b3c7442d1c32e8bc4628cf157c954b34.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Mt. S-ISL-SUD-SDNS Statistical Data Collection and Processing System Mt. S-ISL-SUD-SDNS The Czech National Bank, September 2009 Jindra Ivanovova and Irena Zamecnikova Information Systems Department, Monetary and Statistics Department
Mt. S-ISL-SUD-SDNS Statistical Data Collection and Processing System Mt. S-ISL-SUD-SDNS The Czech National Bank, September 2009 Jindra Ivanovova and Irena Zamecnikova Information Systems Department, Monetary and Statistics Department
 Contents Ø Introduction of the System for data collection and processing at the CNB Ø Basic features of the solution Ø Architecture of the system Ø The organizational arrangement and operation
Contents Ø Introduction of the System for data collection and processing at the CNB Ø Basic features of the solution Ø Architecture of the system Ø The organizational arrangement and operation
 The Areas of the System Usage Ø The data collection for : Ø statistics (Monetary and financial statistics, Balance of payments statistics, National accounts statistics, Security - by - Security ) Ø supervision (Banks, Insurance industry, Capital market, Pension scheme industry, Credit Unions ) Ø Wide range of information for the core CNB´s activities (monetary policy, financial stability policy, financial market supervision, national accounts, statistics, etc. ) Ø The group of our respondents : Banks , Funds, Investment companies, Pension funds, Insurance companies, Brokers, Credit Unions, Other financial intermediaries, Non-financial institutions.
The Areas of the System Usage Ø The data collection for : Ø statistics (Monetary and financial statistics, Balance of payments statistics, National accounts statistics, Security - by - Security ) Ø supervision (Banks, Insurance industry, Capital market, Pension scheme industry, Credit Unions ) Ø Wide range of information for the core CNB´s activities (monetary policy, financial stability policy, financial market supervision, national accounts, statistics, etc. ) Ø The group of our respondents : Banks , Funds, Investment companies, Pension funds, Insurance companies, Brokers, Credit Unions, Other financial intermediaries, Non-financial institutions.
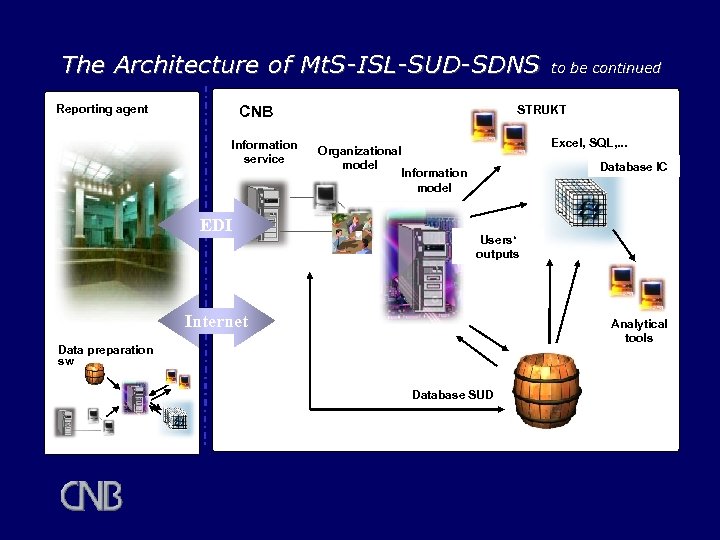 The Architecture of Mt. S-ISL-SUD-SDNS Reporting agent CNB Information service EDI to be continued STRUKT Excel, SQL, . . . Organizational model Information model Database IC Users‘ outputs Internet Analytical tools Data preparation sw Database SUD
The Architecture of Mt. S-ISL-SUD-SDNS Reporting agent CNB Information service EDI to be continued STRUKT Excel, SQL, . . . Organizational model Information model Database IC Users‘ outputs Internet Analytical tools Data preparation sw Database SUD
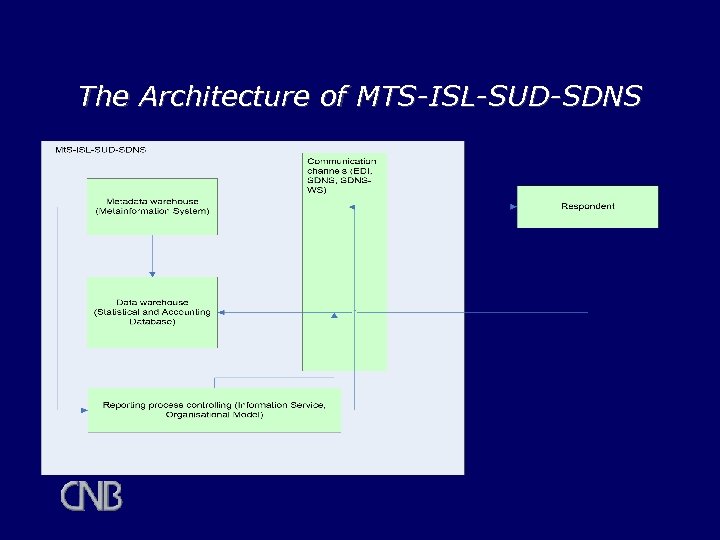 The Architecture of MTS-ISL-SUD-SDNS
The Architecture of MTS-ISL-SUD-SDNS
 The Basic Features of the System Ø No programming during the implementation of new statements and changes Ø The unified description of statements by using metadata Ø The fully automatic data processing controlled by metadata Ø One data warehouse only (Data and Metadata)
The Basic Features of the System Ø No programming during the implementation of new statements and changes Ø The unified description of statements by using metadata Ø The fully automatic data processing controlled by metadata Ø One data warehouse only (Data and Metadata)
