bd04adcda8208fb8d2c2a1fc16487d9f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 91
 Msunduzi Municipality Progress Report in terms of Section 139(1)(b) Presentation to City Stakeholder Forum 31 January 2011 1
Msunduzi Municipality Progress Report in terms of Section 139(1)(b) Presentation to City Stakeholder Forum 31 January 2011 1
 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Introduction Background Financial Overview Electricity Water Sanitation Waste Fleet Roads Planning & Human Settlement Risk Analysis Operationalisation Exit Principles 2
PRESENTATION OUTLINE Introduction Background Financial Overview Electricity Water Sanitation Waste Fleet Roads Planning & Human Settlement Risk Analysis Operationalisation Exit Principles 2
 INTRODUCTION The serious financial challenges in Msunduzi Municipality have necessitated an intervention in terms of section 139 of the MFMA. The financial crises came to be because of poor controls, rampant corruption amongst senior staff, failure to prepare the mid-year Adjustments Budget and the 2010/11 Budget in time. 3
INTRODUCTION The serious financial challenges in Msunduzi Municipality have necessitated an intervention in terms of section 139 of the MFMA. The financial crises came to be because of poor controls, rampant corruption amongst senior staff, failure to prepare the mid-year Adjustments Budget and the 2010/11 Budget in time. 3
 BACKGROUND By mid March 2010 when the Provincial Intervention Team (PIT) was appointed, the budget deficit for the budget 2009/10 was estimated at R 162 million. The mid-year Adjustments Budget, indicated a deficit of R 252 million. however, A further deficit of R 50 million will arise from internal funded capital. 4
BACKGROUND By mid March 2010 when the Provincial Intervention Team (PIT) was appointed, the budget deficit for the budget 2009/10 was estimated at R 162 million. The mid-year Adjustments Budget, indicated a deficit of R 252 million. however, A further deficit of R 50 million will arise from internal funded capital. 4
 BACKGROUND The deficit as reflected on the budget has resulted in serious cash flow shortages to maintain adequate operations in the Municipality. The major contributors are amongst others: The funding of Roads projects close to R 111 million out of operations The funding of a remote metering system (not at all budgeted for) of R 240 million Illegal expenditure of at least R 19 million 5
BACKGROUND The deficit as reflected on the budget has resulted in serious cash flow shortages to maintain adequate operations in the Municipality. The major contributors are amongst others: The funding of Roads projects close to R 111 million out of operations The funding of a remote metering system (not at all budgeted for) of R 240 million Illegal expenditure of at least R 19 million 5
 BACKGROUND Non-payment for services close to R 423 million as a result of poor revenue collection processes High Eskom accounts during the summer Eskom accounts treble during the winter months The high electricity demands are negatively influenced by high increments of electricity tariffs Illegal connection to services Financial sustainability with regards to the Rates base 6
BACKGROUND Non-payment for services close to R 423 million as a result of poor revenue collection processes High Eskom accounts during the summer Eskom accounts treble during the winter months The high electricity demands are negatively influenced by high increments of electricity tariffs Illegal connection to services Financial sustainability with regards to the Rates base 6
 FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY There is a clear indication that proper planning must be done for future years in order to balance Revenue and Expenditure There is a need for strategies which will enhance Revenue and Contain Cost Revenue enhancement Strategy Cost Containment Strategy Cost Benefit Analysis and Strategy 7
FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY There is a clear indication that proper planning must be done for future years in order to balance Revenue and Expenditure There is a need for strategies which will enhance Revenue and Contain Cost Revenue enhancement Strategy Cost Containment Strategy Cost Benefit Analysis and Strategy 7
 STATUS QUO ANALYSIS The PIT commenced with the identification of poor service delivery, inadequate controls, failure to conform to legislative requirements, policies, procedures, processes and in general governance. 8
STATUS QUO ANALYSIS The PIT commenced with the identification of poor service delivery, inadequate controls, failure to conform to legislative requirements, policies, procedures, processes and in general governance. 8
 STATUS QUO ANALYSIS General Finding an esteemed City like Msunduzi in disarray politically and administratively, this is what one experienced in general when you entered the city. Streets filled with refuse, visible illegal connections of electricity, potholes in roads, uncut grass, parks and open spaces filled with refuse. A city lamed by the hands of its political leaders and its officials. The state of the municipality has deteriorated to an extent that has rendered the municipality unstable and inoperable. 9
STATUS QUO ANALYSIS General Finding an esteemed City like Msunduzi in disarray politically and administratively, this is what one experienced in general when you entered the city. Streets filled with refuse, visible illegal connections of electricity, potholes in roads, uncut grass, parks and open spaces filled with refuse. A city lamed by the hands of its political leaders and its officials. The state of the municipality has deteriorated to an extent that has rendered the municipality unstable and inoperable. 9
 STATUS QUO ANALYSIS Political Instability Politicians operated in different camps Allegations of dictatorial rule Spending of money on luxuries and parties as if the municipality had enormous cash funds, this is evident from information gathered by the PIT. Allegations that the top politicians ignored the Supply Chain Management policy of the municipality were confirmed by the PIT. 10
STATUS QUO ANALYSIS Political Instability Politicians operated in different camps Allegations of dictatorial rule Spending of money on luxuries and parties as if the municipality had enormous cash funds, this is evident from information gathered by the PIT. Allegations that the top politicians ignored the Supply Chain Management policy of the municipality were confirmed by the PIT. 10
 STATUS QUO ANALYSIS Administrative Instability Whilst all the illegitimate issues occurred the municipality became leaderless and officials started to side with politicians and failed their responsibilities. 62 outstanding reports, some urgent were not presented to the council. Some of these matters related to forensic investigations and implicated some top officials. The forensic report was tabled before council during 2007, but up to now the resolution by council was not adhered to by the Municipal Manager; this was confirmed by the PIT. Immediate action with regard to this had to be taken. The intervention was focusing on all areas of Msunduzi Municipality’s operations, namely Governance and Management control, Financial Management, Sustainable Service Delivery and Infrastructure 11 Development and Maintenance.
STATUS QUO ANALYSIS Administrative Instability Whilst all the illegitimate issues occurred the municipality became leaderless and officials started to side with politicians and failed their responsibilities. 62 outstanding reports, some urgent were not presented to the council. Some of these matters related to forensic investigations and implicated some top officials. The forensic report was tabled before council during 2007, but up to now the resolution by council was not adhered to by the Municipal Manager; this was confirmed by the PIT. Immediate action with regard to this had to be taken. The intervention was focusing on all areas of Msunduzi Municipality’s operations, namely Governance and Management control, Financial Management, Sustainable Service Delivery and Infrastructure 11 Development and Maintenance.
 SWOT ANALYSIS A complete SWOT analysis was done in order to be able to develop and introduce a turnaround strategy. Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats 12
SWOT ANALYSIS A complete SWOT analysis was done in order to be able to develop and introduce a turnaround strategy. Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats 12
 SWOT ANALYSIS Vision A City of Choice Mission To stabilise the affairs of the municipality and ensure that the municipality functions effectively and in a sustainable manner in delivering services to the community. 13
SWOT ANALYSIS Vision A City of Choice Mission To stabilise the affairs of the municipality and ensure that the municipality functions effectively and in a sustainable manner in delivering services to the community. 13
 SWOT ANALYSIS Objectives of Local Government Provide accountable communities government for local Promote social and economic development Promote a safe and healthy environment Encourage the involvement of communities and community organisations in matters of local government 14
SWOT ANALYSIS Objectives of Local Government Provide accountable communities government for local Promote social and economic development Promote a safe and healthy environment Encourage the involvement of communities and community organisations in matters of local government 14
 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS The Municipality did not adhere to required Financial reporting A financial analysis was performed to calculate the cash flow status and the current budget vs. actual It was determined that funds were mixed and no proper fund controls was in place Supply Chain Management was non-existent The municipality was almost bankrupt An eminent shortfall of cash (R 162 million) A Budget deficit of close to R 252 million 15
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS The Municipality did not adhere to required Financial reporting A financial analysis was performed to calculate the cash flow status and the current budget vs. actual It was determined that funds were mixed and no proper fund controls was in place Supply Chain Management was non-existent The municipality was almost bankrupt An eminent shortfall of cash (R 162 million) A Budget deficit of close to R 252 million 15
 SHORT TERM STRATEGIES Bank and Cash Management Daily cash flow is drafted based on actuals and estimated amounts for the period concerned. All funds must be kept separately in order not to mix capital and operational funding. Matching of expenditure with the month concerned and ensuring that the bank reconciliation is performed on a monthly basis. Creditors are being scheduled according to best practises and payments are made in accordance with the scheduling. At this stage no investments should be made and all possible management information must be submitted in order to control funds. Expenditure management An Expenditure Evaluation Committee for all Operating expenditure requests has been set up 16
SHORT TERM STRATEGIES Bank and Cash Management Daily cash flow is drafted based on actuals and estimated amounts for the period concerned. All funds must be kept separately in order not to mix capital and operational funding. Matching of expenditure with the month concerned and ensuring that the bank reconciliation is performed on a monthly basis. Creditors are being scheduled according to best practises and payments are made in accordance with the scheduling. At this stage no investments should be made and all possible management information must be submitted in order to control funds. Expenditure management An Expenditure Evaluation Committee for all Operating expenditure requests has been set up 16
 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS A Functional analysis was performed in order to establish service delivery performance. It was clear that services rendered was at its lowest level and in some cases non-existent 17
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS A Functional analysis was performed in order to establish service delivery performance. It was clear that services rendered was at its lowest level and in some cases non-existent 17
 FUNCTIONAL AREAS The functional turn around strategies are concerned with the restructuring of the functional areas, which will enable business units to deliver a more effective and efficient service. The functional strategies are built on the following pillars: Financial Infrastructure Development and Maintenance Community Service Corporate Services & Planning Internal Audit Performance Management 18
FUNCTIONAL AREAS The functional turn around strategies are concerned with the restructuring of the functional areas, which will enable business units to deliver a more effective and efficient service. The functional strategies are built on the following pillars: Financial Infrastructure Development and Maintenance Community Service Corporate Services & Planning Internal Audit Performance Management 18
 FUNCTIONAL STRATEGIES UNDERLYING PRINCIPLES OPTIMAL SERVICE DELIVERY INCREASED REVENUE COST BENEFIT ANALYSIS – BALANCED BUDGET ONGOING PROCESS DECREASED EXPENDITURE 19
FUNCTIONAL STRATEGIES UNDERLYING PRINCIPLES OPTIMAL SERVICE DELIVERY INCREASED REVENUE COST BENEFIT ANALYSIS – BALANCED BUDGET ONGOING PROCESS DECREASED EXPENDITURE 19
 FUNCTIONAL STRATEGIES Finance, Corporate Services & Planning Community Services Audit and Performance Management 0 Infrastructure Services Optimal Service Delivery 0 Measure / Review 20
FUNCTIONAL STRATEGIES Finance, Corporate Services & Planning Community Services Audit and Performance Management 0 Infrastructure Services Optimal Service Delivery 0 Measure / Review 20
 FINANCIAL STRATEGY To provide end-to-end financial governance and support, in order to ensure optimal utilisation of financial resources. The financial strategy has been divided into various Key Performance Areas to ensure optimal performance. This will be achieved by: Designing organogram and related KPA’s and KPI’s Ensuring financial resources are in accordance with the human resource structures of the business units Introducing Revenue enhancement processes Revision of Policies Online auditing of active accounts 21
FINANCIAL STRATEGY To provide end-to-end financial governance and support, in order to ensure optimal utilisation of financial resources. The financial strategy has been divided into various Key Performance Areas to ensure optimal performance. This will be achieved by: Designing organogram and related KPA’s and KPI’s Ensuring financial resources are in accordance with the human resource structures of the business units Introducing Revenue enhancement processes Revision of Policies Online auditing of active accounts 21
 FINANCE Financial Performance Municipality under severe financial pressure Debtor Management Credit control & debt collection policy introduced Measures introduced to speed up payment rate Connections & disconnections of services Collection rate currently 75% Creditor Management Payment terms of 30 days after statement introduced to capitalise on free credit availability Management Accounting Introduced to track & analyse financial performances 22
