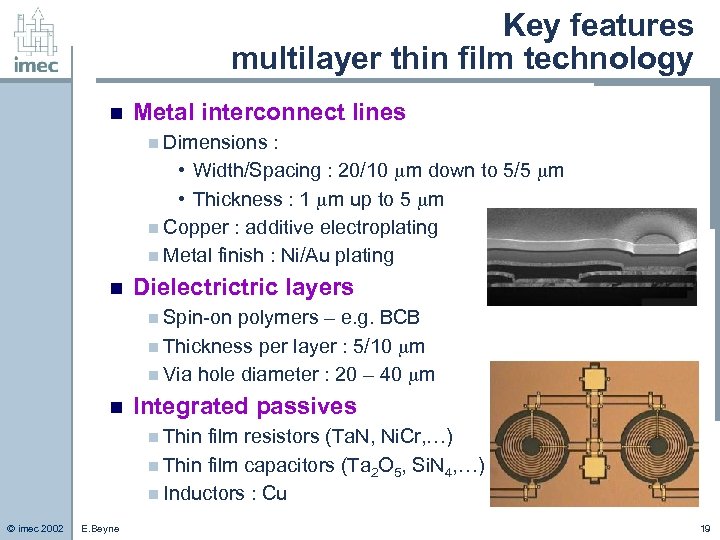
Key features multilayer thin film technology n Metal interconnect lines n Dimensions : • Width/Spacing : 20/10 m down to 5/5 m • Thickness : 1 m up to 5 m n Copper : additive electroplating n Metal finish : Ni/Au plating n Dielectric layers n Spin-on polymers – e. g. BCB n Thickness per layer : 5/10 m n Via hole diameter : 20 – 40 m n Integrated passives n Thin film resistors (Ta. N, Ni. Cr, …) n Thin film capacitors (Ta 2 O 5, Si. N 4, …) n Inductors : Cu © imec 2002 E. Beyne 19
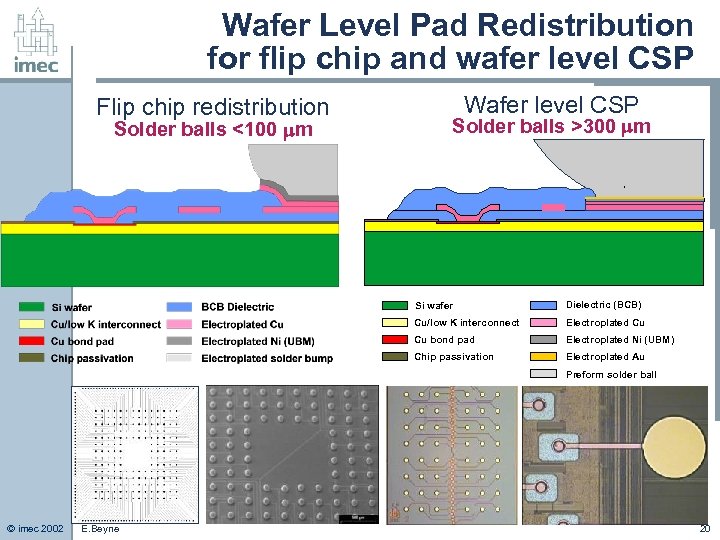
Wafer Level Pad Redistribution for flip chip and wafer level CSP Flip chip redistribution Solder balls <100 m Wafer level CSP Solder balls >300 m Si wafer Dielectric (BCB) Cu/low K interconnect Electroplated Cu Cu bond pad Electroplated Ni (UBM) Chip passivation Electroplated Au Preform solder ball © imec 2002 E. Beyne 20
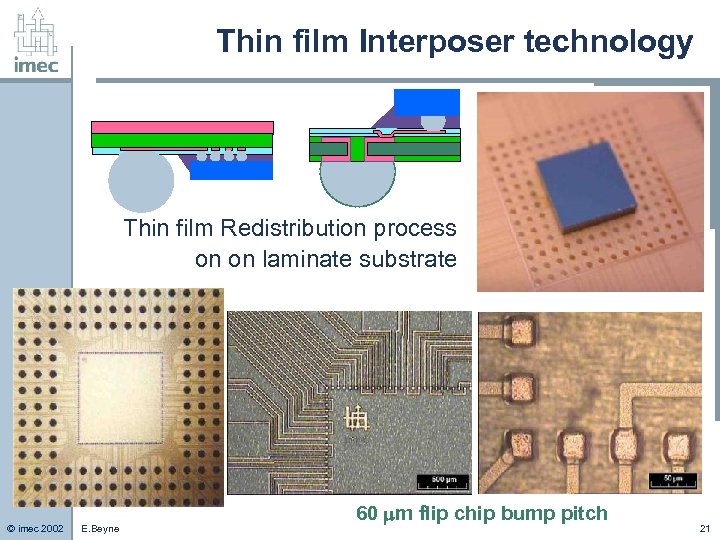
Thin film Interposer technology Thin film Redistribution process on on laminate substrate © imec 2002 E. Beyne 60 m flip chip bump pitch 21
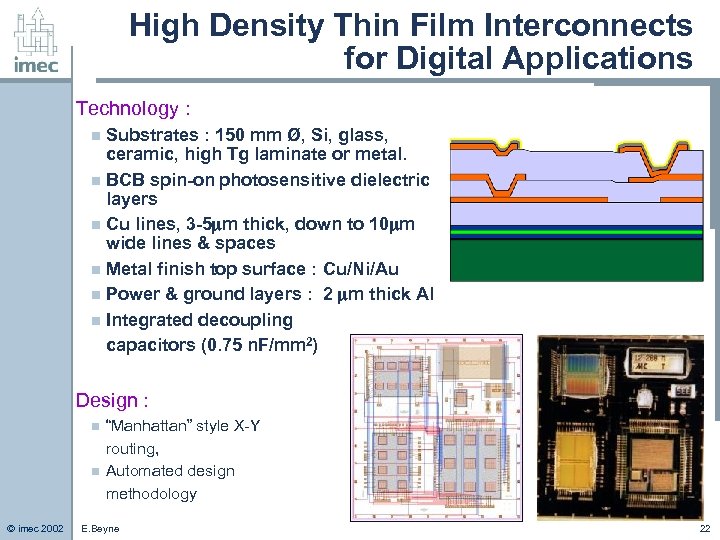