 The Methodology Ø What does the methodology contain : Ø Ø Methodical specification of data (contents of data and reports = WHAT ) Reporting duties ( WHO and WHEN ) Validation rules (for quality - checking ) Semantic data description (No tables) Ø The unified principle of methodical description in all business areas Ø The basic phases of methodology (creation, validation, presentation. . ) Ø Particularity – an update of one object implies automatically changes of the dependent objects
The Methodology Ø What does the methodology contain : Ø Ø Methodical specification of data (contents of data and reports = WHAT ) Reporting duties ( WHO and WHEN ) Validation rules (for quality - checking ) Semantic data description (No tables) Ø The unified principle of methodical description in all business areas Ø The basic phases of methodology (creation, validation, presentation. . ) Ø Particularity – an update of one object implies automatically changes of the dependent objects
 The Data Warehouse Ø Basic principle Multidimensional cube Ø The definition of data is included Ø Ø The semantic description of the data Ø D 1 = IP 1 ( P 1. a, P 2. b, P 3. b) Ø Time series from 1993 Ø The history of statements (all data including canceled data are accessible to users ) Ø New data, correction and cancelation Ø On-line users‘ access
The Data Warehouse Ø Basic principle Multidimensional cube Ø The definition of data is included Ø Ø The semantic description of the data Ø D 1 = IP 1 ( P 1. a, P 2. b, P 3. b) Ø Time series from 1993 Ø The history of statements (all data including canceled data are accessible to users ) Ø New data, correction and cancelation Ø On-line users‘ access
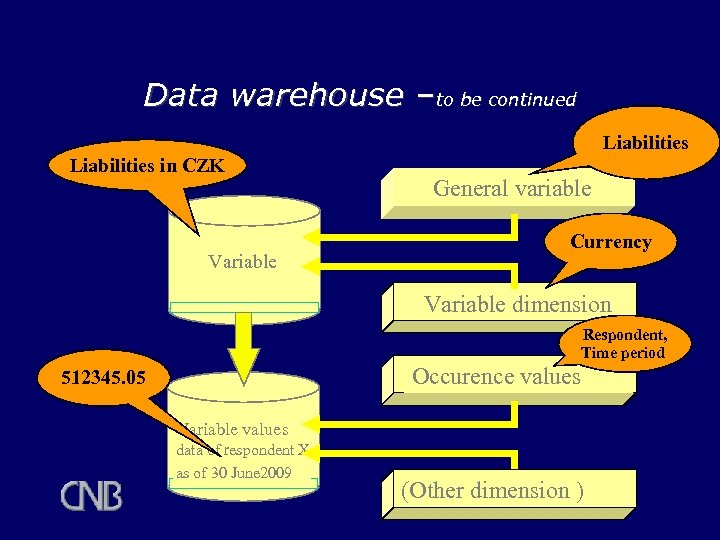 Data warehouse –to be continued Liabilities in CZK Variable General variable Currency Variable dimension Respondent, Time period Occurence values 512345. 05 Variable values data of respondent X as of 30 June 2009 (Other dimension )
Data warehouse –to be continued Liabilities in CZK Variable General variable Currency Variable dimension Respondent, Time period Occurence values 512345. 05 Variable values data of respondent X as of 30 June 2009 (Other dimension )
 Communication and Solution on the Respondents‘ Side to be continued 1. EDI solution: Ø Interfaces defined by the CNB : data, communication and security Ø Detailed procedural and organizational rules defined by the CNB Ø The CNB´s application and the respondents‘ applications based on the similar principles Ø A high level of security: electronic signature and possible encryption
Communication and Solution on the Respondents‘ Side to be continued 1. EDI solution: Ø Interfaces defined by the CNB : data, communication and security Ø Detailed procedural and organizational rules defined by the CNB Ø The CNB´s application and the respondents‘ applications based on the similar principles Ø A high level of security: electronic signature and possible encryption
 Communication and Solution on the Respondents‘ Side 2. 3. Internet solution (SDNS) Ø On-line reporting Ø Secure logon (PKI Entrust certificate or user‘s name & password) Ø Electronic signature (based on PKI Entrust certificate or on the qualified certificates), encrypted communication Web services solution (SDNS-Web-Services) Ø Ten Web-Services for methodological and operating information retrieval defined by the CNB Ø Web-Service for sending data defined by the CNB Ø Secure logon (user‘s name & password) Ø Electronic signature (based on the qualified certificates) , encrypted communication
