3fbf3d4877d61fd0415260c5fa5bb58b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55

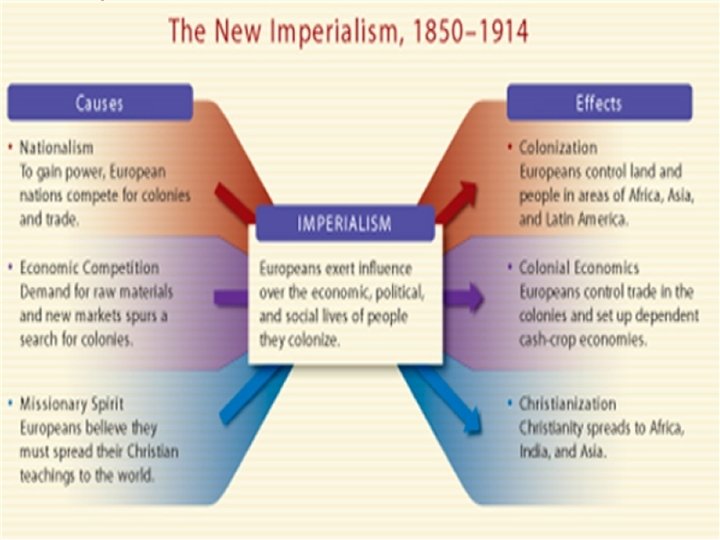
 Mughal India (1526 -1857)
Mughal India (1526 -1857)
 What is India Like? ? ? v 5, 000 year old civilization v 325 languages spoken – 1, 652 dialects v 18 official languages v 29 states, 5 union territories v 3. 28 million sq. kilometers - Area v 7, 516 kilometers - Coastline v 1, 000, 000 people in 2000
What is India Like? ? ? v 5, 000 year old civilization v 325 languages spoken – 1, 652 dialects v 18 official languages v 29 states, 5 union territories v 3. 28 million sq. kilometers - Area v 7, 516 kilometers - Coastline v 1, 000, 000 people in 2000
 Mughal Empire Decline of the Mughals • Persecution of Hindus • Increased taxation and decentralization • Foreign Involvement – France and Britain
Mughal Empire Decline of the Mughals • Persecution of Hindus • Increased taxation and decentralization • Foreign Involvement – France and Britain