FINANCE Financial Performance Municipality under severe financial pressure Debtor Management Credit control & debt collection policy introduced Measures introduced to speed up payment rate Connections & disconnections of services Collection rate currently 75% Creditor Management Payment terms of 30 days after statement introduced to capitalise on free credit availability Management Accounting Introduced to track & analyse financial performances 22
 FINANCE The Outdated financial system does not provide online, integrated reporting, nor adequate Management Accounting information to enable management to analyse operating and financial performance Continuous software changes create a very unstable information environment A System is still to be designed and implemented before the new financial year 23
FINANCE The Outdated financial system does not provide online, integrated reporting, nor adequate Management Accounting information to enable management to analyse operating and financial performance Continuous software changes create a very unstable information environment A System is still to be designed and implemented before the new financial year 23
 BUDGETING The newly adopted budget policy and principles are in accordance with the Municipal Finance Management Act No. 56 of 2003 (MFMA), the Municipal Systems Act, No. 32 of 2000 (MSA) and the Municipal Budget and Reporting Regulations, which have been designed to achieve a range of objectives, including improving the local government sphere’s ability to deliver services by facilitating improved financial sustainability and better medium term planning. The municipality will also adhere to MFMA circulars issued by National Treasury that provide up to date guidance on budgetary policy, budget process and submissions, etc. The National Treasury will also provide further guidelines on budget formats and sample budgets. 24
BUDGETING The newly adopted budget policy and principles are in accordance with the Municipal Finance Management Act No. 56 of 2003 (MFMA), the Municipal Systems Act, No. 32 of 2000 (MSA) and the Municipal Budget and Reporting Regulations, which have been designed to achieve a range of objectives, including improving the local government sphere’s ability to deliver services by facilitating improved financial sustainability and better medium term planning. The municipality will also adhere to MFMA circulars issued by National Treasury that provide up to date guidance on budgetary policy, budget process and submissions, etc. The National Treasury will also provide further guidelines on budget formats and sample budgets. 24
 SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT The existing purchasing system is to be revived so that all SCM processes will be fully automated thus removing the human element and combating manipulation. SCM personnel will receive full training on Intenda thereby adding value to the whole SCM process, the creditor’s data base will simultaneously be scrutinized. It is envisaged that the fully automated process will be a reality by 1 July 2011. Order clerks have been centralised to the SCM unit to combat irregular and wasteful expenditure. The existing SCM policy has been revised and adopted by Council enforcing stricter controls and compliance with the Municipal Finance Management Act (MFMA) and related regulations. In future business units will only submit online purchasing requests to the SCM Unit so that they may be dealt with professionally and in line with the new policy. 25
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT The existing purchasing system is to be revived so that all SCM processes will be fully automated thus removing the human element and combating manipulation. SCM personnel will receive full training on Intenda thereby adding value to the whole SCM process, the creditor’s data base will simultaneously be scrutinized. It is envisaged that the fully automated process will be a reality by 1 July 2011. Order clerks have been centralised to the SCM unit to combat irregular and wasteful expenditure. The existing SCM policy has been revised and adopted by Council enforcing stricter controls and compliance with the Municipal Finance Management Act (MFMA) and related regulations. In future business units will only submit online purchasing requests to the SCM Unit so that they may be dealt with professionally and in line with the new policy. 25
 SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT No orders will be processed unless budget is available for such request. Service providers who provide services without an official order will not be paid by the municipality. Employees, who obtain services without the proper process being followed, will become personally liable for the payment thereof. Goods received from service providers must be signed for in order to confirm delivery, such Goods Received Notes (GRN) will form the first basis for the payment of services provided and will be linked to the requisition and invoice (three way match principle). 26
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT No orders will be processed unless budget is available for such request. Service providers who provide services without an official order will not be paid by the municipality. Employees, who obtain services without the proper process being followed, will become personally liable for the payment thereof. Goods received from service providers must be signed for in order to confirm delivery, such Goods Received Notes (GRN) will form the first basis for the payment of services provided and will be linked to the requisition and invoice (three way match principle). 26
 EXPENDITURE MANAGEMENT The majority of expenditure was reduced during the budget process in order to produce a balanced budget as required by the Municipal Finance Management Act. Nice to have items were not included in the budget. A surplus achieved in the second quarter will be used to cover for these reductions in expenditure incurred during the budget process. Introduction of cost containment by the PIT has yielded positive results in the control of unnecessary expenditure. Also included in the adjustment budget are service delivery items e. g. grass cutting programme, maintenance of roads, provision made for the landfill sites legislative requirements etc. 27
EXPENDITURE MANAGEMENT The majority of expenditure was reduced during the budget process in order to produce a balanced budget as required by the Municipal Finance Management Act. Nice to have items were not included in the budget. A surplus achieved in the second quarter will be used to cover for these reductions in expenditure incurred during the budget process. Introduction of cost containment by the PIT has yielded positive results in the control of unnecessary expenditure. Also included in the adjustment budget are service delivery items e. g. grass cutting programme, maintenance of roads, provision made for the landfill sites legislative requirements etc. 27
 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING The Msunduzi Municipality has introduced Management Accounting whereby the results of the analysis of key financial and non financial information is communicated to all stakeholders in order to enable informed business decisions and sustainable operation. Management Accounting will encompass the following: Obtaining a thorough understanding of the business processes within each business unit. Implementation of controls that will facilitate accurate financial and non-financial output. Tracking and analysis of output of all municipal activities. Consultation with various business units and feedback in respect of variances. Preparation and submission of reports for Council, Exco, Executives and the Portfolio Committee with corrective recommendations on a monthly basis to assist management with decision making. 28
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING The Msunduzi Municipality has introduced Management Accounting whereby the results of the analysis of key financial and non financial information is communicated to all stakeholders in order to enable informed business decisions and sustainable operation. Management Accounting will encompass the following: Obtaining a thorough understanding of the business processes within each business unit. Implementation of controls that will facilitate accurate financial and non-financial output. Tracking and analysis of output of all municipal activities. Consultation with various business units and feedback in respect of variances. Preparation and submission of reports for Council, Exco, Executives and the Portfolio Committee with corrective recommendations on a monthly basis to assist management with decision making. 28
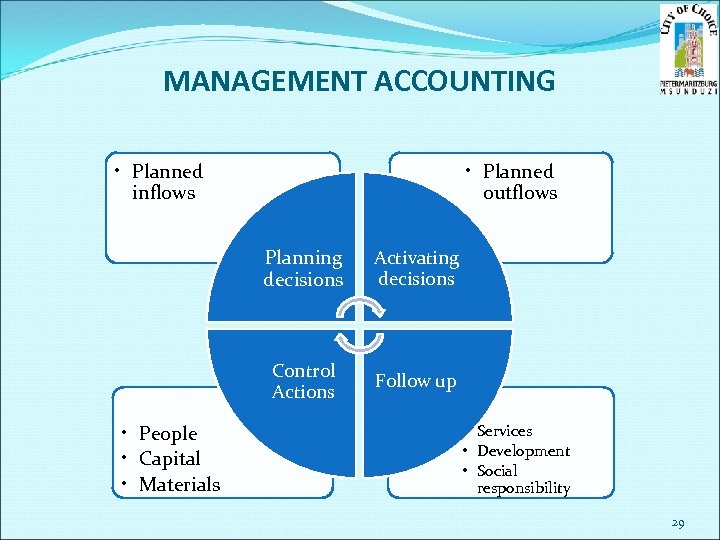 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING • Planned inflows • Planned outflows Planning decisions Control Actions • People • Capital • Materials Activating decisions Follow up • Services • Development • Social responsibility 29
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING • Planned inflows • Planned outflows Planning decisions Control Actions • People • Capital • Materials Activating decisions Follow up • Services • Development • Social responsibility 29
 INFRASTRUCTURE SERVICES DELIVERY STRATEGY To ensure that the municipality provides an end-toend service delivery governance and support in order to ensure optimisation of resources. All areas must be redesigned to ensure optimal performance Designing organogram and related KPA’s and KPI’s Ensuring financial resources are in accordance with the human resource structures of the business units Introducing Efficient and Effective Human Resources Management (Productivity) Revision of Policies Online auditing of actual performance 30
INFRASTRUCTURE SERVICES DELIVERY STRATEGY To ensure that the municipality provides an end-toend service delivery governance and support in order to ensure optimisation of resources. All areas must be redesigned to ensure optimal performance Designing organogram and related KPA’s and KPI’s Ensuring financial resources are in accordance with the human resource structures of the business units Introducing Efficient and Effective Human Resources Management (Productivity) Revision of Policies Online auditing of actual performance 30
 COMMUNITY SERVICES DELIVERY STRATEGY To provide end-to-end community service delivery governance and support to ensure optimisation of resources. Designing organogram and related KPA’s and KPI’s Ensuring financial resources are in accordance with the human resource structures of the business units Introducing Efficient and Effective Human Resources Management (Productivity) Revision of Policies Online auditing of actual performance 31
COMMUNITY SERVICES DELIVERY STRATEGY To provide end-to-end community service delivery governance and support to ensure optimisation of resources. Designing organogram and related KPA’s and KPI’s Ensuring financial resources are in accordance with the human resource structures of the business units Introducing Efficient and Effective Human Resources Management (Productivity) Revision of Policies Online auditing of actual performance 31
 CORPORATE SERVICES AND PLANNING STRATEGY To provide end-to-end community service delivery governance and support to ensure optimisation of resources. Designing organogram and related KPA’s and KPI’s Ensuring financial resources are in accordance with the human resource structures of the business units Introducing Efficient and Effective Human Resources Management (Productivity) Revision of Policies Online auditing of actual performance 32
CORPORATE SERVICES AND PLANNING STRATEGY To provide end-to-end community service delivery governance and support to ensure optimisation of resources. Designing organogram and related KPA’s and KPI’s Ensuring financial resources are in accordance with the human resource structures of the business units Introducing Efficient and Effective Human Resources Management (Productivity) Revision of Policies Online auditing of actual performance 32
 INTERNAL AUDIT STRATEGY To provide an all-encompassing internal audit service to the audit committee and management by: Covering internal audit functions Compiling a comprehensive risk assessment of all council systems, processes and procedures Undertaking or outsource where necessary, concerns raised which require investigation with possible criminal, civil and departmental disciplinary actions Auditing the organisational score card, individual section 57 performance plans and report thereon to management and the Performance Audit Committee 33
INTERNAL AUDIT STRATEGY To provide an all-encompassing internal audit service to the audit committee and management by: Covering internal audit functions Compiling a comprehensive risk assessment of all council systems, processes and procedures Undertaking or outsource where necessary, concerns raised which require investigation with possible criminal, civil and departmental disciplinary actions Auditing the organisational score card, individual section 57 performance plans and report thereon to management and the Performance Audit Committee 33
 INTERNAL AUDIT PROGRESS A Risk Management register has been developed for each Business Unit: Managers to develop strategies to mitigate the risks Managers take full responsibility for managing their risks Implementation of controls is audited Effectiveness of Risk management is measured Opportunity for fraud is prevented Favourable Annual Audit for Msunduzi 34
INTERNAL AUDIT PROGRESS A Risk Management register has been developed for each Business Unit: Managers to develop strategies to mitigate the risks Managers take full responsibility for managing their risks Implementation of controls is audited Effectiveness of Risk management is measured Opportunity for fraud is prevented Favourable Annual Audit for Msunduzi 34
 LEGAL SERVICES & LEGISLATIVE COMPLIANCE Corporate and Legal Services Management were not up to standard and a great number of by-laws were lacking as well as the enforcement thereof. Several by-laws have been adopted since the intervention and we envisage that the process will be concluded by the end of March 2011. Contract Administration Support was inadequate and not completely supportive of the operational functions of the Municipality. An appropriate contract administration and support service has been introduced and is fully functional. 35
LEGAL SERVICES & LEGISLATIVE COMPLIANCE Corporate and Legal Services Management were not up to standard and a great number of by-laws were lacking as well as the enforcement thereof. Several by-laws have been adopted since the intervention and we envisage that the process will be concluded by the end of March 2011. Contract Administration Support was inadequate and not completely supportive of the operational functions of the Municipality. An appropriate contract administration and support service has been introduced and is fully functional. 35
 MARKETING & PUBLIC RELATIONS A fully integrated Customer Care Call Centre is being set up This will ensure an efficient Customer service Phased implementation, with the first phase anticipated to be fully functional by the end of February 2011 Customers will be able to report on complaints, problems and faults reported on Electricity, Water and Sanitation, Roads and other infrastructure related issues Service operational for 24 hrs seven days a week All reported problems and complaints will be referenced and a reference number issued A follow up process will unfold to ensure that the problem is tracked to a point where it is resolved, all in very good response time 36
