ed682382d882e3de161dbcd856b75a59.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 MULTIDISCIPLINARY DESIGN OPTIMIZATION -A Paradigm Shift in Design Methodology for Complex Engineering Systems K Sudhakar, PM Mujumdar, Amitay Isaacs Centre for Aerospace Systems Design & Engineering Dept. of Aerospace Engineering, IIT Bombay Dec. 6, 2002 0
MULTIDISCIPLINARY DESIGN OPTIMIZATION -A Paradigm Shift in Design Methodology for Complex Engineering Systems K Sudhakar, PM Mujumdar, Amitay Isaacs Centre for Aerospace Systems Design & Engineering Dept. of Aerospace Engineering, IIT Bombay Dec. 6, 2002 0
 ENGINEERING DESIGN OPTIMIZATION n Decision is objective and not subjective n Forces a mathematical statement of the problem n n Dec. 6, 2002 Forces modeling system performance & ‘goodness criteria’ Captures knowledge - What was the problem solved, how was it analyzed, how were the decisions taken, . . . 1
ENGINEERING DESIGN OPTIMIZATION n Decision is objective and not subjective n Forces a mathematical statement of the problem n n Dec. 6, 2002 Forces modeling system performance & ‘goodness criteria’ Captures knowledge - What was the problem solved, how was it analyzed, how were the decisions taken, . . . 1
 ISSUES IN POSING THE PROBLEM • Of all variables that influence the design which to pick as design variables? x X • How to confirm that all constraints are g specified (g, h)? • Which one(s) f F to choose as objectives? • How to evaluate f, g, h ? • How to handle coupled multi-disciplinary (iterative) analysis Dec. 6, 2002 2
ISSUES IN POSING THE PROBLEM • Of all variables that influence the design which to pick as design variables? x X • How to confirm that all constraints are g specified (g, h)? • Which one(s) f F to choose as objectives? • How to evaluate f, g, h ? • How to handle coupled multi-disciplinary (iterative) analysis Dec. 6, 2002 2
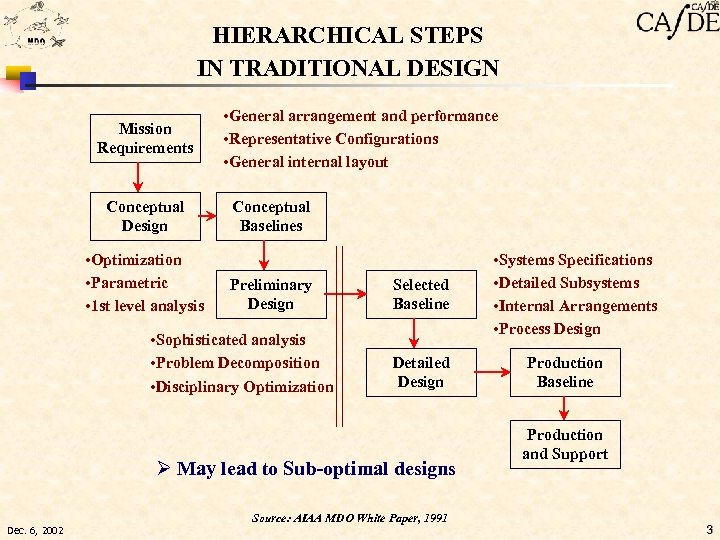 HIERARCHICAL STEPS IN TRADITIONAL DESIGN Mission Requirements Conceptual Design • Optimization • Parametric • 1 st level analysis • General arrangement and performance • Representative Configurations • General internal layout Conceptual Baselines Preliminary Design • Sophisticated analysis • Problem Decomposition • Disciplinary Optimization Selected Baseline Detailed Design Ø May lead to Sub-optimal designs Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 • Systems Specifications • Detailed Subsystems • Internal Arrangements • Process Design Production Baseline Production and Support 3
HIERARCHICAL STEPS IN TRADITIONAL DESIGN Mission Requirements Conceptual Design • Optimization • Parametric • 1 st level analysis • General arrangement and performance • Representative Configurations • General internal layout Conceptual Baselines Preliminary Design • Sophisticated analysis • Problem Decomposition • Disciplinary Optimization Selected Baseline Detailed Design Ø May lead to Sub-optimal designs Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 • Systems Specifications • Detailed Subsystems • Internal Arrangements • Process Design Production Baseline Production and Support 3
