53ea6b5794ef2670fbb40c6015c89ebf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Multi Frequency Laser Driver for Near Infrared Optical Spectroscopy in Biomedical Application Chenpeng Mu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Drexel Univ, Philadelphia, PA, 19104
Multi Frequency Laser Driver for Near Infrared Optical Spectroscopy in Biomedical Application Chenpeng Mu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Drexel Univ, Philadelphia, PA, 19104
 Introduction What is tissue spectroscopy? Near infrared spectroscopy system introduction. Driver design Gain, frequency response, linearity and noise System evaluation Optical property extraction Conclusion
Introduction What is tissue spectroscopy? Near infrared spectroscopy system introduction. Driver design Gain, frequency response, linearity and noise System evaluation Optical property extraction Conclusion
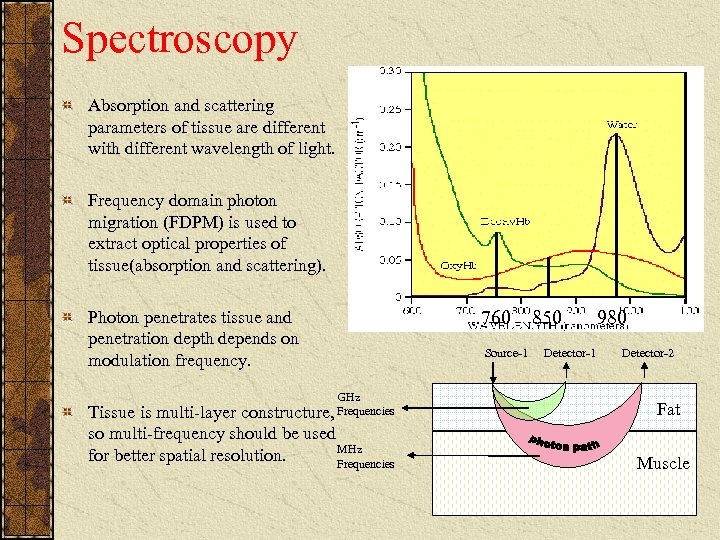 Spectroscopy Absorption and scattering parameters of tissue are different with different wavelength of light. Frequency domain photon migration (FDPM) is used to extract optical properties of tissue(absorption and scattering). Photon penetrates tissue and penetration depth depends on modulation frequency. GHz Tissue is multi-layer constructure, Frequencies so multi-frequency should be used MHz for better spatial resolution. Frequencies 760 Source-1 850 Detector-1 980 Detector-2 Fat Muscle