MARKETING & PUBLIC RELATIONS A fully integrated Customer Care Call Centre is being set up This will ensure an efficient Customer service Phased implementation, with the first phase anticipated to be fully functional by the end of February 2011 Customers will be able to report on complaints, problems and faults reported on Electricity, Water and Sanitation, Roads and other infrastructure related issues Service operational for 24 hrs seven days a week All reported problems and complaints will be referenced and a reference number issued A follow up process will unfold to ensure that the problem is tracked to a point where it is resolved, all in very good response time 36
 INFORMATION SYSTEMS PROGRESS Information Technology and Systems are outdated with malfunctioning networks. Infrastructure Management was lacking whereby there was no system and security control. All systems have been evaluated and certain measures are being introduced to ensure uniformity and standardisation 37
INFORMATION SYSTEMS PROGRESS Information Technology and Systems are outdated with malfunctioning networks. Infrastructure Management was lacking whereby there was no system and security control. All systems have been evaluated and certain measures are being introduced to ensure uniformity and standardisation 37
 ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT & PLANNING Economic Development was part of a broader Business unit called Development Services. Due to the restructuring it is now a fully focused business unit. The unit is now focussing on facilitating business opportunities through the re-establishment of a development facilitation committee which interacts directly with prospective developers. There is now also a focus on Informal Economy and Street Trading, and specific targets have been set for the sub unit. This unit is also co-ordinating an initiative by the Municipality to clean up the City through the implementation of Municipal By-laws. 38
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT & PLANNING Economic Development was part of a broader Business unit called Development Services. Due to the restructuring it is now a fully focused business unit. The unit is now focussing on facilitating business opportunities through the re-establishment of a development facilitation committee which interacts directly with prospective developers. There is now also a focus on Informal Economy and Street Trading, and specific targets have been set for the sub unit. This unit is also co-ordinating an initiative by the Municipality to clean up the City through the implementation of Municipal By-laws. 38
 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT STRATEGY To provide an all-encompassing Performance management function for: The Msunduzi Municipality as a Business Units of the Municipality Individual performance management Indicators, Targets and Reporting Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation Corrective Measures – Council Committee System 39
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT STRATEGY To provide an all-encompassing Performance management function for: The Msunduzi Municipality as a Business Units of the Municipality Individual performance management Indicators, Targets and Reporting Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation Corrective Measures – Council Committee System 39
 CENTRALISATION AND REGIONALISATION There is a strong indication that the Municipality must have a re-look at the centralisation of some functions, but also to look at the regionalisation of services. The principle of bringing to service nearer to the public All indications is that the following services have to be centralised, due to control, uniformity, etc. , namely: Supply Chain Management Human Resources Support Services Finance Support Services 40
CENTRALISATION AND REGIONALISATION There is a strong indication that the Municipality must have a re-look at the centralisation of some functions, but also to look at the regionalisation of services. The principle of bringing to service nearer to the public All indications is that the following services have to be centralised, due to control, uniformity, etc. , namely: Supply Chain Management Human Resources Support Services Finance Support Services 40
 CENTRALISATION AND REGIONALISATION All indications is that the following services have to be regionalised, due to improved service delivery, namely: Parks and Recreational Services Roads and transport Services Refuse Service Fire, Traffic and Public Safety Health Services Water Electricity 41
CENTRALISATION AND REGIONALISATION All indications is that the following services have to be regionalised, due to improved service delivery, namely: Parks and Recreational Services Roads and transport Services Refuse Service Fire, Traffic and Public Safety Health Services Water Electricity 41
 INFRASTRUCTURE PLANNING & ASSET MANAGEMENT Strategy Integrated infrastructure development plans (timing, capacities & limitations), to be driven by SDF, and LED and Housing development programmes and available technology. Prepare a realistic Infrastructure Investment Plan Work towards an infrastructure-efficient City. Establish a Fleet Management System for optimum management, maintenance and replacement of fleet. Put in place an efficient Asset Management System for all infrastructure assets. 42
INFRASTRUCTURE PLANNING & ASSET MANAGEMENT Strategy Integrated infrastructure development plans (timing, capacities & limitations), to be driven by SDF, and LED and Housing development programmes and available technology. Prepare a realistic Infrastructure Investment Plan Work towards an infrastructure-efficient City. Establish a Fleet Management System for optimum management, maintenance and replacement of fleet. Put in place an efficient Asset Management System for all infrastructure assets. 42
 SERVICE DELIVERY: ELECTRICITY Strategy Clear maintenance backlogs (cable faults street lights, switch gear) so that maintenance can be planned on 1 year cycle. Reduce electricity losses by installation of protective structures, including remote meter reading. Refurbishment programme to replace primary transformers (33 k. V to 132 k. V) Encourage use of alternative energy sources to curb electricity demand. 43
SERVICE DELIVERY: ELECTRICITY Strategy Clear maintenance backlogs (cable faults street lights, switch gear) so that maintenance can be planned on 1 year cycle. Reduce electricity losses by installation of protective structures, including remote meter reading. Refurbishment programme to replace primary transformers (33 k. V to 132 k. V) Encourage use of alternative energy sources to curb electricity demand. 43
 SERVICE DELIVERY: ELECTRICITY A process mapping exercise was conducted identifying all risk areas in the current system which have been addressed Risk Areas: Application Register Estimated Cost process Job Cost finalisation Reconciliation of Receipts to Requests Cashier + Filing Clerk Duplication of Activities Billing / Finance / Invoicing 44
SERVICE DELIVERY: ELECTRICITY A process mapping exercise was conducted identifying all risk areas in the current system which have been addressed Risk Areas: Application Register Estimated Cost process Job Cost finalisation Reconciliation of Receipts to Requests Cashier + Filing Clerk Duplication of Activities Billing / Finance / Invoicing 44
 SERVICE DELIVERY: ELECTRICITY Risk Areas : Stock Control Management control Separate data bases for registration and technician resulting in loss & manipulation of information Management information Credit Control and recovery of outstanding Municipal debt Circuit breaker control Works Order and Job Card control 45
SERVICE DELIVERY: ELECTRICITY Risk Areas : Stock Control Management control Separate data bases for registration and technician resulting in loss & manipulation of information Management information Credit Control and recovery of outstanding Municipal debt Circuit breaker control Works Order and Job Card control 45
 SERVICE DELIVERY: WATER A Management maintenance plan has been introduced to: Eradication of basic water and sanitation backlogs Adequate provision and maintenance of water and sanitation infrastructure Non-Revenue Water [Water losses] Infiltration Control Programme Bulk Water & Sanitation Master Plans 46
SERVICE DELIVERY: WATER A Management maintenance plan has been introduced to: Eradication of basic water and sanitation backlogs Adequate provision and maintenance of water and sanitation infrastructure Non-Revenue Water [Water losses] Infiltration Control Programme Bulk Water & Sanitation Master Plans 46
 SERVICE DELIVERY: WATER A large-scale initiative, with the assistance of the Department of Water Affairs, to reduce the high levels of water losses commenced in December 2010 after the preparation of a detailed intervention plan to be complete the following over the next three years: Move towards a planned mains replacement program, initially replacing approximately 30 km of pipe in those areas most regularly affected by pipe bursts Carry out leak detection surveys and leak repair on the entire water reticulation system at least twice a year (totally approximately 7000 km) Reduce the maximum supplied pressure to consumers to 60 m through the installation of 40 new pressure reducing valves 47
SERVICE DELIVERY: WATER A large-scale initiative, with the assistance of the Department of Water Affairs, to reduce the high levels of water losses commenced in December 2010 after the preparation of a detailed intervention plan to be complete the following over the next three years: Move towards a planned mains replacement program, initially replacing approximately 30 km of pipe in those areas most regularly affected by pipe bursts Carry out leak detection surveys and leak repair on the entire water reticulation system at least twice a year (totally approximately 7000 km) Reduce the maximum supplied pressure to consumers to 60 m through the installation of 40 new pressure reducing valves 47
 SERVICE DELIVERY: WATER Repair all leaking reservoirs and improve reservoir security Ensure that all key infrastructure is placed on a preventative maintenance program Identify and regularise all illegal connections by ensuring that all connections are metered, registered and not tampered with Improve the efficiency of meter readings and billing Undertake a comprehensive consumer awareness and education campaign targeting the responsible use of water and efficient water use habits 48
SERVICE DELIVERY: WATER Repair all leaking reservoirs and improve reservoir security Ensure that all key infrastructure is placed on a preventative maintenance program Identify and regularise all illegal connections by ensuring that all connections are metered, registered and not tampered with Improve the efficiency of meter readings and billing Undertake a comprehensive consumer awareness and education campaign targeting the responsible use of water and efficient water use habits 48
 SERVICE DELIVERY: SANITATION A Management maintenance plan has been introduced to: Promote free flow of water sanitation Accurate measures of e. coli at strategic river points Maintain the existing infrastructure which is outdated Highlight the lack of available funds for upgrade Underline challenges facing the Sanitation Department Understand health hazards 49
SERVICE DELIVERY: SANITATION A Management maintenance plan has been introduced to: Promote free flow of water sanitation Accurate measures of e. coli at strategic river points Maintain the existing infrastructure which is outdated Highlight the lack of available funds for upgrade Underline challenges facing the Sanitation Department Understand health hazards 49
 SERVICE DELIVERY: WASTE Domestic refuse process was mapped & divided into three regional areas to ensure balancing of volumes of refuse and number of collection points. Domestic Refuse Collections increased by +3000 households as a result of previous private contracts being cancelled ADHOC overtime totally eliminated Total overhaul of personal / attendance records – unauthorised absences significantly reduced Not one day of lost operation in the last 7 months. 50
SERVICE DELIVERY: WASTE Domestic refuse process was mapped & divided into three regional areas to ensure balancing of volumes of refuse and number of collection points. Domestic Refuse Collections increased by +3000 households as a result of previous private contracts being cancelled ADHOC overtime totally eliminated Total overhaul of personal / attendance records – unauthorised absences significantly reduced Not one day of lost operation in the last 7 months. 50
 SERVICE DELIVERY: WASTE Domestic refuse process was mapped & divided into three regional areas to ensure balancing of volumes of refuse and number of collection points. Funds are now available to repair broken skips. TLB’s and tipper trucks have now been hired to clean up all the illegal dump sites and garden sites so that a baseline is achieved and then it will be seen which areas are the culprits. This operation is currently underway. No dumping signs have been ordered and made and these will be distributed where required. A task team has been established to prosecute illegal dumping offenders 51
SERVICE DELIVERY: WASTE Domestic refuse process was mapped & divided into three regional areas to ensure balancing of volumes of refuse and number of collection points. Funds are now available to repair broken skips. TLB’s and tipper trucks have now been hired to clean up all the illegal dump sites and garden sites so that a baseline is achieved and then it will be seen which areas are the culprits. This operation is currently underway. No dumping signs have been ordered and made and these will be distributed where required. A task team has been established to prosecute illegal dumping offenders 51
 SERVICE DELIVERY: WASTE A large number of the street cleaners working 24/7 are posted in the city to endeavour to keep the city centre clean. The night shift staff reduces the number of cleaners available on a daily basis. Teams are sent out to the other areas on an adhoc basis to clean specific areas on request and when sporting events occur. Waste Management has 6 peace officers who are issuing warnings to the public as an advance warning to prosecutions. The new operation to prosecute littering offenders will assist greatly with keeping the streets clean and thus allow for cleaners to spend mote time in the suburbs Waste Management Summit and all assessments and consultations at the landfill site undertaken at no cost to council. 52
SERVICE DELIVERY: WASTE A large number of the street cleaners working 24/7 are posted in the city to endeavour to keep the city centre clean. The night shift staff reduces the number of cleaners available on a daily basis. Teams are sent out to the other areas on an adhoc basis to clean specific areas on request and when sporting events occur. Waste Management has 6 peace officers who are issuing warnings to the public as an advance warning to prosecutions. The new operation to prosecute littering offenders will assist greatly with keeping the streets clean and thus allow for cleaners to spend mote time in the suburbs Waste Management Summit and all assessments and consultations at the landfill site undertaken at no cost to council. 52
