fd1834ce9595da10ecf7013cee60bb67.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Multi-Agent Auction, Bidding and Contracting Support Systems D. -J. Wu, Yanjun Sun FMEC May 11 -12, 2000 Philadelphia

ABC in Human History • Marrying daughter in ancient China using bidding, Song Dynasty • Auction women as wives in Babylonia, Fifth Century, B. C. • Farming contracting in ancient China, 452 B. C.

Auction Literature • Tradition auction (single item) • • English, Dutch Sealed bid, open cry First price winner and second price winner Goods are storable • Combinatorial auction (multi item) • i. Bundle (Auction. Bot) • Generalized Vickery auction
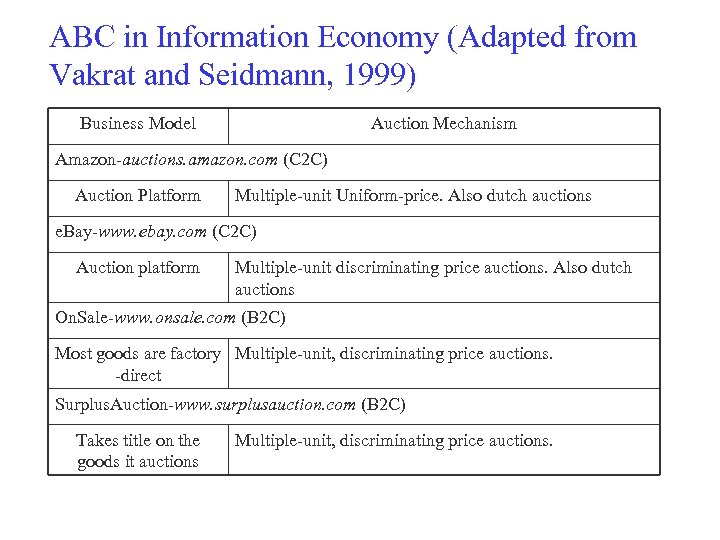
ABC in Information Economy (Adapted from Vakrat and Seidmann, 1999) Business Model Auction Mechanism Amazon-auctions. amazon. com (C 2 C) Auction Platform Multiple-unit Uniform-price. Also dutch auctions e. Bay-www. ebay. com (C 2 C) Auction platform Multiple-unit discriminating price auctions. Also dutch auctions On. Sale-www. onsale. com (B 2 C) Most goods are factory Multiple-unit, discriminating price auctions. -direct Surplus. Auction-www. surplusauction. com (B 2 C) Takes title on the goods it auctions Multiple-unit, discriminating price auctions.
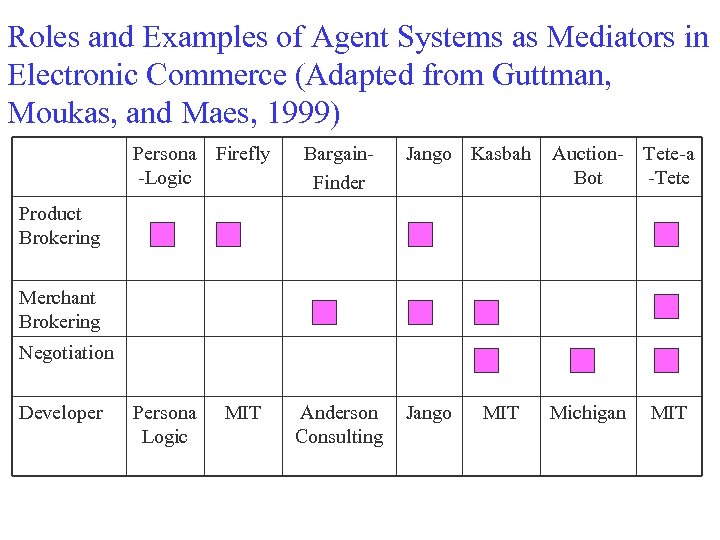
Roles and Examples of Agent Systems as Mediators in Electronic Commerce (Adapted from Guttman, Moukas, and Maes, 1999) Persona Firefly -Logic Bargain. Finder Jango Kasbah Auction- Tete-a Bot -Tete Jango Michigan Product Brokering Merchant Brokering Negotiation Developer Persona Logic MIT Anderson Consulting MIT

e. BAC Auction Literature e. BAC Bid Discrete Continuous Storability YES NO Seller Single Many Market One Two