Communication and Solution on the Respondents‘ Side 2. 3. Internet solution (SDNS) Ø On-line reporting Ø Secure logon (PKI Entrust certificate or user‘s name & password) Ø Electronic signature (based on PKI Entrust certificate or on the qualified certificates), encrypted communication Web services solution (SDNS-Web-Services) Ø Ten Web-Services for methodological and operating information retrieval defined by the CNB Ø Web-Service for sending data defined by the CNB Ø Secure logon (user‘s name & password) Ø Electronic signature (based on the qualified certificates) , encrypted communication
 The Internet Application SDNS Ø Public access Ø Presentation of methodologies for all business areas in structured form Ø Registered access Ø Ø Ø Presentation of methodology of all respondent-related statements Presentation of data transmitting schedule Data input Ø Data typing supported by detailed methodological description Ø File upload in the xml format prepared by the suitable application Ø Possibility to compute summary values from detailed values Ø Possibility of preliminary checks Data sending Presentation of processing results
The Internet Application SDNS Ø Public access Ø Presentation of methodologies for all business areas in structured form Ø Registered access Ø Ø Ø Presentation of methodology of all respondent-related statements Presentation of data transmitting schedule Data input Ø Data typing supported by detailed methodological description Ø File upload in the xml format prepared by the suitable application Ø Possibility to compute summary values from detailed values Ø Possibility of preliminary checks Data sending Presentation of processing results
 The Automated processing – to be continued Ø The basic phases of data processing: collection, quality checking, storing, sending response Ø Operation is controlled via metadata: Ø Ø What kind of information: described by methodology What kind of checks: described by methodology What kind of activity: described by operational metadata Operational parameters: Statement priority Ø Number of currently running batches Ø Maximum duration of one batch processing Ø Time limit for sending processing results to respondents, etc. Ø
The Automated processing – to be continued Ø The basic phases of data processing: collection, quality checking, storing, sending response Ø Operation is controlled via metadata: Ø Ø What kind of information: described by methodology What kind of checks: described by methodology What kind of activity: described by operational metadata Operational parameters: Statement priority Ø Number of currently running batches Ø Maximum duration of one batch processing Ø Time limit for sending processing results to respondents, etc. Ø
 The Automated processing Some facts: Ø Ø Ø Messages received per year : about 40 000 Processing results and reminders sent per year: about 50 000 Daily received messages in the peak: about 500 Daily sent messages in the peak: about 700 Time limit between receiving messages and sending processing results: 20 min. at least for 95% messages received in a month