 SERVICE DELIVERY: LANDFILL The New England Road Landfill Site is anticipated to have 6 years of operations before closure. Business initiatives being explored to extend the lifespan: Gas to Energy Business negotiations underway to develop & install a Gas Plant enough gas to energy for the next 17 years. Gas Flaring Unit to be installed within 2 months. generate at least R 15 mil per year in electricity savings. settlement of the Landfill Site due to gas being drawn off will in increase the life span. 53
SERVICE DELIVERY: LANDFILL The New England Road Landfill Site is anticipated to have 6 years of operations before closure. Business initiatives being explored to extend the lifespan: Gas to Energy Business negotiations underway to develop & install a Gas Plant enough gas to energy for the next 17 years. Gas Flaring Unit to be installed within 2 months. generate at least R 15 mil per year in electricity savings. settlement of the Landfill Site due to gas being drawn off will in increase the life span. 53
 SERVICE DELIVERY: LANDFILL Recycling The recycling of reusable is imperative to extend the life span of the Landfill Site. In October 2010 a workshop was attended by various role players. As a result of this workshop various projects were identified: Domestic Recyclable program Garden Site chipping and composting Waste entrepreneurs creating work The objective with these initiatives is to extend the lifespan of the Landfill Site, generate income, create work opportunities and to reduce the environmental pollution of the city. 54
SERVICE DELIVERY: LANDFILL Recycling The recycling of reusable is imperative to extend the life span of the Landfill Site. In October 2010 a workshop was attended by various role players. As a result of this workshop various projects were identified: Domestic Recyclable program Garden Site chipping and composting Waste entrepreneurs creating work The objective with these initiatives is to extend the lifespan of the Landfill Site, generate income, create work opportunities and to reduce the environmental pollution of the city. 54
 SERVICE DELIVERY: LANDFILL Recycling E. g. The Buyisa- e-Bag initiative for the Landfill Site is aimed at Regulating the litter pickers on site in terms of training Equipping with safety equipment to deal with each situation at the site Developing a waste material recycling plant Creating job opportunities Creating new income for the city 55
SERVICE DELIVERY: LANDFILL Recycling E. g. The Buyisa- e-Bag initiative for the Landfill Site is aimed at Regulating the litter pickers on site in terms of training Equipping with safety equipment to deal with each situation at the site Developing a waste material recycling plant Creating job opportunities Creating new income for the city 55
 SERVICE DELIVERY: FLEET Feasibility study was conducted to: Ascertain the on-going availability of vehicles Provide continuous support to all service areas Establish the condition of fleet which will need to be replaced Introduce the daily report of vehicle availability To ensure the monitoring of maintenance and usability of vehicles 56
SERVICE DELIVERY: FLEET Feasibility study was conducted to: Ascertain the on-going availability of vehicles Provide continuous support to all service areas Establish the condition of fleet which will need to be replaced Introduce the daily report of vehicle availability To ensure the monitoring of maintenance and usability of vehicles 56
 SERVICE DELIVERY: ROADS Strategy To develop sustainable roads, public transport facilities and building infrastructure in the most effective and efficient manner for the residents of Msunduzi. To maintain and rehabilitate Municipal road network, public transport facilities, building infrastructure and stormwater systems in sustainable and cost-effective manner for the safety purposes of all Msunduzi residents. 57
SERVICE DELIVERY: ROADS Strategy To develop sustainable roads, public transport facilities and building infrastructure in the most effective and efficient manner for the residents of Msunduzi. To maintain and rehabilitate Municipal road network, public transport facilities, building infrastructure and stormwater systems in sustainable and cost-effective manner for the safety purposes of all Msunduzi residents. 57
 SERVICE DELIVERY: ROADS Traffic light Intersections The city has 171 intersections of which 43 critical intersections need to be functional on a continuous basis Road Marking and Traffic Signs Current estimated total km of road is 2, 230 km approx. 40% being gravel A planned maintenance programme is in place to repaint road markings of main routes, speed humps and intersections Revamping of traffic signs and replacing of damaged signs 58
SERVICE DELIVERY: ROADS Traffic light Intersections The city has 171 intersections of which 43 critical intersections need to be functional on a continuous basis Road Marking and Traffic Signs Current estimated total km of road is 2, 230 km approx. 40% being gravel A planned maintenance programme is in place to repaint road markings of main routes, speed humps and intersections Revamping of traffic signs and replacing of damaged signs 58
 SERVICE DELIVERY: ROADS Traffic Calming 150 Evaluated requests are prioritised and awaiting implementation pending the availability of funds. Pot Holes and Road Crack sealing A planned maintenance programme is in place to address same Sporadic maintenance 59
SERVICE DELIVERY: ROADS Traffic Calming 150 Evaluated requests are prioritised and awaiting implementation pending the availability of funds. Pot Holes and Road Crack sealing A planned maintenance programme is in place to address same Sporadic maintenance 59
 PLANNING & HUMAN SETTLEMENTS Strategy Ø Elimination of informal settlements by 2016 Ø Provision of range of Housing opportunities to “rightsize” all Ø Rationalize Housing in the City: Ø Housing backlogs eliminated and range of housing opportunities available for all. Ø Informal settlements eliminated Ø Suitably located land for housing Ø Energy-, Infrastructure-, and resource-efficient housing Ø Encourage Housing Market in lower-income sector. 60
PLANNING & HUMAN SETTLEMENTS Strategy Ø Elimination of informal settlements by 2016 Ø Provision of range of Housing opportunities to “rightsize” all Ø Rationalize Housing in the City: Ø Housing backlogs eliminated and range of housing opportunities available for all. Ø Informal settlements eliminated Ø Suitably located land for housing Ø Energy-, Infrastructure-, and resource-efficient housing Ø Encourage Housing Market in lower-income sector. 60
 PLANNING & HUMAN SETTLEMENTS Strategy Ø Provide an effective and efficient building plan approval system and enforcement of contraventions Ø To provide an accurate Valuation Roll every 5 years with annual update. Ø to ensure fair market value is realised that stabilises and increases the Rates Base – 37% of Council budget is derived from Rates. Ø Timeous processing of Objections and Appeals. Ø Efficient Town Planning and Subdivision of Land approvals Ø Community-Based Planning to ensure sustainable planning for peoples needs. Ø SDF and Reviews to reflect Community Needs leading to Land Use Schemes. Ø Prevention of illegal land uses and overcrowding 61
PLANNING & HUMAN SETTLEMENTS Strategy Ø Provide an effective and efficient building plan approval system and enforcement of contraventions Ø To provide an accurate Valuation Roll every 5 years with annual update. Ø to ensure fair market value is realised that stabilises and increases the Rates Base – 37% of Council budget is derived from Rates. Ø Timeous processing of Objections and Appeals. Ø Efficient Town Planning and Subdivision of Land approvals Ø Community-Based Planning to ensure sustainable planning for peoples needs. Ø SDF and Reviews to reflect Community Needs leading to Land Use Schemes. Ø Prevention of illegal land uses and overcrowding 61
 PLANNING & HUMAN SETTLEMENTS Msunduzi’s Development Application was approved & published in Government Gazette November 2010. This addresses: Subdivision, Rezoning, Special Consent, Removal of Restrictions in Title Deed, Road Closures and Enforcement of Contravention with respect to the Town Planning Scheme Currently reviewing Spatial Development Framework through: Consultation with community for comment & contribution Preparing detailed local area plans for the City Final product of Detailed site specific Land Use Management Scheme 62
PLANNING & HUMAN SETTLEMENTS Msunduzi’s Development Application was approved & published in Government Gazette November 2010. This addresses: Subdivision, Rezoning, Special Consent, Removal of Restrictions in Title Deed, Road Closures and Enforcement of Contravention with respect to the Town Planning Scheme Currently reviewing Spatial Development Framework through: Consultation with community for comment & contribution Preparing detailed local area plans for the City Final product of Detailed site specific Land Use Management Scheme 62
 HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT The Msunduzi Municipality has gone a long way in terms of implementing the turnaround strategy which will see the restructuring of council business. Both political and macro structures have been approved with clear Key Performance Areas and Key Performance Indicators. In order to make sure that service delivery is not compromised; acting appointments have been made. 63
HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT The Msunduzi Municipality has gone a long way in terms of implementing the turnaround strategy which will see the restructuring of council business. Both political and macro structures have been approved with clear Key Performance Areas and Key Performance Indicators. In order to make sure that service delivery is not compromised; acting appointments have been made. 63
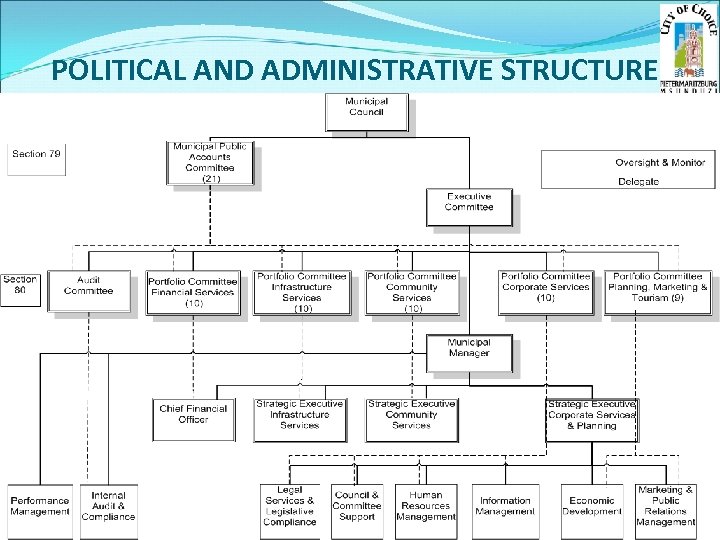 POLITICAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE STRUCTURE
POLITICAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE STRUCTURE
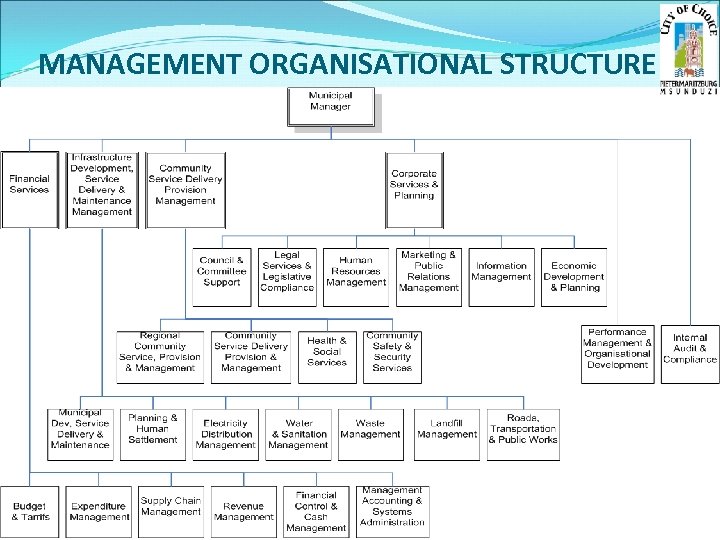 MANAGEMENT ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE
MANAGEMENT ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE
 DISCIPLINARY ACTIONS Various forensic investigations have and are being conducted Reports have been received In terms of the findings: Suspensions – 19 Resignation – 3 Dismissal – 1 Case Closed - 2 In Process – 8 Awaiting Action – 9 Investigation - 35 66
DISCIPLINARY ACTIONS Various forensic investigations have and are being conducted Reports have been received In terms of the findings: Suspensions – 19 Resignation – 3 Dismissal – 1 Case Closed - 2 In Process – 8 Awaiting Action – 9 Investigation - 35 66
 DISCIPLINARY ACTIONS In so far, we wish to brief the press on the critical issues with regard to the Municipality and I would like to start with the Disciplinary processes. I would like to allay all fears that the suspended high ranking officials will be returning to their posts as there is currently disciplinary proceedings to test the allegations. I would like to state that in these proceedings Council will take all necessary actions to ensure that justice prevails, there will be NO Golden Handshakes nor generous payouts. 67
DISCIPLINARY ACTIONS In so far, we wish to brief the press on the critical issues with regard to the Municipality and I would like to start with the Disciplinary processes. I would like to allay all fears that the suspended high ranking officials will be returning to their posts as there is currently disciplinary proceedings to test the allegations. I would like to state that in these proceedings Council will take all necessary actions to ensure that justice prevails, there will be NO Golden Handshakes nor generous payouts. 67
 DISCIPLINARY ACTIONS As far as disciplinary actions are concerned with regard to the suspended high ranking Municipal officials, the DMM of Finance has proposed a settlement. The MEC Co. GTA has given the mandate to settle and this is currently in process. Apart from the disciplinary proceedings the municipality is investigating possible Criminal and Civil action against the DMM of Corporate Services. The defendant has raised a point in limine on unreasonable delay instituting the proceedings. All necessary pleadings in this regard have been filed. The matter will be argued shortly. The acting Manger Public Safety Mr K Chetty was found guilty on all charges and has been dismissed. The Municipality is currently investigating possible Criminal and Civil action against the said staff member. The disciplinary enquiry against the Manager of Procurement Unit is proceeding this week, and that of the DMM Community Services is set down for next week. I would also like to say that there is a strong case to take civil and criminal action against some of these candidates. There are 20 or so other cases, all in various stages of disciplinary proceedings 68
DISCIPLINARY ACTIONS As far as disciplinary actions are concerned with regard to the suspended high ranking Municipal officials, the DMM of Finance has proposed a settlement. The MEC Co. GTA has given the mandate to settle and this is currently in process. Apart from the disciplinary proceedings the municipality is investigating possible Criminal and Civil action against the DMM of Corporate Services. The defendant has raised a point in limine on unreasonable delay instituting the proceedings. All necessary pleadings in this regard have been filed. The matter will be argued shortly. The acting Manger Public Safety Mr K Chetty was found guilty on all charges and has been dismissed. The Municipality is currently investigating possible Criminal and Civil action against the said staff member. The disciplinary enquiry against the Manager of Procurement Unit is proceeding this week, and that of the DMM Community Services is set down for next week. I would also like to say that there is a strong case to take civil and criminal action against some of these candidates. There are 20 or so other cases, all in various stages of disciplinary proceedings 68
 RISK ANALYSIS Risks have been identified across the business operations of the Municipality. These risks have been analysed in order to formulate mitigation factors to ensure business enhancement and continuity. The risks that were identified reflect the burning issues and pressures experienced by the Municipality. These risks have to be addressed in order to ensure long -term sustainability of the Municipality. In many cases these risk areas have to be dealt with, managed and supported by independent external parties and not Municipal officials who may not be adequately skilled to do so or may have a resistance to change. The following table is a listing of identified risks, the progress made on these risks and actions required for the sustainability of the progress & ultimate neutralisation of 69 these risks.
RISK ANALYSIS Risks have been identified across the business operations of the Municipality. These risks have been analysed in order to formulate mitigation factors to ensure business enhancement and continuity. The risks that were identified reflect the burning issues and pressures experienced by the Municipality. These risks have to be addressed in order to ensure long -term sustainability of the Municipality. In many cases these risk areas have to be dealt with, managed and supported by independent external parties and not Municipal officials who may not be adequately skilled to do so or may have a resistance to change. The following table is a listing of identified risks, the progress made on these risks and actions required for the sustainability of the progress & ultimate neutralisation of 69 these risks.