Research Questions: • Can artificial agents discover the equilibrium if it exists? • Can artificial agents learn reasonably good policies when facing automated markets? • What kind of mechanisms will induce coordination, cooperation and information sharing among agents?
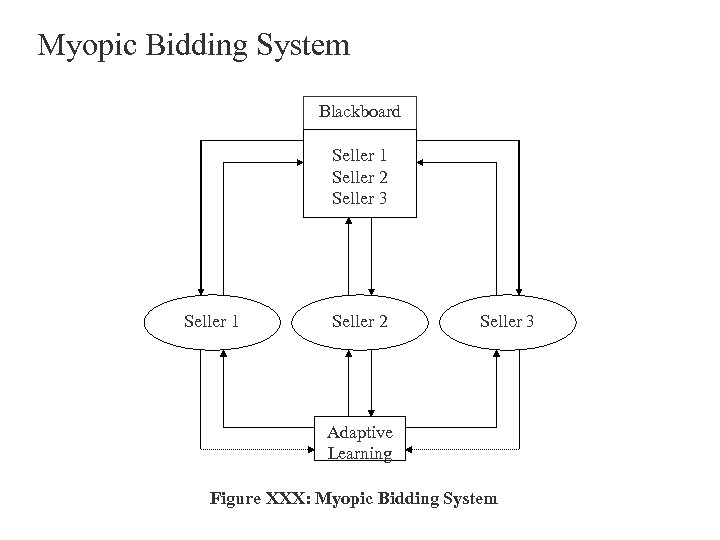
Myopic Bidding System Blackboard Seller 1 Seller 2 Seller 3 Adaptive Learning Figure XXX: Myopic Bidding System
Agents Learning in Myopic System • • • Floating point representation. Identical initial population. Rule strength is current profit. Memory size = 1. Learning via genetic algorithms.