High Density Thin Film Interconnects for Digital Applications Technology : Substrates : 150 mm Ø, Si, glass, ceramic, high Tg laminate or metal. n BCB spin-on photosensitive dielectric layers n Cu lines, 3 -5 m thick, down to 10 m wide lines & spaces n Metal finish top surface : Cu/Ni/Au n Power & ground layers : 2 m thick Al n Integrated decoupling capacitors (0. 75 n. F/mm 2) n Design : n n © imec 2002 “Manhattan” style X-Y routing, Automated design methodology E. Beyne 22
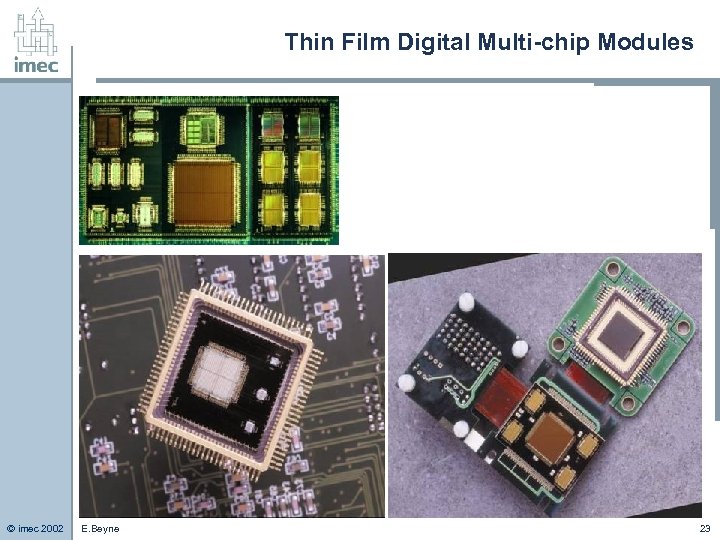
Thin Film Digital Multi-chip Modules © imec 2002 E. Beyne 23
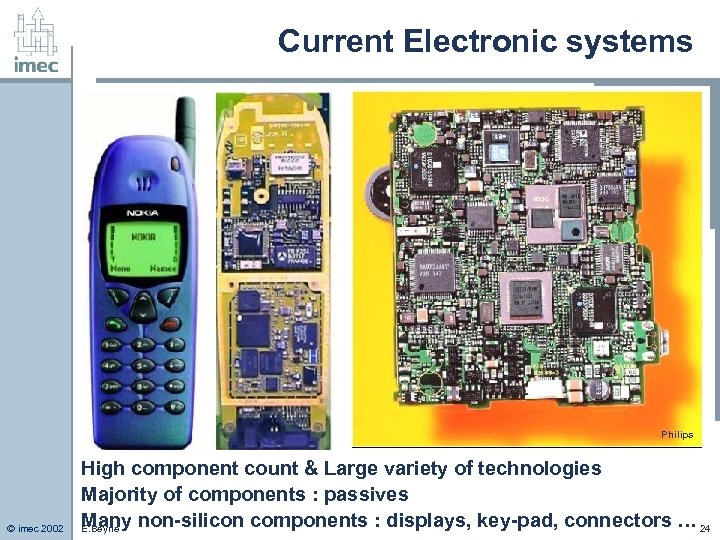
Current Electronic systems Philips © imec 2002 High component count & Large variety of technologies Majority of components : passives Many non-silicon components : displays, key-pad, connectors … 24 E. Beyne
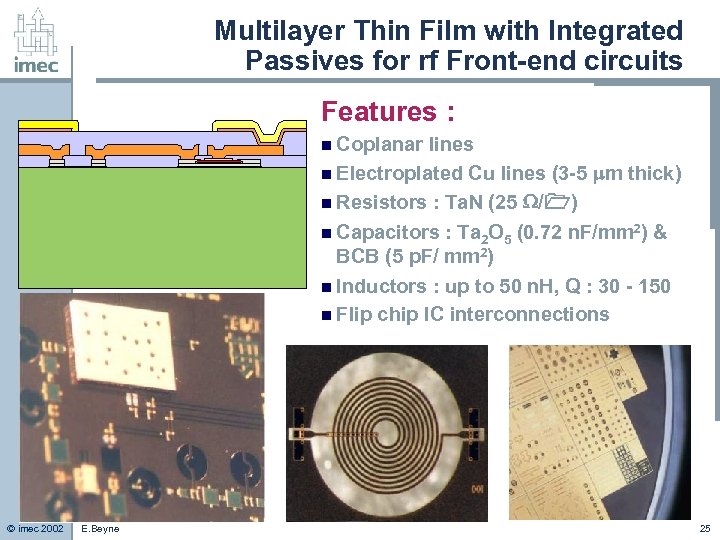
Multilayer Thin Film with Integrated Passives for rf Front-end circuits Features : n Coplanar lines n Electroplated Cu lines (3 -5 m thick) n Resistors : Ta. N (25 / ) n Capacitors : Ta 2 O 5 (0. 72 n. F/mm 2) & BCB (5 p. F/ mm 2) n Inductors : up to 50 n. H, Q : 30 - 150 n Flip chip IC interconnections © imec 2002 E. Beyne 25