 OPERATIONALISATION Optimal Process and Project Control “War” Office – Committee Room 3 Pitbull 6 Critical implementation Strategies Chiwhawha Grass Cut Roads Potholes Waste Legal (Bylaws, contracts, etc. ) Communications Several other general process controls Daily feedback on progress Performance measurement Immediate intervention when targets are not met 70
OPERATIONALISATION Optimal Process and Project Control “War” Office – Committee Room 3 Pitbull 6 Critical implementation Strategies Chiwhawha Grass Cut Roads Potholes Waste Legal (Bylaws, contracts, etc. ) Communications Several other general process controls Daily feedback on progress Performance measurement Immediate intervention when targets are not met 70
 EXIT PRINCIPLES Define the end state for Msunduzi including: Addressing end state objectives, requirements from Exco, Municipal Manager and Operational units. Corporate functions and their boundaries; Departments, their functions and their boundaries; Level of centralisation/decentralisation of functions; Strategic priorities per department, including corporate; KPA’s and KPI’s for corporate and departments; KPA and KPI measures (targets); Requirement for Section 78 ringfencing or the creation of separate departments; 71
EXIT PRINCIPLES Define the end state for Msunduzi including: Addressing end state objectives, requirements from Exco, Municipal Manager and Operational units. Corporate functions and their boundaries; Departments, their functions and their boundaries; Level of centralisation/decentralisation of functions; Strategic priorities per department, including corporate; KPA’s and KPI’s for corporate and departments; KPA and KPI measures (targets); Requirement for Section 78 ringfencing or the creation of separate departments; 71
 EXIT PRINCIPLES Define the end state for Msunduzi including: Decision on outsourcing/in-sourcing/co-sourcing (PPP); Governance and accountabilities at corporate and departmental levels; Define timeframe to achieve the provisions as per the MFMA exit requirements; Agree on the PIT review processes as per MFMA. Define key projects that need to implemented; Finalize the insource/outsource/co-source decisions; Effect the required commercial process to address issues to ensure MFMA exit issues for mandatory interventions are addressed. 72
EXIT PRINCIPLES Define the end state for Msunduzi including: Decision on outsourcing/in-sourcing/co-sourcing (PPP); Governance and accountabilities at corporate and departmental levels; Define timeframe to achieve the provisions as per the MFMA exit requirements; Agree on the PIT review processes as per MFMA. Define key projects that need to implemented; Finalize the insource/outsource/co-source decisions; Effect the required commercial process to address issues to ensure MFMA exit issues for mandatory interventions are addressed. 72
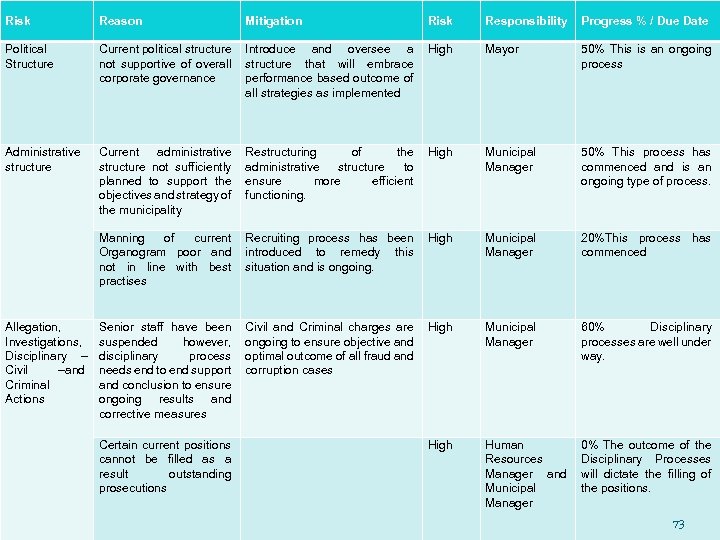 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % / Due Date Political Structure Current political structure not supportive of overall corporate governance Introduce and oversee a structure that will embrace performance based outcome of all strategies as implemented High Mayor 50% This is an ongoing process Administrative structure Current administrative structure not sufficiently planned to support the objectives and strategy of the municipality Restructuring of the administrative structure to ensure more efficient functioning. High Municipal Manager 50% This process has commenced and is an ongoing type of process. Manning of current Organogram poor and not in line with best practises Recruiting process has been introduced to remedy this situation and is ongoing. High Municipal Manager 20%This process has commenced Senior staff have been suspended however, disciplinary process needs end to end support and conclusion to ensure ongoing results and corrective measures Civil and Criminal charges are ongoing to ensure objective and optimal outcome of all fraud and corruption cases High Municipal Manager 60% Disciplinary processes are well under way. High Human Resources Manager and Municipal Manager 0% The outcome of the Disciplinary Processes will dictate the filling of the positions. Allegation, Investigations, Disciplinary – Civil –and Criminal Actions Certain current positions cannot be filled as a result outstanding prosecutions 73
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % / Due Date Political Structure Current political structure not supportive of overall corporate governance Introduce and oversee a structure that will embrace performance based outcome of all strategies as implemented High Mayor 50% This is an ongoing process Administrative structure Current administrative structure not sufficiently planned to support the objectives and strategy of the municipality Restructuring of the administrative structure to ensure more efficient functioning. High Municipal Manager 50% This process has commenced and is an ongoing type of process. Manning of current Organogram poor and not in line with best practises Recruiting process has been introduced to remedy this situation and is ongoing. High Municipal Manager 20%This process has commenced Senior staff have been suspended however, disciplinary process needs end to end support and conclusion to ensure ongoing results and corrective measures Civil and Criminal charges are ongoing to ensure objective and optimal outcome of all fraud and corruption cases High Municipal Manager 60% Disciplinary processes are well under way. High Human Resources Manager and Municipal Manager 0% The outcome of the Disciplinary Processes will dictate the filling of the positions. Allegation, Investigations, Disciplinary – Civil –and Criminal Actions Certain current positions cannot be filled as a result outstanding prosecutions 73
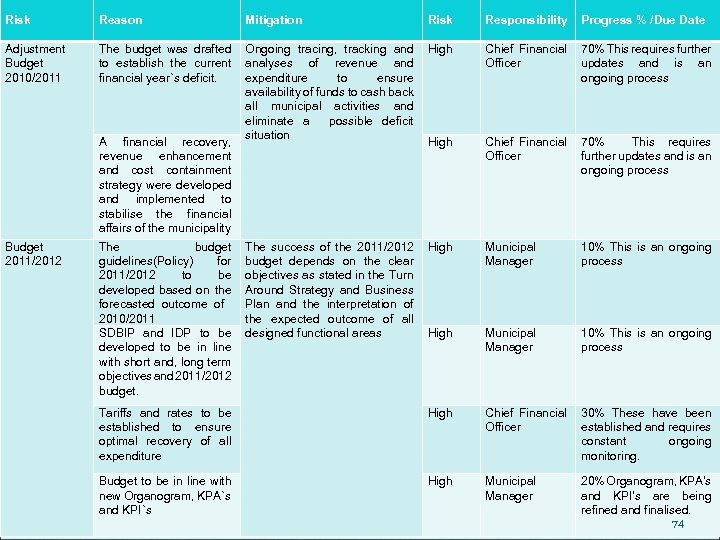 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Adjustment Budget 2010/2011 The budget was drafted to establish the current financial year`s deficit. Ongoing tracing, tracking and analyses of revenue and expenditure to ensure availability of funds to cash back all municipal activities and eliminate a possible deficit situation High Chief Financial Officer 70% This requires further updates and is an ongoing process The success of the 2011/2012 budget depends on the clear objectives as stated in the Turn Around Strategy and Business Plan and the interpretation of the expected outcome of all designed functional areas High Municipal Manager 10% This is an ongoing process Tariffs and rates to be established to ensure optimal recovery of all expenditure High Chief Financial Officer 30% These have been established and requires constant ongoing monitoring. Budget to be in line with new Organogram, KPA`s and KPI`s High Municipal Manager 20% Organogram, KPA’s and KPI’s are being refined and finalised. 74 A financial recovery, revenue enhancement and cost containment strategy were developed and implemented to stabilise the financial affairs of the municipality Budget 2011/2012 The budget guidelines(Policy) for 2011/2012 to be developed based on the forecasted outcome of 2010/2011 SDBIP and IDP to be developed to be in line with short and, long term objectives and 2011/2012 budget.
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Adjustment Budget 2010/2011 The budget was drafted to establish the current financial year`s deficit. Ongoing tracing, tracking and analyses of revenue and expenditure to ensure availability of funds to cash back all municipal activities and eliminate a possible deficit situation High Chief Financial Officer 70% This requires further updates and is an ongoing process The success of the 2011/2012 budget depends on the clear objectives as stated in the Turn Around Strategy and Business Plan and the interpretation of the expected outcome of all designed functional areas High Municipal Manager 10% This is an ongoing process Tariffs and rates to be established to ensure optimal recovery of all expenditure High Chief Financial Officer 30% These have been established and requires constant ongoing monitoring. Budget to be in line with new Organogram, KPA`s and KPI`s High Municipal Manager 20% Organogram, KPA’s and KPI’s are being refined and finalised. 74 A financial recovery, revenue enhancement and cost containment strategy were developed and implemented to stabilise the financial affairs of the municipality Budget 2011/2012 The budget guidelines(Policy) for 2011/2012 to be developed based on the forecasted outcome of 2010/2011 SDBIP and IDP to be developed to be in line with short and, long term objectives and 2011/2012 budget.
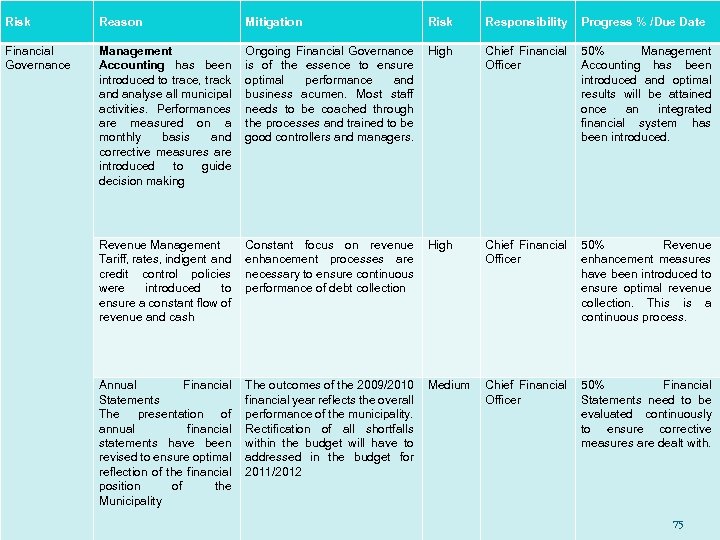 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Financial Governance Management Accounting has been introduced to trace, track and analyse all municipal activities. Performances are measured on a monthly basis and corrective measures are introduced to guide decision making Ongoing Financial Governance is of the essence to ensure optimal performance and business acumen. Most staff needs to be coached through the processes and trained to be good controllers and managers. High Chief Financial Officer 50% Management Accounting has been introduced and optimal results will be attained once an integrated financial system has been introduced. Revenue Management Tariff, rates, indigent and credit control policies were introduced to ensure a constant flow of revenue and cash Constant focus on revenue enhancement processes are necessary to ensure continuous performance of debt collection High Chief Financial Officer 50% Revenue enhancement measures have been introduced to ensure optimal revenue collection. This is a continuous process. Annual Financial Statements The presentation of annual financial statements have been revised to ensure optimal reflection of the financial position of the Municipality The outcomes of the 2009/2010 financial year reflects the overall performance of the municipality. Rectification of all shortfalls within the budget will have to addressed in the budget for 2011/2012 Medium Chief Financial Officer 50% Financial Statements need to be evaluated continuously to ensure corrective measures are dealt with. 75
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Financial Governance Management Accounting has been introduced to trace, track and analyse all municipal activities. Performances are measured on a monthly basis and corrective measures are introduced to guide decision making Ongoing Financial Governance is of the essence to ensure optimal performance and business acumen. Most staff needs to be coached through the processes and trained to be good controllers and managers. High Chief Financial Officer 50% Management Accounting has been introduced and optimal results will be attained once an integrated financial system has been introduced. Revenue Management Tariff, rates, indigent and credit control policies were introduced to ensure a constant flow of revenue and cash Constant focus on revenue enhancement processes are necessary to ensure continuous performance of debt collection High Chief Financial Officer 50% Revenue enhancement measures have been introduced to ensure optimal revenue collection. This is a continuous process. Annual Financial Statements The presentation of annual financial statements have been revised to ensure optimal reflection of the financial position of the Municipality The outcomes of the 2009/2010 financial year reflects the overall performance of the municipality. Rectification of all shortfalls within the budget will have to addressed in the budget for 2011/2012 Medium Chief Financial Officer 50% Financial Statements need to be evaluated continuously to ensure corrective measures are dealt with. 75