Spectroscopy Absorption and scattering parameters of tissue are different with different wavelength of light. Frequency domain photon migration (FDPM) is used to extract optical properties of tissue(absorption and scattering). Photon penetrates tissue and penetration depth depends on modulation frequency. GHz Tissue is multi-layer constructure, Frequencies so multi-frequency should be used MHz for better spatial resolution. Frequencies 760 Source-1 850 Detector-1 980 Detector-2 Fat Muscle
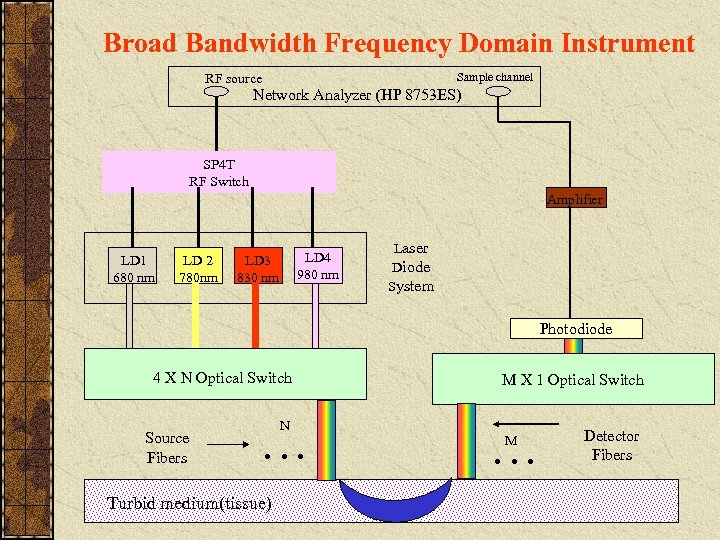 Broad Bandwidth Frequency Domain Instrument Sample channel RF source Network Analyzer (HP 8753 ES) SP 4 T RF Switch Amplifier LD 1 680 nm LD 2 780 nm LD 4 980 nm LD 3 830 nm Laser Diode System Photodiode 4 X N Optical Switch Source Fibers … N M X 1 Optical Switch … M Detector Fibers TURBID MEDIUM Turbid medium(tissue)
Broad Bandwidth Frequency Domain Instrument Sample channel RF source Network Analyzer (HP 8753 ES) SP 4 T RF Switch Amplifier LD 1 680 nm LD 2 780 nm LD 4 980 nm LD 3 830 nm Laser Diode System Photodiode 4 X N Optical Switch Source Fibers … N M X 1 Optical Switch … M Detector Fibers TURBID MEDIUM Turbid medium(tissue)
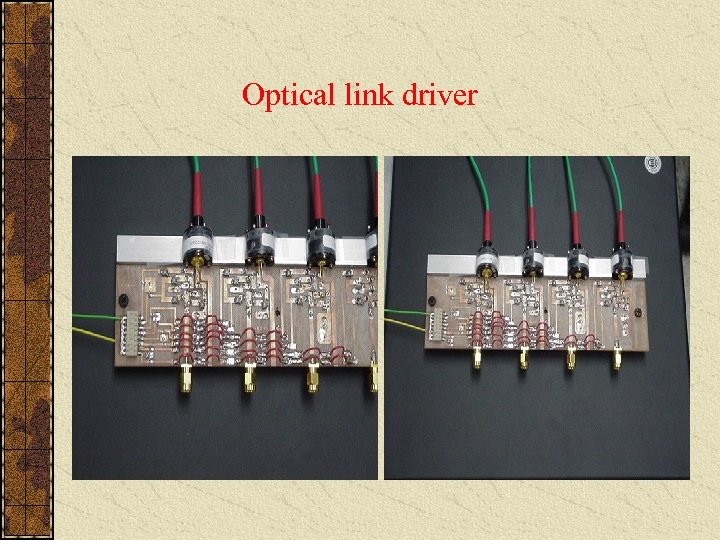 Optical link driver
Optical link driver