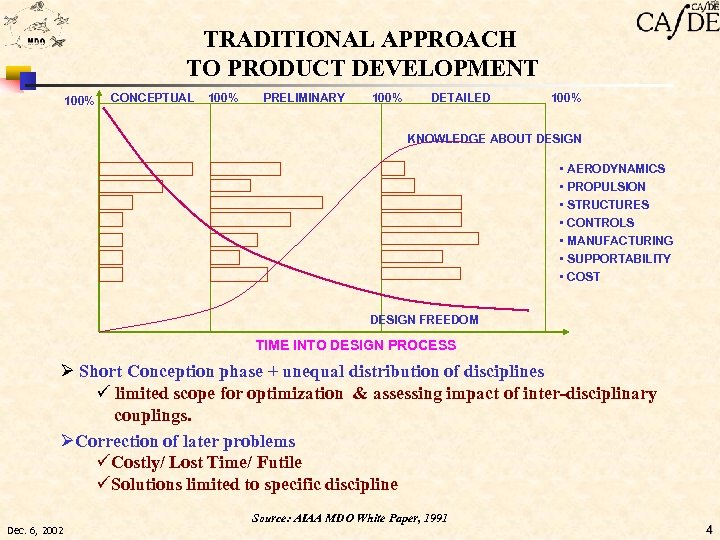 TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 100% CONCEPTUAL 100% PRELIMINARY 100% DETAILED 100% KNOWLEDGE ABOUT DESIGN • AERODYNAMICS • PROPULSION • STRUCTURES • CONTROLS • MANUFACTURING • SUPPORTABILITY • COST DESIGN FREEDOM TIME INTO DESIGN PROCESS Ø Short Conception phase + unequal distribution of disciplines ü limited scope for optimization & assessing impact of inter-disciplinary couplings. ØCorrection of later problems üCostly/ Lost Time/ Futile üSolutions limited to specific discipline Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 4
TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 100% CONCEPTUAL 100% PRELIMINARY 100% DETAILED 100% KNOWLEDGE ABOUT DESIGN • AERODYNAMICS • PROPULSION • STRUCTURES • CONTROLS • MANUFACTURING • SUPPORTABILITY • COST DESIGN FREEDOM TIME INTO DESIGN PROCESS Ø Short Conception phase + unequal distribution of disciplines ü limited scope for optimization & assessing impact of inter-disciplinary couplings. ØCorrection of later problems üCostly/ Lost Time/ Futile üSolutions limited to specific discipline Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 4
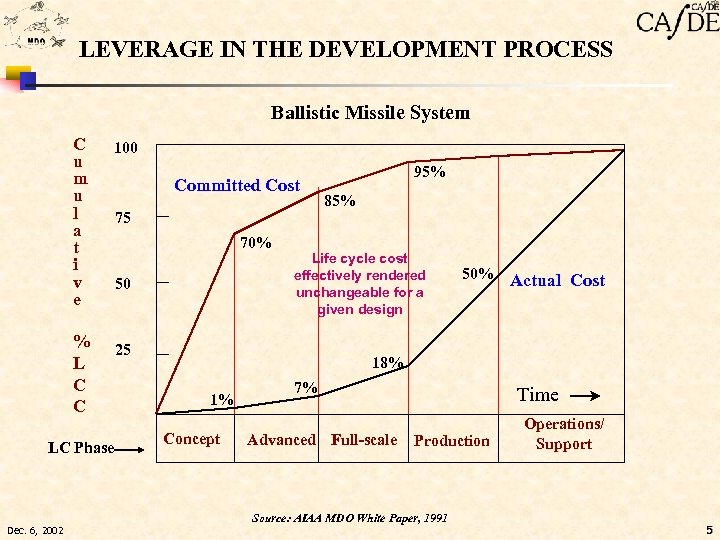 LEVERAGE IN THE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Ballistic Missile System C u m u l a t i v e 100 % L C C LC Phase Committed Cost 75 70% 50 95% 85% Life cycle cost effectively rendered unchangeable for a given design 25 Actual Cost 18% 1% Concept 7% Advanced Full-scale Time Production Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 50% Operations/ Support 5
LEVERAGE IN THE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Ballistic Missile System C u m u l a t i v e 100 % L C C LC Phase Committed Cost 75 70% 50 95% 85% Life cycle cost effectively rendered unchangeable for a given design 25 Actual Cost 18% 1% Concept 7% Advanced Full-scale Time Production Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 50% Operations/ Support 5
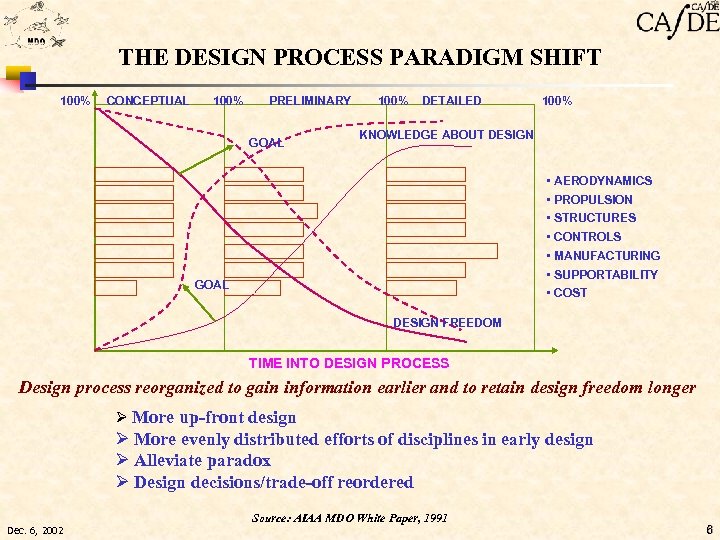 THE DESIGN PROCESS PARADIGM SHIFT 100% CONCEPTUAL 100% PRELIMINARY GOAL 100% DETAILED 100% KNOWLEDGE ABOUT DESIGN • AERODYNAMICS • PROPULSION • STRUCTURES • CONTROLS • MANUFACTURING • SUPPORTABILITY • COST GOAL DESIGN FREEDOM TIME INTO DESIGN PROCESS Design process reorganized to gain information earlier and to retain design freedom longer Ø More up-front design Ø More evenly distributed efforts of disciplines in early design Ø Alleviate paradox Ø Design decisions/trade-off reordered Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 6