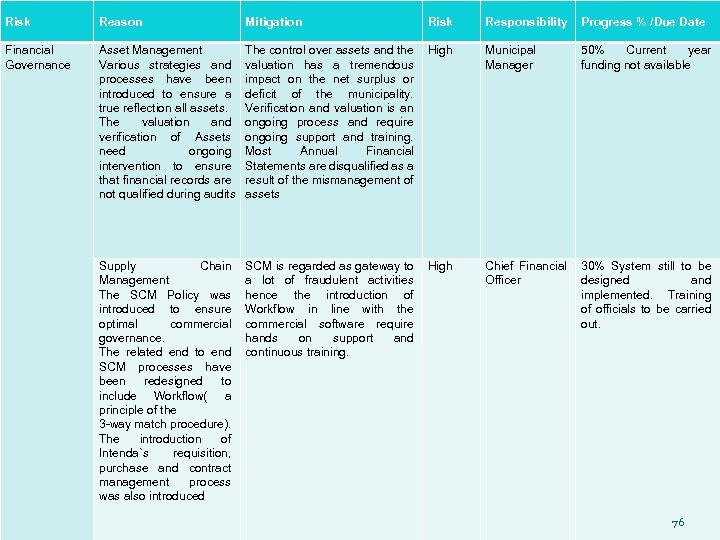 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Financial Governance Asset Management Various strategies and processes have been introduced to ensure a true reflection all assets. The valuation and verification of Assets need ongoing intervention to ensure that financial records are not qualified during audits The control over assets and the valuation has a tremendous impact on the net surplus or deficit of the municipality. Verification and valuation is an ongoing process and require ongoing support and training. Most Annual Financial Statements are disqualified as a result of the mismanagement of assets High Municipal Manager 50% Current year funding not available Supply Chain Management The SCM Policy was introduced to ensure optimal commercial governance. The related end to end SCM processes have been redesigned to include Workflow( a principle of the 3 -way match procedure). The introduction of Intenda`s requisition, purchase and contract management process was also introduced SCM is regarded as gateway to a lot of fraudulent activities hence the introduction of Workflow in line with the commercial software require hands on support and continuous training. High Chief Financial Officer 30% System still to be designed and implemented. Training of officials to be carried out. 76
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Financial Governance Asset Management Various strategies and processes have been introduced to ensure a true reflection all assets. The valuation and verification of Assets need ongoing intervention to ensure that financial records are not qualified during audits The control over assets and the valuation has a tremendous impact on the net surplus or deficit of the municipality. Verification and valuation is an ongoing process and require ongoing support and training. Most Annual Financial Statements are disqualified as a result of the mismanagement of assets High Municipal Manager 50% Current year funding not available Supply Chain Management The SCM Policy was introduced to ensure optimal commercial governance. The related end to end SCM processes have been redesigned to include Workflow( a principle of the 3 -way match procedure). The introduction of Intenda`s requisition, purchase and contract management process was also introduced SCM is regarded as gateway to a lot of fraudulent activities hence the introduction of Workflow in line with the commercial software require hands on support and continuous training. High Chief Financial Officer 30% System still to be designed and implemented. Training of officials to be carried out. 76
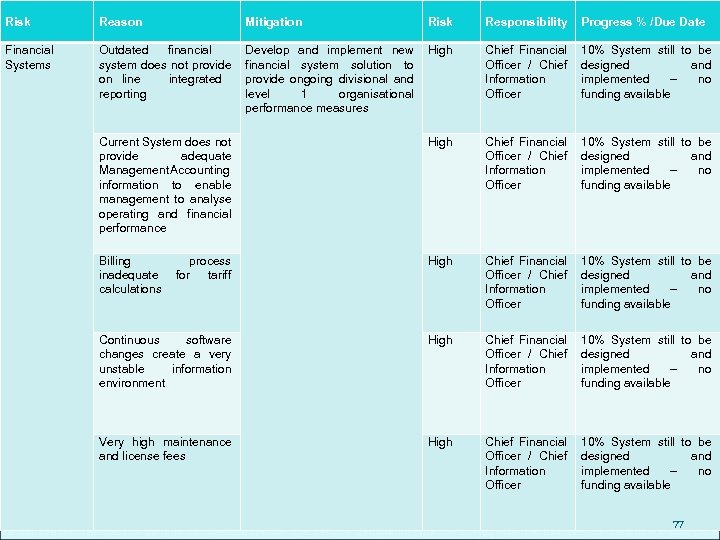 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Financial Systems Outdated financial system does not provide on line integrated reporting Develop and implement new financial system solution to provide ongoing divisional and level 1 organisational performance measures High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available Current System does not provide adequate Management Accounting information to enable management to analyse operating and financial performance High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available Billing inadequate calculations process for tariff High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available Continuous software changes create a very unstable information environment High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available Very high maintenance and license fees High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available 77
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Financial Systems Outdated financial system does not provide on line integrated reporting Develop and implement new financial system solution to provide ongoing divisional and level 1 organisational performance measures High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available Current System does not provide adequate Management Accounting information to enable management to analyse operating and financial performance High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available Billing inadequate calculations process for tariff High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available Continuous software changes create a very unstable information environment High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available Very high maintenance and license fees High Chief Financial Officer / Chief Information Officer 10% System still to be designed and implemented – no funding available 77
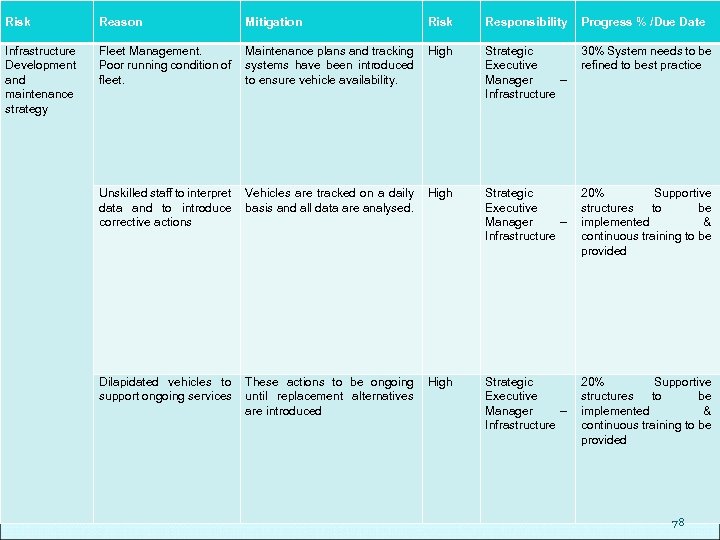 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Fleet Management. Poor running condition of fleet. Maintenance plans and tracking systems have been introduced to ensure vehicle availability. High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% System needs to be refined to best practice Unskilled staff to interpret data and to introduce corrective actions Vehicles are tracked on a daily basis and all data are analysed. High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Supportive structures to be implemented & continuous training to be provided Dilapidated vehicles to support ongoing services These actions to be ongoing until replacement alternatives are introduced High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Supportive structures to be implemented & continuous training to be provided 78
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Fleet Management. Poor running condition of fleet. Maintenance plans and tracking systems have been introduced to ensure vehicle availability. High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% System needs to be refined to best practice Unskilled staff to interpret data and to introduce corrective actions Vehicles are tracked on a daily basis and all data are analysed. High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Supportive structures to be implemented & continuous training to be provided Dilapidated vehicles to support ongoing services These actions to be ongoing until replacement alternatives are introduced High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Supportive structures to be implemented & continuous training to be provided 78
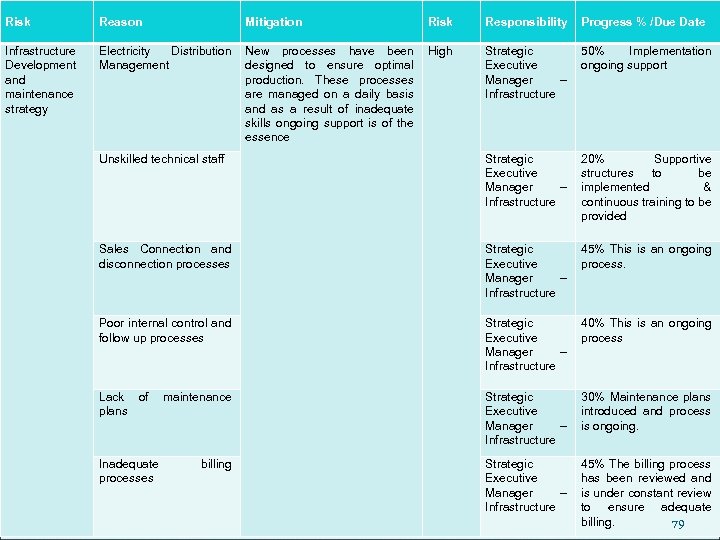 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Electricity Distribution Management New processes have been designed to ensure optimal production. These processes are managed on a daily basis and as a result of inadequate skills ongoing support is of the essence High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 50% Implementation ongoing support Unskilled technical staff Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Supportive structures to be implemented & continuous training to be provided Sales Connection and disconnection processes Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 45% This is an ongoing process. Poor internal control and follow up processes Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 40% This is an ongoing process Lack of plans maintenance Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% Maintenance plans introduced and process is ongoing. billing Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 45% The billing process has been reviewed and is under constant review to ensure adequate billing. 79 Inadequate processes
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Electricity Distribution Management New processes have been designed to ensure optimal production. These processes are managed on a daily basis and as a result of inadequate skills ongoing support is of the essence High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 50% Implementation ongoing support Unskilled technical staff Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Supportive structures to be implemented & continuous training to be provided Sales Connection and disconnection processes Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 45% This is an ongoing process. Poor internal control and follow up processes Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 40% This is an ongoing process Lack of plans maintenance Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% Maintenance plans introduced and process is ongoing. billing Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 45% The billing process has been reviewed and is under constant review to ensure adequate billing. 79 Inadequate processes
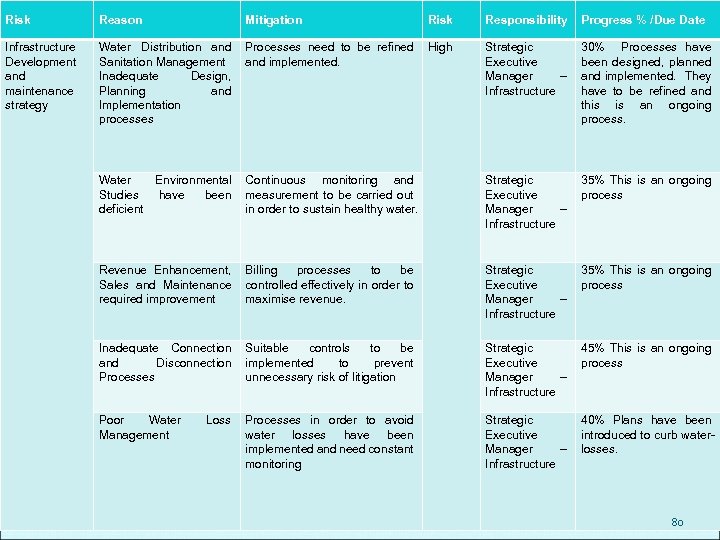 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Water Distribution and Sanitation Management Inadequate Design, Planning and Implementation processes Processes need to be refined and implemented. High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% Processes have been designed, planned and implemented. They have to be refined and this is an ongoing process. Water Environmental Studies have been deficient Continuous monitoring and measurement to be carried out in order to sustain healthy water. Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 35% This is an ongoing process Revenue Enhancement, Sales and Maintenance required improvement Billing processes to be controlled effectively in order to maximise revenue. Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 35% This is an ongoing process Inadequate Connection and Disconnection Processes Suitable controls to be implemented to prevent unnecessary risk of litigation Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 45% This is an ongoing process Poor Water Management Processes in order to avoid water losses have been implemented and need constant monitoring Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 40% Plans have been introduced to curb waterlosses. Loss 80
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Water Distribution and Sanitation Management Inadequate Design, Planning and Implementation processes Processes need to be refined and implemented. High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% Processes have been designed, planned and implemented. They have to be refined and this is an ongoing process. Water Environmental Studies have been deficient Continuous monitoring and measurement to be carried out in order to sustain healthy water. Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 35% This is an ongoing process Revenue Enhancement, Sales and Maintenance required improvement Billing processes to be controlled effectively in order to maximise revenue. Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 35% This is an ongoing process Inadequate Connection and Disconnection Processes Suitable controls to be implemented to prevent unnecessary risk of litigation Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 45% This is an ongoing process Poor Water Management Processes in order to avoid water losses have been implemented and need constant monitoring Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 40% Plans have been introduced to curb waterlosses. Loss 80