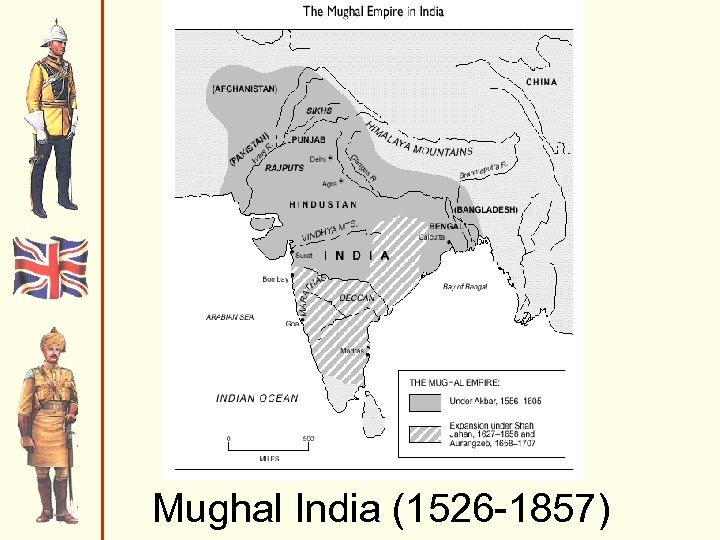
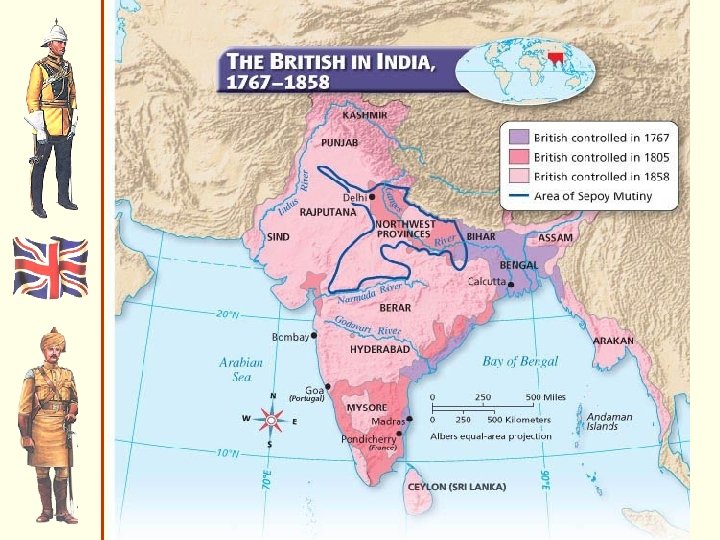
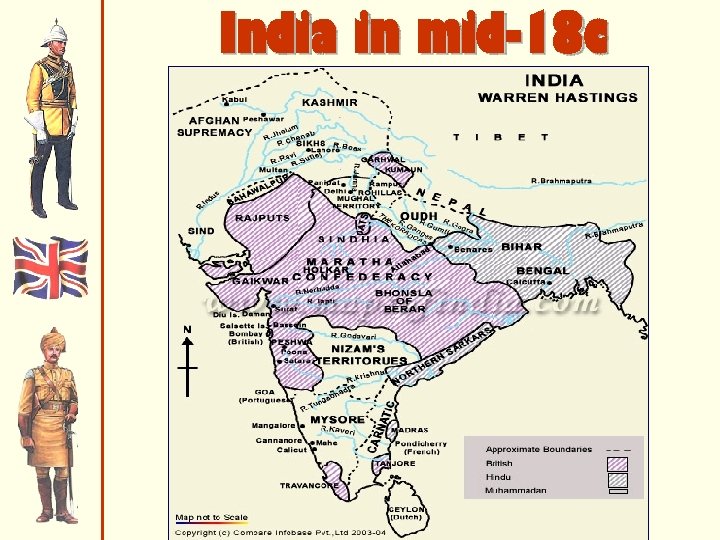 India in mid-18 c
India in mid-18 c
 British East India Company Early British imperialism in India was carried out by the British East India Trading Company. The British Take Control How? Keep India in Chaos • East India Co. limited to • Manipulated rulers of coastal trading cities while states, Played rulers Mughal Empire strong, against each other But… • Company’s army took • Mid-1700 s, when empire over much of India, broke apart East India Co. claiming it had to restore leaders saw chance to order* (Political take over Indian lands Imperialism)
British East India Company Early British imperialism in India was carried out by the British East India Trading Company. The British Take Control How? Keep India in Chaos • East India Co. limited to • Manipulated rulers of coastal trading cities while states, Played rulers Mughal Empire strong, against each other But… • Company’s army took • Mid-1700 s, when empire over much of India, broke apart East India Co. claiming it had to restore leaders saw chance to order* (Political take over Indian lands Imperialism)
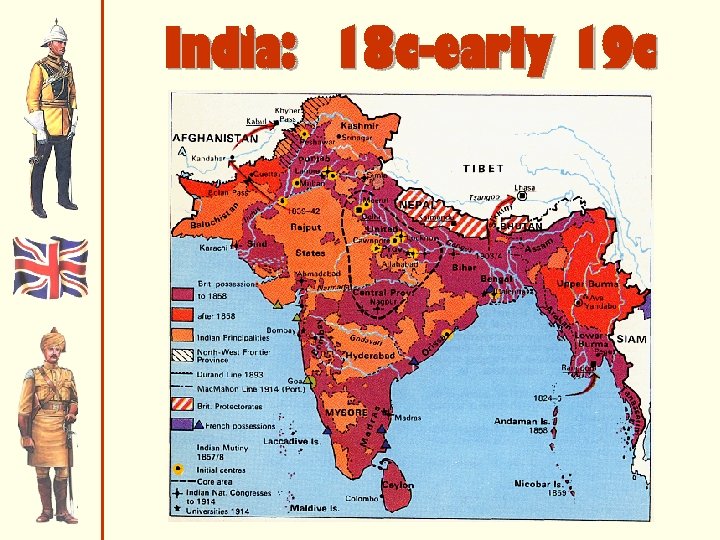 India: 18 c-early 19 c
India: 18 c-early 19 c
 British Expand Control over India East India Company Dominates India • British East India Company rules India until 1850 s • Company has its own army led by British officers • Army is staffed by Sepoys—Indian soldiers*
British Expand Control over India East India Company Dominates India • British East India Company rules India until 1850 s • Company has its own army led by British officers • Army is staffed by Sepoys—Indian soldiers*
 Sepoys, 1850 s
Sepoys, 1850 s
 British East India Company Agents
British East India Company Agents