THE DESIGN PROCESS PARADIGM SHIFT 100% CONCEPTUAL 100% PRELIMINARY GOAL 100% DETAILED 100% KNOWLEDGE ABOUT DESIGN • AERODYNAMICS • PROPULSION • STRUCTURES • CONTROLS • MANUFACTURING • SUPPORTABILITY • COST GOAL DESIGN FREEDOM TIME INTO DESIGN PROCESS Design process reorganized to gain information earlier and to retain design freedom longer Ø More up-front design Ø More evenly distributed efforts of disciplines in early design Ø Alleviate paradox Ø Design decisions/trade-off reordered Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 6
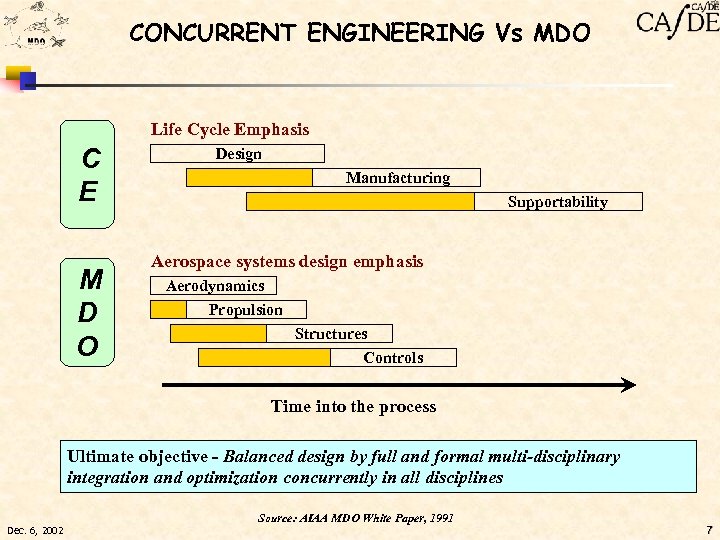 CONCURRENT ENGINEERING Vs MDO Life Cycle Emphasis C E M D O Design Manufacturing Supportability Aerospace systems design emphasis Aerodynamics Propulsion Structures Controls Time into the process Ultimate objective - Balanced design by full and formal multi-disciplinary integration and optimization concurrently in all disciplines Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 7
CONCURRENT ENGINEERING Vs MDO Life Cycle Emphasis C E M D O Design Manufacturing Supportability Aerospace systems design emphasis Aerodynamics Propulsion Structures Controls Time into the process Ultimate objective - Balanced design by full and formal multi-disciplinary integration and optimization concurrently in all disciplines Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 7
 MDO ? n Multi-disciplinary : More than one discipline n Design – Process of translating requirements into n Optimization – Formal mathematical process of plays a role. Eg. In aerospace -aerodynamics, structures, controls, mission, . . . detailed product specifications. locating the ‘best’ under ‘constraints’ Dec. 6, 2002 8
MDO ? n Multi-disciplinary : More than one discipline n Design – Process of translating requirements into n Optimization – Formal mathematical process of plays a role. Eg. In aerospace -aerodynamics, structures, controls, mission, . . . detailed product specifications. locating the ‘best’ under ‘constraints’ Dec. 6, 2002 8
 What is MDO? Some popular definitions of Multidisciplinary Design Optimisation 1. A methodology for the optimal design of complex engineering systems and subsystems that coherently exploits the synergism of mutually interacting phenomena using high fidelity analysis with formal optimization 2. MDO is a methodology that combines analysis and in individual disciplines into that for the entire system for optimization. 3. "How to decide what to change, and to what extent to change it, when everything influences everything else. " Dec. 6, 2002 9