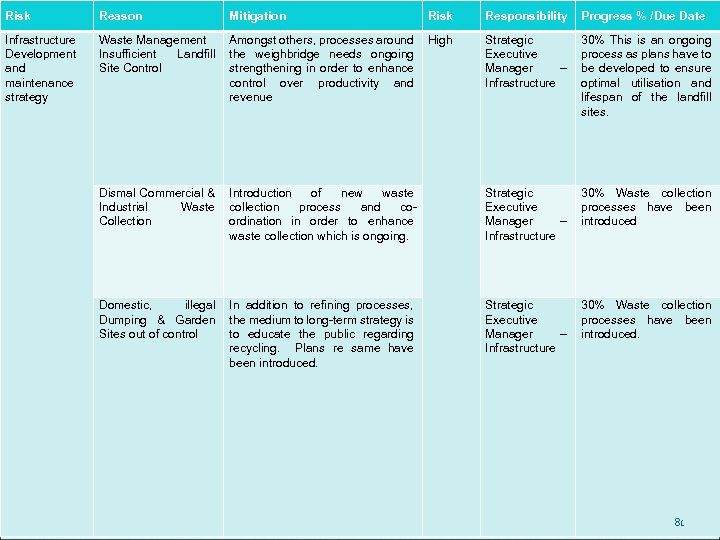 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Waste Management Insufficient Landfill Site Control Amongst others, processes around the weighbridge needs ongoing strengthening in order to enhance control over productivity and revenue High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% This is an ongoing process as plans have to be developed to ensure optimal utilisation and lifespan of the landfill sites. Dismal Commercial & Industrial Waste Collection Introduction of new waste collection process and coordination in order to enhance waste collection which is ongoing. Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% Waste collection processes have been introduced Domestic, illegal Dumping & Garden Sites out of control In addition to refining processes, the medium to long-term strategy is to educate the public regarding recycling. Plans re same have been introduced. Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% Waste collection processes have been introduced. 81
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Waste Management Insufficient Landfill Site Control Amongst others, processes around the weighbridge needs ongoing strengthening in order to enhance control over productivity and revenue High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% This is an ongoing process as plans have to be developed to ensure optimal utilisation and lifespan of the landfill sites. Dismal Commercial & Industrial Waste Collection Introduction of new waste collection process and coordination in order to enhance waste collection which is ongoing. Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% Waste collection processes have been introduced Domestic, illegal Dumping & Garden Sites out of control In addition to refining processes, the medium to long-term strategy is to educate the public regarding recycling. Plans re same have been introduced. Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 30% Waste collection processes have been introduced. 81
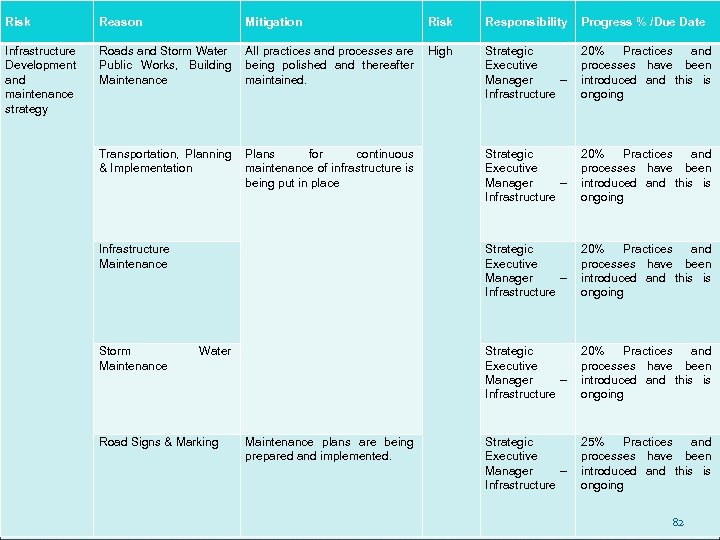 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Roads and Storm Water Public Works, Building Maintenance All practices and processes are being polished and thereafter maintained. High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Practices and processes have been introduced and this is ongoing Transportation, Planning & Implementation Plans for continuous maintenance of infrastructure is being put in place Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Practices and processes have been introduced and this is ongoing Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 25% Practices and processes have been introduced and this is ongoing Infrastructure Maintenance Storm Maintenance Water Road Signs & Marking Maintenance plans are being prepared and implemented. 82
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Infrastructure Development and maintenance strategy Roads and Storm Water Public Works, Building Maintenance All practices and processes are being polished and thereafter maintained. High Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Practices and processes have been introduced and this is ongoing Transportation, Planning & Implementation Plans for continuous maintenance of infrastructure is being put in place Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 20% Practices and processes have been introduced and this is ongoing Strategic Executive Manager – Infrastructure 25% Practices and processes have been introduced and this is ongoing Infrastructure Maintenance Storm Maintenance Water Road Signs & Marking Maintenance plans are being prepared and implemented. 82
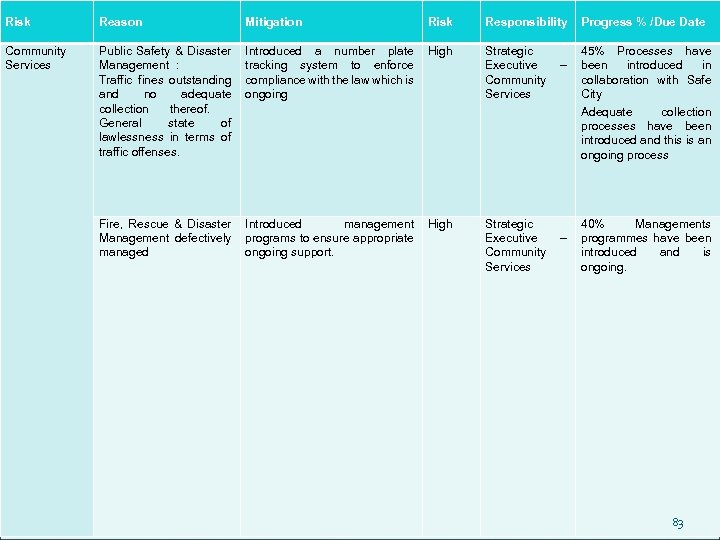 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Community Services Public Safety & Disaster Management : Traffic fines outstanding and no adequate collection thereof. General state of lawlessness in terms of traffic offenses. Introduced a number plate tracking system to enforce compliance with the law which is ongoing High Strategic Executive Community Services 45% Processes have been introduced in collaboration with Safe City Adequate collection processes have been introduced and this is an ongoing process Fire, Rescue & Disaster Management defectively managed Introduced management programs to ensure appropriate ongoing support. High Strategic Executive Community Services – – 40% Managements programmes have been introduced and is ongoing. 83
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Community Services Public Safety & Disaster Management : Traffic fines outstanding and no adequate collection thereof. General state of lawlessness in terms of traffic offenses. Introduced a number plate tracking system to enforce compliance with the law which is ongoing High Strategic Executive Community Services 45% Processes have been introduced in collaboration with Safe City Adequate collection processes have been introduced and this is an ongoing process Fire, Rescue & Disaster Management defectively managed Introduced management programs to ensure appropriate ongoing support. High Strategic Executive Community Services – – 40% Managements programmes have been introduced and is ongoing. 83
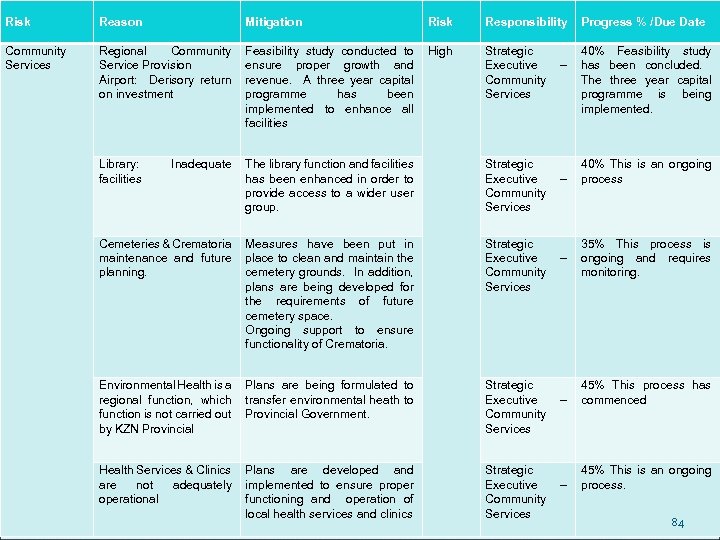 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Community Services Regional Community Service Provision Airport: Derisory return on investment Feasibility study conducted to ensure proper growth and revenue. A three year capital programme has been implemented to enhance all facilities High Strategic Executive Community Services 40% Feasibility study has been concluded. The three year capital programme is being implemented. Library: facilities The library function and facilities has been enhanced in order to provide access to a wider user group. Strategic Executive Community Services Cemeteries & Crematoria maintenance and future planning. Measures have been put in place to clean and maintain the cemetery grounds. In addition, plans are being developed for the requirements of future cemetery space. Ongoing support to ensure functionality of Crematoria. Strategic Executive Community Services Environmental Health is a regional function, which function is not carried out by KZN Provincial Plans are being formulated to transfer environmental heath to Provincial Government. Strategic Executive Community Services Health Services & Clinics are not adequately operational Plans are developed and implemented to ensure proper functioning and operation of local health services and clinics Strategic Executive Community Services Inadequate – – – 40% This is an ongoing process 35% This process is ongoing and requires monitoring. – 45% This process has commenced – 45% This is an ongoing process. 84
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Community Services Regional Community Service Provision Airport: Derisory return on investment Feasibility study conducted to ensure proper growth and revenue. A three year capital programme has been implemented to enhance all facilities High Strategic Executive Community Services 40% Feasibility study has been concluded. The three year capital programme is being implemented. Library: facilities The library function and facilities has been enhanced in order to provide access to a wider user group. Strategic Executive Community Services Cemeteries & Crematoria maintenance and future planning. Measures have been put in place to clean and maintain the cemetery grounds. In addition, plans are being developed for the requirements of future cemetery space. Ongoing support to ensure functionality of Crematoria. Strategic Executive Community Services Environmental Health is a regional function, which function is not carried out by KZN Provincial Plans are being formulated to transfer environmental heath to Provincial Government. Strategic Executive Community Services Health Services & Clinics are not adequately operational Plans are developed and implemented to ensure proper functioning and operation of local health services and clinics Strategic Executive Community Services Inadequate – – – 40% This is an ongoing process 35% This process is ongoing and requires monitoring. – 45% This process has commenced – 45% This is an ongoing process. 84
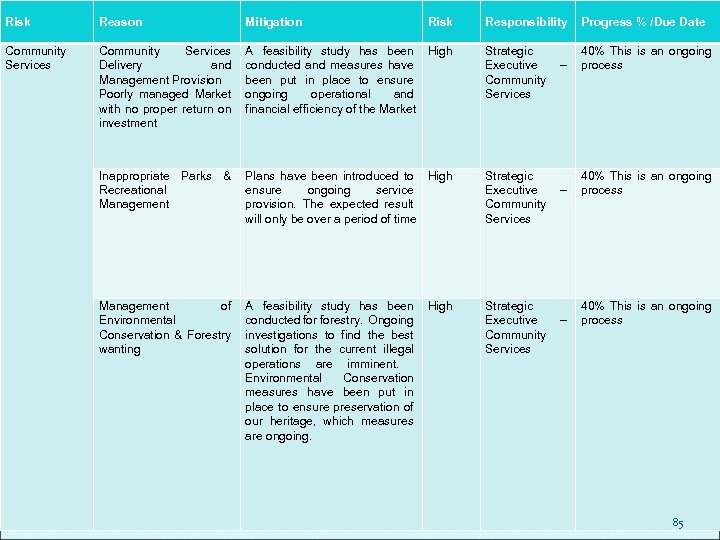 Risk Reason Mitigation Community Services Delivery and Management Provision Poorly managed Market with no proper return on investment Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date A feasibility study has been High conducted and measures have been put in place to ensure ongoing operational and financial efficiency of the Market Strategic Executive Community Services – 40% This is an ongoing process Inappropriate Parks & Recreational Management Plans have been introduced to High ensure ongoing service provision. The expected result will only be over a period of time Strategic Executive Community Services – 40% This is an ongoing process Management of Environmental Conservation & Forestry wanting A feasibility study has been conducted forestry. Ongoing investigations to find the best solution for the current illegal operations are imminent. Environmental Conservation measures have been put in place to ensure preservation of our heritage, which measures are ongoing. Strategic Executive Community Services – 40% This is an ongoing process High 85
Risk Reason Mitigation Community Services Delivery and Management Provision Poorly managed Market with no proper return on investment Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date A feasibility study has been High conducted and measures have been put in place to ensure ongoing operational and financial efficiency of the Market Strategic Executive Community Services – 40% This is an ongoing process Inappropriate Parks & Recreational Management Plans have been introduced to High ensure ongoing service provision. The expected result will only be over a period of time Strategic Executive Community Services – 40% This is an ongoing process Management of Environmental Conservation & Forestry wanting A feasibility study has been conducted forestry. Ongoing investigations to find the best solution for the current illegal operations are imminent. Environmental Conservation measures have been put in place to ensure preservation of our heritage, which measures are ongoing. Strategic Executive Community Services – 40% This is an ongoing process High 85
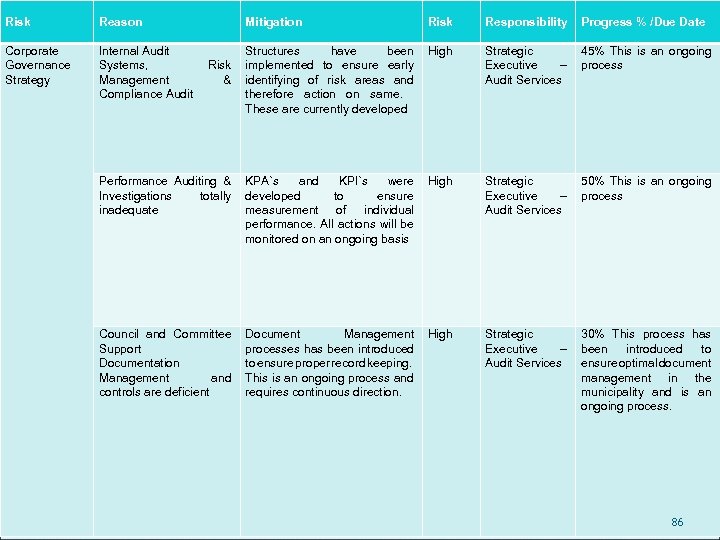 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Corporate Governance Strategy Internal Audit Systems, Management Compliance Audit Structures have been implemented to ensure early identifying of risk areas and therefore action on same. These are currently developed High Strategic Executive – Audit Services 45% This is an ongoing process Performance Auditing & Investigations totally inadequate KPA`s and KPI`s were developed to ensure measurement of individual performance. All actions will be monitored on an ongoing basis High Strategic Executive – Audit Services 50% This is an ongoing process Council and Committee Support Documentation Management and controls are deficient Document Management processes has been introduced to ensure proper record keeping. This is an ongoing process and requires continuous direction. High Strategic Executive – Audit Services 30% This process has been introduced to ensure optimal document management in the municipality and is an ongoing process. Risk & 86