Model for Myopic Bidding • Bidding Price • Bidding Capacity
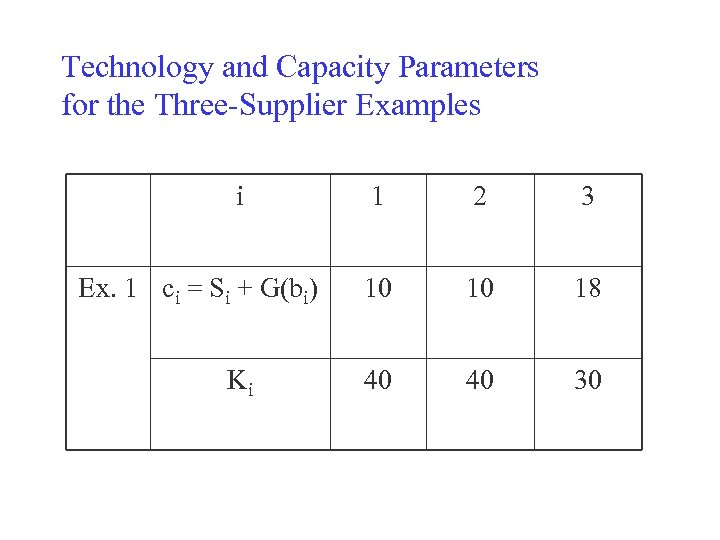
Technology and Capacity Parameters for the Three-Supplier Examples i Ex. 1 ci = Si + G(bi) Ki 1 2 3 10 10 18 40 40 30
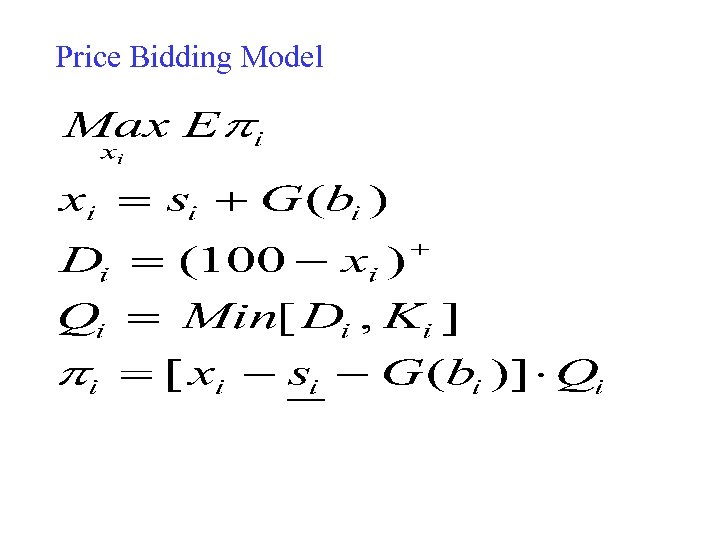
Price Bidding Model
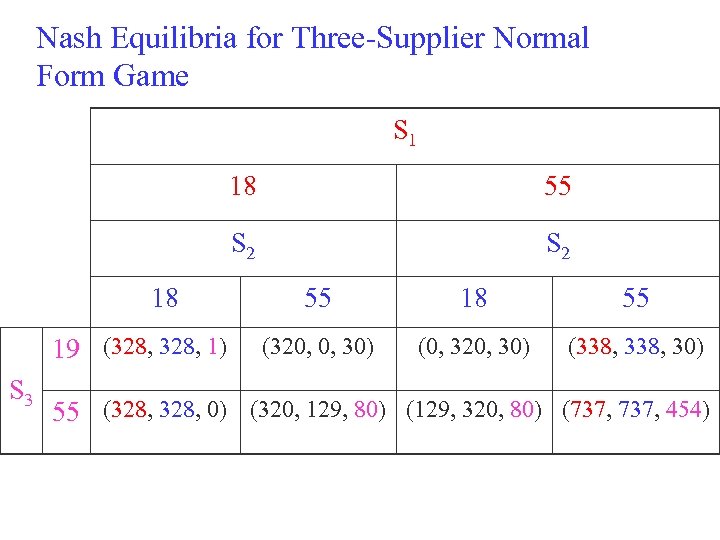
Nash Equilibria for Three-Supplier Normal Form Game S 1 18 S 2 18 19 (328, 1) S 3 55 S 2 55 18 55 (320, 0, 30) (0, 320, 30) (338, 30) 55 (328, 0) (320, 129, 80) (129, 320, 80) (737, 454)
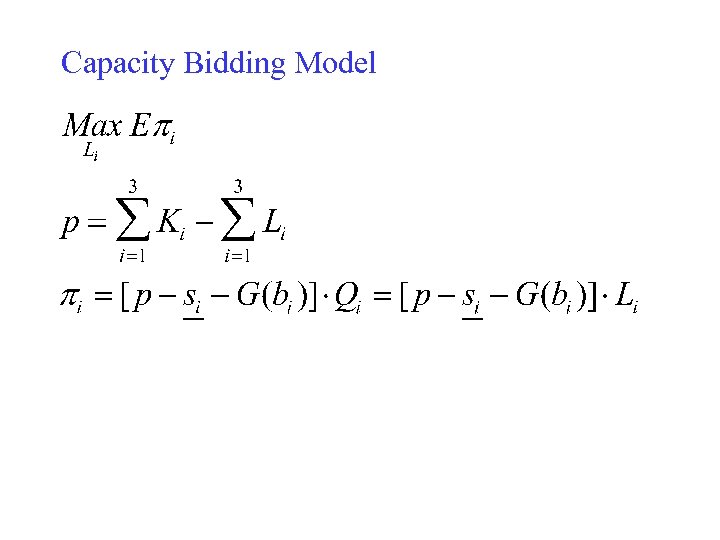
Capacity Bidding Model
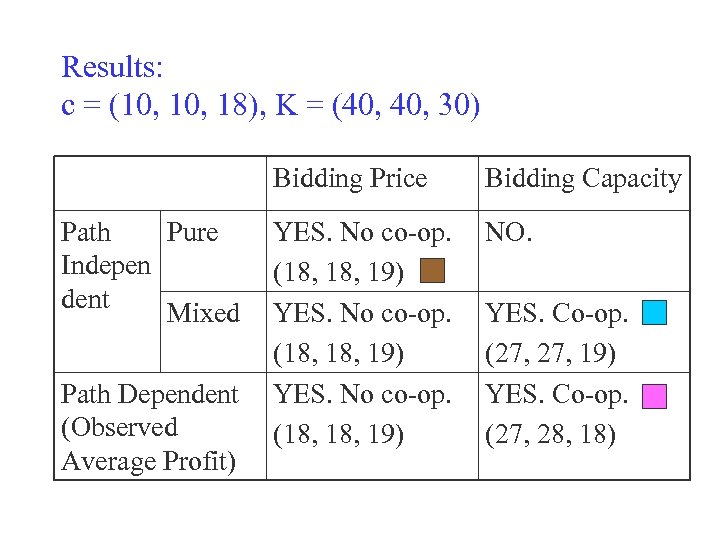
Results: c = (10, 18), K = (40, 30) Bidding Price Path Pure Indepen dent Mixed YES. No co-op. (18, 18, 19) Path Dependent YES. No co-op. (Observed (18, 19) Average Profit) Bidding Capacity NO. YES. Co-op. (27, 19) YES. Co-op. (27, 28, 18)