What is MDO? Some popular definitions of Multidisciplinary Design Optimisation 1. A methodology for the optimal design of complex engineering systems and subsystems that coherently exploits the synergism of mutually interacting phenomena using high fidelity analysis with formal optimization 2. MDO is a methodology that combines analysis and in individual disciplines into that for the entire system for optimization. 3. "How to decide what to change, and to what extent to change it, when everything influences everything else. " Dec. 6, 2002 9
 Dec. 6, 2002 10
Dec. 6, 2002 10
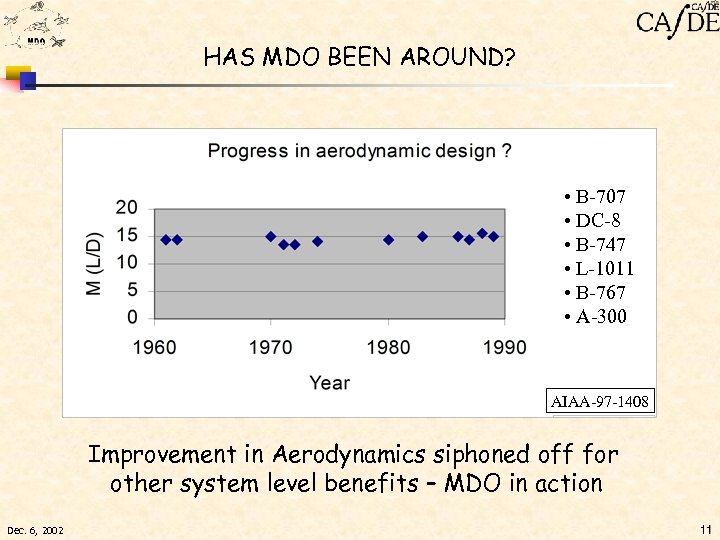 HAS MDO BEEN AROUND? • B-707 • DC-8 • B-747 • L-1011 • B-767 • A-300 AIAA-97 -1408 Improvement in Aerodynamics siphoned off for other system level benefits – MDO in action Dec. 6, 2002 11
HAS MDO BEEN AROUND? • B-707 • DC-8 • B-747 • L-1011 • B-767 • A-300 AIAA-97 -1408 Improvement in Aerodynamics siphoned off for other system level benefits – MDO in action Dec. 6, 2002 11
 CONVENTIONAL DESIGN V/S MDO 1. Conventional Aerospace Design Practice ¨ ¨ Dependence on Parameter trends and trade-off studies ¨ Independent disciplinary design + System level reviews ¨ Optimization limited to disciplines ¨ Resolution of interdisciplinary conflicts nonautomated ¨ Relying heavily on previous experience ¨ Dec. 6, 2002 Heirarchichal Overall – more heuristic, than formal mathematical optimization 12
CONVENTIONAL DESIGN V/S MDO 1. Conventional Aerospace Design Practice ¨ ¨ Dependence on Parameter trends and trade-off studies ¨ Independent disciplinary design + System level reviews ¨ Optimization limited to disciplines ¨ Resolution of interdisciplinary conflicts nonautomated ¨ Relying heavily on previous experience ¨ Dec. 6, 2002 Heirarchichal Overall – more heuristic, than formal mathematical optimization 12
 CONVENTIONAL DESIGN V/S MDO Multi-disciplinary Design Optimization ¨ Low fidelity models => Conceptual design ¨ Tightly coupled inter-disciplinary codes. (Close knit group) ? ? ¨ All or most of the following, ü ü ü Dec. 6, 2002 Largely automated within a formal framework Formal mathematical methods and high fidelity computations indispensable Interdisciplinary couplings formally modeled/retained Design freedom to significantly affect system performance in multiple disciplines simultaneously Disciplinary authority. Parallel execution. 13
CONVENTIONAL DESIGN V/S MDO Multi-disciplinary Design Optimization ¨ Low fidelity models => Conceptual design ¨ Tightly coupled inter-disciplinary codes. (Close knit group) ? ? ¨ All or most of the following, ü ü ü Dec. 6, 2002 Largely automated within a formal framework Formal mathematical methods and high fidelity computations indispensable Interdisciplinary couplings formally modeled/retained Design freedom to significantly affect system performance in multiple disciplines simultaneously Disciplinary authority. Parallel execution. 13