The Automated processing Some facts: Ø Ø Ø Messages received per year : about 40 000 Processing results and reminders sent per year: about 50 000 Daily received messages in the peak: about 500 Daily sent messages in the peak: about 700 Time limit between receiving messages and sending processing results: 20 min. at least for 95% messages received in a month
 Organizational Arrangement to be continued Ø Matter-of-fact administration Ø Ø Methodical supervision of all business area methodologies Administration of shared objects: dimensions (parameters), code lists , hierarchic classifications, data types, … Ø Technical administration Ø Ø Ø Administration of system and operational parameters Monitoring of data processing Users‘ support
Organizational Arrangement to be continued Ø Matter-of-fact administration Ø Ø Methodical supervision of all business area methodologies Administration of shared objects: dimensions (parameters), code lists , hierarchic classifications, data types, … Ø Technical administration Ø Ø Ø Administration of system and operational parameters Monitoring of data processing Users‘ support
 Organizational Arrangement Ø Users – methodical designer Ø Design of a statement methodological description with the aid of the system rules, objects and tools Ø Users Ø Ø Ø Data selection and data aggregation Numerical series (time, respondents) Information about the data quality at the users‘ disposal Ø Users – programmer Ø Design and programming of output applications
Organizational Arrangement Ø Users – methodical designer Ø Design of a statement methodological description with the aid of the system rules, objects and tools Ø Users Ø Ø Ø Data selection and data aggregation Numerical series (time, respondents) Information about the data quality at the users‘ disposal Ø Users – programmer Ø Design and programming of output applications
 Basic Feature at the Outset Ø Ø Ø The conception of the whole system at the outset The system has been outsourced (larger expenses but saved personnel resources - thousands of man-days) The users used the same methods, tools: prescribed (limited) rules increased the efficiency
Basic Feature at the Outset Ø Ø Ø The conception of the whole system at the outset The system has been outsourced (larger expenses but saved personnel resources - thousands of man-days) The users used the same methods, tools: prescribed (limited) rules increased the efficiency
 Summary Ø Advantage for respondents Ø Ø one system for all reporting to the CNB no software is needed („small“ reporting extent) possibility to check data before transmitting quick result response Ø Advantage for the CNB Ø Ø Ø one system for all reporting agents (large, small, financial, non-financial, . . ) no software distribution increasing data quality
Summary Ø Advantage for respondents Ø Ø one system for all reporting to the CNB no software is needed („small“ reporting extent) possibility to check data before transmitting quick result response Ø Advantage for the CNB Ø Ø Ø one system for all reporting agents (large, small, financial, non-financial, . . ) no software distribution increasing data quality
 Finally Thank you for your attention ! Any questions? Ø The web-side of the internet application SDNS (in Czech only) https: //wsn. cnb. cz/ewi/
Finally Thank you for your attention ! Any questions? Ø The web-side of the internet application SDNS (in Czech only) https: //wsn. cnb. cz/ewi/