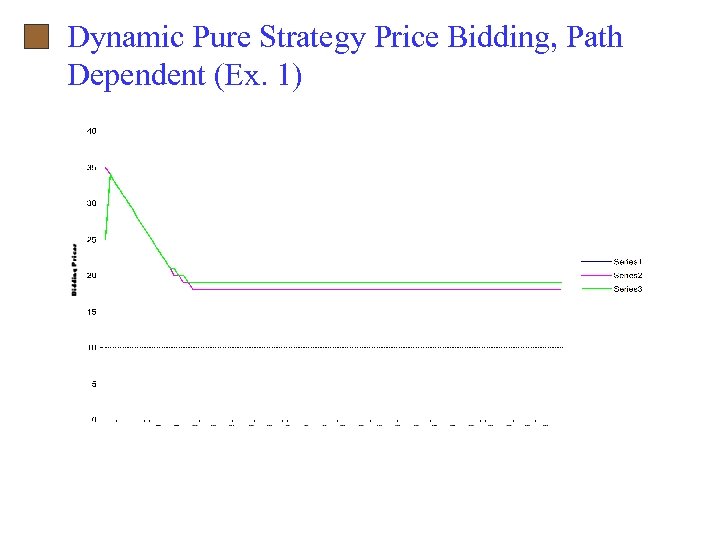
Dynamic Pure Strategy Price Bidding, Path Dependent (Ex. 1)
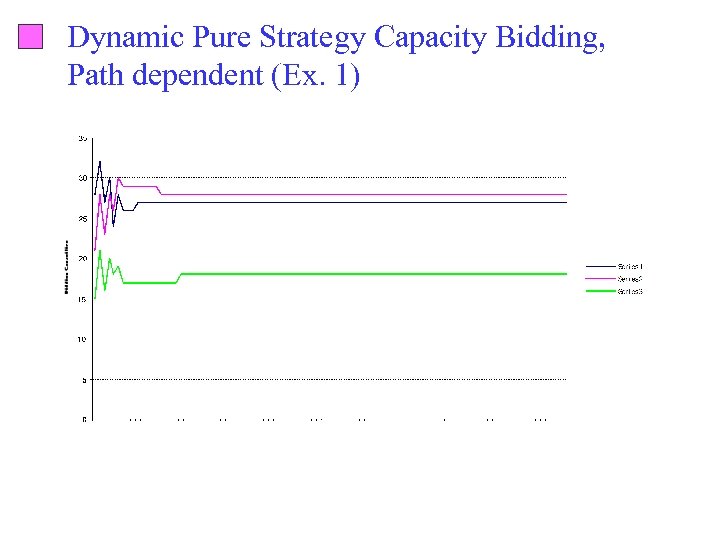
Dynamic Pure Strategy Capacity Bidding, Path dependent (Ex. 1)
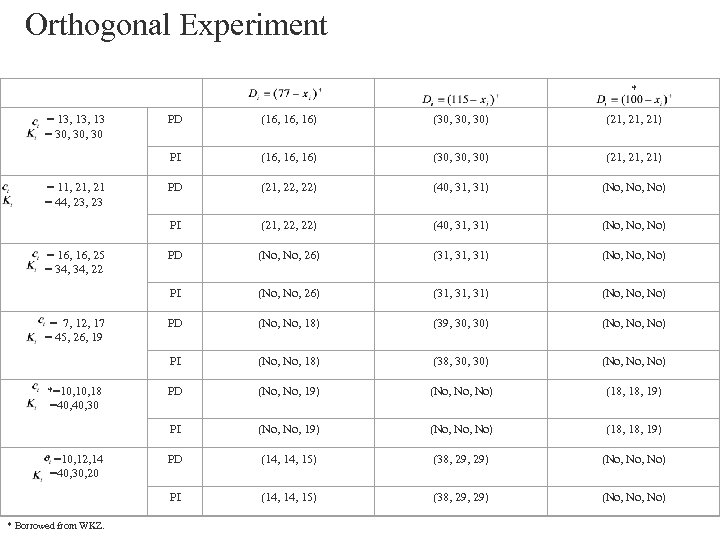
Orthogonal Experiment * = 13, 13 = 30, 30 (21, 21) PD (21, 22, 22) (40, 31, 31) (No, No, No) PD (No, No, 26) (31, 31, 31) (No, No, No) PD (No, 18) (39, 30) (No, No) (No, 18) (38, 30) (No, No) PD (No, No, 19) (No, No, No) (18, 18, 19) PD (14, 15) (38, 29) (No, No) PI * Borrowed from WKZ. (30, 30) PI * =10, 12, 14 =40, 30, 20 (16, 16) PI *=10, 18 =40, 30 (21, 21) PI = 7, 12, 17 = 45, 26, 19 (30, 30) PI = 16, 25 = 34, 22 (16, 16) PI = 11, 21 = 44, 23 PD (14, 15) (38, 29) (No, No)