 CONVENTIONAL DESIGN V/S MDO Multi-disciplinary Design Optimization (contd. ) ¨ Special architectures for problem formulation/ decomposition • • Coupling variables and constraints • Dec. 6, 2002 Disciplinary (local) constraints, variables • ¨ System level objectives, constraints, variables System level and discipline level optimizations Human expertise & judgement given due weightage 14
CONVENTIONAL DESIGN V/S MDO Multi-disciplinary Design Optimization (contd. ) ¨ Special architectures for problem formulation/ decomposition • • Coupling variables and constraints • Dec. 6, 2002 Disciplinary (local) constraints, variables • ¨ System level objectives, constraints, variables System level and discipline level optimizations Human expertise & judgement given due weightage 14
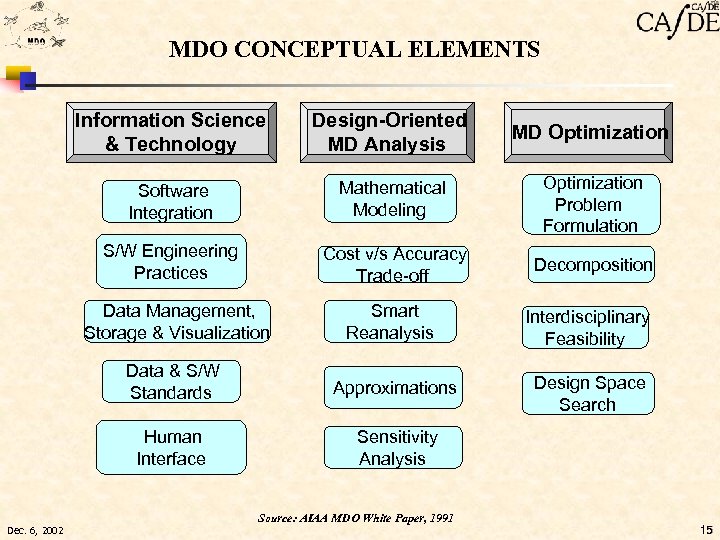 MDO CONCEPTUAL ELEMENTS Information Science & Technology Design-Oriented MD Analysis MD Optimization Software Integration Mathematical Modeling Optimization Problem Formulation S/W Engineering Practices Cost v/s Accuracy Trade-off Decomposition Data Management, Storage & Visualization Smart Reanalysis Data & S/W Standards Approximations Human Interface Sensitivity Analysis Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 Interdisciplinary Feasibility Design Space Search 15
MDO CONCEPTUAL ELEMENTS Information Science & Technology Design-Oriented MD Analysis MD Optimization Software Integration Mathematical Modeling Optimization Problem Formulation S/W Engineering Practices Cost v/s Accuracy Trade-off Decomposition Data Management, Storage & Visualization Smart Reanalysis Data & S/W Standards Approximations Human Interface Sensitivity Analysis Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1991 Dec. 6, 2002 Interdisciplinary Feasibility Design Space Search 15
 CHALLENGES IN MDO IMPLEMENTATION Information Science & Technology • Computational resources (CPU, memory, disk space) § Distributed parallel processing • Common parametric geometric model • Software support § s/w integration of proprietary, legacy, commercial, . . § configuration control and data management § collaborative work environment, person-person/machine • Human expertise/experience capture Dec. 6, 2002 16
CHALLENGES IN MDO IMPLEMENTATION Information Science & Technology • Computational resources (CPU, memory, disk space) § Distributed parallel processing • Common parametric geometric model • Software support § s/w integration of proprietary, legacy, commercial, . . § configuration control and data management § collaborative work environment, person-person/machine • Human expertise/experience capture Dec. 6, 2002 16
 CHALLENGES IN MDO IMPLEMENTATION Ø Multidisciplinary Analysis • Well posed interfaces for disciplines • Discipline and MD sensitivities • Mathematical modeling of LC disciplines • Automated grid generation for CFD, FEM • Cost & run-time of high fidelity analysis Ø MD Optimization • Problem definition • MDO architectures Dec. 6, 2002 • Design Space Search 17