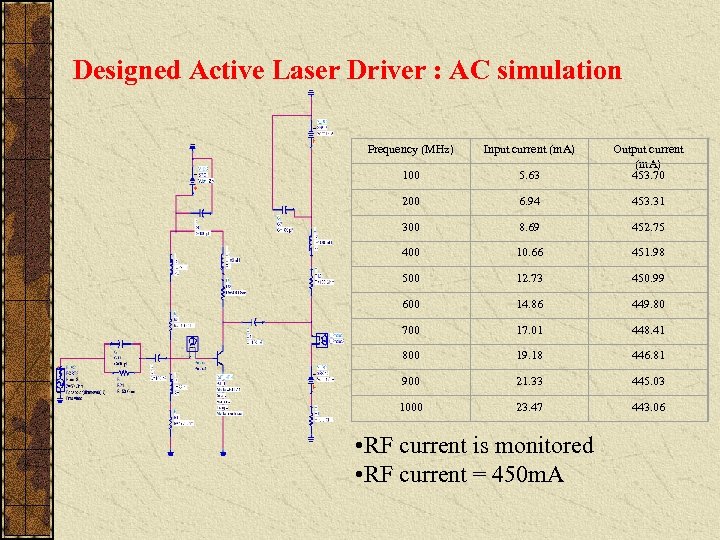 Designed Active Laser Driver : AC simulation Frequency (MHz) Input current (m. A) 100 5. 63 Output current (m. A) 453. 70 200 6. 94 453. 31 300 8. 69 452. 75 400 10. 66 451. 98 500 12. 73 450. 99 600 14. 86 449. 80 700 17. 01 448. 41 800 19. 18 446. 81 900 21. 33 445. 03 1000 23. 47 443. 06 • RF current is monitored • RF current = 450 m. A
Designed Active Laser Driver : AC simulation Frequency (MHz) Input current (m. A) 100 5. 63 Output current (m. A) 453. 70 200 6. 94 453. 31 300 8. 69 452. 75 400 10. 66 451. 98 500 12. 73 450. 99 600 14. 86 449. 80 700 17. 01 448. 41 800 19. 18 446. 81 900 21. 33 445. 03 1000 23. 47 443. 06 • RF current is monitored • RF current = 450 m. A
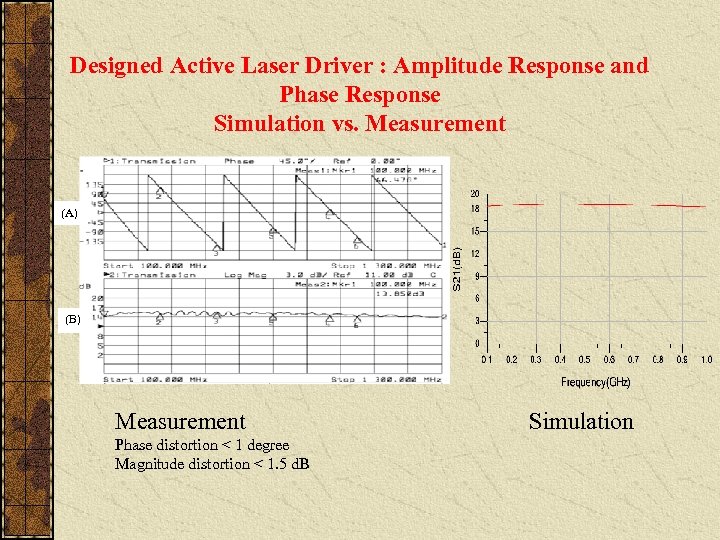 Designed Active Laser Driver : Amplitude Response and Phase Response Simulation vs. Measurement (A) (B) Measurement Phase distortion < 1 degree Magnitude distortion < 1. 5 d. B Simulation
Designed Active Laser Driver : Amplitude Response and Phase Response Simulation vs. Measurement (A) (B) Measurement Phase distortion < 1 degree Magnitude distortion < 1. 5 d. B Simulation
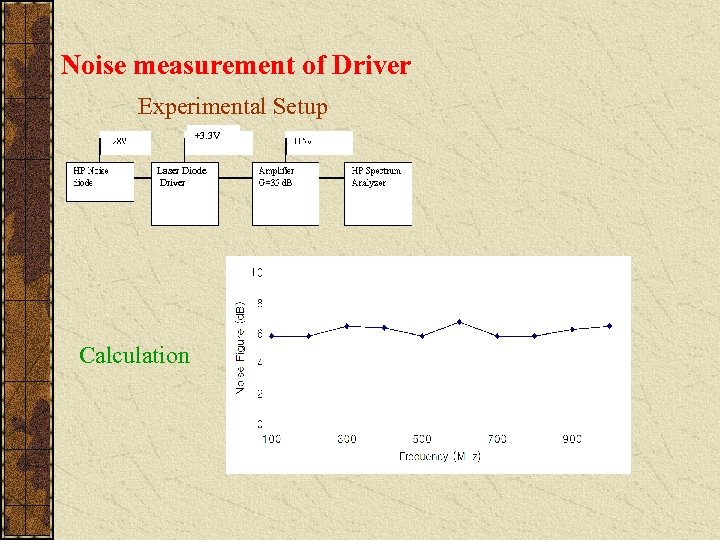 Noise measurement of Driver Experimental Setup +3. 3 V Laser Diode Driver Calculation
Noise measurement of Driver Experimental Setup +3. 3 V Laser Diode Driver Calculation
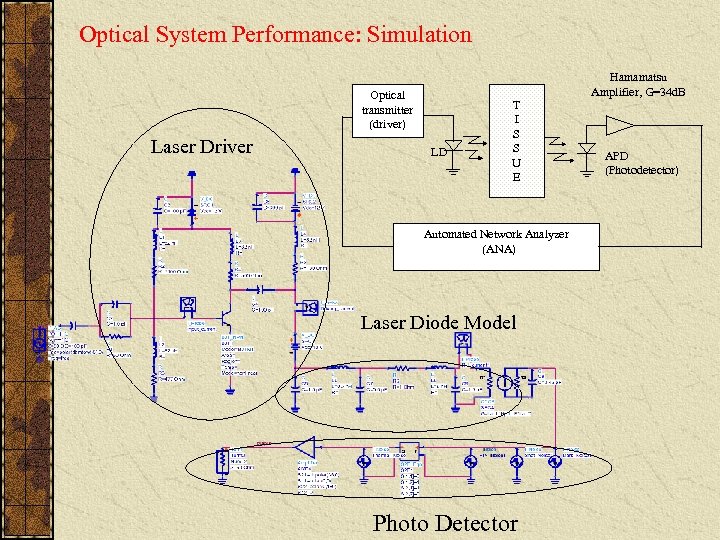 Optical System Performance: Simulation Hamamatsu Amplifier, G=34 d. B Optical transmitter (driver) Laser Driver LD T I S S U E Automated Network Analyzer (ANA) Laser Diode Model Photo Detector APD (Photodetector)