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Corporate Governance Strategy Internal Audit Systems, Management Compliance Audit Structures have been implemented to ensure early identifying of risk areas and therefore action on same. These are currently developed High Strategic Executive – Audit Services 45% This is an ongoing process Performance Auditing & Investigations totally inadequate KPA`s and KPI`s were developed to ensure measurement of individual performance. All actions will be monitored on an ongoing basis High Strategic Executive – Audit Services 50% This is an ongoing process Council and Committee Support Documentation Management and controls are deficient Document Management processes has been introduced to ensure proper record keeping. This is an ongoing process and requires continuous direction. High Strategic Executive – Audit Services 30% This process has been introduced to ensure optimal document management in the municipality and is an ongoing process. Risk & 86
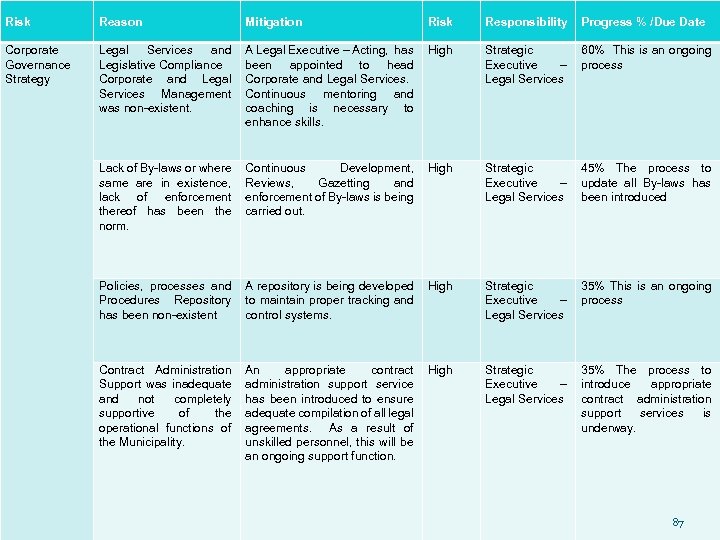 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Corporate Governance Strategy Legal Services and Legislative Compliance Corporate and Legal Services Management was non-existent. A Legal Executive – Acting, has been appointed to head Corporate and Legal Services. Continuous mentoring and coaching is necessary to enhance skills. High Strategic Executive – Legal Services 60% This is an ongoing process Lack of By-laws or where same are in existence, lack of enforcement thereof has been the norm. Continuous Development, Reviews, Gazetting and enforcement of By-laws is being carried out. High Strategic Executive – Legal Services 45% The process to update all By-laws has been introduced Policies, processes and Procedures Repository has been non-existent A repository is being developed to maintain proper tracking and control systems. High Strategic Executive – Legal Services 35% This is an ongoing process Contract Administration Support was inadequate and not completely supportive of the operational functions of the Municipality. An appropriate contract administration support service has been introduced to ensure adequate compilation of all legal agreements. As a result of unskilled personnel, this will be an ongoing support function. High Strategic Executive – Legal Services 35% The process to introduce appropriate contract administration support services is underway. 87
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Corporate Governance Strategy Legal Services and Legislative Compliance Corporate and Legal Services Management was non-existent. A Legal Executive – Acting, has been appointed to head Corporate and Legal Services. Continuous mentoring and coaching is necessary to enhance skills. High Strategic Executive – Legal Services 60% This is an ongoing process Lack of By-laws or where same are in existence, lack of enforcement thereof has been the norm. Continuous Development, Reviews, Gazetting and enforcement of By-laws is being carried out. High Strategic Executive – Legal Services 45% The process to update all By-laws has been introduced Policies, processes and Procedures Repository has been non-existent A repository is being developed to maintain proper tracking and control systems. High Strategic Executive – Legal Services 35% This is an ongoing process Contract Administration Support was inadequate and not completely supportive of the operational functions of the Municipality. An appropriate contract administration support service has been introduced to ensure adequate compilation of all legal agreements. As a result of unskilled personnel, this will be an ongoing support function. High Strategic Executive – Legal Services 35% The process to introduce appropriate contract administration support services is underway. 87
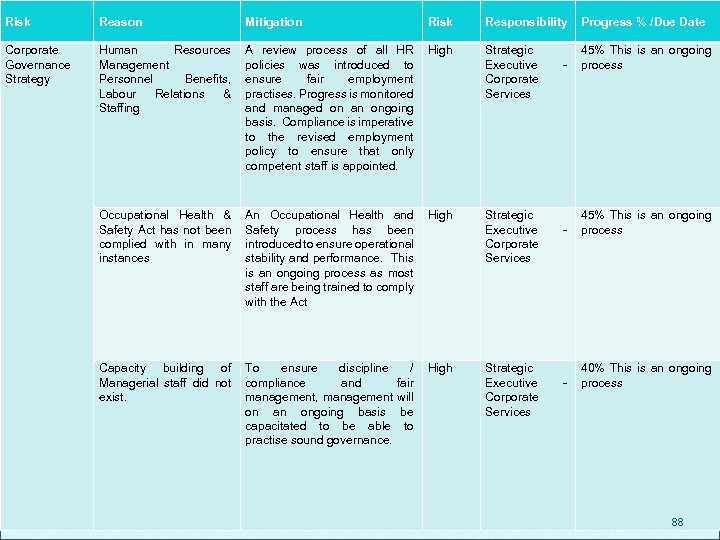 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Corporate Governance Strategy Human Resources Management Personnel Benefits, Labour Relations & Staffing A review process of all HR policies was introduced to ensure fair employment practises. Progress is monitored and managed on an ongoing basis. Compliance is imperative to the revised employment policy to ensure that only competent staff is appointed. High Strategic Executive Corporate Services - 45% This is an ongoing process Occupational Health & Safety Act has not been complied with in many instances An Occupational Health and Safety process has been introduced to ensure operational stability and performance. This is an ongoing process as most staff are being trained to comply with the Act High - 45% This is an ongoing process Capacity building of Managerial staff did not exist. To ensure discipline compliance and management, management on an ongoing basis capacitated to be able practise sound governance. High - 40% This is an ongoing process / fair will be to Strategic Executive Corporate Services 88
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Corporate Governance Strategy Human Resources Management Personnel Benefits, Labour Relations & Staffing A review process of all HR policies was introduced to ensure fair employment practises. Progress is monitored and managed on an ongoing basis. Compliance is imperative to the revised employment policy to ensure that only competent staff is appointed. High Strategic Executive Corporate Services - 45% This is an ongoing process Occupational Health & Safety Act has not been complied with in many instances An Occupational Health and Safety process has been introduced to ensure operational stability and performance. This is an ongoing process as most staff are being trained to comply with the Act High - 45% This is an ongoing process Capacity building of Managerial staff did not exist. To ensure discipline compliance and management, management on an ongoing basis capacitated to be able practise sound governance. High - 40% This is an ongoing process / fair will be to Strategic Executive Corporate Services 88
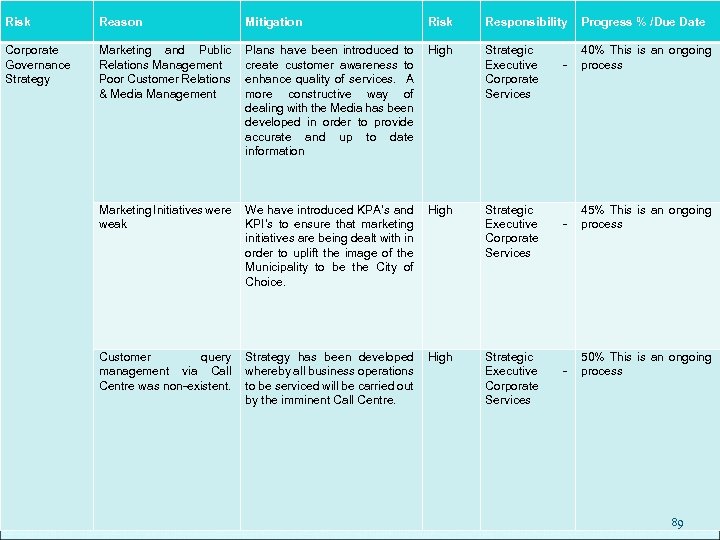 Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Corporate Governance Strategy Marketing and Public Relations Management Poor Customer Relations & Media Management Plans have been introduced to create customer awareness to enhance quality of services. A more constructive way of dealing with the Media has been developed in order to provide accurate and up to date information High Strategic Executive Corporate Services - 40% This is an ongoing process Marketing Initiatives were weak We have introduced KPA’s and KPI’s to ensure that marketing initiatives are being dealt with in order to uplift the image of the Municipality to be the City of Choice. High - 45% This is an ongoing process Customer query management via Call Centre was non-existent. Strategy has been developed whereby all business operations to be serviced will be carried out by the imminent Call Centre. High - 50% This is an ongoing process Strategic Executive Corporate Services 89
Risk Reason Mitigation Risk Responsibility Progress % /Due Date Corporate Governance Strategy Marketing and Public Relations Management Poor Customer Relations & Media Management Plans have been introduced to create customer awareness to enhance quality of services. A more constructive way of dealing with the Media has been developed in order to provide accurate and up to date information High Strategic Executive Corporate Services - 40% This is an ongoing process Marketing Initiatives were weak We have introduced KPA’s and KPI’s to ensure that marketing initiatives are being dealt with in order to uplift the image of the Municipality to be the City of Choice. High - 45% This is an ongoing process Customer query management via Call Centre was non-existent. Strategy has been developed whereby all business operations to be serviced will be carried out by the imminent Call Centre. High - 50% This is an ongoing process Strategic Executive Corporate Services 89
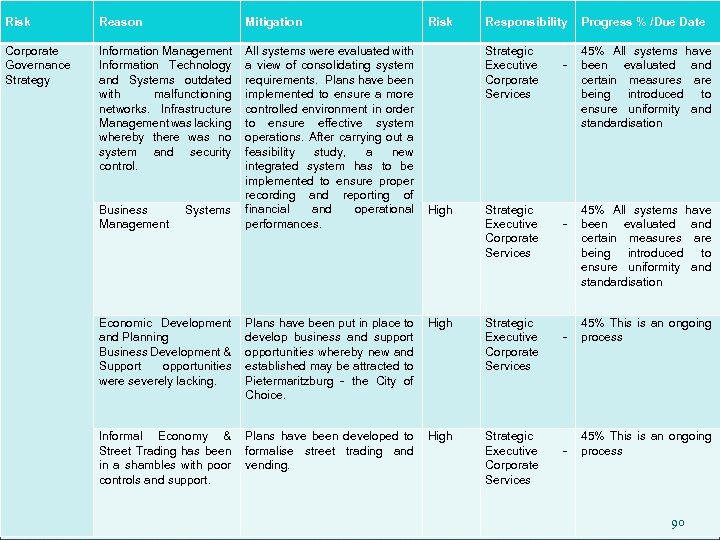 Risk Reason Mitigation Corporate Governance Strategy Information Management Information Technology and Systems outdated with malfunctioning networks. Infrastructure Management was lacking whereby there was no system and security control. All systems were evaluated with a view of consolidating system requirements. Plans have been implemented to ensure a more controlled environment in order to ensure effective system operations. After carrying out a feasibility study, a new integrated system has to be implemented to ensure proper recording and reporting of financial and operational performances. Business Management Systems Risk Economic Development and Planning Business Development & Support opportunities were severely lacking. Plans have been put in place to develop business and support opportunities whereby new and established may be attracted to Pietermaritzburg - the City of Choice. High Informal Economy & Street Trading has been in a shambles with poor controls and support. Plans have been developed to formalise street trading and vending. High Progress % /Due Date Strategic Executive Corporate Services High Responsibility 45% All systems have been evaluated and certain measures are being introduced to ensure uniformity and standardisation Strategic Executive Corporate Services - - 45% All systems have been evaluated and certain measures are being introduced to ensure uniformity and standardisation - 45% This is an ongoing process 90
Risk Reason Mitigation Corporate Governance Strategy Information Management Information Technology and Systems outdated with malfunctioning networks. Infrastructure Management was lacking whereby there was no system and security control. All systems were evaluated with a view of consolidating system requirements. Plans have been implemented to ensure a more controlled environment in order to ensure effective system operations. After carrying out a feasibility study, a new integrated system has to be implemented to ensure proper recording and reporting of financial and operational performances. Business Management Systems Risk Economic Development and Planning Business Development & Support opportunities were severely lacking. Plans have been put in place to develop business and support opportunities whereby new and established may be attracted to Pietermaritzburg - the City of Choice. High Informal Economy & Street Trading has been in a shambles with poor controls and support. Plans have been developed to formalise street trading and vending. High Progress % /Due Date Strategic Executive Corporate Services High Responsibility 45% All systems have been evaluated and certain measures are being introduced to ensure uniformity and standardisation Strategic Executive Corporate Services - - 45% All systems have been evaluated and certain measures are being introduced to ensure uniformity and standardisation - 45% This is an ongoing process 90
 Questions? 91
Questions? 91