CHALLENGES IN MDO IMPLEMENTATION Ø Multidisciplinary Analysis • Well posed interfaces for disciplines • Discipline and MD sensitivities • Mathematical modeling of LC disciplines • Automated grid generation for CFD, FEM • Cost & run-time of high fidelity analysis Ø MD Optimization • Problem definition • MDO architectures Dec. 6, 2002 • Design Space Search 17
 OPTIMIZATION ISSUES IN MDO Single level monolithic optimization (conventional) 2. Decomposition • Decomposed Analysis - System level optimization - Parallel disciplinary analysis • Decomposed optimization - Multi-level (system and subspace) optimization - Parallel disciplinary analysis 3. System sensitivity analysis 4. Design oriented analysis, Surrogates 5. Improved optimization algorithms • Large number of design variables & constraints • Gradient free 1. Dec. 6, 2002 18
OPTIMIZATION ISSUES IN MDO Single level monolithic optimization (conventional) 2. Decomposition • Decomposed Analysis - System level optimization - Parallel disciplinary analysis • Decomposed optimization - Multi-level (system and subspace) optimization - Parallel disciplinary analysis 3. System sensitivity analysis 4. Design oriented analysis, Surrogates 5. Improved optimization algorithms • Large number of design variables & constraints • Gradient free 1. Dec. 6, 2002 18
 OPTIMISATION ISSUES IN MDO • Which optimisation algorithm to use? – Gradient based? How to generate gradients? – Evolutionary? How many function evaluations? • Evaluation of gradients? Requirements on convergence more severe than that required for engineering analysis. • Noisy functions? f X Dec. 6, 2002 19
OPTIMISATION ISSUES IN MDO • Which optimisation algorithm to use? – Gradient based? How to generate gradients? – Evolutionary? How many function evaluations? • Evaluation of gradients? Requirements on convergence more severe than that required for engineering analysis. • Noisy functions? f X Dec. 6, 2002 19
 MDO GROWTH OVER THE YEARS 1982 : Holt Ashley AIAA lecture "Making things Best. . . " "There are over 8073 papers in Optimal Control, Aerodynamic Optimisation & Structural Optimisation. Not one paper on Optimization in Aircraft Design” 1991 : AIAA White Paper on MDO; & Special issue of Journal of Aircraft 1996 : Over 200 papers on MDO application to A/C Design, including from Industry 1998 : AIAA White Paper on MDO. “Summary of Industry MDO Applications & Needs”, Geising & Barthelemy 1999 : Second Special Issue of Journal of Aircraft Dec. 6, 2002 20