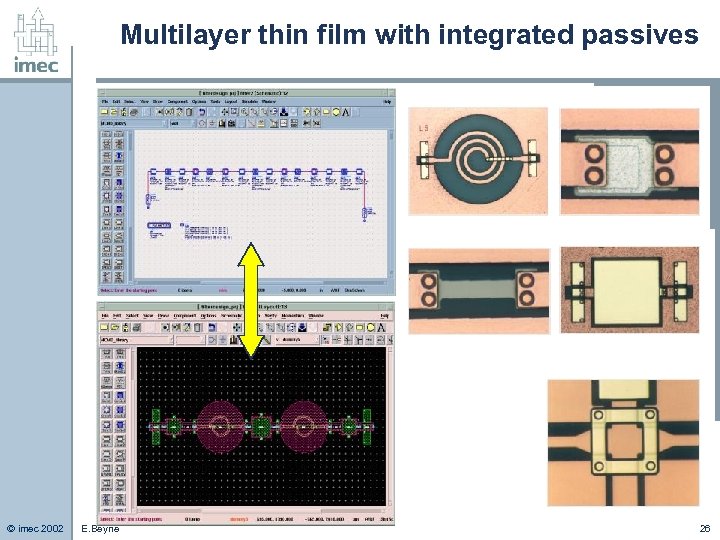
Multilayer thin film with integrated passives Design library © imec 2002 E. Beyne 26
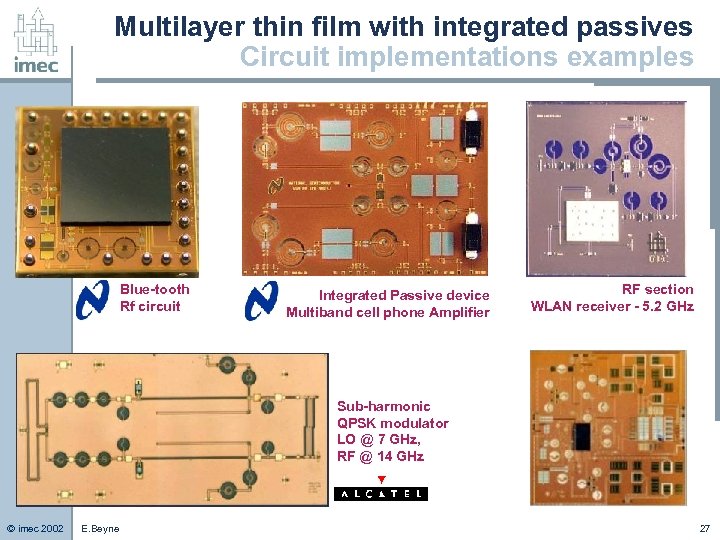
Multilayer thin film with integrated passives Circuit implementations examples Blue-tooth Rf circuit Integrated Passive device Multiband cell phone Amplifier RF section WLAN receiver - 5. 2 GHz Sub-harmonic QPSK modulator LO @ 7 GHz, RF @ 14 GHz © imec 2002 E. Beyne 27

Conclusion n Interconnect technology scales much slower than integrated circuit technology, creating an “Interconnect Gap”. n Multilayer thin film n can bridge the interconnect Gap n Key technology for flip chip and on-chip pad redistribution n Can be used for building high density interposer substrates n is an enabling technology for true “Systems In a Package” (SIPs) n Enables n Offers © imec 2002 E. Beyne integration of high quality passive components excellent high frequency performance 28
Questions ? © imec 2002 E. Beyne 29
feb1afaf2cfe7bc77186e352353769db.ppt