 British Expand Control over India East India Company Dominates India (sub-continent) • British East India Company rules India until 1850 s • Company has its own army led by British officers • Army is staffed by sepoys—Indian soldiers • India is Britain’s most valuable colony, or “jewel in the crown” • Forced to produce raw materials for British manufacturing (cotton, tea, lumber, opium) • Also forced to buy British industrial goods *
British Expand Control over India East India Company Dominates India (sub-continent) • British East India Company rules India until 1850 s • Company has its own army led by British officers • Army is staffed by sepoys—Indian soldiers • India is Britain’s most valuable colony, or “jewel in the crown” • Forced to produce raw materials for British manufacturing (cotton, tea, lumber, opium) • Also forced to buy British industrial goods *
 Coins of the British East India Co. 1719 coin 1804 coin
Coins of the British East India Co. 1719 coin 1804 coin
 British Soldiers in India, 1830 s
British Soldiers in India, 1830 s
 Coffee House in mid-19 c British India
Coffee House in mid-19 c British India
 British Opium Warehouse in Patna, India Selling Patna Opium in China
British Opium Warehouse in Patna, India Selling Patna Opium in China
 The Sepoy Mutiny Indians Rebel • Sepoys refuse to use cartridges of new rifles for religious reasons Hindus believe they use cow fat. . Muslins believe they use pig fat… • Many Sepoys are jailed; others start the Sepoy Mutiny against British. Thousands are killed. • GB punishes India by Taking over from the Dutch E. India Company. *
The Sepoy Mutiny Indians Rebel • Sepoys refuse to use cartridges of new rifles for religious reasons Hindus believe they use cow fat. . Muslins believe they use pig fat… • Many Sepoys are jailed; others start the Sepoy Mutiny against British. Thousands are killed. • GB punishes India by Taking over from the Dutch E. India Company. *
 The Sepoy Mutiny The Supoy Mutiny is the Turning Point for GB control • Raj—term for British rule over India, lasts from 1857 to 1947 • GB now turns India into a mirror of GB They use a “parliamentary” system of govt. English becomes the most common spoken language…. this brings people together*
The Sepoy Mutiny The Supoy Mutiny is the Turning Point for GB control • Raj—term for British rule over India, lasts from 1857 to 1947 • GB now turns India into a mirror of GB They use a “parliamentary” system of govt. English becomes the most common spoken language…. this brings people together*
 The Sepoy Mutiny: 1857
The Sepoy Mutiny: 1857

 Execution of Sepoys: “The Devil’s Wind” Punishment of the Sepoys
Execution of Sepoys: “The Devil’s Wind” Punishment of the Sepoys

 1877: Queen Victoria Becomes “Empress of India”
1877: Queen Victoria Becomes “Empress of India”
 Queen Victoria in India
Queen Victoria in India
 Queen Victoria: Receiving the Crown of India
Queen Victoria: Receiving the Crown of India
 Sikhs – Bengal Cavalry of the British Army
Sikhs – Bengal Cavalry of the British Army

 Outlawing Suttee (sati)
Outlawing Suttee (sati)
 Fighting the Thuggees
Fighting the Thuggees
 Fighting the Thuggees Thuggee- (from Hindi thag ‘thief’, from Sanskrit sthaga ‘scoundrel’, from sthagati ‘to conceal’) was an Indian network of secret fraternities engaged in murdering and robbing travelers, operating from at least the 17 th century (and possibly as early as 13 th century) to the 19 th century. The group are the origin of the term "thug", as many Indian words passed into common English during British Imperial rule of India.
Fighting the Thuggees Thuggee- (from Hindi thag ‘thief’, from Sanskrit sthaga ‘scoundrel’, from sthagati ‘to conceal’) was an Indian network of secret fraternities engaged in murdering and robbing travelers, operating from at least the 17 th century (and possibly as early as 13 th century) to the 19 th century. The group are the origin of the term "thug", as many Indian words passed into common English during British Imperial rule of India.
 Medical Service, 1860
Medical Service, 1860
 A Life of Leisure for GB citizians
A Life of Leisure for GB citizians
 Br. Viceroy’s Daughter: Simla, 1863
Br. Viceroy’s Daughter: Simla, 1863