MDO GROWTH OVER THE YEARS 1982 : Holt Ashley AIAA lecture "Making things Best. . . " "There are over 8073 papers in Optimal Control, Aerodynamic Optimisation & Structural Optimisation. Not one paper on Optimization in Aircraft Design” 1991 : AIAA White Paper on MDO; & Special issue of Journal of Aircraft 1996 : Over 200 papers on MDO application to A/C Design, including from Industry 1998 : AIAA White Paper on MDO. “Summary of Industry MDO Applications & Needs”, Geising & Barthelemy 1999 : Second Special Issue of Journal of Aircraft Dec. 6, 2002 20
 MDO STATUS AT A GLANCE Ø Ø Generalized MDO environment – far from reach Most common applications • One discipline (structures) with other discipline as constraints • Simultaneous aerodynamic and structural optimization § Wings § Aircraft configurations (HSCT, BWB) § Rotor blades • Coupling of preliminary design with mission and performance optimization catching up • Trajectory optimization in Space vehicles § Disciplines - propulsion, trajectory analysis, weights, sizing • Simultaneous structures, aerodynamics and control optimization Dec. 6, 2002 21
MDO STATUS AT A GLANCE Ø Ø Generalized MDO environment – far from reach Most common applications • One discipline (structures) with other discipline as constraints • Simultaneous aerodynamic and structural optimization § Wings § Aircraft configurations (HSCT, BWB) § Rotor blades • Coupling of preliminary design with mission and performance optimization catching up • Trajectory optimization in Space vehicles § Disciplines - propulsion, trajectory analysis, weights, sizing • Simultaneous structures, aerodynamics and control optimization Dec. 6, 2002 21
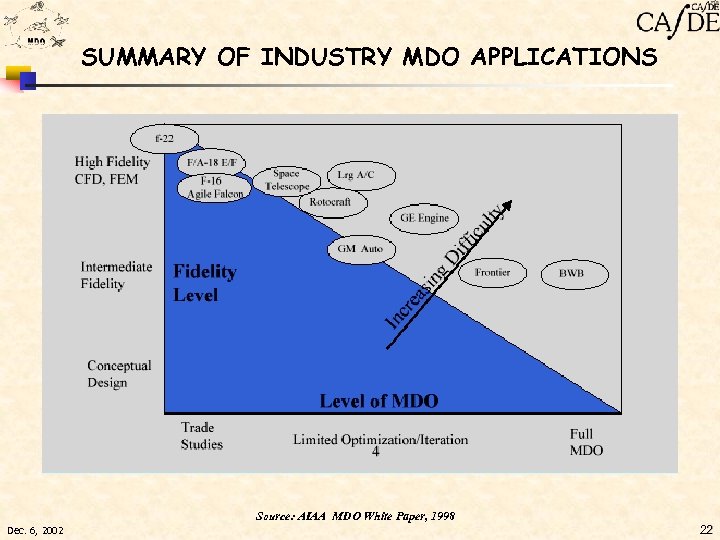 SUMMARY OF INDUSTRY MDO APPLICATIONS Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1998 Dec. 6, 2002 22
SUMMARY OF INDUSTRY MDO APPLICATIONS Source: AIAA MDO White Paper, 1998 Dec. 6, 2002 22
 An Example – HSCT (1991 -’ 99)! n HSCT-2 n n HSCT-3 n n 5 design variables, 6 constraints WINGDES, ELAPS, Range equation, engine deck Time for one cycle = 10 minutes 7 design variables, 6 constraints ISAAC, COMET, Range equation. Engine deck Time for one cycle = 3 hours HSCT-4 n n 271 design variables, 31, 868 constraints CFL 3 D, USSAERO, GENESIS, FLOPS, ENG 10 Time for one cycle = 3 days (Analysis, sensitivity, optimizer step) 32 P Origin 2000, n x {Sun Ultra-2, SGI R 10000} CFL 3 D - CFD in Euler mode; Dec. 6, 2002 USSAERO – Panel code, GENESIS - FEM 23
An Example – HSCT (1991 -’ 99)! n HSCT-2 n n HSCT-3 n n 5 design variables, 6 constraints WINGDES, ELAPS, Range equation, engine deck Time for one cycle = 10 minutes 7 design variables, 6 constraints ISAAC, COMET, Range equation. Engine deck Time for one cycle = 3 hours HSCT-4 n n 271 design variables, 31, 868 constraints CFL 3 D, USSAERO, GENESIS, FLOPS, ENG 10 Time for one cycle = 3 days (Analysis, sensitivity, optimizer step) 32 P Origin 2000, n x {Sun Ultra-2, SGI R 10000} CFL 3 D - CFD in Euler mode; Dec. 6, 2002 USSAERO – Panel code, GENESIS - FEM 23