Summary of Myopic Price Bidding • No cooperation exists under any climate. • Bidding tends to have equilibrium under amenable climate. • No difference between path dependent and independent.

Non-Myopic Bidding • No learning (Fixed strategy tournament) • One agent learning • All agents learning
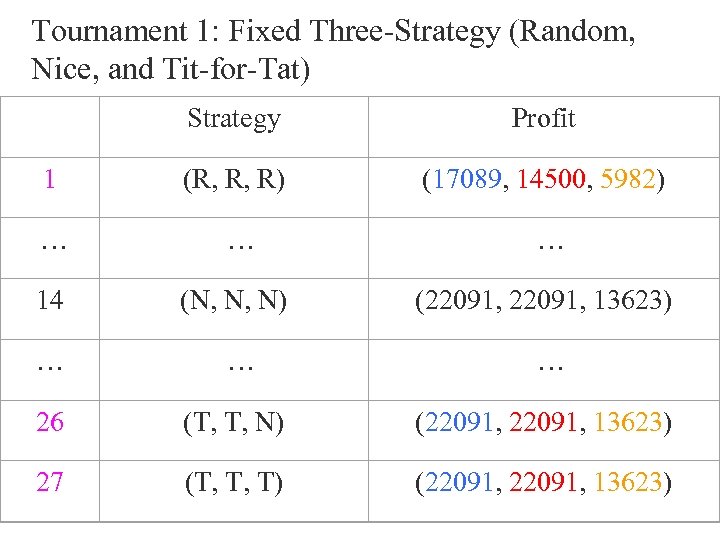
Tournament 1: Fixed Three-Strategy (Random, Nice, and Tit-for-Tat) Strategy Profit 1 (R, R, R) (17089, 14500, 5982) … … … 14 (N, N, N) (22091, 13623) … … … 26 (T, T, N) (22091, 13623) 27 (T, T, T) (22091, 13623)
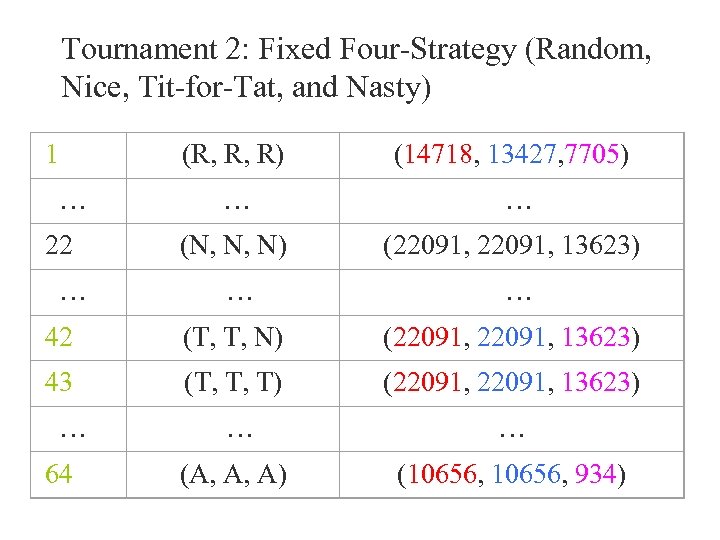
Tournament 2: Fixed Four-Strategy (Random, Nice, Tit-for-Tat, and Nasty) 1 (R, R, R) (14718, 13427, 7705) … … … 22 (N, N, N) (22091, 13623) … … … 42 (T, T, N) (22091, 13623) 43 (T, T, T) (22091, 13623) … … … 64 (A, A, A) (10656, 934)