Optical System Performance: Simulation Hamamatsu Amplifier, G=34 d. B Optical transmitter (driver) Laser Driver LD T I S S U E Automated Network Analyzer (ANA) Laser Diode Model Photo Detector APD (Photodetector)
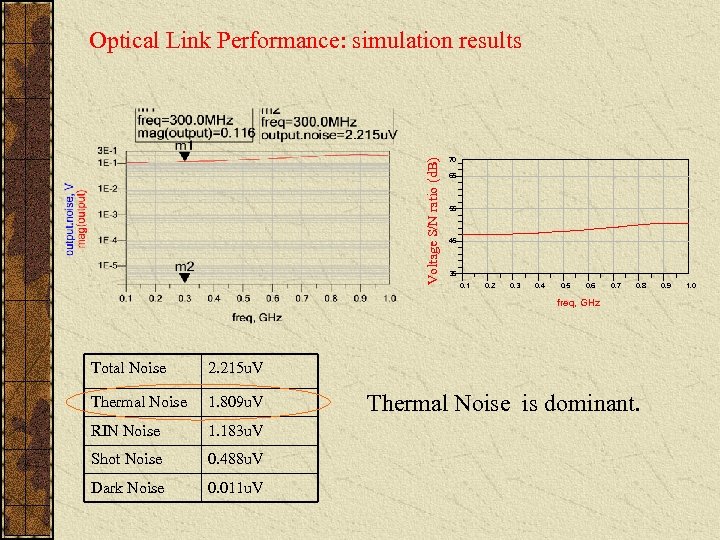 Voltage S/N ratio (d. B) Optical Link Performance: simulation results 70 65 55 45 35 0. 1 0. 2 0. 3 0. 4 0. 5 0. 6 0. 7 0. 8 freq, GHz Total Noise 2. 215 u. V Thermal Noise 1. 809 u. V RIN Noise 1. 183 u. V Shot Noise 0. 488 u. V Dark Noise 0. 011 u. V Thermal Noise is dominant. 0. 9 1. 0
Voltage S/N ratio (d. B) Optical Link Performance: simulation results 70 65 55 45 35 0. 1 0. 2 0. 3 0. 4 0. 5 0. 6 0. 7 0. 8 freq, GHz Total Noise 2. 215 u. V Thermal Noise 1. 809 u. V RIN Noise 1. 183 u. V Shot Noise 0. 488 u. V Dark Noise 0. 011 u. V Thermal Noise is dominant. 0. 9 1. 0
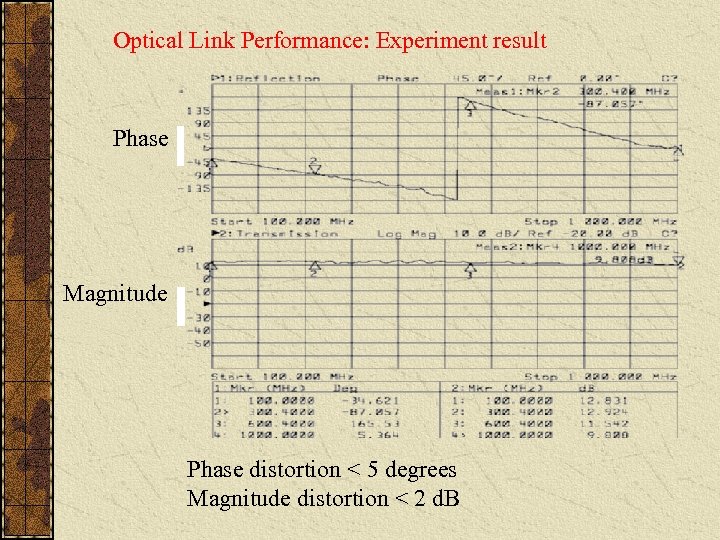 Optical Link Performance: Experiment result A Phase Magnitude B Phase distortion < 5 degrees Magnitude distortion < 2 d. B
Optical Link Performance: Experiment result A Phase Magnitude B Phase distortion < 5 degrees Magnitude distortion < 2 d. B
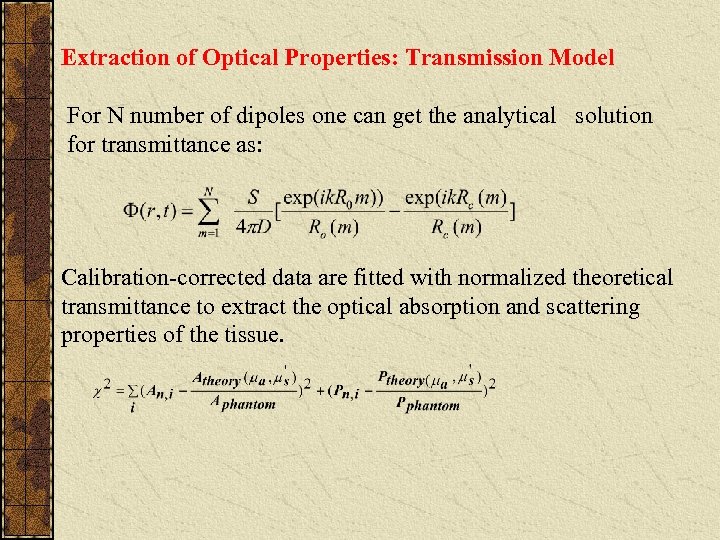 Extraction of Optical Properties: Transmission Model For N number of dipoles one can get the analytical solution for transmittance as: Calibration-corrected data are fitted with normalized theoretical transmittance to extract the optical absorption and scattering properties of the tissue.