 Darjeeling Railroad, 1880 s
Darjeeling Railroad, 1880 s
 Simla: Little England in the mountains of India
Simla: Little England in the mountains of India
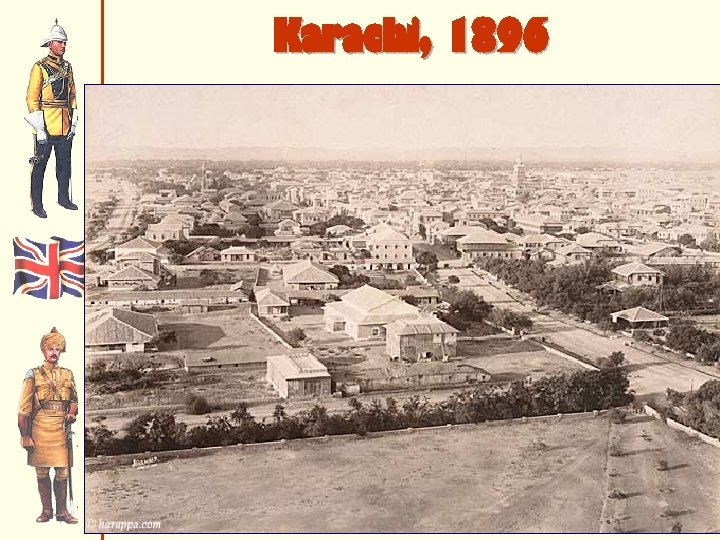 Karachi, 1896
Karachi, 1896
 Victoria Station, Bombay
Victoria Station, Bombay
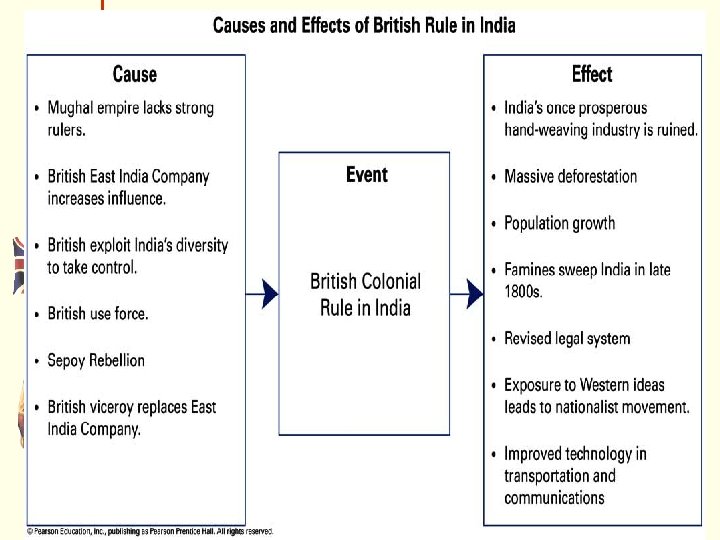
 Nationalism Surfaces in India • In 1800 s, GB modernized India RR, roads and ports to assist GB in getting goods raw materials out of the country. • Many Indians adopt western ways and call for social reforms, like getting rid of the “caste” system. • Indians resent being second-class citizens in own country Indians start to realize they now have a common language, history, geography, culture…. . And now a common goal……. . What is it? Independence from GB
Nationalism Surfaces in India • In 1800 s, GB modernized India RR, roads and ports to assist GB in getting goods raw materials out of the country. • Many Indians adopt western ways and call for social reforms, like getting rid of the “caste” system. • Indians resent being second-class citizens in own country Indians start to realize they now have a common language, history, geography, culture…. . And now a common goal……. . What is it? Independence from GB

 § 1885 The Indian National Congress was founded in Bombay. § swaraj “independence. ” * the goal of the movement.
§ 1885 The Indian National Congress was founded in Bombay. § swaraj “independence. ” * the goal of the movement.
 § 1905 partition of Bengal based on religions and languages. § 1906 creation of the Muslim League.
§ 1905 partition of Bengal based on religions and languages. § 1906 creation of the Muslim League.
 Jawaharlal nehru 1889 - 1964
Jawaharlal nehru 1889 - 1964
 Young Mohandas K. Gandhi, 6 1869 - 1948
Young Mohandas K. Gandhi, 6 1869 - 1948
 Gandhi with the london vegetarian society, 1890
Gandhi with the london vegetarian society, 1890
 Gandhi as a Young Barrister in Natal
Gandhi as a Young Barrister in Natal
 Gandhi as a Lawyer in Johannesburg, So. Africa
Gandhi as a Lawyer in Johannesburg, So. Africa
 The Indian Players Gandhi Nehru Jinnah Hear them.
The Indian Players Gandhi Nehru Jinnah Hear them.
 Amritsar Massacre, 1919 379 dead; over 1200 wounded!
Amritsar Massacre, 1919 379 dead; over 1200 wounded!
 The New Imperialism: Section 4 Note Taking Transparency 163 5 of 6
The New Imperialism: Section 4 Note Taking Transparency 163 5 of 6