One Agent Learning
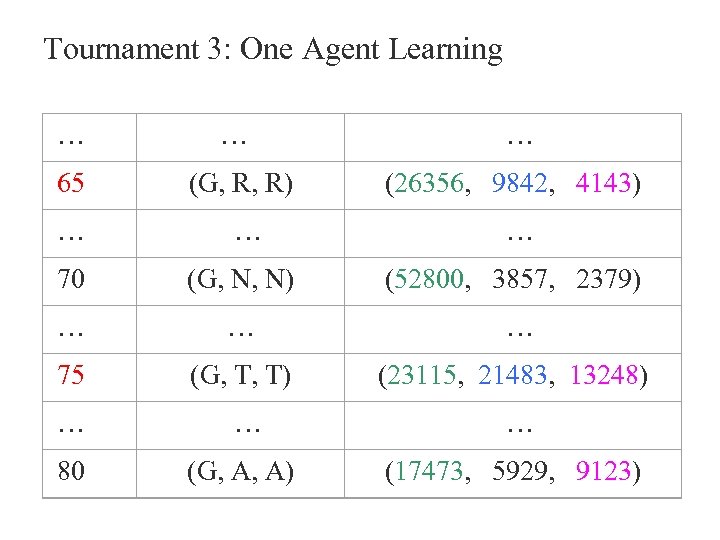
Tournament 3: One Agent Learning … … … 65 (G, R, R) (26356, 9842, 4143) … … … 70 (G, N, N) (52800, 3857, 2379) … … … 75 (G, T, T) (23115, 21483, 13248) … … … 80 (G, A, A) (17473, 5929, 9123)
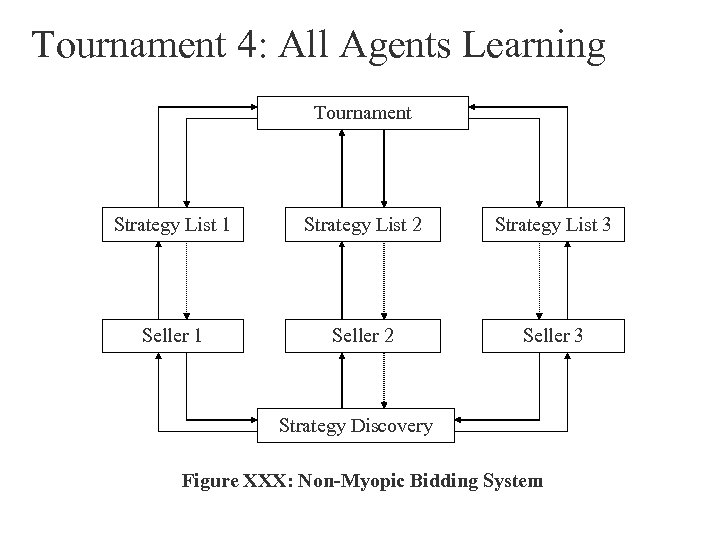
Tournament 4: All Agents Learning Tournament Strategy List 1 Strategy List 2 Strategy List 3 Seller 1 Seller 2 Seller 3 Strategy Discovery Figure XXX: Non-Myopic Bidding System

Agent Learning in Non-Myopic System • Representation: Each rule specifies multiperiod bidding strategy. • Randomly generated initial population. • Rule learning via genetic algorithms. • Rule strength is expected tournament profit.