 HSCT - 4 n n n Dec. 6, 2002 Detailed problem definition took more than 1 year to extract from people Requirements document touched 100 pages merely to define analysis process, tools used and data flow 90% of work went into preparing analysis codes for MDA and integrating them in a proper sequence. (Such experiences have prompted development of MDO Frameworks) 24
HSCT - 4 n n n Dec. 6, 2002 Detailed problem definition took more than 1 year to extract from people Requirements document touched 100 pages merely to define analysis process, tools used and data flow 90% of work went into preparing analysis codes for MDA and integrating them in a proper sequence. (Such experiences have prompted development of MDO Frameworks) 24
 MDO@CASDE OVER THE YEARS n Aug 1999 n Aug 2000 - First meeting of SIG-MDO n Jan 2001 - Professional Development Course on MDO n Jun 2002 - Second meeting of SIG-MDO n Mar 2003 - Third Meeting of SIG-MDO n Sep 2003 - International Conference on MDO n Feb 2004 - Fourth Meeting SIG-MDO n Jan 2005 - Fifth Meeting of SIG-MDO Dec. 6, 2002 - CASDE asked to spur initiatives in MDO 25
MDO@CASDE OVER THE YEARS n Aug 1999 n Aug 2000 - First meeting of SIG-MDO n Jan 2001 - Professional Development Course on MDO n Jun 2002 - Second meeting of SIG-MDO n Mar 2003 - Third Meeting of SIG-MDO n Sep 2003 - International Conference on MDO n Feb 2004 - Fourth Meeting SIG-MDO n Jan 2005 - Fifth Meeting of SIG-MDO Dec. 6, 2002 - CASDE asked to spur initiatives in MDO 25
 End of MDO Introduction Dec. 6, 2002 26
End of MDO Introduction Dec. 6, 2002 26
 MDO STATUS AT A GLANCE Ø MDO Elements • Decomposition, Approximations, Sensitivity Analysis well researched but not matured to industry requirements • Other issues ? ? 1. Recent Trends - Generic MDO Technologies (NASA, EC ) 1. Distributed heterogeneous environment 2. Problem specification and setup, decision support systems 3. Generic software framework for MDO 4. Multi-objective design optimization 1. MADIC, FRONTIER, FIDO, i. SIGHT, USMADE 2. IPPD system for aircraft design (ASDL, GIT Atlanta) 3. Knowledge Based Engineering (Boeing) 1. MDO in preliminary design focused on aero-elasticity Dec. 6, 2002 with FEM, CFD 27
MDO STATUS AT A GLANCE Ø MDO Elements • Decomposition, Approximations, Sensitivity Analysis well researched but not matured to industry requirements • Other issues ? ? 1. Recent Trends - Generic MDO Technologies (NASA, EC ) 1. Distributed heterogeneous environment 2. Problem specification and setup, decision support systems 3. Generic software framework for MDO 4. Multi-objective design optimization 1. MADIC, FRONTIER, FIDO, i. SIGHT, USMADE 2. IPPD system for aircraft design (ASDL, GIT Atlanta) 3. Knowledge Based Engineering (Boeing) 1. MDO in preliminary design focused on aero-elasticity Dec. 6, 2002 with FEM, CFD 27