Extraction of Optical Properties: Transmission Model For N number of dipoles one can get the analytical solution for transmittance as: Calibration-corrected data are fitted with normalized theoretical transmittance to extract the optical absorption and scattering properties of the tissue.
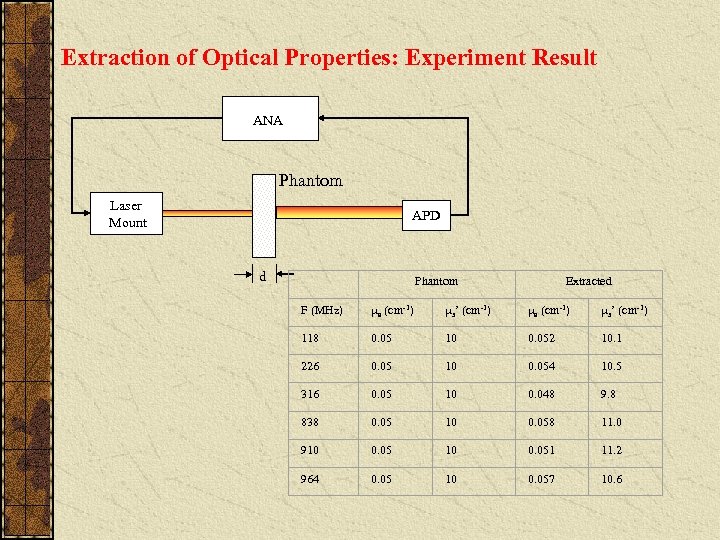 Extraction of Optical Properties: Experiment Result ANA Phantom Laser Mount APD d Phantom Extracted F (MHz) a (cm-1) s’ (cm-1) 118 0. 05 10 0. 052 10. 1 226 0. 05 10 0. 054 10. 5 316 0. 05 10 0. 048 9. 8 838 0. 05 10 0. 058 11. 0 910 0. 051 11. 2 964 0. 05 10 0. 057 10. 6
Extraction of Optical Properties: Experiment Result ANA Phantom Laser Mount APD d Phantom Extracted F (MHz) a (cm-1) s’ (cm-1) 118 0. 05 10 0. 052 10. 1 226 0. 05 10 0. 054 10. 5 316 0. 05 10 0. 048 9. 8 838 0. 05 10 0. 058 11. 0 910 0. 051 11. 2 964 0. 05 10 0. 057 10. 6
 Conclusion An active laser driver is developed for a broadband operation of four-color sources in near IR. A multi-frequency domain instrument is reported for near infrared light spectroscopy applications. High power (up to 1. 2 W) and high-speed (up to 1 GHz) laser diode driver exhibited a flat frequency response. Extracted optical parameters a and s for phantom resembling breast tissue demonstrates the high accuracy of this measurement technique and extraction method.
Conclusion An active laser driver is developed for a broadband operation of four-color sources in near IR. A multi-frequency domain instrument is reported for near infrared light spectroscopy applications. High power (up to 1. 2 W) and high-speed (up to 1 GHz) laser diode driver exhibited a flat frequency response. Extracted optical parameters a and s for phantom resembling breast tissue demonstrates the high accuracy of this measurement technique and extraction method.