Model for Non-Myopic Bidding

The Emergence of Trust • Learning to cooperate • Conditions for cooperation • Impact of climate

Agent Learning in Dynamic Environment: Experiment 1
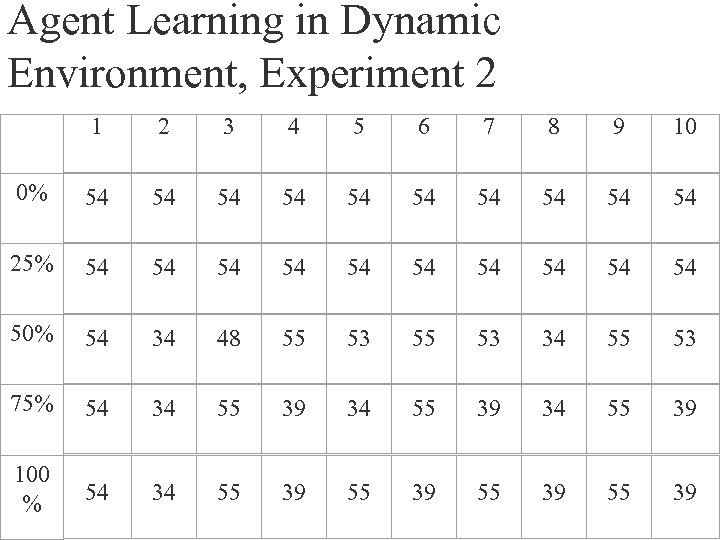
Agent Learning in Dynamic Environment, Experiment 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0% 54 54 54 25% 54 54 54 50% 54 34 48 55 53 34 55 53 75% 54 34 55 39 100 % 54 34 55 39
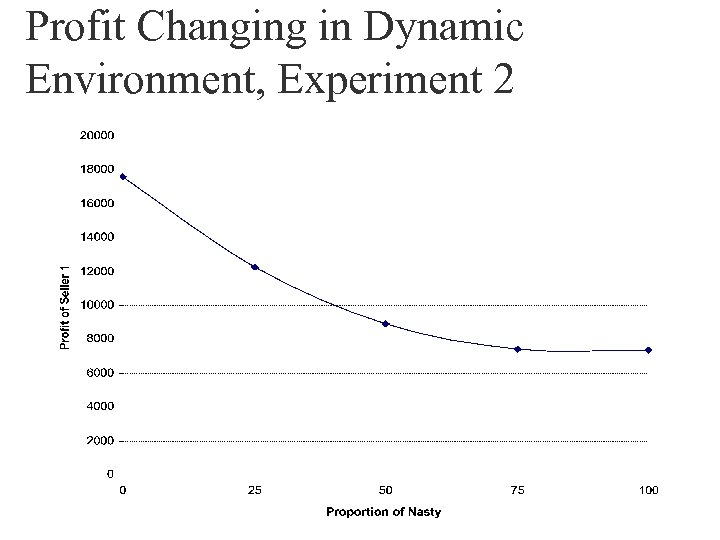
Profit Changing in Dynamic Environment, Experiment 2

Ongoing Research • The ring of King Solomon • Agent communication • Computational principles of trust • Agent coalition and Bargaining • Role of Larmarcian learning

Summary • Artificial agents are viable in automated marketplace. • • Discover optimal bidding and contracting strategies in the equilibrium if exist. Find better strategies in a complex dynamic environment where equilibrium do not exist. • The emergence of trust. • • • Depends on the auction mechanism: Capacity bidding induces cooperation. Non-myopic bidding leads to cooperation while myopic bidding does not. Climate has impact on agents cooperation.
fd1834ce9595da10ecf7013cee60bb67.ppt